Neurophysiological Evaluation of Students’ Experience during Remote and Face-to-Face Lessons: A Case Study at Driving School
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Protocol
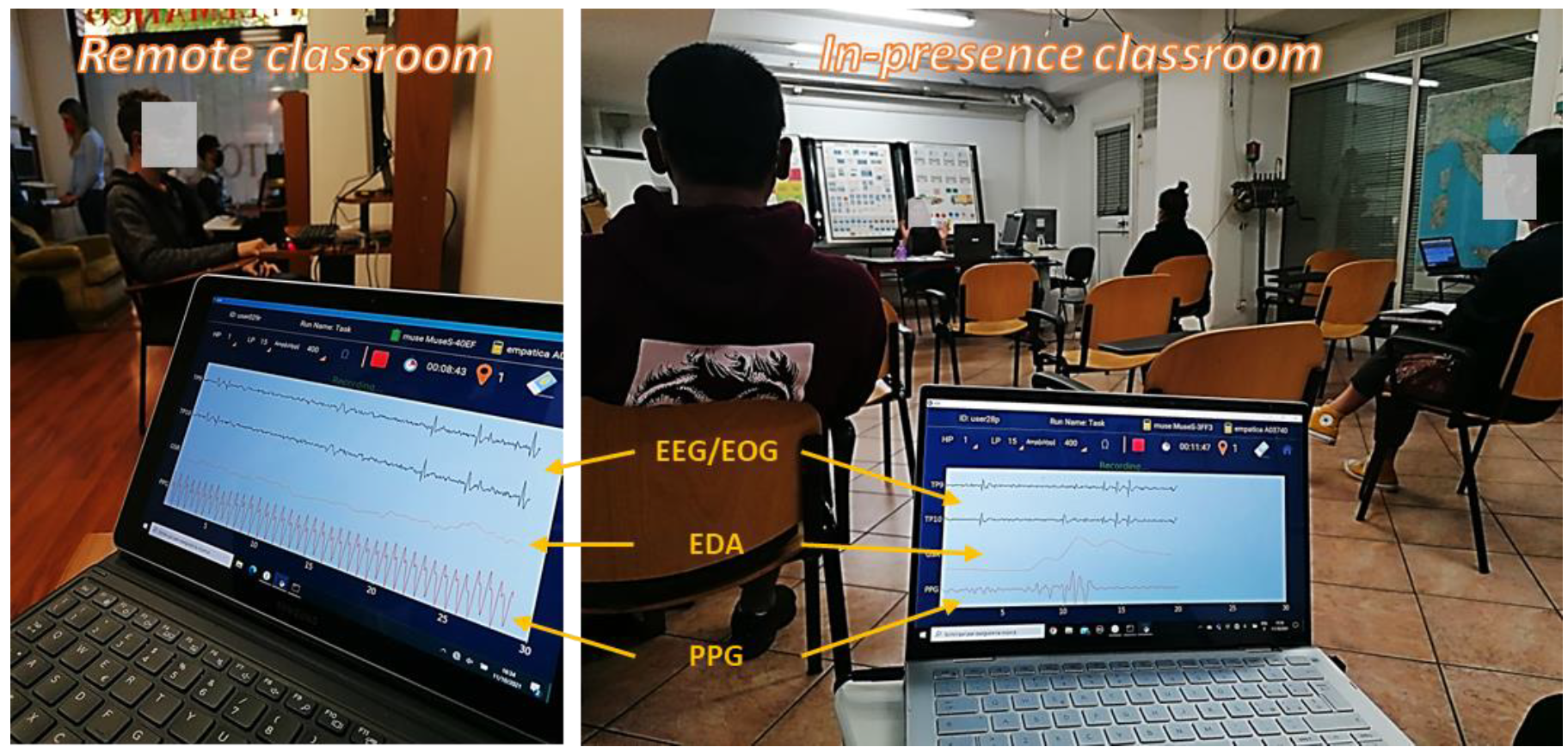
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. EOG Signal Acquisition and Analysis
2.3.2. PPG Signal Acquisition and Analysis
2.3.3. EDA Signal Acquisition and Analysis
2.3.4. Questionnaire
2.3.5. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
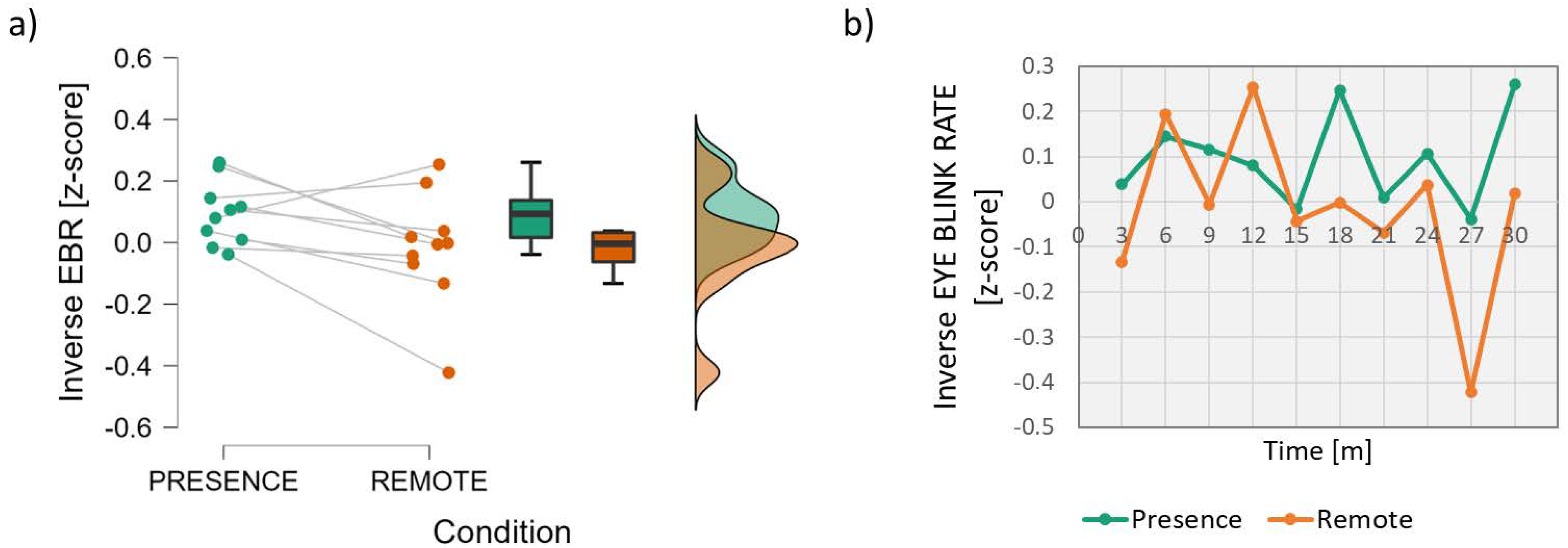
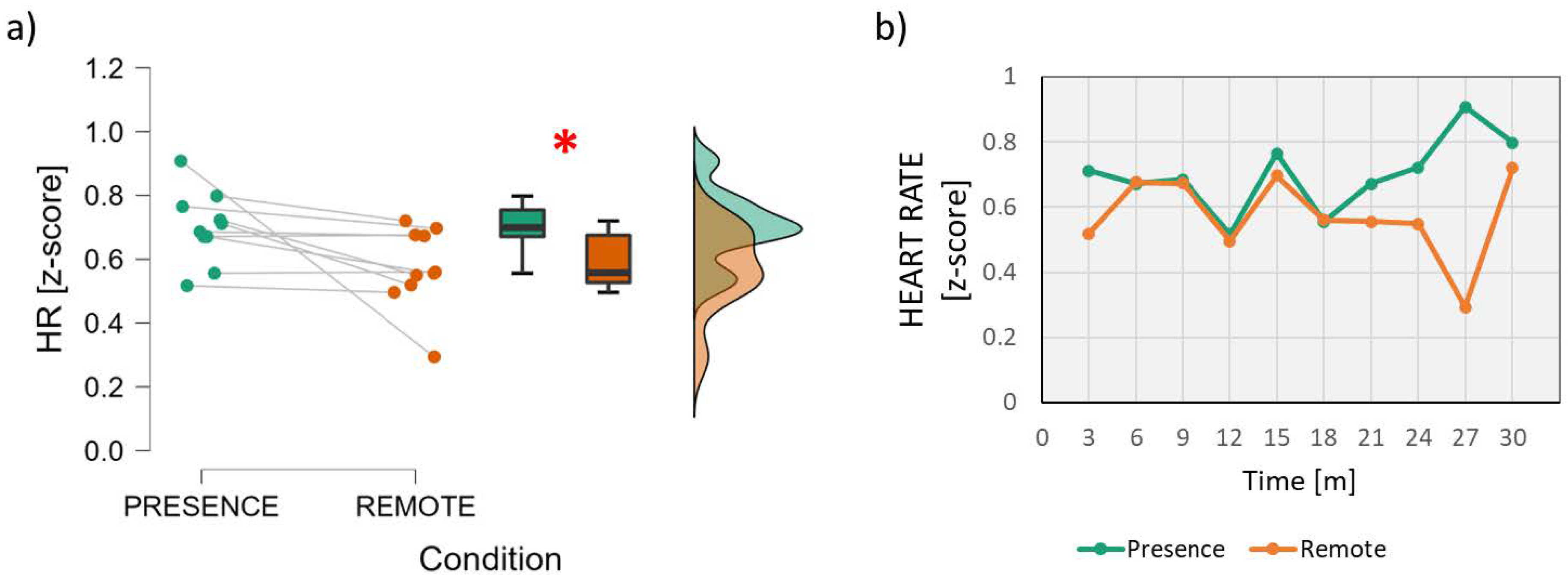
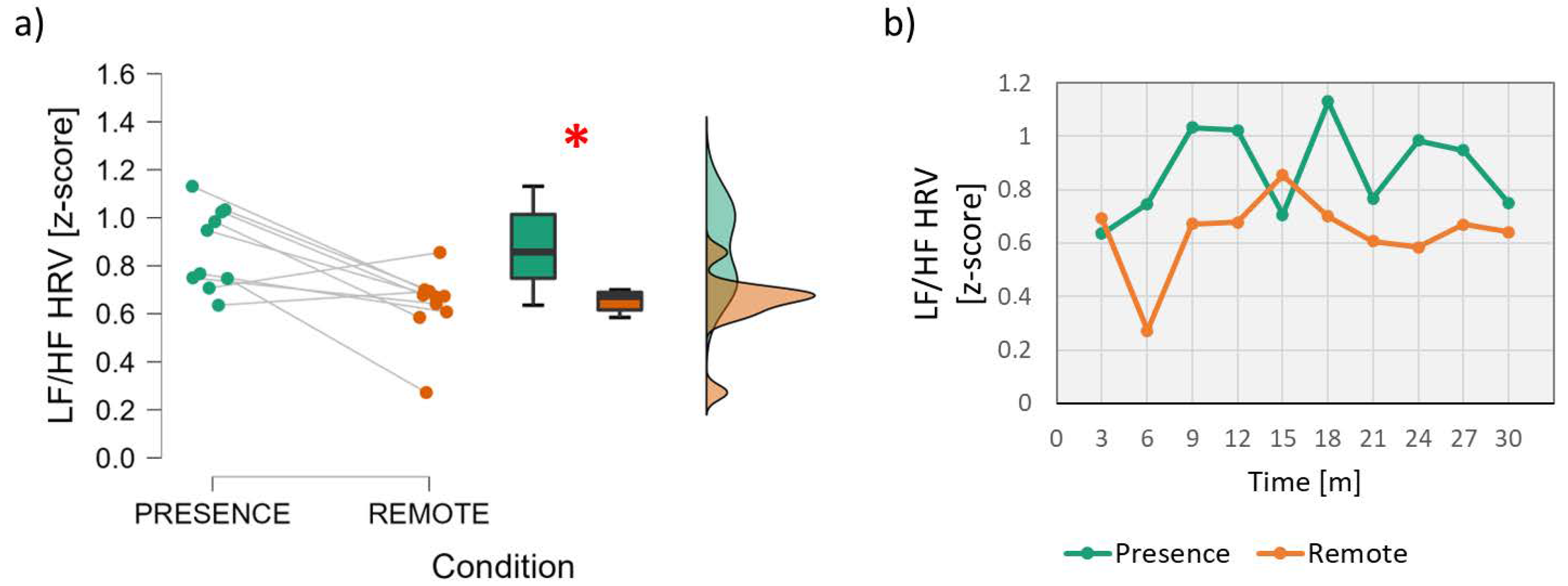
3.1. Neurophysiological Parameters
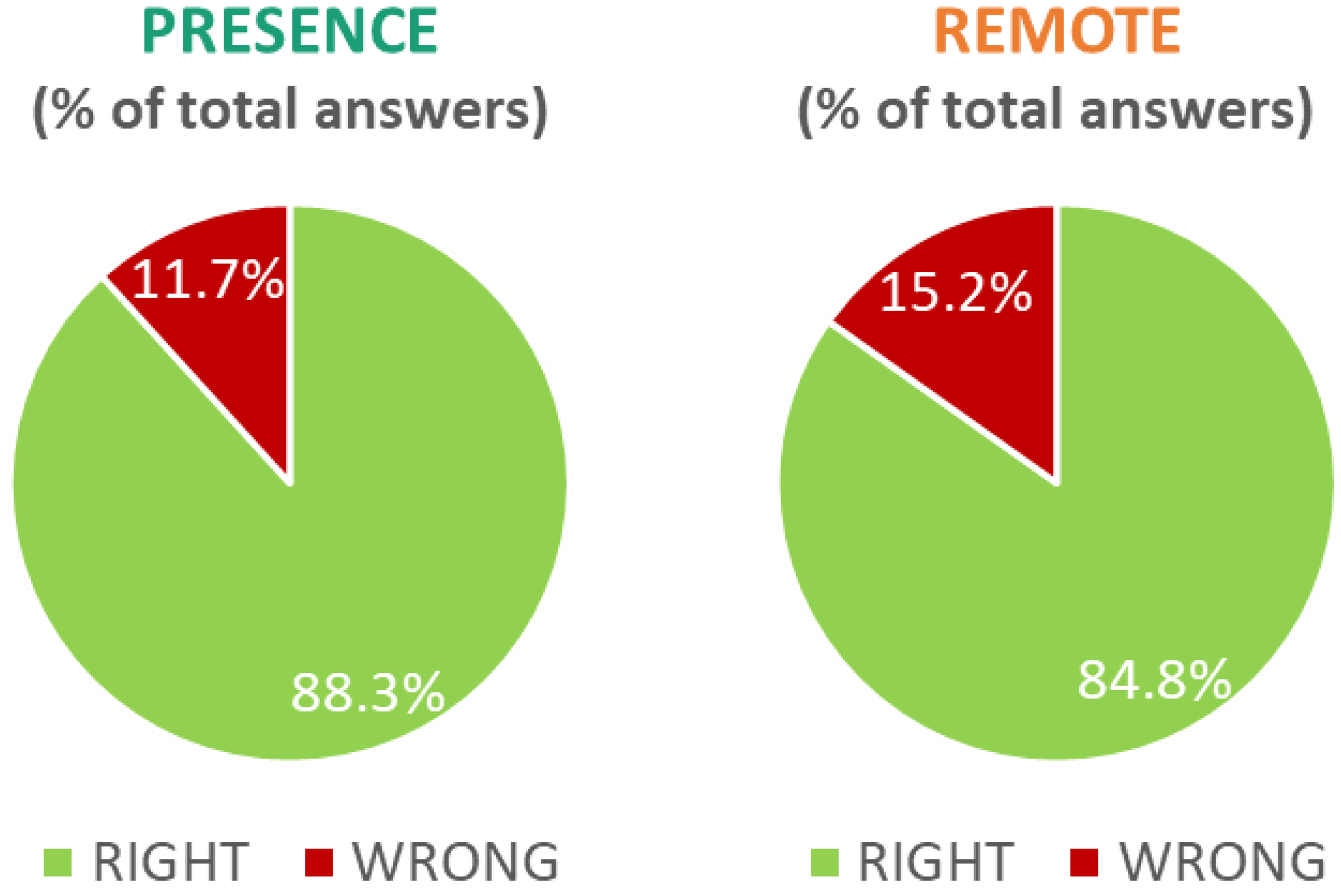
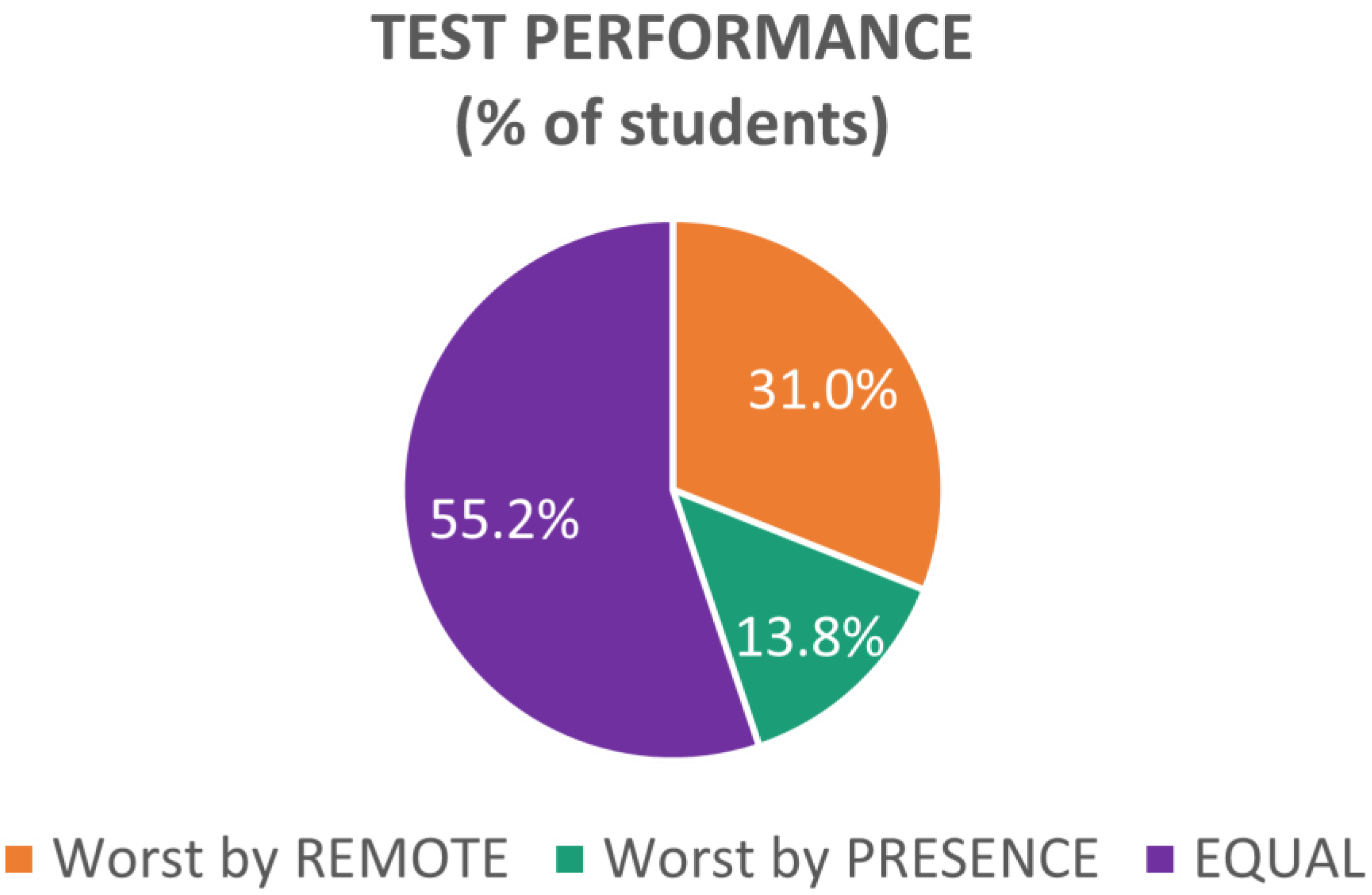
3.2. Questionnaires
- “Worst by PRESENCE”, if the participant gave more wrong answers for subjects covered in the In-presence condition;
- “Worst by REMOTE”, if the participant gave more wrong answers for subjects covered in the Remote condition;
- “EQUAL”, if the number of wrong answers was the same between the two conditions.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palvia, S.; Aeron, P.; Gupta, P.; Mahapatra, D.; Parida, R.; Rosner, R.; Sindhi, S. Online Education: Worldwide Status, Challenges, Trends, and Implications. J. Glob. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 21, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuban, C.; Picciano, A.G.; Graham, C.R.; Moskal, P.D. Research in Online and Blended Learning: New Challenges, New Opportunities. In Conducting Research in Online and Blended Learning Environments, 1st ed.; New Pedagogical Frontiers; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- AACSB Data and Research Blog. Continued Growth in Accessibility of AACSB-Accredited Online Degrees. Available online: https://aacsbblogs.typepad.com/dataandresearch/2016/10/continued-growth-in-accessibility-of-aacsb-accredited-online-degrees.html (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.; Palvia, S.; Verma, S. Online business education research: Systematic analysis and a conceptual model. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2019, 17, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, I.E.; Seaman, J.; Babson Survey Research Group. Online Report Card: Tracking Online Education in the United States. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED572777 (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Marinoni, G.; Van’t Land, H.; Jensen, T. The impact of COVID-19 on Higher Education Around the World: IAU Global Survey Report; International Association of Universities (IAU): Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Unger, S.; Meiran, W. Student Attitudes Towards Online Education during the COVID-19 Viral Outbreak of 2020: Distance Learning in a Time of Social Distance. Int. J. Technol. Educ. Sci. 2020, 4, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Antonenko, P.; Keil, A.; Dawson, K. Converging Subjective and Psychophysiological Measures of Cognitive Load to Study the Effects of Instructor-Present Video. Mind. Brain. Educ. 2020, 14, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berka, C.; Levendowski, D.J.; Lumicao, M.N.; Yau, A.; Davis, G.; Zivkovic, V.T.; Olmstead, R.E.; Tremoulet, P.D.; Craven, P.L. EEG correlates of task engagement and mental workload in vigilance, learning, and memory tasks. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2007, 78, B231–B244. [Google Scholar]
- Flumeri, G.D.; Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; Colosimo, A.; Pozzi, S.; Bonelli, S.; Golfetti, A.; Kong, W.; Babiloni, F. On the Use of Cognitive Neurometric Indexes in Aeronautic and Air Traffic Management Environments. In Symbiotic Interaction; Blankertz, B., Jacucci, G., Gamberini, L., Spagnolli, A., Freeman, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9359, pp. 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- John, E.R. Neurometrics: Clinical Applications of Quantitative Electrophysiology; Routledge: London, UK; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.routledge.com/Neurometrics-Clinical-Applications-of-Quantitative-Electrophysiology/John/p/book/9780367753986 (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Babiker, A.; Faye, I.; Mumtaz, W.; Malik, A.S.; Sato, H. EEG in classroom: EMD features to detect situational interest of students during learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 78, 16261–16281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.H.; Galloway, T.; Berka, C. EEG-Related Changes in Cognitive Workload, Engagement and Distraction as Students Acquire Problem Solving Skills. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Conati, C., McCoy, K., Paliouras, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4511, pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, H.-C.; Jung, T.-P.; Chou, W.-C.; Huang, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lin, G.-Y. EEG Dynamics Reflect the Distinct Cognitive Process of Optic Problem Solving. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaldo, R.M.; Iglesias, J.; Gómez, V.F.; Crespo, J.; Pérez, L.; Alonso, J.F.; Sanz, A.R. Computerized Brain Interfaces for Adaptive Learning and Assessment. In Intelligent Human Systems Integration; Karwowski, W., Ahram, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 722, pp. 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gwizdka, J.; Chaovalitwongse, W.A. Using Wireless EEG Signals to Assess Memory Workload in the n-Back Task. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2015, 46, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammer, J.K.; Xu, K.; Lenartowicz, A. Effects of context on the neural correlates of attention in a college classroom. npj Sci. Learn 2021, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, L.-W.; Komarov, O.; Hairston, W.D.; Jung, T.-P.; Lin, C.-T. Sustained Attention in Real Classroom Settings: An EEG Study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu-Bayraktar, D.; Ozel, P.; Altindis, F.; Yilmaz, B. Split-attention effects in multimedia learning environments: Eye-tracking and EEG analysis. Multimed. Tools Appl 2022, 81, 8259–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larmuseau, C.; Cornelis, J.; Lancieri, L.; Desmet, P.; Depaepe, F. Multimodal learning analytics to investigate cognitive load during online problem solving. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2020, 51, 1548–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Meneses, L.J.; Kruger, J.-L.; Doherty, S. Validating theta power as an objective measure of cognitive load in educational video. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2019, 68, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spüler, M.; Walter, C.; Rosenstiel, W.; Gerjets, P.; Moeller, K.; Klein, E. EEG-based prediction of cognitive workload induced by arithmetic: A step towards online adaptation in numerical learning. ZDM 2016, 48, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Arpaia, P.; Frosolone, M.; Improta, G.; Moccaldi, N.; Pollastro, A. EEG-based measurement system for monitoring student engagement in learning 4.0. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedher, A.B.; Jraidi, I.; Frasson, C. Tracking Students’ Mental Engagement Using EEG Signals during an Interaction with a Virtual Learning Environment. J. Intell. Learn. Syst. Appl. 2019, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inventado, P.S.; Legaspi, R.; Suarez, M.; Numao, M. Predicting Student Emotions Resulting from Appraisal of Its Feedback; Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning; Asia-Pacific Society for Computers in Education: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2011; Volume 6, pp. 107–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ghergulescu, I.; Muntean, C.H. A Novel Sensor-Based Methodology for Learner's Motivation Analysis in Game-Based Learning. Interact. Comput. 2014, 26, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijeira-Díaz, H.J.; Drachsler, H.; Järvelä, S.; Kirschner, P.A. Sympathetic arousal commonalities and arousal contagion during collaborative learning: How attuned are triad members? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 92, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.T.; Picard, R.W. Advancing Neuroscience through Wearable Devices. Neuron 2020, 108, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Di Florio, A.; Babiloni, F. The Dry Revolution: Evaluation of Three Different EEG Dry Electrode Types in Terms of Signal Spectral Features, Mental States Classification and Usability. Sensors 2019, 19, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikenfeld, J.; Jajack, A.; Rogers, J.; Gutruf, P.; Tian, L.; Pan, T.; Li, R.; Khine, M.; Kim, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Wearable sensors: Modalities, challenges, and prospects. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciaraffa, N.; Di Flumeri, G.; Germano, D.; Giorgi, A.; Di Florio, A.; Borghini, G.; Vozzi, A.; Ronca, V.; Babiloni, F.; Aricò, P. Evaluation of a New Lightweight EEG Technology for Translational Applications of Passive Brain-Computer Interfaces. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 901387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Di Flumeri, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Babiloni, F. Passive BCI beyond the lab: Current trends and future directions. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 08TR02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vozzi, A.; Ronca, V.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Cherubino, P.; Trettel, A.; Babiloni, F.; Di Flumeri, G. The Sample Size Matters: To What Extent the Participant Reduction Affects the Outcomes of a Neuroscientific Research. A Case-Study in Neuromarketing Field. Sensors 2021, 21, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acabchuk, R.L.; Simon, M.A.; Low, S.; Brisson, J.M.; Johnson, B.T. Measuring Meditation Progress with a Consumer-Grade EEG Device: Caution from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Mindfulness 2020, 12, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przegalinska, A.; Ciechanowski, L.; Magnuski, M.; Gloor, P. Muse Headband: Measuring Tool or a Collaborative Gadget? In Collaborative Innovation Networks; Grippa, F., Leitão, J., Gluesing, J., Riopelle, K., Gloor, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, G.; Coles, M.G.H.; Donchin, E. A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1983, 55, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, R.; Barry, R. Removal of ocular artifact from the EEG: A review. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2000, 30, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Arico, P.; Borghini, G.; Colosimo, A.; Babiloni, F. A new regression-based method for the eye blinks artifacts correction in the EEG signal, without using any EOG channel. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 3187–3190. [Google Scholar]
- McIntire, L.K.; McKinley, R.A.; Goodyear, C.; McIntire, J.P. Detection of vigilance performance using eye blinks. Appl. Ergon. 2014, 45, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A Real-Time QRS Detection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramshur, J.T. Design, Evaluation, and Application of Heart Rate Variability Analysis Software (HRVAS); University of Memphis: Memphis, TN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ruf, T. The Lomb-Scargle Periodogram in Biological Rhythm Research: Analysis of Incomplete and Unequally Spaced Time-Series. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 1999, 30, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, G.D.; Tarassenko, L. Quantifying Errors in Spectral Estimates of HRV Due to Beat Replacement and Resampling. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Őri, Z.; Monir, G.; Weiss, J.; Sayhouni, X.; Singer, D.H. Heart Rate Variability. Cardiol. Clin. 1992, 10, 499–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, C.O.; Morris, P.E.; Richler, J.J. Effect size estimates: Current use, calculations, and interpretation. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2012, 141, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghini, G.; Astolfi, L.; Vecchiato, G.; Mattia, D.; Babiloni, F. Measuring neurophysiological signals in aircraft pilots and car drivers for the assessment of mental workload, fatigue and drowsiness. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 44, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Ronca, V.; Giorgi, A.; Vozzi, A.; Aricò, P.; Sciaraffa, N.; Zeng, H.; Dai, G.; Kong, W.; Babiloni, F.; et al. EEG-Based Index for Timely Detecting User’s Drowsiness Occurrence in Automotive Applications. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daza, R.; DeAlcala, D.; Morales, A.; Tolosana, R.; Cobos, R.; Fierrez, J. ALEBk: Feasibility Study of Attention Level Estimation via Blink Detection applied to e-Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.09165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettivel, N.; Jeyaratnam, N.; Ravindran, V.; Sumathipala, S.; Amarakecrthi, S. System for Detecting Student Attention Pertaining and Alerting. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Information Technology Research (ICITR), Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 5–7 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, H.D.; Corfield, D.R.; Chandler, M.P.; Mathias, C.J.; Dolan, R.J. Cerebral correlates of autonomic cardiovascular arousal: A functional neuroimaging investigation in humans. J. Physiol. 2000, 523, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, T.C.; Wilson, G.F. A comparison of heart rate, eye activity, EEG and subjective measures of pilot mental workload during flight. Aviat Space Environ. Med 1998, 69, 360–367. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Yadav, R.; Yung, I.; Zajdel, D.P.; Oken, B.S. Sensitivity to mental effort and test—retest reliability of heart rate variability measures in healthy seniors. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocua, A.C.L.; Gonzalez, J.P.C.; Jimenez, I.A.C.; Acevedo, J.S.G.; Marcolin, F.; Vezzetti, E. Assessment of Cognitive Student Engagement Using Heart Rate Data in Distance Learning during COVID-19. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, K.N.; Tiettmeyer, J.M.; Chuprinko, B.C.; Jordan, S.; Grove, N.P. Measuring Load on Working Memory: The Use of Heart Rate as a Means of Measuring Chemistry Students’ Cognitive Load. J. Chem. Educ. 2014, 91, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, D.K.; Krieg, P.A. Student engagement, assessed using heart rate, shows no reset following active learning sessions in lectures. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scavone, A.; Kadziolka, M.J.; Miller, C.J. State and Trait Mindfulness as Predictors of Skin Conductance Response to Stress. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2020, 45, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosebrock, L.E.; Hoxha, D.; Norris, C.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Gollan, J.K. Skin Conductance and Subjective Arousal in Anxiety, Depression, and Comorbidity. Psychophysiology 2017, 31, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, G.; Bandini, A.; Orlandi, S.; Di Flumeri, G.; Arico, P.; Sciaraffa, N.; Ronca, V.; Bonelli, S.; Ragosta, M.; Tomasello, P.; et al. Stress Assessment by Combining Neurophysiological Signals and Radio Communications of Air Traffic Controllers. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, T.; Wells, J.; Boisvert, D.L.; Lewis, R.; Cooke, E.M.; Woeckener, M.; Kavish, N. Skin conductance, heart rate and aggressive behavior type. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 141, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, M.A. Psychophysiologic Stress Responsivity in Type A and B Female College Students and Community Women. Psychophysiology 1989, 26, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangaroska, K.; Giannakos, M.N. Learning Analytics for Learning Design: A Systematic Literature Review of Analytics-Driven Design to Enhance Learning. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2018, 12, 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blikstein, P. Multimodal learning analytics. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge, Leuven, Belgium, 8–13 April 2013; pp. 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simonetti, I.; Tamborra, L.; Giorgi, A.; Ronca, V.; Vozzi, A.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Trettel, A.; Babiloni, F.; et al. Neurophysiological Evaluation of Students’ Experience during Remote and Face-to-Face Lessons: A Case Study at Driving School. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010095
Simonetti I, Tamborra L, Giorgi A, Ronca V, Vozzi A, Aricò P, Borghini G, Sciaraffa N, Trettel A, Babiloni F, et al. Neurophysiological Evaluation of Students’ Experience during Remote and Face-to-Face Lessons: A Case Study at Driving School. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimonetti, Ilaria, Luca Tamborra, Andrea Giorgi, Vincenzo Ronca, Alessia Vozzi, Pietro Aricò, Gianluca Borghini, Nicolina Sciaraffa, Arianna Trettel, Fabio Babiloni, and et al. 2023. "Neurophysiological Evaluation of Students’ Experience during Remote and Face-to-Face Lessons: A Case Study at Driving School" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010095
APA StyleSimonetti, I., Tamborra, L., Giorgi, A., Ronca, V., Vozzi, A., Aricò, P., Borghini, G., Sciaraffa, N., Trettel, A., Babiloni, F., Picardi, M., & Di Flumeri, G. (2023). Neurophysiological Evaluation of Students’ Experience during Remote and Face-to-Face Lessons: A Case Study at Driving School. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010095









