Abnormalities of EEG Functional Connectivity and Effective Connectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
Highlights
- Our findings indicated that patients with ASD exhibited local hyper-connectivity of brain regions in functional connectivity and a significant decrease in effective connectivity across hemispheres.
- These resting-state EEG connectivity abnormalities may help to find biomarkers of ASD.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
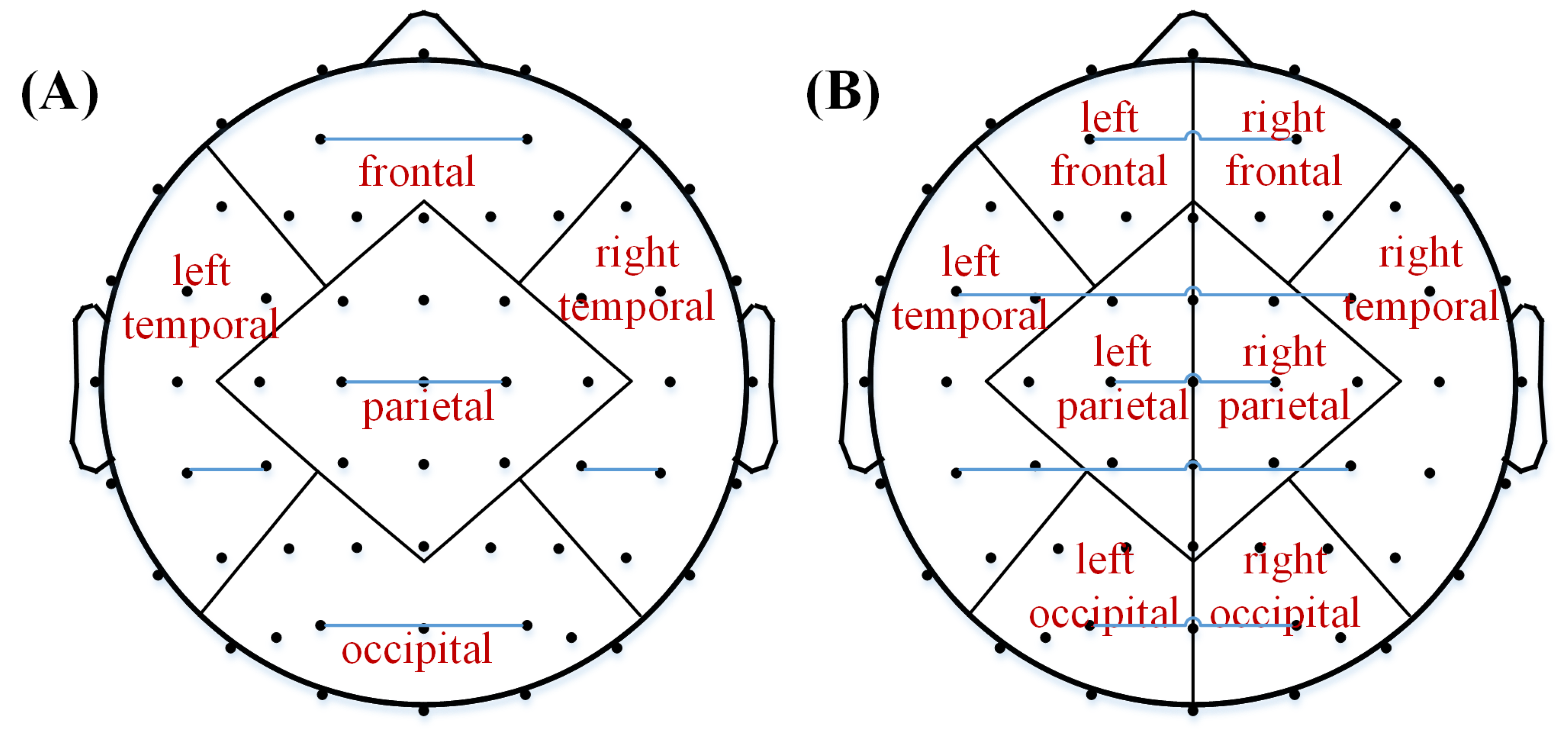
2.4. Functional Connectivity
2.5. Effective Connectivity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
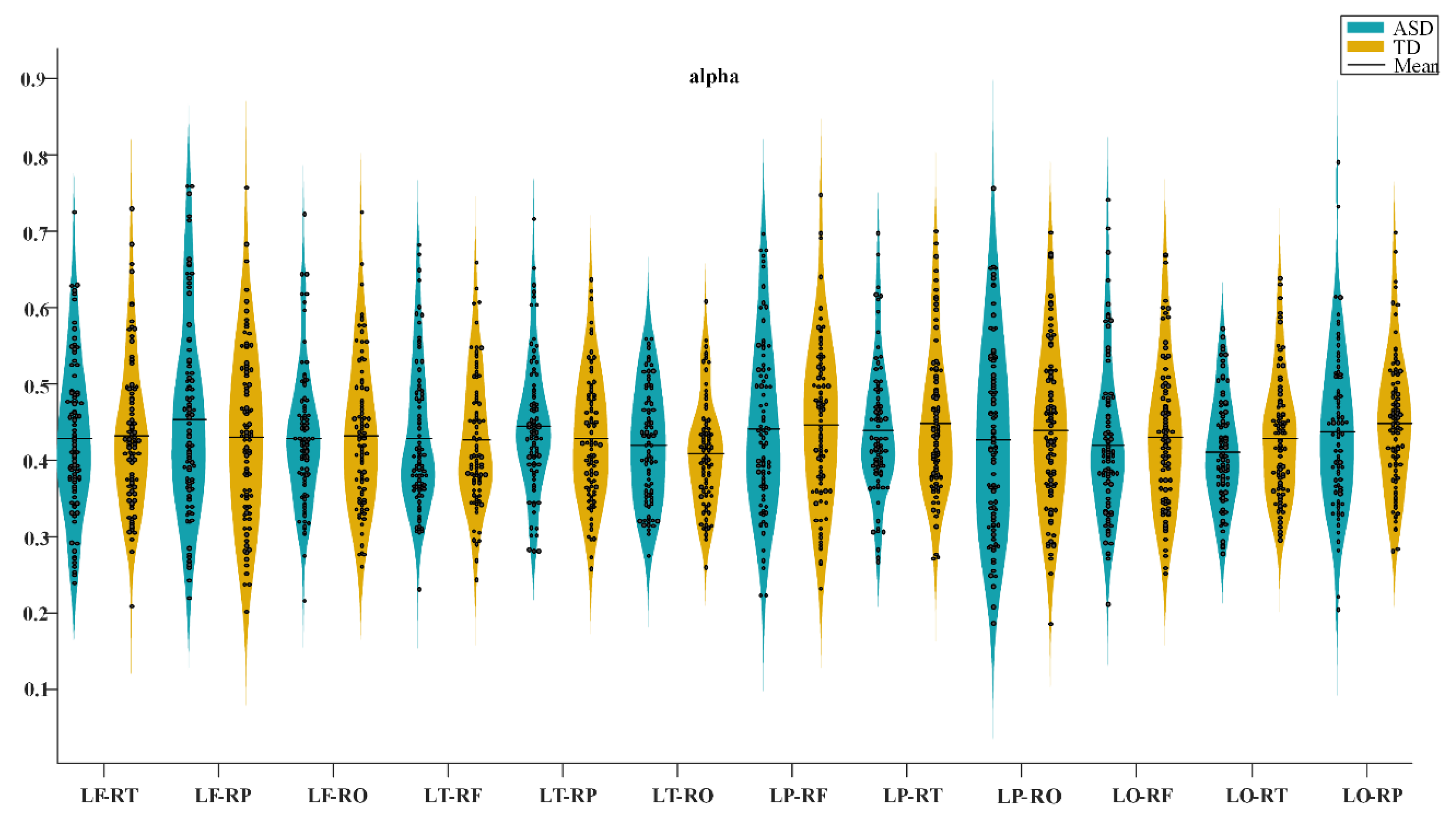
3.1. Functional Connectivity Differences in Two Groups
3.2. Effective Connectivity Differences between the Two Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Functional Connectivity Differences between the ASD and TD Groups
4.2. Analysis of Effective Connectivity Differences between the ASD and TD Groups
5. Limitations of This Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roehr, B. American Psychiatric Association explains DSM-5. BMJ 2013, 346, f3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.; Lee, J.; Chiu, S.; Charm, J.; So, W.Y.; Yuen, F.P.; Kwok, C.; Tsoi, J.; Lin, Y.; Zee, B. A machine learning approach for retinal images analysis as an objective screening method for children with autism spectrum disorder. Eclinicalmedicine 2020, 28, 100588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, P.; Baumeister, S.; Mason, L.; Chatham, C.H.; Holiga, S.; Dukart, J.; Jones, E.J.H.; Banaschewski, T.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Bölte, S.; et al. Resting state EEG power spectrum and functional connectivity in autism: A cross-sectional analysis. Mol. Autism 2022, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.J.; de Miranda, D.M.; Albuquerque, M.R.; Indredavik, M.S.; Evensen, K.A.I.; Van Lieshout, R.; Saigal, S.; Taylor, H.G.; Raikkonen, K.; Kajantie, E.; et al. Psychiatric disorders in individuals born very preterm / very low-birth weight: An individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis. Eclinicalmedicine 2021, 42, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.J.; Gu, H.; Gerig, G.; Elison, J.T.; Styner, M.; Gouttard, S.; Botteron, K.N.; Dager, S.R.; Dawson, G.; Estes, A.M.; et al. Differences in White Matter Fiber Tract Development Present From 6 to 24 Months in Infants With Autism. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.-T.; Ni, D.; Thung, K.-H.; Shi, F.; Wee, C.-Y.; Jin, Y.; Shen, D. Identification of Infants at High-Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Multiparameter Multiscale White Matter Connectivity Networks. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 4880–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, B. The elusive concept of brain connectivity. Neuroimage 2003, 19, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Onge, E.; Al-Sharif, N.; Girard, G.; Theaud, G.; Descoteaux, M. Cortical Surfaces Integration with Tractography for Structural Connectivity Analysis. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.M.Y.; Chan, M.-C.; Lai, O.L.-H.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Han, Y.M.Y. Abnormal Prefrontal Functional Connectivity Is Associated with Inflexible Information Processing in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): An fNIRS Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharan, A.L.; Bowden, S.C.; Lai, A.; Peterson, A.D.; Cheung, M.W.-L.; Woldman, W.; D’Souza, W.J. Source data from a systematic review and meta-analysis of EEG and MEG studies investigating functional connectivity in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Data Brief 2021, 39, 107665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, X.; Wei, H.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Erkoyuncu, J.A.; Sarrigiannis, P.G. Brain functional and effective connectivity based on electroencephalography recordings: A review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 43, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, F.; La Porta, F.; Petrone, V.; Battaglia, S.; Orlandi, S.; Ippolito, G.; Romei, V.; Piperno, R.; Lullini, G. Accuracy of EEG Biomarkers in the Detection of Clinical Outcome in Disorders of Consciousness after Severe Acquired Brain Injury: Preliminary Results of a Pilot Study Using a Machine Learning Approach. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, A.; Andrade, A.; Churches, O.; Wagner, A.P.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Ring, H. Task-related functional connectivity in autism spectrum conditions: An EEG study using wavelet transform coherence. Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, F.H.; Shankardass, A.; McAnulty, G.B.; Als, H. The relationship of Asperger’s syndrome to autism: A preliminary EEG coherence study. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, J.; Martien, K.; Grieve, P.; Stark, R.; Herbert, M. Reduced functional connectivity in visual evoked potentials in children with autism spectrum disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiker, I.; David, N.; Schneider, T.R.; Nolte, G.; Schöttle, D.; Engel, A.K. Perceptual Integration Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorders Are Associated with Reduced Interhemispheric Gamma-Band Coherence. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 16352–16361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barttfeld, P.; Wicker, B.; Cukier, S.; Navarta, S.; Lew, S.; Sigman, M. A big-world network in ASD: Dynamical connectivity analysis reflects a deficit in long-range connections and an excess of short-range connections. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Chan, A.S.; Sze, S.L.; Cheung, M.-C.; Wong, C.-K.; Lam, J.M.; Poon, P.M. Altered immune function associated with disordered neural connectivity and executive dysfunctions: A neurophysiological study on children with autism spectrum disorders. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2013, 7, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, Y.; Bloy, L.; Shankar, V.; Edgar, J.C.; Roberts, T.P.L.; Schultz, R.T.; Verma, R. Functionally Driven Brain Networks Using Multi-layer Graph Clustering. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention - MICCAI; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 17, pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coben, R.; Clarke, A.R.; Hudspeth, W.; Barry, R.J. EEG power and coherence in autistic spectrum disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Domínguez, L.; Stieben, J.; Pérez Velázquez, J.L.; Shanker, S. The imaginary part of coherency in autism: Differences in cortical functional connectivity in preschool children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, M.; Kemner, C.; de Reus, M.A.; Collin, G.; Snijders, T.M.; Hofman, D.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Stam, C.J.; Heuvel, M.P.V.D. Disrupted Functional Brain Networks in Autistic Toddlers. Brain Connect. 2013, 3, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righi, G.; Tierney, A.L.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Functional Connectivity in the First Year of Life in Infants at Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder: An EEG Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keehn, B.; Vogel-Farley, V.; Tager-Flusberg, H.; Nelson, C.A. Atypical Hemispheric Specialization for Faces in Infants at Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2015, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Qu, H.; Chen, A.; Du, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W. Alteration of Effective Connectivity in the Default Mode Network of Autism After an Intervention. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 796437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jin, H.; Feng, J.; Qin, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, B.; et al. Attenuated effective connectivity of large-scale brain networks in children with autism spectrum disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 987248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, E.T.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, W.; Gilson, M.; Deco, G.; Feng, J. Effective connectivity in autism. Autism Res. 2019, 13, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, F.; Jaloli, M.; Coben, R.; Nasrabadi, A.M. Estimating brain effective connectivity from EEG signals of patients with autism disorder and healthy individuals by reducing volume conduction effect. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2021, 16, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Velázquez, J.L.; Galán, R.F. Information gain in the brain’s resting state: A new perspective on autism. Front. Neuroinform. 2013, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Am. Psychiatr. Assoc. 2013, 21, 591–643.
- Kang, J.-N.; Song, J.-J.; Casanova, M.F.; Sokhadze, E.M.; Li, X.-L. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on children with low-function autism. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, C.J.; Nolte, G.; Daffertshofer, A. Phase lag index: Assessment of functional connectivity from multi channel EEG and MEG with diminished bias from common sources. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinck, M.; Oostenveld, R.; Van Wingerden, M.; Battaglia, F.; Pennartz, C.M. An improved index of phase-synchronization for electrophysiological data in the presence of volume-conduction, noise and sample-size bias. Neuroimage 2011, 55, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating Causal Relations by Econometric Models and Cross-spectral Methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.F. The neuropathology of autism. Brain Pathol. 2007, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucewicz, M.T.; Cimbalnik, J.; Matsumoto, J.Y.; Brinkmann, B.H.; Bower, M.R.; Vasoli, V.; Sulc, V.; Meyer, F.; Marsh, W.R.; Stead, S.M.; et al. High frequency oscillations are associated with cognitive processing in human recognition memory. Brain 2014, 137, 2231–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, J.J.; Thiagarajan, T.C. EEG Frequency Bands in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review of Resting State Studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Son, S.J.; Morris, J.A.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, C.; Rah, J.-C. Comprehensive Analysis of Long-Range Connectivity from and to the Posterior Parietal Cortex of the Mouse. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 31, 356–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopell, N.; Ermentrout, G.B.; Whittington, M.A.; Traub, R.D. Gamma rhythms and beta rhythms have different synchronization properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1867–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Shi, Y.; Huang, L.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhan, L.; Ding, Q.; et al. The Atypical Effective Connectivity of Right Temporoparietal Junction in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Multi-Site Study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 927556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TD (n = 90) | ASD (n = 89) | Differences between Two Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 5.09 ± 2.27 | 5.17 ± 1.89 | t = −0.497, p = 0.638 |
| Male/Female | 76/14 | 71/18 | , p = 0.359 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, X.; Fan, X.; Zhong, Y.; Casanova, M.F.; Sokhadze, E.M.; Li, X.; Kang, J. Abnormalities of EEG Functional Connectivity and Effective Connectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010130
Geng X, Fan X, Zhong Y, Casanova MF, Sokhadze EM, Li X, Kang J. Abnormalities of EEG Functional Connectivity and Effective Connectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010130
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Xinling, Xiwang Fan, Yiwen Zhong, Manuel F. Casanova, Estate M. Sokhadze, Xiaoli Li, and Jiannan Kang. 2023. "Abnormalities of EEG Functional Connectivity and Effective Connectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010130
APA StyleGeng, X., Fan, X., Zhong, Y., Casanova, M. F., Sokhadze, E. M., Li, X., & Kang, J. (2023). Abnormalities of EEG Functional Connectivity and Effective Connectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010130






