Abstract
IQ has been found to correlate with alcohol consumption, with a higher IQ being a risk for alcohol misuse. Furthermore, recent research has shown that the microstructure of the arcuate fasciculus is associated with IQ. This study therefore aimed to examine the association between the arcuate fasciculus microstructure, IQ, and alcohol dependence risk. In this study, we performed probabilistic tractography between Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas in the left and right hemispheres to examine the association of the arcuate fasciculus’s integrity with IQ and alcohol dependence risk, using DTI data from 344 individuals. Data regarding IQ were obtained from the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II). Alcohol substance involvement (SI) score was derived using the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Quick Screen and was used as an index for alcohol dependence risk. Both the left arcuate fasciculus and IQ were found to have a significant association with alcohol dependence risk. A mediation analysis revealed that this association between the left arcuate fasciculus microstructure and an alcohol dependence risk was mediated by IQ. It is suggested that the left arcuate fasciculus microstructure is associated with IQ which is associated with alcohol dependence risk. While alcohol consumption is known to be robustly toxic to the brain, the left arcuate fasciculus shows exceptional characteristics in which its microstructure integrity is positively associated with an alcohol dependence risk through higher IQ. Clinical implications are discussed.
1. Introduction
The microstructure of the arcuate fasciculus (AF) was recently shown to be associated with IQ (Ikuta et al., 2019). The arcuate fasciculus bridges two distant structures: Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe and Broca’s area in the frontal lobe. This structure has been shown to be highly elaborate in humans as compared to non-human primates [1]. Therefore, the AF may represent intelligence unique to humans.
IQ has been found to be associated with alcohol use. For example, a study of 99 countries showed that a higher IQ predicts a greater level of alcohol consumption [2]. A longitudinal study over 37 years has shown that a higher IQ in adolescence is a risk for alcohol-related hospitalization [3]. IQ has also been shown to be associated with a preference for wine over other beverages [4]. These results indicate that higher IQ is a risk for alcohol misuse.
At the same time, it should be noted that the toxicity of alcohol consumption has been well established, and that the influence of this toxicity is known to be relatively widespread across the brain [5]. Additionally, higher levels of alcohol consumption and alcoholism have been found to result in a reduction of cortical gray matter [6,7,8] and white matter [9,10,11], as well as in subcortical structures extending to the brain stem and cerebellum [12,13]. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies found reduced fractional anisotropy in alcoholism, suggesting damaged myelination in the white matter [14,15]. Such research demonstrates that alcohol misuse has negative effects on the brain.
Despite the fact that alcohol has been found to cause harm to the brain, associations have been independently found between both the AF & IQ as well as between alcohol use and IQ. In this study, we aimed to examine this triangular relationship between the AF, alcohol use, and IQ. Using diffusion tensor imaging data and probabilistic tractography of the AF, we examined whether the AF microstructure is associated with alcohol addiction as well as IQ.
2. Materials and Methods
The AF data used in this study followed our previous study [16]. Briefly, the Nathan Kline Institute-Rockland Sample (NKI-RS: http://fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/enhanced/) [17] data were obtained from the Collaborative Informatics and Neuroimaging Suite (https://coins.trendscenter.org/). From the database, data were obtained from both the Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST), which is a self-administered questionnaire, and the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II) including a full-scale IQ composite score. The alcohol substance involvement (SI) score was used as an index of alcohol dependence risk.
The DTI series consisted of 128 volumes of noncolinear directions as well as nine volumes without diffusion weighting (TR = 2400 ms, TE = 85 ms, matrix = 128 × 128, FOV = 256 mm, b ≈ 1500 (except the first volume b = 0)). Each volume consisted of 64 contiguous 2-mm slices with 2mm3 isotropic resolution.
Image data were processed using the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain Software Library (FSL version 4.1.8; Oxford, UK; http://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl). Eddy-current-induced distortions were corrected and head-motion displacements were corrected through affine registration of the 128 diffusion volumes to the first b = 0 volume using FSL’s Linear Registration Tool. The b-vector table (i.e., gradient directions) for each participant was then adjusted according to the rotation parameters of these corrections. Non-brain tissue was removed using FSL’s Brain Extraction Tool. Fractional anisotropy (FA), an index of white matter integrity, was calculated at each voxel of the brain by fitting a diffusion tensor model to the raw diffusion data along with using weighted least squares in FSL’s Diffusion Toolbox.
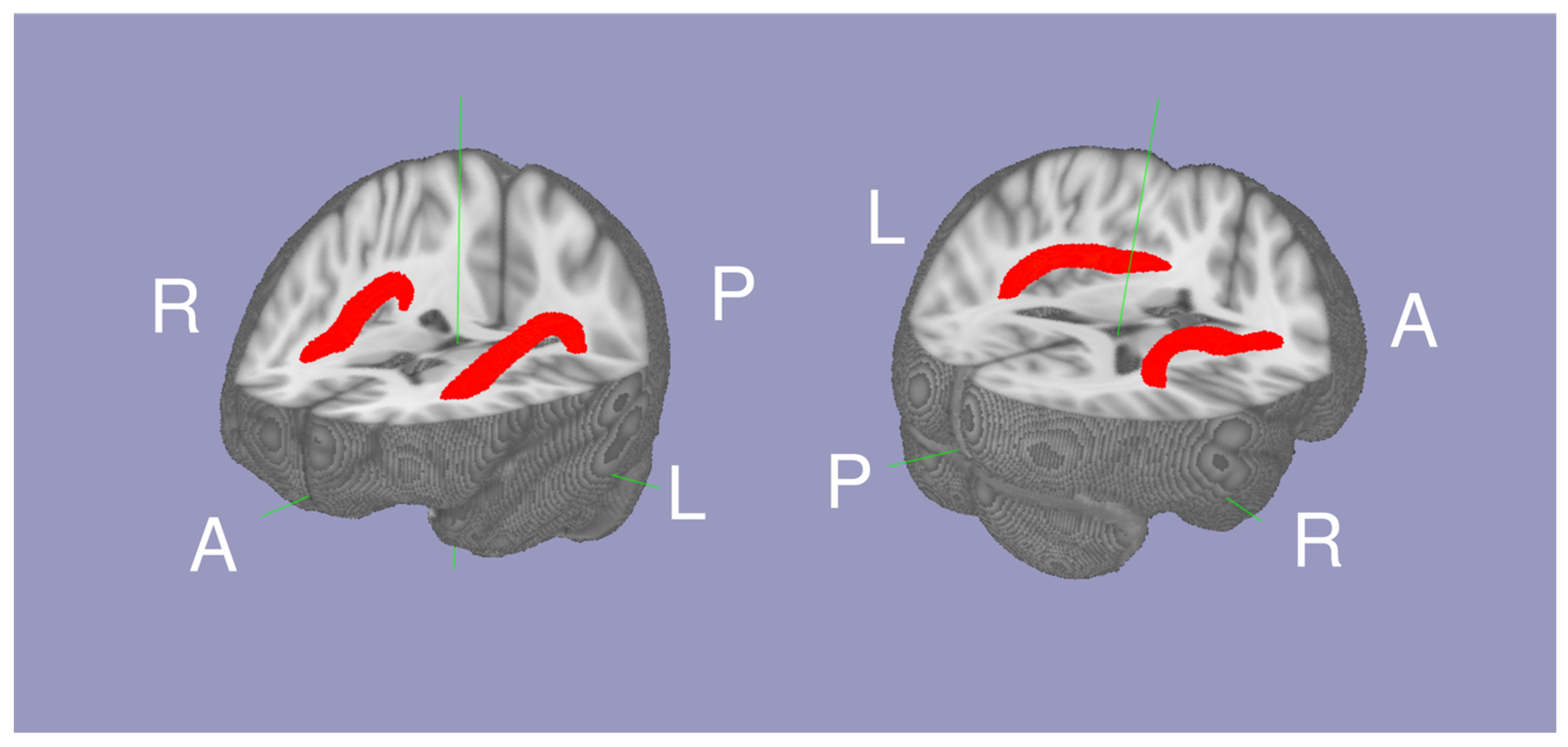
The white matter tract between Broca’s and Wernicke’s area was isolated as the AF using probabilistic tractography as described in our previous study [16]. The script to conduct probabilistic tractography is also available online (https://olemiss.edu/projects/dnl/codes.html). Briefly, tractography was conducted within the white matter of each hemisphere above MNI Z = 0 by having two seed regions: Broca’s area (the pars triangularis and pars opercularis) and Wernicke’s area (the posterior superior temporal gyrus and planum temporale) defined in the the HarvardOxford cortical atlas [18]. The mean FA within the left and right AF (thresholded at a normalized probability value of 0.04) was calculated for each individual. In 334 individuals, (42.99 ± 22.78 range 16 to 85 years old, 113 males and 221 females; Table 1), the Arcuate Fasciculus FA (AFFA), IQ, and National Institute of Drug Abuse addiction data were available. The mean AF is shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Subject Demographics.
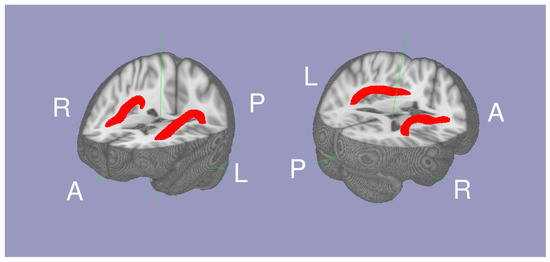
Figure 1.
The mean probabilistic tractography of the arcuate fasciculi (red) between Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area white matter.
Statistical analyses were conducted independently for left and right AFFA. A multiple linear regression was calculated to predict alcohol dependence risk based on AFFA and age. Another linear regression was tested to predict alcohol dependence risk based on IQ. In order to test whether the relationship between the AFFA and alcohol dependence risk was mediated by IQ, a mediation analysis was conducted using the MBESS package [19] on R 3.6.1. In the mediation analysis, the residual from a regression to predict AFFA based on age was tested to examine the age-independent association between AFFA and alcohol dependence risk.
3. Results
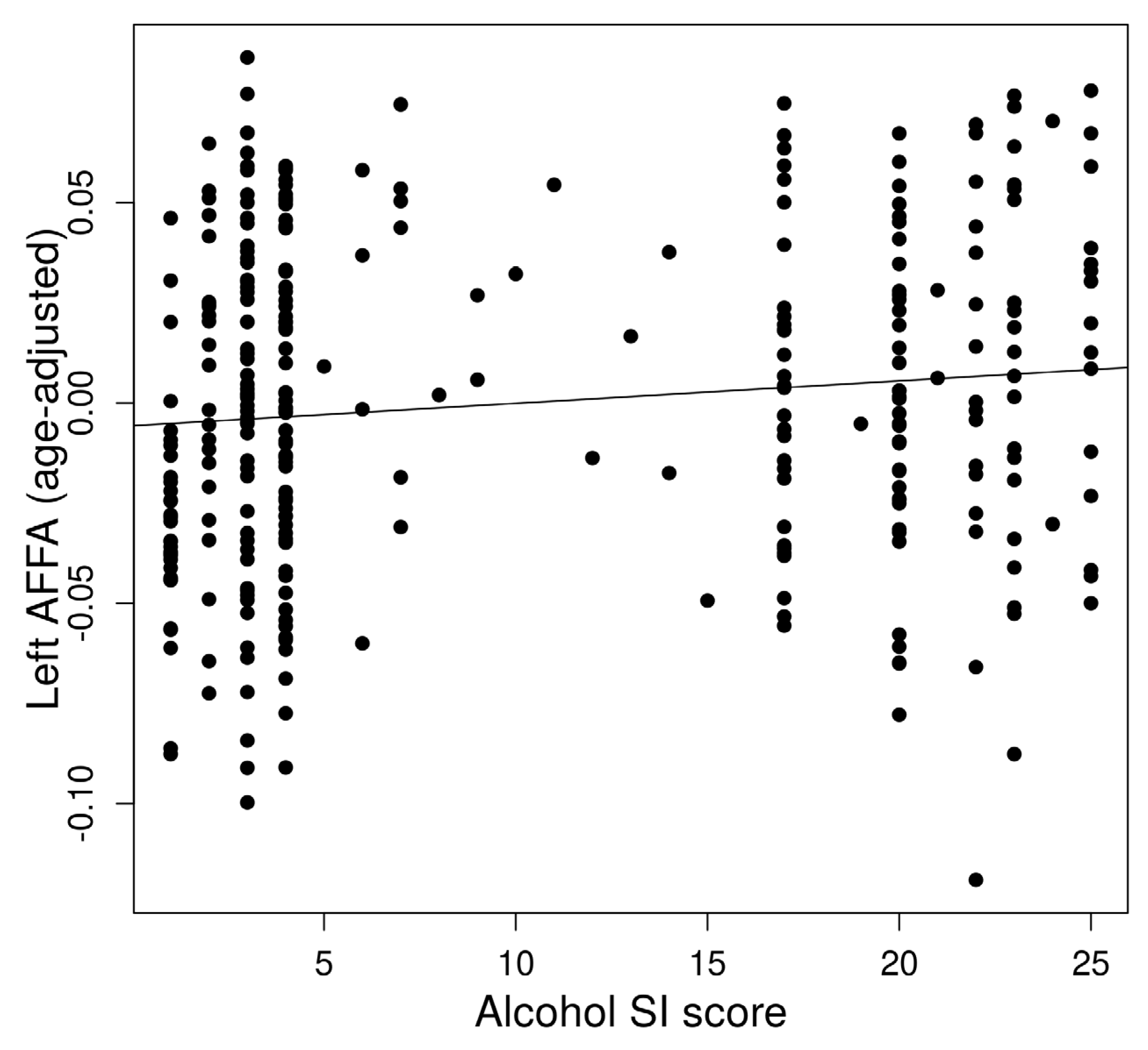
The left AFFA was associated with alcohol dependence risk (Figure 2). In a multiple regression to predict alcohol dependence risk based on AFFA and age, a significant regression equation was found (F(2,321) = 5.813, p = 0.0033) with an R2 of 0.29 in the left AFFA. The predicted alcohol dependence risk is −3.18 + 26.02 (left AFFA) + 0.067 (age). The left AFFA (p = 0.028) and age (p = 0.0044) significantly predicted alcohol dependence risk. However, the right AFFA did not show a significant association with alcohol dependence risk.
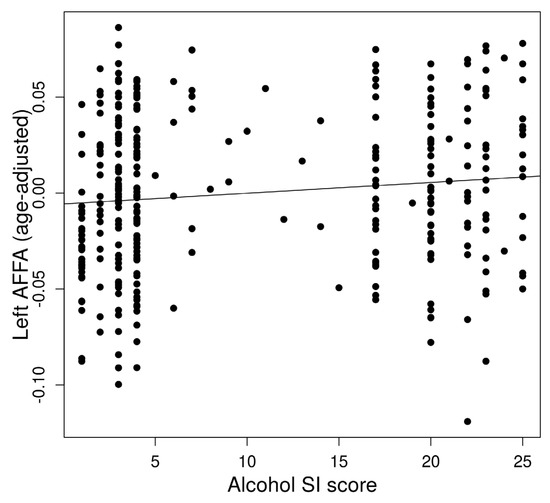
Figure 2.
Association between alcohol dependence risk and left Arcuate Fasciculus FA (AFFA).
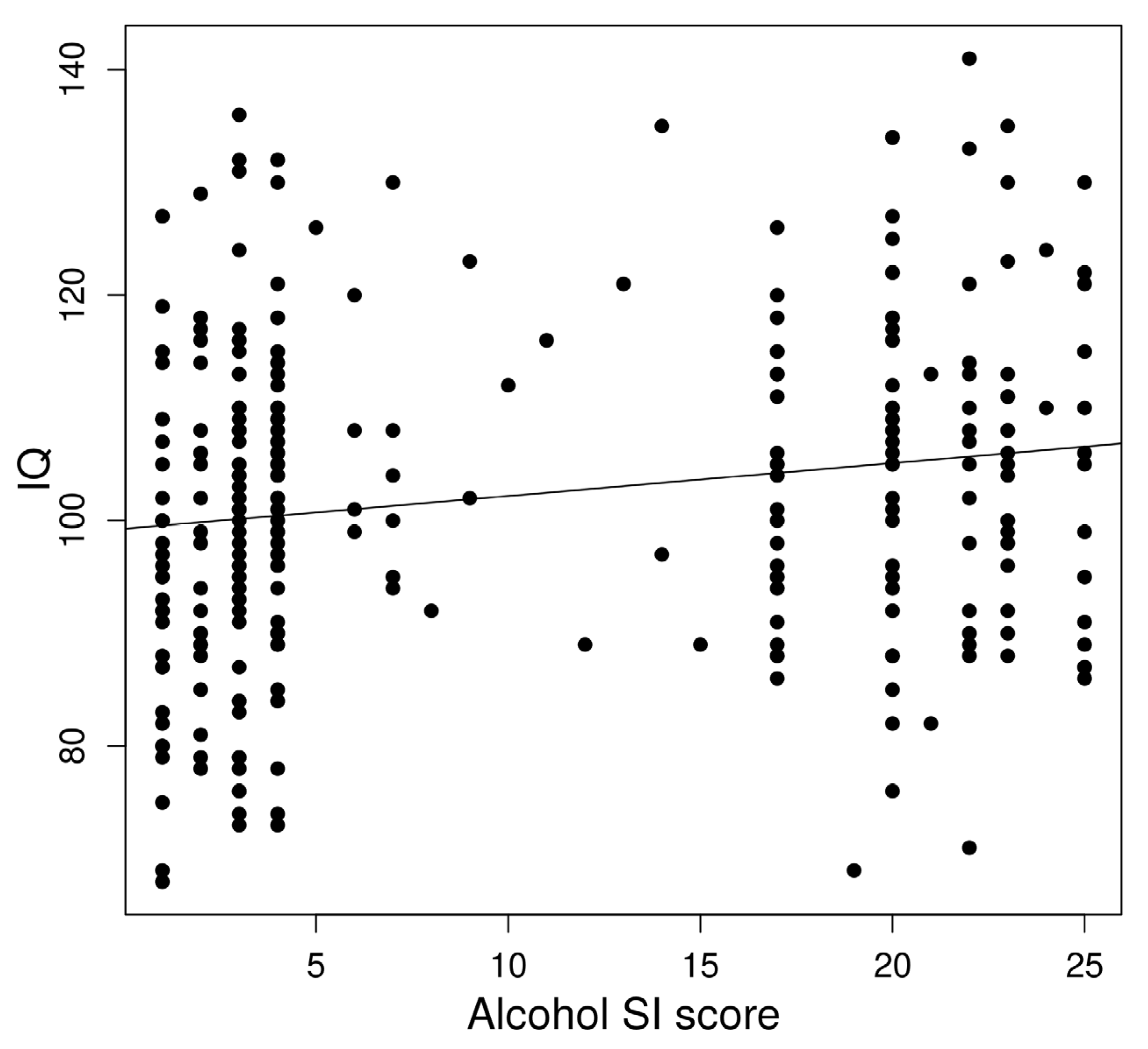
In a linear regression to predict IQ based on age-adjusted left AFFA, a significant regression equation was found (F(1,322) = 8.53, p = 0.0037) with an R2 of 0.023 (Figure 3).
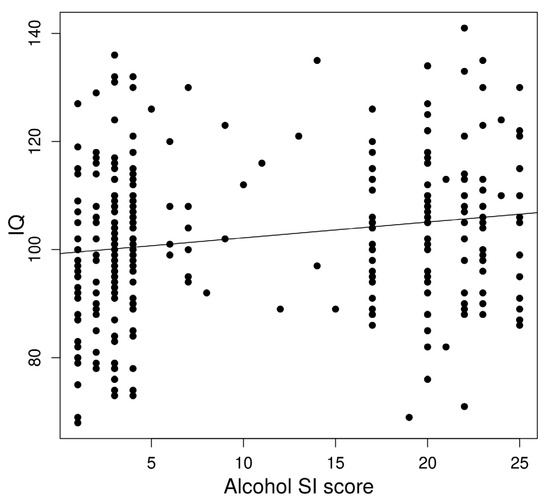
Figure 3.
Association between alcohol dependence risk and IQ.
IQ significantly predicted alcohol dependence risk. In a linear regression, a significant regression equation was found (F(1,322) = 10.76, p = 0.0012) with an R2 of 0.29.
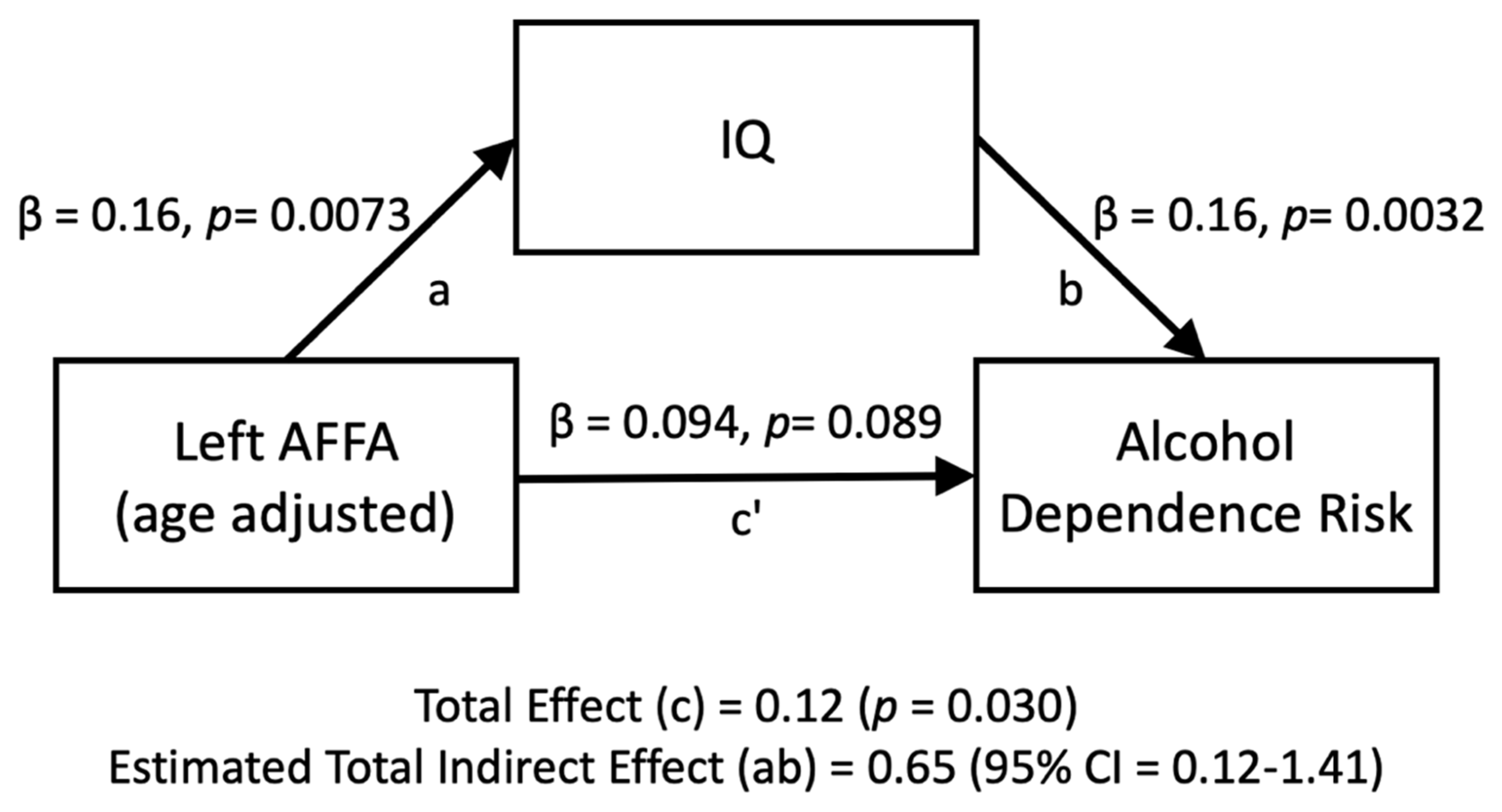
The relationship between the left AFFA and alcohol dependence risk was mediated by IQ (Figure 4). The standardized regression coefficient between the left AFFA and IQ was statistically significant, as was the standardized regression coefficient between IQ and alcohol dependence risk. The standardized indirect effect was (0.16) × (0.16) = 0.026. We tested the significance of this indirect effect using bootstrapping procedures. Unstandardized indirect effects and partially standardized indirect effects were computed for each of 10,000 bootstrapped samples, and the 95% confidence interval was computed by determining the indirect effects at the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles. The bootstrapped partially standardized indirect effect was 0.65, and the 95% confidence interval ranged from 0.12 to 1.41. Thus, the indirect effect was statistically significant.
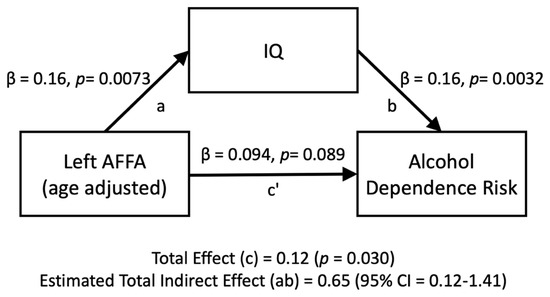
Figure 4.
Mediation analyses for the left AFFA (age-adjusted) on the number of alcohol dependence risk, directly (c’) and indirectly through IQ (ab).
4. Discussion
This study examined the association between the arcuate fasciculus and alcohol dependence risk. Despite findings that alcohol consumption is harmful to the brain, alcohol dependence risk was positively associated with the microstructure of the left arcuate fasciculus (left AFFA). It is known that the arcuate fasciculus is positively associated with IQ and that IQ is positively associated with increased consumption of alcohol. We found that IQ mediates the positive association between the left AFFA and alcohol dependence risk. This suggests that stronger AF connectivity increases the risk for alcohol dependence through higher IQ.
Our current finding is primarily inconsistent with previous studies. The microstructure of the left AFFA showed a positive association with alcohol dependence risk. Previously, brain white matter microstructure was shown to be negatively associated with alcohol consumption [14,15], and consistent with the well-known toxicity of alcohol to the whole brain [5]. The left arcuate fasciculus in this study showed exceptional characteristics in which its microstructure and was positively associated with alcohol dependence risk.
Although the left AFFA microstructure showed a positive association with alcohol dependence risk, the mediation analysis revealed that this positive association was mediated by higher IQ, rather than being a direct association. The positive association between IQ and alcohol consumption is well established [2,3,4]. Stronger left AFFA is associated with alcohol dependence risk through greater IQ.
Our results need to be carefully interpreted since we have no direct knowledge about causality though it may appear that greater left AFFA causes higher IQ which causes alcohol dependence risk. Instead, we are detecting a tendency for alcohol dependence risk to be more common with greater left AFFA through its tendency for higher IQ.
Age may have a ineligible influence on the association between AFFA and alcohol dependence risk. In order to test the significance of the effect of age, additional multiple linear regressions were calculated to predict alcohol dependence risk based on left AFFA and age, for the group at the median age (45 years old) and younger, as well as for the older group. The younger group maintained a significant association but the association was not significant in the older group. It suggests the possibility that the influence of left AFFA is more profound in a younger population.
The current study was motivated by anecdotal reports from clinicians that the vast majority of clients who struggle with Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) are quite intelligent, which contrasts with the current understanding that heavy alcohol use often negatively affects cognitive functioning. For instance, Ioime et al. [20] found functional deficits in verbal memory, visuospatial abilities, and executive functions. Widely accepted clinical implications of the harm to white matter by alcohol misuse are increased impulsive behavior and impairments in the response inhibition [21]. In worst-case situations, chronic alcohol use can result in Wernicke’s encephalopathy, Korsakoff’s syndrome, and alcohol-related dementia, all of which are permanent forms of brain damage [22]. From a neuroimaging standpoint, brain white matter microstructure was previously shown to be negatively associated with alcohol consumption [14,15].
The current study’s findings are intriguing in light of Mulhauser and colleagues’ findings that the language domain was less affected by heavy alcohol users than other domains [22]. Of further interest is the effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) [23] in treating AUD [24,25]. A central component of ACT is a focus on language/“mind” as a major source of clinical distress [26]. If the AFFA, heavily influential in language, is indeed associated with AUD through greater IQ, then this information has the potential for assisting the design of clinical interventions.
Clinicians need to know how cognitive functioning is affected to plan clinical interventions. It has been said that “the literature is unanimous in considering that cognitive impairment reduces effectiveness of psychological treatments” [20] and that a better understanding of cognitive functioning is necessary to plan individualized treatment. While many researchers state the need for assessing both deficits and strengths, most studies focus only on cognitive impairment [20,22]. However, there is a long-standing clinical awareness of the importance of knowing what is not impaired (client strengths) when engaging in assessment and treatment planning. Indeed, studies have shown that clinicians who are aware of the neuropsychological status of their clients not only provide better care but also have better treatment outcomes [22,27,28]. The importance of awareness of clients’ cognitive strengths is also emerging in other fields such as the treatment of psychosis [29].
5. Conclusions
The current study’s findings revealed that although the left AFFA microstructure showed a positive association with alcohol dependence risk, this positive association is mediated by higher IQ, rather than the left AFFA itself being directly associated with alcohol dependence risk. If the AFFA, heavily influential in language and human sentience, is indeed associated with AUD through greater IQ, this information has the potential to be quite useful when designing clinical interventions. A possibility is suggested that assessment of the left AF may provide helpful information in the future treatment of AUD.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.I. and A.K.F.; statistical analysis, T.I.; writing—review and editing, P.B.K. and A.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data is available on the NKI-RS website. The tractography code will be available at https://olemiss.edu/projects/dnl/.
Acknowledgments
Principal support for the enhanced NKI-RS project is provided by the NIMH BRAINS R01MH094639-01 (PI Milham). Funding for key personnel was also provided in part by the New York State Office of Mental Health and Research Foundation for Mental Hygiene. Funding for the decompression and augmentation of administrative and phenotypic protocols was provided by a grant from the Child Mind Institute (1FDN2012-1). Additional personnel support was provided by the Center for the Developing Brain at the Child Mind Institute, as well as NIMH R01MH081218, R01MH083246, and R21MH084126. Project support was also provided by the NKI Center for Advanced Brain Imaging (CABI), the Brain Research Foundation, and the Stavros Niarchos Foundation. Image preprocessing was performed using the supercomputer cluster at the Mississippi Center for Supercomputing Research and partly funded by the National Science Foundation (EPS-0903787).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rilling, J.K.; Glasser, M.F.; Preuss, T.M.; Ma, X.; Zhao, T.; Hu, X.; Behrens, T.E.J. The Evolution of the Arcuate Fasciculus Revealed with Comparative DTI. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belasen, A.; Hafer, R.W. IQ and Alcohol Consumption: International Data. Intelligence 2013, 41, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölund, S.; Allebeck, P.; Hemmingsson, T. Intelligence Quotient (IQ) in Adolescence and Later Risk of Alcohol-Related Hospital Admissions and Deaths—37-Year Follow-up of Swedish Conscripts. Addiction 2012, 107, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, L.H.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; Grønbæk, M. Intelligence in Relation to Later Beverage Preference and Alcohol Intake. Addiction 2005, 100, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, L.K.; Fennema-Notestine, C.; Elman, J.A.; Eyler, L.T.; Franz, C.E.; Hagler, D.J.; Hatton, S.N.; Lyons, M.J.; Panizzon, M.S.; Dale, A.M.; et al. Alcohol Intake and Brain White Matter in Middle Aged Men: Microscopic and Macroscopic Differences. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 18, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fein, G.; Sclafani, V.D.; Cardenas, V.A.; Goldmann, H.; Tolou-Shams, M.; Meyerhoff, D.J. Cortical Gray Matter Loss in Treatment-Naïve Alcohol Dependent Individuals. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernigan, T.L.; Butters, N.; DiTraglia, G.; Schafer, K.; Smith, T.; Irwin, M.; Grant, I.; Schuckit, M.; Cermak, L.S. Reduced Cerebral Grey Matter Observed in Alcoholics Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1991, 15, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V.; Rosenbloom, M.J.; Mathalon, D.H.; Lim, K.O. A Controlled Study of Cortical Gray Matter and Ventricular Changes in Alcoholic Men Over a 5-Year Interval. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Yuzuriha, T.; Kinukawa, N.; Murakawa, R.; Takashima, Y.; Uchino, A.; Ibayashi, S.; Iida, M.; Yao, H.; Hirano, M. Alcohol Intake and Quantitative MRI Findings among Community Dwelling Japanese Subjects. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 278, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazdzinski, S.; Durazzo, T.C.; Studholme, C.; Song, E.; Banys, P.; Meyerhoff, D.J. Quantitative Brain MRI in Alcohol Dependence: Preliminary Evidence for Effects of Concurrent Chronic Cigarette Smoking on Regional Brain Volumes. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Lim, K.O.; Zipursky, R.B.; Mathalon, D.H.; Rosenbloom, M.J.; Lane, B.; Ha, C.N.; Sullivan, E.V. Brain Gray and White Matter Volume Loss Accelerates with Aging in Chronic Alcoholics: A Quantitative MRI Study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1992, 16, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Deshmukh, A.; Desmond, J.E.; Lim, K.O.; Pfefferbaum, A. Cerebellar Volume Decline in Normal Aging, Alcoholism, and Korsakoff’s Syndrome: Relation to Ataxia. Neuropsychology 2000, 14, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Deshmukh, A.; Rosa, E.D.; Rosenbloom, M.J.; Pfefferbaum, A. Striatal and Forebrain Nuclei Volumes: Contribution to Motor Function and Working Memory Deficits in Alcoholism. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, S.; Bach, P.; Pérez-Cervera, L.; Cosa-Linan, A.; Weil, G.; Vollstädt-Klein, S.; Hermann, D.; Kiefer, F.; Kirsch, P.; Ciccocioppo, R.; et al. Microstructural White Matter Alterations in Men with Alcohol Use Disorder and Rats with Excessive Alcohol Consumption During Early Abstinence. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V. Disruption of Brain White Matter Microstructure by Excessive Intracellular and Extracellular Fluid in Alcoholism: Evidence from Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, T.; Gollnick, H.M.; Rutledge, A.N. Age Associated Decline in the Arcuate Fasciculus and IQ. Brain Imaging Behav. 2020, 14, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooner, K.; Colcombe, S.; Tobe, R.; Mennes, M.; Benedict, M.; Moreno, A.; Panek, L.; Brown, S.; Zavitz, S.; Li, Q.; et al. The NKI-Rockland Sample: A Model for Accelerating the Pace of Discovery Science in Psychiatry. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An Automated Labeling System for Subdividing the Human Cerebral Cortex on MRI Scans into Gyral Based Regions of Interest. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K. MBESS: The MBESS R Package 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MBESS/index.html.
- Ioime, L.; Guglielmo, R.; Affini, G.F.; Quatrale, M.; Martinotti, G.; Callea, A.; Savi, E.; Janiri, L. Neuropsychological Performance in Alcohol Dependent Patients: A One-Year Longitudinal Study. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, C.B.; Leritz, E.C.; Salat, D.H.; Lindemer, E.; Maksimovskiy, A.L.; Shepel, J.; Williams, V.; Venne, J.R.; Milberg, W.P.; McGlinchey, R.E. Widespread Effects of Alcohol on White Matter Microstructure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhauser, K.; Weinstock, J.; Ruppert, P.; Benware, J. Changes in Neuropsychological Status during the Initial Phase of Abstinence in Alcohol Use Disorder: Neurocognitive Impairment and Implications for Clinical Care. Subst. Use Misuse 2018, 53, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.C.; Strosahl, K.D.; Wilson, K.G. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy, Second Edition: The Process and Practice of Mindful Change; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-60918-962-4. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, C.; Zettle, R. Treating Inpatients with Comorbid Depression and Alcohol Use Disorders: A Comparison of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy Versus Treatment as Usual. Psychol. Rec. 2010, 59, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.B.; An, W.; Levin, M.E.; Twohig, M.P. An Initial Meta-Analysis of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Treating Substance Use Disorders. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 155, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R. ACT Made Simple: An Easy-to-Read Primer on Acceptance and Commitment Therapy; New Harbinger Publications: Oakland, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-57224-705-5. [Google Scholar]
- Grohman, K.; Fals-Stewart, W. Computer-Assisted Cognitive Rehabilitation with Substance-Abusing Patients: Effects on Treatment Response. J. Cogn. Rehabil. 2003, 21, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, M.E.; Voelbel, G.T.; Buckman, J.F.; Labouvie, E.W.; Barry, D. Short-Term Neuropsychological Recovery in Clients with Substance Use Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allott, K.; Steele, P.; Boyer, F.; de Winter, A.; Bryce, S.; Alvarez-Jimenez, M.; Phillips, L. Cognitive Strengths-Based Assessment and Intervention in First-Episode Psychosis: A Complementary Approach to Addressing Functional Recovery? Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 79, 101871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).