Heart Rate Variability Analyses in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
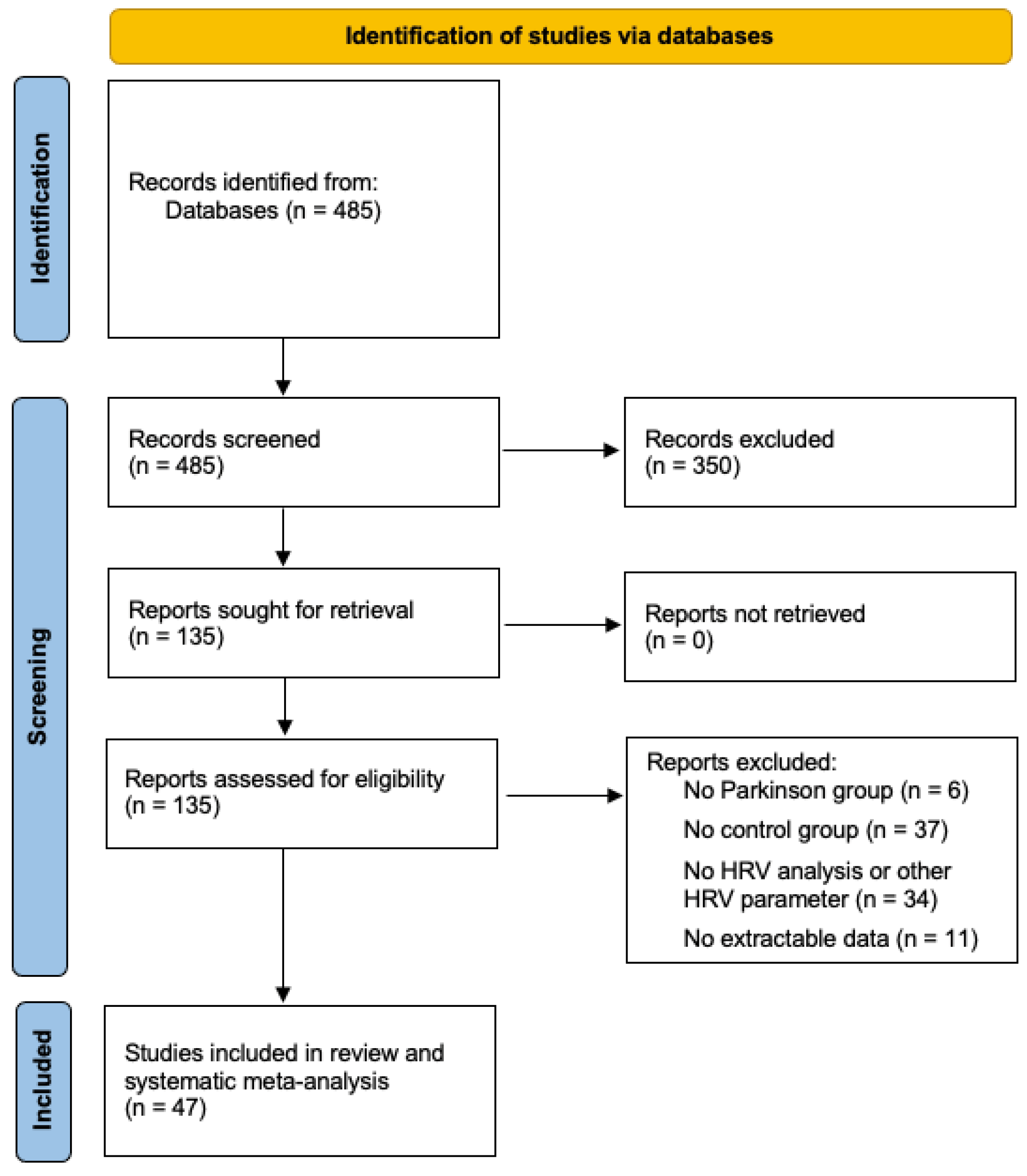
3.1. Selection and Study Population
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Random-Effects Meta-Analyses
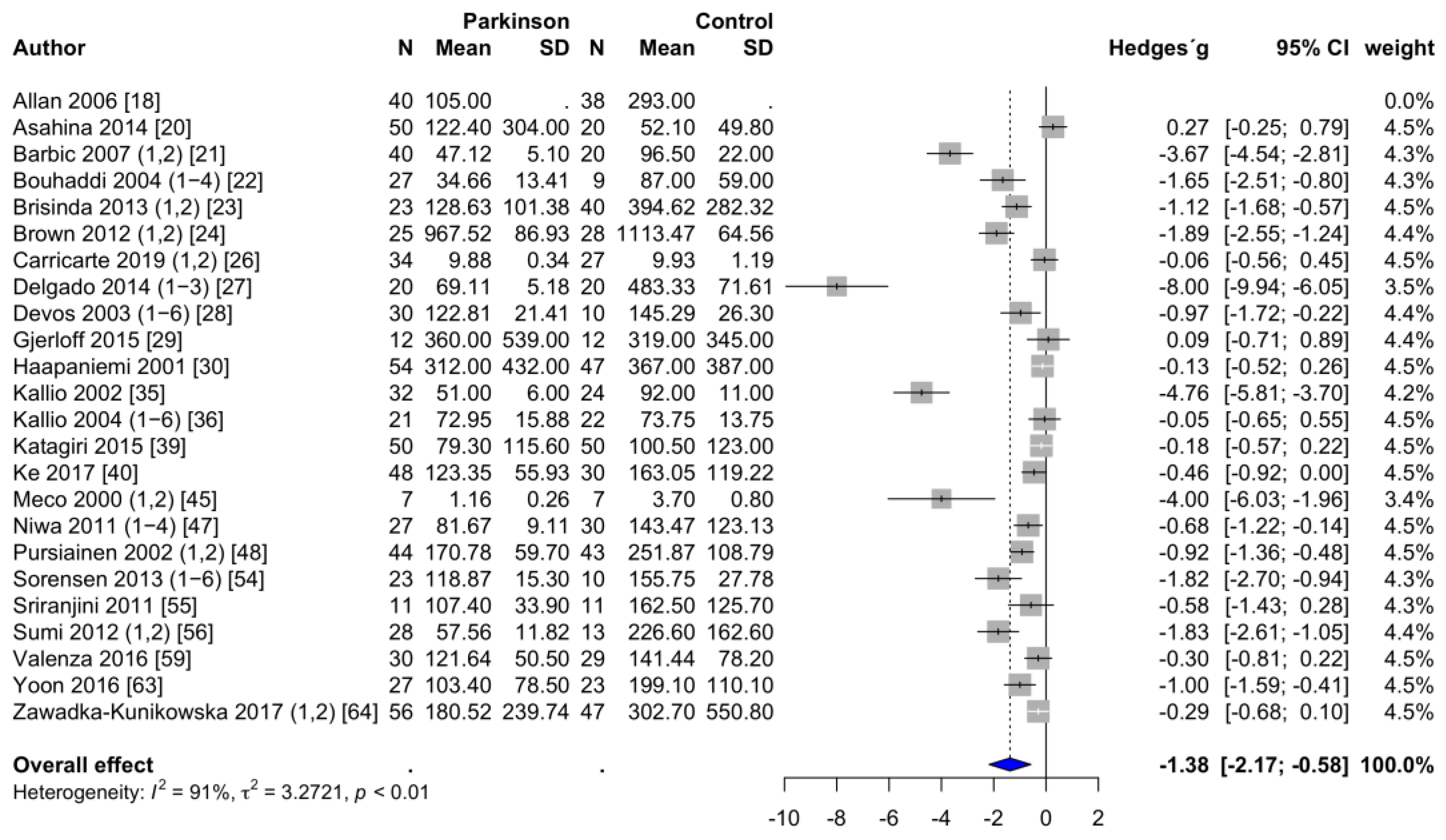
3.3.1. Frequency-Domain Parameters of HRV
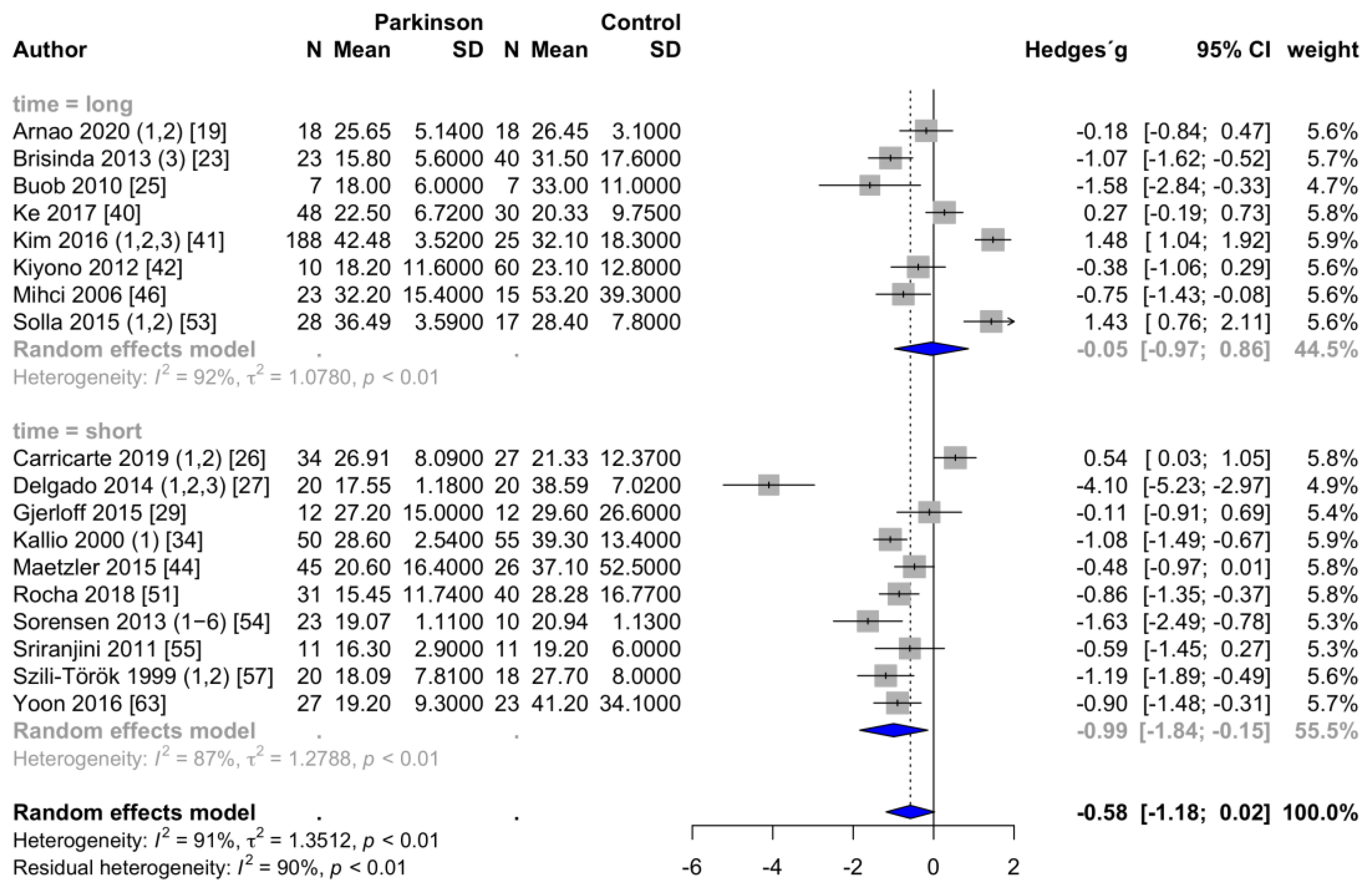
3.3.2. Time-Domain Parameters of HRV
3.4. Between-Study Heterogeneity
3.5. Subgroup Analyses
3.6. Meta-Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Study | Group | HRV Analysis | Measurement | N | Age (y) | N | Age (y) | Disease | Hoehn/Yahr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Duration | (PD) | (PD) | (HC) | (HC) | Duration (y) | Stage | ||
| Allan (2006) [18] | PD patients with dementia | HFms2 | short | 40 | 72 | 38 | 76 | 5.0 | na |
| Arnao (2020), 1 [19] | ambulatory setting, daytime | RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 18 | 56 | 18 | 56 | 5.0 | na |
| Arnao (2020), 2 [19] | ambulatory setting, nighttime | RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 18 | 56 | 18 | 56 | 5.0 | na |
| Asahina (2014) [20] | PD patients, early untreated | HFms2 | short | 50 | 64 | 20 | 64 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| Barbic (2007), 1 [21] | PD patients without orthostatic hypotension | HFms2, HFnu | short | 19 | 66 | 20 | 64 | 7.5 | 2.7 |
| Barbic (2007), 2 [21] | PD patients with orthostatic hypotension | HFms2, HFnu | short | 21 | 69 | 20 | 64 | 10.5 | 2.8 |
| Bouhaddi (2004), 1 [22] | involvement of L-dopa therapy, newly diagnosed without L-dopa | HFms2 | short | 9 | 61 | 9 | 63 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| Bouhaddi (2004), 2 [22] | involvement of L-dopa therapy, newly diagnosed with L-dopa | HFms2 | short | 9 | 61 | 9 | 63 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| Bouhaddi (2004), 3 [22] | involvement of L-dopa therapy, long-term treated without L-dopa | HFms2 | short | 18 | 69 | 9 | 63 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| Bouhaddi (2004), 4 [22] | involvement of L-dopa therapy, long-term treated with L-dopa | HFms2 | short | 18 | 69 | 9 | 63 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| Brisinda (2013), 1 [23] | PD patients, frequency analysis, during sleep | HFms2, HFnu | short | 23 | 63 | 40 | na | na | 2.0 |
| Brisinda (2013), 2 [23] | PD patients, frequency analysis, daily activity | HFms2, HFnu | short | 23 | 63 | 40 | na | na | 2.0 |
| Brisinda (2013), 3 [23] | PD patients, time-domain analysis | RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 23 | 63 | 40 | na | na | 2.0 |
| Brown (2012), 1 [24] | resting condition, compared to older healthy controls | HFms2, HFnu | short | 25 | na | 28 | na | na | na |
| Brown (2012), 2 [24] | deep breathing, compared to older healthy controls | HFms2, HFnu | short | 25 | na | 28 | na | na | na |
| Buob (2010) [25] | early stages of PD | RMSSD | long | 7 | 50 | 7 | 50 | 4.0 | na |
| Carricarte (2019), 1 [26] | PD patients, LRRK2-associated | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD | short | 14 | 63 | 27 | 59 | 10.8 | na |
| Carricarte (2019), 2 [26] | PD patients, idiopathic | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD | short | 20 | 64 | 27 | 59 | 6.3 | na |
| Delgado (2014), 1 [27] | Mexican PD patients, supine resting | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 20 | 61 | 20 | 38 | 3.7 | na |
| Delgado (2014), 2 [27] | Mexican PD patients, active standing | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 20 | 61 | 20 | 38 | 3.7 | na |
| Delgado (2014), 3 [27] | Mexican PD patients, controlled breathing | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 20 | 61 | 20 | 38 | 3.7 | na |
| Devos (2003), 1 [28] | untreated PD patients, disease duration less than 2 years, daytime | HFms2 | long | 10 | 60 | 10 | 61 | 1.5 | na |
| Devos (2003), 2 [28] | untreated PD patients, disease duration less than 2 years, nighttime | HFms2, pNN50 | long | 10 | 60 | 10 | 61 | 1.5 | na |
| Devos (2003), 3 [28] | treated PD patients, disease duration more than 2 years, daytime | HFms2 | long | 10 | 63 | 10 | 61 | 8.0 | na |
| Devos (2003), 4 [28] | treated PD patients, disease duration more than 2 years, nighttime | HFms2, pNN50 | long | 10 | 63 | 10 | 61 | 8.0 | na |
| Devos (2003), 5 [28] | treated PD patients, advanced PD with motor complications, daytime | HFms2 | long | 10 | 62 | 10 | 61 | 8.6 | na |
| Devos (2003), 6 [28] | treated PD patients, advanced PD with motor complications, nighttime | HFms2, pNN50 | long | 10 | 62 | 10 | 61 | 8.6 | na |
| Gjerloff (2015) [29] | association with Donepezil positron emission tomography | HFms2, RMSSD | short | 12 | 64 | 12 | 62 | 5.3 | 2.2 |
| Haapaniemi (2001) [30] | ambulatory setting, 24 h | HFms2 | long | 54 | 61 | 47 | 60 | 1.7 | 1.5 # |
| Harnod (2014) [31] | association with motor symptom duration | HF (ln) * | short | 32 | 62 | 32 | na | 9.8 | 2.7 |
| Jain (2011) [32] | association with pupil measures | HF (*10−1s2/Hz) * | short | 17 | 65 | 18 | 60 | na | 1.7 |
| Jaipurkar (2018), 1 [33] | PD patients, supine resting | HFms2 * | short | 31 | 61 | 31 | 60 | 3.6 | na |
| Jaipurkar (2018), 2 [33] | PD patients, head-up tilt table test | HFms2 * | short | 31 | 61 | 31 | 60 | 3.6 | na |
| Kallio (2000), 1 [34] | PD patients, untreated | RMSSD | short | 50 | 60 | 55 | 56 | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| Kallio (2000), 2 [34] | PD patients, untreated, fast Fourier transform analysis | HFnu, pNN50 | short | 20 | na | 24 | na | na | na |
| Kallio (2002) [35] | PD patients, untreated, fast Fourier transform analysis | HFms2, HFnu | short | 32 | 58 | 24 | 54 | na | na |
| Kallio (2004), 1 [36] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, awake | HFms2, HFnu | long | 21 | 58 | 22 | 56 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Kallio (2004), 2 [36] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, REM | HFms2, HFnu | long | 21 | 58 | 22 | 56 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Kallio (2004), 3 [36] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, sleep stage 1 | HFms2, HFnu | long | 21 | 58 | 22 | 56 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Kallio (2004), 4 [36] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, sleep stage 2 | HFms2, HFnu | long | 21 | 58 | 22 | 56 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Kallio (2004), 5 [36] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, sleep stage 3 | HFms2, HFnu | long | 21 | 58 | 22 | 56 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Kallio (2004), 6 [36] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, sleep stage 4 | HFms2, HFnu | long | 21 | 58 | 22 | 56 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Kanegusuku (2017), 1 [37] | effect of progressive resistance training, PD training group | HFnu | short | 15 | 67 | 16 | 68 | 8.5 | 2.5 |
| Kanegusuku (2017), 2 [37] | effect of progressive resistance training, PD control group | HFnu | short | 12 | 63 | 16 | 68 | 9.0 | 2.4 |
| Kang (2012) [38] | association with olfactory dysfunction | HFms2 * | short | 15 | 66 | 18 | 60 | na | 1.7 |
| Katagiri (2015) [39] | association with myocardial scintigraphy | HFms2 | short | 50 | 66 | 50 | 67 | na | na |
| Ke (2017) [40] | association with sympathetic skin response | HFms2, RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 48 | 69 | 30 | 63 | 5.4 | na |
| Kim (2016), 1 [41] | PD patients, mild stage | RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 106 | 66 | 25 | 67 | 2.2 | 1.1 |
| Kim (2016), 2 [41] | PD patients, moderate stage | RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 51 | 72 | 25 | 67 | 4.5 | 2.2 |
| Kim (2016), 3 [41] | PD patients, severe stage | RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 31 | 71 | 25 | 67 | 5.8 | 3.2 |
| Kiyono (2012) [42] | ambulatory setting, daytime | HF (ln) *, RMSSD | long | 10 | 69 | 60 | 69 | 10.7 | 3.6 |
| Liou (2013), 1 [43] | association with electroencephalography, quiet breathing | HFnu | short | 26 | 67 | 23 | 65 | 2.6 | 1.3 |
| Liou (2013), 2 [43] | association with electroencephalography, deep breathing | HFnu | short | 26 | 67 | 23 | 65 | 2.6 | 1.3 |
| Maetzler (2015) [44] | association with sympathetic skin response, metronomic breathing | HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 45 | 66 | 26 | 65 | 3.8 | 2.1 |
| Meco (2000), 1 [45] | effect of treatment with Tolcapone (before treatment), daytime | HFms2 | long | 7 | 70 | 7 | na | 14.1 | 2.1 |
| Meco (2000), 2 [45] | effect of treatment with Tolcapone (before treatment), nighttime | HFms2 | long | 7 | 70 | 7 | na | 14.1 | 2.1 |
| Mihci (2006) [46] | ambulatory setting, 24 h | RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 23 | 66 | 15 | 67 | 5.5 | 2.5 # |
| Niwa (2011), 1 [47] | PD patients, early stage, daytime | HFms2 | long | 9 | 71 | 30 | 69 | 4.8 | na |
| Niwa (2011), 2 [47] | PD patients, early stage, nighttime | HFms2 | long | 9 | 71 | 30 | 69 | 4.8 | na |
| Niwa (2011), 3 [47] | PD patients, advanced stage, daytime | HFms2 | long | 18 | 69 | 30 | 69 | 7.1 | na |
| Niwa (2011), 4 [47] | PD patients, advanced stage, nighttime | HFms2 | long | 18 | 69 | 30 | 69 | 7.1 | na |
| Pursiainen (2002), 1 [48] | PD patients, untreated, daytime | HFms2 | long | 44 | 63 | 43 | 60 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| Pursiainen (2002), 2 [48] | PD patients, untreated, nighttime | HFms2 | long | 44 | 63 | 43 | 60 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| Pyatigorskaya (2016), 1 [49] | association with magnetic resonance imaging, slow wave sleep | HFnu | long | 47 | 62 | 23 | 60 | na | 2.0 |
| Pyatigorskaya (2016), 2 [49] | association with magnetic resonance imaging, REM sleep | HFnu | long | 47 | 62 | 23 | 60 | na | 2.0 |
| Rocchi (2018) [50] | comparison to second control group (REM sleep behavior disorder) | HFnu | short | 17 | 68 | 12 | 69 | 2.3 | na |
| Rocha (2018) [51] | effect of game therapy training (before training) | HFnu, RMSSD | short | 31 | 78 | 40 | 72 | 8.0 | 2.0 |
| Sauvageot (2011), 1 [52] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, Non REM | HFnu, pNN50 | long | 35 | 66 | 35 | 65 | 6.6 | 2.4 |
| Sauvageot (2011), 2 [52] | association with nocturnal sleep patterns, REM | HFnu, pNN50 | long | 35 | 66 | 35 | 65 | 6.6 | 2.4 |
| Solla (2015), 1 [53] | PD patients, tremor dominant subtype | HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 17 | 63 | 17 | 65 | 6.0 | 2.1 |
| Solla (2015), 2 [53] | PD patients, akinetic-rigid subtype | HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | long | 11 | 66 | 17 | 65 | 7.9 | 2.7 |
| Sorensen (2013), 1 [54] | association with rapid-eye movement sleep behavior, awake | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 10 | 63 | 10 | 59 | na | 1.4 |
| Sorensen (2013), 2 [54] | association without rapid-eye movement sleep behavior, awake | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 13 | 61 | 10 | 59 | na | 0.9 |
| Sorensen (2013), 3 [54] | association with rapid-eye movement sleep behavior, Non REM | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 10 | 63 | 10 | 59 | na | 1.4 |
| Sorensen (2013), 4 [54] | association without rapid-eye movement sleep behavior, Non REM | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 13 | 61 | 10 | 59 | na | 0.9 |
| Sorensen (2013), 5 [54] | association with rapid-eye movement sleep behavior, REM | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 10 | 63 | 10 | 59 | na | 1.4 |
| Sorensen (2013), 6 [54] | association without rapid-eye movement sleep behavior, REM | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 13 | 61 | 10 | 59 | na | 0.9 |
| Sriranjini (2011) [55] | effect of a single dose L-dopa (before intake) | HFms2, HFnu, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 11 | 57 | 11 | 55 | 4.1 | 2.1 |
| Sumi (2012), 1 [56] | effect of deep brain stimulation (before stimulation), off medication | HFms2 | short | 28 | 62 | 13 | 58 | 22.0 | 3.9 |
| Sumi (2012), 2 [56] | effect of deep brain stimulation (before stimulation), on medication | HFms2 | short | 28 | 62 | 13 | 58 | 22.0 | 2.4 |
| Szili-Török (1999), 1 [57] | association with baroreflex sensitivity, normal | HF (ms/Hz) *, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 12 | 64 | 18 | 65 | na | 2.0 |
| Szili-Török (1999), 2 [57] | association with baroreflex sensitivity, impaired | HF (ms/Hz) *, RMSSD, pNN50 | short | 8 | 67 | 18 | 65 | na | 2.1 |
| Trachani (2012) [58] | effect of deep brain stimulation (before stimulation) | HFms2 *, HFnu * | short | 24 | 62 | 24 | na | 12.8 | 3.1 |
| Valenza (2016) [59] | computational assessment of heartbeat dynamics | HFms2 | short | 30 | 67 | 29 | 61 | na | na |
| Visanji (2017), 1 [60] | PD patients, LRRK2-associated | HF (log) *, RMSSD * | short | 20 | 64 | 32 | 59 | 11.5 | na |
| Visanji (2017), 2 [60] | PD patients, idiopathic | HF (log) *, RMSSD * | short | 26 | 64 | 32 | 59 | 6.2 | na |
| Walter (2018) [61] | association with vagus nerve atrophy | RMSSD * | short | 20 | 73 | 20 | 70 | 10.1 | na |
| Weise (2015) [62] | association with auricular branch of vagus nerve stimulation | HF (ln) * | short | 50 | 64 | 50 | 64 | 6.4 | 2.3 |
| Yoon (2016) [63] | PD patients, tremor dominant subtype, drug naiv | HFms2, RMSSD | short | 27 | 64 | 23 | 63 | 1.6 | na |
| Zawadka-Kunikowska (2017), 1 [64] | association with peripheral vascular resistance, vasodilation reaction | HFms2 | short | 15 | 67 | 47 | 66 | 9.0 | 2.9 |
| Zawadka-Kunikowska (2017), 2 [64] | association with peripheral vascular resistance, vasoconstriction reaction | HFms2 | short | 41 | 69 | 47 | 66 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
References
- Antony, P.M.; Diederich, N.J.; Kruger, R.; Balling, R. The hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5981–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titova, N.; Qamar, M.A.; Chaudhuri, K.R. The Nonmotor Features of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2017, 132, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, E.J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Ciesielski-Jones, A.J.; Justice, M.A.; Cousins, D.S.; Peddada, S. Meta-analyses on prevalence of selected Parkinson’s nonmotor symptoms before and after diagnosis. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C.H.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. Parkinson’s disease: A dual-hit hypothesis. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwiertz, A.; Spiegel, J.; Dillmann, U.; Grundmann, D.; Burmann, J.; Fassbender, K.; Schafer, K.H.; Unger, M.M. Fecal markers of intestinal inflammation and intestinal permeability are elevated in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 50, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Shannon, K.M.; Kordower, J.H.; Voigt, R.M.; Shaikh, M.; Jaglin, J.A.; Estes, J.D.; Dodiya, H.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Rub, U.; Gai, W.P.; Del Tredici, K. Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: Possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J. Neural Transm. 2003, 110, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ask, T.F.; Lugo, R.G.; Sutterlin, S. The Neuro-Immuno-Senescence Integrative Model (NISIM) on the Negative Association Between Parasympathetic Activity and Cellular Senescence. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.S. Dysautonomia in Parkinson disease. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zis, P.; Erro, R.; Walton, C.C.; Sauerbier, A.; Chaudhuri, K.R. The range and nature of non-motor symptoms in drug-naive Parkinson’s disease patients: A state-of-the-art systematic review. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2015, 1, 15013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology; The North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karemaker, J.M. Counterpoint: Respiratory sinus arrhythmia is due to the baroreflex mechanism. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2009, 106, 1742–1743; discussion 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, B.R.; Cevallos, M.; Altman, D.G.; Rutjes, A.W.; Egger, M. Uses and misuses of the STROBE statement: Bibliographic study. BMJ Open 2011, 1, e000048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrer, M.; Cuijpers, P.; Furukawa, T.A.; Ebert, D. Doing Meta-Analysis in R: A Hands-on Guide. Available online: https://bookdown.org/MathiasHarrer/Doing_Meta_Analysis_in_R/ (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Allan, L.M.; Ballard, C.G.; Allen, J.; Murray, A.; Davidson, A.W.; McKeith, I.G.; Kenny, R.A. Autonomic dysfunction in dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, V.; Cinturino, A.; Mastrilli, S.; Butta, C.; Maida, C.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Aridon, P.; D’Amelio, M. Impaired circadian heart rate variability in Parkinson’s disease: A time-domain analysis in ambulatory setting. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahina, M.; Mathias, C.J.; Katagiri, A.; Low, D.A.; Vichayanrat, E.; Fujinuma, Y.; Yamanaka, Y.; Kuwabara, S. Sudomotor and cardiovascular dysfunction in patients with early untreated Parkinson’s disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2014, 4, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbic, F.; Perego, F.; Canesi, M.; Gianni, M.; Biagiotti, S.; Costantino, G.; Pezzoli, G.; Porta, A.; Malliani, A.; Furlan, R. Early abnormalities of vascular and cardiac autonomic control in Parkinson’s disease without orthostatic hypotension. Hypertension 2007, 49, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhaddi, M.; Vuillier, F.; Fortrat, J.O.; Cappelle, S.; Henriet, M.T.; Rumbach, L.; Regnard, J. Impaired cardiovascular autonomic control in newly and long-term-treated patients with Parkinson’s disease: Involvement of L-dopa therapy. Auton. Neurosci. 2004, 116, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisinda, D.; Sorbo, A.R.; Di Giacopo, R.; Venuti, A.; Bentivoglio, A.R.; Fenici, R. Cardiovascular autonomic nervous system evaluation in Parkinson disease and multiple system atrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 336, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Duma, S.; Piguet, O.; Broe, G.A.; Macefield, V.G. Cardiovascular variability in Parkinson’s disease and extrapyramidal motor slowing. Clin. Auton. Res. 2012, 22, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buob, A.; Winter, H.; Kindermann, M.; Becker, G.; Moller, J.C.; Oertel, W.H.; Bohm, M. Parasympathetic but not sympathetic cardiac dysfunction at early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2010, 99, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carricarte Naranjo, C.; Marras, C.; Visanji, N.P.; Cornforth, D.J.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, L.; Schule, B.; Goldman, S.M.; Estevez, M.; Stein, P.K.; Lang, A.E.; et al. Increased markers of cardiac vagal activity in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2-associated Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, G.; Estanol, B.; Rodriguez-Violante, M.; Martinez-Memije, R.; Infante-Vazquez, O.; Bertado-Ramirez, N. Cardiovascular variability in Mexican patients with Parkinson’s disease. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2014, 72, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devos, D.; Kroumova, M.; Bordet, R.; Vodougnon, H.; Guieu, J.D.; Libersa, C.; Destee, A. Heart rate variability and Parkinson’s disease severity. J. Neural. Transm. 2003, 110, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerloff, T.; Fedorova, T.; Knudsen, K.; Munk, O.L.; Nahimi, A.; Jacobsen, S.; Danielsen, E.H.; Terkelsen, A.J.; Hansen, J.; Pavese, N.; et al. Imaging acetylcholinesterase density in peripheral organs in Parkinson’s disease with 11C-donepezil PET. Brain 2015, 138, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapaniemi, T.H.; Pursiainen, V.; Korpelainen, J.T.; Huikuri, H.V.; Sotaniemi, K.A.; Myllyla, V.V. Ambulatory ECG and analysis of heart rate variability in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnod, D.; Wen, S.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Harnod, T. The association of heart rate variability with parkinsonian motor symptom duration. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Siegle, G.J.; Gu, C.; Moore, C.G.; Ivanco, L.S.; Jennings, J.R.; Steinhauer, S.R.; Studenski, S.; Greenamyre, J.T. Autonomic insufficiency in pupillary and cardiovascular systems in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jaipurkar, R.; Mohan, L.; Tomar, R. Autonomic cardiovascular regulation in Parkinson’s disease by head-up tilt tes-A cross-sectional study. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 8, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, M.; Haapaniemi, T.; Turkka, J.; Suominen, K.; Tolonen, U.; Sotaniemi, K.; Heikkila, V.P.; Myllyla, V. Heart rate variability in patients with untreated Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2000, 7, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, M.; Suominen, K.; Bianchi, A.M.; Makikallio, T.; Haapaniemi, T.; Astafiev, S.; Sotaniemi, K.A.; Myllya, V.V.; Tolonen, U. Comparison of heart rate variability analysis methods in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallio, M.; Suominen, K.; Haapaniemi, T.; Sotaniemi, K.; Myllyla, V.V.; Astafiev, S.; Tolonen, U. Nocturnal cardiac autonomic regulation in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Auton. Res. 2004, 14, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanegusuku, H.; Silva-Batista, C.; Pecanha, T.; Nieuwboer, A.; Silva, N.D., Jr.; Costa, L.A.; de Mello, M.T.; Piemonte, M.E.; Ugrinowitsch, C.; Forjaz, C.L. Effects of Progressive Resistance Training on Cardiovascular Autonomic Regulation in Patients With Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Kloke, J.; Jain, S. Olfactory dysfunction and parasympathetic dysautonomia in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Auton. Res. 2012, 22, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, A.; Asahina, M.; Araki, N.; Poudel, A.; Fujinuma, Y.; Yamanaka, Y.; Kuwabara, S. Myocardial (123)I-MIBG Uptake and Cardiovascular Autonomic Function in Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2015, 2015, 805351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.Q.; Shao, S.M.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Fu, F.W.; Zheng, G.Q.; Liu, C.F. Sympathetic skin response and heart rate variability in predicting autonomic disorders in patients with Parkinson disease. Medicine 2017, 96, e6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, Y.S.; Park, J.W.; An, J.Y.; Park, S.K.; Han, S.R.; Lee, K.S. Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction in Mild and Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. J. Mov. Disord. 2016, 9, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyono, K.; Hayano, J.; Kwak, S.; Watanabe, E.; Yamamoto, Y. Non-gaussianity of low frequency heart rate variability and sympathetic activation: Lack of increases in multiple system atrophy and Parkinson disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, L.M.; Ruge, D.; Chang, Y.P.; Wu, M.N.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Tsai, C.L.; Lai, C.L. Functional connectivity between lateral premotor-parietal circuits and the cardiac autonomic system in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 326, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetzler, W.; Karam, M.; Berger, M.F.; Heger, T.; Maetzler, C.; Ruediger, H.; Bronzova, J.; Lobo, P.P.; Ferreira, J.J.; Ziemssen, T.; et al. Time- and frequency-domain parameters of heart rate variability and sympathetic skin response in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neura.l Transm. 2015, 122, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meco, G.; Vanacore, N.; Locuratolo, N.; Bonifati, V.V.; Vella, C.; Giovani, A.; Tubani, L.; Baratta, L.; Mastrocola, C. Heart rate variability in Parkinson’s disease patients treated with tolcapone. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2000, 6, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihci, E.; Kardelen, F.; Dora, B.; Balkan, S. Orthostatic heart rate variability analysis in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2006, 113, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, F.; Kuriyama, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Imanishi, J. Circadian rhythm of rest activity and autonomic nervous system activity at different stages in Parkinson’s disease. Auton. Neurosci. 2011, 165, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pursiainen, V.; Haapaniemi, T.H.; Korpelainen, J.T.; Huikuri, H.V.; Sotaniemi, K.A.; Myllyla, V.V. Circadian heart rate variability in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatigorskaya, N.; Mongin, M.; Valabregue, R.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Ewenczyk, C.; Poupon, C.; Debellemaniere, E.; Vidailhet, M.; Arnulf, I.; Lehericy, S. Medulla oblongata damage and cardiac autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2016, 87, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, C.; Placidi, F.; Liguori, C.; Del Bianco, C.; Lauretti, B.; Diomedi, M.; Pisani, A.; Mercuri, N.B.; Izzi, F. Daytime autonomic activity in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: A preliminary study. Sleep Med. 2018, 52, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.S.B.; De Oliveira Rocha, L.S.; Pena, E.S.M.; Caldas, L.C.P.; Moreno, M.A. Analysis of autonomic modulation of heart rate in patients with Parkinson’s disease and elderly individuals submitted to game therapy training. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvageot, N.; Vaillant, M.; Diederich, N.J. Reduced sympathetically driven heart rate variability during sleep in Parkinson’s disease: A case-control polysomnography-based study. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solla, P.; Cadeddu, C.; Cannas, A.; Deidda, M.; Mura, N.; Mercuro, G.; Marrosu, F. Heart rate variability shows different cardiovascular modulation in Parkinson’s disease patients with tremor dominant subtype compared to those with akinetic rigid dominant subtype. J. Neural. Transm. 2015, 122, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, G.L.; Mehlsen, J.; Jennum, P. Reduced sympathetic activity in idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease. Auton. Neurosci. 2013, 179, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriranjini, S.J.; Ganesan, M.; Datta, K.; Pal, P.K.; Sathyaprabha, T.N. Effect of a single dose of standard levodopa on cardiac autonomic function in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. India 2011, 59, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, K.; Katayama, Y.; Otaka, T.; Obuchi, T.; Kano, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Oshima, H.; Fukaya, C.; Yamamoto, T.; Ogawa, Y.; et al. Effect of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation on the autonomic nervous system in Parkinson’s disease patients assessed by spectral analyses of R-R interval variability and blood pressure variability. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2012, 90, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szili-Török, T.; Rudas, L.; Dibó, G.; Paprika, D.; Kardos, A. Abnormal cardiovascular autonomic regulation in Parkinson´s disease. J. Clin. Basic Cardiol. 1999, 2, 245–247. [Google Scholar]
- Trachani, E.; Constantoyannis, C.; Sakellaropoulos, G.C.; Stavrinou, M.L.; Nikiforidis, G.; Chroni, E. Heart rate variability in Parkinson’s disease unaffected by deep brain stimulation. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 126, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, G.; Orsolini, S.; Diciotti, S.; Citi, L.; Scilingo, E.P.; Guerrisi, M.; Danti, S.; Lucetti, C.; Tessa, C.; Barbieri, R.; et al. Assessment of spontaneus cardiovascular oscillations in Parkinson´s disease. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 26, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visanji, N.P.; Bhudhikanok, G.S.; Mestre, T.A.; Ghate, T.; Udupa, K.; AlDakheel, A.; Connolly, B.S.; Gasca-Salas, C.; Kern, D.S.; Jain, J.; et al. Heart rate variability in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2-associated Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, U.; Tsiberidou, P.; Kersten, M.; Storch, A.; Lohle, M. Atrophy of the Vagus Nerve in Parkinson’s Disease Revealed by High-Resolution Ultrasonography. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, D.; Adamidis, M.; Pizzolato, F.; Rumpf, J.J.; Fricke, C.; Classen, J. Assessment of brainstem function with auricular branch of vagus nerve stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, J.M. Heart rate variability to differentiate essential tremor from early-stage tremor-dominant Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 368, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawadka-Kunikowska, M.; Slomko, J.; Tafil-Klawe, M.; Klawe, J.J.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A.; Newton, J.L.; Zalewski, P. Role of peripheral vascular resistance as an indicator of cardiovascular abnormalities in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Rub, U.; Bratzke, H.; Del Tredici, K. Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.G.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stebbins, G.T.; Stern, M.B.; Tilley, B.C.; Dodel, R.; Dubois, B.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Process, format, and clinimetric testing plan. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, D.; Sandercock, G.R.; Brodie, D.A. A quantitative systematic review of normal values for short-term heart rate variability in healthy adults. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2010, 33, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geovanini, G.R.; Vasques, E.R.; de Oliveira Alvim, R.; Mill, J.G.; Andreao, R.V.; Vasques, B.K.; Pereira, A.C.; Krieger, J.E. Age and Sex Differences in Heart Rate Variability and Vagal Specific Patterns-Baependi Heart Study. Glob. Heart 2020, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammito, S.; Bockelmann, I. Reference values for time- and frequency-domain heart rate variability measures. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishekh, H.A.; Nisarga, P.; Kisan, R.; Meghana, A.; Chandran, S.; Trichur, R.; Sathyaprabha, T.N. Influence of age and gender on autonomic regulation of heart. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2013, 27, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, J.; Thayer, J.F. Sex differences in healthy human heart rate variability: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 64, 288–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayano, J.; Yuda, E. Pitfalls of assessment of autonomic function by heart rate variability. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2019, 38, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelban, V.; Vichayanrat, E.; Schottlaende, L.; Iodice, V.; Houlden, H. Autonomic dysfunction in genetic forms of synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuma, F.; Hayano, J. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: Why does the heartbeat synchronize with respiratory rhythm? Chest 2004, 125, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | PD Patients (n = 1566) | Controls (n = 1206) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender (male, %) | 60.8 | 55.3 |
| Age (years) | 65.0 ± 0.6 | 62.6 ± 1.0 |
| Disease duration (years) | 5.8 ± 0.5 | - |
| Hoehn and Yahr stage | 2.2 ± 0.1 | - |
| UPDRS | 32.3 ± 3.6 | - |
| UPDRSIII | 21.4 ± 2.2 | - |
| (A) Raw Analyses | PD Patients | Controls | SMD | ci.lb | ci.ub | p value | I2 (%) | Tau2 | k |
| HF (ms2) | 145.2 ± 41.1 | 219.4 ± 48.8 | −1.38 | −2.17 | −0.58 | 0.002 | 91 | 3.27 | 23 |
| HF (nu) | 34.7 ± 1.8 | 33.2 ± 1.9 | 0.08 | −0.93 | 1.09 | 0.867 | 96 | 3.99 | 18 |
| RMSSD (ms) | 23.4 ± 1.9 | 28.9 ± 1.8 | −0.58 | −1.18 | 0.02 | 0.059 | 92 | 1.35 | 18 |
| pNN50 (%) | 4.7 ± 1.1 | 6.8 ± 1.3 | −0.46 | −1.54 | 0.63 | 0.378 | 96 | 3.39 | 14 |
| (B) Heterogeneity Analyses | PD Patients | Controls | SMD | ci.lb | ci.ub | p value | I2 (%) | Tau2 | k |
| HF (ms2) | 107.7 ± 11.0 | 183.0 ± 22.0 | −0.79 | −1.13 | −0.45 | <0.001 | 67 | 0.28 | 14 |
| HF (nu) | 34.5 ± 3.3 | 33.8 ± 3.2 | 0.04 | −0.29 | 0.36 | 0.810 | 53 | 0.12 | 9 |
| RMSSD (ms) | 21.7 ± 1.2 | 24.7 ± 1.1 | −0.65 | −0.97 | −0.32 | 0.001 | 66 | 0.18 | 12 |
| pNN50 (%) | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 0.8 | −0.59 | −1.06 | −0.12 | 0.020 | 64 | 0.28 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heimrich, K.G.; Lehmann, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Prell, T. Heart Rate Variability Analyses in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080959
Heimrich KG, Lehmann T, Schlattmann P, Prell T. Heart Rate Variability Analyses in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(8):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080959
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeimrich, Konstantin G., Thomas Lehmann, Peter Schlattmann, and Tino Prell. 2021. "Heart Rate Variability Analyses in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Brain Sciences 11, no. 8: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080959
APA StyleHeimrich, K. G., Lehmann, T., Schlattmann, P., & Prell, T. (2021). Heart Rate Variability Analyses in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences, 11(8), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11080959







