A Recent Investigation on Detection and Classification of Epileptic Seizure Techniques Using EEG Signal
Abstract
1. Introduction
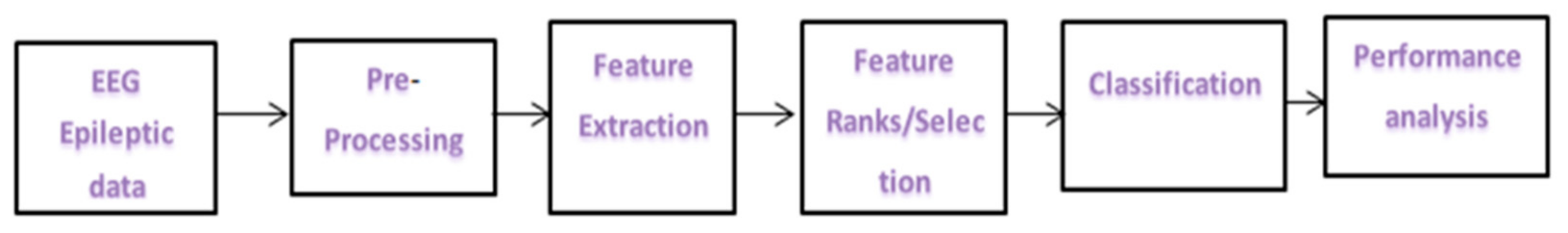
2. Epileptic Seizure Detection System
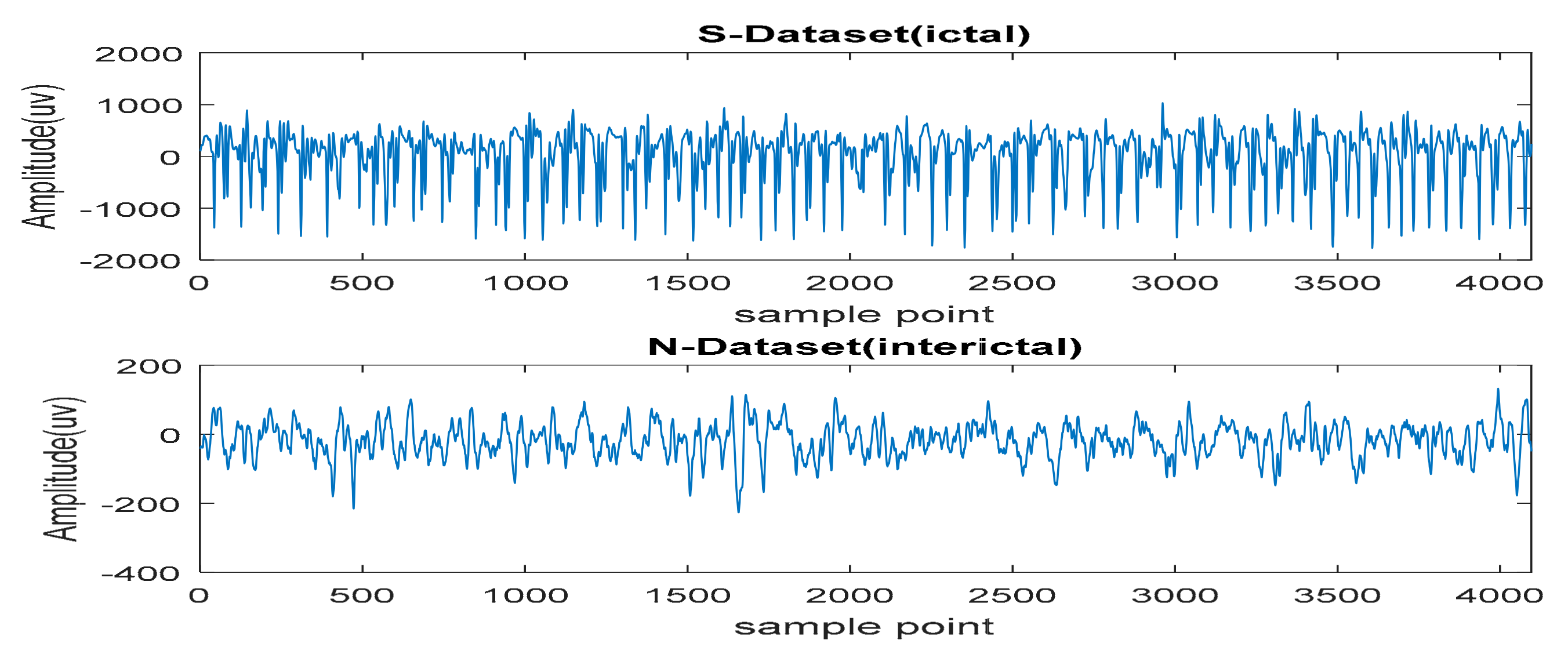
2.1. Data Acquisition and EEG Database
2.2. Preprocessing
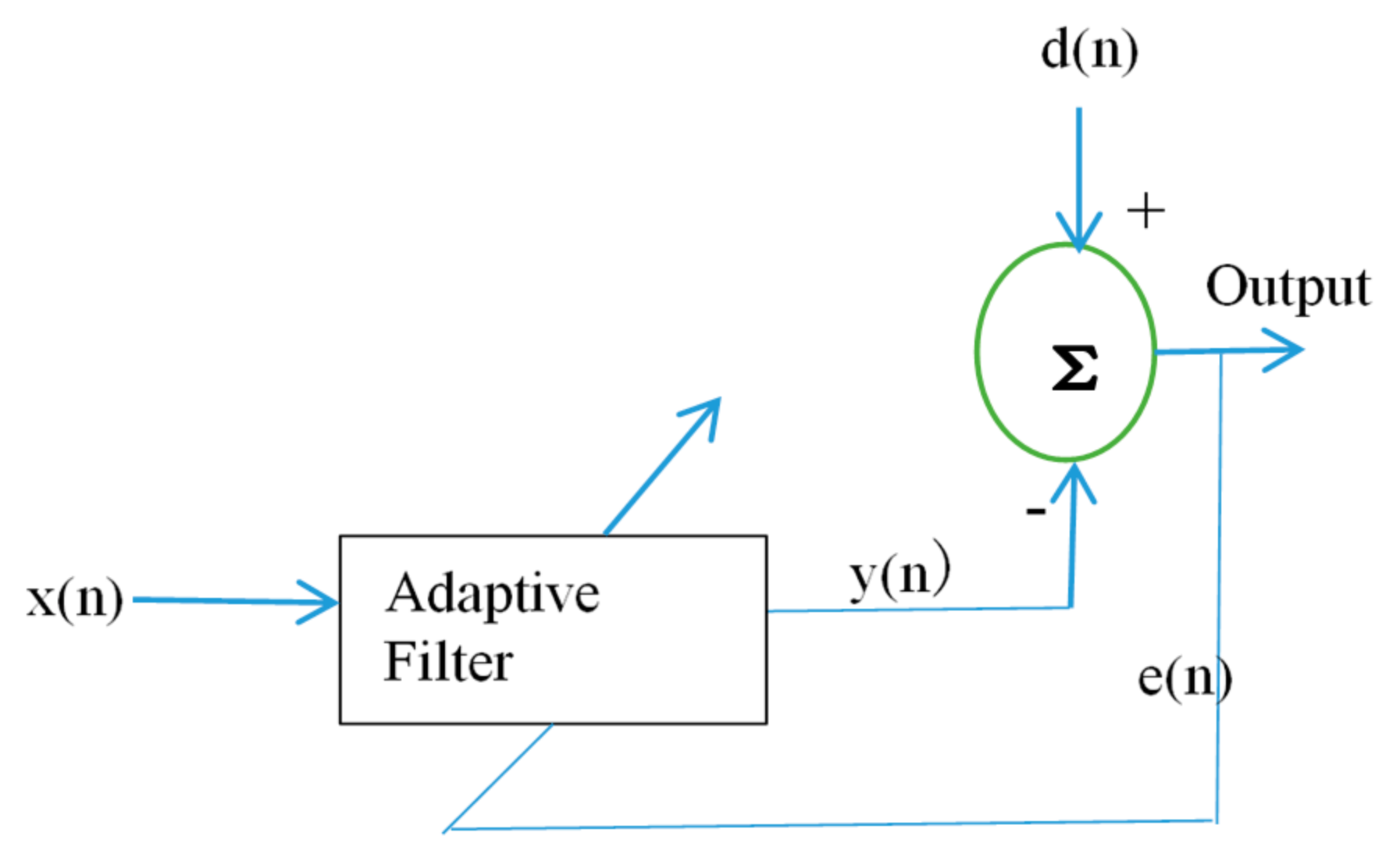
2.2.1. Filtering Technique
2.2.2. Blind Source Separation Techniques
3. Feature Extraction Techniques
3.1. Time Domain Analysis
Statistical Parameters
3.2. Frequency Domain
3.3. Time–Frequency Domain
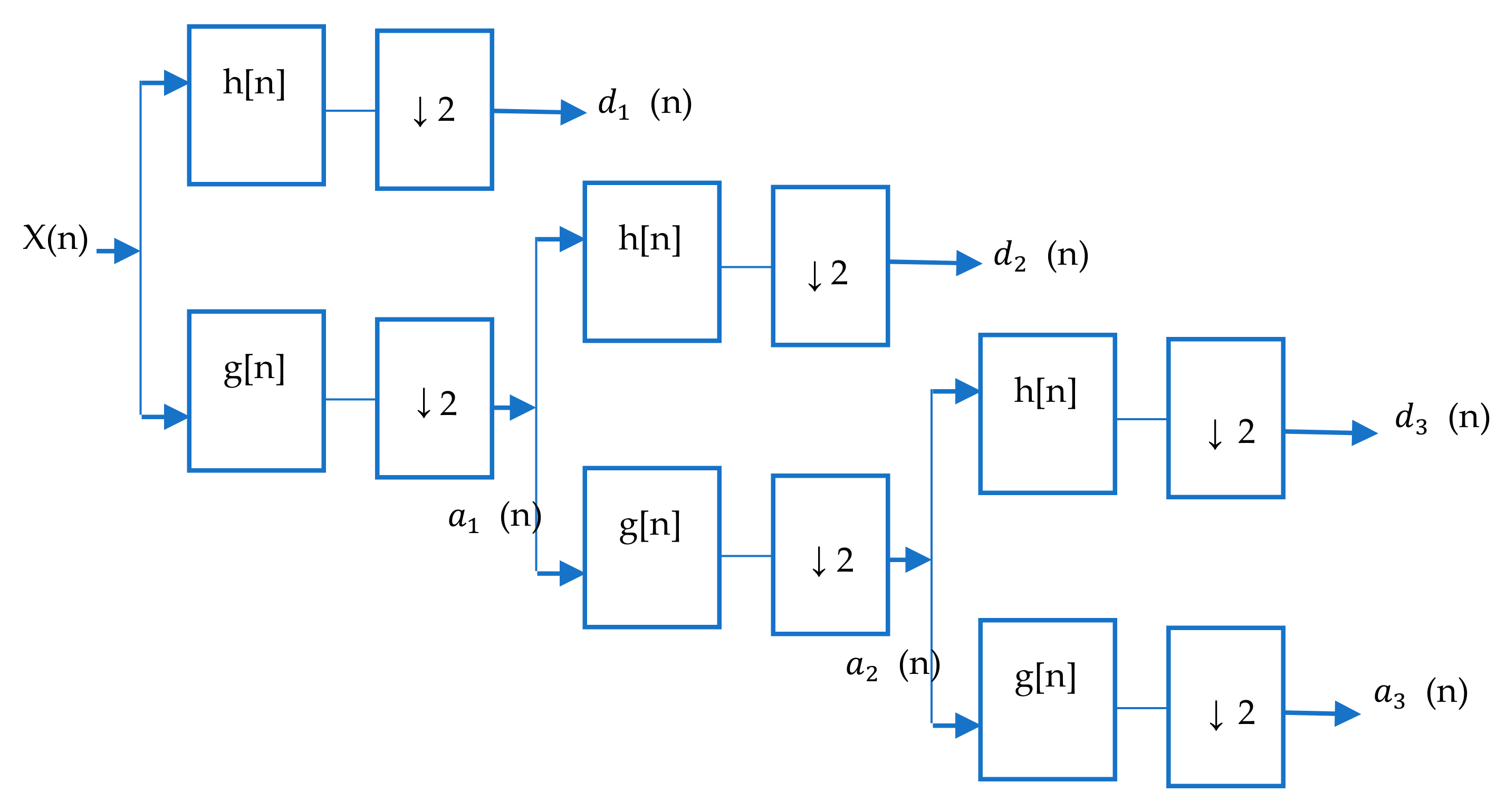
3.4. Wavelet Analysis
3.5. Non-Linear Analysis
Entropy Analysis
4. Classification Techniques
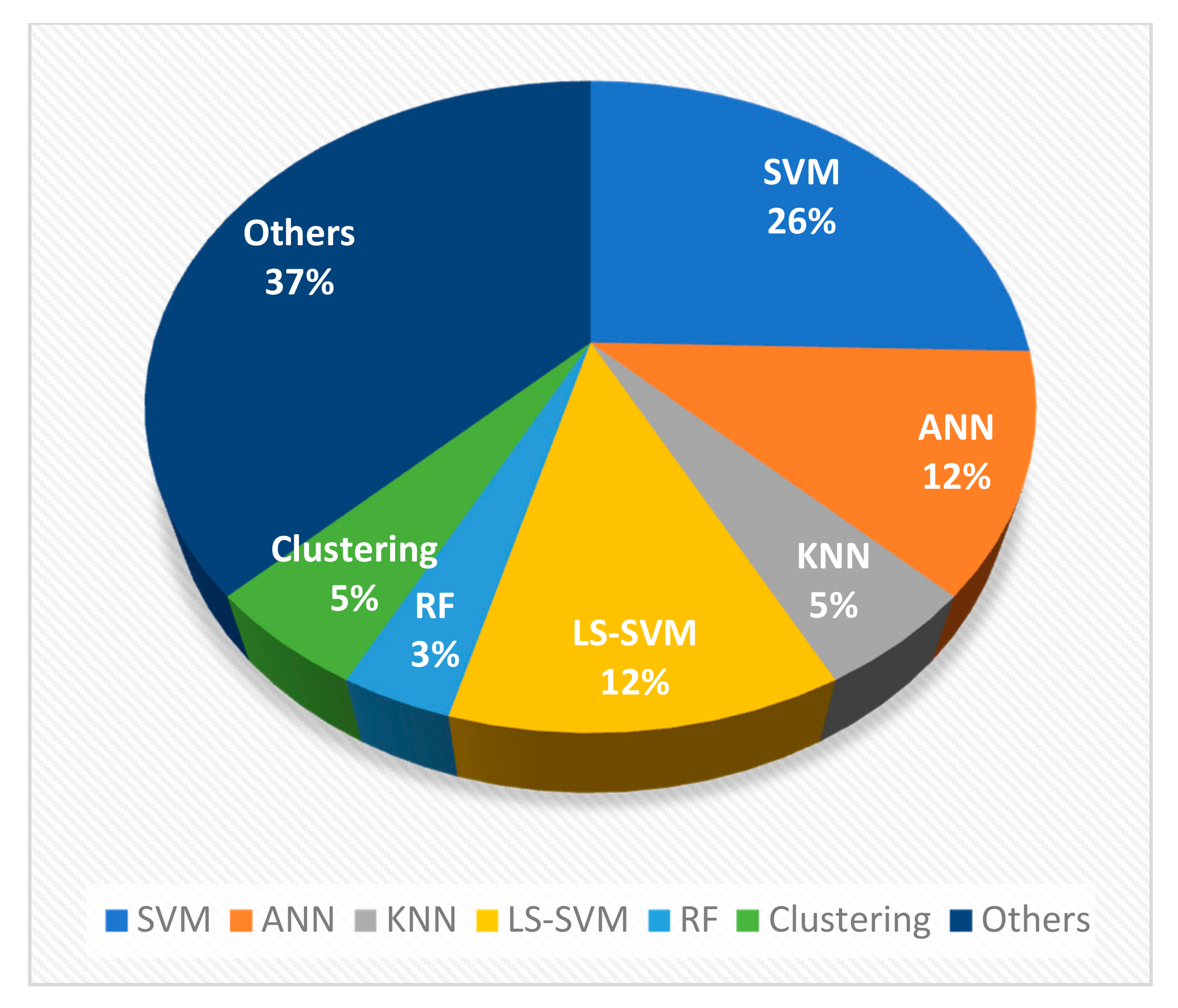
4.1. Machine Learning Techniques
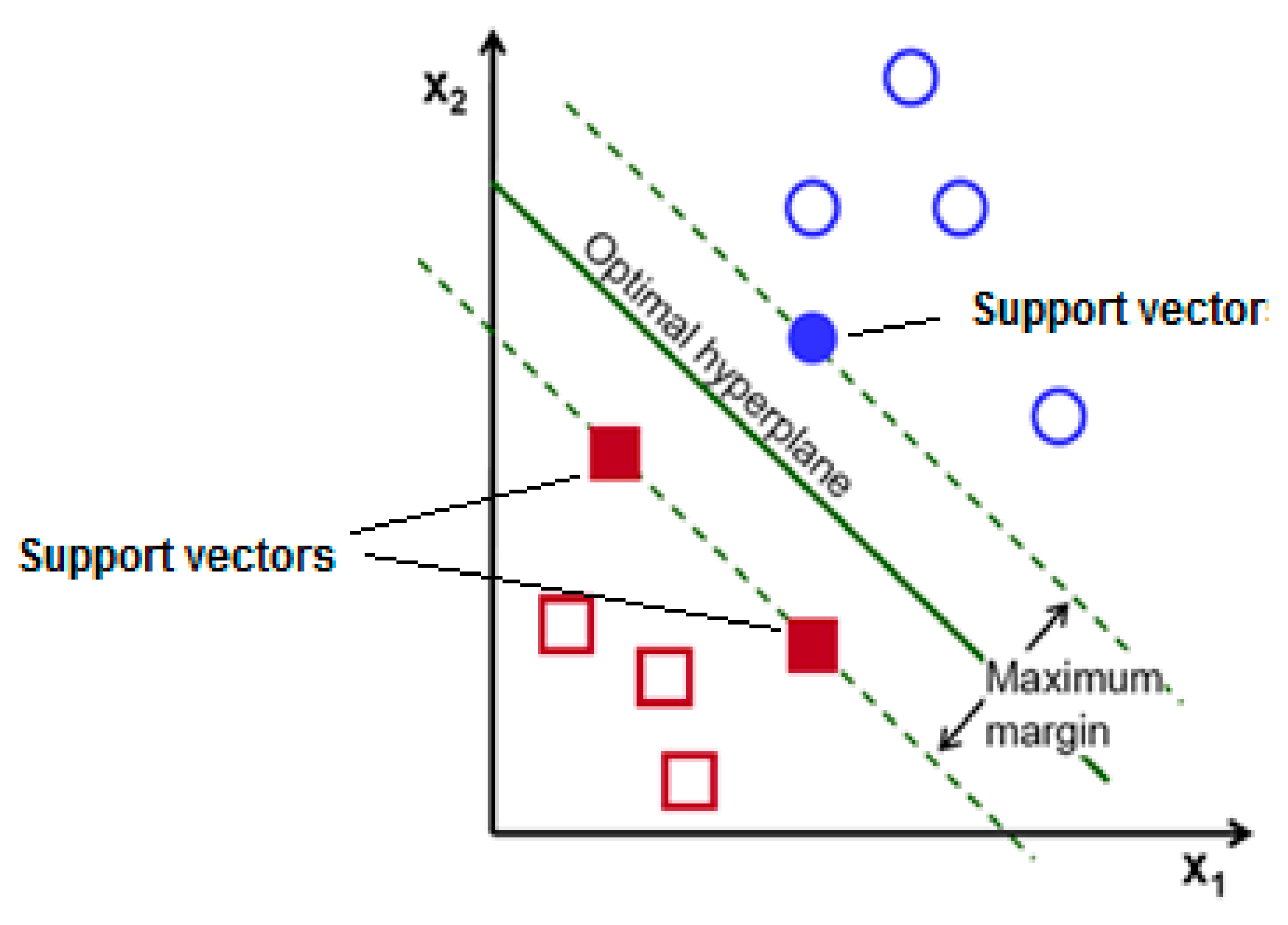
Overview of Support Vector Machine
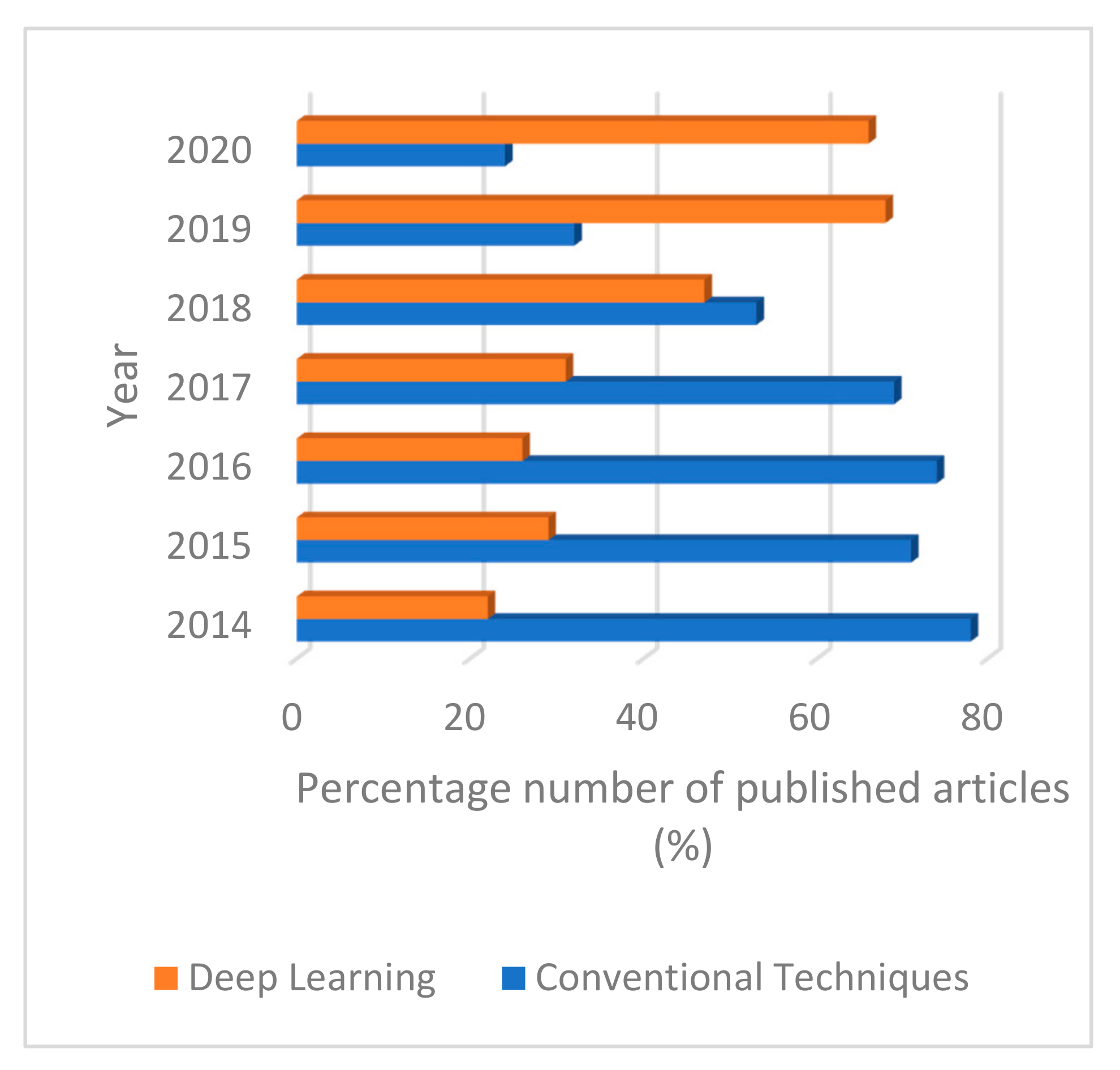
4.2. Deep Learning Techniques
5. Discussion
5.1. Challenges
5.2. Future Research Direction
- With a large volume and high dimension of epileptic seizure datasets, dimensional reduction techniques that reduce the dataset dimension and still retain the significant signal information need to be further investigated.
- Suitable features that reduce the classifier’s computational complexity and time should be considered.
- For models that use invasive recordings, the developed methods must identify seizure onset and measure the seizure strength.
- Researchers should choose a classifier that will not miss or skip all the relevant EEG channels and electrodes.
- Deep learning structures must be carefully selected based on the problem’s peculiarities and involve relevant datasets for real-time, online and offline detection.
- Hybrid deep learning techniques should be extensively explored.
- EEG signal analysis is a neurophysiological approach which holds great potential for enhanced diagnosis and classification of acute disorders of consciousness (ADOCs) such as a vegetative state (VS) and a minimally conscious state (MCS), among others. It can be used to predict the dynamics in the thalamocortical connections as it depicts changes in the activities of the reticular system. Detection and classification of epileptic seizures using EEG signals are a significant step towards advanced diagnosis of unresponsive wakefulness syndrome (UWS) and MCS by characterizing the level of awareness as they share some common features with epileptic seizures. Previous work such as that of Naro et al. [193] used γ-band transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) as a non-invasive neurostimulation protocol on DOC patients to differentiate UWS and MCS individuals. Another neuromodulation approach was also applied in [194], while electrophysiologically based approaches were discussed in [195]. Further research on deep learning techniques could be employed in the classification of VS, MCS and UWS.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACD | acute consciousness disorder |
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| ApEn | approximate entropy |
| AR | autoregressive |
| CAD | computer-aided diagnosis |
| CCA | canonical correlation analysis |
| CD | correlation dimension |
| CDOC | chronic disorder of consciousness |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| DBF | deep belief network |
| DCNN | deep convoluted neural network |
| DOC | disorder of consciousness |
| DNN | deep neural network |
| DWT | discrete wavelet transform |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| EESC | epileptic EEG signal classification |
| EOG | Electrooculogram |
| FDR | Fisher discriminant ratio |
| FA | firefly optimization |
| GMM | Gaussian mixer model |
| GRU | gated recurrent unit |
| HOS | higher-order spectra |
| HRS | hierarchical region splitting |
| ICA | independent component analysis |
| ICGA | integer coded genetic algorithm |
| IMF | intrinsic mode function |
| IoMT | internet of medical things |
| KNN | k-nearest neighbor |
| LLC | locally linear classification |
| LMS | least mean square |
| LMTS | long short-term memory |
| MCA | morphological component analysis |
| MCS | minimally conscious state |
| MRF | Markov random field |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NB | naive Bayes |
| NLMS | non-local means |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PSD | power spectral density |
| PNN | probabilistic neural network |
| PSO | particle swarm optimization |
| RMS | root mean square |
| RLS | recursive least square |
| STFT | short time Fourier transform |
| SVM | support vector machine |
| SLSA | step-wise least square estimation algorithm |
| SRS | simple random Sampling |
| SSDA | stacked sparce density autoencoders |
| TCNN | temporal CNN |
| TGCN | temporal graph convolutional networks |
| TQWT | tunable Q-wavelet decomposition |
| UWS | unresponsive wakefulness syndrome |
| VS | vegetative state |
| WPE | wavelet packet entropy |
| WT | wavelet transform |
| WVD | Weiner–Ville distribution |
References
- Falco-Walter, J.J.; Scheffer, I.E.; Fisher, R.S. The new definition and classification of seizures and epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2018, 139, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M. ILAE official report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Yuen, A.W.; Keezer, M.R.; Sander, J.W. Epilepsy is a neurological and a systemic disorder. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 78, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuly, S.; Zhang, Y. Medical big data: Neurological diseases diagnosis through medical data analysis. Data Sci. Eng. 2016, 1, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, H. Epilepsy and the consciousness system: Transient vegetative state? Neurol. Clin. 2011, 29, 801–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laureys, S.; Schiff, N.D. Disorders of Consciousness. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Laureys, S.; Tononi, G. The Neurology of Consciousness: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuropathology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrò, R.S.; Milardi, D.; Cacciola, A.; Marra, A.; Digangi, G.; Casella, C.; Manuli, A.; De Luca, R.; Silvestri, R.; Bramanti, P. Moving into the wide clinical spectrum of consciousness disorders: Pearls, perils and pitfalls. Medicina 2016, 52, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, H. Impaired consciousness in epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ziemann, U. Managing disorders of consciousness: The role of electroencephalography. J. Neurol. 2020, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorena, O.; Agustina, G.C.; Eric, L. Review: A survey of performance and techniques for automatic epilepsy detection. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2013, 33, 526–537. [Google Scholar]
- Varsavsky, A.; Mareels, I.; Cook, M. Epileptic Seizures and the EEG; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gotman, J. Automatic recognition of epileptic seizures in the EEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1982, 54, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuly, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. EEG Signal Analysis and Classification: Techniques and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, S.; Thakor, N.V. Quantitative EEG Analysis Methods and Clinical Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, Z. EEG Signal Processing and Feature Extraction; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gavvala, J.; Abend, N.; LaRoche, S.; Hahn, C.; Herman, S.T.; Claassen, J.; Macken, M.; Schuele, S.; Gerard, E.; Critical Care EEG Monitoring Research Consortium (CCEMRC). Continuous EEG monitoring: A survey of neurophysiologists and neurointensivists. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, N.R. Foundations of Physiological Psychology, 5th ed.; Allyn and Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mike, C.X. Analyzing Neural Time Series Data: Theory and Practice; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Hall, W.C.; LaMantia, A.S.; McNamara, J.O.; Williams, S.M. Neuroscience, Sinauer Associates, 3rd ed.; Inc. Publishers: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, G.M.; Armando, M.T.; Angel, N.V. EEG Signal Processing for Epilepsy, Epilepsy—Histological, Electroencephalographic and Psychological Aspects, Dejan Stevanovic; Intech-Open: London, UK, 2012; pp. 49–74. [Google Scholar]
- Atwood, H.L.; MacKay, W.A. Essentials of Neurophysiology; B. C. Decker: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sanei, S.; Chambers, J.A. EEG Signal Processing; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Steven, J.L. An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique, 2nd ed.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Sree, S.V.; Swapna, G.; Martis, R.J.; Suri, J.S. Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: A review. Knowl. Based Syst. 2013, 45, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Bhat, S.; Koh, J.E.W. Application of entropies for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using EEG signals: A review. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 88, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Saeed, M.; Saleem, S.; Kamboh, A.M. Seizure detection using EEG: A survey of different techniques. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Emerging Technologies, Islamabad, Pakistan, 18–19 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dattaprasad, T.; Veena, D.; Rajashri, K. A review on seizure detection systems with emphasis on multi-domain feature extraction and classification using machine learning. BRAIN 2017, 8, 109–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmila, A. Epilepsy detection from EEG signals: A review. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2018, 42, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, U.R.; Hagiwara, Y.; Deshpande, S.N.; Sure, S.; WeiKoh, J.E.; Lih Oh, S.; Arunkumar, N.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Min Lim, C. Characterization of focal EEG signals: A review. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 91, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.H.; Arunkumar, N.; Chandima, G.; Alzubaidi, A.K.; Habash, Q.A.; Santamaria-Grana, L.; Mendoza-Moreno, J.F.; Ramirez-Gonzalez, G. Focal and non-focal epilepsy localization: A review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49306–49324. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, M.T.; Desgent, S.; Duss, S.; Carmant, L.; Nguyen, D.K.; Sawan, M. New subdural electrode contacts for intracerebral electroencephalographic recordings: Comparative studies on neural signal recording in vivo. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS 2011), San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 November 2011; pp. 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- EEG Time Series. Available online: http://epileptologiebonn.de/cms/upload/workgroup/ehnertzeegdata.html (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- The University of Freiburg, EEG Database at the Epilepsy Center of the University Hospital of Freiburg, Germany. 2003. Available online: http://epilepsy.uni-freiburg.de (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejak, R.G.; Schindler, K.; Rummel, C. Nonrandomness, non-linear dependence and non-stationarity of electroencephalographic recordings from epilepsy patients. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 046206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Feldwisch-Drentrup, H.; Ihle, M. The role of high-quality EEG databases in improving and assessing seizure prediction methods. Epilepsy Behav. 2011, 22, S88–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.A.; Sturges, B.K.; Vite, C.H.; Ruedebusch, V.; Worrell, G.; Gardner, A.B.; Leyde, K.; Sheffield, W.D.; Litt, B. A novel implanted device to wirelessly record and analyze continuous intracranial canine EEG. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 96, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, B.H.; Patterson, E.E.; Vite, C.; Vasoli, V.M.; Crepeau, D.; Stead, M.; Howbert, J.J.; Cherkassky, V.; Wagenaar, J.B.; Litt, B.; et al. Forecasting Seizures Using Intracranial EEG Measures and SVM in Naturally Occurring Canine Epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urigüen, J.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. EEG artifact removal-state-of the-art and guidelines. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, K.T.; Ward, T.E.; McLoone, S.F. Artifact removal in physiological signals Practices and possibilities. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2012, 16, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatourechi, M.; Bashashati, A.; Ward, R.K.; Birch, G.E. EMG and EOG artifacts in brain computer interface systems: A survey. Clinical neurophysiology: Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Rastegarnia, A.; Yang, Z. Methods for artifact detection and removal from scalp EEG: A review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 46, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamune, R.S.; Laskar, S.H. A review on artefacts removal techniques for Electroencephalogram signals. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on innovations in Electronics, Signal Processing, Communication (IESC), Shillong, India, 1–2 March 2019; pp. 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Khatwani, P.; Tiwari, A. A survey on different noise removal techniques of EEG signals. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2013, 2, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, H.; Whelan, R.; Reilly, R.B. FASTER: Fully automated statistical thresholding for EEG artifact rejection. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 192, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, T.; Lutzenberger, W.; Rockstroh, B.; Birbaumer, N. Removal of ocular artefacts from the EEG—A biophysical approach to the EOG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 60, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Bertrand, A. Removal of eye blink artefacts in wireless EEG sensor networks using reduced-bandwidth canonical correlation analysis. J. Neural. Eng. 2016, 13, 066008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddirala, A.K.; Shaik, R.A. Removal of EOG artefacts from single-channel EEG signals using combined singular spectrum analysis and adaptive noise canceler. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 8279–8287. [Google Scholar]
- O’Regan, S.; Faul, S.; Marnane, W. Automatic detection of EEG artefacts from head movements using EEG and gyroscope signals. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.S.; Bhatnagar, M.; Kumar, S.; Sinha, R.K. A comparative study of applying different non-conventional filters on electroencephalogram. Biomed. Res. 2020, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cheveign, A. ZapLine: A simple and effective method to remove power line artefacts. NeuroImage 2019, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnachandra, R.M.; Srinivasa, R.E. Performance analysis of adaptive filters with various wavelets for noise removal in EEG signals. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 9, 2278–3075. [Google Scholar]
- Kher, R.; Gandhi, R. Adaptive filtering based artifact removal from electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 6–8 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Surya, P.M.; Rafi, A.S. Low-area and high throughput architecture for an adaptive filter using distributed arithmetic. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2013, 69, 781–785. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.C.; Lee, J. A new variable step-size NLMS algorithm and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. Dual adaptive noise cancellation method based on least mean m-estimate of noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 29 June–4 July 2014; pp. 5741–5746. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Mehra, R.; Sharma, L. Effective adaptive noise cancellaer desing using normalized LMS. In IEEE Conference on Next Generation Computing Technologies; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 571–575. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, K.H.; Fung, P.C.W.; Chang, C.Q.; Chan, F.H.Y. Automatic correction of artifact from single-trial event-related potentials by blind source separation using second-order statistics only. Med. Eng. Phys. 2006, 28, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallstrom, G.L.; Kass, R.E.; Miller, A.; Cohn, J.F.; Fox, N.A. Automatic correction of ocular artefacts in the EEG: A comparison of regression-based and component-based methods. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2004, 53, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillon, J.; Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Pelayo, F. Trends in EEG-BCI for daily-life: Requirements for artifact removal. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.P.; Makeig, S.; Humphries, C.; Lee, T.W.; McKeown, M.J.; Iragui, V.; Sejnowski, T.J. Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saminu, S.; Xu, G.; Zhang, S.; Isselmou, A.E.K.; Jabire, A.H.; Karaye, I.A.; Ahmad, I.S. Hybrid feature extraction technique for multi-classification of ictal and non-ictal EEG epilepsy signals. Elektrika, J. Electr. Eng. 2020, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diykh, M.; Li, Y.; Wen, P. EEG sleep stages classification based on time-domain features and structural graph similarity. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minasyan, G.R.; Chatten, J.B.; Harner, R.N. Patient-specific early seizure detection from scalp EEG. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 27, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Wen, P.P. Epileptic seizure detection in EEGs signals using a fast weighted horizontal visibility algorithm, Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 115, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E. Hilbert-Huang Transform and Its Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2014; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Sree, S.V.; Suri, J.S. Automatic detection of epileptic EEG signals using higher-order cumulant features. Int. J. Neural. Syst. 2011, 21, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Dua, S.; Acharya, U.R.; Chua, K.C. Classification of epilepsy using high-order spectra features and principle component analysis. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 36, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.C.; Chandran, V.; Acharya, U.R.; Lim, C.M. Application of higher-order spectra to identify epileptic EEG. J. Med. Syst. 2011, 35, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosco, L.; Correa, A.G.; Leber, E.L. Epileptic seizures detection based on empirical mode decomposition of EEG signals. In Management of Epilepsy-Research, Results and Treatment; Günel, M.K., Ed.; In-Tech Publishing: Vienna, Austria, 2011; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Frei, M.G.; Zaveri, H.P.; Arthurs, S.; Bergey, G.K.; Jouny, C.C.; Lehnertz, K.; Gotman, J.; Osorio, I.; Netoff, T.I.; Freeman, W.J.; et al. Controversies in epilepsy: Debates held during the fourth international workshop on seizure prediction. Epilepsy Behav. 2010, 19, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, R.; Muhammad, K.; Nachiappan, A.; Ramírez-Gonzalez, G. Hash-based encryption for keyframes of diagnostic hysteroscopy. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 60160–60170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serap, A. Determination of autoregressive model orders for seizure detection. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2010, 18, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelouahab, A.; Abdelouahab, M.; Youssef, C. Epileptic seizures identification with autoregressive model and firefly optimization-based classification. Evol. Syst. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, G.; Sinha, D.H. Biomedical Signal Analysis through Wavelets: A Review. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 2012, 2, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zubair, A.R.; Ahmed, Y.K.; Akande, K.A. Electromyography noise suppression in electrocardiogram signal using modified garrote threshold shrinkage function. Afr. J. Comput. ICT 2018, 11, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Faust, O.; Acharya, U.R.; Adeli, H.; Adeli, A. Wavelet-based EEG processing for computer-aided seizure detection and epilepsy diagnosis. Seizure Eur. J. Epilepsy 2015, 26, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A theory for multi-resolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saminu, S.; Özkurt, N. Stationary wavelet transform and entropy-based features for ECG beat classification. Int. J. Res. Stud. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Elhoseny, M.; Ramírez-Gonzalez, G.; Abu-Elnasr, O.M.; Shawkat, S.A.; Arunkumar, N.; Farouk, A. Secure medical data transmission model for IoT-based healthcare systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 20596–20608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logesparan, L.; Rodriguez-Villegas, E.; Casson, A.J. The impact of signal normalization on seizure detection using line length features. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, A.; Geethanjali, P. DWT-based detection of epileptic seizure from EEG signals using naive Bayes and k-nn classifiers. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 7716–7727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ghayab, H.R.; Li, Y.; Siuly, S.; Abdulla, S.A. Feature extraction technique based on tunable q-factor wavelet transform for brain signal classification. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 312, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Karmakar, C.; Yearwood, J.; Venkatesh, S.; Palaniswami, M.; Liu, C. Detection of epileptic seizure based on entropy analysis of short-term EEG. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Banka, H. Local pattern transformation-based feature extraction techniques for classification of epileptic EEG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 34, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, N.S.; Youssef, S.M.; Kholief, M. A hybrid automated detection of epileptic seizures in EEG records. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 53, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Kader, I.; Xu, G.; Shuai, Z.; Saminu, S.; Javaid, I.; Ahmad, I.S. Differential deep convolutional neural network model for brain tumor classification. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, O.; Acharya, U.R.; Min, L.C.; Sputh, B.C.H. Automatic identification of epileptic and background EEG signals using frequency-domain parameters. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2010, 20, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subasi, A.; Gursoy, M.I. EEG signal classification using PCA.; ICA.; LDA and support vector machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 8659–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Rivero, D.; Dorado, J.; Rabunal, J.R.; Pazos, A. Automatic epileptic seizure detection in EEGs based on line length feature and artificial neural networks. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 191, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oweis, R.J.; Abdulhay, E.W. Seizure classification in EEG signals utilizing Hilbert-Huang transform. Biomed. Eng. Online 2011, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, U.; Hekim, M.; Ozer, M. EEG signals classification using the K-means clustering and a multilayer perceptron neural network model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 13475–13481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.; Cai, D. Epileptic EEG classification based on extreme learning machine and non-linear features. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 96, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, M.; Dragan, D. Time-frequency distributions in the classification of epilepsy from EEG signals. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 11413–11422. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, S.; Nidal, K.; Aamir, S.M.; Ali, J.M. Epileptic seizure detection using the singular values of EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2013 ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering, Beijing, China, 25–28 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gajic, D.; Djurovic, Z.; di Gennaro, S.; Fredrik, G. Classification of EEG signals to detect epileptic seizures based on wavelets and statistical pattern recognition. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2014, 2, 1450021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, A.; Thasneem, F.; Paul, J. Detection of epileptic seizure event and onset using EEG. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 450573. [Google Scholar]
- Yatindra, K.; Dewal, M.L.; Anand, R.S. Epileptic seizure detection using DWT based fuzzy approximate entropy and support vector machine. Neuro Comput. 2014, 133, 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, J.; Rupali, K. EEG signal classification using modified fuzzy clustering algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2015, 6, 2031–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Harikumar, R.; Vijayakumar, T. Wavelets and morphological operators based classification of epilepsy risk levels. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 813197. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Sharma, M.; Pachori, R.B.; Sircar, P.; Acharya, U.R. A novel approach for automated detection of focal EEG signals using empirical wavelet transform. Neural. Comput. Applic. 2018, 29, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T. Automatic epilepsy detection using wavelet-based non-linear analysis and optimized SVM. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 36, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Karmakar, C.; Yan, C.; Palaniswami, M.; Liu, C. Classification of 5-S epileptic EEG recordings using distribution entropy and sample entropy. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, M.; Sen, B.; Delen, D. A novel method for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using complex-valued classifiers. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, F.; Hassan, A.; Rehman, S.; Niazi, I.K.; Dremstrup, K. EMD-based temporal and spectral features for the classification of EEG signals using supervised learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ghayab, H.R.; Li, Y.; Abdulla, S.; Diykh, M.; Wan, X. Classification of epileptic EEG signals based on simple random sampling and sequential feature selection. Brain Inform. 2016, 3, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, R.; Padhy, P.; Kankar, P. A comparative study of feature ranking techniques for epileptic seizure detection using wavelet transform. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 53, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, E.; Zhang, Y.S. Epileptic seizure detection from EEG signals using logistic model trees. Brain Inform. 2016, 3, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippa, E.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Mporas, I.; Tsirka, V.; Richardson, M.P.; Koutroumanidis, M.; Megalooikonomoua, V. Improving classification of epileptic and non-epileptic EEG events by feature selection. Neuro Comput. 2016, 171, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Banka, H. Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signal using machine learning techniques. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2018, 41, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Pachori, R.B. A novel approach to detect epileptic seizures using a combination of tunable-q wavelet transform and fractal dimension. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2017, 17, 1740003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, S.; Panigrahi, T. Detection of epileptic seizure using Kraskov entropy applied on tunable-q wavelet transform of EEG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 34, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diykh, M.; Li, Y.; Wen, P. Classify epileptic EEG signals using complex weighted networks based community structure detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 90, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T. Application of MODWT and log-normal distribution model for automatic epilepsy identification. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 37, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Pachori, R.B.; Kanhangad, V.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Panigrahi, B. Automated diagnosis of epilepsy using a key-point-based local binary pattern of EEG signals. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mursalin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chawla, N.V. Automated epileptic seizure detection using improved correlation-based feature selection with random forest classifier. Neuro Comput. 2017, 241, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.; Farooq, O.; Chandel, G. Advances in System Optimization and Control: Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2017; p. 509. [Google Scholar]
- Kocadagli, O.; Langari, R. Classification of EEG signals for epileptic seizures using hybrid artificial neural networks based wavelet transforms and fuzzy relations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 88, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torse, D.; Desai, V.; Khanai, R. Classification of EEG signals in seizure detection system using ellipse area features and support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Engineering and Communication Technology (ICDECT), Maharashtra, India, 15–16 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Bhuraneb, A.A.; Acharya, U.R. MMSFL-OWFB: A novel class of orthogonal wavelet filters for epileptic seizure detection. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 160, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimourta, K.; Tzallas, A.; Giannakeas, N.; Astrakas, L.G.; Angelidis, L.; Tsalikakis, D.G.; Tsipouras, M.G. A robust methodology for the classification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals. Health Technol. 2019, 9, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriraam, N.; Tamanna, K.; Narayan, L.; Khanum, M.; Raghu, S.; Hegde, A.S.; Kumar, A.B. Multichannel EEG based inter-ictal seizures detection using Teager energy with backpropagation neural network classifier. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2018, 41, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudalaimani, C.; Sivakumaran, N.; Elizabeth, T.T.; Rominus, V.S. Automated detection of the pre-seizure state in EEG signal using neural networks. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 39, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, S.; Sriraam, N. Classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals using neighborhood component analysis and machine learning algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 113, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, W.; Luo, M.; Li, K.; Wang, L. Epileptic seizure detection based on time-frequency images of EEG signals using gaussian mixture model and gray level co-occurrence matrix features. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2018, 28, 1850003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cooman, T.; Varon, C.; van de Vel, A.; Jansen, K.; Ceulemans, B.; Lagae, L.; Van Huffel, S. Adaptive nocturnal seizure detection using heart rate low-complexity novelty detection. Seizure 2018, 59, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T. A novel seizure diagnostic model based on kernel density estimation and least squares support vector machine. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 41, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, N.E.; Solarte, J.; Varghas, A. Automated epileptic seizure detection system based on a wearable prototype and cloud computing to assist people with epilepsy. In Applied Computer Sciences in Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, W.; Li, M. Fuzzy distribution entropy and its application in automated seizure detection technique. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 39, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhao, J.; Fu, W. Automated classification of epileptic EEG signals based on multi-feature extraction. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 23–25 November 2018; pp. 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Tanveer, M.; Pachori, R.; Angami, N. Entropy-based features in FAWT framework for automated detection of epileptic seizure EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Bangalore, India, 18–21 November 2018; pp. 1946–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, N.R.; Roy, S.S.; Pal, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Bose, R. Epileptic seizure detection employing cross-hyperbolic stockwell transform. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Research in Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (ICRCICN), Kolkata, India, 22–23 November 2018; pp. 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wani, S.; Sabut, S.; Nalbalwar, S. Detection of epileptic seizure using wavelet transform and neural network classifier. In Computing, Communication and Signal Processing; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Naser, A.; Tantawi, M.; Shedeed, H.; Tolba, M. Detecting epileptic seizures using abe entropy, line length and SVM classifier. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Machine Learning Technologies and Applications, Cairo, Egypt, 28–30 March 2019; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Lahmiri, S.; Shmuel, A. Accurate classification of seizure and seizure-free intervals of intracranial EEG signals from epileptic patients. IEEE Trans Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, S.; Sriraam, N.; Temel, Y.; Rao, S.V.; Hegde, A.S.; Kubben, P.L. Performance evaluation of DWT-based sigmoid entropy in time and frequency domains for automated detection of epileptic seizures using SVM classifier. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 110, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Li, N. Automated recognition of epileptic EEG states using a combination of symlet wavelet processing, gradient boosting machine, and grid search optimizer. Sensors 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, R.; Pratiher, S.; Chatterjee, S. Detection of epileptic seizure employing a novel set of features extracted from a multifractal spectrum of electroencephalogram signals. IET Signal Process. 2019, 13, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, M.; Tanveer, M.; Pachori, R.B. Machine Intelligence and Signal Analysis; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, A.H.; Alzahrani, A.A. New approach for automated epileptic disease diagnosis using an integrated self-organization map and radial basis function neural network algorithm. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 4741–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasil, O.K.; Rajesh, R. Time-domain exponential energy for epileptic EEG signal classification. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 694, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Saminu, S.; Xu, G.; Zhang, S.; Isselmou, A.E.K.; Zakariyya, R.S.; Jabire, A.H. Epilepsy detection and classification for smart IoT devices using hybrid technique. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Electronics, Computer and Computation (ICECCO), Abuja, Nigeria, 10–12 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mahjoub, C.; Jeannès, R.L.B.; Lajnef, T.; Kachouri, A. Epileptic seizure detection on EEG signals using machine learning techniques and advanced preprocessing methods. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 65, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raluca, M.A.; Sever, P.; Adriana, F. EEG-brain activity monitoring and predictive analysis of signals using artificial neural networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 3346. [Google Scholar]
- Ozlem, K.C.; Sibel, K.A.; Hatice, S.T.; Aydin, A. Epileptic seizure classifications using empirical mode decomposition and its derivative. BioMed Eng. Online 2020, 19, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Khaled, M.A. Classification of epileptic seizure dataset using different machine learning algorithms. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 21, 100444. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, M.B.A.; Afzaal, M.; Qureshi, M.S.; Fayaz, M. Machine learning-based EEG signals classification model for epileptic seizure detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, S.; Choudhary, A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, R.; Swetapadma, A. A machine learning-based method to detect epilepsy. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2018, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y. Machine learning applications for electroencephalograph signals in epilepsy: A quick review. Acta Epileptol. 2020, 2, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhrajit, R.; Umar, A.; Jianbin, T.; Stefan, H. Seizure type classification using EEG signals and machine learning: Setting a benchmark. IEEE SPMB 2020, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Alickovic, E.; Kevric, J.; Subasi, A. Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 39, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, K.; Nour, M. Epileptic Seizure Detection Based on New Hybrid Models with Electroencephalogram Signals. IRBM 2020, 41, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, B.; Sung, N.-J.; Min, S.; Hong, M. Deep learning in physiological signal data: A survey. Sensors 2020, 20, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabeff, V.; Teijeiro, T.; Zapater, M.; Cammoun, L.; Rheims, S.; Ryvlin, P.; Atienza, D. Interpreting deep learning models for epileptic seizure detection on EEG signals. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 117, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, A.D.; Navelkar, A.; Gore, M.; Kalbande, D. Methodologies for epilepsy detection: Survey and review. In International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 207–222. [Google Scholar]
- Sunandan, M.; Manvendra, T.; Kavita, T.; Bikesh, K.S. Comparative investigation of different classification techniques for epilepsy detection using EEG signals. In Advances in Biomedical Engineering and Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nogay, H.S.; Adeli, H. Detection of epileptic seizure using pretrained deep convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Eur. Neurol. 2020, 83, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olokodana, I.; Mohanty, S.; Kougianos, E. Distributed kriging-bootstrapped DNN model for fast, accurate seizure detection from EEG signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Limassol, Cyprus, 6–8 July 2020; pp. 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Alzahab, N.A.; Apollonio, L.; di Iorio, A.; Alshalak, M.; Iarlori, S.; Ferracuti, F.; Monteriù, A.; Porcaro, C. Hybrid Deep Learning (HDL)-based Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) systems: A systematic review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, G.C.; Sharma, R.; Agrawal, A. A 1D-CNN-spectrogram-based approach for seizure detection from EEG signal. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, X. Robust deep network with maximum correntropy criterion for seizure detection. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 703816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thodoroff, P.; Pineau, J.; Lim, A. Learning robust features using deep learning for automatic seizure detection. In Proceedings of the 1st Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 19–20 August 2016; pp. 178–190. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, A.R.; Jin, J.; Maszczyk, T.; Dauwels, J.; Cash, S.S.; Westover, M.B. Epileptiform spike detection via convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades, A.; Spyrou, L.; Took, C.C.; Sanei, S. Deep learning for epileptic intracranial EEG data. In Proceedings of the IEEE 26th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), Salerno, Italy, 13–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Ye, S.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Xue, Y.; Chen, W. Classification of epileptic EEG signals with stacked sparse autoencoder based on deep learning. In Intelligent Computing Methodologies. ICIC 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Huang, D.S., Han, K., Hussain, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Achilles, F.; Tombari, F.; Belagiannis, V.; Loesch, A.; Noachtar, S.; Navab, N. Convolutional neural networks for real-time epileptic seizure detection. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2016, 1163, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y. Automatic seizure detection using three-dimensional CNN based on multi-channel EEG. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2018, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xun, G.; Jia, K.; Zhang, A. A multiview deep learning method for epileptic seizure detection using short-time fourier transform. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics—ACM-BCB, Boston, MA, USA, 20–23 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gogna, A.; Majumdar, A.; Ward, R. Semi-supervised stacked label consistent autoencoder for reconstruction and analysis of biomedical signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Hussain, M.; Qazi, E.H.; Aboalsamh, H. An automated system for epilepsy detection using EEG brain signals based on deep learning approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 107, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adeli, H. Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 100, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjepkema-Cloostermans, M.C.; de Carvalho, R.C.; van Putten, M.J. Deep learning for detection of focal epileptiform discharges from scalp EEG recordings. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, R.; Thomas, J.; Kluge, T.; Dauwels, J. A deep learning scheme for automatic seizure detection from long-term scalp EEG. In Proceedings of the 2018 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Hügle, M.; Heller, S.; Watter, M.; Blum, M.; Manzouri, F.; Dumpelmann, M.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Woias, P.; Boedecker, J. Early Seizure Detection with an Energy-Efficient Convolutional Neural Network on an Implantable Microcontroller; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.; Comoretto, L.; Jin, J.; Dauwels, J.; Cash, S.; Westover, M. EEG classification via convolutional neural network-based interictal epileptiform event detection. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; pp. 3148–3151. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, R.; Palangi, H.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Optimized deep neural network architecture for robust detection of epileptic seizures using EEG signals. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, A.; Kunii, N.; Matsuo, T.; Shinozaki, T.; Kawai, K.; Takahashi, H. Seizure detection by convolutional neural network-based analysis of scalp electroencephalography plot images. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.J.; Cho, K.O. Dual deep neural network-based classifiers to detect experimental seizures. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 23, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haotian, L.; Lin, X.; Ying, Z.; Zhixiang, L. Using deep learning and machine learning to detect epileptic seizure with electroencephalography (EEG) data. Mach. Learn. Res. 2019, 4, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rohan, A. Wavelet-based deep learning approach for epilepsy detection. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Thara, T.D.K.; Prema, P.S.; Xiong, F. Auto-detection of epileptic seizure events using a deep neural network with different feature scaling techniques. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 128, 544–550. [Google Scholar]
- Türk, Ö.; Özerdem, M.S. Epilepsy detection by using scalogram based convolutional neural network from EEG signals. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, K. Stacking ensemble-based deep neural networks are modeling for effective epileptic seizure detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 148, 113239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahib, A.; Murat, A.; John, B.I.; Boran, S.; Ahmet, I. Identification of epileptic EEG signals using convolutional neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4089. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Li, X. Epilepsy EEG signal classification algorithm based on improved RBF. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilakiyaselvan, N.; Nayeemulla, K.A.; Shahina, A. Deep learning approach to detect seizure using reconstructed phase space images. J. Biomed. Res. 2020, 34, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Deep convolutional neural network-based epileptic electroencephalogram (EEG) signal classification. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, P.; Giuliana, S.; Alessandra, F.; Barbara, C.; Antonio, D.; Barbara, P.; Cesar, A.T. Convolutional neural network for seizure detection of nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy. Hindawi Complex. 2020, 2020, 4825767. [Google Scholar]
- Kyung-Ok, C.; Hyun-Jong, J. Comparison of different input modalities and network structures for deep learning-based seizure detection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Wenbing, Z.; Wenfeng, W.; Xiaolu, J.; Xiaodong, Z.; Yonghong, P.; Baocan, Z.; Guokai, Z. A novel deep neural network for robust detection of seizures using EEG signals. Hindawi Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 9689821. [Google Scholar]
- Naro, A.; Bramanti, P.; Leo, A.; Russo, M.; Calabrò, R.S. Transcranial alternating current stimulation in patients with chronic disorder of consciousness, a possible way to cut the diagnostic gordian knot? Brain Topogr. 2016, 29, 623–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naro, A.; Leo, A.; Manuli, A.; Cannavò, A.; Bramanti, A.; Bramanti, P.; Calabrò, R.S. How far can we go in chronic disorders of consciousness differential diagnosis? The use of neuromodulation in detecting internal and external awareness. Neuroscience 2017, 349, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Billeri, L.; Filoni, S.; Russo, E.F.; Portaro, S.; Militi, D.; Calabrò, R.S.; Naro, A. Toward improving diagnostic strategies in chronic disorders of consciousness: An overview on the (re-)emergent role of neurophysiology. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Frequency Band Name | Frequency Bandwidth (Hz) |
|---|---|
| Alpha | <4 |
| Beta | 4–8 |
| Gamma | 8–12 |
| Delta | 12–30 |
| Theta | <30 |
| Interior Artifacts | Exterior Artifacts |
|---|---|
| Blinking of the eye (EOG) | Power line |
| Heartbeat (ECG) | Machine fault |
| Muscle movements (EMG) | Faulty electrode/poor placement |
| Skin resistance | ventilation |
| Subject’s movement | Digital artefacts (loose wiring, etc.) |
| Author | Year | Features | Classifier | Performance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [90] O. Faust et al. | 2010 | PSD | RBF SVM | Acc = 98.33 |
| [91] Subasi et al. | 2010 | PCA, LDA, LDA | SVM | Acc = 98.75 |
| [92] Guo et al. | 2010 | DWT | ANN | Acc = 99.60 |
| [93] Oweis | 2011 | EMD + MEMD | Euclidean Clustering | Acc = 94.00 |
| [94] Orhan et al. | 2011 | DWT | K-Means Clustering | Acc = 96.67 |
| [95] Yuan et al. | 2011 | Entropy/Hurst exponent | ANN/PD | Acc = 96.50 |
| [96] Marcus and Dragan | 2012 | Bilinear TFD | SVM/ | Acc = 99.30 |
| [97] Arslan et al. | 2013 | SVD | SVM | Acc = 99.00 |
| [98] Gajic et al. | 2014 | Wavelet | Quadratic Classifier | Acc = 98.50 |
| [99] Nabeel | 2014 | Statistical, Non-linear | Linear Classifier | Acc = 99.85 |
| [100] Yatindra et al. | 2014 | Wavelet entropy | SVM | Acc = 90.00 |
| [101] Jaiswal et al. | 2015 | EMD, Wavelet, Morphological filters | Fuzzy Clustering | PI = 98.03, QV = 23.82 |
| [102] Rajaguru et al. | 2015 | Morphological filters | ANN | Acc = 98.33 |
| [103] Bhattacharyya et al. | 2015 | Focal and non-focal, EWT | SVD, EM, MEM | Acc = 90.00 |
| [104] Li et al. | 2016 | DD-DWT | LS-SVM | Acc = 99.36 |
| [105] Li et al. | 2016 | Entropy | GA-SVM | AUC = 0.97 |
| [106] Peker et al. | 2016 | DTCWT | CVNN | Acc = 100 |
| [107] Riaz et al. | 2016 | EMD | SVM | Acc = 96.20 |
| [108] Ghayab et al. | 2016 | SRS and SFS | LS-SVM | Acc = 99.90 |
| [109] Upadhyay et al. | 2016 | DWT | LS-SVM | Acc = 100 |
| [110] Kabir et al. | 2016 | Optimum allocation technique | LMT | Acc = 95.33 |
| [111] Pippa et al. | 2016 | Time domain and frequency domain features | Bayesian Net | Acc = 95.00 |
| [112] Jaiswal and Banka | 2016 | SpPCA and SubXPCA | SVM | Acc = 94.60 |
| [113] Sharma and Pachori | 2017 | TQWT | LS-SVM + FD | Acc = 100 |
| [114] Patidar et al. | 2017 | TQWT and Kraskov entropy | LS-SVM | Acc = 97.75 |
| [115] Diykh et al. | 2017 | Weighted complex network combined with time domain features | LS-SVM | Acc = 98.00 |
| [116] Li et al. | 2017 | MODWT and LND | RFC | Acc = 100 |
| [117] Tiwari et al. | 2017 | Pyramid scheme for keypoint localization and LBP | SVM | Acc = 99.89 |
| [118] Mursalin et al. | 2017 | ICFS | RFC | Acc = 100 |
| [119] Shaikh et al. | 2017 | EMD | ANN | Acc = 96.10 |
| [120] Kocadagli and Langari | 2017 | DWT and fuzzy relations | ANN | Acc = 99.90 |
| [121] Torse et al. | 2017 | EMD | CSM-SVM | Acc = 96.40 |
| [122] Sharma et al. | 2018 | MMSFL-OWFB-based KE | SVM | Acc = 100 |
| [123] Tzimourta et al. | 2018 | Wavelet transform-based features | Random Forest Classifier | Acc = 95.00 |
| [124] Sriraam et al. | 2018 | Teager energy feature | Supervised Backpropagation Neural Network | Acc = 96.66 |
| [125] Sudalaimani et al. | 2018 | Sub-frequency band features | GRNN | Acc = 91.60 |
| [126] Raghu and Sriram | 2018 | NCA | SVM | Acc = 98.80 |
| [127] Li et al. | 2018 | GMM and GLCM features, RFE-SVM | SVM | Acc = 100 |
| [128] Cooman et al. | 2018 | HRI features |
SVM + Adaptive Heuristic classifier | EPsen = 83.30 |
| [129] Li et al. | 2018 | WPT and KDE | LS-SVM | Acc = 99.60 |
| [130] Cruz et al. | 2018 | ACC and EMG | SVM on CloudComputing Platform | Acc = 83.30 |
| [131] Zhang et al. | 2018 | WPD, fDistIn | KNN | Acc = 98.33 |
| [132] Feng et al. | 2018 | WPD | SVM | Acc = 98.67 |
| [133] Tanveer et al. | 2018 | FAWT and entropy-based features | RELS-TSVM | Acc = 100 |
| [134] Choudhury et al. | 2018 | XHST | KNN | Acc = 100 |
| [135] Wani et al. | 2018 | DWT | ANN | Acc = 95.00 |
| [136] Naser et al. | 2019 | DWT and approximation and abe entropies | SVM | Acc = 98.75 |
| [137] Lamhiri and Shmuel | 2019 | Hurst exponent | k-ANN | Acc = 100 |
| [138] Raghu et al. | 2019 | Sigmoid entropy | SVM | Acc = 100 |
| [139] Wang et al. | 2019 | Symlet wavelet processing, and grid search optimizer |
Gradient Boosting Machine | Acc = 96.10 |
| [140] Bose et al. | 2019 | Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis | SVM | Acc = 100 |
| [141] Dalal et al. | 2019 | FAWT and FD | RELS-TSVM | Acc = 90.20 |
| [142] Osman and Alzahrani | 2019 | SOM | RBFNN | Acc = 97.47 |
| [143] Fasil O.K.; Rajesh R | 2019 | Time domain | Exponential Energy | Acc = 99.50 |
| [144] Saminu et al. | 2019 | DWT, Entropies, Energy | SVM, FFANN | Acc = 99.00 |
| [145] Mahjoub et al. | 2020 | TQWT, IMFs, MEMD | SVM | Acc = 98.78 |
| [146] Raluca et al. | 2020 | DWT | ANN | Acc = 91.10 |
| [147] Ozlem et al. | 2020 | Ensemble EMD | KNN | Acc = 97.00 |
| [148] Khaled | 2020 | NA | Random Forest | Acc = 97.08 |
| Authors | Year | Features | Performance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [163] Qi et al. | 2014 | MCC-based R-SAE model | EPsen = 100 |
| [164] Thodoroff et al. | 2016 | CNN + RNN | EPsen = 85.00 |
| [165] Johansen et al. | 2016 | CNN | AUC = 94.70 |
| [166] Antoniades et al. | 2016 | CNN | EPacc = 87.51 |
| [167] Lin et al. | 2016 | SSAE | EPacc = 96.00 |
| [168] Achilles et al. | 2016 | CNN | AUC = 78.33 |
| [169] Wei et al. | 2016 | Multichannel CNN | EPacc = 92.40 |
| [170] Yuan et al. | 2017 | STFT-Mssda | EPacc = 93.82 |
| [171] Gogna et al. | 2017 | Semi-supervised stacked autoencoder | EPacc = 96.90 |
| [172] Ullah et al. | 2018 | P-1D-CNN | EPacc = 99.90 |
| [173] Acharya et al. | 2018 | CNN | EPacc = 88.67 |
| [174] Tjepkema-Cloostermans et al. | 2018 | CNN (1D and 2D) and/or LSTMs | EPspe = 99.90 |
| [175] Yuvaraj et al. | 2018 | CNN | EPsen = 86.29 |
| [176] Maria Hugle et al. | 2018 | CNN | EPsen = 96.00 |
| [177] Thomas et al. | 2018 | CNN | EPacc = 83.86 |
| [178] Hussein et al. | 2019 | LSTM + FC | EPspe = 100 |
| [179] Emami et al. | 2019 | CNN | DR = 100 |
| [180] Jang and Cho | 2019 | Dual deep neural network | EPsen = 100 |
| [181] Haotian Liu | 2019 | CNN, LSTM, GRU | Acc = 0.96 |
| [182] Rohan Akut | 2019 | WT-CNN | Acc = 99.40 |
| [183] Thara et al. | 2019 | DNN | Acc = 97.21 |
| [184] Turk et al. | 2019 | CNN | Acc = 93.6 |
| [185] Akyol | 2020 | SEA | Acc = 97.17 |
| [186] Rahib et al. | 2020 | Deep CNN | Acc = 98.67 |
| [187] Zhou and Li | 2020 | Improved RBF | NA |
| [188] Ilakiyaselva et al. | 2020 | CNN | Acc = 98.50 |
| [189] Gao et al. | 2020 | Deep CNN | Acc = 92.60 |
| [190] Fabio et al. | 2020 | CNN | Acc = 98.82 |
| [191] Kyung-Ok et al. | 2020 | CNN, FCNN, RNN | AUC = 0.993 |
| [192] Wei Zhao et al. | 2020 | 1D DNN | Acc = 99.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saminu, S.; Xu, G.; Shuai, Z.; Abd El Kader, I.; Jabire, A.H.; Ahmed, Y.K.; Karaye, I.A.; Ahmad, I.S. A Recent Investigation on Detection and Classification of Epileptic Seizure Techniques Using EEG Signal. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11050668
Saminu S, Xu G, Shuai Z, Abd El Kader I, Jabire AH, Ahmed YK, Karaye IA, Ahmad IS. A Recent Investigation on Detection and Classification of Epileptic Seizure Techniques Using EEG Signal. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(5):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11050668
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaminu, Sani, Guizhi Xu, Zhang Shuai, Isselmou Abd El Kader, Adamu Halilu Jabire, Yusuf Kola Ahmed, Ibrahim Abdullahi Karaye, and Isah Salim Ahmad. 2021. "A Recent Investigation on Detection and Classification of Epileptic Seizure Techniques Using EEG Signal" Brain Sciences 11, no. 5: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11050668
APA StyleSaminu, S., Xu, G., Shuai, Z., Abd El Kader, I., Jabire, A. H., Ahmed, Y. K., Karaye, I. A., & Ahmad, I. S. (2021). A Recent Investigation on Detection and Classification of Epileptic Seizure Techniques Using EEG Signal. Brain Sciences, 11(5), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11050668







