Modulation of Motor Cortex Plasticity by Repetitive Paired-Pulse TMS at Late I-Wave Intervals Is Influenced by Intracortical Excitability
Abstract
1. Introduction
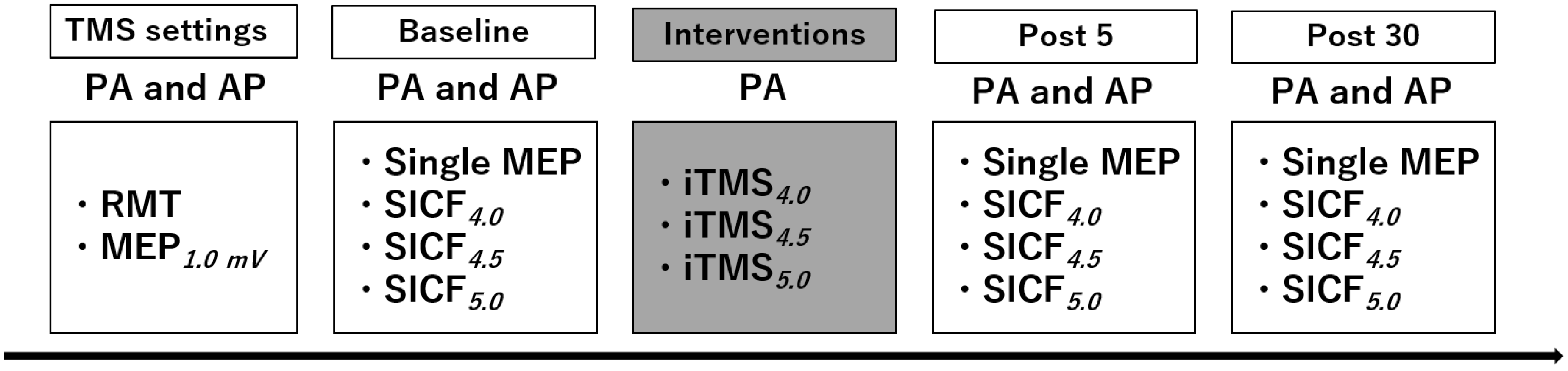
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Arrangement
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.2.1. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
2.2.2. Short-Interval Intracortical Facilitation (SICF)
2.2.3. I-Wave Periodicity Repetitive TMS (iTMS)
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
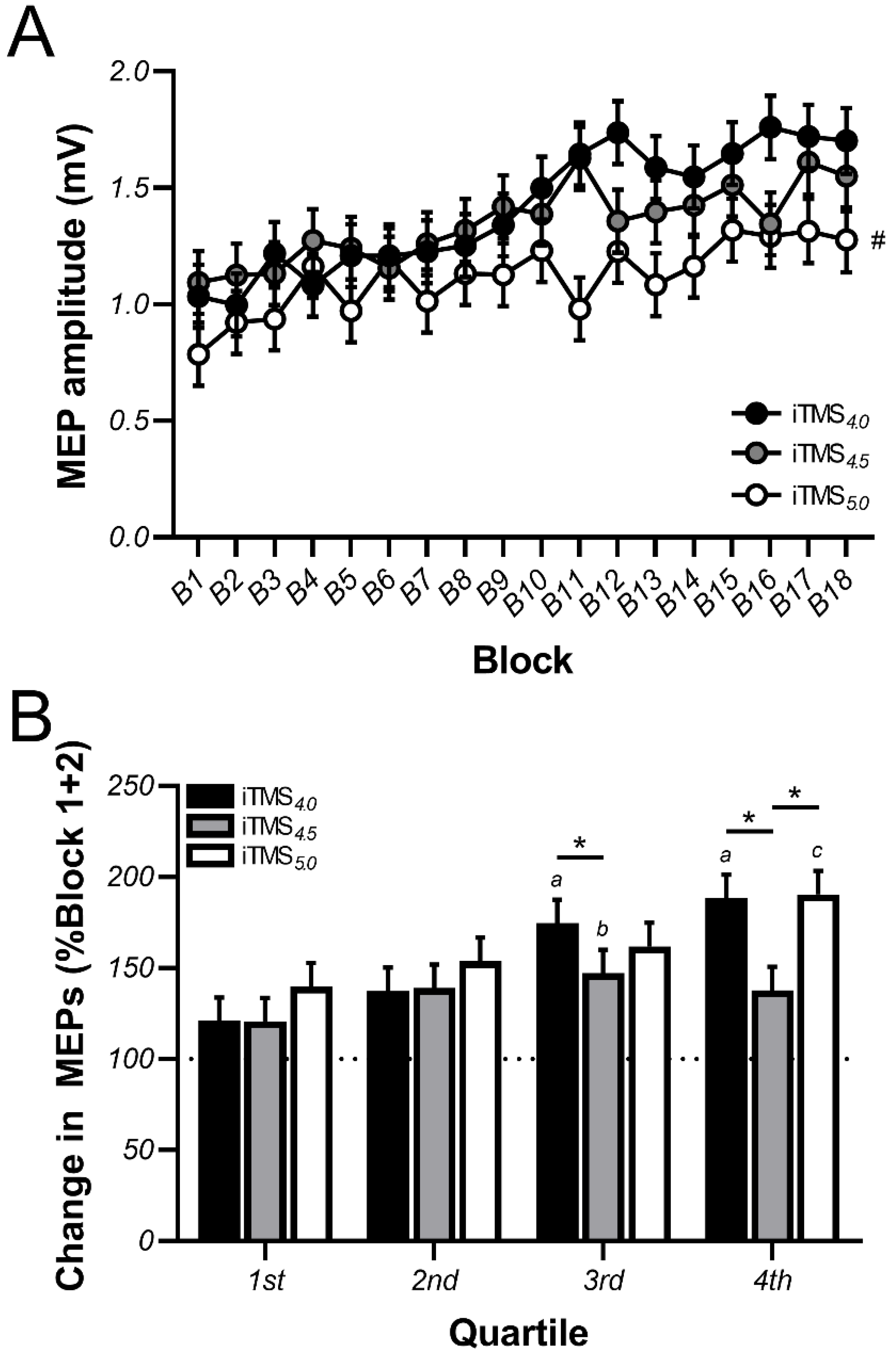
3.1. Changes in Motor Evoked Potential (MEP) Amplitude during iTMS
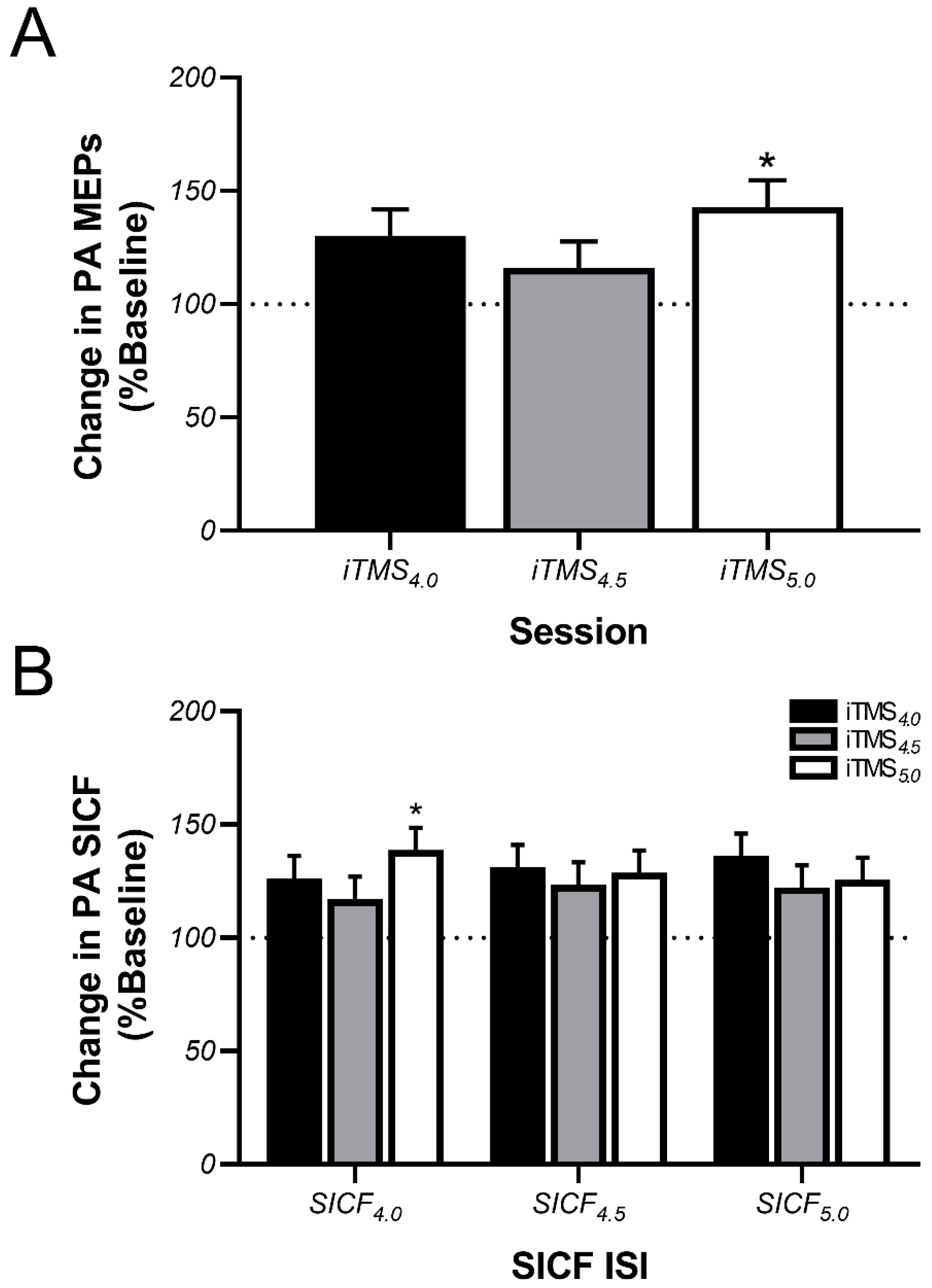
3.2. Effects of iTMS on PA-Sensitive Circuits
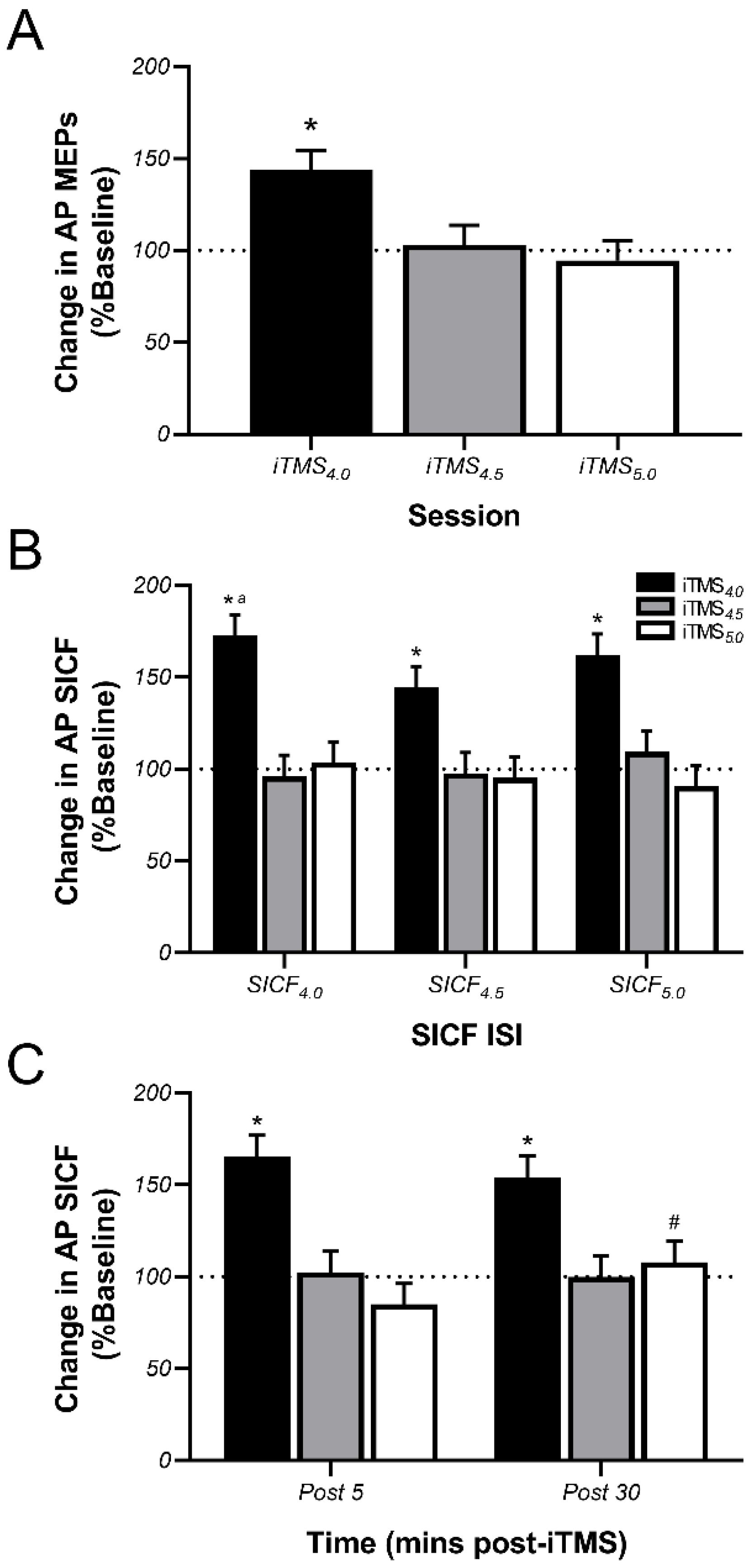
3.3. Effects of iTMS on AP-Sensitive Circuits
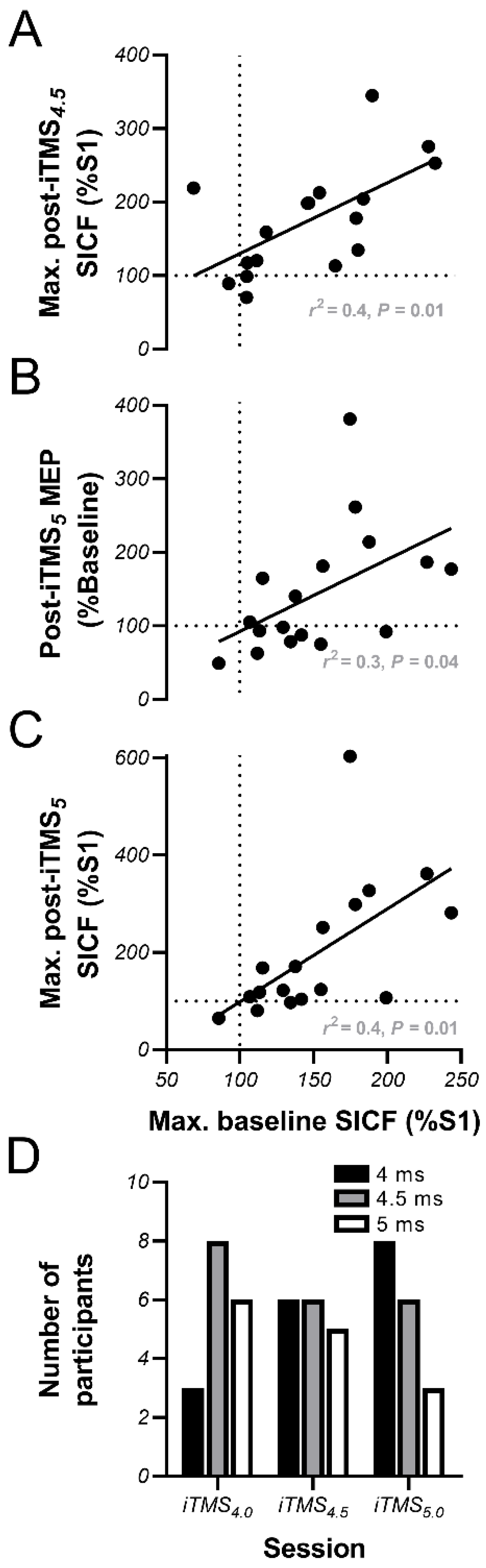
3.4. Linear Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of iTMS on PA-Sensitive Circuits
4.2. Effects of iTMS on AP-Sensitive Circuits
4.3. Baseline Facilitation Predicts iTMS Response, but Not in the Expected Way
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallett, M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and the human brain. Nature 2000, 406, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U.; Paulus, W.; Nitsche, M.A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Byblow, W.D.; Berardelli, A. Consensus: Motor cortex plasticity protocols. Brain Stimul. 2008, 1, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, S.; Bliss, T. Plasticity in the human central nervous system. Brain 2006, 129, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, E.; Cohen Leonardo, G. Neuroplasticity subserving motor skill learning. Neuron 2011, 72, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudo, R.J.; Plautz, E.J.; Frost, S.B. Role of adaptive plasticity in recovery of function after damage to motor cortex. Muscle Nerve 2001, 24, 1000–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, J.C. Techniques and mechanisms of action of transcranial stimulation of the human motor cortex. J. Neurosci. Meth. 1997, 74, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Restuccia, D.; Oliviero, A.; Profice, P.; Ferrara, L.; Insola, A. Effects of voluntary contraction on descending volleys evoked by transcranial stimulation in conscious humans. J. Physiol. 1998, 508, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tsuji, H. Direct and indirect activation of human corticospinal neurons by transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 210, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Rothwell, J.; Capogna, M. Noninvasive stimulation of the human brain: Activation of multiple cortical circuits. Neuroscientist 2018, 24, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U. I-waves in motor cortex revisited. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U.; Tergau, F.; Wischer, S.; Hildebrandt, J.; Paulus, W. Pharmacological control of facilitatory I-wave interaction in the human motor cortex. A paired transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 109, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U.; Tergau, F.; Wassermann, E.M.; Wischer, S.; Hildebrandt, J.; Paulus, W. Demonstration of facilitatory I wave interaction in the human motor cortex by paired transcranial magnetic stimulation. J. Physiol. 1998, 511, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanajima, R.; Ugawa, Y.; Terao, Y.; Enomoto, H.; Shiio, Y.; Mochizuki, H. Mechanisms of intracortical I—Wave facilitation elicited with paired—Pulse magnetic stimulation in humans. J. Physiol. 2002, 538, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemann, U.; Reis, J.; Schwenkreis, P.; Rosanova, M.; Strafella, A.; Badawy, R. TMS and drugs revisited 2014. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 126, 1847–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidgell, D.J.; Mason, J.; Frazer, A.; Pearce, A.J. I-wave periodicity transcranial magnetic stimulation (iTMS) on corticospinal excitability. A systematic review of the literature. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 322, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cash, R.; Benwell, N.; Murray, K.; Mastaglia, F.; Thickbroom, G. Neuromodulation by paired-pulse TMS at an I-wave interval facilitates multiple I-waves. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 193, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thickbroom, G.W.; Byrnes, M.L.; Edwards, D.J.; Mastaglia, F.L. Repetitive paired-pulse TMS at I-wave periodicity markedly increases corticospinal excitability: A new technique for modulating synaptic plasticity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Federico, P.; Perez, M.A. A novel cortical target to enhance hand motor output in humans with spinal cord injury. Brain 2017, 140, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, G.M.; Cirillo, J.; Semmler, J.G. Age—Related changes in late I—Waves influence motor cortex plasticity induction in older adults. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 2597–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, R.F.; Ziemann, U.; Thickbroom, G.W. Inhibitory and disinhibitory effects on I-wave facilitation in motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 105, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Murase, N.; Hasan, A.; Balaratnam, M.; Rothwell, J.C. The role of interneuron networks in driving human motor cortical plasticity. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, J.; Perez, M.A. Subcortical contribution to late TMS-induced I-waves in intact humans. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sewerin, S.; Taubert, M.; Vollmann, H.; Conde, V.; Villringer, A.; Ragert, P. Enhancing the effect of repetitive I-wave paired-pulse TMS (iTMS) by adjusting for the individual I-wave periodicity. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiethoff, S.; Hamada, M.; Rothwell, J.C. Variability in response to transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor cortex. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCambridge, A.B.; Stinear, J.W.; Byblow, W.D. ‘I-wave’recruitment determines response to tDCS in the upper limb, but only so far. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Galea, J.M.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Mazzone, P.; Ziemann, U.; Rothwell, J.C. Two distinct interneuron circuits in human motor cortex are linked to different subsets of physiological and behavioral plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 12837–12849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, G.M.; Semmler, J.G. Preferential activation of unique motor cortical networks with TMS: A review of the physiological, functional and clinical evidence. Neuromodulation 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spampinato, D. Dissecting two distinct interneuronal networks in M1 with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Rossini, P.; Burke, D.; Chen, R.; Cohen, L.; Daskalakis, Z.; Di Iorio, R. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: Basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an IFCN Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1071–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, G.M.; Hand, B.J.; Semmler, J.G. Age-related changes in late synaptic inputs to corticospinal neurons and their functional significance: A paired-pulse TMS study. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, R.F.; Mastaglia, F.L.; Thickbroom, G.W. Evidence for high-fidelity timing-dependent synaptic plasticity of human motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 109, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peurala, S.H.; Muller-Dahlhaus, J.F.; Arai, N.; Ziemann, U. Interference of short-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI) and short-interval intracortical facilitation (SICF). Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2291–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujirai, T.; Caramia, M.D.; Rothwell, J.C.; Day, B.L.; Thompson, P.D.; Ferbert, A. Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 1993, 471, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvendahl, I.; Lindemann, H.; Jung, N.H.; Pechmann, A.; Siebner, H.R.; Mall, V. Influence of waveform and current direction on short-interval intracortical facilitation: A paired-pulse TMS study. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Ugawa, Y.; Terao, Y.; Hanajima, R.; Furubayashi, T.; Kanazawa, I. Preferential activation of different I waves by transcranial magnetic stimulation with a figure-of-eight-shaped coil. Exp. Brain Res. 1997, 113, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammer, T.; Beck, S.; Thielscher, A.; Laubis-Herrmann, U.; Topka, H. Motor thresholds in humans: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study comparing different pulse waveforms, current directions and stimulator types. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, R.; Rothwell, J.C. Pulse duration as well as current direction determines the specificity of transcranial magnetic stimulation of motor cortex during contraction. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.; Ciocca, M.; Chieffo, R.; Hammond, P.; Neef, A.; Paulus, W. TMS of primary motor cortex with a biphasic pulse activates two independent sets of excitable neurones. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.W.; Sullivan, C.M.; Rogasch, N.C.; Hoy, K.E.; Bailey, N.W.; Cash, R.F. The effects of individualised intermittent theta burst stimulation in the prefrontal cortex: A TMS—EEG study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 608–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| iTMS4.0 | iTMS4.5 | iTMS5.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMT (% MSO) | PA | 48.8 ± 1.9 | 48.1 ± 1.9 | 49.2 ± 1.9 |
| AP | 64.8 ± 2.0 * | 64.5 ± 2.0 * | 65.2 ± 2.0 * | |
| MEP1mV intensity (% MSO) | PA | 58.4 ± 2.7 | 58.5 ± 2.7 | 59.4 ± 2.7 |
| AP | 77.7 ± 2.3 * | 75.9 ± 2.4 * | 77.5 ± 2.4 * | |
| MEP1mV amplitude (mV) | PA | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 0.9 ± 0.06 | 0.8 ± 0.06 |
| AP | 0.8 ± 0.06 | 0.7 ± 0.06 | 0.8 ± 0.06 |
| iTMS4.0 | iTMS4.5 | iTMS5.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | SICF4.0 | 111.1 ± 8.1 | 121.3 ± 8.2 | 123.4 ± 8.2 |
| SICF4.5 | 122.9 ± 8.2 | 136.6 ± 8.3 | 130.0 ± 8.2 | |
| SICF5.0 | 111.7 ± 8.2 | 117. 5 ± 8.2 | 126.6 ± 8.2 | |
| AP | SICF4.0 | 122.2 ± 9.2 | 136.4 ± 9.2 | 117.4 ± 9.2 |
| SICF4.5 | 118.7 ± 9.2 | 130.0 ± 9.2 | 118.2 ± 9.1 | |
| SICF5.0 | 99.0 ± 9.1 | 108.2 ± 9.1 | 109.3 ± 9.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Opie, G.M.; Sasaki, R.; Hand, B.J.; Semmler, J.G. Modulation of Motor Cortex Plasticity by Repetitive Paired-Pulse TMS at Late I-Wave Intervals Is Influenced by Intracortical Excitability. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010121
Opie GM, Sasaki R, Hand BJ, Semmler JG. Modulation of Motor Cortex Plasticity by Repetitive Paired-Pulse TMS at Late I-Wave Intervals Is Influenced by Intracortical Excitability. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010121
Chicago/Turabian StyleOpie, George M., Ryoki Sasaki, Brodie J. Hand, and John G. Semmler. 2021. "Modulation of Motor Cortex Plasticity by Repetitive Paired-Pulse TMS at Late I-Wave Intervals Is Influenced by Intracortical Excitability" Brain Sciences 11, no. 1: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010121
APA StyleOpie, G. M., Sasaki, R., Hand, B. J., & Semmler, J. G. (2021). Modulation of Motor Cortex Plasticity by Repetitive Paired-Pulse TMS at Late I-Wave Intervals Is Influenced by Intracortical Excitability. Brain Sciences, 11(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010121






