Effects of Various Doses of Caffeine Ingestion on Intermittent Exercise Performance and Cognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Drug Treatment
2.4. Stroop Task
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Exercise Performance
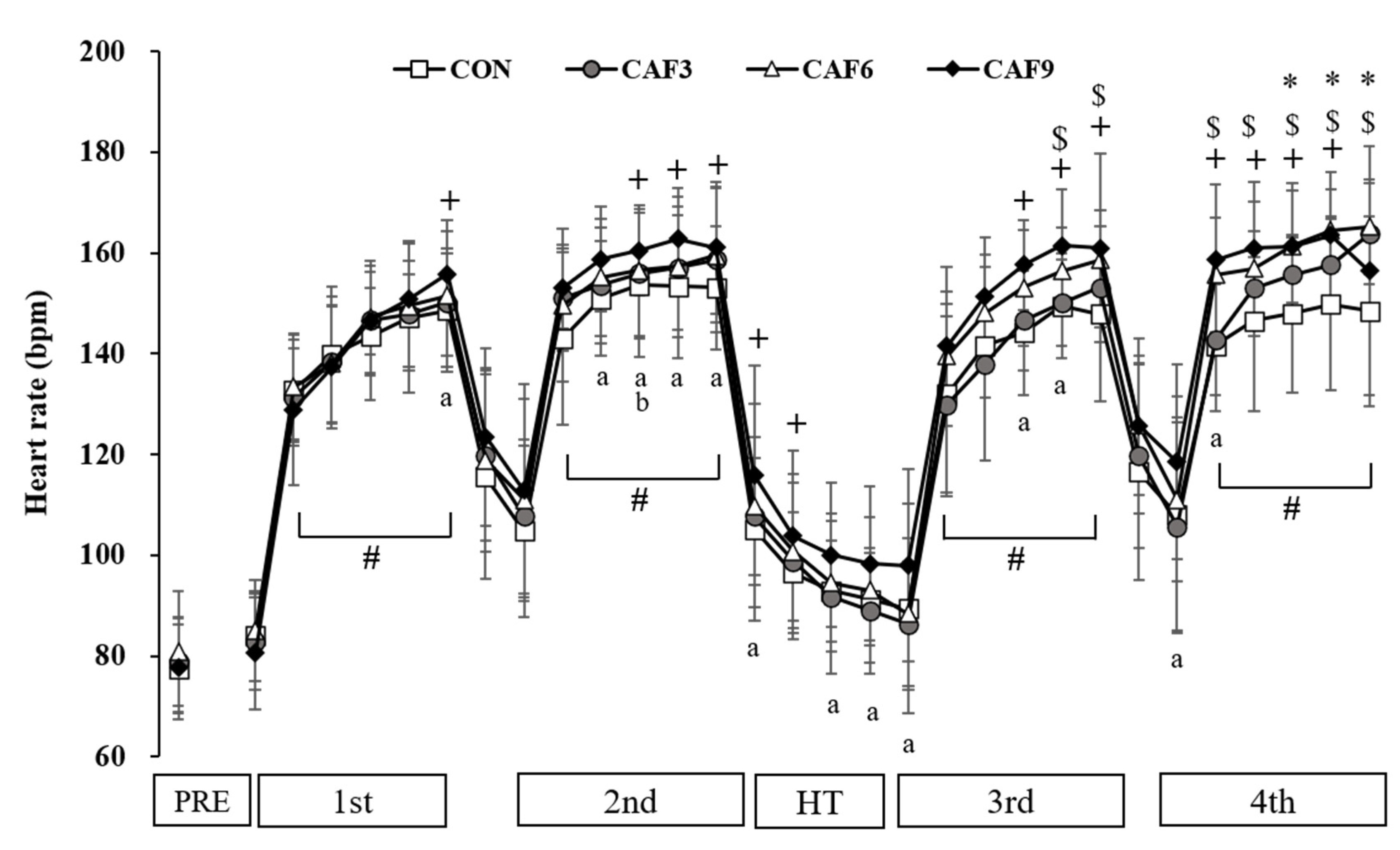
3.2. HR
3.3. RPE
3.4. Stroop Task: Incongruent Condition
3.5. Stroop Task: Congruent Condition
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bishop, D. Dietary supplements and team-sport performance. Sports. Med. 2010, 40, 995–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, N.; Wojek, N. Caffeine consumption amongst british athletes following changes to the 2004 wada prohibited list. Int. J. Sports. Med. 2008, 29, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, N.W.; Fell, J.W.; Leveritt, M.D.; Desbrow, B.; Shing, C.M. Effect of caffeine on cycling time-trial performance in the heat. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2014, 17, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, A.B.; Randell, R.K.; Jeukendrup, A.E.; Earnest, C.P. The metabolic and performance effects of caffeine compared to coffee during endurance exercise. PLoS ONE 2013, 38, e59561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.W.; Haeberlin, E.; Rohde, T. The effect of different dosages of caffeine on endurance performance time. Int. J Sports Med. 1995, 16, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Desbrow, B.; Biddulph, C.; Devlin, B.; Grant, G.D.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; Leveritt, M.D. The effects of different doses of caffeine on endurance cycling time trial performance. J. Sports. Sci. 2012, 30, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.E. Caffeine and exercise: Metabolism, endurance and performance. Sports. Med. 2001, 31, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.R.; Desbrow, B.; Montgomery, P.G.; Anderson, M.E.; Bruce, C.R.; Macrides, T.A.; Burke, L.M. Effect of different protocols of caffeine intake on metabolism and endurance performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.E.; Spriet, L.L. Metabolic, catecholamine, and exercise performance responses to various doses of caffeine. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 78, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spriet, L.L. Exercise and sport performance with low doses of caffeine. Sports Med. 2014, 2, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Macpherson, T.; Spears, I.; Weston, M. The effects of repeated-sprint training on field-based fitness measures: A meta-analysis of controlled and non-controlled trials. Sports. Med. 2015, 45, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaven, C.M.; Maulder, P.; Pooley, A.; Kilduff, L.; Cook, C. Effects of caffeine and carbohydrate mouth rinses on repeated sprint performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 38, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiker, K.T.; Bishop, D.; Dawson, B.; Hackett, L.P. Effects of caffeine on prolonged intermittent-sprint ability in team-sport athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, M.J.; Leicht, A.S.; Spinks, W.L. Physiological and cognitive responses to caffeine during repeated, high-intensity exercise. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2006, 16, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinero, J.; Lara, B.; Ruiz-Vicente, D.; Areces, F.; Puente-Torres, C.; Gallo-Salazar, C.; Coso, J.D. CYP1A2 genotype variations do not modify the benefits and drawbacks of caffeine during exercise: A pilot study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y. Transcranial direct current stimulation with Halo Sport enhances repeated sprint cycling and cognitive performance. Front. Physol. 2019, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.L.; Walker, A.J.; McFadden, B.A.; Sanders, D.J.; Arent, S.M. Effects of TeaCrine and caffein on endurance and cognitive performance during a simulated match in high-level soccer players. J. Int. Soc. Sports. Nutr. 2019, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogervorst, E.; Riedel, W.J.; Kovacs, E.; Brouns, F.; Jolles, J. Caffeine improves cognitive performance after strenuous physical exercise. Int. J. Sports. Med. 1999, 20, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, A.; Kendrick, A.; Maben, A.; Salmon, J. Effects of breakfast and caffeine on cognitive performance, mood and cardiovascular functioning. Appetite 1994, 22, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, H.; Dan, I.; Tsuzuki, D.; Kato, M.; Okamoto, M.; Kyutoku, Y.; Soya, H. Acute moderate exercise elicits increased dorsolateral prefrontal activation and improves cognitive performance with stroop test. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; O’Donnell, J.; Hurst, P.V.; Foskett, A.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K. Caffeine ingestion enhances perceptual responses during intermittent exercise in female team-game players. J. Sports. 2016, 34, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottoms, L.; Greenhalgh, A.; Gregory, K. The effect of caffeine ingestion on skill maintenance and fatigue in epee fencers. J. Sports. Sci. 2013, 31, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods. 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaen, Y.; Onitsuka, S.; Hasegawa, H. Wearing a cooling vest during half-time improves intermittent exercise in the heat. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.A. Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1970, 2, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pauw, K.D.; Roelands, B.; Knaepen, K.; Polfliet, M.; Stiens, J.; Meeusen, R. Effects of caffeine and maltodextrin mouth rinsing on P300, brain imaging and cognitive performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.; Dawson, B.; Schneiker, K.; Goodman, C.; Lay, B. Effect of caffeine supplementation on repeated sprint running performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 93, 990–999. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.; Tierney, P.; Gray, N.; Hawe, G.; Macken, M.; Egan, B. Acute ingestion of caffeinated chewing gum improves repeated sprint performance of team sports athletes with low habitual caffeine consumption. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaister, M.; Howatson, G.; Abraham, C.S.; Lockey, R.A.; Goodwin, J.E.; Foley, P.; McInnes, G. Caffeine supplementation and multiple sprint running performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 20, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, B.J.; Dawson, B.T.; Buck, C.; Wallman, K.E. Effects of sodium phosphate and caffeine ingestion on repeated-sprint ability in male athletes. J. Sci. Sports 2016, 19, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.D.; Hopkins, W.G.; Vollebregt, L. Little effect of caffeine ingestion on repeated sprints in team-sport athletes. Med. Sci. Sports. Exerc. 2001, 33, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.D.; Lowe, T.; Irvine, A. Caffeinated chewing gum increases repeated sprint performance and augments increases in testosterone in competitive cyclists. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranchordas, M.K.; King, G.; Russell, M.; Lynn, A.; Russell, M. Effects of caffeinated gum on a battery of soccer-specific tests in trained university-standard male soccer players. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Cheng, C.F.; Lin, L.C.; Huang, H.W. Caffeine’s effect on intermittent sprint cycling performance with different rest intervals. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Cheng, C.F.; Astorino, T.A.; Lee, C.J.; Huang, H.W.; Chang, W.D. Effects of carbohydrate combined with caffeine on repeated sprint cycling and agility performance in female athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports. Nutr. 2014, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmar, J.M.; Cafarelli, E. Caffeine: A valuable tool to study central fatigue in humans? Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2004, 32, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.K.; Green, J.M. Caffeine and anaerobic performance: Ergogenic value and mechanisms of action. Sports. Med. 2008, 39, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.C.; Deng, Y.Q.; Zheng, X. Cognition and brain activation in response to various doses of caffeine: A near-infrared spectroscopy study. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.J.; Stanley, M.; Parkhouse, N.; Cook, K.; Smith, M. Acute caffeine ingestion enhances strength performance and reduces perceived exertion and muscle pain perception during resistance exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 13, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astorino, T.A.; Terzi, M.N.; Roberson, D.W.; Burnett, T.R. Effect of two doses of caffeine on muscular function during isokinetic exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 2205–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, K.; Matsukawa, K.; Liang, N.; Nakatsuka, C.; Tsuchimochi, H.; Okamura, H.; Hamaoka, T. Dynamic exercise improves cognitive function in association with increased prefrontal oxygenation. J. Physiol. Sci. 2013, 63, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogervorst, E.; Riedel, W.; Jeukendrup, A.; Jolles, J. Cognitive performance after strenuous physical exercise. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1996, 83, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujach, S.; Byun, K.; Hyodo, K.; Suwabe, K.; Soya, H. A transferable high-intensity intermittent exercise improves executive performance in association with dorsolateral prefrontal activation in young adults. Neuroimage 2018, 169, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, Y.; Morishita, S.; Suzuki, R.; Endo, G.; Tsubaki, A. Comparison of the effects of continuous and intermittent exercise on cerebral oxygenation and cognitive function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1232, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst, E.; Bandelow, S.; Schmitt, J.; Jentjens, R.; Oliveira, M.; Allgrove, J.; Carter, T.; Gleeson, M. Caffeine improves physical and cognitive performance during exhaustive exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehlig, A. Is caffeine a cognitive enhancer? J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, S85–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, Y.; Souissi, M.; Chtourou, H. Effects of caffeine ingestion on the diurnal variation of cognitive and repeated high-intensity performances. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 177, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Measurements | Condition | Pre-Ingestion | Post-Ingestion | Post- Exercise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT of incongruent (ms) | CON | 604.85 ± 45.39 | 603.78 ± 45.15 *,# | 562.20 ± 30.79 $ |
| CAF3 | 614.98 ±50.56 | 564.68 ± 41.21 ! | 529.77 ± 35.96 !,$ | |
| CAF6 | 630.38 ± 61.66 | 582.75 ± 38.74 *,! | 549.84 ± 37.82 !,$ | |
| CAF9 | 623.96 ± 68.73 | 609.00 ± 62.00 *,# | 575.60 ±38.37 $ | |
| RT of congruent (ms) | CON | 573.14 ± 32.76 | 573.08 ± 43.00 | 547.76 ± 38.09 $ |
| CAF3 | 582.61 ± 56.39 | 537.15 ± 43.01 ! | 518.58 ± 36.69 !,$ | |
| CAF6 | 582.31 ± 57.07 | 566.69 ± 43.99 | 531.93 ± 56.47 $ | |
| CAF9 | 577.45 ± 62.58 | 570.14 ± 45.18 | 544.71 ± 36.58 $ | |
| ACC | CON | 0.89 ± 0.08 | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 0.89 ± 0.07 |
| of incongruent | CAF3 | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 0.92 ± 0.06 |
| CAF6 | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 0.90 ± 0.05 | 0.90 ± 0.06 | |
| CAF9 | 0.89 ± 0.08 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 0.89 ± 0.11 | |
| ACC | CON | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 0.93 ± 0.04 |
| of congruent | CAF3 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 0.95 ± 0.03 |
| CAF6 | 0.91 ± 0.11 | 0.94 ± 0.03 | 0.93 ± 0.06 | |
| CAF9 | 0.92 ± 0.09 | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.92 ± 0.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, X. Effects of Various Doses of Caffeine Ingestion on Intermittent Exercise Performance and Cognition. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090595
Wang C, Zhu Y, Dong C, Zhou Z, Zheng X. Effects of Various Doses of Caffeine Ingestion on Intermittent Exercise Performance and Cognition. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(9):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090595
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cuicui, Yuechuan Zhu, Cheng Dong, Zigui Zhou, and Xinyan Zheng. 2020. "Effects of Various Doses of Caffeine Ingestion on Intermittent Exercise Performance and Cognition" Brain Sciences 10, no. 9: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090595
APA StyleWang, C., Zhu, Y., Dong, C., Zhou, Z., & Zheng, X. (2020). Effects of Various Doses of Caffeine Ingestion on Intermittent Exercise Performance and Cognition. Brain Sciences, 10(9), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090595




