A Preliminary Study on Cranio-Facial Characteristics Associated with Minor Neurological Dysfunctions (MNDs) in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Morphological Assessment
2.3. Neurological Assessment
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodier, P.M.; Bryson, S.E.; Welch, J.P. Minor Malformations and Physical Measurements in Autism: Data from Nova Scotia. Teratology 1997, 55, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourion, D.; Gourevitch, R.; Le Provost, J.-B.; Olié, J.-P.; Lôo, H.; Krebs, M.-O. L’hypothèse neurodéveloppementale dans la schizophrénie. L’Encéphale 2004, 30, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavan, M.S.; Sanders, R.D.; Sweeney, J.A.; Diwadkar, V.A.; Goldstein, G.; Pettegrew, J.W.; Schooler, N.R. Diagnostic Specificity and Neuroanatomical Validity of Neurological Abnormalities in First-Episode Psychoses. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.F.; Pederson, F.A.; Bell, R.Q. Minor Physical Anomalies and Behavior in Preschool Children. Child Dev. 1968, 39, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgen, H.M.; Hop, J.W.; Hox, J.J.; Beemer, F.A.; Van Engeland, H. Minor physical anomalies in autism: A meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 15, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tripi, G.; Roux, S.; Canziani, T.; Brilhault, F.B.; Barthélémy, C.; Canziani, F. Minor physical anomalies in children with autism spectrum disorder. Early Hum. Dev. 2008, 84, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.; McAlonan, G.; Fung, Y.Y.; Fung, G.; Yu, K.K.; Tai, K.-S.; Sham, P.C.; Chua, S.E. MRI Study of Minor Physical Anomaly in Childhood Autism Implicates Aberrant Neurodevelopment in Infancy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boutrus, M.; Maybery, M.T.; Alvares, G.A.; Tan, D.W.; Varcin, K.J.; Whitehouse, A.J.O. Investigating Facial Phenotype in Autism Spectrum Conditions: The Importance of a Hypothesis Driven Approach. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldridge, K.; George, I.D.; Cole, K.K.; Austin, J.R.; Takahashi, N.; Duan, Y.; Miles, J.H. Facial phenotypes in subgroups of prepubertal boys with autism spectrum disorders are correlated with clinical phenotypes. Mol. Autism 2011, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obafemi-Ajayi, T.; Miles, J.H.; Takahashi, T.N.; Qi, W.; Aldridge, K.; Zhang, M.; Xin, S.-Q.; He, Y.; Duan, Y. Facial Structure Analysis Separates Autism Spectrum Disorders into Meaningful Clinical Subgroups. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 45, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripi, G.; Roux, S.; Matranga, D.; Maniscalco, L.; Glorioso, P.; Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Roccella, M. Cranio-Facial Characteristics in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, X.; Brimacombe, M.; Wagner, G.C. Prevalence of motor impairment in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Dev. 2007, 29, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touwen, B.C.L. Examination of the Child with Minor Neurological Dysfunction; Heinemann Medical Books: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Hadders-Algra, M. Two distinct forms of minor neurological dysfunction: Perspectives emerging from a review of data of the Groningen Perinatal Project. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavas, N.; Arısoy, A.E.; Bayhan, A.; Kara, B.; Günlemez, A.; Türker, G.; Oruç, M.; Gökalp, A.S. Neonatal sepsis and simple minor neurological dysfunction. Pediatr. Int. 2017, 59, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, K.A.; Hass, C.J.; Naik, S.K.; Lodha, N.; Cauraugh, J.H. Motor Coordination in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Synthesis and Meta-Analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2010, 40, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadders-Algra, M.; Touwen, B.C. Minor Neurological Dysfunction Is More Closely Related to Learning Difficulties than to Behavioral Problems. J. Learn. Disabil. 1992, 25, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, M.T.; Bollini, A.; Mack, L.M.; Kryda, A.D.; Rutland, J.; Weiss, P.S.; Bercu, Z.; Esterberg, M.L.; Walker, E.F. Neurological soft signs and minor physical anomalies in patients with schizophrenia and related disorders, their first-degree biological relatives, and non-psychiatric controls. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 94, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; Le Couteur, A. Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1994, 24, 659–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopler, E.; Reichler, R.J.; Renner, B.R. The Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS); Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 3rd ed.; The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, G.H.; Froster, U.G.; Allanson, J.E. Handbook of Normal Physical Measurements; Oxford Medical Publications; Oxford University Press: Cary, NC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, L.G.; Munro, I.R.; Kolar, J.C. Anthropometric Facial Proportions in Medicine; Charles Thomas Publisher Ltd.: Springfield, IL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, L.H.; Maathuis, K.G.; Kouw, E.; Hamming, M.; Hadders-Algra, M. Test-retest, inter-assessor and intra-assessor reliability of the modified Touwen examination. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2008, 12, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapin, I. Preschool Children with Inadequate Communication: Developmental Language Disorder, Autism, Low IQ; Mac Keith Press: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Militerni, R.; Bravaccio, C.; Falco, C.; Fico, C. Palermo MT Repetitive Behaviors in Autistic Disorder. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2002, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, J.H. Autism subgroups from a medical genetics perspective. In Autism Spectrum Disorders; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 705–721. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, J.H.; Hillman, R.E. Value of a Clinical Morphology Examination in Autism. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 91, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirmiya, N.; Charman, T. The prodrome of autism: Early behavioral and biological signs, regression, peri- and post-natal development and genetics. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2010, 51, 432–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.B.; Enticott, P.G.; Rinehart, N.J. Motor Development and Delay: Advances in Assessment of Motor Skills in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Rajerison, T.A.; Paillet, C.; Guimard-Brunault, M.; Saby, A.; Ponson, L.; Tripi, G.; Malvy, J.; Roux, S. Autism is a prenatal disorder: Evidence from late gestation brain overgrowth. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, M.; Punt, M.; De Groot, E.; Minderaa, R.B.; Hadders-Algra, M. Minor neurological dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorder. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamiri, B.; Nelson, C.; Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Murphy, J.M.; Gilman, S.E. Neurological Soft Signs and Cognitive Performance in Early Childhood. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Armony, J.; Servanschreiber, D.; Cohen, J.; Le Doux, J. Computational modeling of emotion: Explorations through the anatomy and physiology of fear conditioning. Trends Cogn. Sci. 1997, 1, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaspe, P.; Schwartz, S.; Vuilleumier, P. Fear and stop: A role for the amygdala in motor inhibition by emotional signals. Neuroimage 2011, 55, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbard, C.R.; Ren, J.; Skuse, D.H.; Clayden, J.D.; Clark, C.A. Structural connectivity of the amygdala in young adults with autism spectrum disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 39, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angkustsiri, K.; Krakowiak, P.; Moghaddam, B.; Wardinsky, T.; Gardner, J.; Kalamkarian, N.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.L.; Wardisky, T. Minor physical anomalies in children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism 2011, 15, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, M.; Jones, K.L. A review of the physical features of the fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 60, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Demographic and Clinical Variables | Anthropometric Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Z-Score | ||
| Age in months | 91.5 (26.7) | Cephalic Index | 74.2 (5.1) | −0.51 (1.2) |
| CARS | 30.4 (5.3) | Facial Index | 83.9 (6.6) | −0.17 (1.3) |
| Global QI | 59.9 (24.2) | Intercanthal Index | 38.7 (2.2) | 0.20 (1.0) |
| VQ | 50 (24.4) | Nasal Index | 72.5 (5.9) | 0.27 (0.9) |
| nVQ | 70 (26.8) | Mouth-Face Index | 36.7 (2.1) | −0.09 (0.9) |
| MND Total | 2.2 (1.5) | |||
| Type of Mild Neurological Dysfunction | |
|---|---|
| n (%) | |
| Posture and muscle tone | 10 (30%) |
| Reflex abnormalities | 1 (3%) |
| Involuntary movements | 3 (9%) |
| Coordination and balance | 10 (30%) |
| Fine motor dysfunction | 11 (33%) |
| Associated Movements | 19 (58%) |
| Sensory deficits | 17 (52%) |
| Cranial nerve dysfunction | 3 (9%) |
| s-MND | 15 (45%) |
| c-MND | 14 (42%) |
| Cephalic Index Z-Score | Facial Index Z-Score | Intercanthal Index Z-Score | Nasal Index Z-Score | Mouth-Face Index Z-Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.330 | 0.060 | −0.061 | 0.732 | 0.143 | 0.426 | −0.044 | 0.807 | 0.001 | 0.999 |
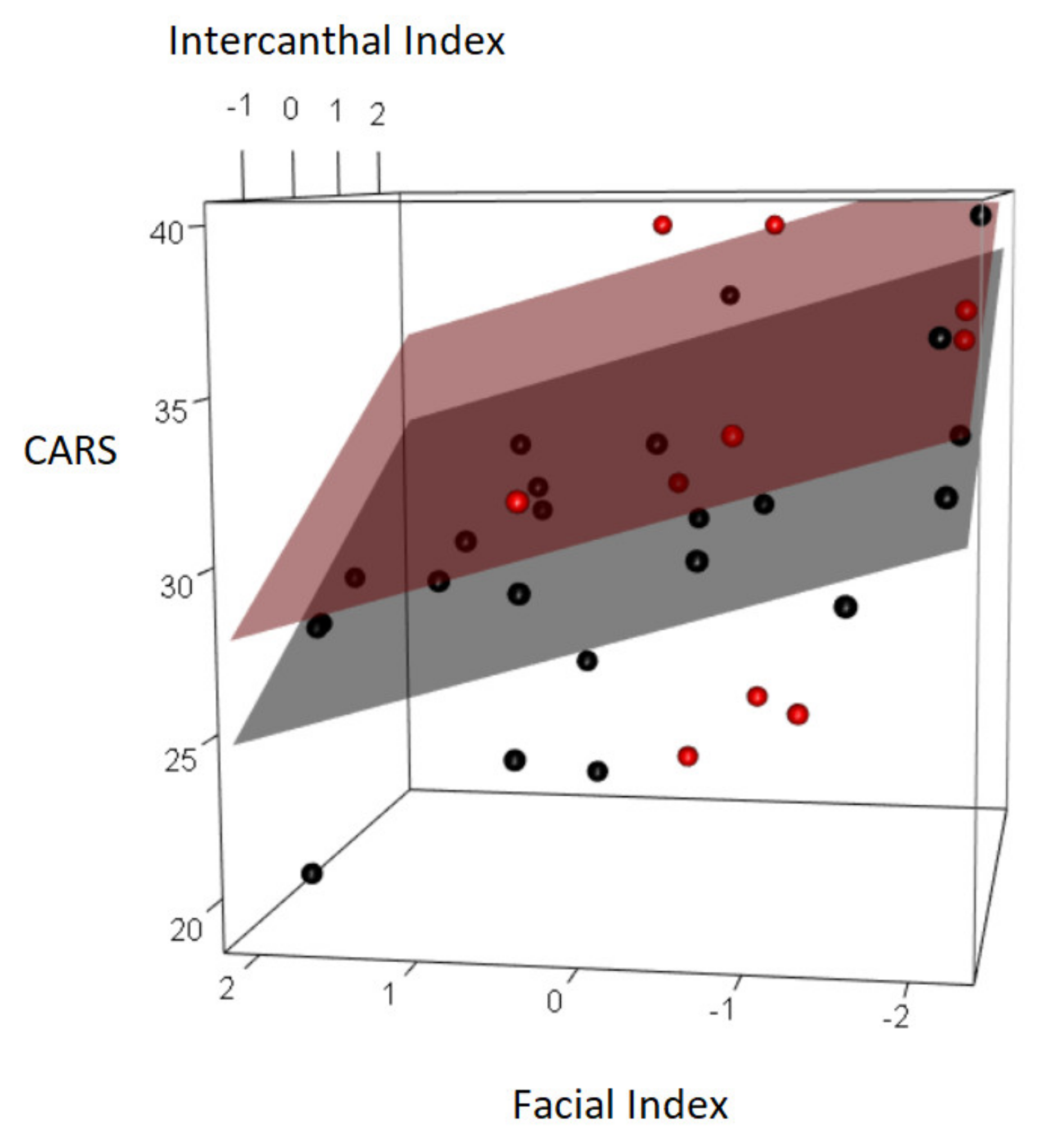
| CARS | 0.315 | 0.073 | −0.505 | 0.002 | 0.384 | 0.027 | −0.274 | 0.122 | −0.029 | 0.870 |
| Global IQ | −0.231 | 0.194 | 0.348 | 0.046 | −0.121 | 0.499 | 0.137 | 0.444 | 0.074 | 0.678 |
| VQ | −0.290 | 0.101 | 0.316 | 0.072 | −0.253 | 0.154 | 0.119 | 0.506 | 0.058 | 0.747 |
| nVQ | −0.182 | 0.308 | 0.328 | 0.061 | 0.012 | 0.944 | 0.208 | 0.244 | 0.036 | 0.838 |
| Posture and muscle tone | 0.432 | 0.012 | −0.293 | 0.097 | 0.278 | 0.116 | −0.196 | 0.272 | 0.192 | 0.283 |
| Reflex abnormalities | 0.186 | 0.299 | 0.049 | 0.785 | 0.381 | 0.028 | −0.259 | 0.145 | 0.174 | 0.332 |
| Involuntary movements | 0.042 | 0.812 | −0.145 | 0.419 | 0.276 | 0.118 | 0.184 | 0.304 | −0.205 | 0.252 |
| Coordination and balance | 0.203 | 0.255 | −0.081 | 0.652 | 0.132 | 0.461 | −0.233 | 0.191 | −0.015 | 0.933 |
| Fine motor dysfunction | −0.094 | 0.609 | 0.011 | 0.948 | 0.296 | 0.096 | −0.093 | 0.604 | −0.322 | 0.067 |
| Associated Movements | 0.158 | 0.378 | −0.298 | 0.091 | 0.154 | 0.391 | −0.021 | 0.906 | −0.048 | 0.788 |
| Sensory deficits | 0.547 | <0.001 | −0.532 | 0.001 | 0.064 | 0.720 | −0.088 | 0.626 | 0.206 | 0.248 |
| Cranial nerve dysfunction | 0.034 | 0.846 | −0.015 | 0.931 | 0.175 | 0.329 | 0.278 | 0.116 | −0.099 | 0.581 |
| s-MND | −0.448 | 0.008 | 0.271 | 0.126 | −0.244 | 0.170 | 0.118 | 0.511 | −0.083 | 0.644 |
| c-MND | 0.469 | 0.005 | −0.468 | 0.005 | 0.245 | 0.168 | −0.150 | 0.403 | 0.013 | 0.941 |
| Coef | 95%CI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cephalic Index | ||||
| Intercept | −5.455 | −10.786 | −0.125 | 0.045 |
| Fine motor dysfunction | −0.899 | −1.827 | 0.028 | 0.056 |
| Sensory deficits | 1.100 | 0.253 | 1.948 | 0.013 |
| Facial Index | ||||
| Intercept | 4.017 | −1.591 | 9.626 | 0.150 |
| CARS | −0.118 | −0.227 | −0.009 | 0.035 |
| Reflex abnormalities | 2.070 | −0.355 | 4.497 | 0.090 |
| Sensory deficits | −1.332 | −2.225 | −0.441 | 0.005 |
| Intercanthal Index | ||||
| Intercept | −4.229 | −9.392 | 0.933 | 0.102 |
| Global IQ | 0.025 | −0.001 | 0.051 | 0.063 |
| Mouth-Face Index | ||||
| Intercept | 0.016 | −5.156 | 5.188 | 0.995 |
| Fine motor dysfunction | −0.842 | −1.742 | 0.059 | 0.065 |
| Coef | 95%CI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CARS | ||||
| Intercept | 39.035 | 35.286 | 42.784 | <0.001 |
| Global QI | −0.138 | −0.191 | −0.085 | <0.001 |
| Posture and muscle tone | −3.155 | −5.944 | −0.367 | 0.027 |
| Facial Index | −1.410 | −2.338 | −0.482 | 0.004 |
| Intercanthal Index | 1.877 | 0.751 | 3.004 | 0.001 |
| Global QI | ||||
| Intercept | 162.072 | 126.819 | 197.326 | <0.001 |
| CARS | −2.674 | −3.894 | −1.455 | <0.001 |
| Total MND | −11.646 | −16.631 | −6.663 | <0.001 |
| Coordination and balance | 9.262 | −3.752 | 22.278 | 0.155 |
| Facial Index | −4.016 | −8.620 | 0.587 | 0.084 |
| Intercanthal Index | 8.805 | 3.281 | 14.331 | 0.002 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniscalco, L.; Frédérique, B.-B.; Roccella, M.; Matranga, D.; Tripi, G. A Preliminary Study on Cranio-Facial Characteristics Associated with Minor Neurological Dysfunctions (MNDs) in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10080566
Maniscalco L, Frédérique B-B, Roccella M, Matranga D, Tripi G. A Preliminary Study on Cranio-Facial Characteristics Associated with Minor Neurological Dysfunctions (MNDs) in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(8):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10080566
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiscalco, Laura, Bonnet-Brilhault Frédérique, Michele Roccella, Domenica Matranga, and Gabriele Tripi. 2020. "A Preliminary Study on Cranio-Facial Characteristics Associated with Minor Neurological Dysfunctions (MNDs) in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD)" Brain Sciences 10, no. 8: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10080566
APA StyleManiscalco, L., Frédérique, B.-B., Roccella, M., Matranga, D., & Tripi, G. (2020). A Preliminary Study on Cranio-Facial Characteristics Associated with Minor Neurological Dysfunctions (MNDs) in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). Brain Sciences, 10(8), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10080566







