Cortical Thickness and Natural Scene Recognition in the Child’s Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
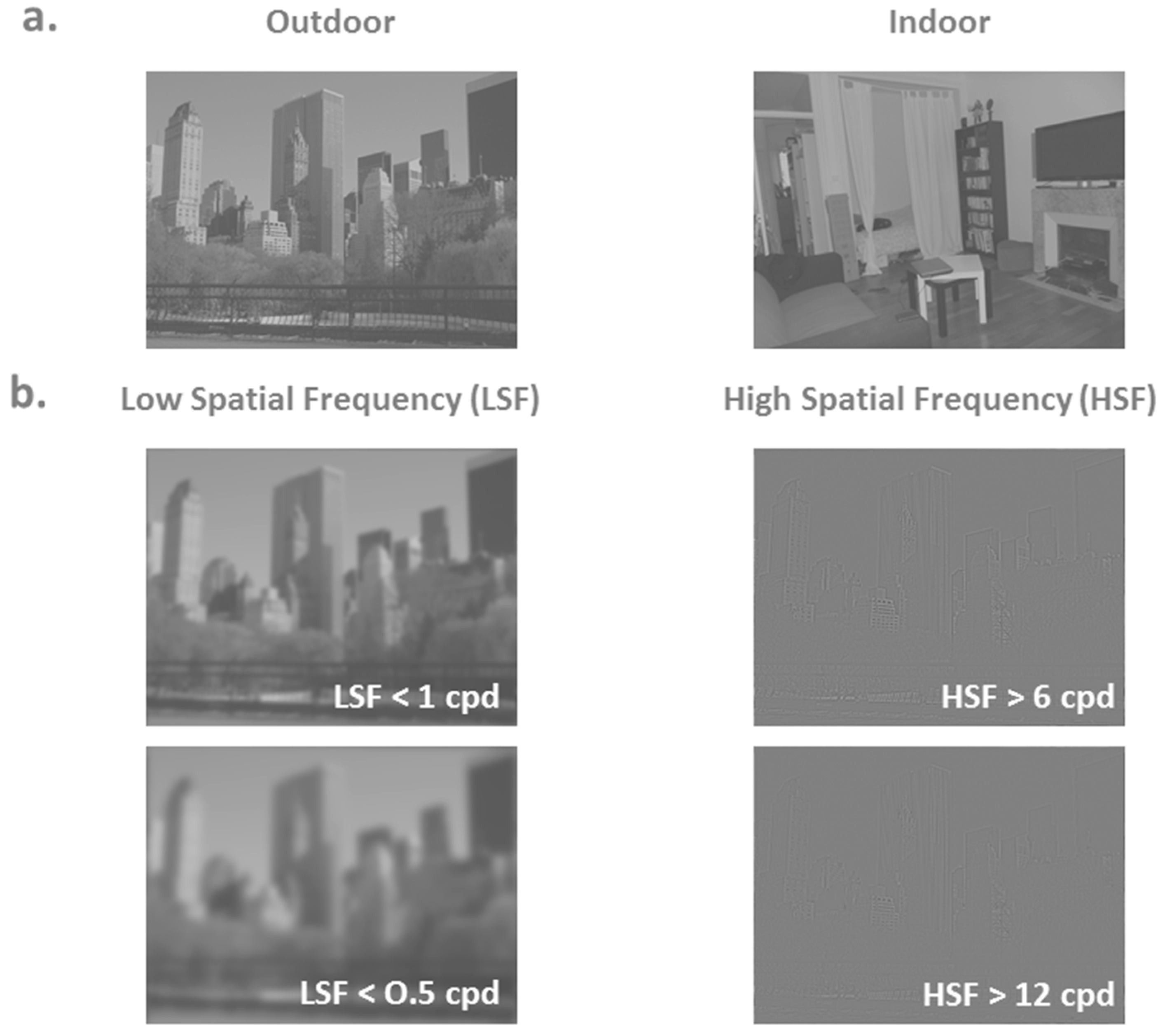
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Behavioral Data
2.3. Cortical Thickness
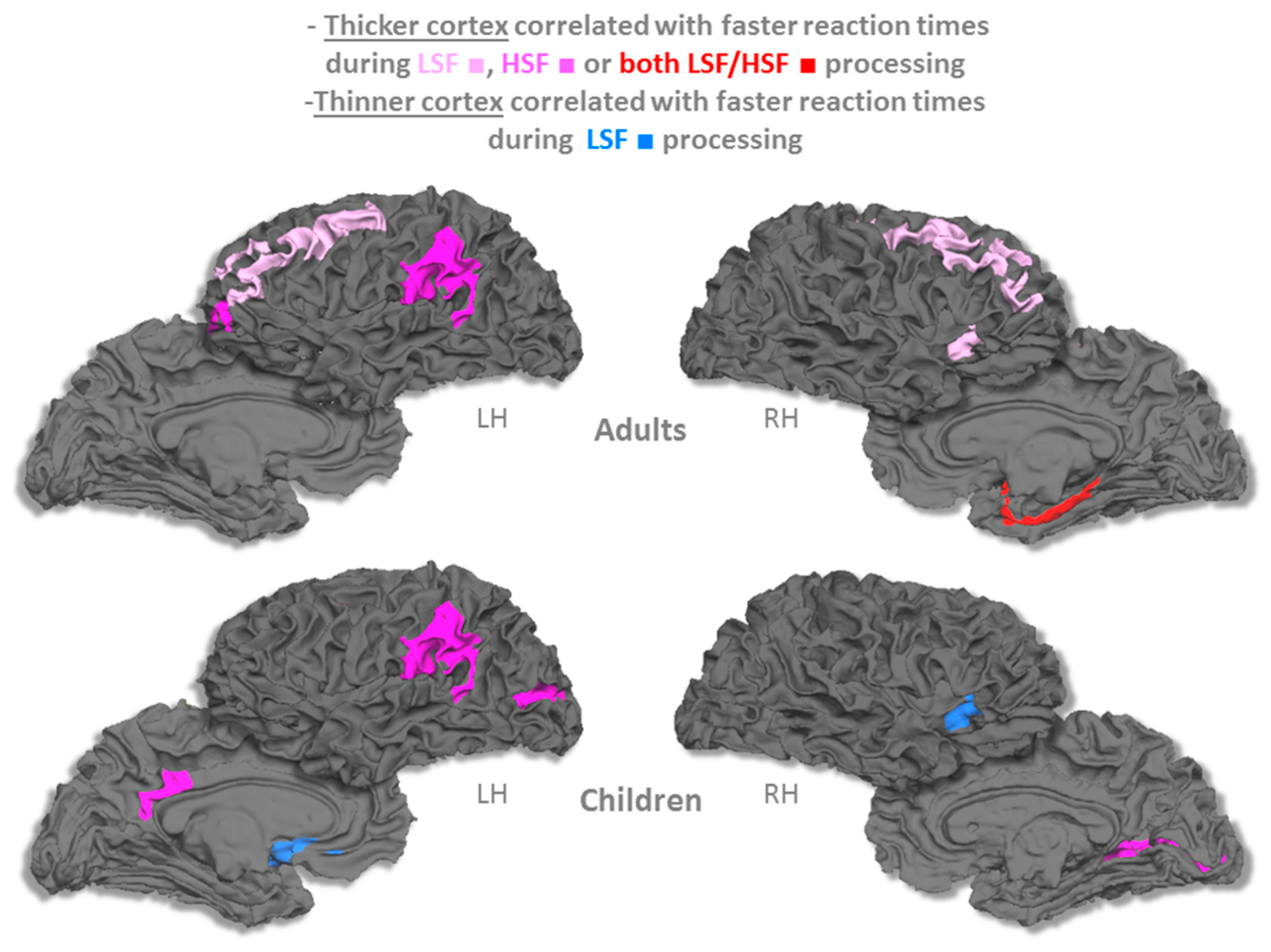
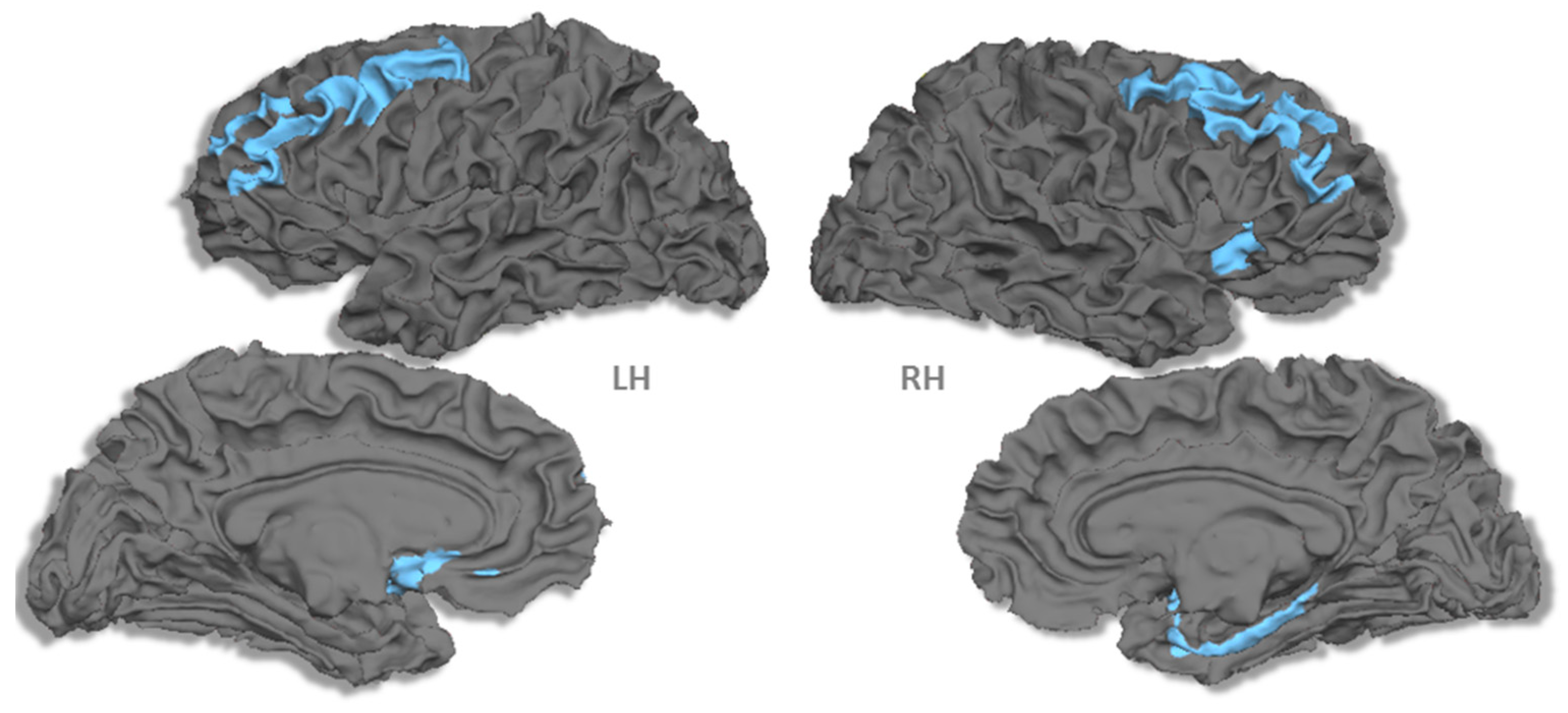
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Data
3.2. Cortical Thickness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Data Availability
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HSF | high spatial frequencies |
| LSF | low spatial frequencies |
| OPA | occipital place area |
| PPA | parahippocampal place area |
| RSC | retrosplenial cortex |
| RTs | reaction times |
References
- Bar, M. Visual objects in context. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, L.; Ramanoël, S.; Peyrin, C. The neural bases of spatial frequency processing during scene perception. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegdé, J. Time course of visual perception: Coarse-to-fine processing and beyond. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 84, 405–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, L.; Chauvin, A.; Guyader, N.; Peyrin, C. Rapid scene categorization: Role of spatial frequency order, accumulation mode and luminance contrast. Vis. Res. 2015, 107, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schyns, P.G.; Oliva, A. From blobs to boundary edges: Evidence for time- and spatial-scale-dependent scene recognition. Psychol. Sci. 1994, 5, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, M.; Kassam, K.S.; Ghuman, A.S.; Boshyan, J.; Schmid, A.M.; Dale, A.M.; Hämäläinen, M.S.; Marinković, K.; Schacter, D.L.; Rosen, B.R.; et al. Top-down facilitation of visual recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauffmann, L.; Chauvin, A.; Pichat, C.; Peyrin, C. Effective connectivity in the neural network underlying coarse-to-fine categorization of visual scenes. A dynamic causal modeling study. Brain Cogn. 2015, 99, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kveraga, K.; Boshyan, J.; Bar, M. Magnocellular projections as the trigger of top-down facilitation in recognition. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 13232–13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilks, D.D.; Julian, J.B.; Paunov, A.M.; Kanwisher, N. The occipital place area is causally and selectively involved in scene perception. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, R.A.; Higgins, J.S.; Jablonski, K.; Feiler, A.M. Visual scene processing in familiar and unfamiliar environments. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 3670–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, R.A.; Kanwisher, N. A cortical representation of the local visual environment. Nature 1998, 392, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, L.; Ramanoël, S.; Guyader, N.; Chauvin, A.; Peyrin, C. Spatial frequency processing in scene-selective cortical regions. NeuroImage 2015, 112, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajimehr, R.; Devaney, K.J.; Bilenko, N.Y.; Young, J.C.; Tootell, R.B.H. The “parahippocampal place area” responds preferentially to high spatial frequencies in humans and monkeys. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1000608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorpe, S.; Fize, D.; Marlot, C. Speed of processing in the human visual system. Nature 1996, 381, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRullen, R.; Thorpe, S.J. Is it a bird? Is it a plane? Ultra-rapid visual categorisation of natural and artifactual objects. Perception 2001, 30, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill-Spector, K.; Kanwisher, N. Visual recognition: As soon as you know it is there, you know what it is. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 16, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellemberg, D.; Hansen, B.C.; Johnson, A. The developing visual system is not optimally sensitive to the spatial statistics of natural images. Vis. Res. 2012, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovács, I. Human development of perceptual organization. Vis. Res. 2000, 40, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navon, D. Forest before trees: The precedence of global features in visual perception. Cogn. Psychol. 1977, 9, 353–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, N.; Mellet, E.; Houdé, O.; Pineau, A. First came the trees, then the forest: Developmental changes during childhood in the processing of visual local-global patterns according to the meaningfulness of the stimuli. Dev. Psychol. 2008, 44, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondloch, C.J.; Geldart, S.; Maurer, D.; de Schonen, S. Developmental changes in the processing of hierarchical shapes continue into adolescence. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2003, 84, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destrieux, C.; Fischl, B.; Dale, A.; Halgren, E. Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanoël, S.; Kauffmann, L.; Cousin, E.; Dojat, M.; Peyrin, C. Age-Related Differences in Spatial Frequency Processing during Scene Categorization. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, P.J.; Makous, W. Spatial frequency, phase, and the contrast of natural images. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2002, 19, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.; Chee, M.W.L.; Zagorodnov, V. Improvement of brain segmentation accuracy by optimizing non-uniformity correction using N3. NeuroImage 2009, 48, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumon, M.; Kveraga, K.; Barrett, L.F.; Bar, M. Visual predictions in the orbitofrontal cortex rely on associative content. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trapp, S.; Bar, M. Prediction, context, and competition in visual recognition. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1339, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenhav, A.; Barrett, L.F.; Bar, M. Affective value and associative processing share a cortical substrate. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 13, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminoff, E.M.; Kveraga, K.; Bar, M. The role of the parahippocampal cortex in cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 1717, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paus, T. Location and function of the human frontal eye-field: A selective review. Neuropsychologia 1996, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schall, J.D.; Stuphorn, V.; Brown, J.W. Monitoring and control of action by the frontal lobes. Neuron 2002, 36, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyrin, C.; Michel, C.M.; Schwartz, S.; Thut, G.; Seghier, M.; Landis, T.; Marendaz, C.; Vuilleumier, P. The neural substrates and timing of top-down processes during coarse-to-fine categorization of visual scenes: A combined fMRI and ERP study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 2768–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganis, G.; Thompson, W.L.; Kosslyn, S.M. Brain areas underlying visual mental imagery and visual perception: An fMRI study. Cogn. Brain Res. 2004, 20, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellet, E.; Briscogne, S.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Ghaëm, O.; Petit, L.; Zago, L.; Etard, O.; Berthoz, A.; Mazoyer, B.; Denis, M. Neural correlates of topographic mental exploration: The impact of route versus survey perspective learning. NeuroImage 2000, 12, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sack, A.T.; Schuhmann, T. Hemispheric Differences within the Fronto-Parietal Network Dynamics Underlying Spatial Imagery. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musel, B.; Kauffmann, L.; Ramanoël, S.; Giavarini, C.; Guyader, N.; Chauvin, A.; Peyrin, C. Coarse-to-fine categorization of visual scenes in scene-selective cortex. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2014, 26, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Kawashima, R.; Sato, N.; Nakamura, A.; Sugiura, M.; Kato, T.; Hatano, K.; Ito, K.; Fukuda, H.; Schormann, T.; et al. Functional delineation of the human occipito-temporal areas related to face and scene processing. A PET study. Brain 2000, 123, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasr, S.; Liu, N.; Devaney, K.J.; Yue, X.; Rajimehr, R.; Ungerleider, L.G.; Tootell, R.B.H. Scene-selective cortical regions in human and nonhuman primates. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13771–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamps, F.S.; Julian, J.B.; Kubilius, J.; Kanwisher, N.; Dilks, D.D. The occipital place area represents the local elements of scenes. NeuroImage 2016, 132, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, R.A. Parahippocampal and retrosplenial contributions to human spatial navigation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2008, 12, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciaramelli, E.; Grady, C.L.; Moscovitch, M. Top-down and bottom-up attention to memory: A hypothesis (AtoM) on the role of the posterior parietal cortex in memory retrieval. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 1828–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, N.; Leroux, E.; Pineau, A.; Houdé, O.; Simon, G. Changes in cortical thickness in 6-year-old children open their mind to a global vision of the world. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 362349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganski, B.; Gaser, C.; Busch, V.; Schuierer, G.; Bogdahn, U.; May, A. Neuroplasticity: Changes in grey matter induced by training. Nature 2004, 427, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatorre, R.J.; Fields, R.D.; Johansen-Berg, H. Plasticity in gray and white: Neuroimaging changes in brain structure during learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenger, E.; Brozzoli, C.; Lindenberger, U.; Lövdén, M. Expansion and Renormalization of Human Brain Structure During Skill Acquisition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2017, 21, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tau, G.Z.; Peterson, B.S. Normal development of brain circuits. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scherf, K.S.; Behrmann, M.; Kimchi, R.; Luna, B. Emergence of global shape processing continues through adolescence. Child Dev. 2009, 80, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sowell, E.R.; Thompson, P.M.; Leonard, C.M.; Welcome, S.E.; Kan, E.; Toga, A.W. Longitudinal mapping of cortical thickness and brain growth in normal children. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8223–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Kabani, N.J.; Lerch, J.P.; Eckstrand, K.; Lenroot, R.; Gogtay, N.; Greenstein, D.; Clasen, L.; Evans, A.; Rapoport, J.L.; et al. Neurodevelopmental trajectories of the human cerebral cortex. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3586–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Label | Hemisphere | p-Value | Pearson’s ρ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | ||||
| LSF | ||||
| G_front_middle | L | 0.046 | −0.49 | |
| G_front_middle | R | 0.048 | −0.49 | |
| G_oc-temp_med-Parahip | R | 0.024 | −0.55 | |
| S_circular_insula_ant | R | 0.021 | −0.55 | |
| S_precentral-sup-part | R | 0.026 | −0.54 | |
| HSF | ||||
| G_and_S_frontomargin | L | 0.046 | −0.49 | |
| G_pariet_inf-Supramar | L | 0.025 | −0.54 | |
| G_oc-temp_med-Parahip | R | 0.030 | −0.53 | |
| Children | ||||
| LSF | ||||
| G_subcallosal | L | 0.031 | 0.58 | |
| S_circular_insula_ant | R | 0.005 | 0.70 | |
| HSF | ||||
| G_cingul-Post-dorsal | L | 0.033 | −0.57 | |
| G_pariet_inf-Supramar | L | 0.018 | −0.62 | |
| S_oc_middle_and_Lunatus | L | 0.033 | −0.57 | |
| S_calcarine | R | 0.027 | −0.59 |
| Label | Hemisphere | F(1,27) | p-Value | η2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G_front_middle | L | 4.98 | 0.03 | 0.16 |
| G_subcallosal | L | 7.79 | 0.01 | 0.22 |
| G_front_middle | R | 4.35 | 0.047 | 0.14 |
| G_oc-temp_med-Parahip | R | 5.92 | 0.02 | 0.18 |
| S_circular_insula_ant | R | 17.30 | <0.001 | 0.39 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orliac, F.; Borst, G.; Simon, G.; Mevel, K.; Vidal, J.; Dollfus, S.; Houdé, O.; Peyrin, C.; Poirel, N. Cortical Thickness and Natural Scene Recognition in the Child’s Brain. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060329
Orliac F, Borst G, Simon G, Mevel K, Vidal J, Dollfus S, Houdé O, Peyrin C, Poirel N. Cortical Thickness and Natural Scene Recognition in the Child’s Brain. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(6):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060329
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrliac, François, Grégoire Borst, Grégory Simon, Katell Mevel, Julie Vidal, Sonia Dollfus, Olivier Houdé, Carole Peyrin, and Nicolas Poirel. 2020. "Cortical Thickness and Natural Scene Recognition in the Child’s Brain" Brain Sciences 10, no. 6: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060329
APA StyleOrliac, F., Borst, G., Simon, G., Mevel, K., Vidal, J., Dollfus, S., Houdé, O., Peyrin, C., & Poirel, N. (2020). Cortical Thickness and Natural Scene Recognition in the Child’s Brain. Brain Sciences, 10(6), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060329





