Mini-Basketball Training Program Improves Social Communication and White Matter Integrity in Children with Autism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Usual Care and Mini-Basketball Training Program
2.4. Behavioral Measurements
2.5. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Acquisition and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Analyses
3.2. Social Communication Performance
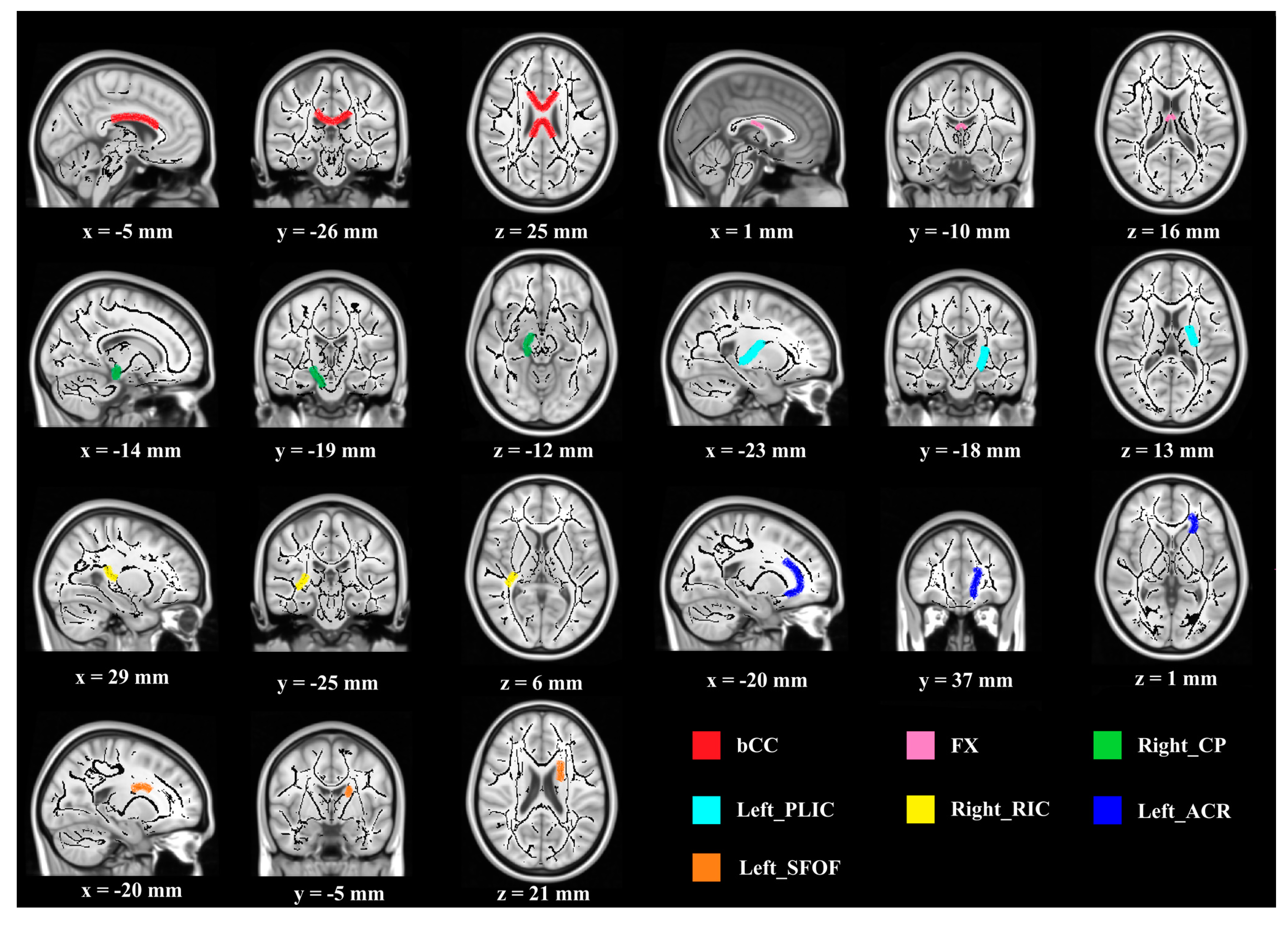
3.3. White Matter Structure
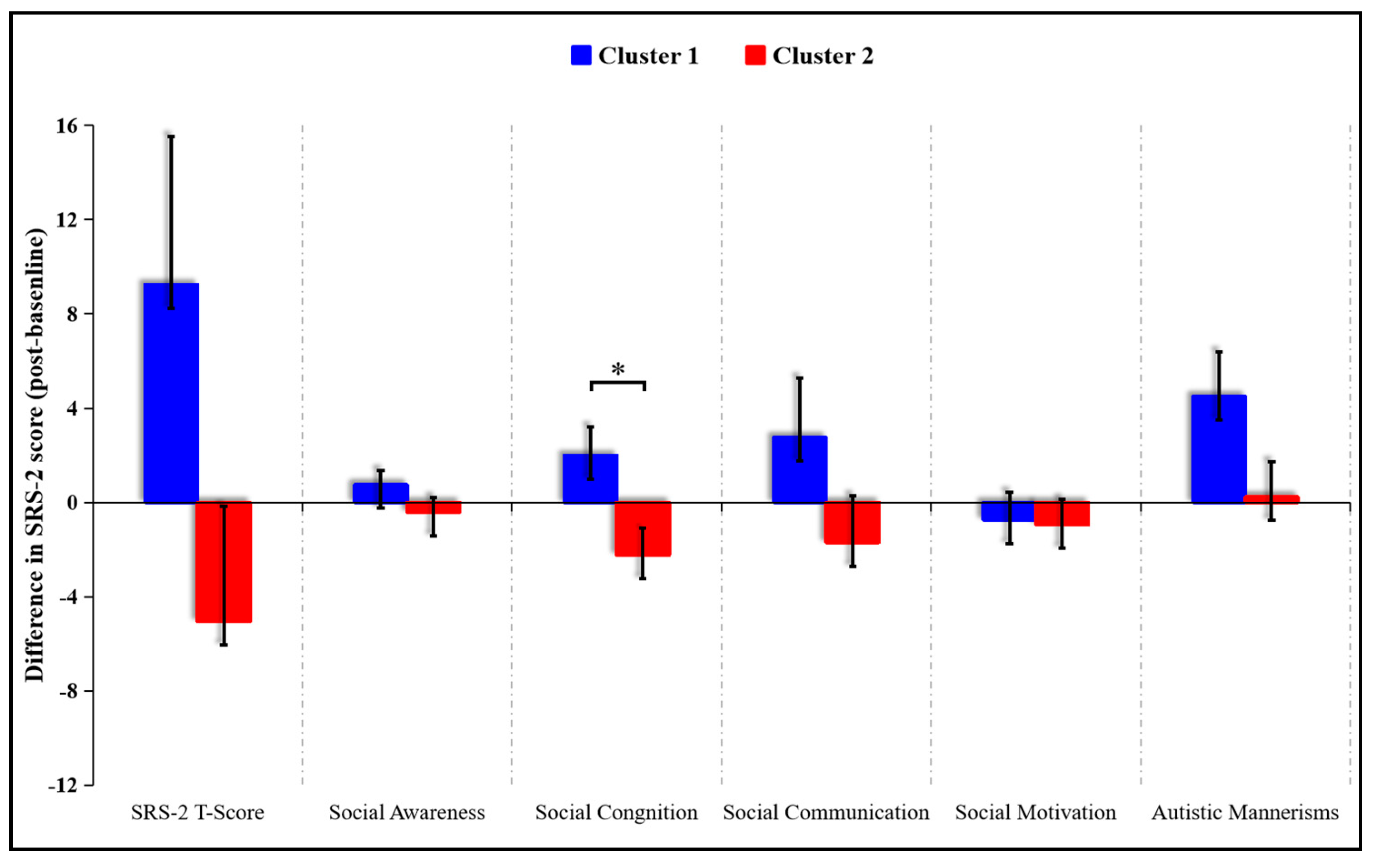
3.4. Exploratory K-Means Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lord, C.; Brugha, T.S.; Charman, T.; Cusack, J.; Dumas, G.; Frazier, T.; Jones, E.J.H.; Jones, R.M.; Pickles, A.; State, M.W.; et al. Autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.R.; Fox, N.A.; Zeanah, C.H., Jr.; Nelson, C.A. Social communication difficulties and autism in previously institutionalized children. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 54, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landa, R.J.; Holman, K.C.; Garrett-Mayer, E. Social and communication development in toddlers with early and later diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Classification of Diseases for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics, 11th Revision. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en (accessed on 27 June 2018).
- Association, A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, S.L.; Havdahl, K.A.; Huerta, M.; Lord, C. Subdimensions of social-communication impairment in autism spectrum disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2016, 57, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Data & Statistics on Autism Spectrum Disorder. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Roane, H.S.; Fisher, W.W.; Carr, J.E. Applied behavior analysis as treatment for autism spectrum disorder. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 175, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.R.; Radley, K.C.; Jenson, W.R.; West, R.P.; Clare, S.K. Peer-facilitated discrete trial training for children with autism spectrum disorder. Sch. Psychol. Q. 2016, 31, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahmer, A.C. Teaching symbolic play skills to children with autism using pivotal response training. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1995, 25, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, A.C.Y. Brief report: Impact of a physical exercise intervention on emotion regulation and behavioral functioning in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2020, 50, 4191–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.Y. Effects of water exercise swimming program on aquatic skills and social behaviors in children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism 2010, 14, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.L.; Wang, J.G.; Liu, Z.M.; Zhu, L.N.; Xiong, X.; Klich, S.; Maszczyk, A.; Chen, A.G. Mini-basketball training program improves physical fitness and social communication in preschool children with autism spectrum disorders. J. Hum. Kinet. 2020, 73, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, D.J.; Krafft, C.E.; Schwarz, N.F.; Chi, L.; Rodrigue, A.L.; Pierce, J.E.; Allison, J.D.; Yanasak, N.E.; Liu, T.; Davis, C.L.; et al. An 8-month exercise intervention alters frontotemporal white matter integrity in overweight children. Psychophysiology 2014, 51, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddock-Heyman, L.; Erickson, K.I.; Holtrop, J.L.; Voss, M.W.; Pontifex, M.B.; Raine, L.B.; Hillman, C.H.; Kramer, A.F. Aerobic fitness is associated with greater white matter integrity in children. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krafft, C.E.; Schaeffer, D.J.; Schwarz, N.F.; Chi, L.; Weinberger, A.L.; Pierce, J.E.; Rodrigue, A.L.; Allison, J.D.; Yanasak, N.E.; Liu, T.; et al. Improved frontoparietal white matter integrity in overweight children is associated with attendance at an after-school exercise program. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, X.; Shu, Y. Martial arts for health benefits in children and youth with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Arch. Budo 2017, 13, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chaddock-Heyman, L.; Erickson, K.I.; Kienzler, C.; Drollette, E.S.; Raine, L.B.; Kao, S.C.; Bensken, J.; Weisshappel, R.; Castelli, D.M.; Hillman, C.H.; et al. Physical activity increases white matter microstructure in children. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Verdejo-Roman, J.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Chaddock-Heyman, L.; Raine, L.B.; Stillman, C.M.; Kramer, A.F.; Erickson, K.I.; et al. Physical fitness, white matter volume and academic performance in children: Findings from the active brains and fit kids 2 projects. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chou, K.H.; Chen, I.Y.; Fan, Y.T.; Decety, J.; Lin, C.P. Atypical development of white matter microstructure in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. NeuroImage 2010, 50, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.J.; Gerig, G.; Lewis, J.D.; Soda, T.; Styner, M.A.; Vachet, C.; Botteron, K.N.; Elison, J.T.; Dager, S.R.; Estes, A.M.; et al. Altered corpus callosum morphology associated with autism over the first 2 years of life. Brain 2015, 138, 2046–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Yoncheva, Y.N.; Chen, B.; Nath, T.; Sharp, D.; Lazar, M.; Velasco, P.; Milham, M.P.; Di Martino, A. Association of white matter structure with autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.; Chua, S.E.; Cheung, V.; Khong, P.L.; Tai, K.S.; Wong, T.K.; Ho, T.P.; McAlonan, G.M. White matter fractional anisotrophy differences and correlates of diagnostic symptoms in autism. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 2009, 50, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.M.; Copeland, B.A.; Karp, E.L.; Finley, C.I.; Houchins-Juarez, N.J.; Ledford, J.R. Chaining functional basketball sequences (with embedded conditional discriminations) in an adolescent with autism. Behav. Anal. Pract. 2016, 9, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using g*power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotrousi, F.; Bagherly, J.; Ghasemi, A. The compensatory impact of mini-basketball skills on the progress of fundamental movements in children. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 46, 5206–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Wan, Q.; Guo, L.Y. Effects of adapted physical exercise intervention on visual working memory in children with autism spectrum disorder. China Sport Sci. Technol. 2017, 53, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.G.; Cai, K.L.; Liu, Z.M.; Herold, F.; Zou, L.; Zhu, L.N.; Xiong, X.; Chen, A.G. Effects of mini-basketball training program on executive functions and core symptoms among preschool children with autism spectrum disorders. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopler, E.; Reichler, R.J.; DeVellis, R.F.; Daly, K. Toward objective classification of childhood autism: Childhood autism rating scale (cars). J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1980, 10, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, T.V.; Eriksen, W.T.; Souders, M.C.; Pinto-Martin, J.A. Eating behaviors, diet quality, and gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorders: A brief review. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2013, 28, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angriman, M.; Caravale, B.; Novelli, L.; Ferri, R.; Bruni, O. Sleep in children with neurodevelopmental disabilities. Neuropediatrics 2015, 46, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.A.; Spirito, A.; McGuinn, M. The children’s sleep habits questionnaire (cshq): Psychometric properties of a survey instrument for school-aged children. Sleep 2000, 23, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, J.; Guthrie, C.A.; Sanderson, S.; Rapoport, L. Development of the children’s eating behaviour questionnaire. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2001, 42, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantino, J.; Gruber, C.P. The Social Responsiveness Scale (Srs) Manual; Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Zhong, S.; Xu, P.; He, Y.; Gong, G. Panda: A pipeline toolbox for analyzing brain diffusion images. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Ring, H.A.; Wheelwright, S.; Bullmore, E.T.; Brammer, M.J.; Simmons, A.; Williams, S.C. Social intelligence in the normal and autistic brain: An fMRI study. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanfield, A.C.; McIntosh, A.M.; Spencer, M.D.; Philip, R.; Gaur, S.; Lawrie, S.M. Towards a neuroanatomy of autism: A systematic review and meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging studies. Eur. Psychiatry 2008, 23, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, C.S.; Weng, S.J.; Wiggins, J.L.; Kurapati, N.; Louro, H.M.; Carrasco, M.; Maslowsky, J.; Risi, S.; Lord, C. Neural circuitry of emotional face processing in autism spectrum disorders. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2010, 35, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courchesne, E.; Pierce, K. Why the frontal cortex in autism might be talking only to itself: Local over-connectivity but long-distance disconnection. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005, 15, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickelgren, I. Autistic brains out of synch? Science 2005, 308, 1856–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.C.; Catani, M.; Deeley, Q.; Latham, R.; Daly, E.; Kanaan, R.; Picchioni, M.; McGuire, P.K.; Fahy, T.; Murphy, D.G. Altered connections on the road to psychopathy. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, Y.; She, L.; Sui, Y.N.; Liu, L.; Richards, L.J.; Poo, M.M. Axon position within the corpus callosum determines contralateral cortical projection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2714–E2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellani, M.; Yeh, P.H.; Tansella, M.; Balestrieri, M.; Soares, J.C.; Brambilla, P. Dti studies of corpus callosum in bipolar disorder. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 1096–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, G.M.; Ansermet, F.; Parnas, J. Schizophrenia, neurodevelopment and corpus callosum. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.L.; Lee, J.E.; Lazar, M.; Boudos, R.; DuBray, M.B.; Oakes, T.R.; Miller, J.N.; Lu, J.; Jeong, E.K.; McMahon, W.M.; et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the corpus callosum in autism. NeuroImage 2007, 34, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Miller, J.H.; Shimony, J.S.; Conturo, T.E.; Lee, B.C.; Almli, C.R.; McKinstry, R.C. Normal brain maturation during childhood: Developmental trends characterized with diffusion-tensor MRI. Radiology 2001, 221, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, R.J.; Mateljevic, N.; Kaiser, M.D.; Sugrue, D.R.; Volkmar, F.R.; Pelphrey, K.A. Structural neural phenotype of autism: Preliminary evidence from a diffusion tensor imaging study using tract-based spatial statistics. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, J.; Brogna, C.; Robles, S.G.; Vergani, F.; Duffau, H. Anatomic dissection of the inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus revisited in the lights of brain stimulation data. Cortex 2010, 46, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, R.P. The autistic child’s appraisal of expressions of emotion: A further study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1986, 27, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippi, C.L.; Mehta, S.; Grabowski, T.; Adolphs, R.; Rudrauf, D. Damage to association fiber tracts impairs recognition of the facial expression of emotion. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15089–15099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D.; Sherman, J.C. The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 1998, 121, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.Q.; Xie, J.X.; Yuan, H.S.; Pei, X.L.; Dong, W.T.; Liu, P.C. Diffusion tensor imaging study of the anterior limb of internal capsules in neuroleptic-naive schizophrenia. Acad. Radiol. 2008, 15, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendlebury, S.T.; Blamire, A.M.; Lee, M.A.; Styles, P.; Matthews, P.M. Axonal injury in the internal capsule correlates with motor impairment after stroke. Stroke 1999, 30, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luna, B.; Minshew, N.J.; Garver, K.E.; Lazar, N.A.; Thulborn, K.R.; Eddy, W.F.; Sweeney, J.A. Neocortical system abnormalities in autism: An fMRI study of spatial working memory. Neurology 2002, 59, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.A.; Kana, R.K.; Just, M.A. A developmental study of the structural integrity of white matter in autism. Neuroreport 2007, 18, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, M.; Jones, D.K.; Daly, E.; Embiricos, N.; Deeley, Q.; Pugliese, L.; Curran, S.; Robertson, D.; Murphy, D.G. Altered cerebellar feedback projections in Asperger syndrome. NeuroImage 2008, 41, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, G.; Courchesne, E. The cerebellum and non-motor function: Clinical implications. Mol. Psychiatry 1998, 3, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Penn, H.E. Neurobiological correlates of autism: A review of recent research. Child Neuropsychol. 2006, 12, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsetos, C.D.; Hyde, T.M.; Herman, M.M. Neuropathology of the cerebellum in schizophrenia–An update: 1996 and future directions. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 42, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, F.X.; Giedd, J.N.; Marsh, W.L.; Hamburger, S.D.; Vaituzis, A.C.; Dickstein, D.P.; Sarfatti, S.E.; Vauss, Y.C.; Snell, J.W.; Lange, N.; et al. Quantitative brain magnetic resonance imaging in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1996, 53, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Venuti, P.; Apicella, F.; Muratori, F. Analysis of unsupported gait in toddlers with autism. Brain Dev. 2011, 33, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayate, A.; Tonge, B.J.; Bradshaw, J.L.; McGinley, J.L.; Iansek, R.; Rinehart, N.J. Differentiation of high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder based on neuromotor behaviour. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.S.; Hong, J.H.; Hong, C.; Yeo, S.S.; Lee, D.; Cho, H.K.; Jang, S.H. Location of the corticospinal tract at the corona radiata in human brain. Brain Res. 2010, 1326, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | Content | Goal | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom routine | Line up, classroom greetings, roll call, etc. | Communication and social interaction | 2 min |
| Warm-up activities | Stretching, jogging, limbs exercise, etc. | Warm-up | 8 min |
| Mini-basketball training program | Phase I: simple basketball training Phase II: mini-basketball skill learning Phase III: game based on mini-basketball | Social interaction and mini-basketball skills development | 25 min |
| Cool-down activities | Relaxation exercise and summary | Review, summary, reward, clean-up | 5 min |
| Phase | Goal | Content | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I | Standardize classroom routines Increase children’s interest in mini- basketball | Classroom routines (taking turns, waiting, obeying, etc.) Simple basketball training (roll and throw the ball, etc.) | 2 weeks |
| Phase II | Improve children’s mini-basketball skills Improve their social communication skills | Basic basketball skill (dribbling, passing, shooting, etc.) Peer coordination training (passing and catching ball, relay racing, etc.) | 8 weeks |
| Phase III | Improve children’s cooperative ability, social skills, and collectivization | Group game based on mini-basketball (basketball-dribbling relay, basketball-passing relays, basket-moving shooting, playing ducks, etc.) | 2 weeks |
| Variable | Control Group | Exercise Group |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 14 | 15 |
| Gender (boys/girls) | 13/1 | 12/3 |
| Age (years) | 4.68 ± 0.72 | 5.13 ± 0.61 |
| BMI (height/weight2) | 16.08 ± 1.69 | 15.65 ± 1.17 |
| CARS a | 38.86 ± 3.90 | 41.20 ± 7.23 |
| CSHQ b | 58.00 ± 12.53 | 56.80 ± 5.06 |
| CEBQ c | 53.50 ± 20.49 | 55.20 ± 7.67 |
| Variable | Control Group (n = 14) | Exercise Group (n = 15) | F | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Post-Test | Baseline | Post-Test | ||
| SRS-2 T-score a | 84.64 ± 20.65 | 97.14 ± 22.14 | 96.53 ± 26.28 | 85.27 ± 29.41 | 11.869 ** |
| Social awareness | 10.36 ± 2.50 | 11.36 ± 2.68 | 12.40 ± 3.11 | 11.87 ± 4.37 | 3.243 |
| Social cognition | 17.21 ± 3.68 | 19.42 ± 4.01 | 20.27 ± 5.15 | 17.07 ± 5.23 | 11.872 ** |
| Social communication | 30.71 ± 8.34 | 35.43 ± 8.37 | 33.80 ± 11.37 | 29.80 ± 10.705 | 10.094 ** |
| Social motivation | 14.36 ± 4.55 | 14.50 ± 4.35 | 15.80 ± 4.13 | 13.47 ± 5.37 | 2.902 |
| Autistic mannerisms | 12.00 ± 5.46 | 16.43 ± 6.38 | 14.27 ±6.45 | 13.07 ± 5.95 | 6.283 ** |
| WM Region | Control Group (n = 14) | Exercise Group (n = 15) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Post-Test | Baseline | Post-Test | |
| Fractional Anisotropy | ||||
| Body of corpus callosum | 0.557 ± 0.031 | 0.551 ± 0.038 | 0.556 ± 0.024 | 0.497 ± 0.051 |
| Fornix | 0.477 ± 0.078 | 0.463 ± 0.078 | 0.479 ± 0.055 | 0.654 ± 0.025 |
| Right cerebral peduncle | 0.621 ± 0.024 | 0.617 ± 0.042 | 0.637 ± 0.031 | 0.672 ± 0.025 |
| Left posterior limb of internal capsule | 0.656 ± 0.024 | 0.653 ± 0.034 | 0.658 ± 0.025 | 0.672 ± 0.019 |
| Right retrolenticular part of internal capsule | 0.557 ± 0.018 | 0.553 ± 0.023 | 0.561 ± 0.043 | 0.582 ± 0.030 |
| Left anterior corona radiate | 0.390 ± 0.025 | 0.388 ± 0.031 | 0.393 ± 0.028 | 0.415 ± 0.029 |
| Left superior fronto-occipital fasciculus | 0.446 ± 0.029 | 0.436 ± 0.033 | 0.450 ± 0.024 | 0.469 ± 0.041 |
| Mean Diffusivity (10−3 mm2/s) | ||||
| Left corticospinal tract | 0.799 ± 0.059 | 0.833 ± 0.012 | 0.805 ± 0.072 | 0.761 ± 0.076 |
| Right corticospinal tract | 0.793 ± 0.037 | 0.824 ± 0.010 | 0.799 ± 0.072 | 0.744 ± 0.080 |
| Left anterior corona radiate | 0.866 ± 0.461 | 0.871 ± 0.069 | 0.858 ± 0.047 | 0.820 ± 0.048 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, K.; Yu, Q.; Herold, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Xiong, X.; Chen, A.; Müller, P.; Kramer, A.F.; et al. Mini-Basketball Training Program Improves Social Communication and White Matter Integrity in Children with Autism. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110803
Cai K, Yu Q, Herold F, Liu Z, Wang J, Zhu L, Xiong X, Chen A, Müller P, Kramer AF, et al. Mini-Basketball Training Program Improves Social Communication and White Matter Integrity in Children with Autism. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(11):803. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110803
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Kelong, Qian Yu, Fabian Herold, Zhimei Liu, Jingui Wang, Lina Zhu, Xuan Xiong, Aiguo Chen, Patrick Müller, Arthur F. Kramer, and et al. 2020. "Mini-Basketball Training Program Improves Social Communication and White Matter Integrity in Children with Autism" Brain Sciences 10, no. 11: 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110803
APA StyleCai, K., Yu, Q., Herold, F., Liu, Z., Wang, J., Zhu, L., Xiong, X., Chen, A., Müller, P., Kramer, A. F., Müller, N. G., & Zou, L. (2020). Mini-Basketball Training Program Improves Social Communication and White Matter Integrity in Children with Autism. Brain Sciences, 10(11), 803. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110803








