Abstract
The relationship between physical activity amount and cognitive function in elderly Koreans has received little attention. This study therefore aimed to understand the independent and common link between cognitive function and physical activity levels among elderly Korean adults. This study recruited a total of 2746 elderly adults (1348 males and 1398 females). All participants were assessed for cognitive functioning using the Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire Cognition (KDSQ-C). The computerized Korean version short form of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) used in this study was entirely based on the long, self-administered, usual week-long IPAQ found in the IPAQ manual of operation. In the unadjusted model, elderly adults who met the recommended level of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity were more likely to have a sufficient level of cognitive function. Hemoglobin, creatinine, cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), LDL-C, and HDL-C differed significantly between groups. A negative correlation was found between KDSQ-C score and the moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) amount per week. Physical activity amount is associated with cognition function in Korean elderly adults. Increasing physical activity may improve hemoglobin and creatinine and be involved in improving serum lipid profiles in elderly adults. Thus, physical activity has been suggesting as a useful tool to reduce the risk of cognitive function associated with aging.
1. Introduction
Due to a super-aged population, weakness has become an increasingly important issue in Korea [1]. In a study among South Korean women, The Lancet reported a 90% probability that life expectancy at birth in 2030 would exceed 86.7 years of age, which matches the highest worldwide life expectancy rate from 2012, and a 57% probability of exceeding 90 years of age [2].
Public health problems are increasing worldwide. This includes cognitive impairment, which is prevalent among the elderly at 10% to 22% [3]. Cognitive decline is a common part of aging that may instill fear [4]. For this reason, there is continual research into whether the condition indicates the early stages of dementia or is a part of a healthy continuum [5]. There are also a variety of effective preventive strategies that majorly impact public health by improving the quality of life while reducing associated economic and social burdens [6].
In the context of a substantially aging world population, many studies are now focusing on the potential positive effects of physical activity on cognitive impairment [7]. Current global guidelines for using physical activity to improve health encourage older adults to perform moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) for at least 150 min each week [8,9]. Previous studies have also shown that endurance exercises can protect against cognitive decline among the elderly, especially in regard to elements of executive planning and the working memory [10], while aerobic exercise has been found to increase brain volume in the frontal region, thereby resulting in higher levels of processing, attention control, and working memory [11]. In this regard, regular exercise and other forms of physical activity are highly important for promoting cognitive function and health not only in the cognitively impaired, but also in the healthy elderly.
Additionally, low hemoglobin [12], low creatinine [13], low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and high triglycerides (TG) [14] are potential contributing factors for progressive cognitive decline in the elderly. These biomarkers are associated with vascular risk factors [15], leading to vascular dementia in elderly people [16]. Moreover, a lower hemoglobin level was independently associated with mortality in this elderly cohort study [17]. The low creatinine might simultaneously reflect decreased muscle mass in elderly populations [13].
Although previous studies have investigated cognitive impairment in the elderly, there has been relatively little focus on the relationship between the amount of physical activity and cognitive function in elderly Korean adults. This study therefore aimed to understand the independent and common link between cognitive function and physical activity levels among elderly Korean adults.
2. Methodology
2.1. Participants
This study recruited a total of 2746 elderly adults (1348 males and 1398 females). All participants were 65 years of age or older and were specifically recruited from Nasaret International Hospital (Incheon, South Korea) from January 2018 to December 2019.
All participants were screened for cognitive function using the Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire Cognition (KDSQ-C) from the Ministry of Health and Welfare [18]. According to a baseline KDSQ-C cutoff score of 6 points, participants were divided into two groups, including the cognitive impairment group (scores ≥ 6 points) and normal group (scores < 6 points).
The data set was drawn from a retrospective cohort based on Nasaret International Hospital Medical Informatics Data (NIHMID), and separate patient recruitment procedures were not carried out. As the data were de-identified, the informed consent of the subject was not applicable. In the NIHMID, de-identified join keys replacing personal identifiers are used to secure ethical clearance. Therefore, the researcher cannot receive informed consent from individual patients for the use of personal information. However, the use of NIHMID for research purposes requires approval from the institutional review board. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Kangwon National University (KWNUIRB-2019-07-009-003).
The characteristics of the participants are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The characteristics of the participants.
2.2. Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire Cognition (KDSQ-C)
As mentioned in the previous section, all participants were assessed for cognitive function using the Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire Cognition (KDSQ-C) [18]. The KDSQ-C is self-administered and consists of 15 cognitive dysfunction items, each of which are rated on a three-point scale: 0 (no), 1 (sometimes/occasional), and 2 (often/frequent). The KDSQ-C is not influenced by age or educational level and has previously shown scores of 0.79 for sensitivity and 0.80~0.86 for specificity among dementia [19,20]. According to a baseline KDSQ-C cutoff score of 6 points, participants were divided into two groups, including the cognitive impairment group (scores ≥ 6 points) and normal group (scores < 6 points).
2.3. The International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)
This study used the computerized Korean version of the IPAQ, which is entirely based on the long, self-administered, usual week-long IPAQ found in the IPAQ manual of operation. The 7-item IPAQ identifies the total minutes over the previous seven days that were spent on moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA), walking physical activity, and inactivity [21]. It is specifically designed to collect information on the amounts of time (i.e., the number of sessions and average amounts of time per session) spent walking, in moderate-intensity physical activity, in vigorous-intensity physical activity, and sitting on weekdays and weekend days. Questions regarding participation in moderate and vigorous physical activities were supplemented by concrete examples of commonly performed activities. Data obtained via the questionnaires were then summed for each item (i.e., vigorous intensity, moderate intensity, and walking) in order to estimate the total amount of time spent in physical activity on a weekly basis.
Based on the self-reported amount of time spent in MVPA, participants were categorized as either sufficiently or insufficiently active. This was done according to guidelines set forth by the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM)/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) [9] stating that individuals should accumulate at least 150 min of moderate-intensity activity per week.
2.4. Blood Collection and Hemoglobin, Creatinine, and Serum Lipid Analysis
Fasting venous blood samples were collected from all participants. Fasting was maintained for nine hours. Blood samples were collected on the following day. Participants were instructed to obtain sufficient sleep and refrain from radical movements as much as possible. Samples were immediately centrifuged at 3500× g at 4 °C for 10 min and analyzed within 24 h. Serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and creatinine were measured using a biochemical automatic analyzer using commercial kits (Hitachi 7180, Tokyo, Japan). Hemoglobin levels were determined using a hemoglobin assay kit (Sysmex XN-1000, Kobe, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS statistical package for Windows, version 25.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Means and standard deviations were computed for all variables. Binary logistic regression analyses were also conducted to examine the independent and joint associations of sufficient MVPA levels with cognitive function; odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for these associations. The participant group consisting of individuals who met the recommended MVPA levels (150 min per week) was set as the reference during the joint association analyses. The aforementioned covariates were adjusted for in the adjusted models. The relationships between KDSQ-C scores and weekly MVPA amounts were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. The participant’s characteristics (age, height, weight, body mass index, waist circumference, systolic and diastolic blood pressure) and blood variables (hemoglobin, creatinine, TC, TG, LDL-C, and HDL-C) were further analyzed for significant difference among the groups using a one-way ANOVA. Finally, a post-hoc analysis (Bonferroni) was used to compare specific differences in cases of significance, which was statistically accepted at the 0.05 level.
3. Results
3.1. Associations between Physical Activity and Cognitive Function
Table 2 shows the independent associations between physical activity amounts and cognitive function in elderly adult participants. In the unadjusted model, participants who met the recommended MVPA levels (OR = 1.63, 95% CI = 1.28–2.08) were more likely to have a sufficient level of cognitive functioning. Those not meeting the recommended MVPA levels were 1.63 fold more likely to have cognitive decline. Additionally, the associations between meeting the recommended MVPA levels (OR = 1.35, 95% CI = 1.05–1.4) were attenuated after adjusting (age, sex, body mass index, and waist circumference) for covariates. Even with adjusting, elderly Korean adults who did not meet the recommended MVPA levels were 1.35 times more likely to have cognitive decline.

Table 2.
Independent associations between objectively measured physical activity and cognitive function in elderly adults.
3.2. Hemoglobin, Creatinine, and Serum Lipids
Table 3 presents the hemoglobin, creatinine, and serum lipid profiles. A one-way ANOVA showed that hemoglobin (p < 0.001), creatinine (p < 0.001), TC (p < 0.001), TG (p = 0.018), LDL-C (p = 0.002), and HDL-C (p = 0.001) were significantly different between groups.

Table 3.
Blood variables for each group.
A post-hoc analysis using the Bonferroni test indicated that hemoglobin and creatinine levels in both the normal elderly and ≥150 min groups were significantly higher than those in the <150 min group (normal and cognitive impairment). Next, TC and LDL-C in the normal elderly and ≥150 min groups were significantly lower than those in the normal elderly and <150 min groups as well as in the cognitive impairment and ≥150 min groups.
3.3. Correlations Coefficients between KDSQ-C Scores and MVPA Amounts
Figure 1 shows the correlation coefficients between KDSQ-C scores and weekly MVPA amounts. As shown, a negative correlation was found between KDSQ-C scores and weekly MVPA amounts (p < 0.000).
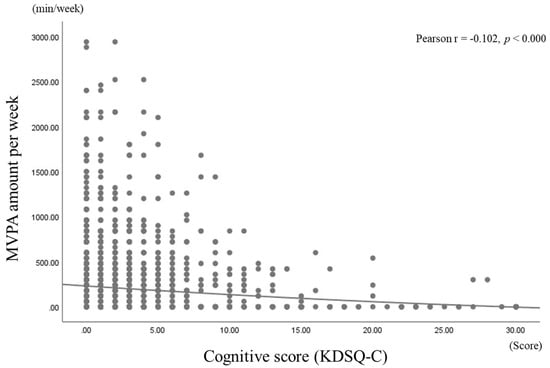
Figure 1.
Pearson’s correlation coefficients for cognitive scores and weekly MVPA amounts.
4. Discussion
This study found that elderly Korean adults who did not engage in recommended MVPA levels exhibited approximately double the amount of decline in cognitive function when compared to those who met the recommendations. There was a negative correlation in which KDSQ-C scores increased as weekly MVPA amounts decreased. In addition, hemoglobin and creatinine levels were higher in the ≥150 min group than in the <150 min group, while TC and LDL-C were lower in the ≥150 min group than in the <150 min group.
Most clinical practice guidelines recommend screening to identify these patients at an early time in the primary care setting [22]. Research has shown that cognitive impairments are associated with decreased hippocampal capacity and reduced processing speed in both mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) groups [23]. Further, research into muscle mass and other possible confounding factors has shown that participants with cognitive impairment have significantly diminished physical function when compared to those without cognitive impairment [24]. In addition, low upper and lower extremity performance levels are associated with increased disorder and dysfunction in the range of motion, even after considering the impacts of cognitive performance; this supports the suggestion that motor performance contributes to functional impairments in AD patients [25]. We produced strong evidence showing that elderly Korean adults who did not engage in recommended MVPA levels exhibited approximately double the amount of decline to cognitive function when compared to those who met the recommendations. In addition, we found a negative correlation in which KDSQ-C scores increased as weekly MVPA amounts decreased. Muscle strength is known to decrease in the elderly due to skeletal muscle atrophy [26]. As a result of aging, all body systems are inevitably reduced, thus leading to “weakness, fatigue, and slowing of movement” [27]. This shows that regular physical activity is essential, especially among the aging. Indeed, a substantial amount of evidence has been reported on cognitive function in this regard. For instance, a large sample size (n = 4615) of elderly Canadian women showed an association between lower cognitive loss risk and regular physical activity [28]. Further, a study among 732 healthy Greek adults aged 60 years or older at baseline (after about 6–13 years) showed a strong positive association between physical activity and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores upon registration; this relationship supports the protective role of physical activity against cognitive impairment [29]. In this study, 150 min of MVPA per week was set as a cut-off following previous studies conducted by the WHO [8] and Pate et al. [9]. Korea has instituted a periodic general national health examination program that screens for cognitive impairment using the KDSQ-C [19]. A previous study examined questionnaire scores, finding that the area under the curve for the KDSQ-C was 0.75 for diagnosing dementia [30]. This study also used the KDSQ-C questionnaire to assess cognitive function.
We also found noticeably significant differences in which hemoglobin and creatinine levels in the normal elderly and ≥150 min groups were higher than those in the <150 min group (normal and cognitive impairment). As two routine laboratory tests, low levels of hemoglobin and creatinine clearance are known to significantly increase the risk of death [31]. Low hemoglobin levels have been shown to be statistically significant with a prospective nonlinear association between hemoglobin concentrations and cognitive function [32]. The association between low creatinine levels and functional limitations suggests that creatinine levels are affected by factors other than renal function and muscle mass in the elderly [33]. Cognitive function also decreases in patients with slight decreases in the glomerular filtration rate [34]. Moreover, a previous study found that a group of participants who had completed at least six months of physical activity had higher hemoglobin and glomerular filtration rates when compared to a group consisting of sedentary individuals [35]. In both men and women, increased weekly amounts of either aerobic or strength exercise have been associated with significantly higher levels of creatinine [36]. Because creatinine is a metabolite of creatine decomposition, active individuals and those with large amounts of muscle mass are expected to have higher creatine conversion rates, thus leading to higher serum creatinine levels [36]. This study also found that hemoglobin and creatinine levels were higher in patients who met the recommended MVPA levels, regardless of cognitive function. In addition, TC, TG, and LDL-C levels were significantly lower, while HDL-C levels were higher in those who met the recommended MVPA levels. Research has shown that low TC and HDL-C concentrations are associated with cognitive impairment [37]. While the mechanism by which low levels of HDL-C are associated with cognitive impairment is currently unknown, HDL-C has been described as a negative risk factor for the development of cognitive impairment [38]. This may be because HDL-C slows or prevents the development of AD by preventing the aggregation and polymerization of β-amyloid [39]. As opposed to lowering TC, He et al. [40] reported that increasing HDL-C may prevent the development of cognitive impairment and dementia.
This study also had some limitations that point to suggestions for future research. First, hemoglobin levels were not separately assessed between men and women and were also expressed as means and standard deviations according to MVPA amounts. Second, kidney function was not evaluated during the assessment of creatinine. Third, physical activity amounts were solely investigated using the IPAQ. Future studies should therefore continue to investigate hemoglobin levels and glomerular filtration rates in addition to more objectively measuring physical activity levels.
5. Conclusions
This study shows that in elderly Korean adults, the amount of physical activity is associated with the level of cognition function. Results also indicate that increased physical activity may enhance hemoglobin and creatinine levels and improve serum lipid profiles among this group.
In sum, physical activity engagement constitutes a useful method for reducing the risk of cognitive impairment associated with aging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-T.L. and E.L.; Data curation, S.-T.L., Y.Z.J., and E.L.; Formal analysis, S.-T.L., Y.Z.J., and E.L.; Investigation, S.-T.L., T.A., and E.L.; Methodology, S.-T.L., T.A., and E.L.; Writing—original draft, S.-T.L. and E.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2019S1A5B5A02035423).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ACSM | American College of Sports Medicine |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) |
| KDSQ-C | Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire Cognition |
| IPAQ | International Physical Activity Questionnaire |
| MVPA | Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity |
| NIHMID | Nasaret International Hospital Medical Informatics Data |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| ORs | Odds ratios |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| SPSS | Statistical package for social science |
References
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Seo, Y.M.; Seo, A.R.; Kim, B.; Yoo, J.I.; Park, K.S. The Association between Frailty and Disability among the Elderly in Rural Areas of Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontis, V.; Bennett, J.E.; Mathers, C.D.; Li, G.; Foreman, K.; Ezzati, M. Future life expectancy in 35 industrialised countries: Projections with a Bayesian model ensemble. Lancet 2017, 389, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, B.; Dale-McGrath, S.; Tierney, M.C. Sex differences in the prevalence and incidence of mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 176–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langa, K.M.; Levine, D.A. The diagnosis and management of mild cognitive impairment: A clinical review. JAMA 2014, 312, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lee, D.W.; Cho, S.J.; Na, D.L.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, Y.R.; Youn, J.H.; Kwon, M.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Brief screening for mild cognitive impairment in elderly outpatient clinic: Validation of the Korean version of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2008, 21, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etgen, T.; Sander, D.; Huntgeburth, U.; Poppert, H.; Förstl, H.; Bickel, H. Physical activity and incident cognitive impairment in elderly persons: The INVADE study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenschlager, N.T.; Cox, K.; Kurz, A.F. Physical activity and mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2010, 10, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pate, R.R.; Pratt, M.; Blair, S.N.; Haskell, W.L.; Macera, C.A.; Bouchard, C.; Buchner, D.; Ettinger, W.; Heath, G.H.; King, A.C. Physical activity and public health. A recommendation from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American College of Sports Medicine. JAMA 1995, 273, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.E.; Yaffe, K.; Satariano, W.A.; Tager, I.B. A longitudinal study of cardiorespiratory fitness and cognitive function in healthy older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colcombe, S.J.; Erickson, K.I.; Scalf, P.E.; Kim, J.S.; Prakash, R.; McAuley, D.; Elavsky, S.; Marquez, D.X.; Hu, L.; Kramer, A.F. Aerobic exercise training increases brain volume in aging humans. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2006, 61, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajani, S.; Archana, R.; Indla, Y.R.; Rajesh, P. Correlation between hemoglobin levels and visual memory among an older adult population in Chennai. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 604–608. [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe, K.; Lindquist, K.; Shlipak, M.G.; Simonsick, E.; Fried, L.; Rosano, C.; Satterfield, S.; Atkinson, H.; Windham, B.G.; Kurella-Tamura, M. Cystatin C as a marker of cognitive function in elders: Findings from the health ABC study. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, C. Subgroup analysis of the influence of body mass index on the association between serum lipids and cognitive function in Chinese population. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabadi, M.H.; Vincent, A.S. Do vascular risk factors contribute to the prevalence of pressure ulcer in veterans with spinal cord injury? J. Spinal Cord Med. 2011, 34, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Xia, R.; Li, N.; Liao, X.; Chen, Z. Chinese herbal medicine for vascular cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2020, 99, e22455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakai, N.A.; Katz, R.; Hirsch, C.; Shlipak, M.G.; Chaves, P.H.M.; Newman, A.B.; Cushman, M. A prospective study of anemia status, hemoglobin concentration, and mortality in an elderly cohort: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2018 National Health Examination Doctor Consultation Manual; Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention: Cheongju-si, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.W.; Cho, B.; Chey, J.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, B.S. The development and validation of Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire (KDSQ). J. Korean Neurol. Assoc. 2002, 20, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.H.; Park, M.H. Three screening methods for cognitive dysfunction using the Mini-Mental State Examination and Korean Dementia Screening Questionnaire. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)–Short and Long Forms. 2011. Available online: www.ipaq.ki.se (accessed on 24 January 2011).
- Boustani, M.; Peterson, B.; Hanson, L.; Harris, R.; Lohr, K.N. Screening for dementia in primary care: A summary of the evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.J.; Devanand, D.P.; Liu, X.; Caccappolo, E. Functional impairment in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer disease. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyeung, T.W.; Kwok, T.; Lee, J.; Leung, P.C.; Leung, J.; Woo, J. Functional decline in cognitive impairment--the relationship between physical and cognitive function. Neuroepidemiology 2008, 31, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, L.E.; Bienias, J.L.; McCann, J.J.; Scherr, P.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Evans, D.A. Upper and lower extremity motor performance and functional impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Alzheimer Dis. Other Dement. 2010, 25, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svantesson, U.; Jones, J.; Wolbert, K.; Alricsson, M. Impact of Physical Activity on the Self-Perceived Quality of Life in Non-Frail Older Adults. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2015, 7, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkendall, D.T.; Garrett, W.E. The effects of aging and training on skeletal muscle. Am. J. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurin, D.; Verreault, R.; Lindsay, J.; MacPherson, K.; Rockwood, K. Physical activity and risk of cognitive impairment and dementia in elderly persons. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaltopoulou, T.; Kyrozis, A.; Stathopoulos, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Vassilopoulos, D.; Trichopoulou, A. Diet, physical activity and cognitive impairment among elders: The EPIC-Greece cohort (European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition). Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Kim, S.; Park, K.W.; Park, K.H.; Youn, Y.C.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; et al. A Comparative Evaluation of the KDSQ-C, AD8, and SMCQ as a Cognitive Screening Test to Be Used in National Medical Check-ups in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldez, R.R.; Sabatine, M.S.; Morrow, D.A.; Mohanavelu, S.; McCabe, C.H.; Antman, E.M.; Braunwald, E. Baseline hemoglobin concentration and creatinine clearance composite laboratory index improves risk stratification in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 2009, 157, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.L.; Jonassaint, C.; Sharrett, A.R.; Mosley, T.H.; Astor, B.C.; Selvin, E.; Coresh, C.; Gottesman, R.F. Hemoglobin, Anemia, and Cognitive Function: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2016, 71, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odden, M.C.; Shlipak, M.G.; Tager, I.B. Serum creatinine and functional limitation in elderly persons. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2009, 64, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.F.; Elias, P.K.; Seliger, S.L.; Narsipur, S.S.; Dore, G.A.; Robbins, M.A. Chronic kidney disease, creatinine and cognitive functioning. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2446–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, P.S.; Campos, A.S.D.; Corrêa, C.S.; Dias, C.J.M.; Mostarda, C.T.; Amorim, C.E.N.; Garcia, A.M.C. Effects of Chronic Physical Activity on Glomerular Filtration Rate, Creatinine, and the Markers of Anemia of Kidney Transplantation Patients. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragala, M.S.; Bi, C.; Chaump, M.; Kaufman, H.W.; Kroll, M.H. Associations of aerobic and strength exercise with clinical laboratory test values. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, N.; Piperi, C.; Salonicioti, A.; Psarra, V.; Mitsonis, C.; Liappas, I.; Lea, R.W.; Kalofoutis, A. Characterization of the lipid profile in dementia and depression in the elderly. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2007, 20, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castano, E.M.; Prelli, F.; Wisniewski, T.; Golabek, A.; Kumar, R.A.; Soto, C.; Frangione, B. Fibrillogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease of amyloid beta peptides and apolipoprotein E. Biochem. J. 1995, 306, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockerill, G.W.; Rye, K.A.; Gamble, J.R.; Vadas, M.A.; Barter, P.J. High-density lipoproteins inhibit cytokine-induced expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wu, T.; Ji, L.; Huang, G.; Ma, F. Relationship between plasma lipids and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly Chinese: A case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).