Comprehensive Analysis of RNA-Seq Gene Expression Profiling of Brain Transcriptomes Reveals Novel Genes, Regulators, and Pathways in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
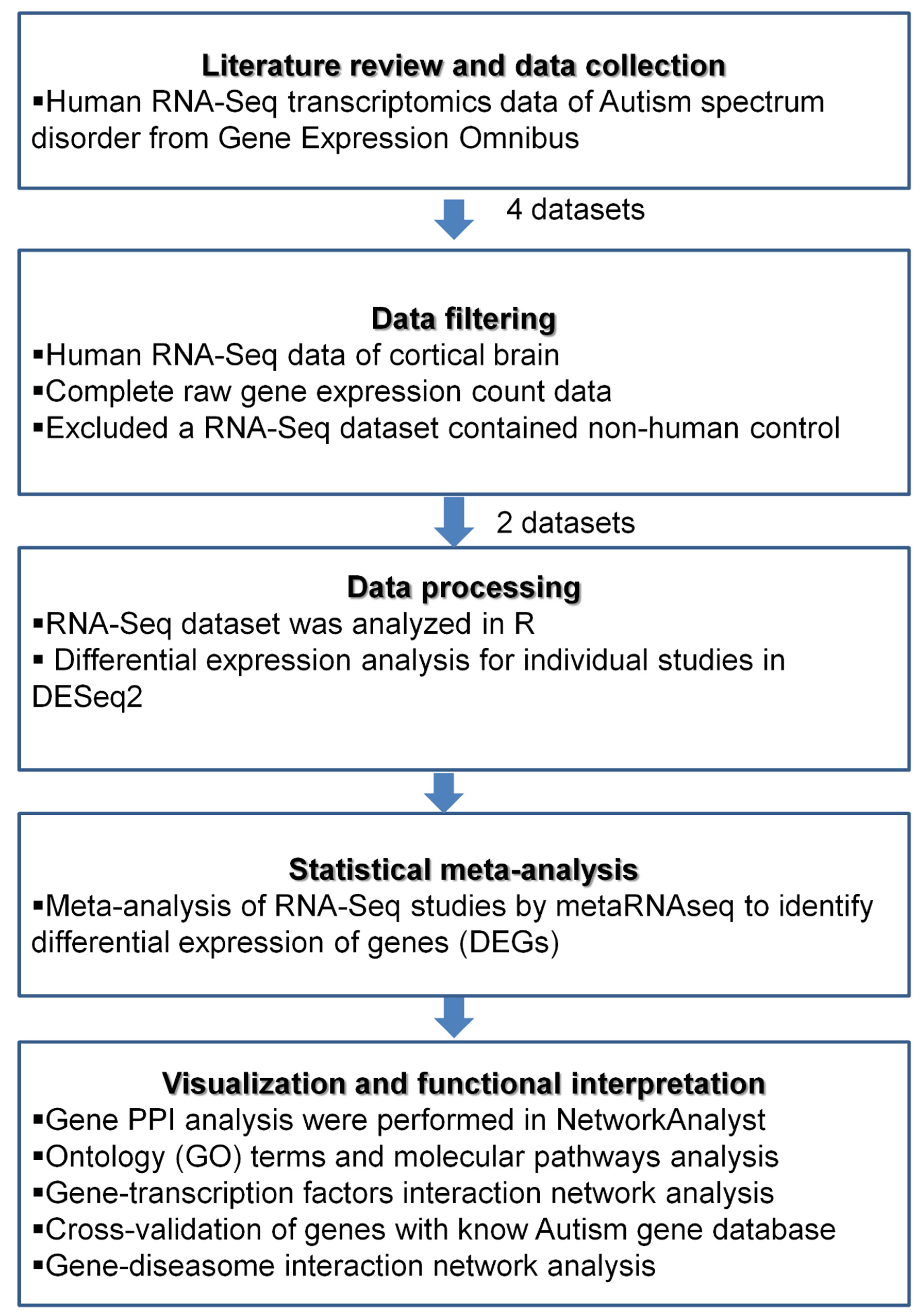
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of the Transcriptomics Data
2.2. Data Processing and Differential Expression Analysis of Individual Datasets
2.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
2.5. Transcriptional Regulators of the DEGs
2.6. In Silico Cross-Validation and Gene Disease Association Network Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Differentially Expressed Genes in Brain Cortex via Meta-Analysis of RNA-Seq Transcriptomics
3.2. Data Visualization and Functional Interpretation
3.3. Hub Proteins: Protein Interactome Analysis
3.4. Regulatory Signature: DEGs-TFs Interaction Network
3.5. Cross-Validation and DEGs–Disease Association Network
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maenner, M.J. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2020, 69, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, T.; Zaman, T.; Shahjaman, M.; Karim, M.R.; Huq, F.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Holsinger, R.M.D.; Gov, E.; Moni, M.A. Identification of molecular signatures and pathways to identify novel therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease: Insights from a systems biomedicine perspective. Genomics 2020, 112, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, T.; Turanli, B.; Zaman, T.; Faruquee, H.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Mollah, M.N.H.; Nanda, R.K.; Arga, K.Y.; Gov, E.; et al. Network-based approach to identify molecular signatures and therapeutic agents in Alzheimer’s disease. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 78, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ch’ng, C.; Kwok, W.; Rogic, S.; Pavlidis, P. Meta-analysis of gene expression in autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2015, 8, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatt, S.J.; Tsuang, M.T.; Winn, M.; Chandler, S.D.; Collins, M.; Lopez, L.; Weinfeld, M.; Carter, C.; Schork, N.; Pierce, K. Blood-based gene expression signatures of infants and toddlers with autism. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2012, 51, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, V.W.; Lai, Y. Developing a predictive gene classifier for autism spectrum disorders based upon differential gene expression profiles of phenotypic subgroups. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. Boston 2013, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Pramparo, T.; Pierce, K.; Lombardo, M.V.; Barnes, C.C.; Marinero, S.; Ahrens-Barbeau, C.; Murray, S.S.; Lopez, L.; Xu, R.; Courchesne, E. Prediction of autism by translation and immune/inflammation coexpressed genes in toddlers from pediatric community practices. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazestani, V.H.; Pramparo, T.; Nalabolu, S.; Kellman, B.P.; Murray, S.; Lopez, L.; Pierce, K.; Courchesne, E.; Lewis, N.E. A perturbed gene network containing PI3K–AKT, RAS–ERK and WNT–β-catenin pathways in leukocytes is linked to ASD genetics and symptom severity. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.H.; Kim, I.B.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, D.H. Predicting autism spectrum disorder using blood-based gene expression signatures and machine learning. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forés-Martos, J.; Catalá-López, F.; Sánchez-Valle, J.; Ibáñez, K.; Tejero, H.; Palma-Gudiel, H.; Climent, J.; Pancaldi, V.; Fañanás, L.; Arango, C. Transcriptomic metaanalyses of autistic brains reveals shared gene expression and biological pathway abnormalities with cancer. Mol. Autism 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T. The Gene Expression Omnibus Database. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1418, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.; Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential analysis of count data–the DESeq2 package. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 10–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Rau, A.; Marot, G.; Jaffrézic, F. Differential meta-analysis of RNA-seq data from multiple studies. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edwards, A.W.R.A. Fischer, Statistical Methods for Research Workers (1925). In Landmark Writings in Western Mathematics 1640–1940; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 856–870. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omi. A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Gill, E.E.; Hancock, R.E.W. NetworkAnalyst for statistical, visual and network-based meta-analysis of gene expression data. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, B.S.; Arking, D.E.; Campbell, D.B.; Mefford, H.C.; Morrow, E.M.; Weiss, L.A.; Menashe, I.; Wadkins, T.; Banerjee-Basu, S.; Packer, A. SFARI Gene 2.0: A community-driven knowledgebase for the autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piñero, J.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Bravo, A.; Deu-Pons, J.; Bauer-Mehren, A.; Baron, M.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. DisGeNET: A discovery platform for the dynamical exploration of human diseases and their genes. Database 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén, M.; Karlsson, M.J.; Hober, A.; Svensson, A.S.; Scheffel, J.; Kotol, D.; Zhong, W.; Tebani, A.; Strandberg, L.; Edfors, F. The human secretome. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalls, M.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Vallerga, C.L.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Chang, D.; Tan, M.; Kia, D.A.; Noyce, A.J.; Xue, A. Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Nakamura, K.; Thanseem, I.; Yamada, K.; Iwayama, Y.; Toyota, T.; Matsuzaki, H.; Miyachi, T.; Yamada, S.; Tsujii, M. Brain region-specific altered expression and association of mitochondria-related genes in autism. Mol. Autism 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronan, J.L.; Wu, W.; Crabtree, G.R. From neural development to cognition: Unexpected roles for chromatin. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; You, Y.; Yue, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, T.; Wu, Z. Chromatin remodeling gene EZH2 involved in the genetic etiology of autism in Chinese Han population. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 610, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, M.; Monteggia, L.M. A role for histone deacetylases in the cellular and behavioral mechanisms underlying learning and memory. Learn. Mem. 2014, 21, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griswold, A.J.; Ma, D.; Cukier, H.N.; Nations, L.D.; Schmidt, M.A.; Chung, R.-H.; Jaworski, J.M.; Salyakina, D.; Konidari, I.; Whitehead, P.L.; et al. Evaluation of copy number variations reveals novel candidate genes in autism spectrum disorder-associated pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3513–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, J.; Jensen, M.; Amini, H.; Hormozdiari, F.; Penn, O.; Shifman, S.; Girirajan, S.; Hormozdiari, F. Dissecting the genetic basis of comorbid epilepsy phenotypes in neurodevelopmental disorders. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lalani, A.I.; Zhu, S.; Gokhale, S.; Jin, J.; Xie, P. TRAF molecules in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Curr. Pharm. Rep. 2018, 4, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldinger, K.A.; Lehmann, O.J.; Hudgins, L.; Chizhikov, V.V.; Bassuk, A.G.; Ades, L.C.; Krantz, I.D.; Dobyns, W.B.; Millen, K.J. FOXC1 is required for normal cerebellar development and is a major contributor to chromosome 6p25. 3 Dandy-Walker malformation. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, S.; Offer, S.M. Epigenetic regulations of GABAergic neurotransmission: Relevance for neurological disorders and epigenetic therapy. Med. Epigenetics 2016, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriele, M.; Vulto-van Silfhout, A.T.; Germain, P.L.; Vitriolo, A.; Kumar, R.; Douglas, E.; Haan, E.; Kosaki, K.; Takenouchi, T.; Rauch, A. YY1 haploinsufficiency causes an intellectual disability syndrome featuring transcriptional and chromatin dysfunction. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristino, A.S.; Williams, S.M.; Hawi, Z.; An, J.Y.; Bellgrove, M.A.; Schwartz, C.E.; da F Costa, L.; Claudianos, C. Neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders represent an interconnected molecular system. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, G.R.; Chung, J.; Mez, J.; Barber, R.; Beecham, G.W.; Bennet, D.A. Transethnic genome-wide scan identifies novel Alzheimer disease loci. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, Y.J.; Wang, H.H.; Lee, M.T.M.; Wang, S.C.; Chiang, H.L.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chung, M.S.; Kuo, C.C.; Liao, D.L. Genome-wide association study of treatment refractory schizophrenia in Han Chinese. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filice, F.; Schwaller, B.; Michel, T.M.; Grünblatt, E. Profiling parvalbumin interneurons using iPSC: Challenges and perspectives for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Mol. Autism 2020, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhr, M.; Orduz, D.; Gregory, P.; Moreno, H.; Khan, U.; Vörckel, K.J.; Wolfer, D.P.; Welzl, H.; Gall, D.; Schiffmann, S.N.; et al. Lack of parvalbumin in mice leads to behavioral deficits relevant to all human autism core symptoms and related neural morphofunctional abnormalities. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, E.; Ariza, J.; Rogers, H.; Noctor, S.C.; Martínez-Cerdeño, V. The Number of Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons Is Decreased in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex in Autism. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, E.; Hernandez, A.V.; Kattan, M.W. Meta-analysis: Its strengths and limitations. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2008, 75, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, F.L.; Kloth, K.; Bley, A.; Denecke, J.; Santer, R.; Lessel, D.; Hempel, M.; Kutsche, K. Activating mutations in PAK1, encoding p21-activated kinase 1, cause a neurodevelopmental disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horn, S.; Au, M.; Basel-Salmon, L.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P.; Chapin, A.; Cohen, L.; Elting, M.W.; Graham, J.M., Jr.; Gonzaga-Jauregui, C.; Konen, O. De novo variants in PAK1 lead to intellectual disability with macrocephaly and seizures. Brain 2019, 142, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rubeis, S.; He, X.; Goldberg, A.P.; Poultney, C.S.; Samocha, K.; Cicek, A.E.; Kou, Y.; Liu, L.; Fromer, M.; Walker, S. Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature 2014, 515, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.; Merico, D.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; Wei, J.; Lionel, A.C.; Sato, D.; Rickaby, J.; Lu, C.; Szatmari, P.; Roberts, W. A discovery resource of rare copy number variations in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2012, 2, 1665–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, K.E.; Sharan, K.; Takumi, T.; Yadav, V.K. Skeletal Site-specific Changes in Bone Mass in a Genetic Mouse Model for Human 15q11-13 Duplication Seen in Autism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calarge, C.A.; Schlechte, J.A. Bone mass in boys with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeyer, A.M.; Sokoloff, N.C.; McDonnell, E.; Macklin, E.A.; McDougle, C.J.; Misra, M. Bone microarchitecture in adolescent boys with autism spectrum disorder. Bone 2017, 97, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekhlaspour, L.; Baskaran, C.; Campoverde, K.J.; Sokoloff, N.C.; Neumeyer, A.M.; Misra, M. Bone density in adolescents and young adults with autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 3387–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karasik, D.; Rivadeneira, F.; Johnson, M.L. The genetics of bone mass and susceptibility to bone diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, J.S.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Wolfe, L.A.; Bone, W.P.; Maduro, V.; Accardi, J.; Adams, D.R.; Schwartz, C.E.; Norris, J.; Wood, T. Impaired osteoblast and osteoclast function characterize the osteoporosis of Snyder-Robinson syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chauhan, A.; Sheikh, A.M.; Patil, S.; Chauhan, V.; Li, X.M.; Ji, L.; Brown, T.; Malik, M. Elevated immune response in the brain of autistic patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 207, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.N.; Van de Water, J. Altered T cell responses in children with autism. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chez, M.G.; Dowling, T.; Patel, P.B.; Khanna, P.; Kominsky, M. Elevation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cerebrospinal fluid of autistic children. Pediatr. Neurol. 2007, 36, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Pan, T.; Kendrick, K.M.; Xu, W. Immunological cytokine profiling identifies TNF-α as a key molecule dysregulated in autistic children. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goines, P.E.; Ashwood, P. Cytokine dysregulation in autism spectrum disorders (ASD): Possible role of the environment. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2013, 36, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masi, A.; Breen, E.J.; Alvares, G.A.; Glozier, N.; Hickie, I.B.; Hunt, A.; Hui, J.; Beilby, J.; Ravine, D.; Wray, J. Cytokine levels and associations with symptom severity in male and female children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Feng, C.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ke, J.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Li, C.; Javed, I. Proteomics study of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in autistic children. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchia, M.; Piras, I.S.; Huentelman, M.J.; Pinna, F.; Zai, C.C.; Kennedy, J.L.; Carpiniello, B. Pattern of gene expression in different stages of schizophrenia: Down-regulation of NPTX2 gene revealed by a meta-analysis of microarray datasets. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| GEO Accession | Brain | No of Sample |
|---|---|---|
| GSE64018 | cortex | Control: 12 ASD:12 |
| GSE30573 | cortex | Control: 3 ASD: 3 |
| Ensemble ID | Gene Symbol | FDR | Average log2FC | Regulation of Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000077420 | APBB1IP | 5.92E-06 | 1.02 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000134516 | DOCK2 | 6.38E-05 | 1.07 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000142102 | PGGHG | 0.000223 | 1.06 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000146192 | FGD2 | 0.000394 | 1.27 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000142583 | SLC2A5 | 0.000449 | 1.31 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000188282 | RUFY4 | 0.000537 | 2.67 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000053918 | KCNQ1 | 0.000553 | 1.11 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000123338 | NCKAP1L | 0.000703 | 1.15 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000107099 | DOCK8 | 0.000823 | 1.04 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000249825 | AC012636.1 | 0.001274 | 1.21 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000128602 | SMO | 0.001487 | 1.19 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000213694 | S1PR3 | 0.001625 | 1.06 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000184574 | LPAR5 | 0.001879 | 1.25 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000198142 | SOWAHC | 0.002218 | 1.07 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000197324 | LRP10 | 0.002269 | 1.22 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000104903 | LYL1 | 0.002295 | -1.01 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000152192 | POU4F1 | 0.002449 | 3.19 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000188511 | C22orf34 | 0.002528 | 1.09 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000132561 | MATN2 | 0.003122 | 1.00 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000137767 | SQOR | 0.003406 | 1.14 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000178623 | GPR35 | 0.003868 | 1.10 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000137693 | YAP1 | 0.004274 | 1.18 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000187554 | TLR5 | 0.004764 | 1.05 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000155465 | SLC7A7 | 0.005133 | 1.10 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000092531 | SNAP23 | 0.005308 | 1.03 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000183508 | TENT5C | 0.005427 | 1.61 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000136732 | GYPC | 0.005534 | 1.03 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000258701 | LINC00638 | 0.005609 | 1.23 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000158516 | CPA2 | 0.005742 | 2.25 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000135245 | HILPDA | 0.006065 | 1.25 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000125398 | SOX9 | 0.006225 | 1.24 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000142512 | SIGLEC10 | 0.006448 | 1.31 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000105137 | SYDE1 | 0.006757 | 1.05 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000084093 | REST | 0.006965 | 1.20 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000167393 | PPP2R3B | 0.007156 | 1.02 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000174348 | PODN | 0.007183 | 1.08 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000143384 | MCL1 | 0.007261 | 1.05 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000231327 | LINC01816 | 0.007409 | 1.07 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000168209 | DDIT4 | 0.007787 | 1.04 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000127418 | FGFRL1 | 0.007833 | 1.05 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000225032 | AL162586.1 | 0.008133 | 1.14 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000101916 | TLR8 | 0.008409 | 2.09 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000155926 | SLA | 0.008477 | 1.07 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000121933 | TMIGD3 | 0.008491 | 1.16 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000205336 | ADGRG1 | 0.008543 | 1.04 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000101057 | MYBL2 | 0.0087 | 3.23 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000165806 | CASP7 | 0.008879 | 1.09 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000223764 | LINC02593 | 0.008879 | 1.67 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000104689 | TNFRSF10A | 0.009434 | 1.10 | Upregulated |
| ENSG00000225684 | FAM225B | 0.009746 | 1.62 | Upregulated |
| Gene Symbol | Description | Regulation | Degree | Biological Significance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAG3 | BAG cochaperone 3 | Up | 23 | Parkinson’s disease | [20] |
| CDK2 | Cyclin dependent kinase 2 | Up | 25 | Involved in cell cycle regulation | GeneCard |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A | Up | 22 | Implicated in ASD in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex region of brain | [21] |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit | Up | 18 | Genetic variation of EZH2-a chromatin remodeling factors is observed in intellectual disabilities and ASD; EZH2 in human embryonic brain suggesting a contributory role of this gene in etiology of ASD in Chinese population | [22,23] |
| HDAC1 | Histone Deacetylase 1 | Up | 35 | Several studies have suggested a role for HDAC1 and HDAC2 in learning and memory behaviors | [24] |
| GABARAPL1 | GABA Type A Receptor Associated Protein Like 1 | Down | 19 | ASD associated pathway | [25] |
| MYC | MYC proto-oncogene | Up | 54 | Implicated in tumorigenesis and metabolism | [26] |
| TRAF1 | TNF receptor associated factor 1 | Up | 16 | Involved in inflammation and aberrant expression leads to inflammatory disease | [27] |
| VIM | Vimentin | Up | 16 | Disease involved in VIM is cataract | Genecards database |
| TFs | Description | Degree | Molecular Significance | Novelty | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOXC1 | forkhead box C1 | 785 | deletion or duplication of FOXC1 are related with cerebellar and cerebellar malformation | Novel | [28] |
| GATA2 | GATA binding protein 2 | 652 | GATA2 is involved in maintaining the development of GABAergic neurons, its association with development of ASD is not known yet. | Novel | [29] |
| YY1 | YY1 transcription factor | 413 | both deletions and de novo point mutations affecting YY1 activity trigger Intellectual Disability syndrome of haploinsufficiency | Novel | [30] |
| FOXL1 | Forkhead Box L1 | 353 | The role of the TF FOXL1 is not known in neurodevelopmental disorder | Novel | [31] |
| USF2 | Upstream Stimulatory Factor 2 | 325 | USF2 is one of the major TFs that bind in brain.12 known ASD SNPs are associated validated TF binding sites of YY1, E2F1 and USF2 enriched in neurodevelopmental and neuropshiatric disorder | Known | [31] |
| NFIC | Nuclear Factor I C | 305 | highly enriched in neurodevelopmental disorder, not known in ASD | Novel | [32] |
| NFKB1 | Nuclear Factor Kappa B Subunit 1 | 297 | identified NFKB1 play crucial role in etiology of treatment refractory schizophrenia in Chinese Han population; not known in ASD | Novel | [33] |
| E2F1 | E2F Transcription Factor 1 | 287 | 12 known ASD SNPs are associated validated TF binding sites of YY1, E2F1 and USF2 enriched in neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorder PPI network. Many of these SNPs are correlated with synaptic transmission. | Known | [31] |
| TFAP2A | Transcription Factor AP-2 Alpha | 263 | The role of the TF TFAP2A is not known in neurodevelopmental disorder. | Novel | - |
| HINFP | Histone H4 Transcription Factor | 258 | The role of the TF TFAP2A is not known in neurodevelopmental disorder. | Novel | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.R.; Petralia, M.C.; Ciurleo, R.; Bramanti, A.; Fagone, P.; Shahjaman, M.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.; Turanli, B.; Arga, K.Y.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of RNA-Seq Gene Expression Profiling of Brain Transcriptomes Reveals Novel Genes, Regulators, and Pathways in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100747
Rahman MR, Petralia MC, Ciurleo R, Bramanti A, Fagone P, Shahjaman M, Wu L, Sun Y, Turanli B, Arga KY, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of RNA-Seq Gene Expression Profiling of Brain Transcriptomes Reveals Novel Genes, Regulators, and Pathways in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(10):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100747
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Rezanur, Maria Cristina Petralia, Rosella Ciurleo, Alessia Bramanti, Paolo Fagone, Md Shahjaman, Lang Wu, Yanfa Sun, Beste Turanli, Kazim Yalcin Arga, and et al. 2020. "Comprehensive Analysis of RNA-Seq Gene Expression Profiling of Brain Transcriptomes Reveals Novel Genes, Regulators, and Pathways in Autism Spectrum Disorder" Brain Sciences 10, no. 10: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100747
APA StyleRahman, M. R., Petralia, M. C., Ciurleo, R., Bramanti, A., Fagone, P., Shahjaman, M., Wu, L., Sun, Y., Turanli, B., Arga, K. Y., Islam, M. R., Islam, T., & Nicoletti, F. (2020). Comprehensive Analysis of RNA-Seq Gene Expression Profiling of Brain Transcriptomes Reveals Novel Genes, Regulators, and Pathways in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sciences, 10(10), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100747







