Arylsulfatase A (ASA) in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Biomarker Potential
Abstract
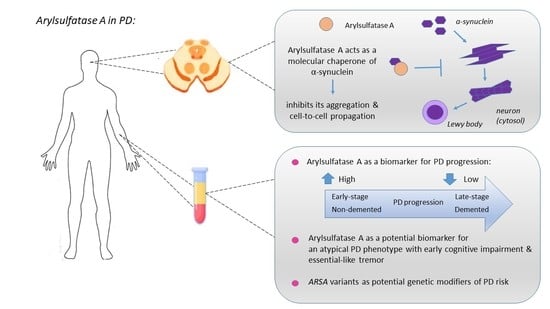
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Evidence on the Emerging Role of ASA in PD
2.1. ASA Levels and Activity as a Potential PD Biomarker
2.2. ASA Localization in the Brain of PD Patients
2.3. Possible Association between ARSA Gene Variants and PD
3. Preclinical Evidence on the Potential Role of ASA in PD Pathogenesis
4. Discussion and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rizek, P.; Kumar, N.; Jog, M. An update on the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2016, 188, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Piperi, C. miR-124 and Parkinson’s disease: A biomarker with therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenganatt, M.A.; Jankovic, J. Parkinson Disease Subtypes. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Bozi, M.; Simitsi, A.M.; Koros, C.; Antonelou, R.; Papagiannakis, N.; Michalopoulos, I. The relationship between environmental factors and different Parkinson’s disease subtypes in Greece: Data analysis of the Hellenic Biobank of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 67, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.-M.; Chan, L.; Chan, D.K.Y.; Kim, J.W. Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease—A Clinical Perspective. J. Mov. Disord. 2012, 5, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, M.; Klein, C. The many faces of alpha-synuclein mutations. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, K.M.; Silveira-Moriyama, L.; Parkkinen, L.; Healy, D.G.; Farrell, M.; Mencacci, N.E.; Ahmed, Z.; Brett, F.M.; Hardy, J.; Quinn, N.; et al. Parkin Disease–A Clinicopathological Entity? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Shaikh, M.F.; Piperi, C. Fractalkine (CX3CL1) signaling and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Potential clinical and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Villa, C.; Shaikh, M.F.; Piperi, C. Lymphocyte-Activation Gene 3 (LAG3) Protein as a Possible Therapeutic Target for Parkinson’s Disease: Molecular Mechanisms Connecting Neuroinflammation to α-Synuclein Spreading Pathology. Biology 2020, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-J.; Chen, S.-D.; Liou, C.-W.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-K.; Lin, K.-L. The Overcrowded Crossroads: Mitochondria, Alpha-Synuclein, and the Endo-Lysosomal System Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bae, E.-J.; Yang, N.-Y.; Song, M.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J.S.; Jung, B.C.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Masliah, E.; Sardi, S.P.; et al. Glucocerebrosidase depletion enhances cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahmoradian, S.H.; Lewis, A.J.; Genoud, C.; Hench, J.; Moors, T.E.; Navarro, P.P.; Castaño-Díez, D.; Schweighauser, G.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Goldie, K.N.; et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fanning, S.; Selkoe, D.J.; Dettmer, U. Vesicle trafficking and lipid metabolism in synucleinopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Imai, Y.; Hattori, N. Lipids: Key Players That Modulate α-Synuclein Toxicity and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemann, C.J.; Martens, G.J.; Sharma, M.; Martens, M.B.; Isacson, O.; Gasser, T.; Poelmans, G. Integrated molecular landscape of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Mazzulli, J.R. Is Parkinson’s disease a lysosomal disorder? Brain 2018, 141, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotegher, N.; Duchen, M.R. Crosstalk between Lysosomes and Mitochondria in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gusdon, A.M.; Zhu, J.; Van Houten, B.; Chu, C.T. ATP13A2 regulates mitochondrial bioenergetics through macroautophagy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalls, M.A.; Pankratz, N.; Lill, C.M.; Do, C.B.; Hernandez, D.G.; Saad, M.; DeStefano, A.L.; Kara, E.; Bras, J.; Sharma, M.; et al. Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeliovich, A.; Gitler, A.D. Defects in trafficking bridge Parkinson’s disease pathology and genetics. Nature 2016, 539, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robak, L.A.; Jansen, I.E.; Van Rooij, J.; Kraaij, R.; Jankovic, J.; Shulman, J.M.; Nalls, M.A.; Plagnol, V.; Hernandez, D.G.; Sharma, M.; et al. Excessive burden of lysosomal storage disorder gene variants in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2017, 140, 3191–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simitsi, A.; Koros, C.; Moraitou, M.; Papagiannakis, N.; Antonellou, R.; Bozi, M.; Angelopoulou, E.; Stamelou, M.; Michelakakis, H.; Stefanis, L. Phenotypic Characteristics in GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease: A Study in a Greek Population. J. Park. Dis. 2018, 8, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrucci, S.; Ginevrino, M.; Trezzi, I.; Monfrini, E.; Ricciardi, L.; Albanese, A.; Bove, F. GBA-Related Parkinson’s Disease: Dissection of Genotype-Phenotype Correlates in a Large Italian Cohort. Mov. Disord. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmann, K.; Srulijes, K.; Pflederer, S.; Hauser, A.K.; Schulte, C.; Maetzler, W.; Berg, D. GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease: Reduced survival and more rapid progression in a prospective longitudinal study. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klüenemann, H.H.; Nutt, J.G.; Davis, M.Y.; Bird, T.D. Parkinsonism syndrome in heterozygotes for Niemann-Pick C1. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 335, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brás, J.; Guerreiro, R.; Hardy, J. SnapShot: Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell 2015, 160, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, T.M.; Cachón-González, M.B. The cellular pathology of lysosomal diseases. J. Pathol. 2011, 226, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shachar, T.; Bianco, C.L.; Recchia, A.; Wiessner, C.; Raas-Rothschild, A.; Futerman, A.H. Lysosomal storage disorders and Parkinson’s disease: Gaucher disease and beyond. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pchelina, S.N.; Nuzhnyi, E.; Emelyanov, A.; Boukina, T.; Usenko, T.; Nikolaev, M.; Salogub, G.; Yakimovskii, A.; Zakharova, E.Y. Increased plasma oligomeric alpha-synuclein in patients with lysosomal storage diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 583, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kanai, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kim, W.S.; Yoo, H.S.; Fu, Y.; Kim, D.-K.; Jung, B.C.; Choi, M.; Oh, K.W.; et al. Arylsulfatase A, a genetic modifier of Parkinson’s disease, is an α-synuclein chaperone. Brain 2019, 142, 2845–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieselmann, V.; Krägeloh-Mann, I. Metachromatic Leukodystrophy—An Update. Neuropediatrics 2010, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciotti, S.; Albi, E.; Parnetti, L.; Beccari, T. Lysosomal Ceramide Metabolism Disorders: Implications in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bindu, P.S.; Mahadevan, A.; Taly, A.B.; Christopher, R.; Gayathri, N.; Shankar, S.K. Peripheral neuropathy in metachromatic leucodystrophy. A study of 40 cases from south India. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troy, S.; Wasilewski, M.; Beusmans, J.; Godfrey, C. Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Intrathecally Administered Recombinant Human Arylsulfatase A (TAK-611) in Children with Metachromatic Leukodystrophy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 107, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molander-Melin, M.; Pernber, Z.; Franken, S.; Gieselmann, V.; Månsson, J.E.; Fredman, P. Accumulation of sulfatide in neuronal and glial cells of arylsulfatase A deficient mice. J. Neurocytol. 2004, 33, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, M. The Role and Metabolism of Sulfatide in the Nervous System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 37, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittke, D.; Hartmann, D.; Gieselmann, V. Lysosomal sulfatide storage in the brain of arylsulfatase A-deficient mice: Cellular alterations and topographic distribution. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 108, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabelo, N.; Martín, M.V.; Santpere, G.; Marín, R.; Torrent, L.; Ferrer, I.; Díaz, M. Severe Alterations in Lipid Composition of Frontal Cortex Lipid Rafts from Parkinson’s Disease and Incidental Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antelmi, E.; Rizzo, G.; Fabbri, M.; Capellari, S.; Scaglione, C.; Martinelli, P. Arylsulphatase A activity in familial parkinsonism: A pathogenetic role? J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgi, S.; Ferlini, A.; Zanetti, A.; Mochi, M. Reduced activity of arylsulfatase A and predisposition to neurological disorders: Analysis of 140 pediatric patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1991, 40, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappler, J.; Watts, R.W.E.; Conzelmann, E.; Gibbs, D.A.; Propping, P.; Gieselmann, V. Low arylsulphatase A activity and choreoathetotic syndrome in three siblings: Differentiation of pseudodeficiency from metachromatic leukodystrophy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 1991, 150, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnetti, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Persichetti, E.; Eusebi, P.; Varghese, S.; Qureshi, M.M.; Dardis, A.; Deganuto, M.; De Carlo, C.; Castrioto, A.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid lysosomal enzymes and alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alcalay, R.N.; Levy, O.A.; Waters, C.C.; Fahn, S.; Ford, B.; Kuo, S.-H.; Mazzoni, P.; Pauciulo, M.W.; Nichols, W.C.; Gan-Or, Z.; et al. Glucocerebrosidase activity in Parkinson’s disease with and without GBA mutations. Brain 2015, 138, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niimi, Y.; Ito, S.; Mizutani, Y.; Murate, K.; Shima, S.; Ueda, A.; Mutoh, T. Altered regulation of serum lysosomal acid hydrolase activities in Parkinson’s disease: A potential peripheral biomarker? Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 61, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.D.; Persichetti, E.; Chiasserini, D.; Eusebi, P.; Beccari, T.; Calabresi, P.; van de Berg, W.D. Changes in endolysosomal enzyme activities in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, P.; Ippoliti, M.; Montanari, M.; Martinelli, A.; Mochi, M.; Giuliani, S.; Sangiorgi, S. Arylsulphatase A (ASA) activity in parkinsonism and symptomatic essential tremor. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1994, 89, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenganatt, M.A.; Jankovic, J. The relationship between essential tremor and Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 22 (Suppl. 1), S162–S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Han, C.; Lu, Y.; Mo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Cai, F.; et al. Characterization of a pathogenic variant in GBA for Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment patients. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, C.; Schüle, B.; Schuele, B.; Munhoz, R.P.; Rogaeva, E.; Langston, J.W.; Kasten, M.; Meaney, C.; Klein, C.; Wadia, P.M.; et al. Phenotype in parkinsonian and nonparkinsonian LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers. Neurology 2011, 77, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, T.; Ross, O.A.; Puschmann, A.; Dickson, D.W.; Wszolek, Z.K. Autosomal dominant Parkinson’s disease caused by SNCA duplications. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 22 (Suppl. 1), S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Chung, S.J.; Ye, B.S.; Sohn, Y.H.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, P.H. Changes in plasma arylsulfatase A level as a compensatory biomarker of early Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morena, F.; Argentati, C.; Trotta, R.; Crispoltoni, L.; Stabile, A.; Pistilli, A.; Di Baldassarre, A.; Calafiore, R.; Montanucci, P.; Basta, G.; et al. A Comparison of Lysosomal Enzymes Expression Levels in Peripheral Blood of Mild- and Severe-Alzheimer’s Disease and MCI Patients: Implications for Regenerative Medicine Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerr, J.; Böckenhoff, A.; Ewald, B.; Ladewig, J.; Eckhardt, M.; Gieselmann, V.; Matzner, U.; Brüstle, O.; Koch, P. Arylsulfatase A Overexpressing Human iPSC-derived Neural Cells Reduce CNS Sulfatide Storage in a Mouse Model of Metachromatic Leukodystrophy. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Boxer, A.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Miller, B.L.; Kapogiannis, D. Altered lysosomal proteins in neural-derived plasma exosomes in preclinical Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappler, J.; Pötter, W.; Gieselmann, V.; Kiessling, W.; Friedl, W.; Propping, P. Phenotypic consequences of low arylsulfatase A genotypes (ASAp/ASAp and ASA-/ASAp): Does there exist an association with multiple sclerosis? Dev. Neurosci. 1991, 13, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegg, M.E.; Burke, D.; Heales, S.J.R.; Cooper, J.M.; Hardy, J.; Wood, N.W.; Schapira, A.H.V. Glucocerebrosidase deficiency in substantia nigra of parkinson disease brains. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moors, T.E.; Paciotti, S.; Ingrassia, A.; Quadri, M.; Breedveld, G.; Tasegian, A.; Chiasserini, D.; Eusebi, P.; Duran-Pacheco, G.; Kremer, T.; et al. Characterization of Brain Lysosomal Activities in GBA-Related and Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 56, 1344–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, E.M.; Smith, G.A.; Park, E.; Cao, H.; Brown, E.; Hallett, P.; Isacson, O. Progressive decline of glucocerebrosidase in aging and Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Sidransky, E.; Verma, A.; Mixon, T.; Sandberg, G.D.; Wakefield, L.K.; Morrison, A.; Lwin, A.; Colegial, C.; Allman, J.M.; et al. Neuropathology provides clues to the pathophysiology of Gaucher disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2004, 82, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Iseki, E.; Togo, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Katsuse, O.; Katsuyama, K.; Kanzaki, S.; Shiozaki, K.; Kawanishi, C.; Yamashita, S.; et al. Neuronal and glial accumulation of α- and β-synucleins in human lipidoses. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, R.; Bar-Joseph, I.; Frosch, M.P.; Walsh, D.M.; Hamilton, J.A.; Selkoe, D.J. The formation of highly soluble oligomers of alpha-synuclein is regulated by fatty acids and enhanced in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 2003, 37, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, S.A.; Romero-Ramos, M. Microglia Response During Parkinson’s Disease: Alpha-Synuclein Intervention. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruan, Y.; Zheng, R.; Lin, Z.-H.; Gao, T.; Xue, N.-J.; Cao, J.; Tian, J.; Zhang, B.; Pu, J. Genetic analysis of arylsulfatase A (ARSA) in Chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 734, 135094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieselmann, V.; Polten, A.; Kreysing, J.; Von Figura, K. Arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency: Loss of a polyadenylylation signal and N-glycosylation site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9436–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makarious, M.B.; Diez-Fairen, M.; Krohn, L.; Blauwendraat, C.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Ding, J.; Pihlstrøm, L.; Houlden, H.; Scholz, S.W.; Gan-Or, Z. ARSA variants in α-synucleinopathies. Brain 2019, 142, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, W.; Nakabayashi, Y.; Mizuta, I.; Hirota, Y.; Ito, C.; Kubo, M.; Tomiyama, H. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Yan, X.; Guo, J.; Xu, Q.; Tang, B.; Sun, Q. Recent Advances in Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hooge, R.; Hartmann, D.; Manil, J.; Colin, F.; Gieselmann, V.; De Deyn, P. Neuromotor alterations and cerebellar deficits in aged arylsulfatase A-deficient transgenic mice. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 273, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X. Potential mechanisms contributing to sulfatide depletion at the earliest clinically recognizable stage of Alzheimer’s disease: A tale of shotgun lipidomics. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alza, N.P.; González, P.A.I.; Conde, M.A.; Uranga, R.M.; Salvador, G.A. Lipids at the Crossroad of α-Synuclein Function and Dysfunction: Biological and Pathological Implications. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullin, S.; Smith, L.; Lee, K.; D’Souza, G.; Woodgate, P.; Elflein, J.; Hällqvist, J.; Toffoli, M.; Streeter, A.; Hosking, J.; et al. Ambroxol for the Treatment of Patients with Parkinson Disease with and Without Glucocerebrosidase Gene Mutations. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Í Dali, C.; Sevin, C.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Giugliani, R.; Sakai, N.; Wu, J.; Wasilewski, M. Safety of intrathecal delivery of recombinant human arylsulfatase A in children with metachromatic leukodystrophy: Results from a phase 1/2 clinical trial. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.A.; Alcalay, R.N. Precision medicine in Parkinson’s disease: Emerging treatments for genetic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maegawa, G.; A Patil, S. Developing therapeutic approaches for metachromatic leukodystrophy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Villa, C.; Piperi, C. Arylsulfatase A (ASA) in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Biomarker Potential. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100713
Angelopoulou E, Paudel YN, Villa C, Piperi C. Arylsulfatase A (ASA) in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Biomarker Potential. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(10):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100713
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelopoulou, Efthalia, Yam Nath Paudel, Chiara Villa, and Christina Piperi. 2020. "Arylsulfatase A (ASA) in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Biomarker Potential" Brain Sciences 10, no. 10: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100713
APA StyleAngelopoulou, E., Paudel, Y. N., Villa, C., & Piperi, C. (2020). Arylsulfatase A (ASA) in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Biomarker Potential. Brain Sciences, 10(10), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100713