The Effect of Aging on the ERP Correlates of Feedback Processing in the Probabilistic Selection Task
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.3. Procedure
2.4. EEG Recording and Analysis
2.5. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Data
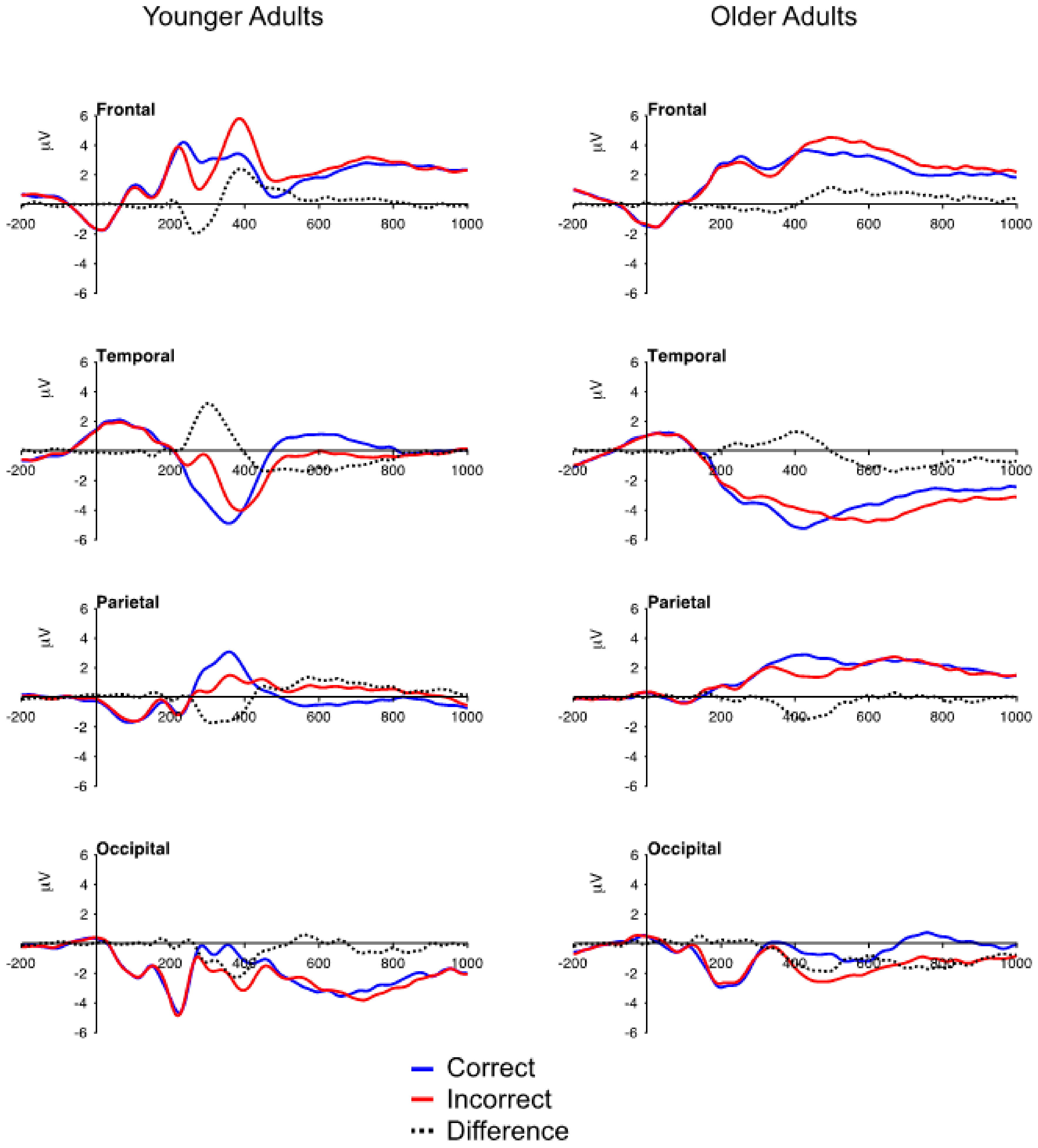
3.2. ERP Data: Mean Voltage
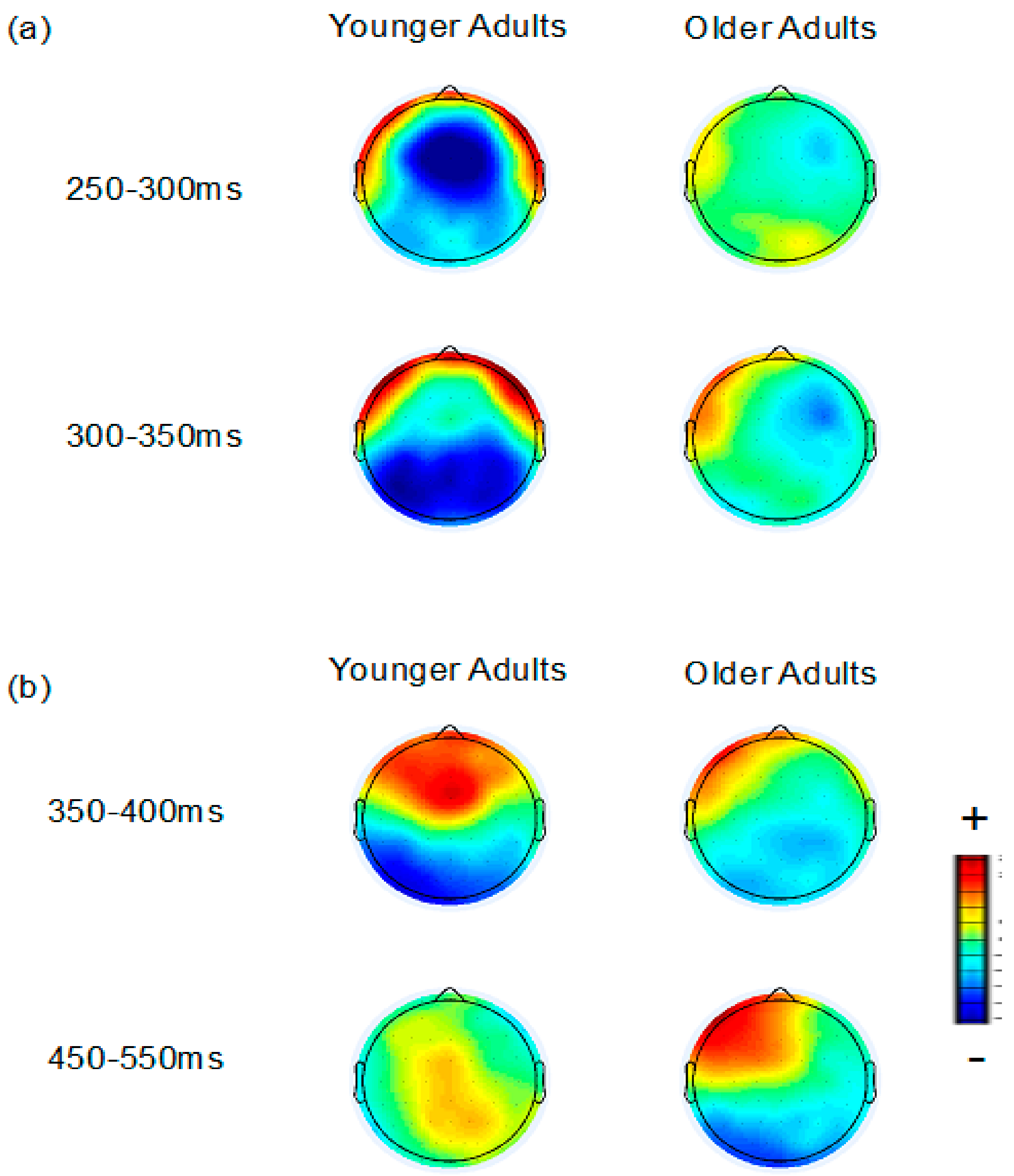
3.2.1. FN and Temporal Positivity
3.2.2. Frontal P3 and Occipital Negativity
3.2.3. Parietal P3
3.2.4. Aging and Correct Feedback
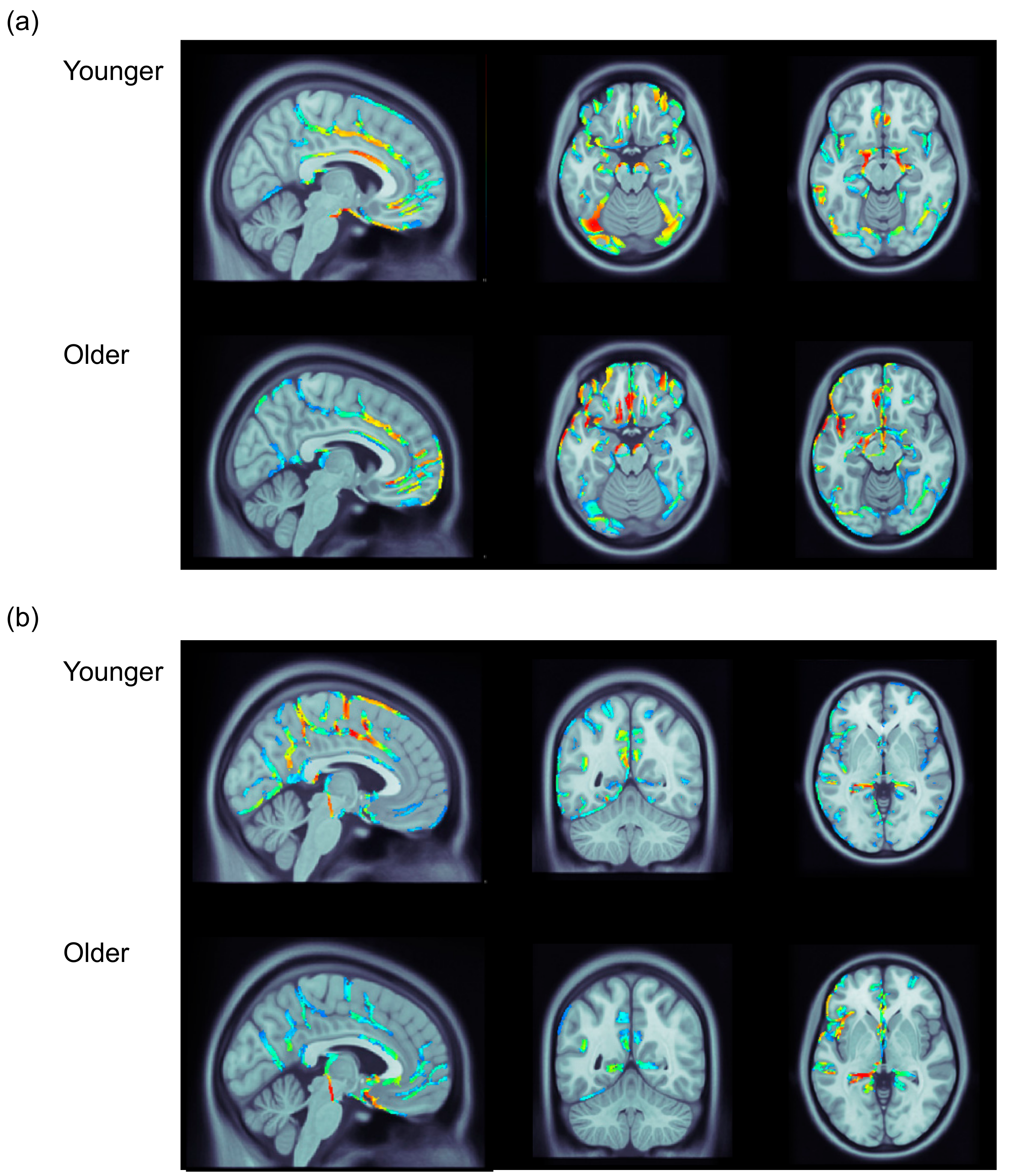
3.3. ERP Data: Distributed Source Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frank, M.J.; Seeberger, L.C.; O’Reilly, R.C. By carrot or by stick: Cognitive reinforcement learning in parkinsonism. Science 2004, 306, 1940–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klucharav, V.; Hytönen, K.; Rijpkema, M.; Smidts, A.; Fernández, G. Reinforcement learning signal predicts social conformity. Neuron 2009, 61, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutson, B.; Samanez-Larkin, G.R.; Kuhnen, C.M. Gain and loss learning differentially contribute to life financial outcomes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, W.J.; Willoughby, A.R. The medial frontal cortex and the rapid processing of monetary gains and losses. Science 2002, 295, 2279–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.W.; Anderson, J.R. Learning from experience: Event-related potential correlates of reward processing, neural adaptation, and behavioral choice. Neurosci. Biobeh. Rev. 2012, 36, 1870–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.; Tiernan, B.N.; Kieffaber, P.D.; Bailey, K.; Anderson, S. The effect of age on the neural correlates of feedback processing in a naturalistic gambling game. Psychophysiology 2012, 51, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, N.; Sanfey, A.G. Independent coding of reward magnitude and valence in the human brain. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6258–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellebaum, C.; Polezzi, D.; Daum, I. It is less than you expected: The feedback-related negativity reflects violations of reward magnitude expectations. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 3343–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyer, J.P.; Woldorff, M.G.; Huettel, S.A. Rapid electrophysiological brain responses are influenced by both valence and magnitude of monetary rewards. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2008, 20, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.; Bailey, K.; Tiernan, B.N.; Boonsuk, W.; Gilbert, S. The temporal dynamics of medial and lateral frontal neural activity related to proactive cognitive control. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 3450–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, X. The P300 and reward valence, magnitude, and expectancy in outcome evaluation. Brain Res. 2009, 1286, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holroyd, C.B.; Pakzad-Vaezi, K.L.; Krigolson, O.E. The feedback correct-related positivity: Sensitivity of the event-related brain potential to unexpected positive feedback. Psychophysiology 2008, 45, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, R.; Bailey, K.; Anderson, S.; Kieffaber, P.D. Beyond the FN: The neural correlates of feedback processing in a virtual blackjack game. Brain Cogn. 2014, 86, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, R.; Bailey, K.; Anderson, S. Transient and sustained ERP activity related to feedback processing in the probabilistic selection task. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2018, 126, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajcak, G.; Moser, J.S.; Holroyd, C.B.; Simons, R.F. It’s worse than you thought: The feedback negativity and violations of reward prediction in gambling tasks. Psychophysiology 2007, 44, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Vijver, I.; van Driel, J.; Hillebrand, A.; Cohen, M.X. Interactions between frontal and posterior oscillatory dynamics support adjustments of stimulus processing during reinforcement learning. NeuroImage 2018, 18, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewig, J.; Straube, T.; Trippe, R.H.; Kretschmer, N.; Hecht, H.; Coles, M.G.H.; Miltner, W.H.R. Decision-making under risk: An fMRI study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2008, 21, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hairston, J.; Schrier, M.; Fan, J. Common and distinct networks underlying reward valence and processing stages: A meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppinger, B.; Kray, J.; Mock, B.; Mecklinger, A. Better or worse than expected? Aging, learning, and the ERN. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämmerer, D.; Li, S.; Müller, V.; Lindenberger, U. Life span differences in electrophysiological correlates of monitoring gains and losses during probabilistic reinforcement learning. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 23, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, S.; Ridderinkhof, K.R.; Talsma, D.; Coles, M.G.H.; Holroyd, C.B.; Kok, A.; van der Molen, M.W. A computational account of altered error processing in older age: Dopamine and the error-related negativity. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2002, 2, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathewson, K.J.; Dyan, J.; Snyder, P.J.; Tays, W.J.; Segalowitz, S.J. Aging and electrocortical response to error feedback during a spatial learning task. Psychophysiology 2008, 45, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness. The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised; The Psychological Corporation, Hartcourt Brace Janovich: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, J.C. Mill Hill Vocabulary Scale; H.K. Lewis: London, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Tadel, F.; Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. Brainstorm: A user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, T.A. The processing-speed theory of adult age differences in cognition. Psychol. Rev. 1996, 103, 403–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.X.; Wilmes, K.A.; van de Vijver, I. Cortical electrophysiological network dynamics of feedback learning. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.W.; Dennis, N.A.; Daseleer, S.M.; Fleck, M.S.; Cabeza, R. Qué PASA? The posterior-anterior shift in aging. Cereb. Cortex. 2008, 18, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.L.; Hazlett, E.A.; Byne, W.; Hof, P.R.; Buchsbaum, M.S.; Cohen, B.H.; Goldstein, K.E.; Haznedar, M.M.; Mitsis, E.M.; Siever, L.J.; et al. Anterior and posterior cingulate cortex volume in healthy adults: Effects of aging and gender differences. Brain Res. 2011, 1401, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, L.L.; Isaacowitz, D.M.; Charles, S.T. Taking time seriously: A theory of socioemotional selectivity. Am. Psychol. 1999, 54, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, M.; Carstensen, L.L. Aging and motivated cognition: The positivity effect in attention and memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weniger, G.; Boucsein, K.; Irle, E. Impaired associative memory in temporal lobe epilepsy subjects after lesions of hippocampus, parahippocampal gyrus, and amygdala. Hippocampus 2004, 14, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgmans, S.; van Boxtel, M.P.J.; van den Berg, K.E.M.; Gronenschild, E.H.B.M.; Jabobs, H.I.L.; Jolles, J.; Uylings, H.B.M. The posterior parahippocampal gyrus is preferentially affected in age-related memory decline. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R. A triarchic model of P300 amplitude. Psychophysiology 1986, 23, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, A. On the utility of P3 amplitude as a measure of processing capacity. Psychophysiology 2001, 38, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.; Kazmerski, V.; Fabiani, M. An overview of age-related changes in the scalp distribution of P3b. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 104, 98–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polich, J. Meta-analysis of P300 normative aging studies. Psychophysiology 1996, 33, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, R.; Schwarb, H.; Johnson, B.N. The influence of age and individual differences in executive function on stimulus processing in the oddball task. Cortex 2010, 46, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Younger | Older | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | M | 19.56 | 71.42 |
| SD | 1.56 | 5.79 | |
| Education | M | 13.94 | 17.36 |
| SD | 0.95 | 2.76 | |
| Vocabulary | M | 14.62 | 23.14 |
| SD | 3.60 | 4.80 | |
| Digit symbol | M | 43.08 | 32.06 |
| SD | 6.01 | 7.30 | |
| Choose A | M | 0.66 | 0.60 |
| SD | 0.22 | 0.23 | |
| Avoid B | M | 0.63 | 0.54 |
| SD | 0.19 | 0.21 | |
| A | B | C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Younger | Older | Younger | Older | Younger | Older | ||
| Block 1 | M | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.57 | 0.51 | 0.57 |
| SD | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.20 | |
| Block 2 | M | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| SD | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.21 | |
| Block 3 | M | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| SD | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.17 | |
| FN | Frontal P3 | Temp. pos. | Occ. neg. | Parietal P3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Younger Adults | ||||||
| Correct feedback | M | 3.18 | 3.33 | −2.88 | −0.57 | 2.87 |
| SD | 2.52 | 2.44 | 2.57 | 2.56 | 2.31 | |
| Incorrect feedback | M | 1.40 | 5.24 | −0.54 | −2.43 | 1.29 |
| SD | 2.43 | 3.21 | 1.71 | 2.97 | 2.75 | |
| Older Adults | ||||||
| Correct feedback | M | 2.44 | 3.43 | −3.73 | −0.87 | 2.85 |
| SD | 3.38 | 3.43 | 3.68 | 3.80 | 2.76 | |
| Incorrect feedback | M | 2.02 | 4.43 | −3.16 | −2.39 | 1.43 |
| SD | 3.55 | 3.68 | 2.99 | 4.24 | 3.22 | |
| F | p | BF10 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FN | 1.09 | 0.30 | 0.60 |
| Temporal positivity | 1.61 | 0.21 | 0.57 |
| Frontal | 0.05 | 0.83 | 0.38 |
| Occipital negativity | 0.23 | 0.64 | 0.37 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
West, R.; Huet, A. The Effect of Aging on the ERP Correlates of Feedback Processing in the Probabilistic Selection Task. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010040
West R, Huet A. The Effect of Aging on the ERP Correlates of Feedback Processing in the Probabilistic Selection Task. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleWest, Robert, and AnnMarie Huet. 2020. "The Effect of Aging on the ERP Correlates of Feedback Processing in the Probabilistic Selection Task" Brain Sciences 10, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010040
APA StyleWest, R., & Huet, A. (2020). The Effect of Aging on the ERP Correlates of Feedback Processing in the Probabilistic Selection Task. Brain Sciences, 10(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010040





