Dry Bio-Decontamination Process in Reduced-Pressure O2 Plasma
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. O2 Plasma Treatment
2.3. Viable Cell Counts and Decontamination Effect
2.4. Determination of Protein Leakage Quantity
2.5. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Production
2.6. DNA Measurement
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Decontamination Effect of UV Radiation in Oxygen Plasma
3.2. Decontamination Effect of Charged Species in Oxygen Plasma
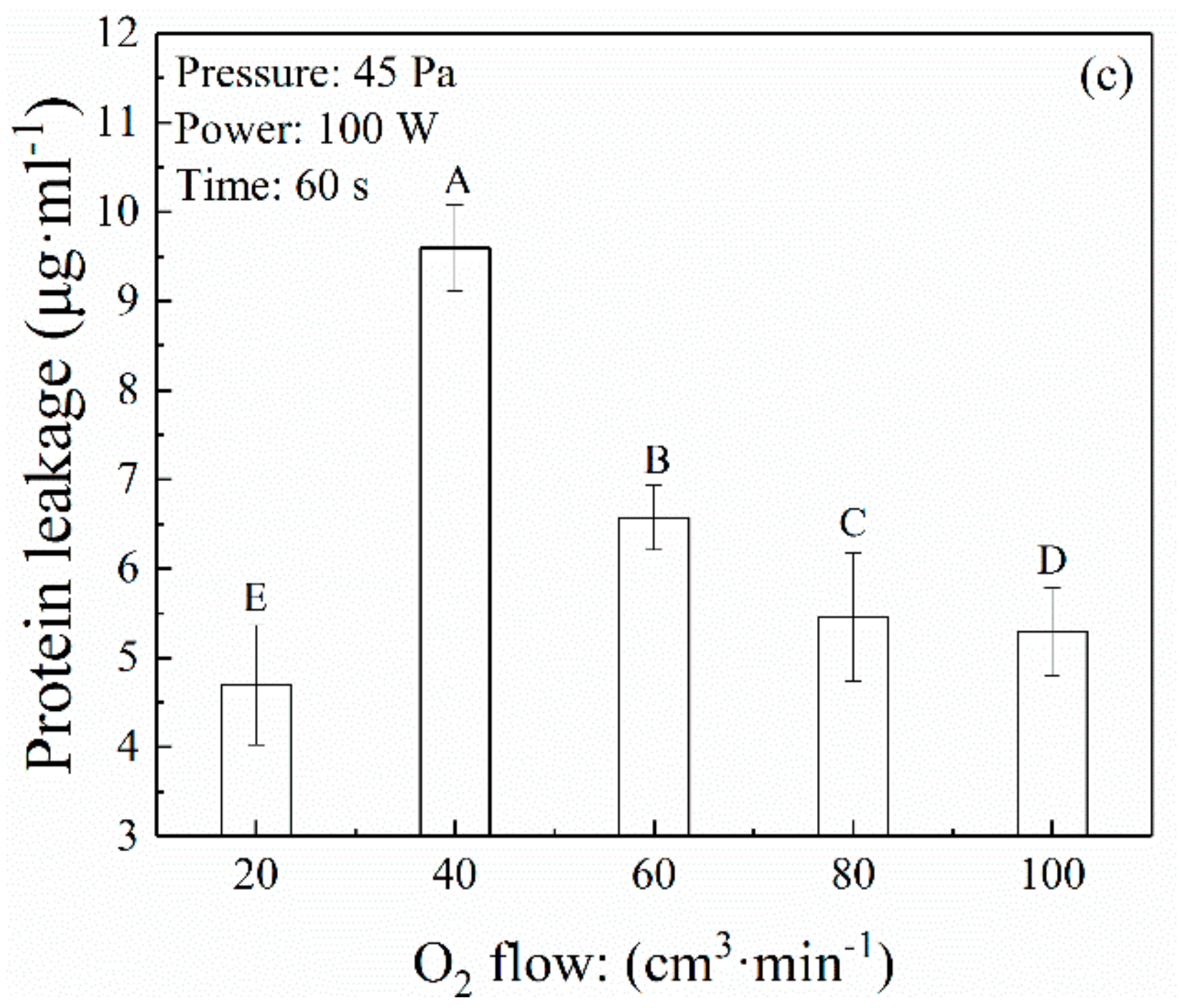
3.3. Decontamination Effect of Free Radicals in Oxygen Plasma
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moisan, M.; Barbeau, J.; Moreau, S.; Pelletier, J.; Tabrizian, M.; Yahia, L. Low-temperature sterilization using gas plasmas: a review of the experiments and an analysis of the inactivation mechanisms. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 226, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Puligundla, P.; Mok, C. Inactivation of foodborne pathogens on the surfaces of different packaging materials using low-pressure air plasma. Food Control. 2015, 51, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Schaudinn, C.; Jaramillo, D.E.; Webster, P.; Costerton, J.W. In vitro antimicrobial effect of a cold plasma jet against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms. ISRN Dent. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.M.; Zhang, G.J.; Yuan, Y.K.; Ma, Y.; Xu, G.M.; Yang, Y. Research on the inactivation effect of low-temperature plasma on Candida albicans. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2008, 36, 498–503. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, N.N.; Tiwari, B.K.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Cullen, P.J. Nonthermal plasma inactivation of food-borne pathogens. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.T.K.; Phan, H.T.; Brennan, C.S.; Phimolsiripol, Y. Nonthermal plasma for pesticide and microbial elimination on fruits and vegetables: An overview. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 52, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, P.; Zuizina, D.; Han, L.; Cullen, P.J.; Gilmore, B.F. Microbiological interactions with cold plasma. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowsky, B.; Schlüter, O.; Knorr, D. Interactions of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma with solid and liquid food systems: A review. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 82–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemira, B.A. Cold plasma decontamination of foods. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, A.; Niemira, B.A.; Gurtler, J.B.; Fan, X.; Sites, J.; Boyd, G.; Chen, H. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of aerobic microorganisms on blueberries and effects on quality attributes. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrynin, D.; Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A. Physical and biological mechanisms of direct plasma interaction with living tissue. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 115020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, S.G.; Cooper, M.; Yost, A.; Paff, M.; Ercan, U.K.; Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Brooks, A.D. Nonthermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma-induced inactivation involves oxidative DNA damage and membrane lipid peroxidation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroussi, M.; Leipold, F. Evaluation of the roles of reactive species, heat, and UV radiation in the inactivation of bacterial cells by air plasmas at atmospheric pressure. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 233, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Chen, J.R. Analysis of surface sterilization and properties of medical poly(tetrafluoroethylene) in remote argon plasma. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2008, 36, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, C.; Reineke, K.; Ehlbeck, J.; Knorr, D.; Schlüter, O. Decontamination of whole black pepper using different cold atmospheric pressure plasma applications. Food Control. 2015, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfmann, H.; Bibinov, N.; Wunderlich, J.; Awakowicz, P.A. Double inductively coupled plasma for sterilization of medical devices. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Chen, J.R. Inactivation of Escherichia coli and properties of medical poly (vinyl chloride) in remote-oxygen plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5690–5697. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Q.; Chen, J.R.; Gao, J.L. Low temperature argon plasma sterilization effect on pseudomonas aeruginosa and its mechanisms. J. Electrostat. 2009, 67, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerouge, S.; Wertheimer, M.R.; Marchand, R.; Tabrizian, M.; Yahia, L. Effect of gas composition on spore mortality and etching during low-pressure plasma sterilization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 51, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Chen, J.R.; Yang, L.Q.; Zhou, Y. Long-distance oxygen plasma sterilization: Effects and mechanisms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, J.M.; Arenas, F.A.; Pradenas, G.A.; Sandoval, J.M.; Vasquez, C.C. Escherichia coli yqhd exhibits aldehyde reductase activity and protects from the harmful effect of lipid peroxidation-derived aldehydes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7346–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Condensed Protocols from Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Translated by Huang, P.T.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 387–396. [Google Scholar]
- Mogul, R.; Bol’shakov, A.A.; Chan, S.L.; Stevens, R.M.; Khare, B.N.; Meyyappan, M.; Trent, J.D. Impact of low-temperature plasmas on deinococcus radiodurans and biomolecules. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.Y.; Xue, G.B.; Ju, X.C. The study on bactericidal mechanism of plasmas ozone against E. coli on the surface. Mod. Prevent. Med. 2004, 31, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Arana, I.; Santorum, P.; Muela, A.; Barcina, I. Chlorination and ozonation of wastewater: comparative analysis of efficacy through the effect on Escherichia coli membranes. J. Appl. Microbial. 1999, 86, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y. Study Method of Free Radical Medicine; Sanitation Press: Beijing, China, 2000; 62p. [Google Scholar]
- Köse, K.; Yazici, C.; Cambay, N.; Aşcioğlu, O.; Doğan, P. Lipid peroxidation and erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes in patients with Behcet’s disease. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2002, 197, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Ma, X.; Xie, J.; He, C. Dry Bio-Decontamination Process in Reduced-Pressure O2 Plasma. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091933
Liu H, Feng X, Ma X, Xie J, He C. Dry Bio-Decontamination Process in Reduced-Pressure O2 Plasma. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(9):1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091933
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongxia, Xinxin Feng, Xin Ma, Jinzhuo Xie, and Chi He. 2019. "Dry Bio-Decontamination Process in Reduced-Pressure O2 Plasma" Applied Sciences 9, no. 9: 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091933
APA StyleLiu, H., Feng, X., Ma, X., Xie, J., & He, C. (2019). Dry Bio-Decontamination Process in Reduced-Pressure O2 Plasma. Applied Sciences, 9(9), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091933




