An Improved A-Star Algorithm Considering Water Current, Traffic Separation and Berthing for Vessel Path Planning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Risk Modelling
2.1. Obstacle Modelling With Current
2.2. Traffic Separation Modelling
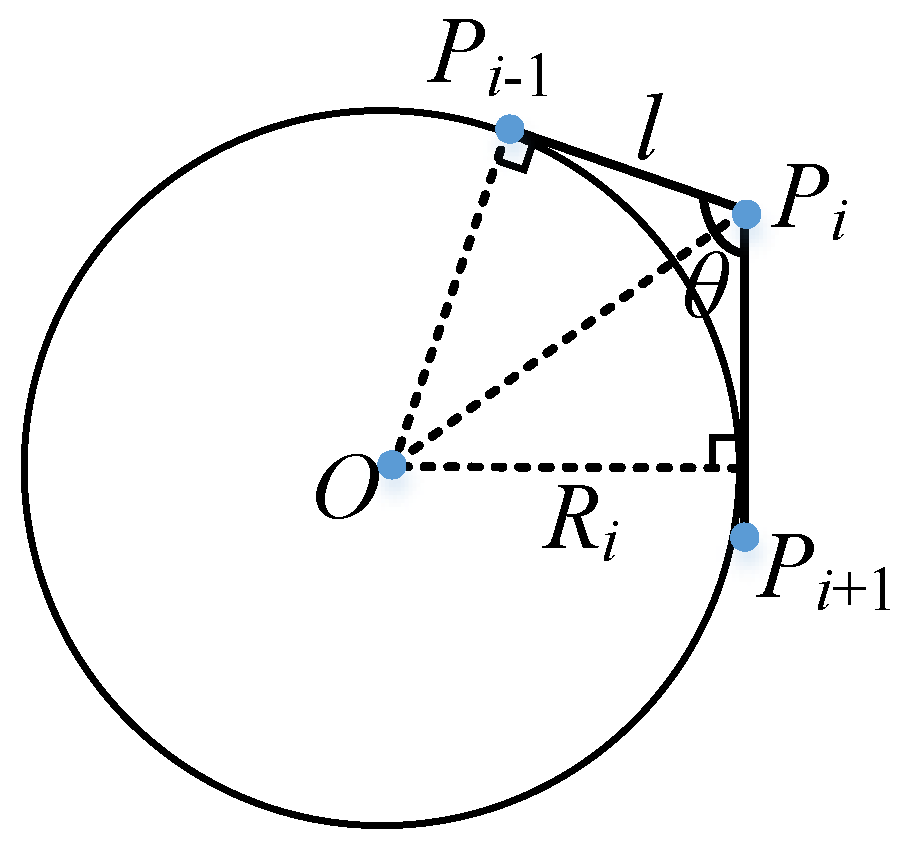
2.3. Berthing Modelling Considering Current
2.4. Manoeuvrability Restriction Modelling
3. Improved A-Star Algorithm
3.1. Traditional A-Star Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Traditional A-Star algorithm () |
|
3.2. A-Star Algorithm Considering Risk Models
3.2.1. Normal Path Generation of Vessels
| Algorithm 2 Normal path generation with the improved A-Star algorithm () |
|
3.2.2. Berthing Path Generation of Vessels
| Algorithm 3 Berthing path generation algorithm () |
|
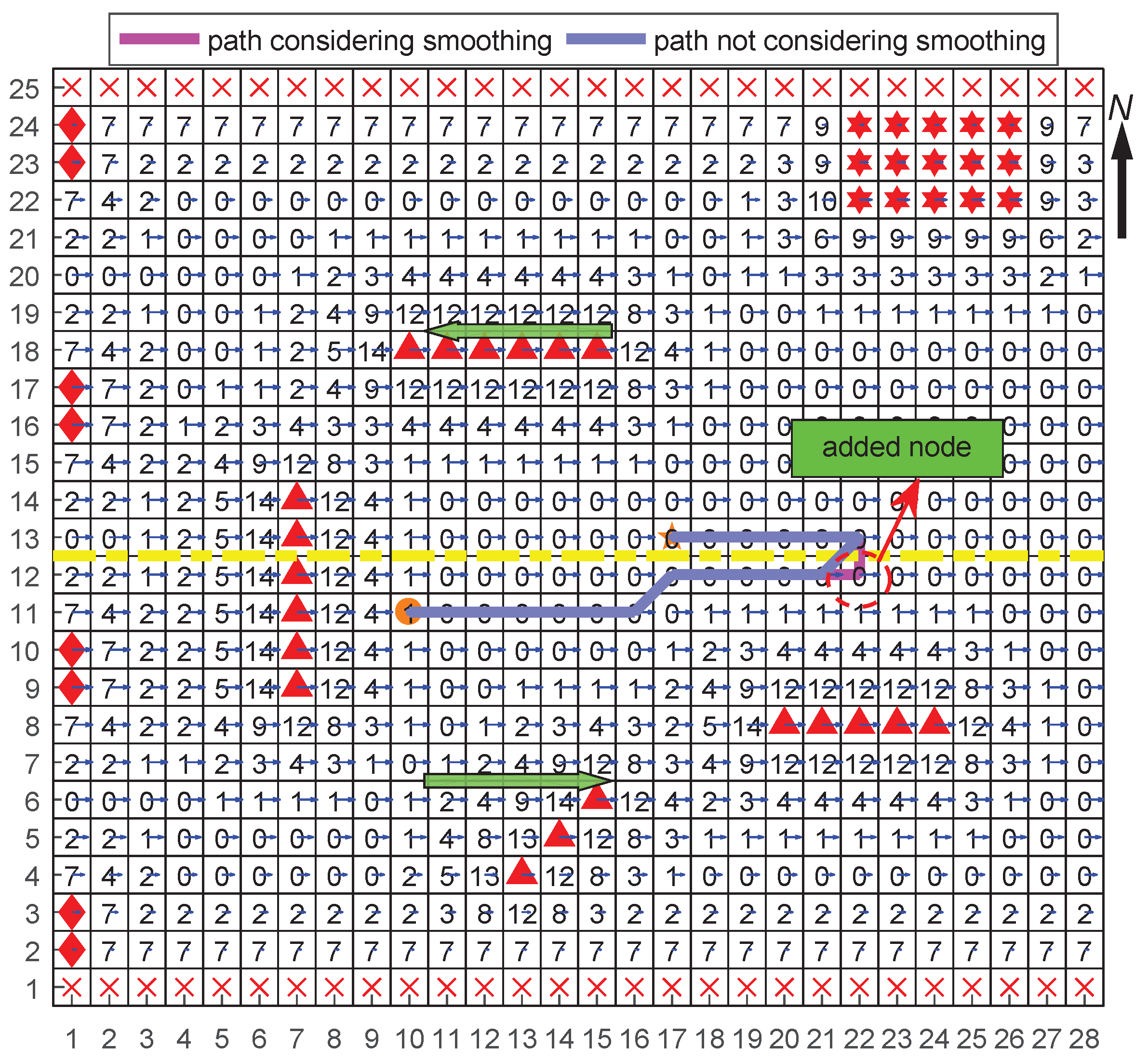
3.2.3. Combined Path Generation of Vessels
| Algorithm 4 Smoothing the combined path algorithm () |
|
4. Case Study
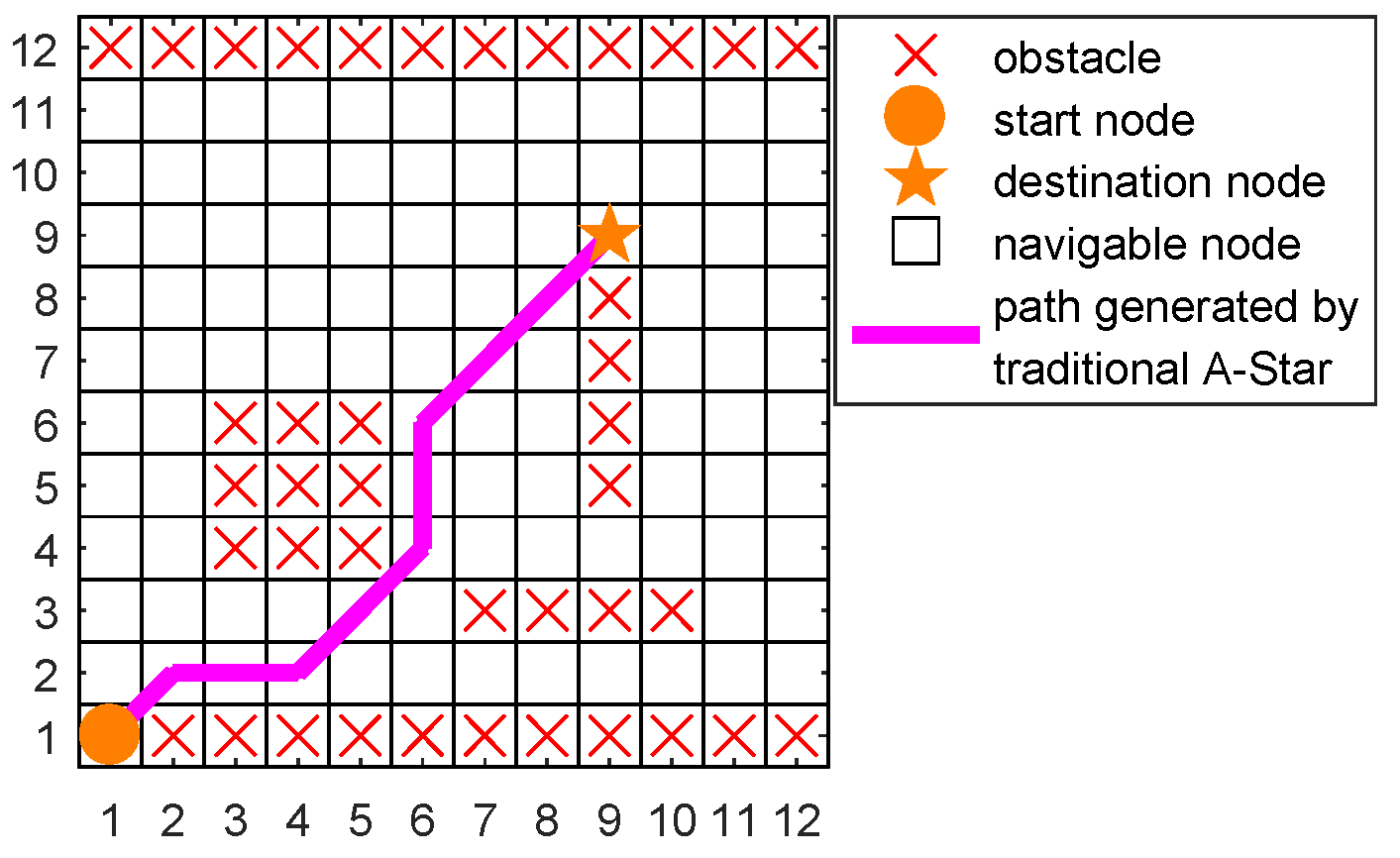
4.1. Case 1: Normal Path Planning
4.1.1. Setup
4.1.2. Results
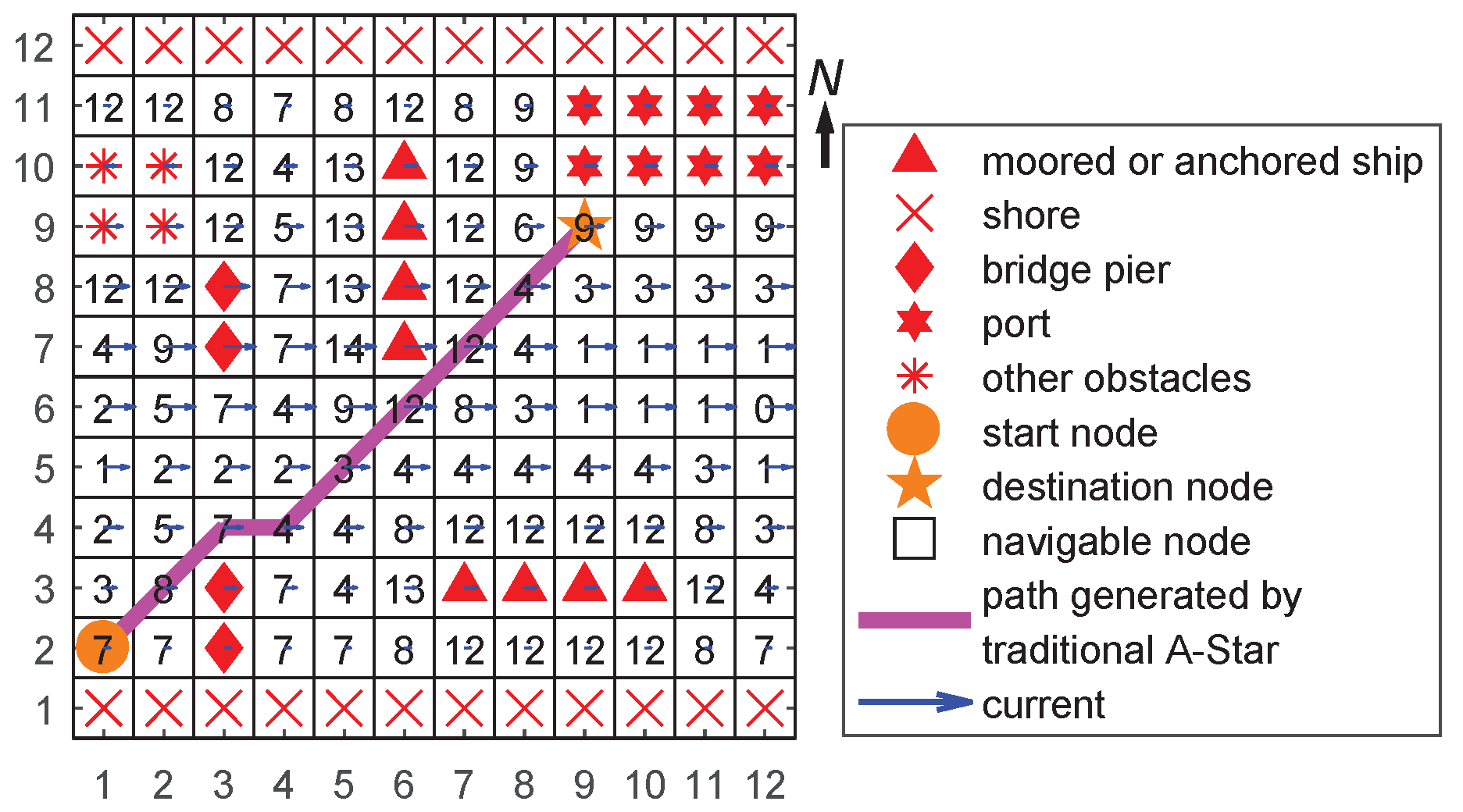
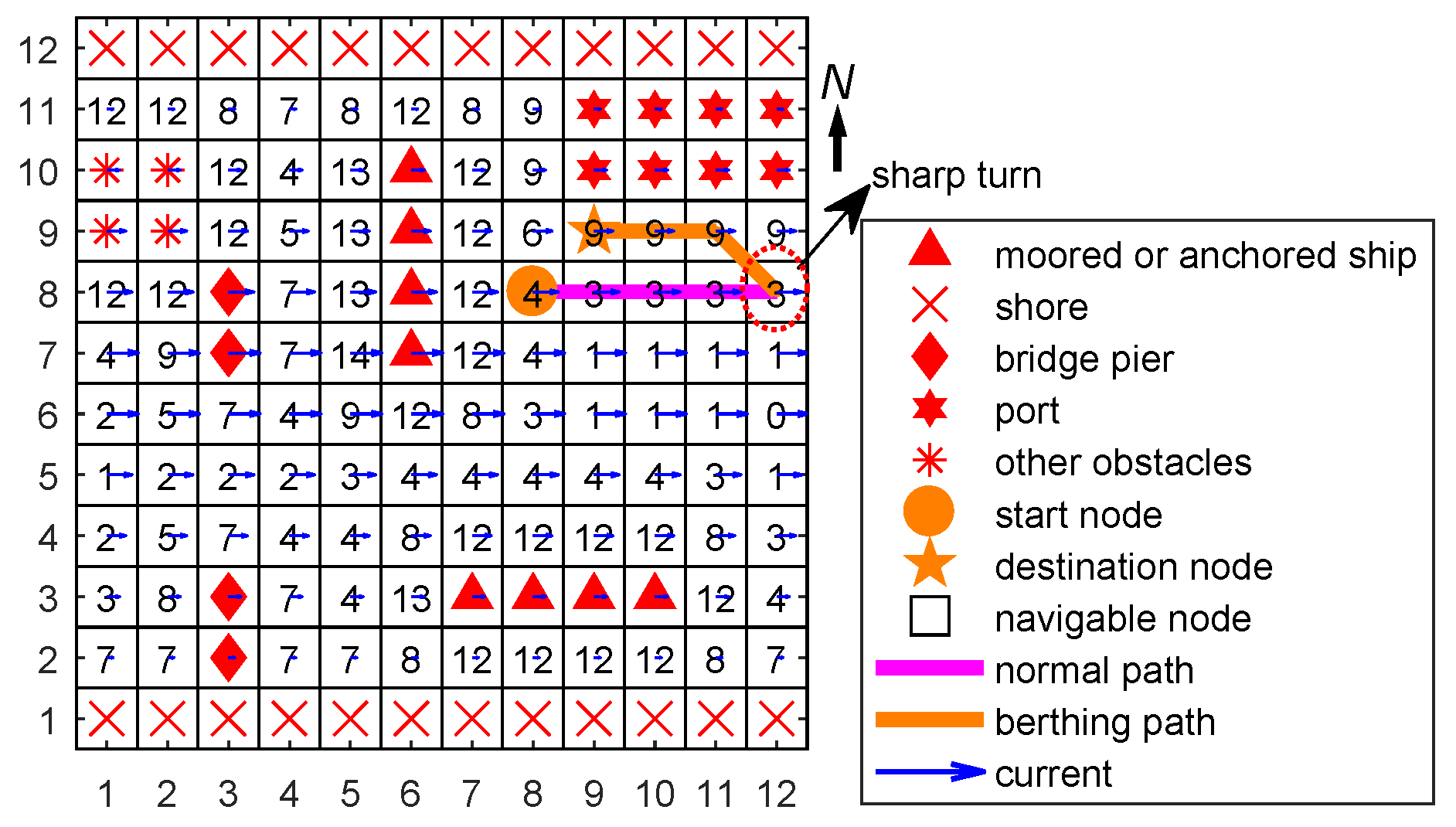
4.2. Case 2: Berthing Path Planning
4.2.1. Setup
4.2.2. Results
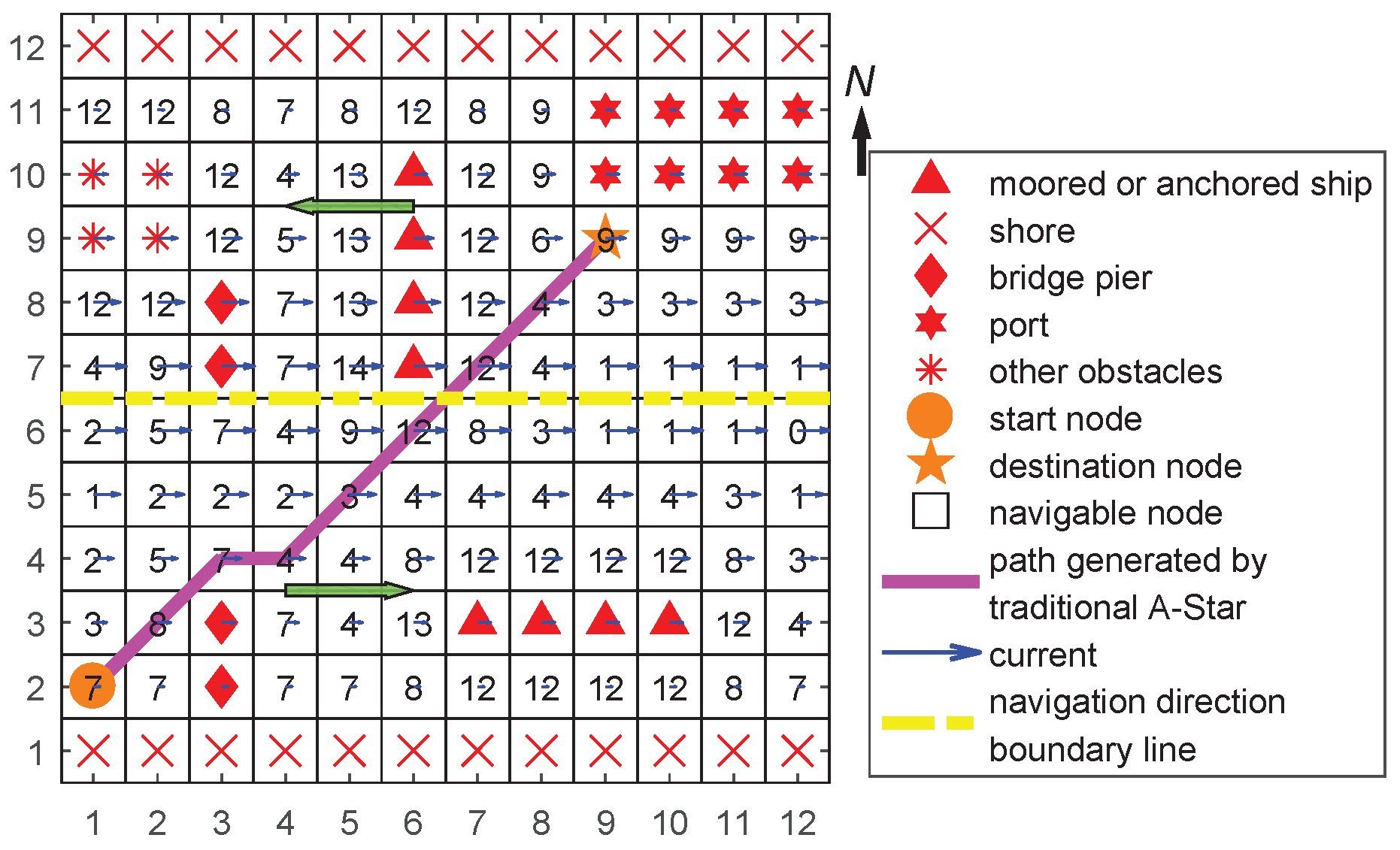
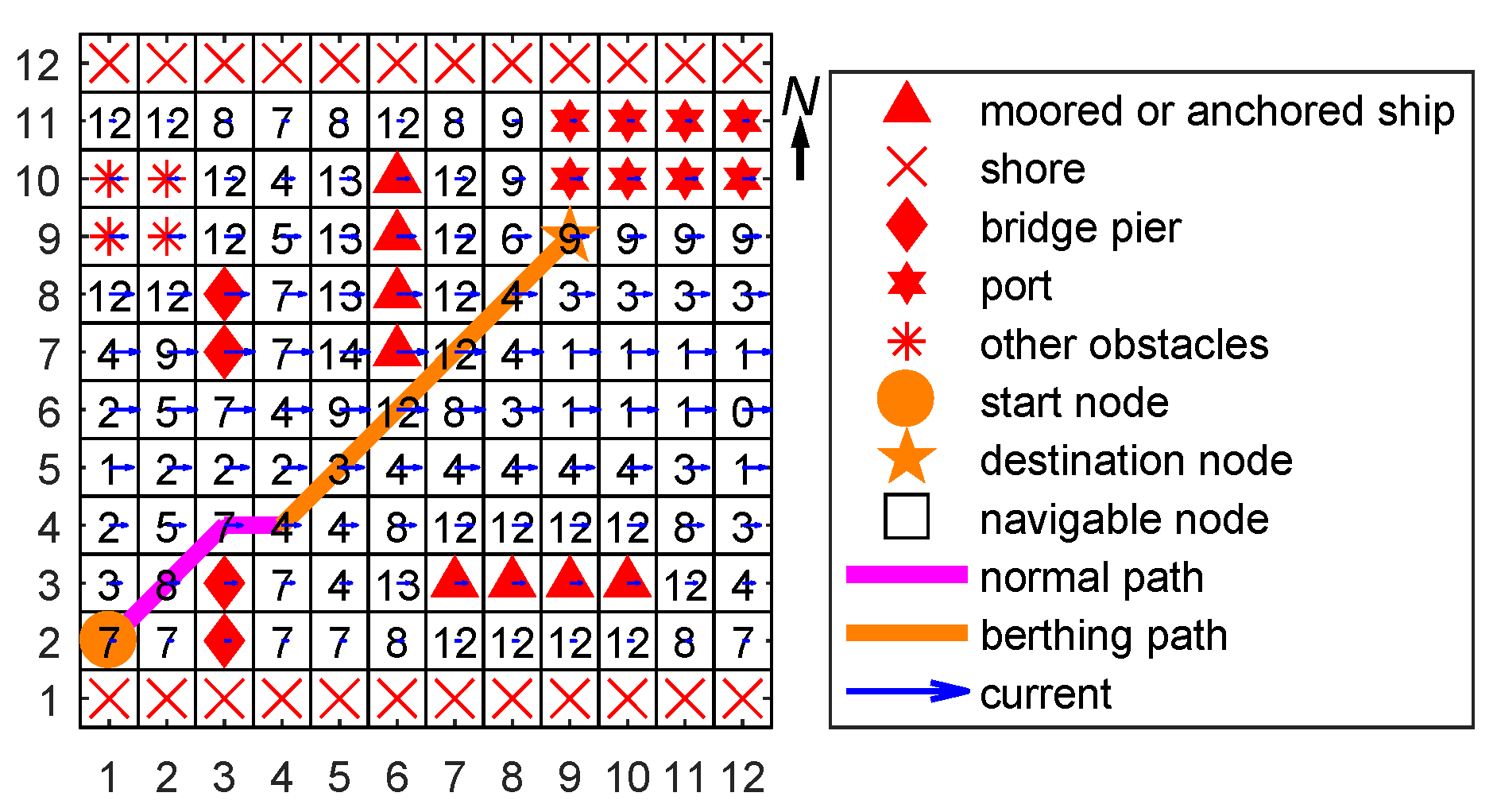
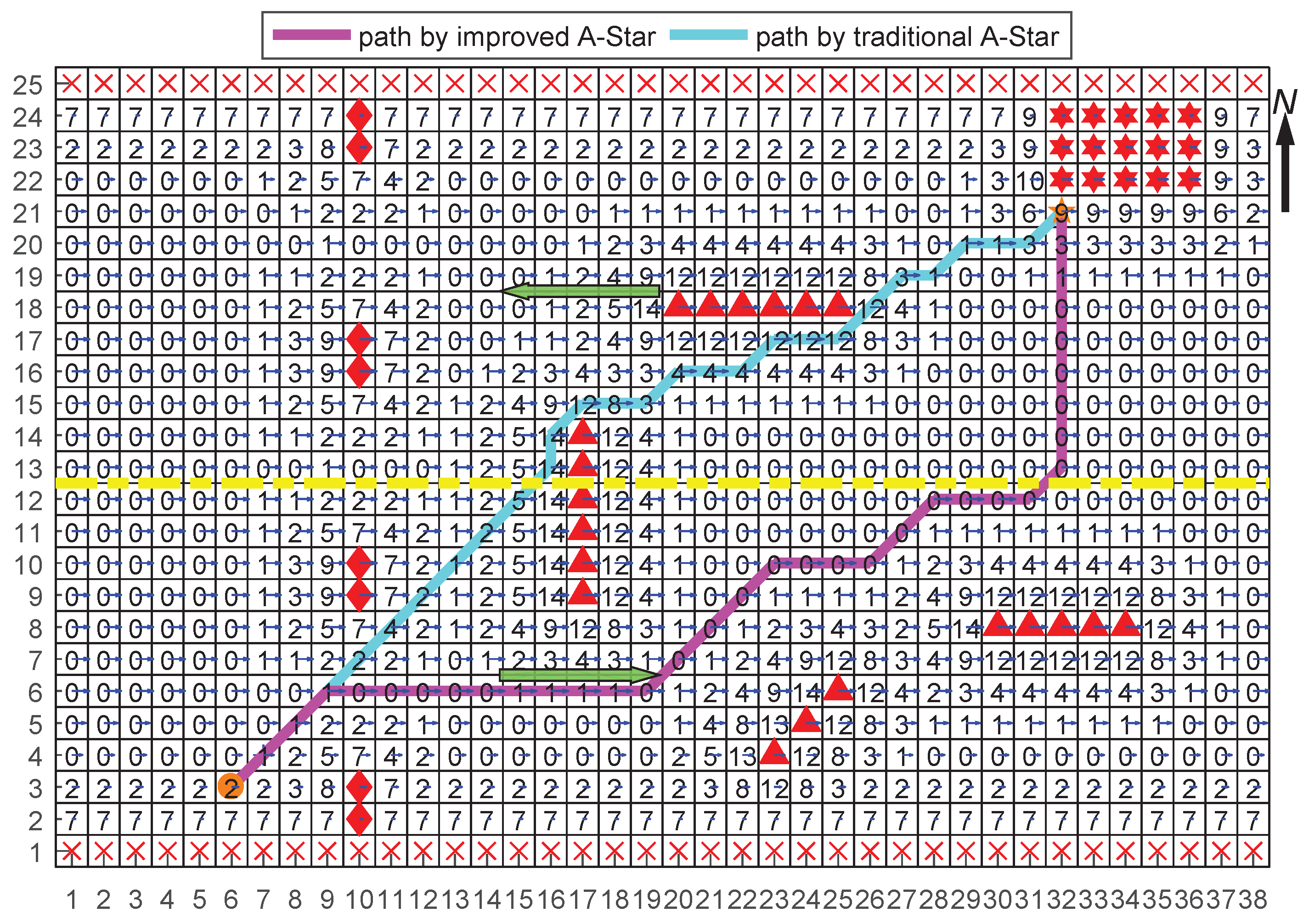
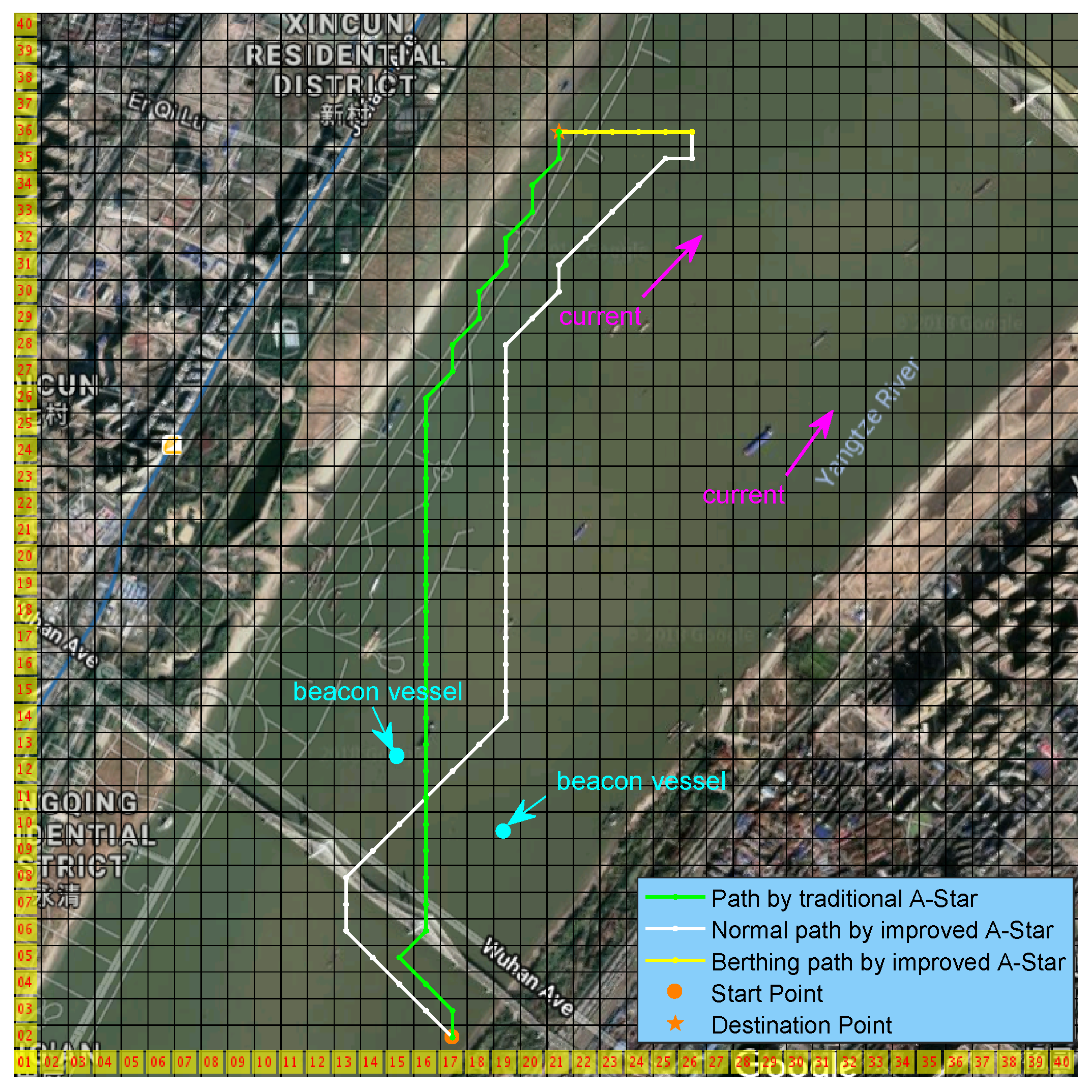
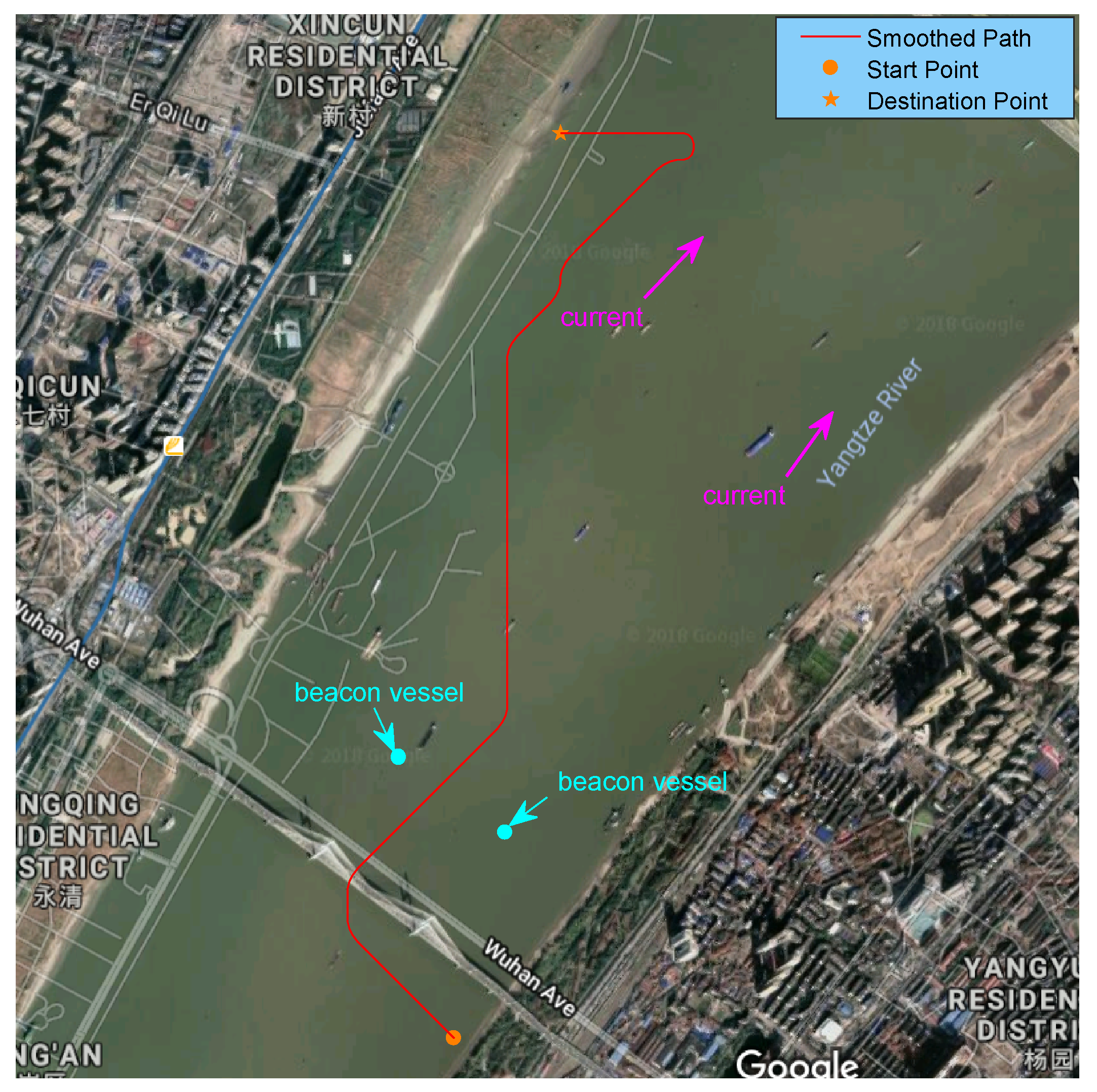
4.3. Case 3: Combined Path Planning
4.3.1. Setup
4.3.2. Results
4.4. Case 4: Path Planning in Real Scenario
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wuthishuwong, C.; Traechtler, A.; Bruns, T. Safe trajectory planning for autonomous intersection management by using vehicle to infrastructure communication. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Networking 2015, 2015, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.; Costa, P.; Lima, J.; Veiga, G. Towards an orientation enhanced Astar algorithm for robotic navigation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Seville, Spain, 18 June 2015; pp. 3320–3325. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, P.; Pugazhenthi, S. Optimal path planning of mobile robots: A review. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2012, 7, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlapczynski, R. A new method of ship routing on raster grids, with turn penalties and collision avoidance. J. Navig. 2005, 59, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, B.; Myung, H. Curvature path planning with high resolution graph for unmanned surface vehicle. In Proceedings of the Robot Intelligence Technology and Applications (RiTA); Springer: Gwangju, Korea, 2013; pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, H.; Yin, Y. Fast path planning for autonomous ships in restricted waters. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Yin, Y. COLREGS-constrained real-time path planning for autonomous ships using modified artificial potential fields. J. Navig. 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hu, M.; Yan, X. Multi-objective path planning for unmanned surface vehicle with currents effects. ISA Trans. 2018, 75, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Kim, H.; Chung, H.; Bang, Y.; Myung, H. Energy efficient path planning for a marine surface vehicle considering heading angle. Ocean Eng. 2015, 107, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, E. A Master’s Guide to Berthing; The Standard; Witherby & Company: Witherby, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rafal, S. Evolutionary Sets of Safe Ship Trajectories Within Traffic Separation Schemes. J. Navig. 2013, 66, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Shin, J.U.; Kim, H.; Myung, H. Angular rate-constrained path planning algorithm for unmanned surface vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2014, 84, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.G.H. Hyperstar: A multi-path Astar algorithm for risk averse vehicle navigation. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2009, 43, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.E.; Nilsson, N.J.; Raphael, B. A formal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1968, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.M.; Al-Arif, A.H.M.; Ferdous, I.; Nizami, M.S.H. Path planning for robotic boats in a rescue system. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 45, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyaraj, B.M.; Jain, L.C.; Finn, A.; Drake, S. Multiple UAVs path planning algorithms: A comparative study. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2008, 7, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Lin, C.; Xie, X.; Wang, A.J.A.; Hung, C.C. Path planning for virtual human motion using improved A* star algorithm. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations (ITNG), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1 July 2010; pp. 1154–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Pochmara, J.; Grygiel, W.; Koppa, R.; Kaminski, K. Mobile robot platform for real-time search algorithms. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, Gdynia, Poland, 10 October 2013; pp. 615–620. [Google Scholar]


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| node range of x axis | |
| node range of y axis | |
| grid length | 30 m |
| minimum radius of vessel | 27 m |
| 100 | |
| 0.2 | |
| 0.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Mao, Q.; Chu, X.; Xie, S. An Improved A-Star Algorithm Considering Water Current, Traffic Separation and Berthing for Vessel Path Planning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061057
Liu C, Mao Q, Chu X, Xie S. An Improved A-Star Algorithm Considering Water Current, Traffic Separation and Berthing for Vessel Path Planning. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(6):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061057
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chenguang, Qingzhou Mao, Xiumin Chu, and Shuo Xie. 2019. "An Improved A-Star Algorithm Considering Water Current, Traffic Separation and Berthing for Vessel Path Planning" Applied Sciences 9, no. 6: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061057
APA StyleLiu, C., Mao, Q., Chu, X., & Xie, S. (2019). An Improved A-Star Algorithm Considering Water Current, Traffic Separation and Berthing for Vessel Path Planning. Applied Sciences, 9(6), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061057







