Investigation on Direct Shear and Energy Dissipation Characteristics of Iron Tailings Powder Reinforced by Polypropylene Fiber
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Material
3. Direct Shear Test
3.1. Sample Preparation and Testing
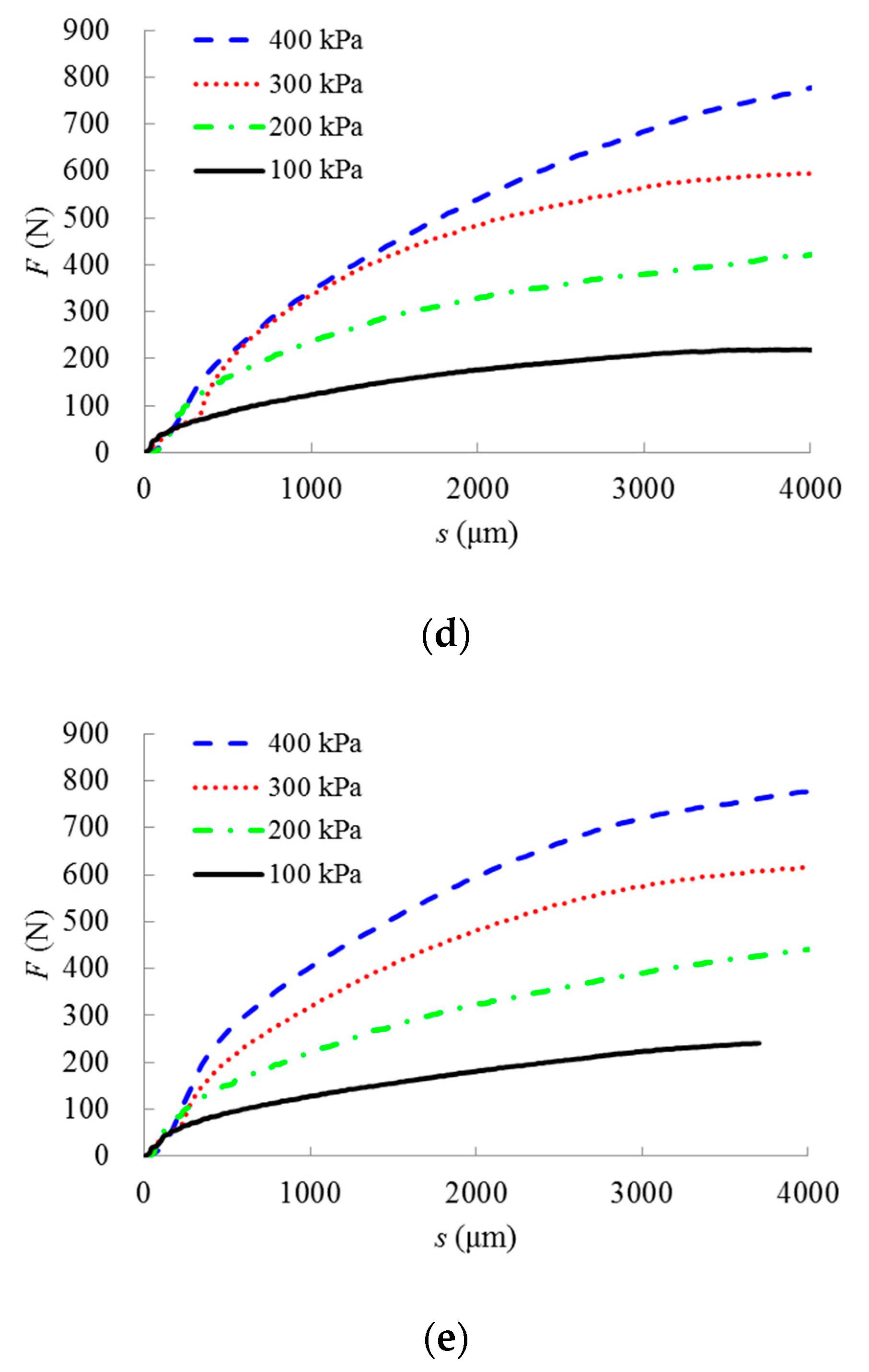
3.2. Test Results and Analysis
4. Shear Energy Dissipation of Fiber-Reinforced Iron Tailings Powder
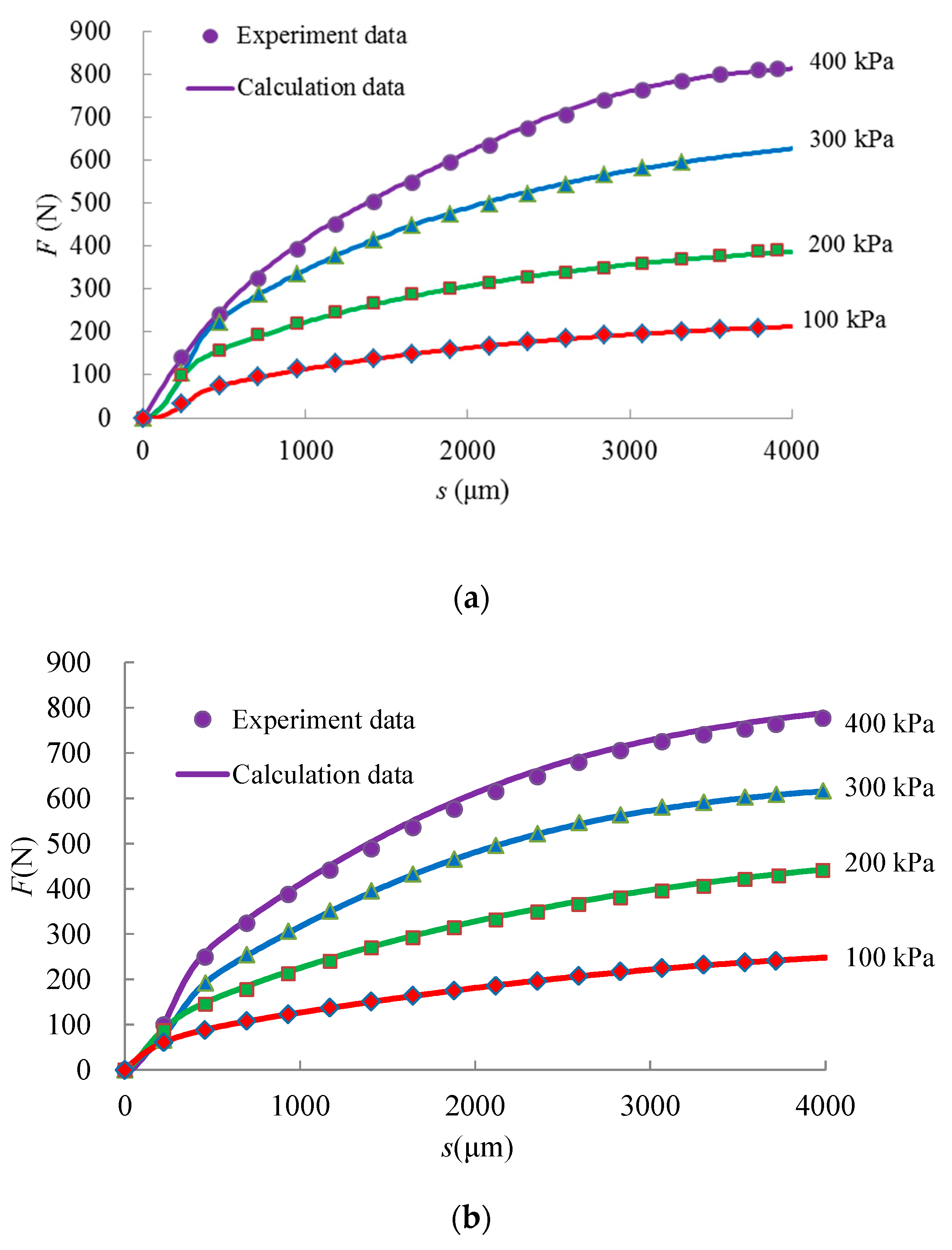
4.1. F-s Curve Fitting Based on a BP Neural Network
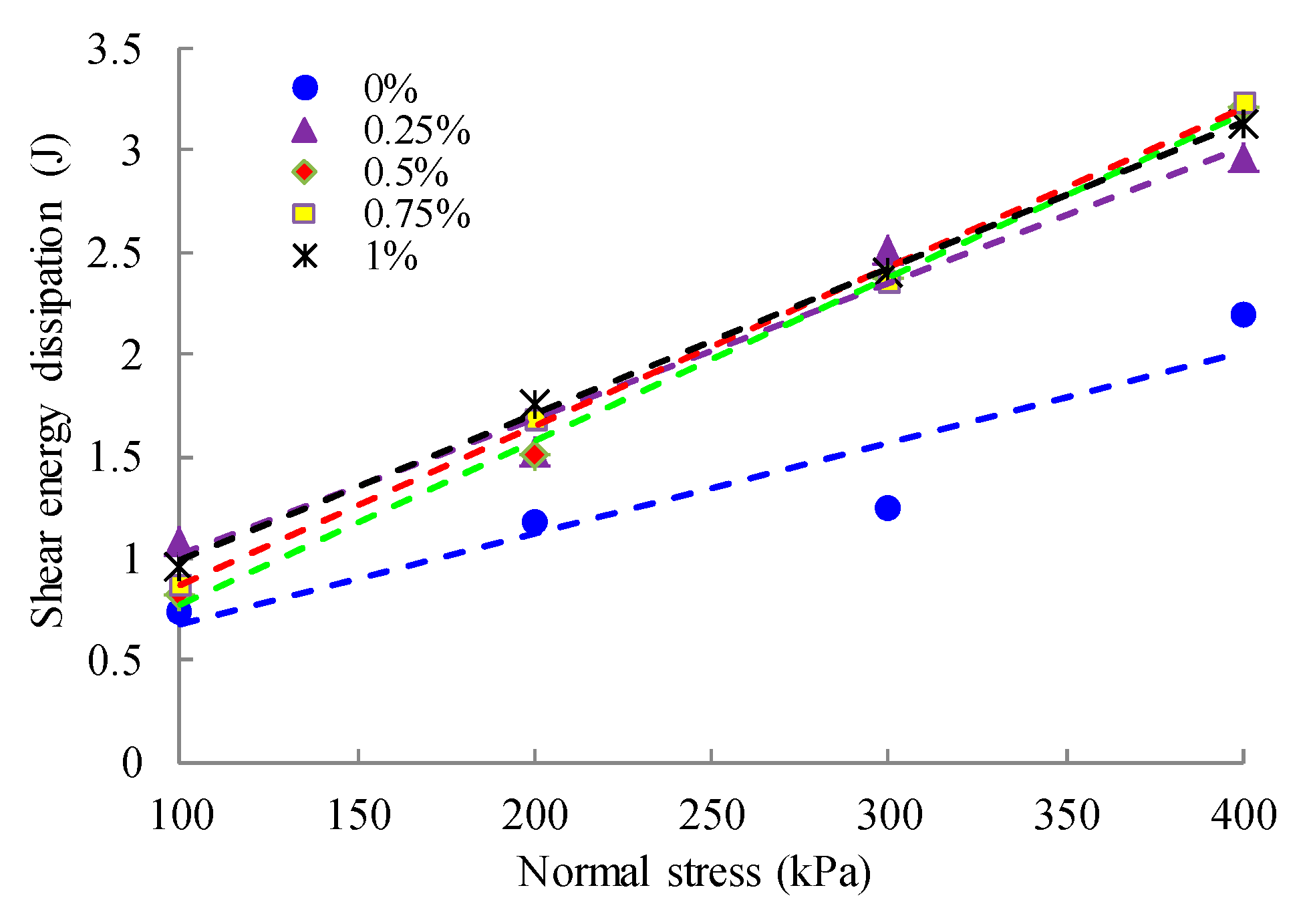
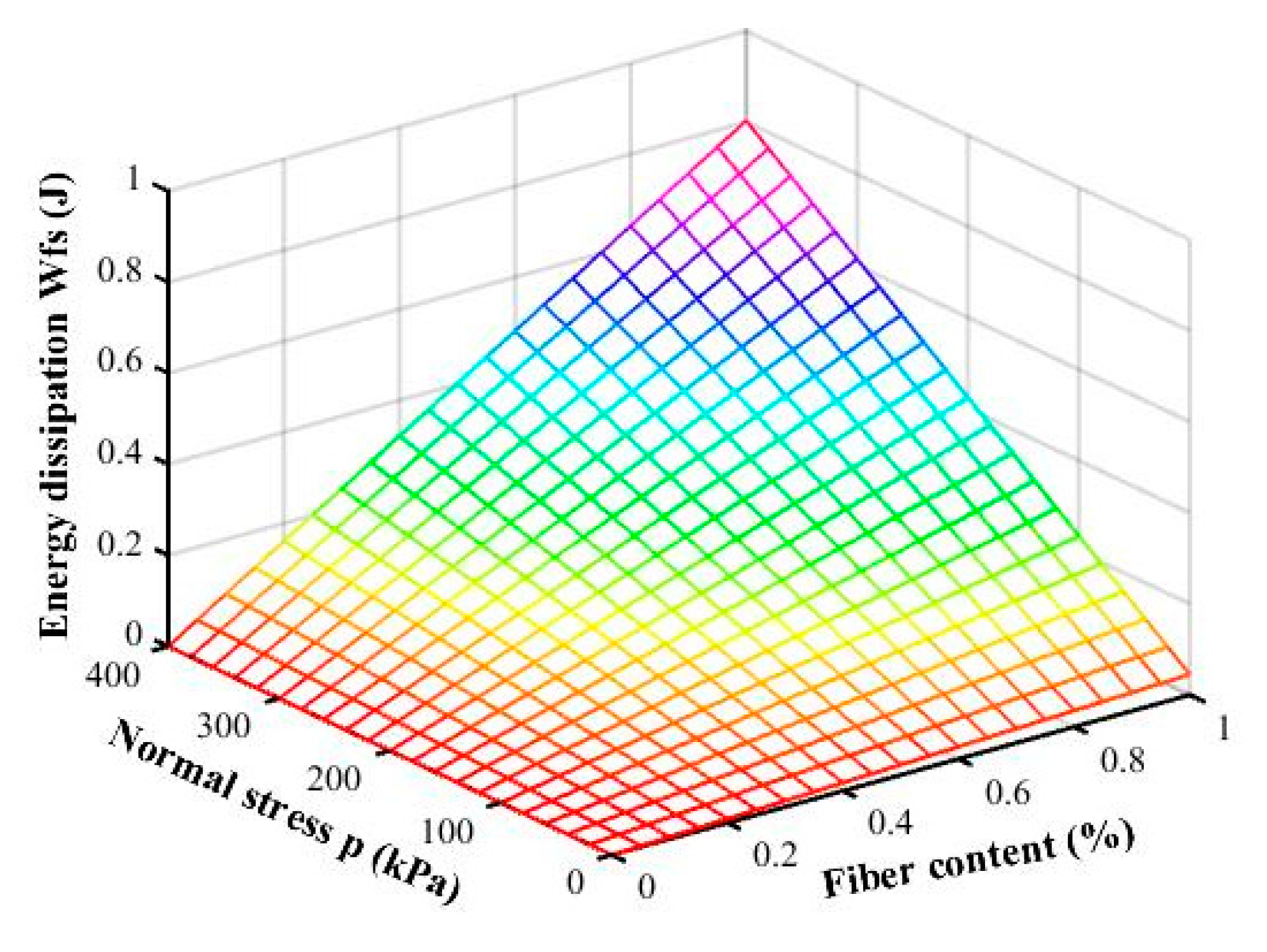
4.2. Calculation of Shear Energy Dissipation of Fiber-Reinforced Iron Tailings Powder
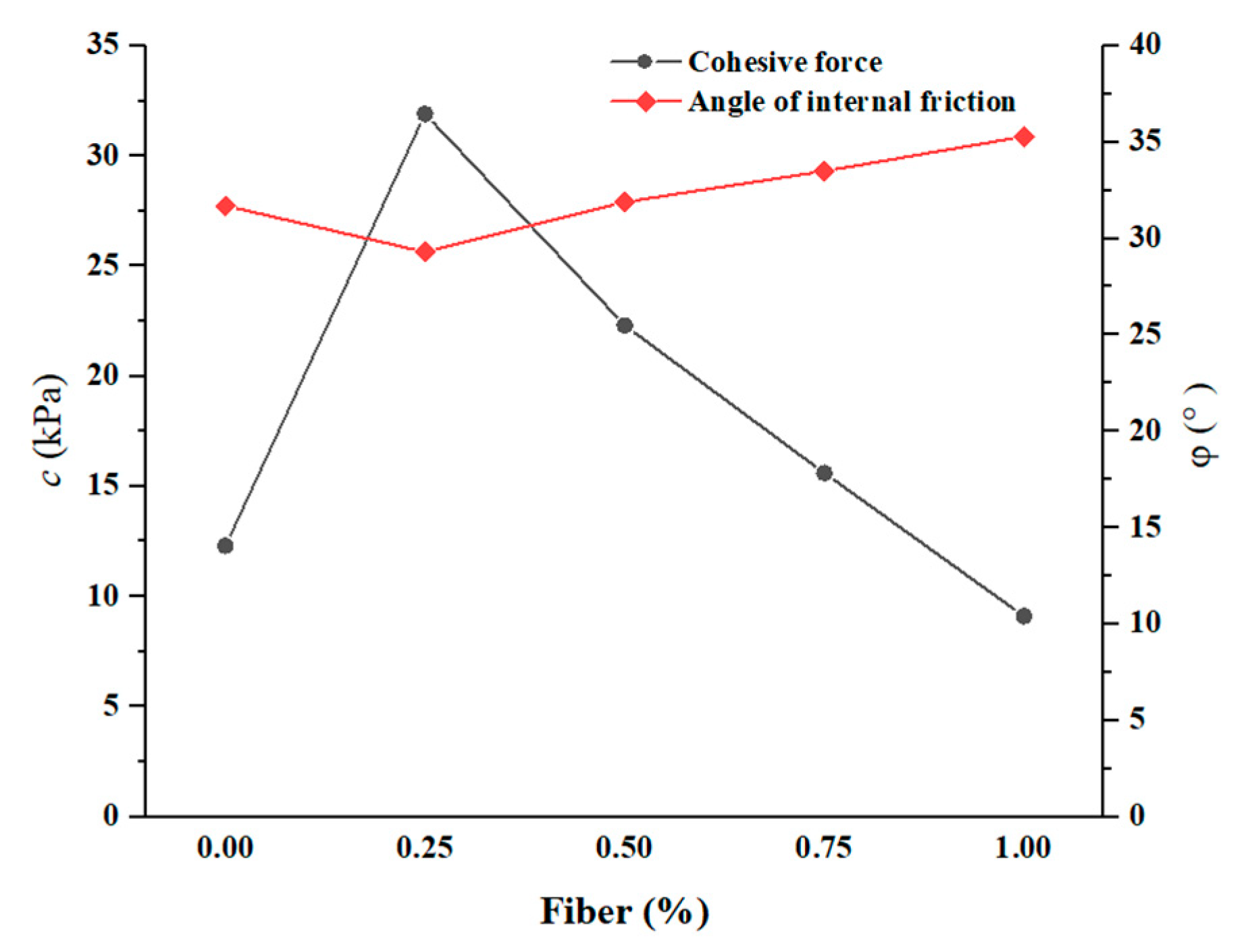
5. Interfacial Strength Parameters of Fiber-Reinforced Iron Tailings Powder
5.1. Fiber Interfacial Energy Dissipation Calculation
5.2. Interfacial Strength Parameters of Fiber-Reinforced Iron Tailings Powder
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, F.; Li, L.; Song, S.; Liu, J. Early-age hydration characteristics of composite binder containing iron tailing powder. Powder Technol. 2017, 315, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W.; Ren, D. Development of fly ash and iron ore tailing based porous geopolymer for removal of Cu(II) from wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13507–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onitiri, M.A.; Akinlabi, E.T. Effects of Particle Size and Particle Loading on the Tensile Properties of Iron-Ore-Tailing-Filled Epoxy and Polypropylene Composites. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2017, 52, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, L.; Biswal, S.K.; Venugopaland, R.; Mandre, N.R. Recovery of Ultra-Fine Iron Ore from Iron Ore Tailings. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, L.A.D.C.; Silva, G.C.; Mendes, J.C.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Using Iron Ore Tailings from Tailing Dams as Road Material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ha, S. Effects of Particle Size on the Shear Behavior of Coarse Grained Soils Reinforced with Geogrid. Materials 2014, 7, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Soltani, A.; Deng, A.; Jaksa, M.B. Mechanical Performance of Jute Fiber-Reinforced Micaceous Clay Composites Treated with Ground-Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag. Materials 2019, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Li, S.; Yu, H.; Gong, X. Interlaminar Bonding Properties on Cement Concrete Deck and Phosphorous Slag Asphalt Pavement. Materials 2019, 12, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Guo, J.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y. Investigation on the Triaxial Mechanical Characteristics of Cement-Treated Subgrade Soil Admixed with Polypropylene Fiber. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.; Consoli, N.C.; Baudet, B. The mechanics of fibre-reinforced sand. Géotechnique 2010, 60, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diambra, A.; Ibraim, E. Fibre-reinforced sand: Interaction at the fibre and grain scale. Géotechnique 2015, 65, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diambra, A.; Ibraim, E.; Wood, D.M.; Russell, A. Fibre reinforced sands: Experiments and modelling. Geotext. Geomembr. 2010, 28, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Senetakis, K. Modulus Reduction and Damping Increase of Two Sands Reinforced with Polypropylene Fibers. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04017299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diambra, A.; Ibraim, E. Modelling of fibre-cohesive soil mixtures. Acta Geotech. 2014, 9, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.A.; Najjar, S.S.; Sadek, S.; Taha, H.; Jaffal, H.; Alahmad, M. Effect of compaction method on the undrained strength of fiber-reinforced clay. Soils Found. 2018, 58, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Deng, A.; Taheri, A. Swell-compression characteristics of a fiber–reinforced expansive soil. Geotext. Geomembr. 2018, 46, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegenizadeh, A.; Keramatikerman, M.; Nikraz, H. Liquefaction resistance of fibre reinforced low-plasticity silt. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 104, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Yao, K.; Li, N.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, C. Strength properties of nano-MgO and cement stabilized coastal silty clay subjected to sulfuric acid attack. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X. Research on the Impact Loading and Energy Dissipation of Concrete after Elevated Temperature under Different Heating Gradients and Cooling Methods. Materials 2018, 11, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Li, Z.W. Factor of Safety of Three-Dimensional Stepped Slopes. Int. J. Géoméch. 2018, 18, 04018036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z. A novel constitutive model for geomaterials in hyperplasticity. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 98, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi, S.; Fonseca, J. A micro finite-element model for soil behavior: Numerical validation. Géotechnique 2018, 68, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.X. Investigation on strength and microstructure characteristics of Nano-MgO admixed with cemented soft soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamás, K. The role of bond and damping in the discrete element model of soil-sweep interaction. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 169, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, K.J.; Huang, X.; O’Sullivan, C. Energy dissipation in soil samples during drained triaxial shearing. Géotechnique 2018, 68, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.W.; Ma, W.; Zhang, S.J.; Mu, Y.H.; Li, G.Y. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles in mechanical behaviors of frozen loess. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 146, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, N.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, A.Z.; Chi, S. Experimental and mathematical investigations on unconfined compressive behavior of coastal soft soil under complicated freezing processes. Pol. Marit. Res. 2016, 23, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.J.; Xiao, H.; Lee, F.H. Determination of representative strength of deep cement-mixed clay from core strength data. Géotechnique 2017, 67, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraim, E.; Camenen, J.-F.; Diambra, A.; Kairelis, K.; Visockaite, L.; Consoli, N.C. Energy efficiency of fibre reinforced soil formation at small element scale: Laboratory and numerical investigation. Geotext. Geomembr. 2018, 46, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, P.F.; Noorzad, R. Energy-based evaluation of liquefaction of fiber-reinforced sand using cyclic triaxial testing. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 104, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, N.; Tao, F.; Yao, K. Characterisation of nano magnesia–cement-reinforced seashore soft soil by direct-shear test. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2019, 37, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, W.; Song, F.; An, D.; Yan, H. Compression Characteristics and Microscopic Mechanism of Coastal Soil Modified with Cement and Fly Ash. Materials 2019, 12, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Qiu, L.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Zhou, A.; Xiao, J. Shearing Performance of Lime-Reinforced Iron Tailing Powder Based on Energy Dissipation. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profession Standard of The People’s Republic of China. Test Method of Soils for Highway Engineering (JTG E40-2007); People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Z. A Modified Back Propagation Artificial Neural Network Model Based on Genetic Algorithm to Predict the Flow Behavior of 5754 Aluminum Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhang, L. Prediction model of end-point phosphorus content in BOF steelmaking process based on PCA and BP neural network. J. Process Control 2018, 66, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, A.; Piotr, L.N. Designing the Composition of Cement Stabilized Rammed Earth Using Artificial Neural Networks. Materials 2019, 12, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Han, J.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Application of a BP neural network in predicting destroyed floor depth caused by underground pressure. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Mao, T.; Li, N.; Jia, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W. Characterization of Short-Term Strength Properties of Fiber/Cement-Modified Slurry. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, R.A.; Wroth, C.P. Direct shear tests on reinforced sand. Géotechnique 1987, 37, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






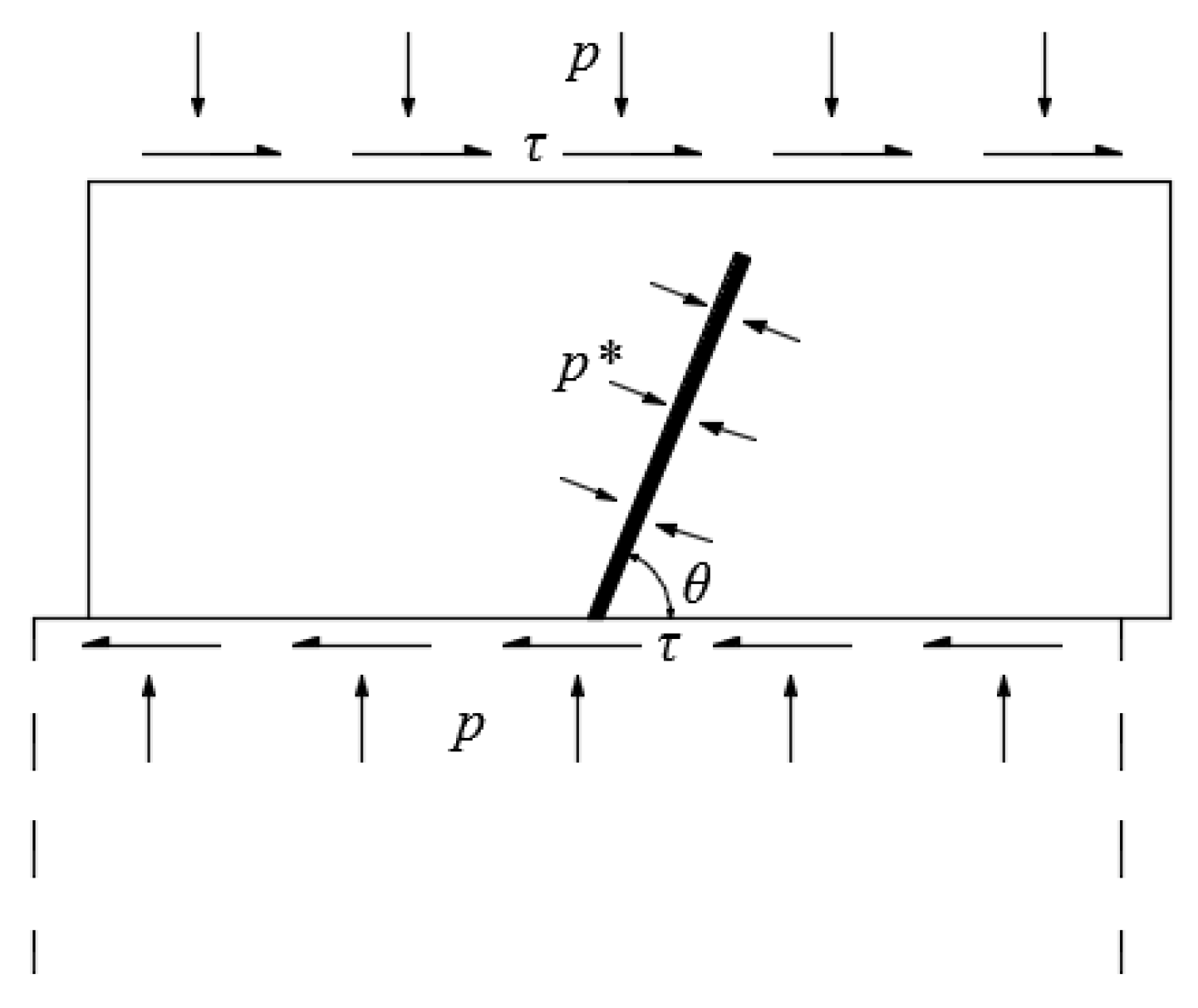

| Particle Diameter (μm) | <45 | 45–75 | 75–100 | 100–150 | >150 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 69.57 | 8.76 | 5.18 | 6.98 | 9.51 |
| Fiber Dosage (%) | Normal Stress (kPa) | a1 | a2 | a3 | a4 | a5 | a6 | a7 | Average Error (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | −49.93 | 0.0023 | −9.71 | 727,324 | 0.00077 | 7.87 | −727,051 | 0.03 |
| 200 | −19.77 | 0.0055 | −29.97 | −4,557,279 | −0.00091 | −9.36 | 399 | 0.06 | |
| 300 | −14.06 | 0.0033 | −17.77 | 317,668 | 0.00037 | 6.33 | −317,062 | 0.05 | |
| 400 | 24.61 | −0.0062 | 34.9 | −38,062 | −0.00067 | −3.79 | 823 | 0.02 | |
| 0.25 | 100 | 111.6 | 0.0022 | −4.46 | 189,740 | 0.0017 | 6.99 | −189,573 | 0.05 |
| 200 | −8044 | −0.00056 | −3.26 | 668 | 0.0053 | 1.41 | −248 | 0.02 | |
| 300 | 1230 | 0.001 | −0.03 | −94 | −0.02 | 6.82 | −514 | 0.07 | |
| 400 | −1634 | −0.00087 | −0.37 | −125 | −0.016 | 2.3 | 775 | 0.02 | |
| 0.5 | 100 | −28,952 | −0.0005 | −4.92 | 39.95 | 0.021 | −5.78 | 202 | 0.38 |
| 200 | 243,556 | 0.00052 | 6.54 | −93.45 | −0.0187 | 3.67 | −243,126 | 0.08 | |
| 300 | 112,578 | 0.0005 | 5.23 | −116 | −0.018 | 4.83 | −111,876 | 0.13 | |
| 400 | −262 | −0.0018 | 3.98 | −17,714 | −0.0011 | −3.4 | 827 | 0.01 | |
| 0.75 | 100 | −270 | −0.001 | 0.56 | 338,718 | 0.0068 | 8.73 | −338,489 | 0.01 |
| 200 | −169,731 | −0.00056 | −6.1 | 80.82 | 0.019 | −3.74 | 375 | 0.13 | |
| 300 | 903 | 0.001 | −0.24 | −101.5 | −0.016 | 6.99 | −294 | 0.01 | |
| 400 | −1737 | −0.0006 | −0.137 | −111 | −0.0117 | 3.08 | 903 | 0.04 | |
| 1 | 100 | 425 | 0.0006 | −0.09 | 295,144 | 0.006 | 8.4 | −295,283 | 0.01 |
| 200 | −81,430 | −0.00038 | −5.16 | 99.53 | 0.0125 | −1.35 | 438 | 0.03 | |
| 300 | 1014 | 0.0009 | −0.18 | −92.58 | −0.0151 | 4.52 | −365 | 0.01 | |
| 400 | −1500 | −0.00076 | −0.114 | 148 | 0.0146 | −3.99 | 693 | 0.02 |
| Normal Stress (kPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber (%) | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 |
| 0 | 0.74 | 1.18 | 1.24 | 2.2 |
| 0.25 | 1.08 | 1.52 | 1.99 | 2.96 |
| 0.5 | 0.83 | 1.51 | 2.38 | 2.36 |
| 0.75 | 0.87 | 1.68 | 2.36 | 3.24 |
| 1 | 0.95 | 1.76 | 2.41 | 3.13 |
| Fiber Dosage (%) | Vf (cm3) | Normal Stress p (kPa) | C1 (m3 × 10−3) | C2 (kPa) | C3 (kPa) | C4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.343 | 100 | 0.066 | 104.75 | 22.32 | 0.82 |
| 200 | 0.066 | 209.51 | 44.63 | 0.82 | ||
| 300 | 0.066 | 314.26 | 66.95 | 0.82 | ||
| 400 | 0.066 | 419.02 | 89.26 | 0.82 | ||
| 0.5 | 0.686 | 100 | 0.132 | 104.75 | 22.32 | 0.82 |
| 200 | 0.132 | 209.51 | 44.63 | 0.82 | ||
| 300 | 0.132 | 314.26 | 66.95 | 0.82 | ||
| 400 | 0.132 | 419.02 | 89.26 | 0.82 | ||
| 0.75 | 1.028 | 100 | 0.198 | 104.75 | 22.32 | 0.82 |
| 200 | 0.198 | 209.51 | 44.63 | 0.82 | ||
| 300 | 0.198 | 314.26 | 66.95 | 0.82 | ||
| 400 | 0.198 | 419.02 | 89.26 | 0.82 | ||
| 1 | 1.373 | 100 | 0.264 | 104.75 | 22.32 | 0.82 |
| 200 | 0.264 | 209.51 | 44.63 | 0.82 | ||
| 300 | 0.264 | 314.26 | 66.95 | 0.82 | ||
| 400 | 0.264 | 419.02 | 89.26 | 0.82 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, P.; Lv, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W. Investigation on Direct Shear and Energy Dissipation Characteristics of Iron Tailings Powder Reinforced by Polypropylene Fiber. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235098
Jiang P, Lv S, Wang Y, Li N, Wang W. Investigation on Direct Shear and Energy Dissipation Characteristics of Iron Tailings Powder Reinforced by Polypropylene Fiber. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(23):5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235098
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Ping, Shaowei Lv, Yue Wang, Na Li, and Wei Wang. 2019. "Investigation on Direct Shear and Energy Dissipation Characteristics of Iron Tailings Powder Reinforced by Polypropylene Fiber" Applied Sciences 9, no. 23: 5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235098
APA StyleJiang, P., Lv, S., Wang, Y., Li, N., & Wang, W. (2019). Investigation on Direct Shear and Energy Dissipation Characteristics of Iron Tailings Powder Reinforced by Polypropylene Fiber. Applied Sciences, 9(23), 5098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235098







