Motion Recognition and an Accuracy Comparison of Left and Right Arms by EEG Signal Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biological Signal Extraction and Processing
2.1. EMG and EEG Signal Abstraction
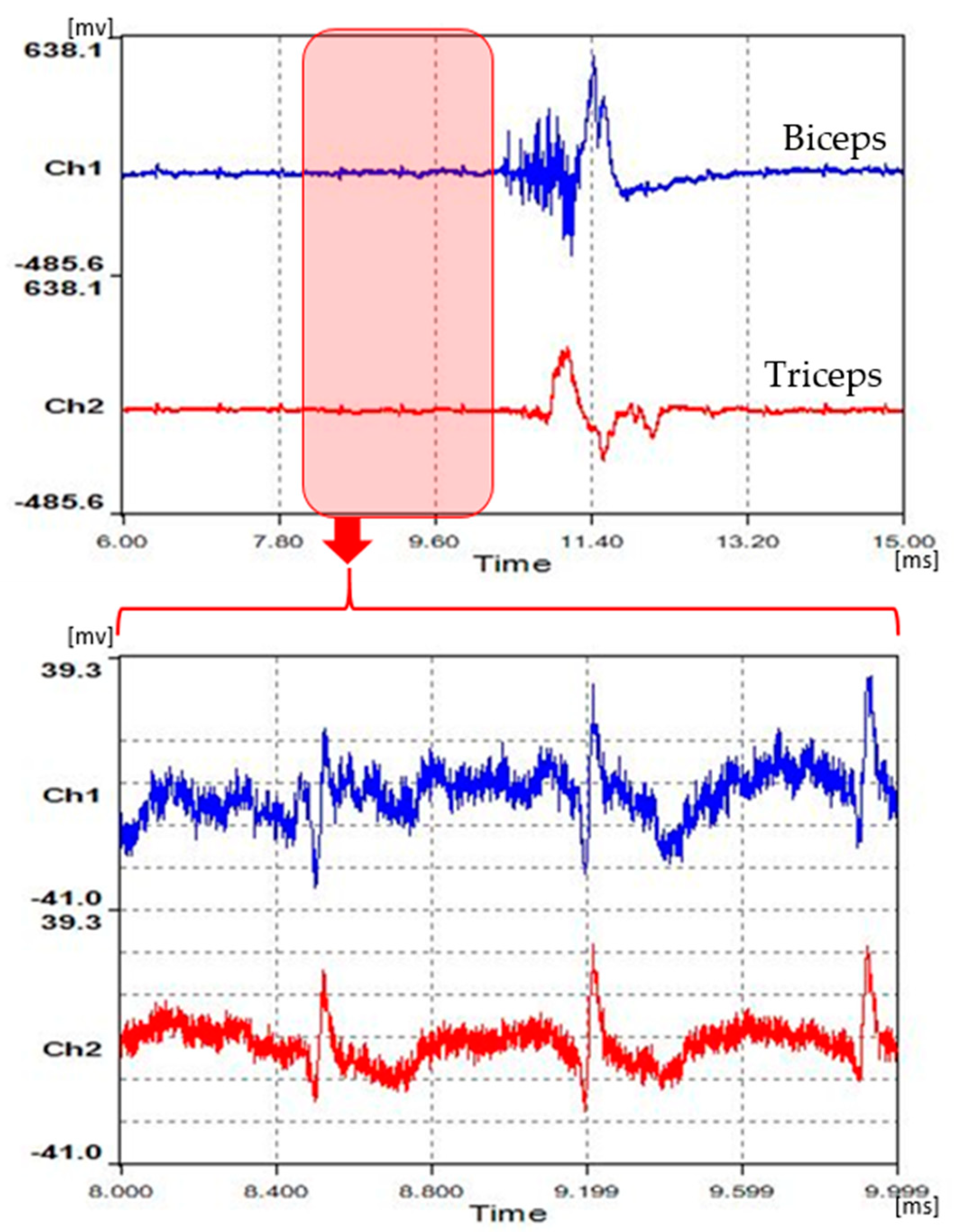
2.1.1. Measurement and Extraction of EMG
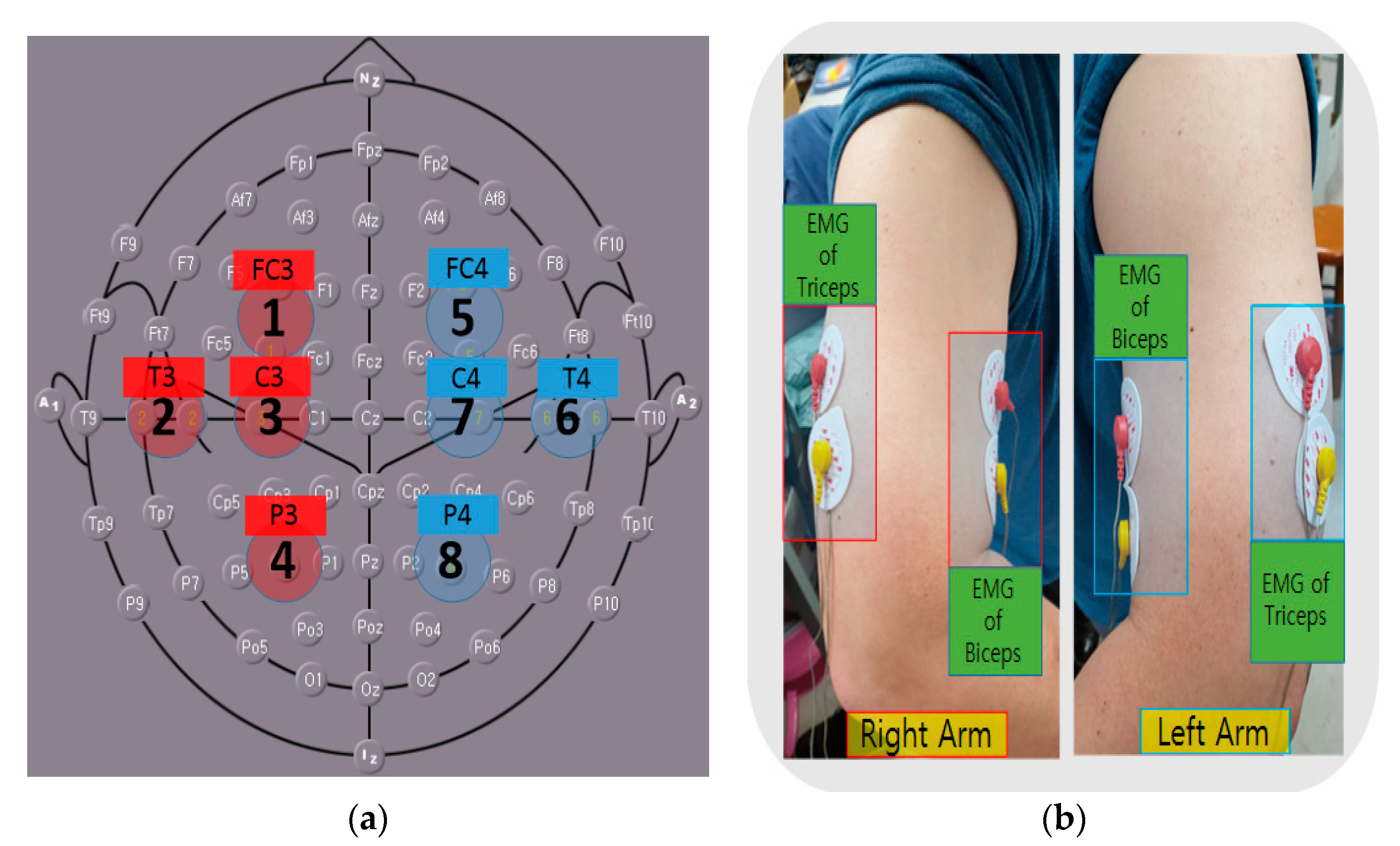
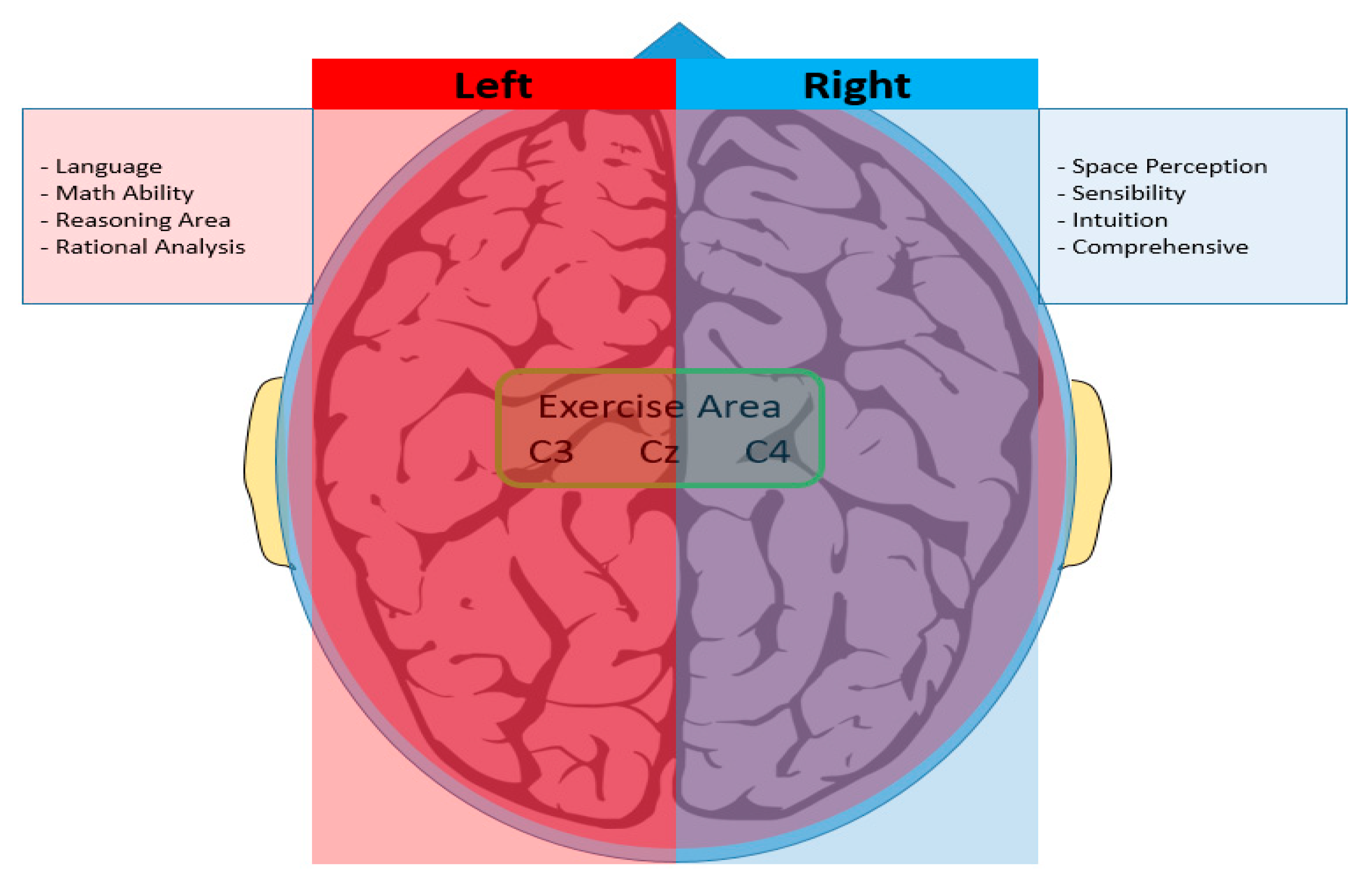
2.1.2. EEG Measurement and Synchronization of Two Signals
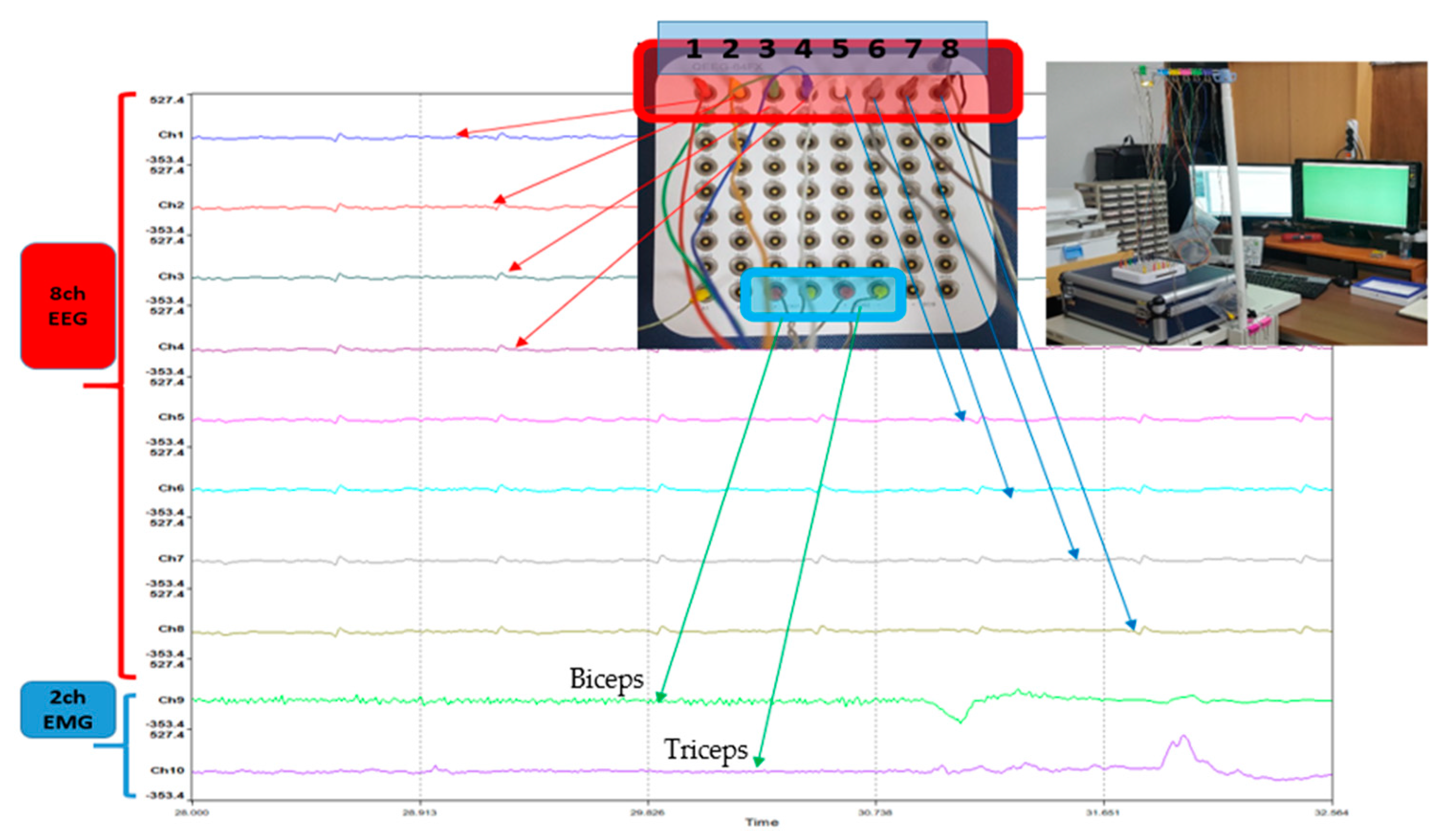
2.2. Configuring the Experimental Environment for Data Extraction
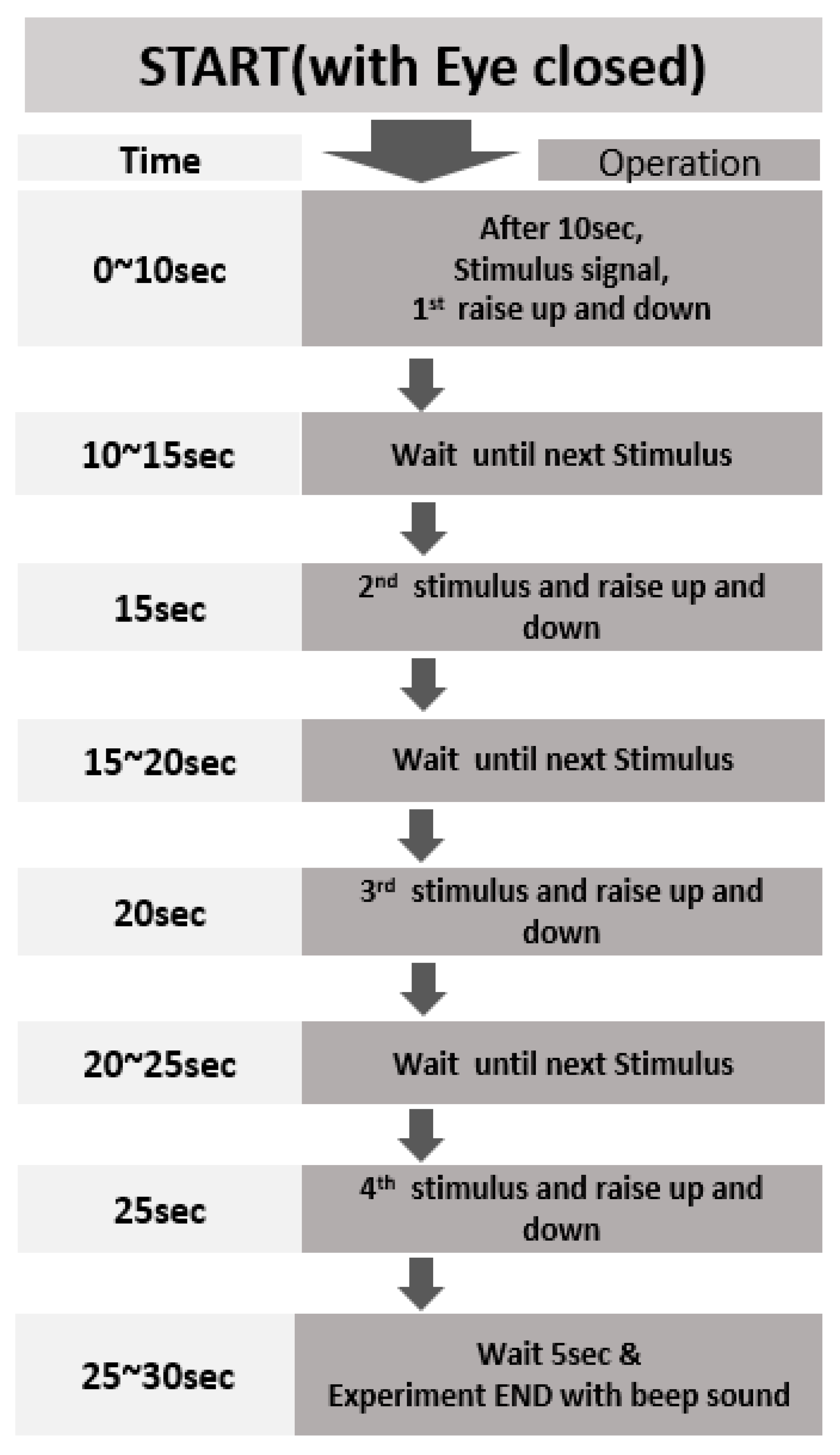
2.3. Data Collection Process
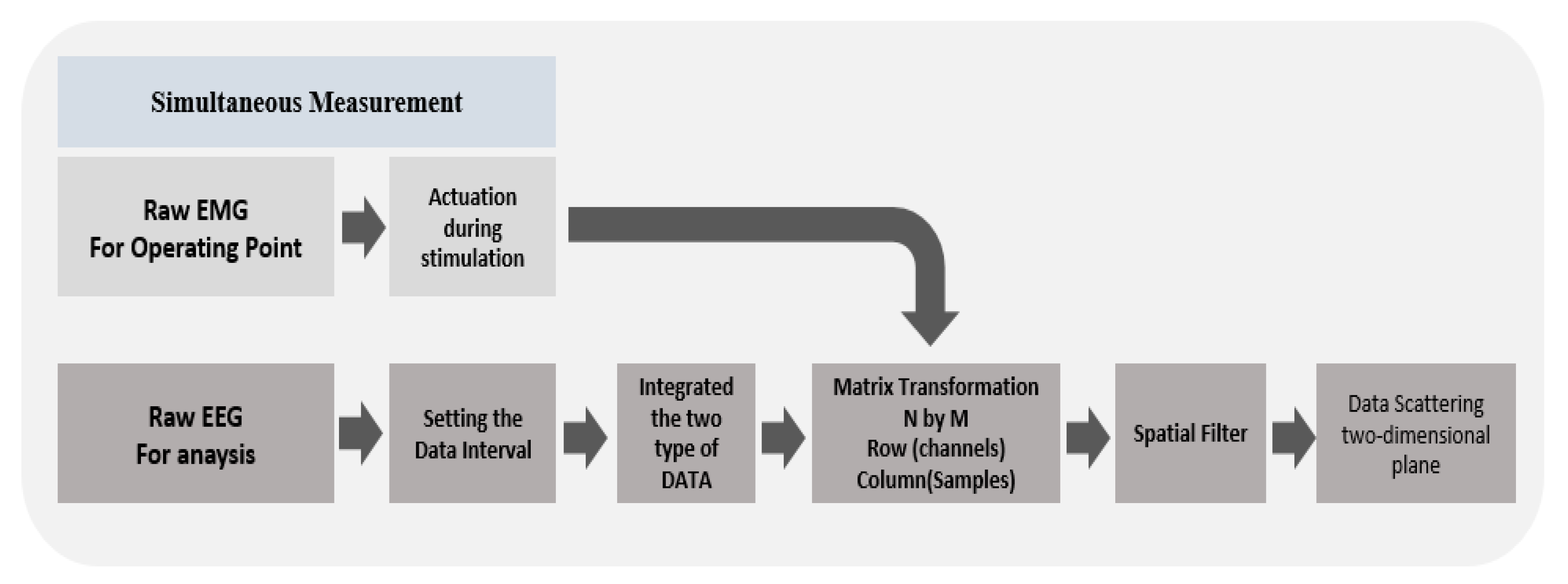
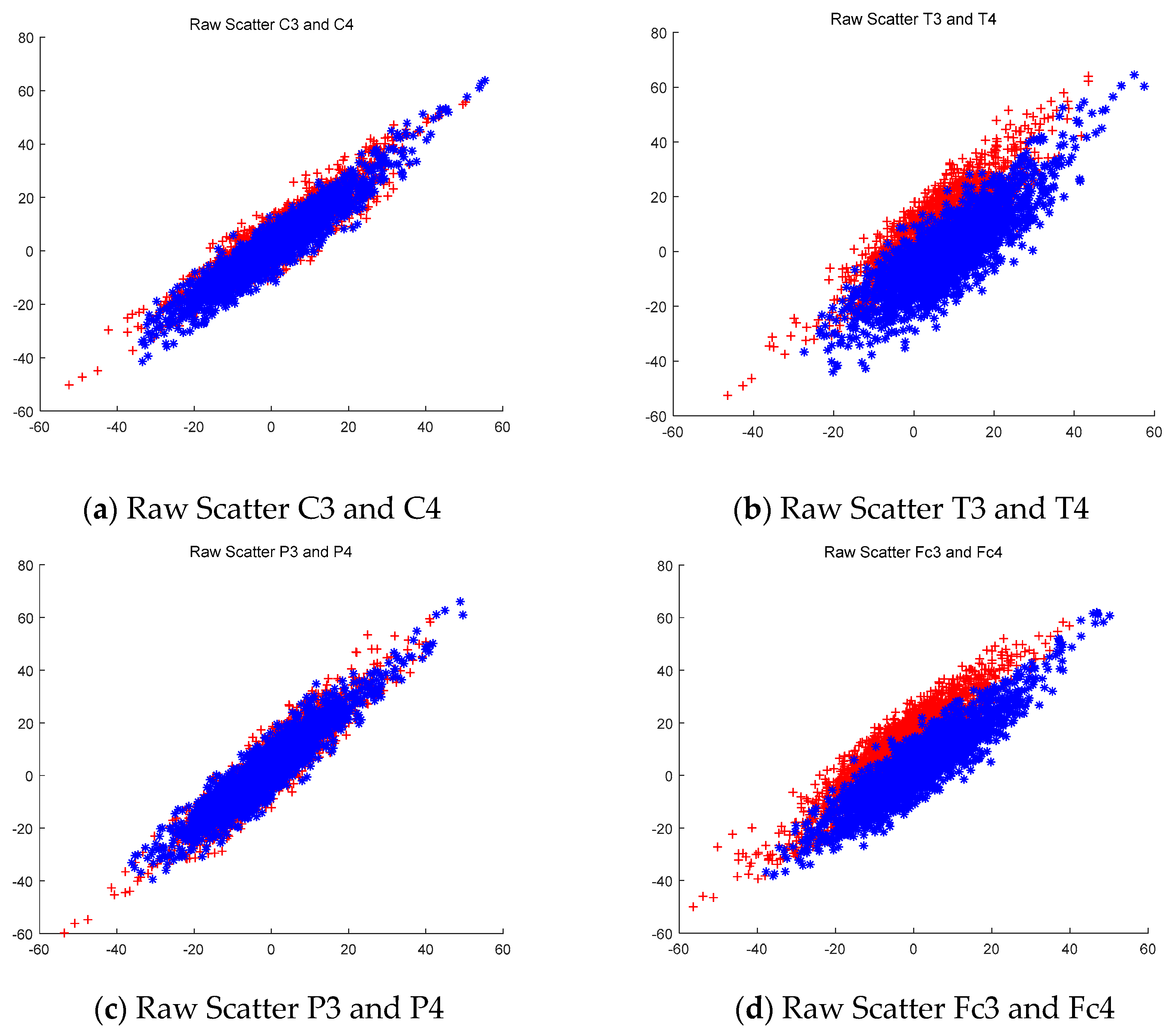
2.4. CSP Filter and Raw Data
3. Data Analysis and Processing Method
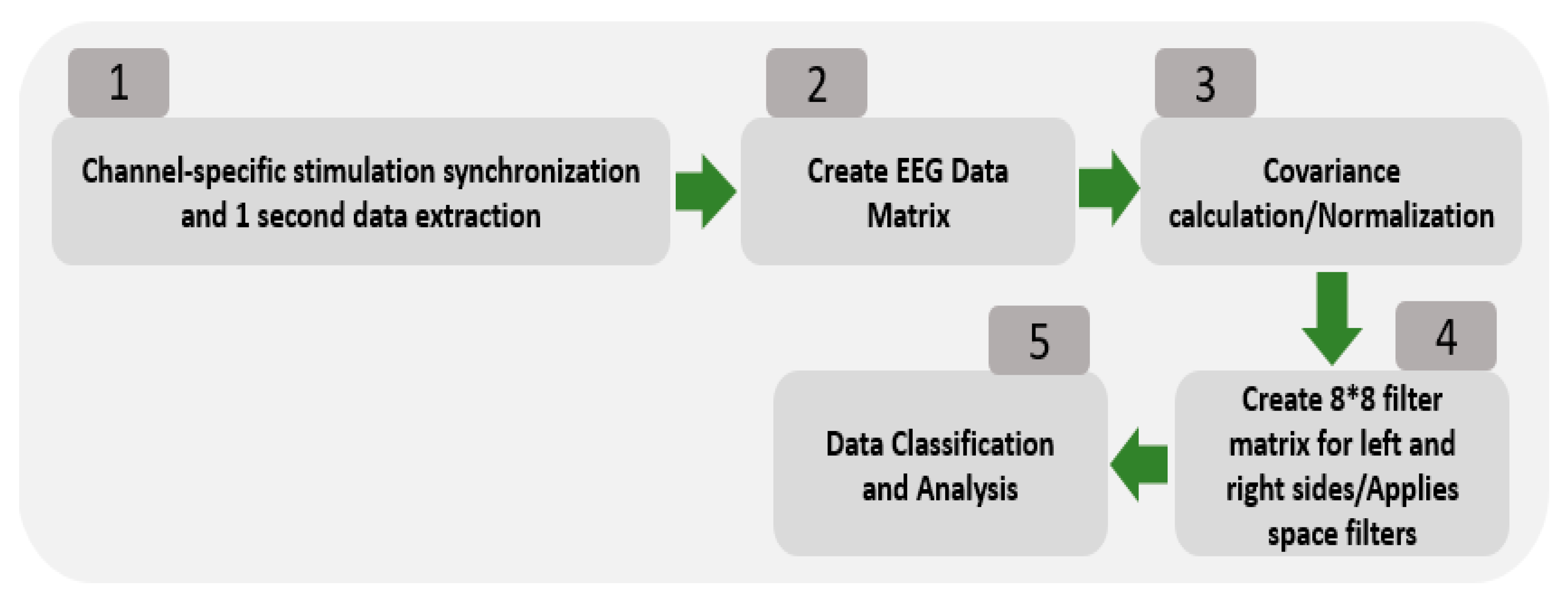
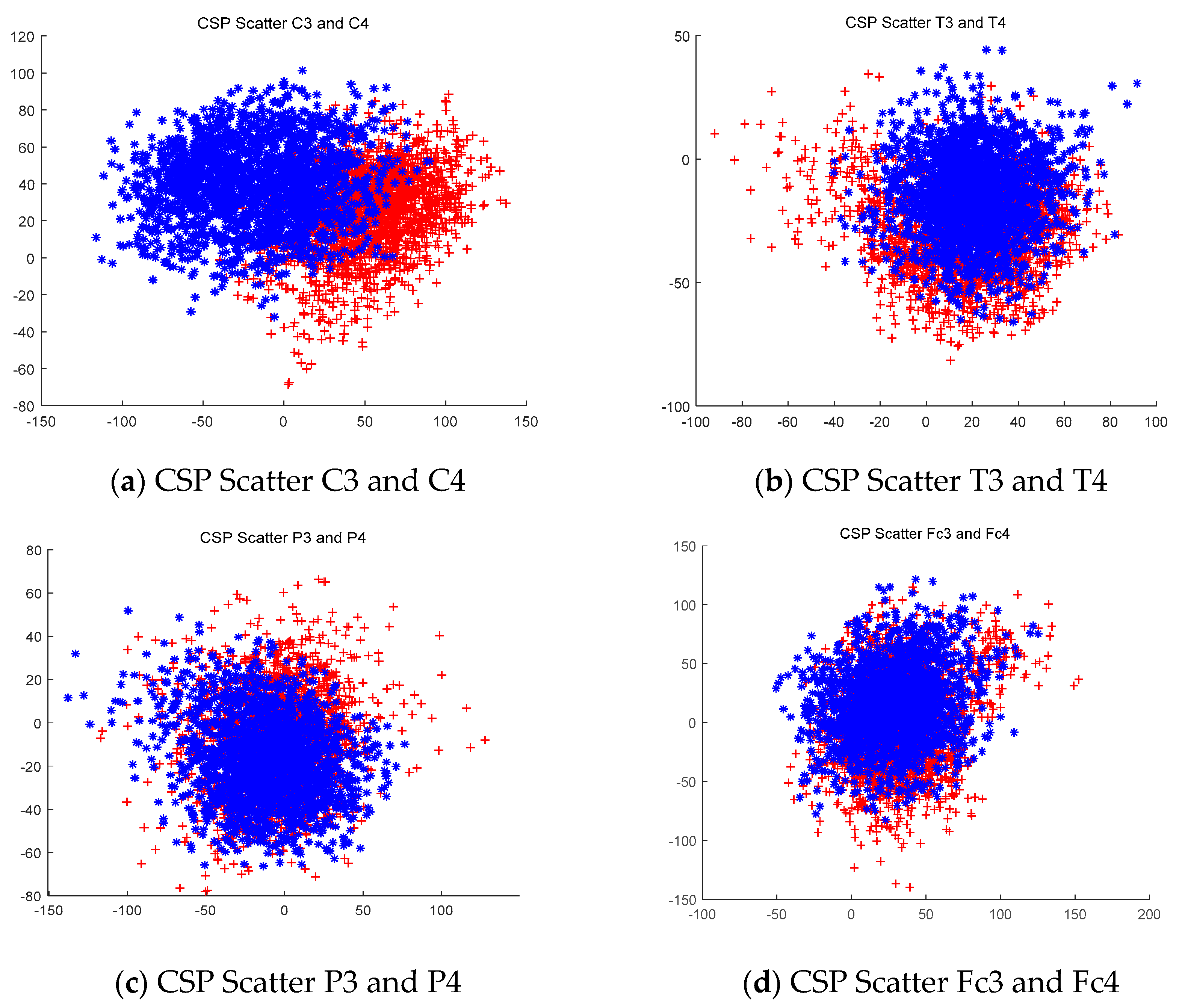
3.1. Data Extraction using the CSP Filtering Method
3.1.1. Analyze the Extracted Data
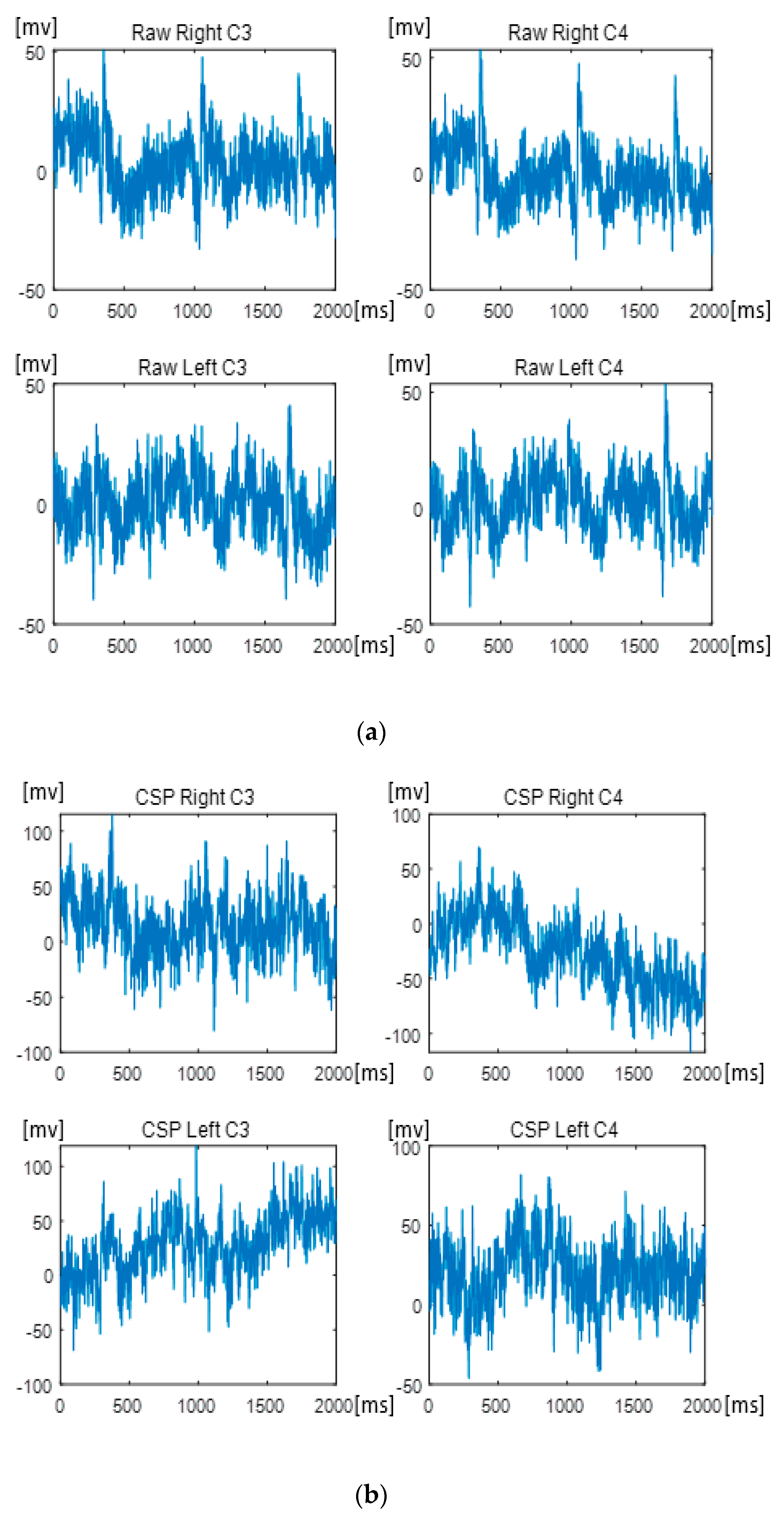
3.1.2. CSP Filtering Method Compared with the Raw Signal
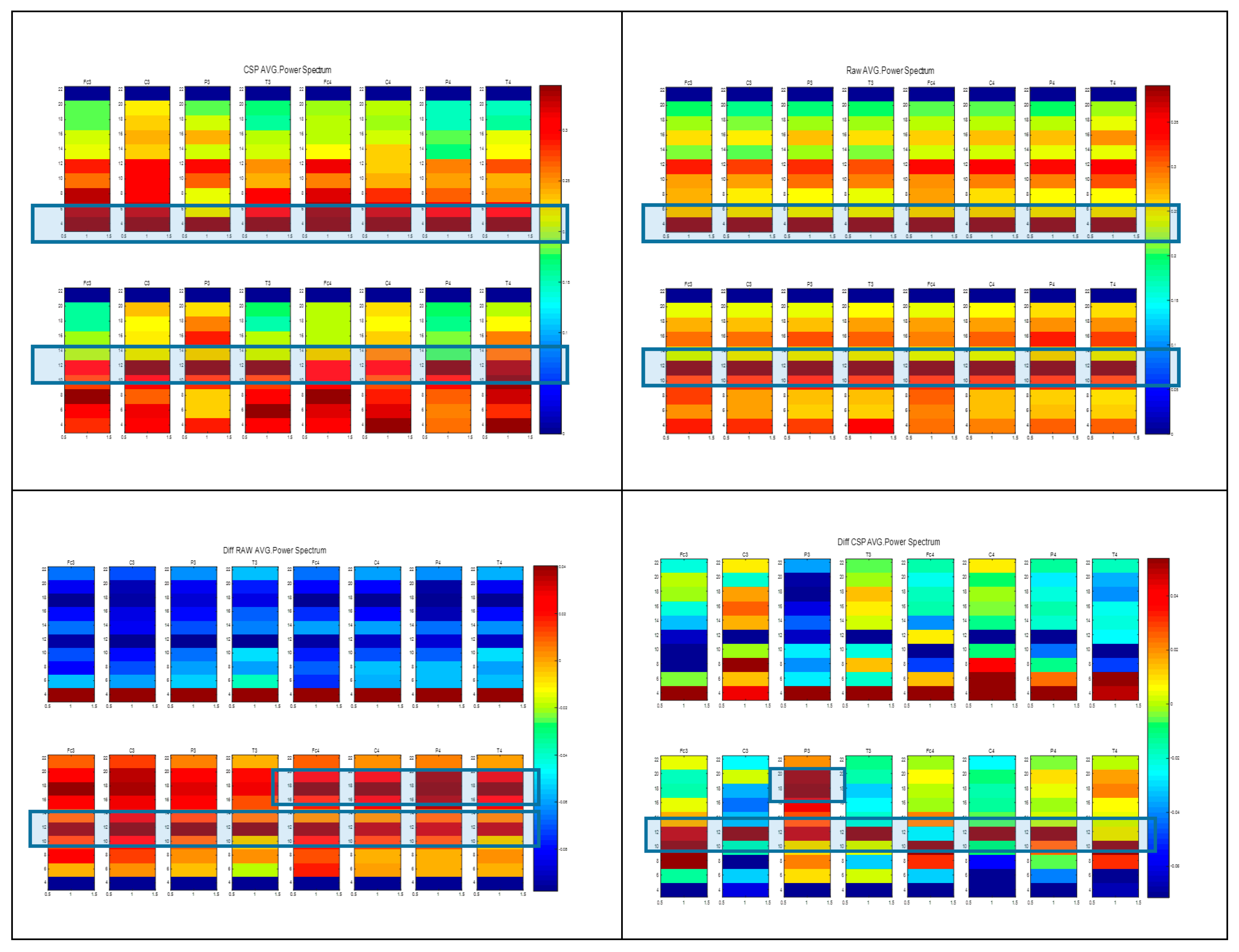
3.2. Spectrum Normalization and Energy Conversion
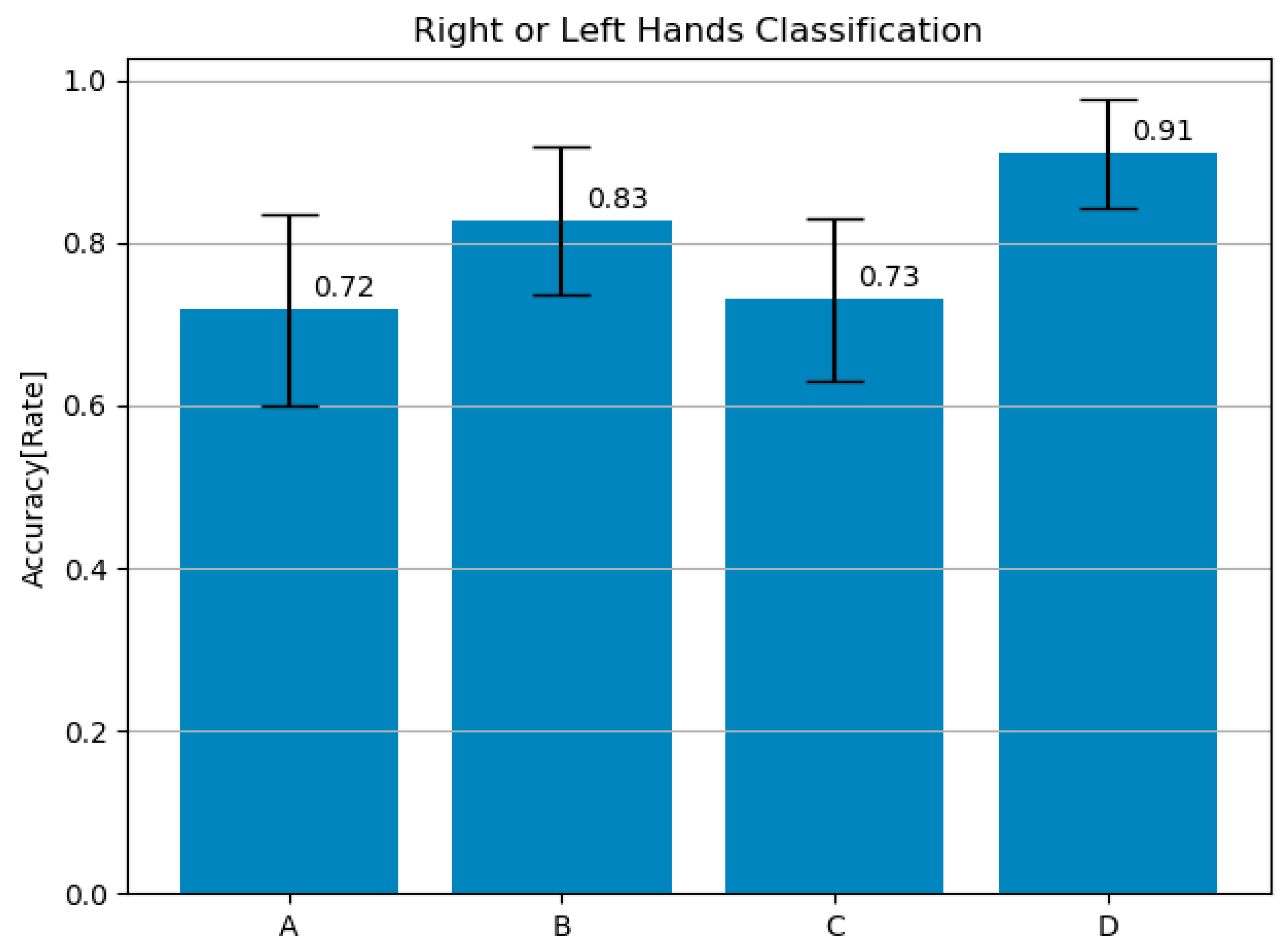
4. Results and Analysis
Separating Left and Right Motion Output by EEG
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suleiman, A.B.R.; Fatehi, T.A.H. Features Extraction Techniques of EEG Signal for BCI Applications; Faculty of Computer and Information Engineering Department College of Electronics Engineering, University of Mosul: Mosul, Iraq, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, G.R.; Nguyen, H.T. Nonnegative matrix factorization for the identification of EMG finger movements: Evaluation using matrix analysis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Caterina, G.D.; Lakany, H.; Petropoulakis, L.; Conway, B.A.; Soraghan, J.J. Study on interaction between temporal and spatial information in the classification of EMG signals in myoelectric prostheses. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Naik, G.R.; Huang, S.; Abraham, A.; Nguyen, H.T. Nonlinear multiscale maximal Lyapunov exponent for accurate myoelectric signal classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 36, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yang, D.; Huang, Q.; Yang, W.; Liu, H. Robust EMG pattern recognition in the presence of confounding factors: Features, classifiers and adaptive learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 96, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Jadhav, P.; Adapa, B.; Acharyya, A.; Naik, G.R. Online and automated reliable system design to remove blink and muscle artifact in EEG. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society(EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 6784–6787. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.; Kim, K.I.; Tompkin, J.; Kim, J.H.; Theobalt, C. Efficient learning of image super-resolution and compression artifact removal with semi-local Gaussian processes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1792–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, P.N.; Shanamugan, D.; Chourasia, A.; Ghole, A.R.; Acharyya, A.A.; Naik, G. Automated detection and correction of eye blink and muscular artefacts in EEG signal for analysis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 1881–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt, C.R.; Bettthauser, J.; Hunt, C.; Thakor, N. Registration of EMG Electrodes to Reduce Classification Errors due to Electrode Shift. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Cleveland, OH, USA, 17–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, B.I.; Cho, H.C.; Jeon, H.T. The Implementation of the Intelligent Exoskeleton Robot Arm Using ElectroMiogram (EMG) vital Signal. J. Korean Inst. Intell. Syst. 2012, 22, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsharipour, B.; Soedirdjo, S.; Merletti, R. Two-dimensional surface EMG: The effects of electrode size, interelectrode distance and image truncation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 49, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hsu, H.-H.; Ho, Y.-E. Scalable Package-level RFI Filter for Digital Clock Noise Mitigation in 5-GHz and future 6-GHz WiFi Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Signal & Power Integrity (EMC+ SIPI), New Orleans, LA, USA, 22–26 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Miskovic, V.; MacDonald, K.J.; Rhodes, L.J.; Cote, K.A. Changes in EEG multiscale entropy and power-law frequency scaling during the human sleep cycle. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.M.; Holm, N.S.; Puthusserypady, S. An Improved Five Class MI Based BCI Scheme for Drone Control Using Filter Bank CSP. In Proceedings of the 7th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface, Jeongseon, Korea, 18–20 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Mousavi, M.; de Sa, V.R. Adaptive CSP with subspace alignment for subject-to-subject transfer in motor imagery brain-computer interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2018 6th International Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), GangWon, Korea, 15–17 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Badruddin, N.; Kiguchi, M. Towards multilevel mental stress assessment using SVM with ECOC: An EEG approach. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lóopez-Larraz, E.; Birbaumer, N.; Ramos-Murguialday, A. A hybrid EEG-EMG BMI improves the detection of movement intention in cortical stroke patients with complete hand paralysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.-L.H.; Yang, W.-W.; Kao, C.-L.; Tsai, M.-W.; Wei, S.-H.; Fregni, F.; Chen, V.C.-F.; Chou, L.-W. Effects of 8-week sensory electrical stimulation combined with motor training on EEG-EMG coherence and motor function in individuals with stroke. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramia, N.; Lotte, F.; Ramat, S. Optimizing spatial filter pairs for EEG classification based on phase-synchronization. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 2049–2053. [Google Scholar]
- Igasaki, T.; Yamashita, K.; Ushijima, T. Force-Temporal Characteristics of EEG-EMG Coherence During Isometric Contraction of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 21–24 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, R.; Marino, M.; Barban, F.; Ganzetti, M.; Mantini, D. Online EEG artifact removal for BCI applications by adaptive spatial filtering. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, B.I.; Kang, B.J.; Cho, H.C.; Kim, J. Motion Recognition and an Accuracy Comparison of Left and Right Arms by EEG Signal Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224885
Jeon BI, Kang BJ, Cho HC, Kim J. Motion Recognition and an Accuracy Comparison of Left and Right Arms by EEG Signal Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224885
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Bu Il, Byung Jun Kang, Hyun Chan Cho, and Jongwon Kim. 2019. "Motion Recognition and an Accuracy Comparison of Left and Right Arms by EEG Signal Analysis" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224885
APA StyleJeon, B. I., Kang, B. J., Cho, H. C., & Kim, J. (2019). Motion Recognition and an Accuracy Comparison of Left and Right Arms by EEG Signal Analysis. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224885




