Characteristics of Arsenic Leached from Sediments: Agricultural Implications of Abandoned Mines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
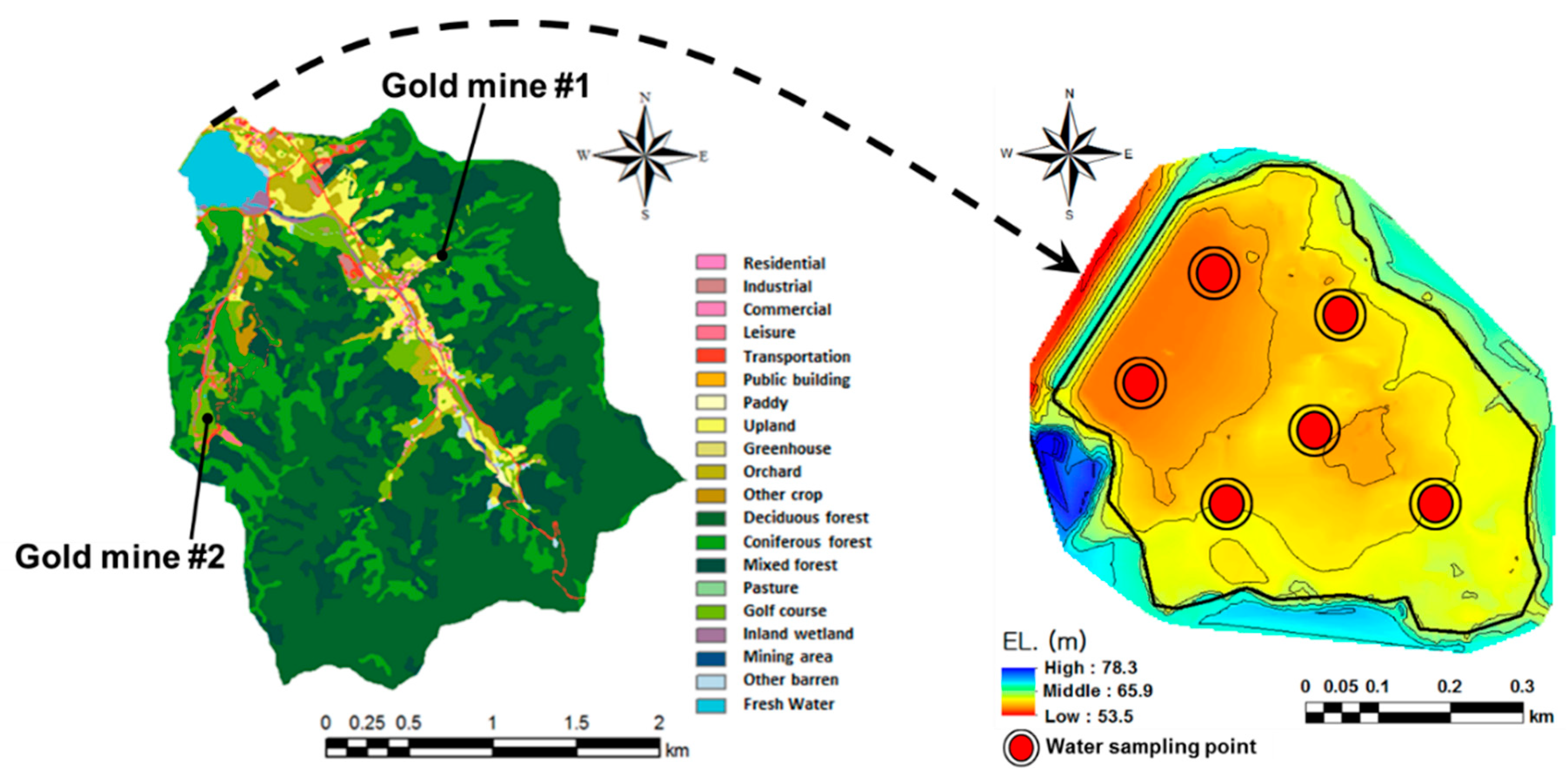
2.1. Study Area and Soil Preparation
2.2. Batch-Leaching Test by Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP)
2.3. Sequential Extraction Procedure
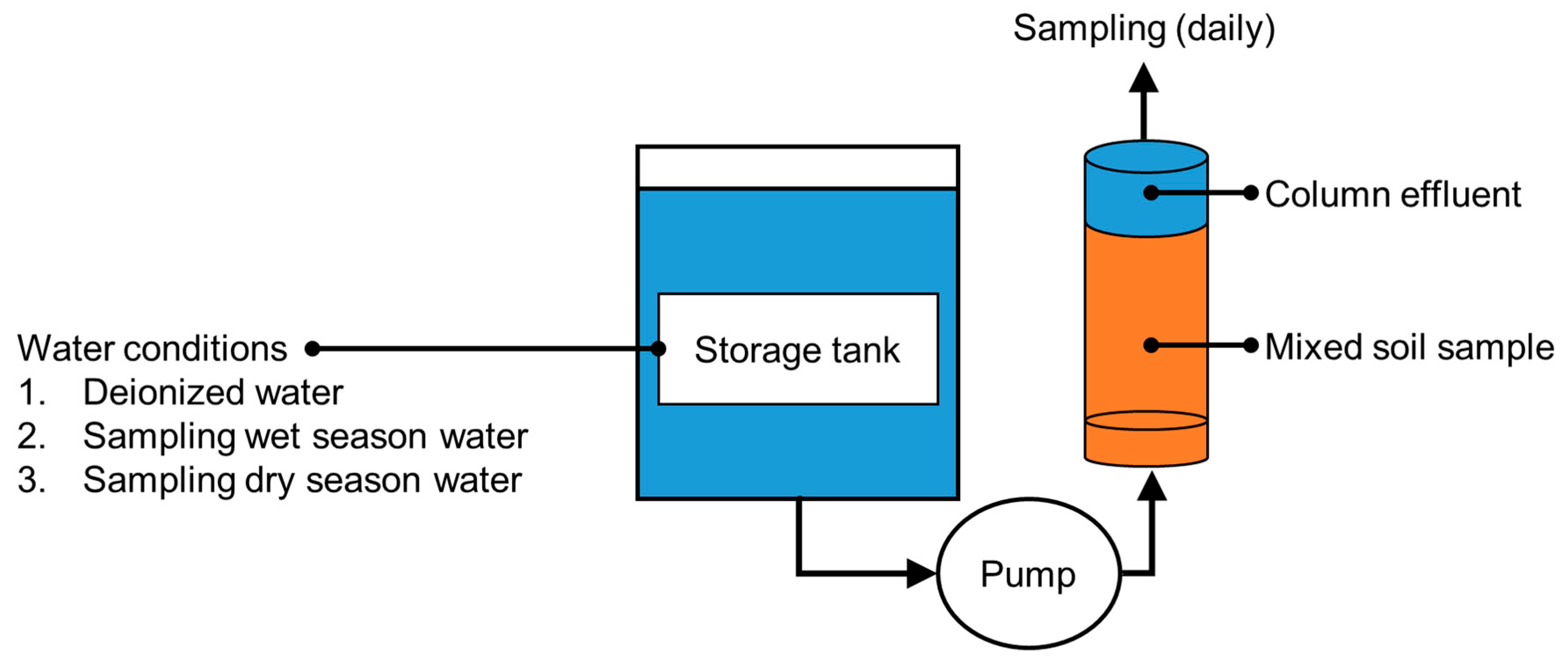
2.4. Column-Leaching Test
3. Results
3.1. Batch-Leaching Test Results
3.2. Sequential Extraction Procedure
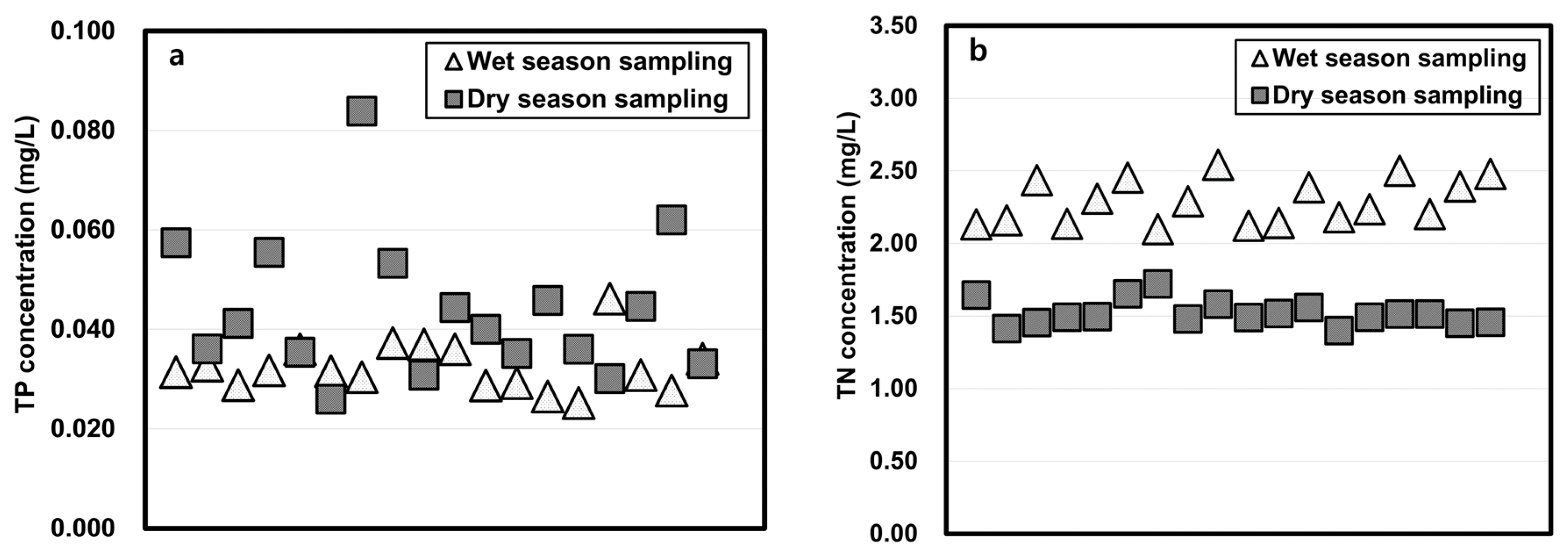
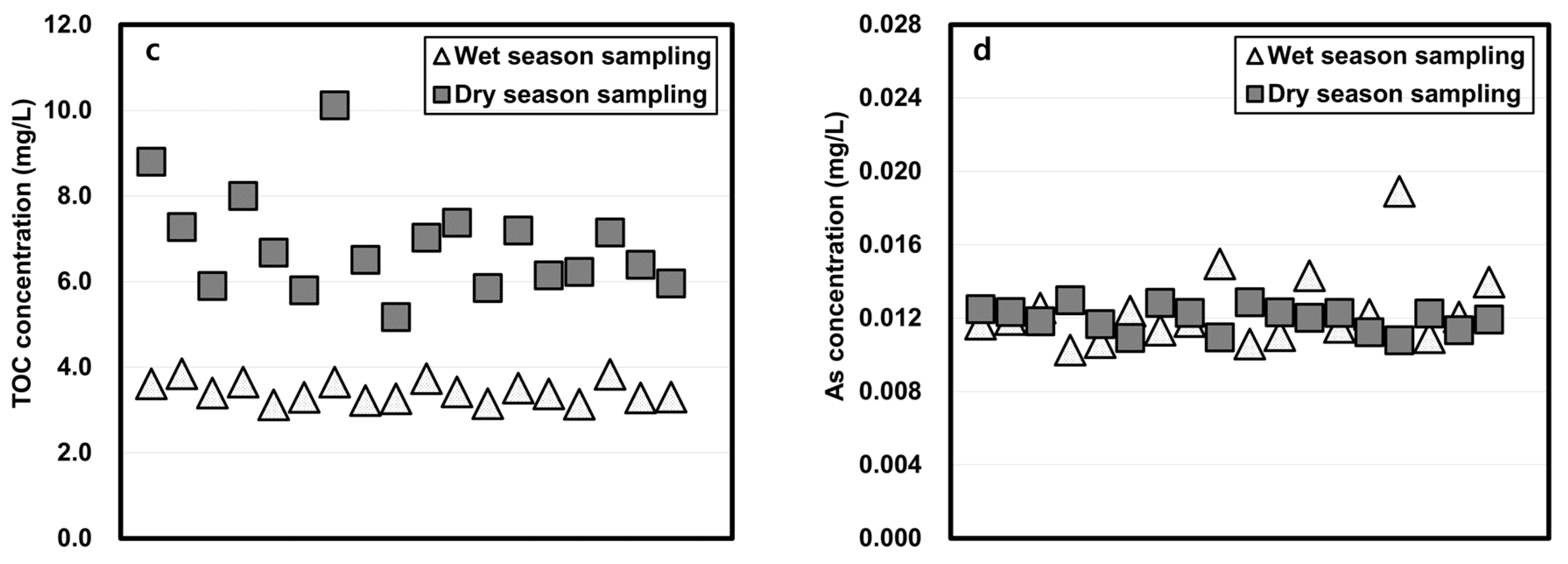
3.3. Column-Leaching Test Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudka, S.; Adriano, D.C. Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Probst, A.; Liao, B.H. Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryer, M.; Collins, C.D.; Ferrier, H.; Colvile, R.N.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Human exposure modelling for chemical risk assessment: A review of current approaches and research and policy implications. Environ. Sci. Policy 2006, 9, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.A.; Faz, A.; Martinez-Martinez, S.; Zornoza, R.; Carmona, D.M.; Kabas, S. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to evaluate heavy metals behavior in mine sites for future reclamation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 109, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Kuijp, T.J.v.d.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhao, F.J.; Lombi, E.; McGrath, S.P. Leaching of heavy metals from contaminated soils using EDTA. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 113, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Qin, Y. Leaching characteristics of heavy metal and As from two urban roadside solids. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.K.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Govil, P.K. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: A case study from Patancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Lu, Y.; Khan, H.; Zakir, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.A. Health risks associated with heavy metals in the drinking water of Swat, northern Pakistan. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Naidu, R. Arsenic in rice: Sources and human health risk. Wheat Rice Dis. Prev. Health 2014, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Naidu, R. Arsenic accumulation in rice: Consequences of rice genotypes and management practices to reduce human health risk. Environ. Int. 2016, 96, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.A.; Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Argos, M.; Slaughter, F.; Pendergrast, C.; Punshon, T.; Gossai, A.; Ahsan, H.; Karagas, M.R. Assessment of human dietary exposure to arsenic through rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka, A.; Yasutaka, T.; Sakanakura, H.; Kalbe, U.; Watanabe, Y.; Inoba, S.; Takeo, M.; Inui, T.; Katsumi, T.; Fujikawa, T.; et al. Column percolation test for contaminated soils: Key factors for standardization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Carrascosa-Chisvert, M.D.; Mena, V.; Souto, R.M.; Santana, J.J.; Nuez, I. Groundwater Quality Assessment in a Volcanic Mountain Range (South of Gran Canaria Island, Spain). Water 2019, 11, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, H. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in an Irrigated Region, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, M.; Senthil Nathan, D. Groundwater quality assessment for domestic and agriculture purposes in Puducherry region. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4037–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wu, M.; Yang, J. Mobilities and leachabilities of heavy metals in sludge with humus soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghanmi, S.I.; Sulami, A.F.A.; El-Zayat, T.A.; Alhogbi, B.G.; Salam, M.A. Acid leaching of heavy metals from contaminated soil collected from Jeddah, Saudi Arabia: Kinetic and thermodynamics studies. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoruha, S.; Elevli, S.; Ergun, S.N.; Demira, G. Assessment of leaching characteristics of heavy metals from industrial leach waste. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 123, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.; Kaya, A. Leaching characteristics of solid wastes from thermal power plants of western Turkey and comparison of toxicity methodologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 73, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, T.M.; Stewart, B.W.; Capo, R.C.; Schroeder, K.T.; Chapman, C.E.; Spivak-Birndorf, L.J.; Vesper, D.J.; Cardone, C.R.; Rohar, P.C. Coal fly ash interaction with environmental fluids: Geochemical and strontium isotope results from combined column and batch leaching experiments. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 32, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.E.; Hower, J.C.; Phillips, A.L.; Rivera, N.; Vengosh, A.; Hsu-Kim, H. Ranking Coal Ash Materials for Their Potential to Leach Arsenic and Selenium: Relative Importance of Ash Chemistry and Site Biogeochemistry. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Lahermo, W.P.; Salminen, R.; Rojstaczer, S.; Peuraniemi, V. Lake and reservoir water quality affected by metals leaching from tropical soils, Bangladesh. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Han, G.; Ahn, J.; You, K.; Kim, H. Leachability of Arsenic and Heavy Metals from Mine Tailings of Abandoned Metal Mines. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 2865–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Zhongqin, T.; Qian, H.; Jianhua, C. Studies of Leaching Characteristics of Arsenic and Antimony for Jinya Gold Mine. Front. Environ. Eng. 2016, 5, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whitmore, T.J.; Riedinger-Whitmore, M.A.; Smoak, J.M.; Kolasa, K.V.; Goddard, E.A.; Bindler, R. Arsenic contamination of lake sediments in Florida: Evidence of herbicide mobility from watershed soils. J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 40, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVries, C.R.; Wang, F. In situ two-dimensional high-resolution profiling of sulfide in sediment interstitial waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, W.; Zhang, H. In situ speciation measurements of trace components in natural waters using thin-film gels. Nature 1994, 367, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panther, J.G.; Stillwell, K.P.; Powell, K.J.; Downard, A.J. Development and application of the diffusive gradients in thin films technique for the measurement of total dissolved inorganic arsenic in waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 622, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Santner, J.; Davison, W. Performance characteristics of diffusive gradients in thin films equipped with a binding gel layer containing precipitated ferrihydrite for measuring arsenic (V), selenium (VI), vanadium (V), and antimony (V). Anal. Chem. 2010, 8903–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.W.; Teasdale, P.R.; Panther, J.G.; Welsh, D.T.; Jolley, D.F. New diffusive gradients in a thin film technique for measuring inorganic arsenic and selenium (IV) using a titanium dioxide based adsorbent. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7401–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Naidu, R. Assessment of toxicity of heavy metal contaminated soils by toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, H.; Du, Y. Strength and leaching characteristics of heavy metal contaminated soils solidified by cement. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 71–98. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, A.; Fine, P. Sequential Selective Extraction Procedures for the Study of Heavy Metals in Soils, Sediments, and Waste Materials-a Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 365–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokalioĝlu, S.; Kartal, S.; Birol, G. Application of a three-stage sequential extraction procedure for the determination of extractable metal contents in highway soils. Turk. J. Chem. 2003, 27, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, W.W.; Kirchbaumer, N.; Prohaska, T.; Stingeder, G.; Lombi, E.; Adriano, D.C. Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 436, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Shin, S.B.; Song, J.H.; Yoon, K.S.; Kang, M.S. Simulating Arsenic Concentration Changes in Small Agricultural Reservoir Using EFDC-WASP Linkage Model. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 60, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Mukherjee, A.B.B.; Bundschuh, J.; Zevenhoven, R.; Loeppert, R.H. Arsenic in Soil and Groundwater Environment: Biogeochemical Interactions, Health Effects and Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leszek, G.; Anna, K.; Bernard, G. Influence of pH on the solubility of arsenic in heavily contaminated soils. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour. 2013, 3, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

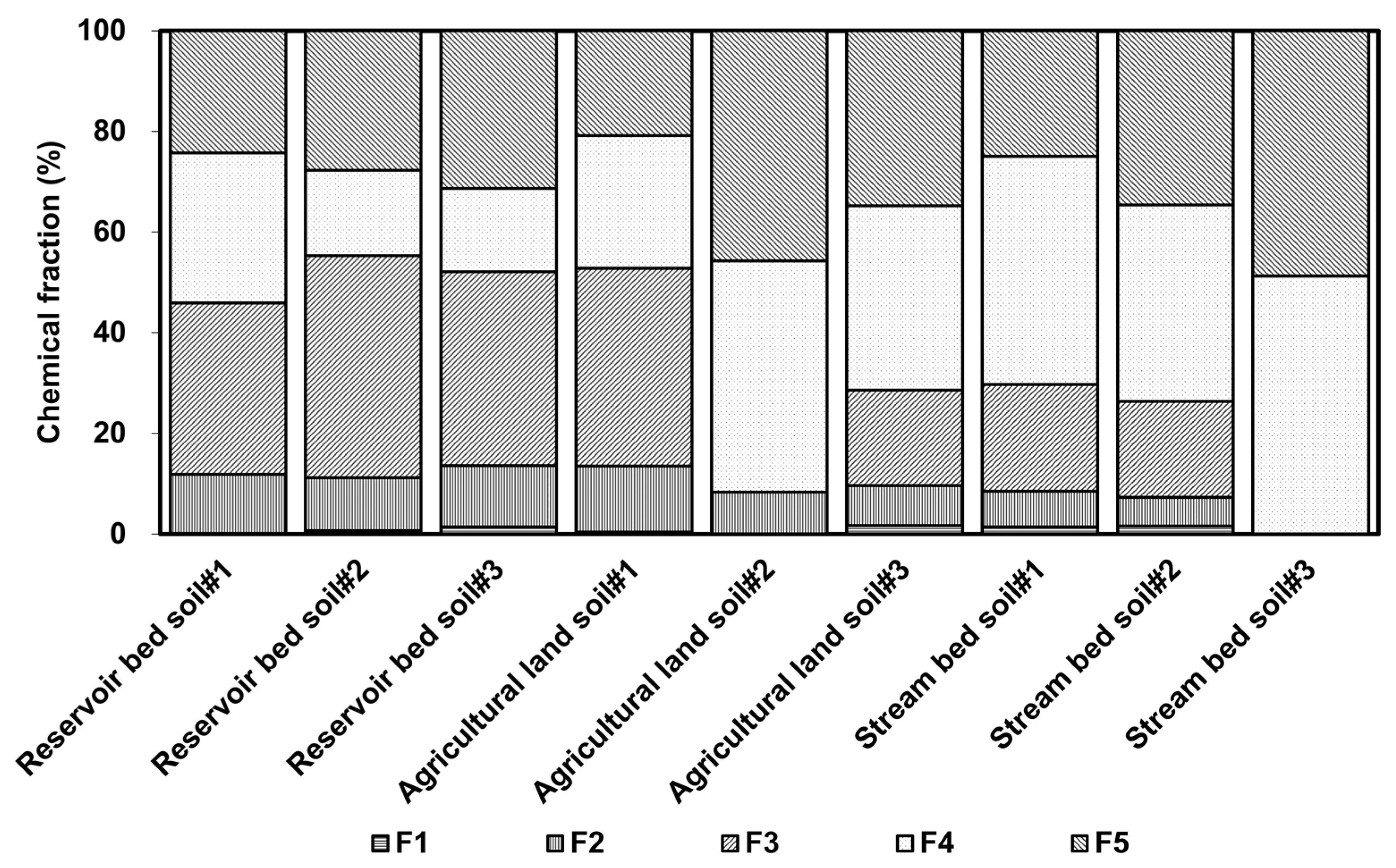
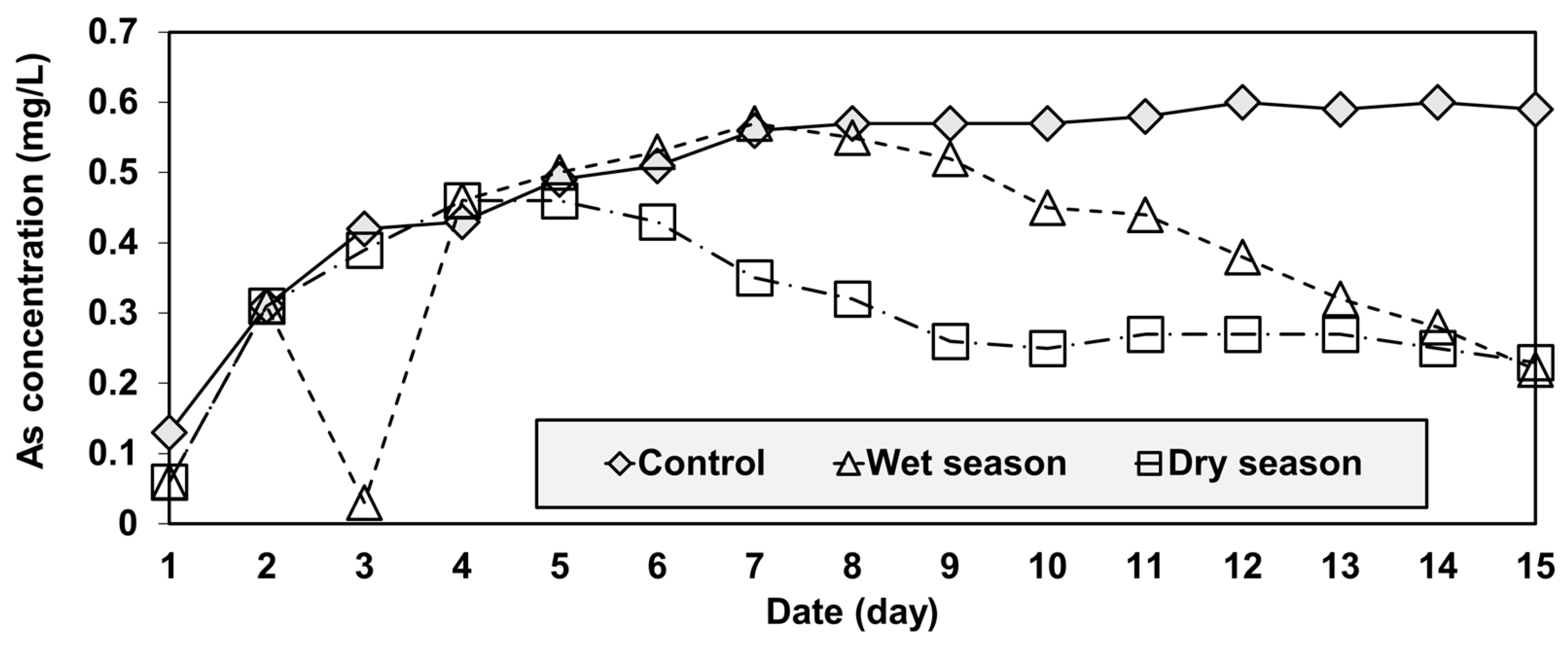
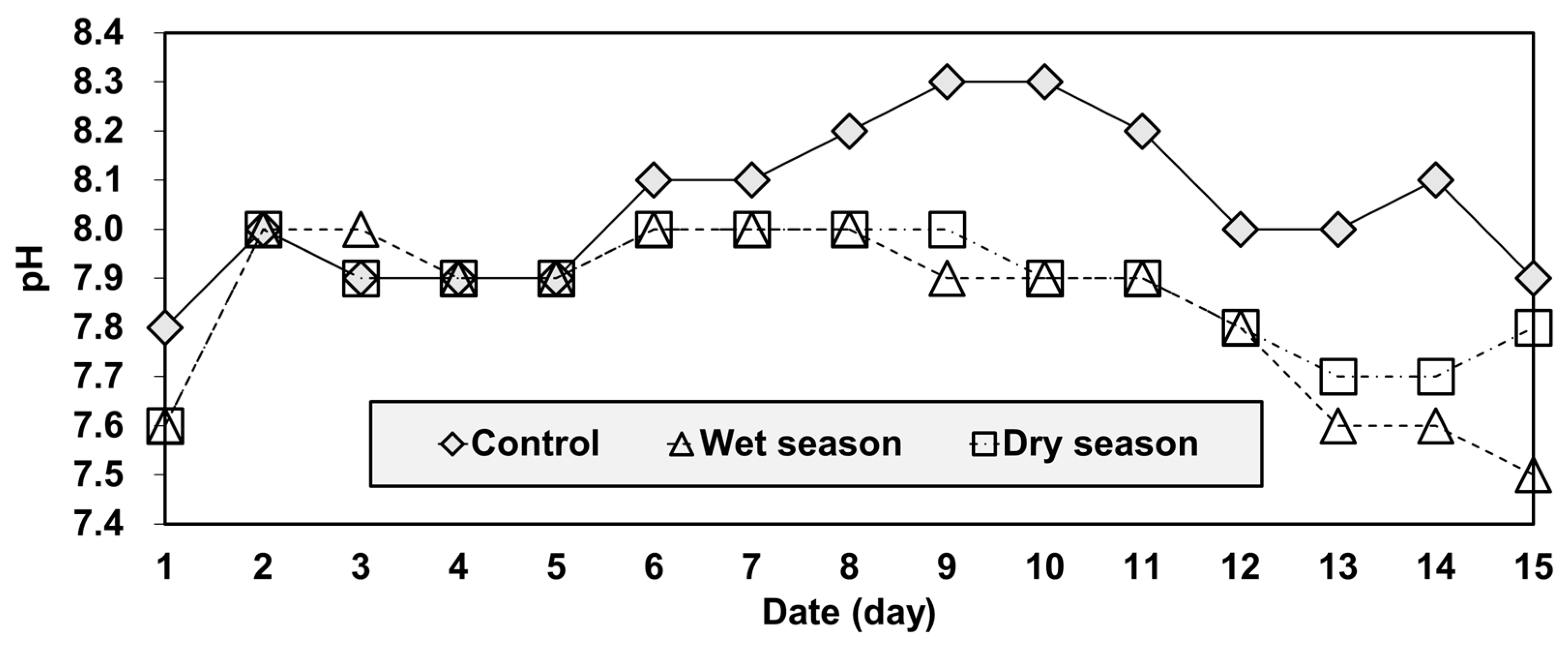
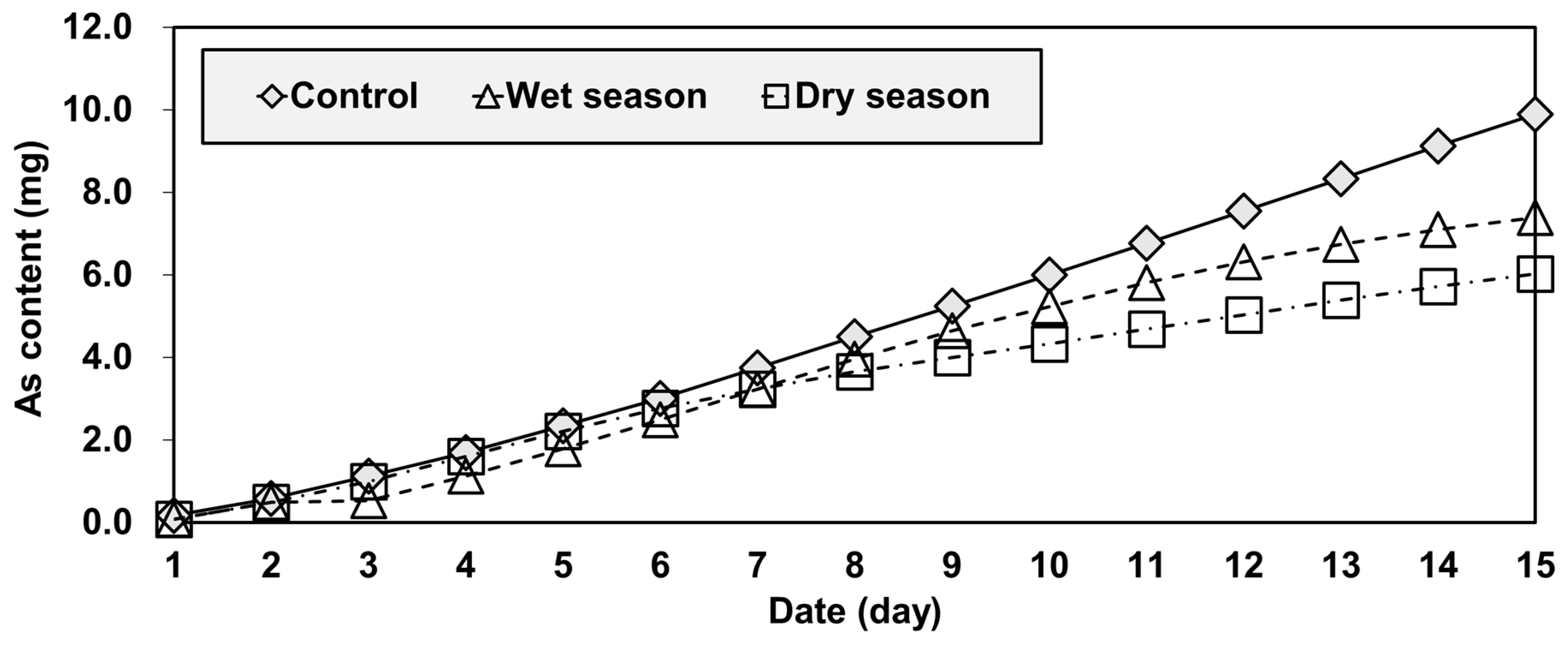
| Form | Phase | Extractant |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nonspecifically sorbed | (NH4)SO4 |
| 2 | Specifically sorbed | (NH4)H2PO4 |
| 3 | Amorphous and poorly crystalline hydrous oxides of Fe and Al phase | NH4 oxalate buffer (pH 3.25) |
| 4 | Well-crystallized hydrous oxides of Fe and Al | NH4 oxalate buffer + ascorbic acid (pH 3.25) |
| 5 | Residual | Residual (HNO3, H2O2) |
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Column specifications and settings | Diameter = 10 cm, height = 44 cm; filled with mixed soil (grain size <2 mm) up to a height of 20 cm (total height = 44 cm); flow rate = 0.91 mL/min and 2 pore volumes (PVs) daily. |
| Sampling | Duration of experiment = 15 days; sampling effluent rate = daily. |
| Soil and water usage | Soil = 2438.4 g/column; amount of water used = 0.658 L/PV × 2 PV/day × 15 days = 19.74 L. |
| pH | Organic Matter (%) | Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) (cmol/kg) | Total Nitrogen (TN) (mg/kg) | Total Phosphorus (TP) (mg/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | As (mg/kg) | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.1 | 2.68 | 6.19 | 1120 | 374.2 | 21.9 | 56.34 | Loamy sand |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, S.; Her, Y.; Jun, S.M.; Song, J.-H.; Lee, G.; Kang, M. Characteristics of Arsenic Leached from Sediments: Agricultural Implications of Abandoned Mines. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4628. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214628
Hwang S, Her Y, Jun SM, Song J-H, Lee G, Kang M. Characteristics of Arsenic Leached from Sediments: Agricultural Implications of Abandoned Mines. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(21):4628. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214628
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Soonho, Younggu Her, Sang Min Jun, Jung-Hun Song, Goontaek Lee, and Moonseong Kang. 2019. "Characteristics of Arsenic Leached from Sediments: Agricultural Implications of Abandoned Mines" Applied Sciences 9, no. 21: 4628. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214628
APA StyleHwang, S., Her, Y., Jun, S. M., Song, J.-H., Lee, G., & Kang, M. (2019). Characteristics of Arsenic Leached from Sediments: Agricultural Implications of Abandoned Mines. Applied Sciences, 9(21), 4628. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214628






