Soft Cationic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Production and Cytotoxicity of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cationic SLNs Production
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization
2.4. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SLNs Production and Characteristics
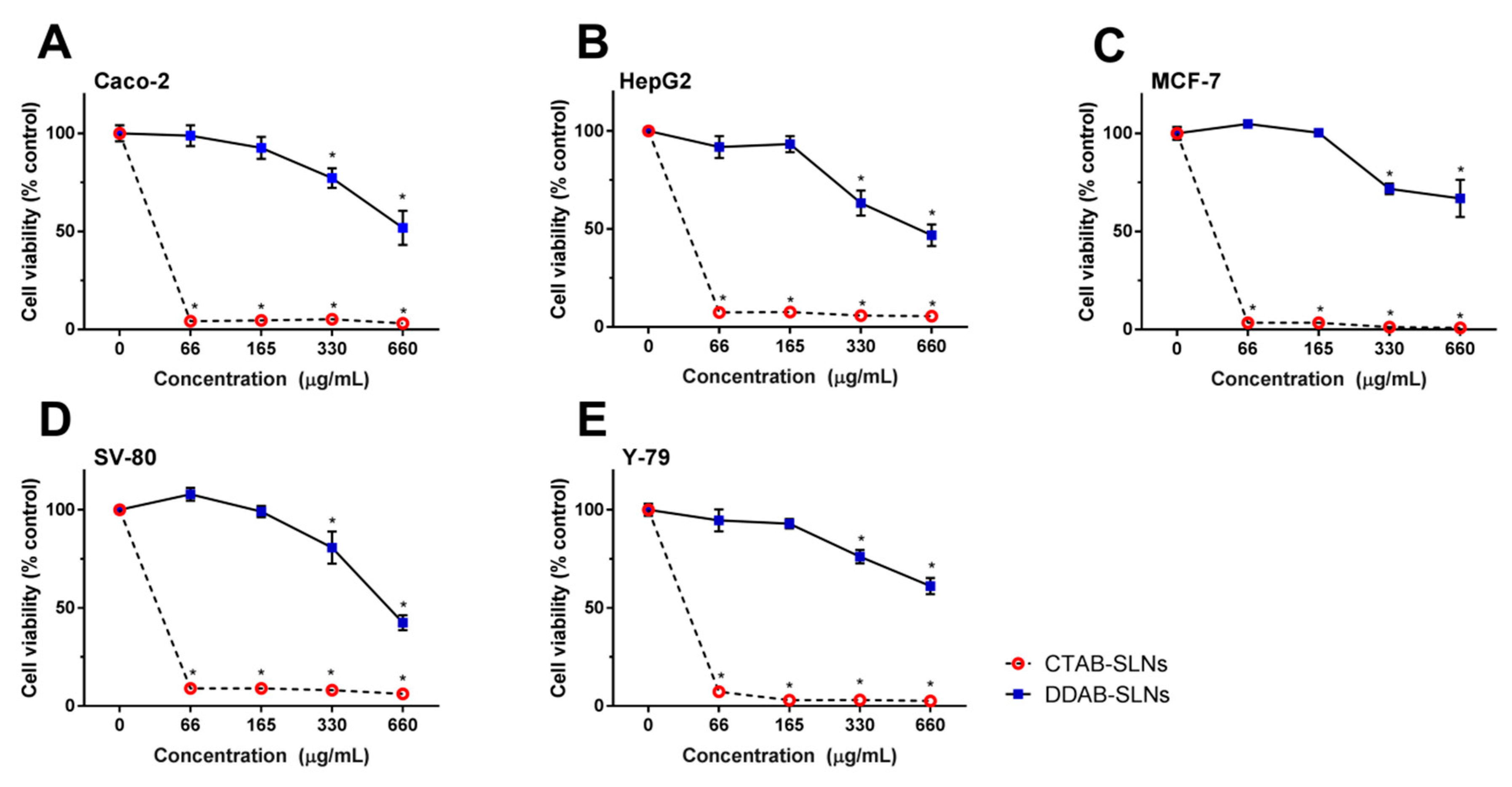
3.2. Assessment of CTAB and DDAB-Decorated SLNs Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muller, R.H.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, C.M. 20 Years of Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN & NLC): Present State of Development & Industrial Applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J.M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Emerging Colloidal Nano Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Nanotoxicology applied to solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carrier—A systematic review of in vitro data. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangueiro, J.F.; Andreani, T.; Egea, M.A.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, S.B.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Design of cationic lipid nanoparticles for ocular delivery: development, characterization and cytotoxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, M.E.; Hotze, M.A.; Johnston, K.P.; Williams, R.O. Drug Nanoparticles by Antisolvent Precipitation: Mixing Energy versus Surfactant Stabilization. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8951–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.M.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.Y.; Xu, L.M.; Zhuang, W.C.; Chai, Y.C.; Yang, C.J. Capping effect of CTAB on positively charged Ag nanoparticles. Phys. E Low-Dimen. Syst. Nanostruct. 2006, 33, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, C.; Mauro, N.; Amore, E.; Martorana, E.; Giammona, G.; Bondi, M.L. Surfactant effect on the physicochemical characteristics of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Akbulut, M.; Kristiansen, K.; Golan, Y.; Israelachvili, J. The role of interparticle and external forces in nanoparticle assembly. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elansezhian, R.; Ramamoorthy, B.; Nair, P.K. The influence of SDS and CTAB surfactants on the surface morphology and surface topography of electroless Ni–P deposits. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 209, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oremusova, J.; Vitkova, Z.; Vitko, A.; Tarnik, M.; Miklovicova, E.; Ivankova, O.; Murgas, J.; Krchnak, D. Effect of Molecular Composition of Head Group and Temperature on Micellar Properties of Ionic Surfactants with C12 Alkyl Chain. Molecules 2019, 24, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, M.; Lauriola, M.M.; Zappaterra, M.; Bianchi, A.; Virgili, A. Surfactants, skin cleansing protagonists. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol.: JEADV 2010, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Luo, D.; Peng, B. Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension Foam System for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivankovic, T.; Hrenovic, J. Surfactants in the environment. Arh. Za Hig. Rada I Toksikologiju 2010, 61, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharipova, A.A.; Aidarova, B.S.; Mutaliyeva, Z.B.; Babayev, A.A.; Issakhov, M.; Issayeva, B.A.; Madybekova, M.G.; Grigoriev, O.D.; Miller, R. The Use of Polymer and Surfactants for the Microencapsulation and Emulsion Stabilization. Colloids Interfaces 2017, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbacova, M.; Verdanova, M.; Mravec, F.; Halasova, T.; Pekar, M. Effect of CTAB and CTAB in the presence of hyaluronan on selected human cell types. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 460, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effendy, I.; Maibach, H.I. Surfactants and experimental irritant contact dermatitis. Contact Dermat. 1995, 33, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, A.; Tasneem, S.; Jesudason, C.G.; Lee, V.S.; Zain, S.B.M. Study of interaction between cationic surfactant (CTAB) and paracetamol by electrical conductivity, tensiometric and spectroscopic methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidamauskas, E.; Cleaver, D.P.; Chatterjee, P.B.; Crans, D.C. Effect of Micellar and Reverse Micellar Interface on Solute Location: 2,6-Pyridinedicarboxylate in CTAB Micelles and CTAB and AOT Reverse Micelles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13153–13161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Santos, D.L.; Costa, I.; Andreani, T.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Cationic solid lipid nanoparticles interfere with the activity of antioxidant enzymes in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Shegokar, R.; Rakovsky, E.; Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Lopes, C.M.; Silva, A.M.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Muller, R.H.; Souto, E.B. Cationic solid lipid nanoparticles (cSLN): Structure, stability and DNA binding capacity correlation studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Shegokar, R.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Silva, A.M.; Lopes, C.M.; Müller, R.H.; Souto, E.B. Modified Rose Bengal assay for surface hydrophobicity evaluation of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles (cSLN). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 45, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Silva, A.M.; Gaivao, I.; Souto, E.B.; Teixeira, J.P.; Martins-Lopes, P. Comet assay reveals no genotoxicity risk of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; Szymanski, M.; Favaro, M.; Azzoni, A.R.; Chaud, M.V.; Santana, M.H.A.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Development and characterization of a cationic lipid nanocarrier as non-viral vector for gene therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 66, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangueiro, J.F.; Andreani, T.; Fernandes, L.; Garcia, M.L.; Egea, M.A.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Physicochemical characterization of epigallocatechin gallate lipid nanoparticles (EGCG-LNs) for ocular instillation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Andreani, T.; Souto, E.B. Comparison of antiproliferative effect of epigallocatechin gallate when loaded into cationic solid lipid nanoparticles against different cell lines. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Andreani, T.; Jager, A.; Chaud, M.V.; Santana, M.H.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Solid lipid nanoparticles for hydrophilic biotech drugs: Optimization and cell viability studies (Caco-2 & HEPG-2 cell lines). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, T.; Kiill, C.P.; de Souza, A.L.R.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Fernandes, L.; Doktorovova, S.; Santos, D.L.; Garcia, M.L.; Gremiao, M.P.D.; Souto, E.B.; et al. Surface engineering of silica nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Characterization and cell toxicity studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.M.; Alvarado, H.L.; Abrego, G.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Garduno-Ramirez, M.L.; Garcia, M.L.; Calpena, A.C.; Souto, E.B. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Oleanolic/Ursolic Acids-Loaded in PLGA Nanoparticles in Different Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, W.; Tovmachenko, O.; Rai, U.S.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. Challenge in understanding size and shape dependent toxicity of gold nanomaterials in human skin keratinocytes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 463, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Bai, R.; Ji, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. Surface chemistry and aspect ratio mediated cellular uptake of Au nanorods. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7606–7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, K.-I.; Ishikawa, T. Didodecyldimethylammonium bromide (DDAB) induces caspase-mediated apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burilova, E.A.; Pashirova, T.N.; Lukashenko, S.S.; Sapunova, A.S.; Voloshina, A.D.; Zhiltsova, E.P.; Campos, J.R.; Souto, E.B.; Zakharova, L.Y. Synthesis, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationships of self-assembled and solubilization properties of amphiphilic quaternary ammonium derivatives of quinuclidine. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashirova, T.; Burilova, E.; Lukashenko, S.; Gaysin, N.; Gnezdilov, O.; Sapunova, A.; Fernandes, A.; Voloshina, A.; Souto, E.B.; Zhiltsova, E.; et al. Nontoxic antimicrobial micellar systems based on mono and di-cationic Dabco-surfactants and furazolidone: Structure-solubilization properties relationships. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y. Self-assembly of cetyl trimethylammonium bromide in ethanol-water mixtures. Front. Chem. China 2006, 1, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Bhawna; Bhasin, K.K.; Kumar, A. An insight into the micellization of dodecyldimethylethylammonium bromide (DDAB) in the presence of bovine serum albumin (BSA). J. Colloids Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partearroyo, M.A.; Ostolaza, H.; Goni, F.M.; Barbera-Guillem, E. Surfactant-induced cell toxicity and cell lysis: A study using B16 melanoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 40, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasun, E.; Li, C.; Barut, I.; Janvier, D.; Qiu, L.; Cui, C.; Tan, W. BSA modification to reduce CTAB induced nonspecificity and cytotoxicity of aptamer-conjugated gold nanorods. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10240–10248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Formulation | DLS | LD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-Ave (nm) | PI | ZP (mV) | d50 (nm) | |
| CTAB-SLNs | 135.1 ± 0.22 | 0.196 ± 0.02 | +28.20 ± 1.33 | 118.3 ± 0.04 |
| DDAB-SLNs | 134.2 ± 1.12 | 0.179 ± 0.07 | +28.20 ± 2.29 | 119.8 ± 0.01 |
| CTAB (*) | µg/mL | 66.0 | 165.0 | 330.0 | 660.0 |
| µM | 181.1 | 452.7 | 905.5 | 1810.9 | |
| DDAB (*) | µg/mL | 66.0 | 165.0 | 330.0 | 660.0 |
| µM | 104.6 | 261.5 | 523.0 | 1046.0 |
| Cell Line | Time | IC50 (µg/mL) * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTAB-SLNs | DDAB-SLNs | ||
| Caco-2 | 24 h | 8.91 ± 0.020 | 983.99 ± 97.01 |
| 48 h | 8.72 ± 0.119 | 845.20 ± 54.98 | |
| HepG2 | 24 h | 9.70 ± 0.158 | 510.25 ± 18.10 |
| 48 h | 9.04 ± 0.026 | 343.53 ± 10.56 | |
| MCF-7 | 24 h | 8.91 ± 0.099 | 1121.14 ± 104.28 |
| 48 h | 9.11 ± 0.099 | 869.88 ± 62.45 | |
| SV-80 | 24 h | 9.31 ± 0.079 | 594.06 ± 16.43 |
| 48 h | 8.91 ± 0.152 | 284.06 ± 17.01 | |
| Y-79 | 24 h | 8.72 ± 0.059 | 1015.28 ± 39.50 |
| 48 h | 9.24 ± 0.059 | 540.21 ± 10.49 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.M.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Pashirova, T.N.; Andreani, T.; Souto, E.B. Soft Cationic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Production and Cytotoxicity of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204438
Silva AM, Martins-Gomes C, Coutinho TE, Fangueiro JF, Sanchez-Lopez E, Pashirova TN, Andreani T, Souto EB. Soft Cationic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Production and Cytotoxicity of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs). Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204438
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Amélia M., Carlos Martins-Gomes, Tiago E. Coutinho, Joana F. Fangueiro, Elena Sanchez-Lopez, Tatiana N. Pashirova, Tatiana Andreani, and Eliana B. Souto. 2019. "Soft Cationic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Production and Cytotoxicity of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs)" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204438
APA StyleSilva, A. M., Martins-Gomes, C., Coutinho, T. E., Fangueiro, J. F., Sanchez-Lopez, E., Pashirova, T. N., Andreani, T., & Souto, E. B. (2019). Soft Cationic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Production and Cytotoxicity of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs). Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204438








