Abstract
Fracture properties are crucial for the applications of structural materials. The fracture behaviors of crystalline alloys have been systematically investigated and well understood. The fracture behaviors of metallic glasses (MGs) are quite different from that of conventional crystalline alloys and have drawn wide interests. Although a few reviews on the fracture and mechanical properties of metallic glasses have been published, an overview on how and why metallic glasses fall out of the scope of the conventional fracture mechanics is still needed. This article attempts to clarify the up-to-date understanding of the question. We review the fracture behaviors of metallic glasses with the related scientific issues including the mode I fracture, brittle fracture, super ductile fracture, impact toughness, and fatigue fracture behaviors. The complex fracture mechanism of MGs is further discussed from the perspectives of discontinuous stress/strain field, plastic zone, and fracture resistance, which deviate from the classic fracture mechanics in polycrystalline alloys. Due to the special deformation mechanism, metallic glasses show a high variability in fracture toughness and other mechanical properties. The outlook presented by this review could help the further studies of metallic glasses. The review also identifies some key questions to be answered.
1. Introduction
Since the discovery of metallic glasses (MGs), especially bulk metallic glasses (BMGs), the mechanical behavior of MGs is attracting increasing attention for both potential structural applications and scientific interests [1]. A series of distinguished mechanical properties, including high compressive plasticity, hardness, ultimate strength, and fracture toughness have been reported [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. These excellent properties and the unusual deformation mechanism of viscous flow and shear band motion make MGs a special member in the family of structural materials.
At room temperature, the deformation behaviors of MGs are controlled by shear bands, which are kinds of localized viscous flow [9]. The shear bands are very different from the slip bands formed via dislocations in crystalline alloys, and result in the special mechanical behaviors of MGs. The information about the topics of shear bands, mechanical properties, and fracture behaviors of MGs can be found in some review papers [9,10,11,12]. However, a review on the topic of how and why MGs fall out of the scope of conventional fracture mechanics is still lacking. In this article, we attempt to summarize the up-to-date understanding on this issue from several aspects about the fracture behaviors and fracture mechanism. We focus on the main fracture behaviors of metallic glasses, including the mode I fracture, brittle fracture, super ductile fracture, impact toughness, and fatigue fracture behaviors. The complex fracture mechanism of metallic glasses are discussed from the perspectives of discontinuous stress/strain field, plastic zone, and fracture resistance, which deviate from the classic fracture mechanics in polycrystalline alloys. This work would help researchers and engineers in their scientific and engineering studies of metallic glasses.
2. Fracture Behaviors of MGs
The fracture criterion is an important parameter to understand the deformation and fracture mechanism of a material. For MGs, due to the lack of work-hardening effect, the fracture strength in uniaxial compression tests generally will be equal to or close to the yielding strength [13]. The intensity and direction of stress at the moment of yielding or fracture reflect the critical stress condition to trigger the shear band avalanche [14,15]. From the microcosmic aspect, the yielding criterion reflects the critical stress condition to trigger the localization of shear transformation of atomic groups [16,17]. Previous studies on this issue were mostly based on the uniaxial tensile and compression experiments or simulations [18,19,20]. It has been discovered that MGs generally show a shear mode failure along a shear/fracture angle (the angle between the shear band/fracture surface and the load axis) near 45° [18,19,20]. The angle will be slightly larger than 45° under tension, and will be slightly smaller than 45° under compression. Some brittle MG systems can show cleavage or split mode failure, which will be discussed later. To understand the asymmetric compression and tension behaviors, Schuh et al. indicates that the microstructure of MGs is analogous to that of randomly packed particles in a granular solid [18]. Therefore, the yielding criterion of MGs could be described by the Mohr-Coulomb criterion:
where τy stands for the shear yield stress, τy is a constant, σn is the normal stress on the shear plane, α is a coefficient that reflects the degree of internal friction in the system. This criterion explains the asymmetric compression and tension strength of MGs, but show deviations in the estimation of shear angle. On this basis, Z.F. Zhang et al. further proposed the elliptical criterion [19,20]:
where τ and σ stand for the shear stress and normal stress on a shear plane, τ0 and σ0 are material dependent constants. The elliptical criterion provides a applicable model to comprehensively explain the strength and shear angle of MGs under the simple loading condition of uniaxial compression/tension. However, the fracture behaviors of MGs under bending, fast loading, fatigue loading and other loading conditions are still complicated to be understood.
2.1. Typical Mode I Fracture of MGs
The fracture properties are very important for the engineering applications of structural materials. The mode I fracture properties of metallic glasses is widely studied by 3-point/4-point bending and compact tension tests [21,22]. The measured fracture toughness of most MGs falls in the range of a few MPa·m1/2 to more than one hundred MPa·m1/2 [11,12]. This value is much lower than that of steel and other commonly used engineering alloys [23]. The fracture brittleness is considered as one of the main problems for the engineering application of MGs.
The low fracture toughness of MGs can be understood by their special fracture mechanism. According to the experiments and literature, a typical mode I fracture process of MGs can roughly be divided into three stages:
2.1.1. Multiple Shear Bands Formation and Sliding
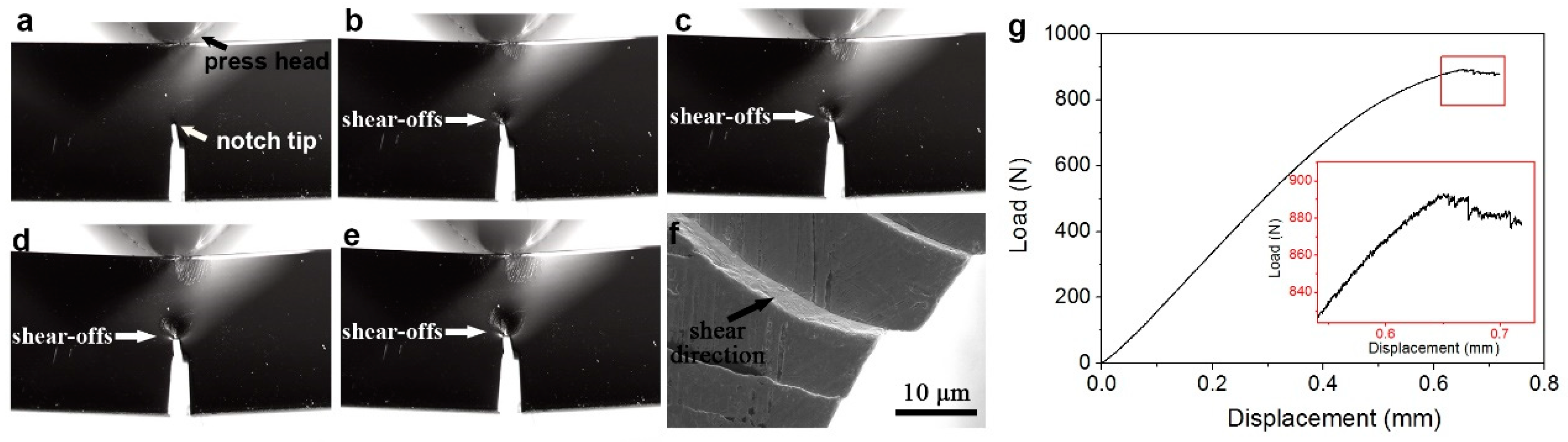
With the increasing notch-tip stress intensity during loading, shear bands are formed. Different from the plane shear bands formed in uniaxial compression/tension tests, the shear bands formed during mode I fracture are curved. This is because the propagation of shear bands in MGs follows the direction of the local maximum shear stress [24]. Therefore, the shear bands will reproduce the shear stress direction in the notch-tip stress field. After formation, the shear bands can slide for a distance, which ranges from less than one micron to tens of microns [25,26]. Figure 1 shows the evolution of shear-offsets and load–displacement curve of a typical ductile Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 metallic glass during 3-point bending test, with a sample size of 3 × 6 × 30 mm3 [27]. Curved shear offsets could be observed on the sample’s side surface (Figure 1a–e, taken by an optical camera, Nikon D810, Japan), and some small stress-drops/serrations could be noticed on the loading curve (Figure 1g), representing the activation and sliding of these shear bands. Enlarged SEM (taken by a LEO-1530 field emission scanning electron microscope, German) image shows that the shear direction of the shear offsets points into the sample (Figure 1f). Due to the randomness in the shear band motions of MGs, it is almost impossible to predict the actual formation moment, sequence, position and sliding distance for each shear band in the real case.
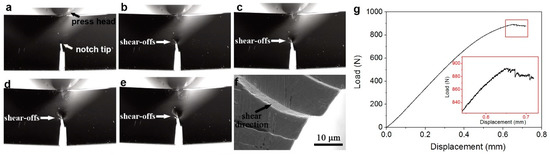
Figure 1.
(a–f) The side view of a Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 metallic glass (MG) sample with a size of 3 × 6 × 30 mm3 during 3-point bending test. (g) The load-displacement curve.
2.1.2. Shear Band Delamination
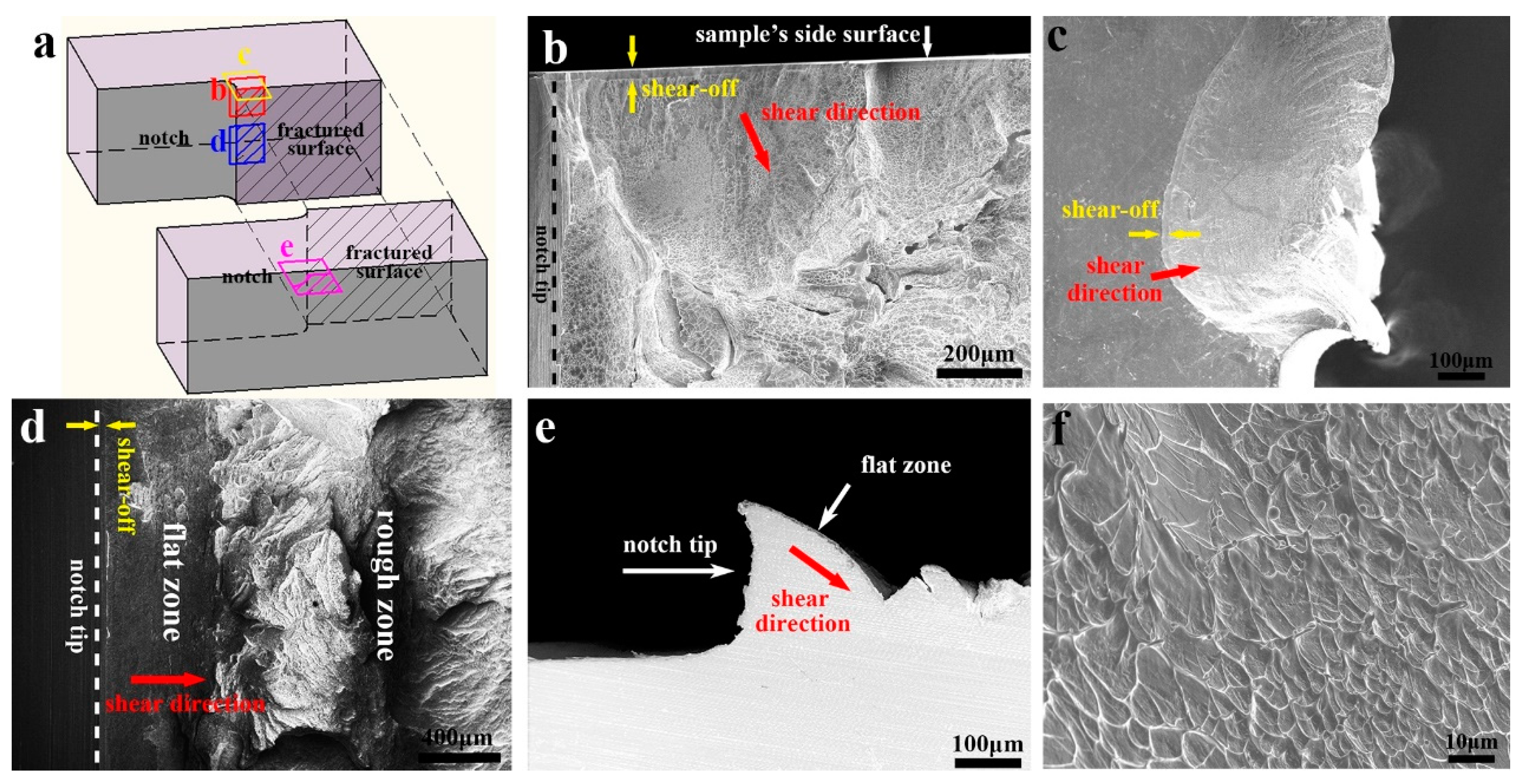
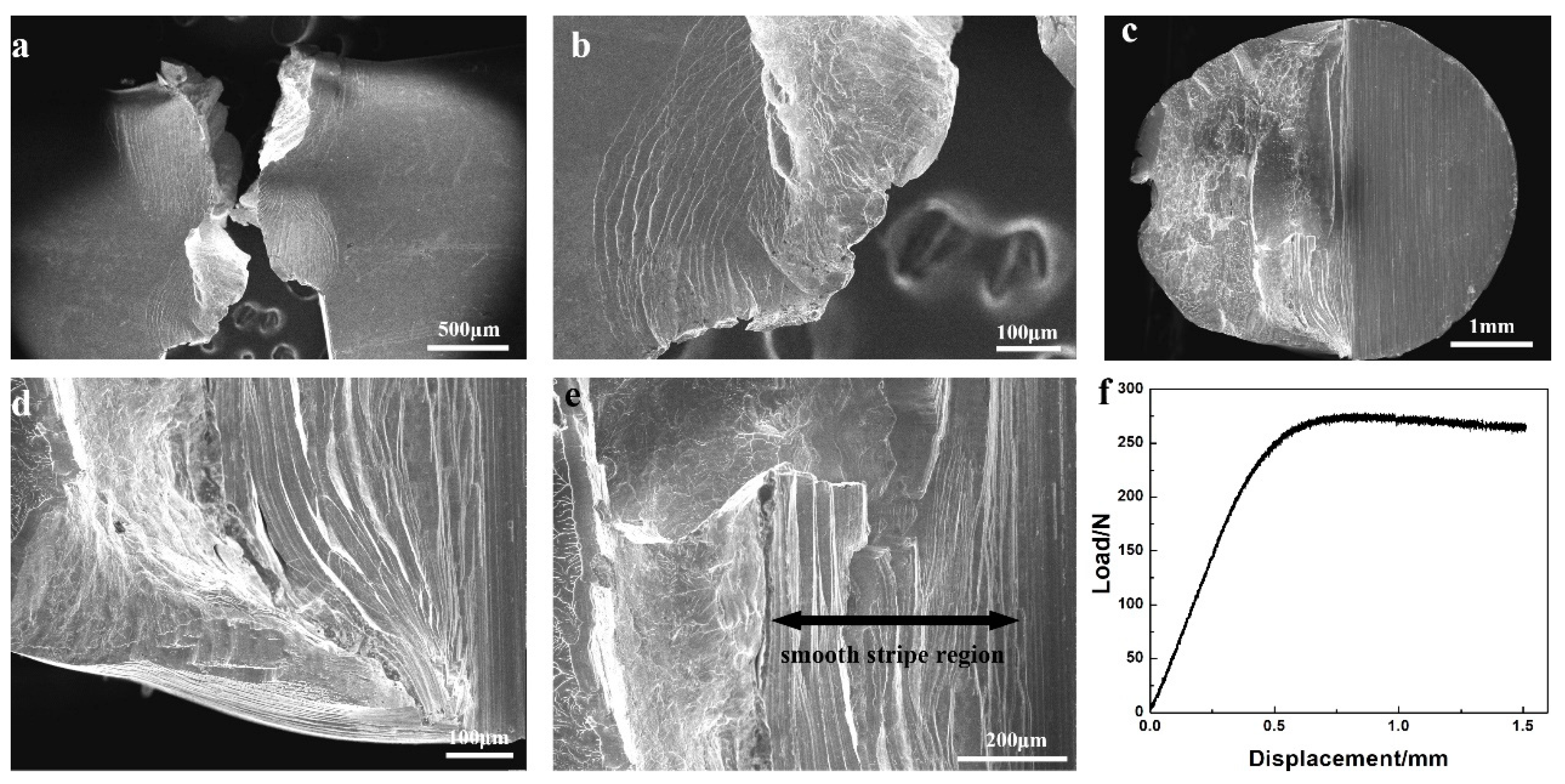
After the multiple shear bands formation and sliding, the material could reach the stage of shear band delamination. At present, the critical condition for shear band delamination is still complicated to be quantitatively predicted. In experiments, the shear bands in MGs will develop into fracture after sliding for a distance of a few tens of microns or less [6,26,28,29,30]. The physics behind the shear band delamination can be understood from different perspectives. As the model of Taylor’s fluid meniscus instability [31,32] suggested, the very thin shear band could be considered as a viscous layer, which would delaminate when a critical stress condition (a critical suction stress gradient along the shear band) is met. On the other hand, the shear band will gradually become looser and softer during sliding, due to the shear dilatation effect [33,34,35]. Irreversible microstructure change (such as nano cavitation [36] and nanocrystallization [37]), micrometer-scale softening and cavitation [38] can also occur during this process and weaken the shear band. Finally, the shear band reaches the critical condition of delamination. When the delamination occurs, the crack tip will propagate rapidly along the shear band path, and the fractograph will reproduce the shape of the shear band, denominated as “flat zone” or “planar zone” in some reports [26,28]. Figure 2 shows the fractograph of a Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 metallic glass, which reveals that the “flat zone” on the fractograph is actually not straightforward but will deviate from the original notch tip direction [27]. The morphologies of the shear bands and the fractograph formed by shear band delamination depend on the local stress condition. Near the side surface of the sample, the local maximum shear stress points into the sample, and cone shape shear bands will form (Figure 2b,c). Near the notch-tip inside the sample, the local maximum shear stress deviates from the notch-tip direction, and curved shape shear bands will form (Figure 2c,d). The shear direction and sliding distance of the shear band before delamination can be determined by the smooth shear-offsets at the edge of the fractograph [26,28,39].
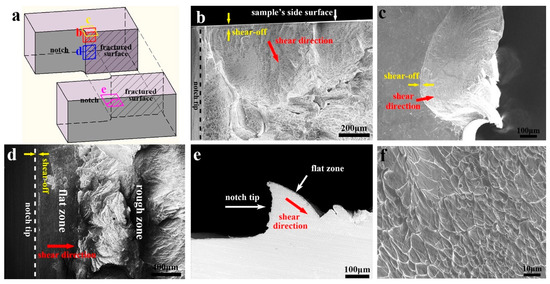
Figure 2.
Fractograph of a Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 metallic glass. (a) Sketch of the fractured sample with four marked regions. (b,c) The fractograph near the side surface of the sample. (d) The fractograph inside the sample. (e) The cross section profile inside the sample. (f) Enlarged image of the viscous features on the fractograph.
2.1.3. Rapid Fracture
After the shear band delamination, the crack can continue propagating rapidly through the sample. As there is no existing shear band and preferred crack propagation direction in this area, irregular rough fractograph is formed (Figure 2d), denominated as “rough zone” in some studies [26,28]. As the external stress is higher than the required stress for crack propagation at this stage, this part of fractograph is also called “over load region” [39]. Due to the lack of measuring method, there still lacks systematic researches on the fracture mechanism of this rapid fracture process.
Through the above three stages of fracture, a typical mode I fractograph of MG consisting of smooth region (shear band formation and sliding), flat zone (shear band delamination) and rough zone (rapid fracture) is formed. Plentiful viscous fracture features including dimples, veins and droplet patterns can be observed on the fractographs [10,39,40] (Figure 2f). These kinds of features are typical in MGs. As MGs are a kind of shear softened material, the deformed position (i.e. shear bands) will go through significant softening and viscosity drop [33,34,35].
When the fracture process develops into the stage of shear band delamination, the stress required for further crack extension will drop dramatically. For most MG samples, the stage of multiple shear bands formation and sliding in the beginning of the fracture process is short and unsustainable. Some brittle MGs can hardly form multiple shear bands at the notch-tip [41]. A large sample size of MGs is also against the multiple shear banding [42,43]. As a result, these MG samples will experience shear band delamination and generally show relatively poor fracture toughness/fracture resistance in the fracture tests.
In the widely used uniaxial compress and tension tests, MGs generally show a shear mode of fracture. In this case, the shear bands can propagate through the sample and are approximately plane. The fracture plane and the applied load direction show an angle near 45° [18,19,20]. Viscous features and smooth shear-offset can be observed on the fractograph [6,44], indicating that the fracture process also consists of shear band formation, sliding, and delamination
2.2. Brittle Fracture of MGs
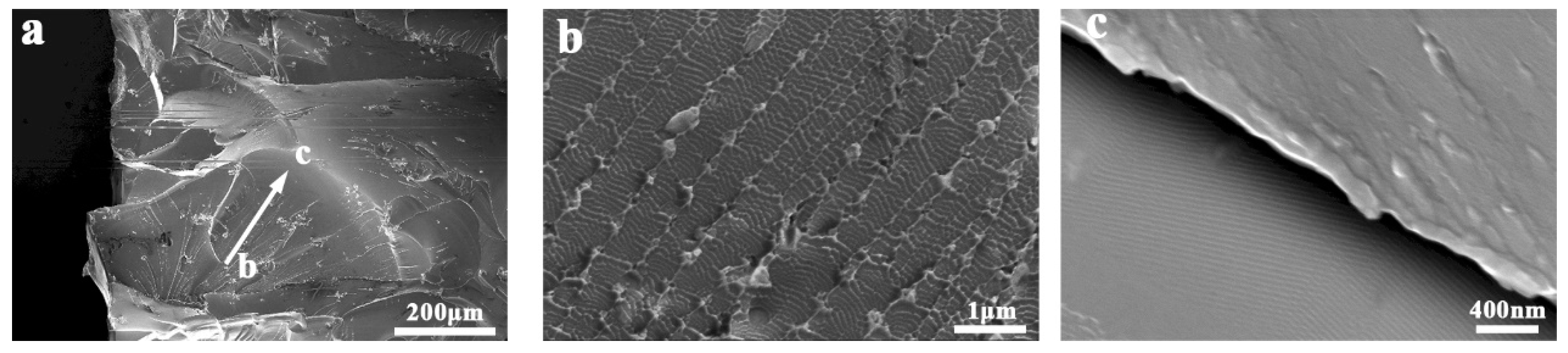
Although the fracture behaviors of most BMGs are controlled by the shear band deformation mechanism, there are exceptions, of course. In some Fe-based, Ca-based, Mg-based, Rare earth-based and other brittle MGs, the fracture mode under compression/tension loading can change from shear mode (fracture along the shear band path, which is ~45°from the loading axis) to cleavage mode (fracture along the plane perpendicular to the applied stress), split mode [45] (fracture along the plane parallel to the applied stress) or fragmentation mode. The cleavage or split surface of these brittle MGs can be divided into mirror, mist, and hackle regions [41,46]. The cleavage surface of MGs is smooth and continuous, with many radial ridge patterns along the crack propagation direction [47]. The split or fragment surface of MGs consists of many smooth conchoidal morphologies [46]. Plentiful periodic nanoscale wavy corrugations can be observed on the enlarged fracture surface (Figure 3). The formation mechanism of such features has been explained within the framework of the meniscus instability, plastic zone theory and local softening mechanism [41,48]. To explain the difference between the ductile and brittle fractographs, some studies point out that there is a positive correlation between the fracture toughness and the dimple size on the fractographs of MGs [49]. Those brittle MGs tends to form small dimples during fracture, and the most brittle MGs will form nanoscale wavy corrugations.
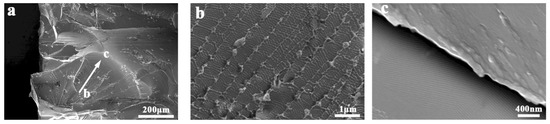
Figure 3.
Fractograph of a brittle Mg54Cu28Ag7Y11 MG with many periodic nanoscale wavy corrugations. (a) The overall appearance of the conchoidal fractograph. (b) Enlarged image of wavy corrugations on the conchoidal fractograph. (c) Enlarged image of nanoscale wavy corrugations at the edge of the conchoidal fractograph.
2.3. “Super Ductile” Fracture of MGs
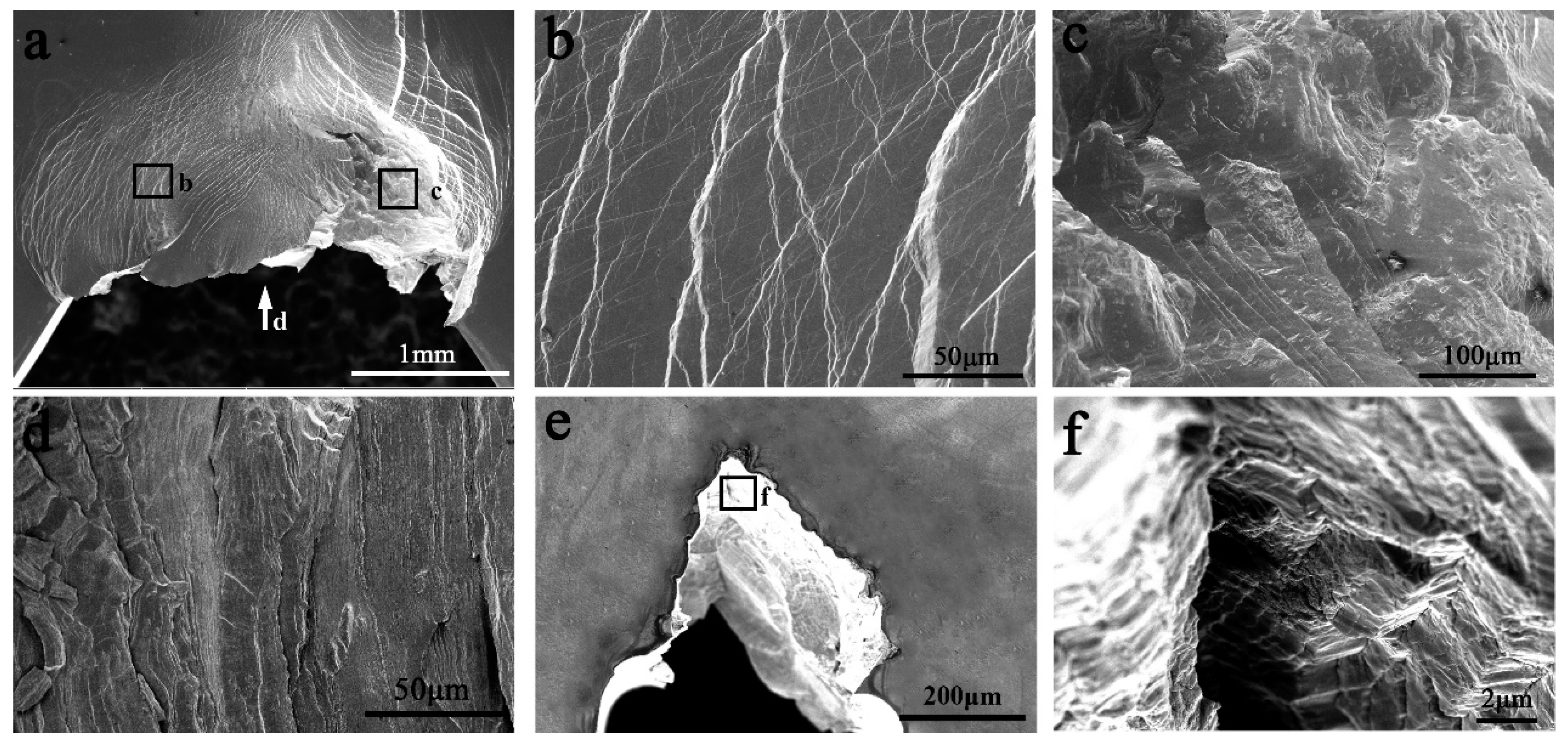
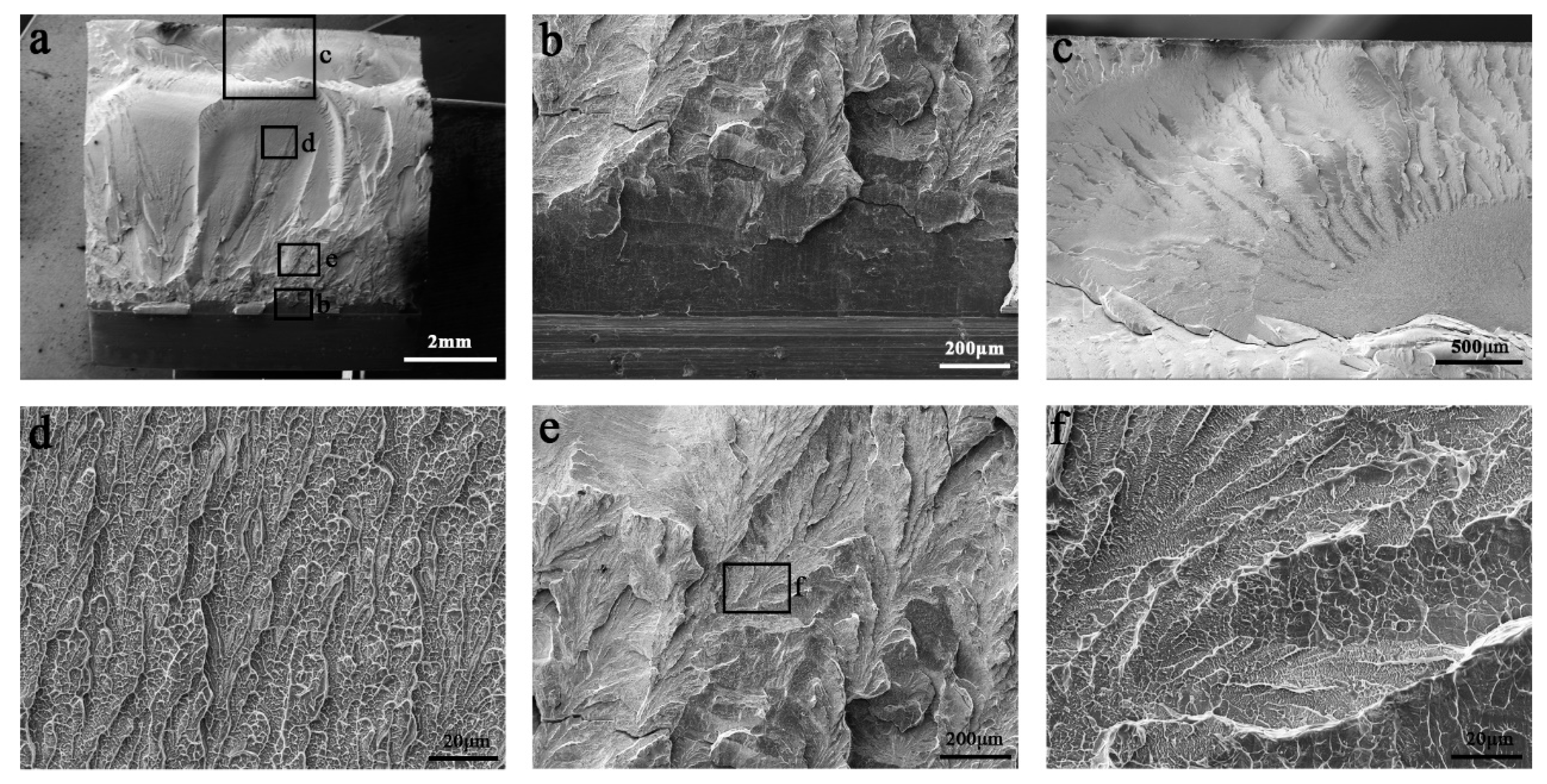
In the last decade, some Zr-based and Pd-based MGs with extremely large fracture toughness have been reported. The measured J-integral toughness of the Zr-based and Pd-based MGs can reach 150 MPa·m1/2 and more than 220 MPa·m1/2, respectively [6,50]. The Zr-based MG can form plentiful multiple shear bands during fracture. The Pd-based MGs can sustain multiple shear bands formation and sliding, without shear band delamination. Figure 4 shows the appearance of another Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 MG sample with a size of size is 2.2 × 3.8 × 25 mm3 during 3-point bending [51]. The sample can be severely deformed without fracture (Figure 4a). Plentiful shear offsets can be observed on the side surface of the sample (Figure 4b). The fractograph shows abundant strip features perpendicular to the crack extension direction (Figure 4d,f), which are formed through multiple shear banding. Such a “Super ductile” fracture behavior is inspiring, however, it is only observed in small size samples. The reasons for this fracture behavior and high toughness can be ascribed to:
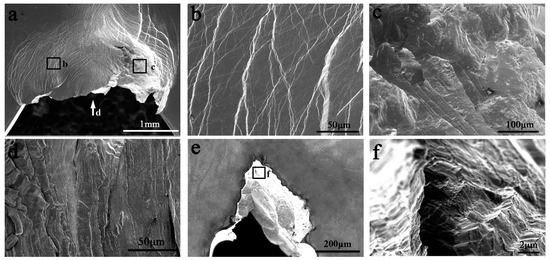
Figure 4.
Appearance of a Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 MG sample with a size of 2.2 × 3.8 × 25 mm3 after 3-point bending. (a–c) Side surface appearance. (d–f) Fracture surface appearance.
- The Pd-based MGs have better deformability than other MG systems and can more easily form multiple shear bands in different loading conditions.
- The size of the samples used in these studies is small (the thickness and ligament width are not more than 3 mm). Since a smaller sliding distance is needed to release the same stress in a smaller sample, it will be less easy for small samples to reach the critical condition of shear band delamination, i.e. small sample show higher shear band stability. Therefore, sustainable multiple shear banding can be achieved.
- The value of J-integral toughness depends on the energy absorption during crack extension, rather than the crack-tip stress intensity [22,52]. Due to the massive energy dissipation via the multiple shear band movements, a high J-integral toughness can be obtained.
Besides this review, another recent report also indicates that with decreasing sample size, the fracture mode of the Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 MG transits from multiple shear banding-shear band delamination to sustainable multiple shear banding [43]. The fracture toughness increases significantly when the transition occurs. Similar transition can also be observed in other MG systems. Figure 5 shows the fractograph of a pre-notched Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 (Vitreloy-1) MG rods after 3-point bending. A long sustainable multiple shear banding can be achieved when the sample size decreases down to φ2 mm. A large region of smooth stripes (shear offsets) can be observed on the fractograph (Figure 5a–e). A long serration process can be observed on the loading curve (Figure 5f). In the previous mechanical studies of MGs, a correlation of better properties and smaller sample size is widely observed [42]. This law is also applicable in the fracture performance.
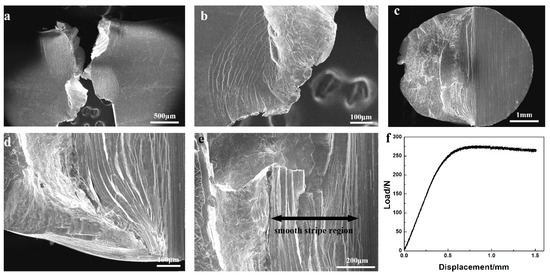
Figure 5.
Appearance of a Vitreloy-1 MG rod with a size of φ2 after 3-point bending. (a,b) Side surface appearance. (c–e) Fracture surface appearance. (f) Loading curve.
2.4. Impact Toughness of MGs
The impact toughness reflects the damage resistance of a material under impact loading. At present, the impact toughness data of MGs are still few. As the size requirement of the standard test (10 × 10 × 55 mm) can hardly be reached by most MGs. Only a small number of MGs can achieve a critical size over 10 mm [53,54,55,56,57,58]. Many impact toughness data are measured through nonstandard small samples. Table 1 shows a collection of reported impact toughness data of several MGs. Although there is doubt about the reliability of the data measured in nonstandard samples, the highest measured impact toughness in MGs is not higher than 160 kJ/m2. This value is relatively smaller than that of AISI-1018 steel [59].

Table 1.
Impact toughness data of different metallic glasses.
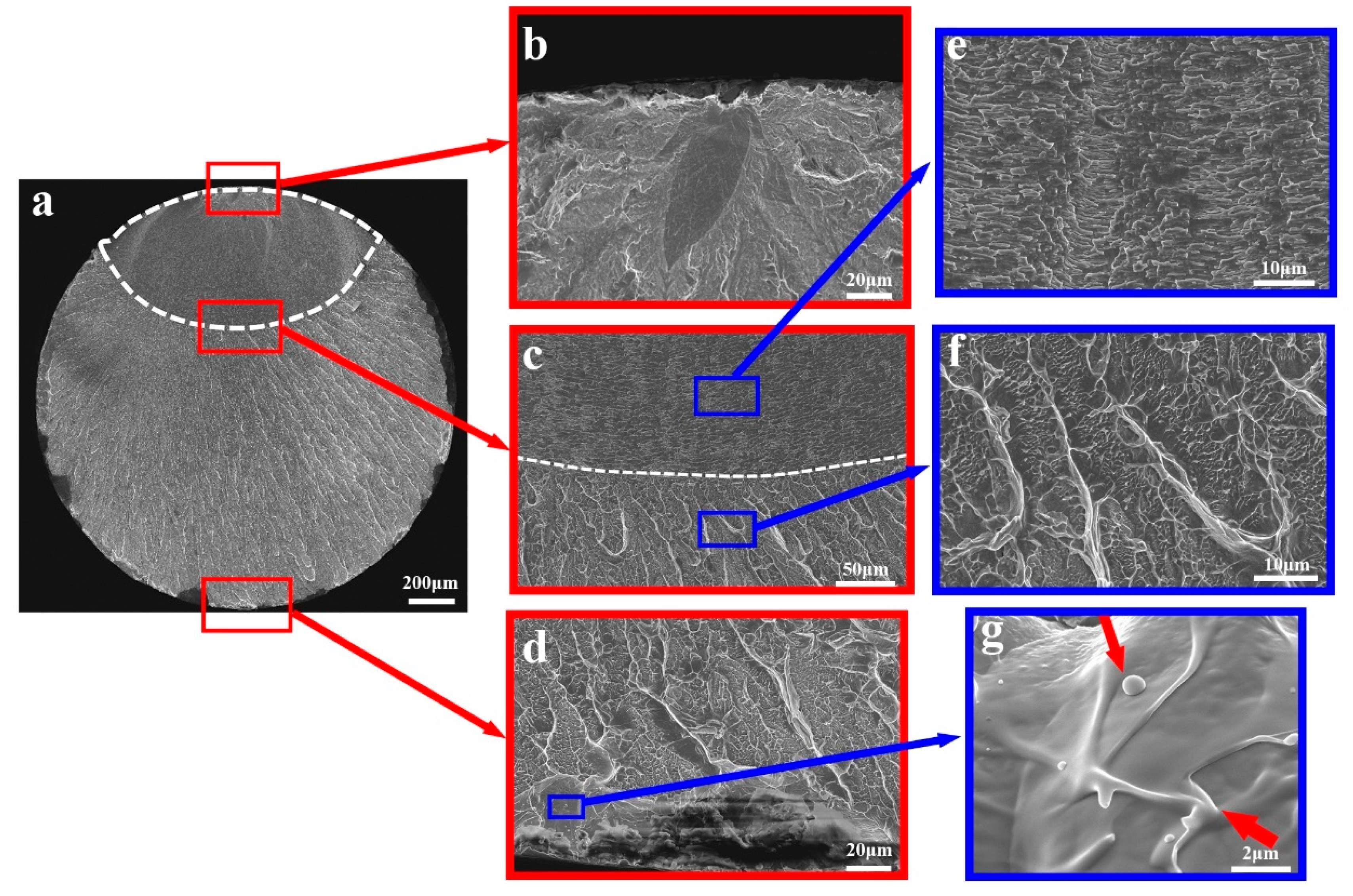
Figure 6 shows a typical impact fracture morphology of a (Ti41Zr25Be28Fe6)91Cu9 MG, which is very similar to that of mode I fracture. The fractograph starts with a smooth region and flat zone (Figure 6b), which are formed during shear band sliding and delamination. The other positions of the fractograph are rough, with many ridge patterns. Plentiful vein patterns and viscous features can be observed on the enlarged images of the fractograph (Figure 5d–f). The fracture direction changes obviously near the end of the sample (Figure 6c), which results from the changed stress condition at this position and the existence of shear bands generated by the impact hammer.
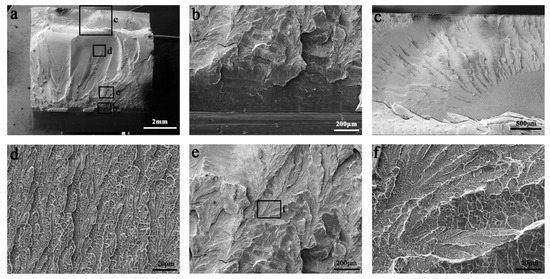
Figure 6.
Fractograph morphology of a (Ti41Zr25Be28Fe6)91Cu9 MG after impact toughness test. (a) The overall appearance of the fractograph. (b) The smooth region and flat zone on the fractograph near the initial notch tip. (c) Changed fracture direction and fractograph morphology near the end of the sample. (d–f) The vein patterns and viscous features at different positions of the fractograph.
The loading rate of impact toughness test is much faster than that of conventional static tests, and is also much faster than that of shear band sliding. Generally, the shear band sliding speed in MGs is at the magnitude of 1 mm/s or less [68,69]. The speed of pendulum hammer in the impact toughness test is at the magnitude of 4 m/s. Therefore, the fractograph of MGs after impact tests is similar to the over load region formed during rapid fracture. It has been reported that the mechanical behaviors of MGs are sensitive to the strain rate [70]. However, systematic researches on the dynamic fracture mechanism and influence of high stain rate in MGs during impact toughness test are still rare.
2.5. Fatigue Performance of MGs
Fatigue rupture is one of the main failure modes in engineering material [71]. The fatigue study of MGs can be traced back to the mid-1970 [72,73]. Due to the size limit, the tests of the early discovered MGs were carried out with ribbon samples. The Pd-Si MG ribbons show a fatigue crack growth threshold as high as ΔKth = 9 MPa·m1/2 [74], which is even higher than that of high-strength steel [75]. With the development of bulk metallic glasses, the fatigue properties can be measured by bulk samples under tension, compression, and bending tests. Although the fatigue ratio (the ratio of the fatigue endurance limit to the yielding stress) of most BMGs is near 0.3 [76], the fatigue endurance limit (the maximum stress amplitude to which the material is subjected for 107 cycles without failure) is still high, due to their high yielding strength. Some Co-based and Fe-based MGs can reach a fatigue limit as high as 2 GPa [77]. Table 2 shows the data of the fatigue endurance limit and the fatigue ratio of some reported MGs with a size larger than 2 mm and other commonly used metal materials including steel and Titanium alloy.

Table 2.
Fatigue properties of some MGs and some commonly used metal materials.
It is noticed that the measured fatigue properties of MGs are sensitive to the test method, test environment, sample quality, sample size, surface condition, and etc. Different results have been reported by different studies [81,89,90]. For example, the pour casting fabricated Zr55Cu30Ni5Al10 MG shows better fatigue properties, as the size and distribution of flaws could be tuned by the fabrication method. Thermal relaxed MGs could show higher fatigue limit, due to the relatively low free volume content [91,92,93]. The Poisson’s ratio, sample size [94] and the content of some alloying elements [87] also have significant influences on the fatigue behavior.
Figure 7 shows a typical fractograph of a brittle Mg-Cu-Ag-Y MG after tension fatigue fracture. The fractograph of the fatigue cracked MGs can be divided into the crack initiation site, the crack growth region and the fast fracture region [86,95]. There can be more than one crack initiation site on one sample. The crack growth region is relative smooth, with many regular fatigue striations perpendicular to the crack growth direction (Figure 7c). The spacing between striations is at micron order or submicron order. The fast fracture region is rough (Figure 7c). Vein patterns and melting features can be observed on the fractograph (Figure 7d), which result from the local heating and viscosity drop during the rapid fracture.
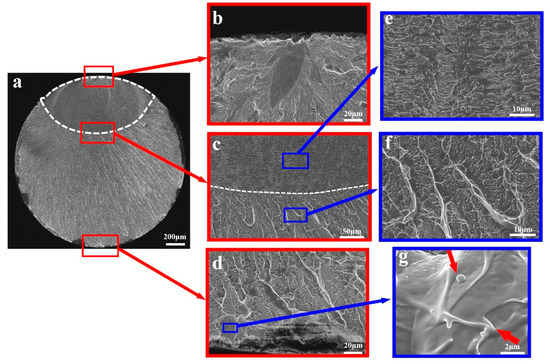
Figure 7.
Fractograph morphology of a brittle Mg-Cu-Ag-Y MG after tension fatigue fracture. (a) The overall appearance of the fractograph. (b) Enlarged image of the crack initiation site. (c) The boundary between the regular fatigue striations and the fast fracture region. (d) The morphology at the end of the fractograph. (e) Enlarge image of the regular fatigue striations. (f) Enlarged image of the fast fracture region (g) Enlarge image of the droplet feature at the end of the fractograph.
3. Fracture Mechanism of MGs
The fracture process in MGs discussed above is very different from that in conventional polycrystalline alloys. With work-hardening effect and the deformation mechanism of dislocations, the deformation of many polycrystalline alloys will experience an elastic, yielding, work-hardening, and fracture process. The mode I fracture process in these materials can be described by the classic linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM), which depicts the plastic zone by the contour line of yielding stress [52]. The material inside the plastic zone could deform plastically, and the material outside the zone will be still elastic. The plastic zone moves accordingly with the extension of crack-tip. The stress intensity for crack extension (fracture toughness) and energy absorption during the crack extension (fracture resistance) can be considered as material dependent constants. Compared to such a fracture process in polycrystalline alloys, the characteristics of fracture behaviors in MGs are summarized as follows:
3.1. Discontinuous Stress/Strain Field
For polycrystalline alloys with work hardening effect, the deformation and stress/strain field can be approximately continuous. For MGs, however, due to the shear softening effect [33,34,96], the viscous flow in MGs at room temperature will localize and form shear bands [16,34]. Since the shear transformations and shear band motions can be considered as thermal activated events [97], the position and the moment of shear band formation are random. After formation, the shear band can slide at a relatively lower stress [16,27,34], with a strain rate much faster than the external load [69,98]. During further loading, the shear bands delaminate and cause rapid fracture of the material [38]. As a result, the spatial and temporal distribution of strain/stress field in MGs during the fracture process will be discontinuous. The global stress/strain will also change discontinuously, observed as the serrations on the loading curves [13,25,99]. The strain in the shear bands is highly localized, while the other places are still elastic.
3.2. Fracture Resistance
Since the fracture process of MGs can be divided into different stages, the fracture resistance and plastic zone size might not be constant during the crack extension. In the stage of multiple shear banding, the stress intensity should be large enough that the shear bands can nucleation from the notch-tip. Part of mechanical energy will be released by plastic deformation in the manner of shear band sliding. It corresponds to a ductile fracture behavior. When the shear band delamination begins, the stress intensity required for further delamination will drop suddenly (due to the stress concentration at the sharp tip of the delaminated shear band and the relatively low viscosity inside the shear band). At the moment, the stress intensity in the sample is higher than the stress required for crack extension. The over load makes the shear band delamination a transient non-static process. Later, the crack extends rapidly and forms the rough zone on the fractograph. In experiments, the rapid fracture of MGs usually takes a very short moment (<<1 s), and sometimes is accompanied by sparking [100]. Since the crack extension rate is much faster than the shear band sliding rate, there will be not enough time for the material to deform by shear band sliding. The plastic deformation and energy absorption during the shear band delamination and rapid fracture will be small. It corresponds to a brittle fracture behavior.
3.3. Plastic Zone
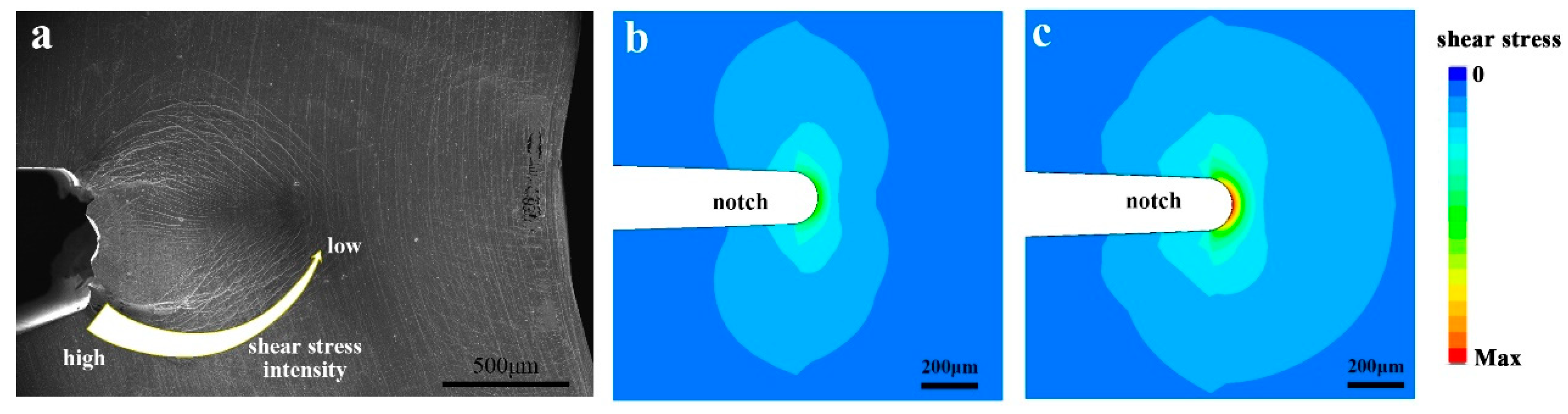
The crack-tip plastic zone of MGs also differs from that of polycrystalline alloys. In the stage of multiple shear banding, the plastic zone depends on the distribution of shear bands. It has been noticed that the notch-tip shear bands distribution on the side surface of MGs during mode I fracture deviates from the local stress distribution [6,27,50] (Figure 8). The reason for such deviation is that the shear bands in MGs propagates along the local maximum shear stress direction (or the direction of the local maximum shear stress gradient) [101]. Due to the stress concentration at shear band tip, the shear band is able to propagate into the region with relatively low stress. Therefore, the actual plastic deformed region of MGs depends on the distribution of shear stress direction, instead of the distribution of stress intensity. With the increasing stress intensity during loading, new shear bands are formed from the notch-tip, and the plastic deformed region gradually extends. Later, the shear band delamination is triggered when the critical condition is reached. At the moment, the sharp crack tip extends rapidly along the shear band path. The plastic zone depends on the softened region near the crack tip. Since the opposite sides of the delaminated shear bands could match well with each other, the plastic zone size might be very small. If the plastic region has a similar size to the dimples on the fractograph (a few microns to tens of microns), it will be much smaller than the shear band itself (the shear bands in BMGs can be millimeter-scale). The decreased plastic zone size explains the reduced fracture resistance during the shear band delamination.
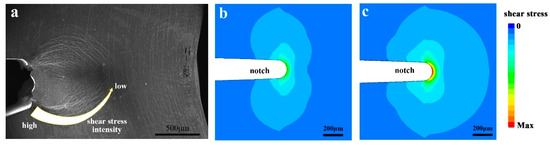
Figure 8.
A comparison of shear band distribution and shear stress distribution near the notch tip of a Pd77.5Cu6Si16.5 MG during 3-point bending. (a) The shear band distribution near the notch tip of the sample. (b) Simulated shear stress distribution on the side surface of the sample. (c) Simulated shear stress distribution in the middle of the sample.
Based on the above discussions, the shear band controlled fracture process of MGs can be considered as a dynamic process, in which the plastic deformation is achieved through individual shear band formation and sliding instead of continuous deformation. With different sample size, sample shape and loading condition, the stability, direction, formation stress, morphology and sliding distance of the shear bands in MGs will change accordingly, which will result in different deformation behaviors. Therefore, those mechanical properties including plasticity and fracture toughness will strongly depend on both the material and the external loading condition. For instance, straightforward shear bands are formed under uniaxial loading, and the material will show a shear mode fracture [18,19,20,44]. Due to the normal stress sensitivity of the shear band nucleation, MGs show different yielding stress and shear directions in compression and tension [18,19,20]. Under different constrained loading conditions, different failure mode, plasticity, and serration behavior can be obtained [102,103], etc. In the case of mode I fracture, the energy absorption is mainly attributed to the stage of multiple shear bands formation and sliding. In small size samples, sustainable multiple shear banding can be more easily achieved and better fracture toughness/fracture resistance can be obtained. Under different loading mode, the notch tip shear band distribution (plastic zone) will change accordingly, which will result in different fracture properties [104]. The ductility and toughness of the material depend on the crucial moment of shear band delamination, which is sensitive to the local structure and stress condition. In different tests, different samples, and different positions of a sample, the critical condition of shear band delamination might show a high degree of variability and randomness. With this understanding, it becomes doubtful to treat those mechanical properties in MGs as intrinsic material properties.
4. Characterizing the Fracture Properties of Metallic Glasses
At present, how to characterize the fracture property of MGs is still under debate. The main points in controversy are summarized as below:
4.1. Size Limit of MGs
According to the standard test method of mode I fracture toughness [21,22], a large sample size is required to ensure the validity of the measured results. For a sample with a fracture toughness of KIC, the required thickness of the sample can be expressed as:
where B represents the sample’s thickness, a represents the crack length, KQ represents the toughness value, and σY represents the yielding strength. As the mode I fracture toughness value of MGs falls in the range of a few to more than one hundred MPa·m0.5 [21,22], the required sample size will be a few millimeters to more than one centimeter. However, such a size requirement can hardly be reached by most MGs, due to their poor glass-forming ability. Until now, the BMGs with a critical size of more than one centimeter are still rare. Most fracture tests of MGs are carried out with a sample size of a few millimeters, which can hardly reach the size requirement of standard test [21,22]. Besides, crack opening displacement should be measured during the fracture process as required by the test standard. However, it will be difficult to install a very small extensometer onto the small MG samples.
4.2. Fatigue Pre-Crack
According to the test standard [21,22], a fatigue pre-crack with enough length should be prepared to ensure the sharpness of the initial crack tip. However, this requirement can hardly be achieved by MGs with small size. As the ligament length of most MG samples is small, the fatigue load should decrease according with the extension of the fatigue crack. Moreover, it is difficult to prepare a straight fatigue crack in MGs. As the shear bands near the notch tip are curved and deviated from the original notch direction, the fatigue crack also will easily deviate from the original direction. A recent report discovered that straightforward fatigue crack can be prepared under the pure shear stress condition achieved by asymmetric four-point bending [105], which provides a feasible solution for this question.
4.3. Variability of Fracture Toughness
As MG samples can hardly meet the requirement of size and fatigue pre-crack in the test standard, some nonstandard measurements were used for substitution. Some studies used the notch toughness (without fatigue pre-crack) as an approximation to characterize the fracture toughness of MGs [30,106]. In some studies, the fatigue pre-cracking process was replaced by machining a notch tip with a very small radius [6]. J-integral toughness tests were also used, as the size requirement of J-integral toughness test is smaller than that of standard measurement [22,52]. In these studies under different loading conditions and different test methods, a high variability in the measured fracture toughness is observed.
Experiments of notch toughness show that with increasing notch-tip radius, the degree of stress concentration at the notch-tip decreases, and a greater load is needed to form shear bands from the notch-tip. A larger fracture toughness can be measured [107]. In small size samples, a shorter shear band sliding distance is required to release the same stress. The material prefers to form multiple shear bands rather than shear band delamination, and a higher fracture resistance can be achieved [42,43,51]. The measured fracture toughness is also sensitive to the temperature [108], loading rate, loading mode [107], heat history [109], residual stress [110], geometry [111] and the distribution of impurities/flaws [112]. For example, the cooling rate directly affects the fracture energy of a Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni-Be MG, which can range from 148.9 to only 0.2 kJ m−2 [26]. The measured fracture toughness of Vitreloy-1 MG can vary widely from ~18 to ~130 MPa·m1/2 in different reports with different test methods [39,75,113].
To understand the variability of fracture toughness in MGs. Some studies suggest that the properties of MGs are “intrinsically variable” [114], as the shear band behaviors of MGs depends on both the material and the loading condition [42,107,115]. Some studies suggest that the sample geometry to measure the fracture toughness of BMGs should be much smaller than suggested by the standards for crystalline alloys [111]. According to the discussions of this review, the variability of mechanical properties of MGs actually reflects the sensibility of the shear band behaviors to the external loading condition and the randomness in the shear band motions. We have seen the tendency that new experimental methods, theoretical criteria, or definitions will be proposed to further study these shear band controlled materials, especially for the engineering important metallic glasses.
5. Prospects
Here a brief review has been provided to understand the fracture behavior and fracture mechanism of MGs. As present, the study of fracture in MGs is still preliminary, due to the complex fracture mechanism of MGs compared to the classic fracture mechanism in polycrystalline alloys. Here we would like to raise some representative unsolved issues in this field, which to our knowledge have relatively high interest and importance.
5.1. Characterizing the Dynamic Fracture Properties of MGs
As discussed above, the different fracture modes, dynamically changing fracture resistance during different stages of fracture, and high variability in the measured fracture toughness of MGs result from their complex fracture mechanism. Due to the limitation of glass-forming ability, standard test methods of fracture properties might not be applicable in those MGs with small critical size. Appropriate experimental methods and theoretical tools are needed to characterize and further study the dynamic fracture behavior of MGs and other shear band controlled materials. For those small size MGs that cannot meet the requirement of test standard, new methods are needed to be developed to characterize their toughness and fracture resistance.
5.2. Toughening Method of MGs
Although some MGs show high damage tolerance, the fracture toughness of the most widely used Fe-based magnetic MGs in industry is still poor. The poor tensile ductility and low impact toughness of MGs also limit their further applications in many cases. How to enhance the mechanical performance of Fe-based MG and their composites without negative effects on their magnetic properties, and how to achieve tensile ductility and toughness in large MG samples are of great significance.
5.3. Performance Under Special Conditions
As the shear band behaviors can be tuned by external loading condition, MGs can possibly show better mechanical performance under special conditions, such as high temperature, cryogenic temperature, small sample size, irregular sample shape, irradiation environment, high strain rate, constrained loading, etc. These factors could provide potential applications for MGs.
5.4. Rapid Fracture Mechanism of MGs
The formation process of the rough zone on the fractograph and the rapid fracture mechanism under impact loading and other rapid loading conditions are still unclear. To optimize the fracture toughness and impact toughness of MGs, the physics behind the rapid fracture of MGs should be studied and clarified.
5.5. Mode II and Mode III Fracture Mechanism of MGs
At present, the studies of fracture mechanism of MGs under Mode II and mode III fracture are still rare. The different fracture properties of MGs under different load mode might provide an approach to understand the correlation between the mechanical behaviors and the loading conditions of MGs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.-N.Y., Y.S. and K.-F.Y.; methodology, G.-N.Y., Y.S. and K.-F.Y.; experiment and simulation, G.-N.Y.; data analysis, G.-N.Y., Y.S. and K.-F.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, G.-N.Y.; writing—review and editing, Y.S. and K.-F.Y.; visualization, G.-N.Y.; supervision, K.-F.Y.; funding acquisition, K.-F.Y. and G.-N.Y.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grand Nos. 51771096 and 51571127) and the Fostering Talents Foundation of Guangdong University of Technology (Grand No. 262511006).
Acknowledgments
We thank Pan Gong and Xin Wang for sharing the precious data and helpful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Inoue, A. Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Dong, C.; Shek, C.H. Bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2004, 44, 45–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S. Processing of bulk metallic glass. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1566–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Greer, A.L.; Ma, E. Bulk metallic glasses: At the cutting edge of metals research. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihisa, I.; Baolong, S.; Hisato, K.; Hidemi, K.; Yavari, A.R. Cobalt-based bulk glassy alloy with ultrahigh strength and soft magnetic properties. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 661–663. [Google Scholar]
- Demetriou, M.D.; Launey, M.E.; Garrett, G.; Schramm, J.P.; Hofmann, D.C.; Johnson, W.L.; Ritchie, R.O. A damage-tolerant glass. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.F.; Ruan, F.; Yang, Y.Q.; Chen, N. Superductile bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 122106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.F.; Zhang, C.Q. Fe-based bulk metallic glass with high plasticity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 061901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Ma, E. Shear bands in metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2013, 74, 71–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Hufnagel, T.C.; Ramamurty, U. Overview No.144—Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4067–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.A.; Wang, W.H. The fracture of bulk metallic glasses. Prog. Mater Sci. 2015, 74, 211–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ramamurty, U.; Ma, E. The fracture toughness of bulk metallic glasses. JOM 2010, 62, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.N.; Chen, S.Q.; Gu, J.L.; Zhao, S.F.; Li, J.F.; Shao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, K.F. Serration behaviours in metallic glasses with different plasticity. Philos. Mag. 2016, 96, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bei, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Lu, Z.P.; George, E.P.; Gao, Y.F. Deformation-induced spatiotemporal fluctuation, evolution and localization of strain fields in a bulk metallic glass. Int. J. Plast. 2015, 71, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Wu, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Z.; Neuefeind, J.; Wang, X.-L. Structure origin of a transition of classic-to-avalanche nucleation in Zr-Cu-Al bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2018, 149, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steif, P.S.; Spaepen, F.; Hutchinson, J.W. Strain localization in amorphous metals. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.J.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Ma, E. Structural processes that initiate shear localization in metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 5146–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Lund, A.C. Atomistic basis for the plastic yield criterion of metallic glass. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; He, G.; Eckert, J.; Schultz, L. Fracture mechanisms in bulk metallic glassy materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 045505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Eckert, J. Unified tensile fracture criterion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 094301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM E399, Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness KIc of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM E1820, Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fracture Toughness; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Zhen, L.; Chao, Y.J. An Assessment of Mechanical Properties of A508-3 Steel Used in Chinese Nuclear Reactor Vessels. J. Press. Vess.Technol. ASME 2015, 137, 031402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaumünzer, D.; Maaß, R.; Löffler, J.F. Stick-slip dynamics and recent insights into shear banding in metallic glasses. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 26, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.A.; Pauly, S.; Tan, J.; Stoica, M.; Wang, W.H.; Kühn, U.; Eckert, J. Serrated flow and stick–slip deformation dynamics in the presence of shear-band interactions for a Zr-based metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4160–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.J.; Poon, S.J.; Shiflet, G.J.; Lewandowski, J.J. Ductile-to-brittle transition in a Ti-based bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.N.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. The shear band controlled deformation in metallic glass: A perspective from fracture. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandaiya, P.; Narasimhan, R.; Ramamurty, U. On the mechanism and the length scales involved in the ductile fracture of a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, J.J.; Gu, X.J.; Shamimi Nouri, A.; Poon, S.J.; Shiflet, G.J. Tough Fe-based bulk metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 091918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zhu, Z.D.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. Notch toughness of Cu-based bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argon, A.S.; Salama, M. Mechanism of fracture in glassy materials capable of some inelastic deformation. Mat. Sci. Eng. 1976, 23, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, P.G.; Taylor, G. The penetration of a fluid into a porous medium or hele-shaw cell containing a more viscous liquid. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 1958, 245, 312–329. [Google Scholar]
- Spaepen, F. A microscopic mechanism for steady state inhomogeneous flow in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 1977, 25, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argon, A.S. Plastic deformation in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 1979, 27, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. Softening and dilatation in a single shear band. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 5146–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, G.N.; Yao, K.F.; Liu, X. Direct experimental evidence of nano-voids formation and coalescence within shear bands. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 181909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fujita, T.; Zeng, Y.Q.; Nishiyama, N.; Inoue, A.; Chen, M.W. Micromechanisms of serrated flow in a Ni50Pd30P20 bulk metallic glass with a large compression plasticity. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2834–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaß, R.; Birckigt, P.; Borchers, C.; Samwer, K.; Volkert, C.A. Long range stress fields and cavitation along a shear band in a metallic glass: The local origin of fracture. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowhaphandu, P.; Ludrosky, L.A.; Montgomery, S.L.; Lewandowski, J.J. Deformation and fracture toughness of a bulk amorphous Zr–Ti–Ni–Cu–Be alloy. Intermetallics 2000, 8, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.; Murali, P.; Ramamurty, U. On factors influencing the ductile-to-brittle transition in a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, D.Q.; Bai, H.Y.; Pan, M.X.; Xia, A.L.; Han, B.S.; Xi, X.K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.H. Nanoscale periodic morphologies on the fracture surface of brittle metallic glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 235501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, C.T. Size effect on stability of shear-band propagation in bulk metallic glasses: An overview. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Granata, D.; Thurston, K.V.S.; Löffler, J.F.; Ritchie, R.O. On the understanding of the effects of sample size on the variability in fracture toughness of bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2017, 126, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, C.P.; Chang, Y.W. Ductility enhancement of a Ti-based bulk metallic glass through annealing treatment below the glass transition temperature. Intermetallics 2012, 20, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, J.; Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B. Fatigue and Fracture Behavior of a Ca-Based Bulk-Metallic Glass. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 1775–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B. The Duality of Fracture Behavior in a Ca-based Bulk-Metallic Glass. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Wu, F.F.; Gao, W.; Tan, J.; Wang, Z.G.; Stoica, M.; Das, J.; Eckert, J.; Shen, B.L.; Inoue, A. Wavy cleavage fracture of bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Han, Y.N.; Xu, X.H.; Ke, F.J.; Han, B.S.; Wang, W.H. Ductile to brittle transition in dynamic fracture of brittle bulk metallic glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 093520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.K.; Zhao, D.Q.; Pan, M.X.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, Y.; Lewandowski, J.J. Fracture of brittle metallic glasses: Brittleness or plasticity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 125510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. Locating bulk metallic glasses with high fracture toughness: Chemical effects and composition optimization. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.N.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. A non-viscous-featured fractograph in metallic glasses. Philos. Mag. 2016, 96, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L. Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.L.; Yang, X.L.; Zhang, A.L.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, S.F.; Yao, K.F. Centimeter-sized Ti-rich bulk metallic glasses with superior specific strength and corrosion resistance. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 512, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.Y.; Shao, Y.; Gong, P.; Li, J.F.; Yao, K.F. A senary TiZrHfCuNiBe high entropy bulk metallic glass with large glass-forming ability. Mater. Lett. 2014, 125, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Yang, G.N.; Ding, H.Y.; Yao, K.F. A quinary Ti-Zr-Hf-Be-Cu high entropy bulk metallic glass with a critical size of 12 mm. Intermetallics 2015, 61, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Chen, N.; Liu, X.; Yao, K.F. A Ti-Zr-Be-Fe-Cu bulk metallic glass with superior glass-forming ability and high specific strength. Intermetallics 2013, 43, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Ding, H.Y.; Yao, K.F. Pseudo-quinary Ti20Zr20Hf20Be20(Cu20-xNix) high entropy bulk metallic glasses with large glass forming ability. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Gong, P.; Li, J.F.; Chen, N.; Yao, K.F. Quaternary Ti-Zr-Be-Ni bulk metallic glasses with large glass-forming ability. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.J.; Ward, J.D., Jr.; Sands, R.G. Charpy impact energy, fracture toughness and ductile–brittle transition temperature of dual-phase 590 Steel. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.Q.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhu, Z.W.; Fu, H.M.; Wang, A.M.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.Q. TiZr-base Bulk Metallic Glass with over 50 mm in Diameter. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Zhang, T. Impact Fracture Energy of Bulk Amorphous Zr55Al10Cu30Ni5 Alloy. Mater. Trans. 1996, 37, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Akeno, Y.; Yamasaki, T.; Liaw, P.K.; Buchanan, R.A.; Inoue, A. Evolution of Mechanical Properties of Cast Zr50Cu40Al10 Glassy Alloys by Structural Relaxation. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2755–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Zachrisson, C.; Kozachkov, H.; Ullah, A.; Shapiro, A.A.; Johnson, W.L.; Hofmann, D.C. Cryogenic Charpy impact testing of metallic glass matrix composites. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.; Murali, P.; Ramamurty, U. Ductile to brittle transition in the Zr 41.2Ti 13.75Cu 12.5Ni 10Be 22.5 bulk metallic glass. Intermetallics 2006, 14, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurty, U.; Lee, M.L.; Basu, J.; Li, Y. Embrittlement of a bulk metallic glass due to low-temperature annealing. Scr. Mater. 2002, 47, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szuecs, F.; Kim, C.P.; Johnson, W.L. Mechanical properties of Zr56.2Ti13.8Nb5.0Cu6.9Ni5.6Be12.5 ductile phase reinforced bulk metallic glass composite. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Fukaura, K.; Sunada, H.; Inoue, A. Rotating-Beam Fatigue Strength of Pd40Cu30Ni10P20 Bulk Amorphous Alloy. Mater. Trans. 1999, 40, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.X.; Nieh, T.G. Flow serration and shear-band viscosity during inhomogeneous deformation of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaß, R.; Löffler, J.F. Shear-Band Dynamics in Metallic Glasses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2353–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.F.; Kou, H.C.; Li, J.S.; Chang, H.; Zhou, L. Effect of strain rate on compressive behavior of Ti-based bulk metallic glass at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 472, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.Y. Fatigue Materials; Melbourne University Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, L.A. Fracture of Ni-Fe base metallic glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 1975, 10, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Masumoto, T.; Fukushima, K. Fatigue fracture of amorphous Pd-20at-percent Si alloy. Scr. Metall. 1975, 9, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Fukushima, K.; Masumoto, T. Propagation of fatigue cracks in amorphous metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1976, 23, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.J.; Schroeder, V.; Ritchie, R.O. Mechanisms for fracture and fatigue-crack propagation in a bulk metallic glass. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S. Glassy metals. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1980, 43, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Zhang, W.; Shen, B.; Amiya, K.; Ma, C.L.; Nishiyama, N. Fatigue properties in high strength bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2012, 30, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnambalam, V.; Poon, S.J.; Shiflet, G.J. Fe-based bulk metallic glasses with diameter thickness larger than one centimeter. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 1320–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.C.; Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Ponnambalam, V.; Poon, S.J.; Shiflet, G.J. Fatigue behavior of an Fe48Cr15Mo14Er2C15B6 amorphous steel. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.J.; Lippmann, J.M.; Ritchie, R.O. Fatigue of a Zr-Ti-Cu-Ni-Be bulk amorphous metal: Stress/life and crack-growth behavior. Scr. Mater. 1998, 38, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Peker, A.; Yang, B.; Benson, M.L.; Yuan, W.; Peter, W.H.; Huang, L.; Freels, A.; Buchanan, R.A.; et al. Fatigue behavior of Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be bulk-metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Peter, W.H.; Yang, B.; Yokoyama, Y.; Benson, M.L.; Green, B.A.; Kirkham, M.J.; White, S.A.; Saleh, T.A.; et al. Fatigue behavior of bulk-metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.C.; Fan, G.J.; Liaw, P.K.; Choo, H. Fatigue behaviors of the Cu47.5Zr47.5Al5 bulk-metallic glass (BMG) and Cu(47.5)Zr(38)Hf(9.5)Al(5)BMG composite. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, W.H.; Liaw, P.K.; Buchanan, R.A.; Liu, C.T.; Brooks, C.R.; Horton, J.A.; Carmichael, C.A.; Wright, J.L. Fatigue behavior of Zr52.5Al10Ti5Cu17.9Ni14.6 bulk metallic glass. Intermetallics 2002, 10, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.L.; Buchanan, R.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Green, B.A.; Wang, G.Y.; Liu, C.; Horton, J.A. Four-point-bending-fatigue behavior of the Zr-based Vitreloy 105 bulk metallic glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2007, 467, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Peter, W.H.; Yang, B.; Freels, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Benson, M.L.; Green, B.A.; Saleh, T.A.; McDaniels, R.L.; et al. Fatigue behavior and fracture morphology of Zr50Al10Cu40 and Zr50Al10Cu30Ni10 bulk-metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Freels, M.; Inoue, A. The influence of Pd on tension-tension fatigue behavior of Zr-based bulk-metallic glasses. Int. J. Fatigue 2010, 32, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liaw, P.K.; Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Morrison, M.L. Mechanical and Fatigue Behavior of Ca65Mg15Zn20 Bulk-Metallic Glass. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.J.; Ritchie, R.O.; Johnson, W.L. Fracture toughness and fatigue-crack propagation in a Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, B.C.; Dauskardt, R.H. The fatigue endurance limit of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launey, M.E.; Busch, R.; Kruzic, J.J. Influence of structural relaxation on the fatigue behavior of a Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10CU12.5Be22.5 bulk amorphous alloy. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 483–487. [Google Scholar]
- Launey, M.E.; Busch, R.; Kruzic, J.J. Effects of free volume changes and residual stresses on the fatigue and fracture behavior of a Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launey, M.E.; Hofmann, D.C.; Johnson, W.L.; Ritchie, R.O. Solution to the problem of the poor cyclic fatigue resistance of bulk metallic glasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4986–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Inoue, A. Size effects on the fatigue behavior of bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Q.; He, Q.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. Fatigue endurance limit and crack growth behavior of a high-toughness Zr61Ti2Cu25Al12 bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2015, 99, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaepen, F. Metallic glasses: Must shear bands be hot? Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, S.G. Activation energy of shear transformation zones: A key for understanding rheology of glasses and liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 195501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaß, R.; Klaumünzer, D.; Löffler, J.F. Propagation dynamics of individual shear bands during inhomogeneous flow in a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3205–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.A.; Yu, H.B.; Jiao, W.; Bai, H.Y.; Zhao, D.Q.; Wang, W.H. Plasticity of Ductile Metallic Glasses: A Self-Organized Critical State. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 035501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.T.; Heatherly, L.; Easton, D.S.; Carmichael, C.A.; Schneibel, J.H.; Chen, C.H.; Wright, J.L.; Yoo, M.H.; Horton, J.A.; Inoue, A. Test environments and mechanical properties of Zr-base bulk amorphous alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1998, 29, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.N.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. The material-dependence of plasticity in metallic glasses: An origin from shear band thermology. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.N.; Gu, J.L.; Chen, S.Q.; Shao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, K.F. Serration Behavior of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass Under Different Constrained Loading Conditions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 5395–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhou, H.F.; Wang, Z.T.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.J. Origin of anomalous inverse notch effect in bulk metallic glasses. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 2015, 84, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandaiya, P.; Ramamurty, U.; Narasimhan, R. Mixed mode (I and II) crack tip fields in bulk metallic glasses. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 2009, 57, 1880–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, C.; Keryvin, V.; Doquet, V.; Hin, S.; Yokoyama, Y. A sequential pre-cracking procedure to measure the mode-I fracture toughness of ultra pure bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2017, 141, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.D.; Jia, P.; Xu, J. Optimization for toughness in metalloid-free Ni-based bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.A.; Kecskes, L.; Lewandowski, J.J. Effects of changes in test temperature and loading conditions on fracture toughness of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, D.; Narayan, R.L.; Tandaiya, P.; Ramamurty, U. Temperature-dependence of mode I fracture toughness of a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, H.F.; Liu, Z.; Ketkaew, J.; Li, N.; Yurko, J.; Hutchinson, N.; Gao, H.J.; Schroers, J. Processing effects on fracture toughness of metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2017, 130, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.H.; Greer, A.L. Making metallic glasses plastic by control of residual stress. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, H.F.; Liu, Z.; Ketkaew, J.; Shao, L.; Li, N.; Gong, P.; Samela, W.; Gao, H.J.; Schroers, J. Test sample geometry for fracture toughness measurements of bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. Reliability of compressive fracture strength of Mg-Zn-Ca bulk metallic glasses: Flaw sensitivity and Weibull statistics. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, R.D.; Rosakis, A.J.; Johnson, W.L.; Owen, D.M. Fracture toughness determination for a beryllium-bearing bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 1997, 37, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.L.; Tandaiya, P.; Garrett, G.R.; Demetriou, M.D.; Ramamurty, U. On the variability in fracture toughness of ‘ductile’ bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2015, 102, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Desai, A.; Schroers, J. Bulk metallic glass: The smaller the better. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).