A Waste Heat-Driven Cooling System Based on Combined Organic Rankine and Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thermodynamics and Operational Conditions of the Proposed System
2.1. System Components
2.2. Thermodynamics Models and Equations
2.2.1. Components of the Exhaust Gas
2.2.2. Thermodynamics Equations
2.3. Operational Conditions
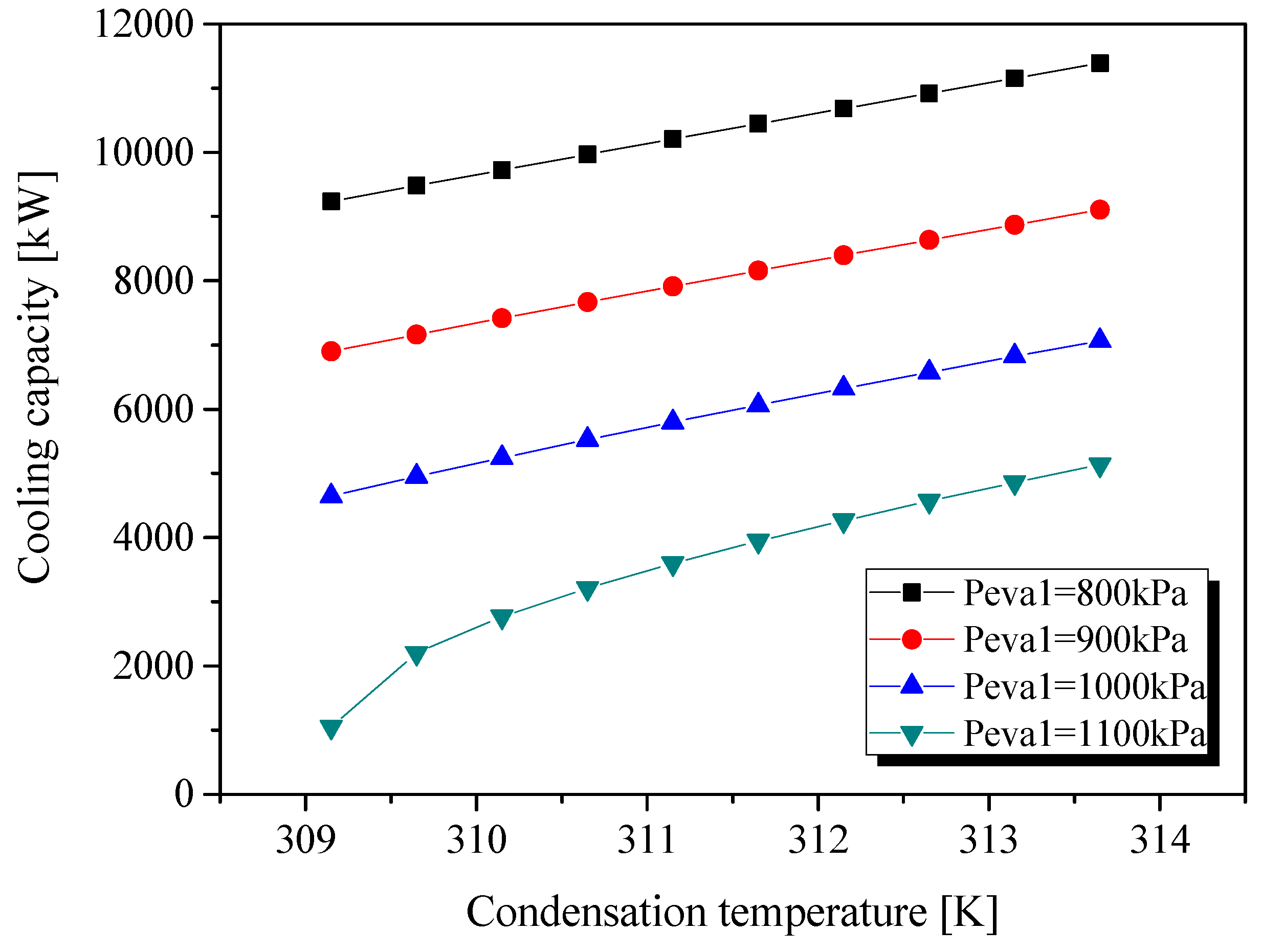
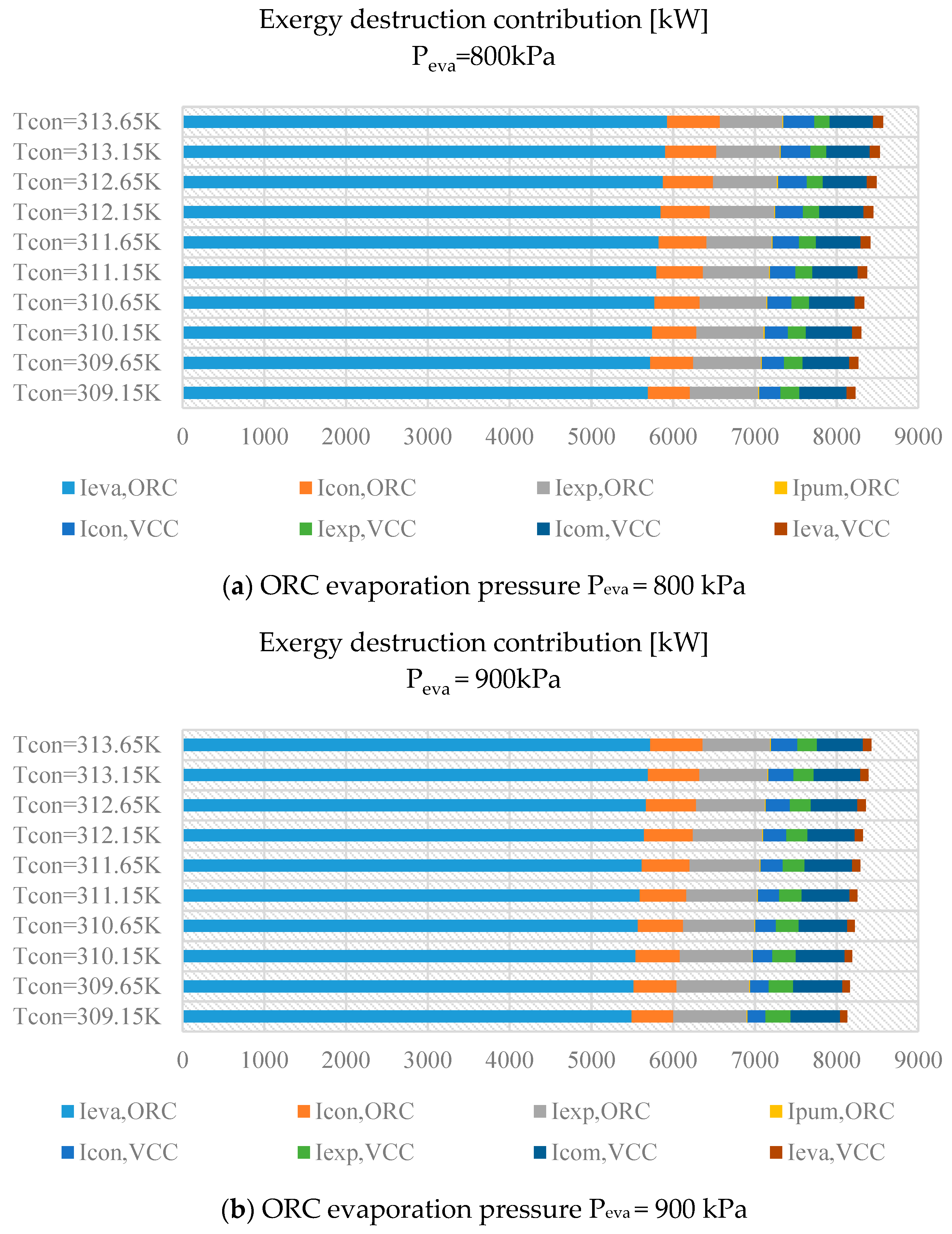
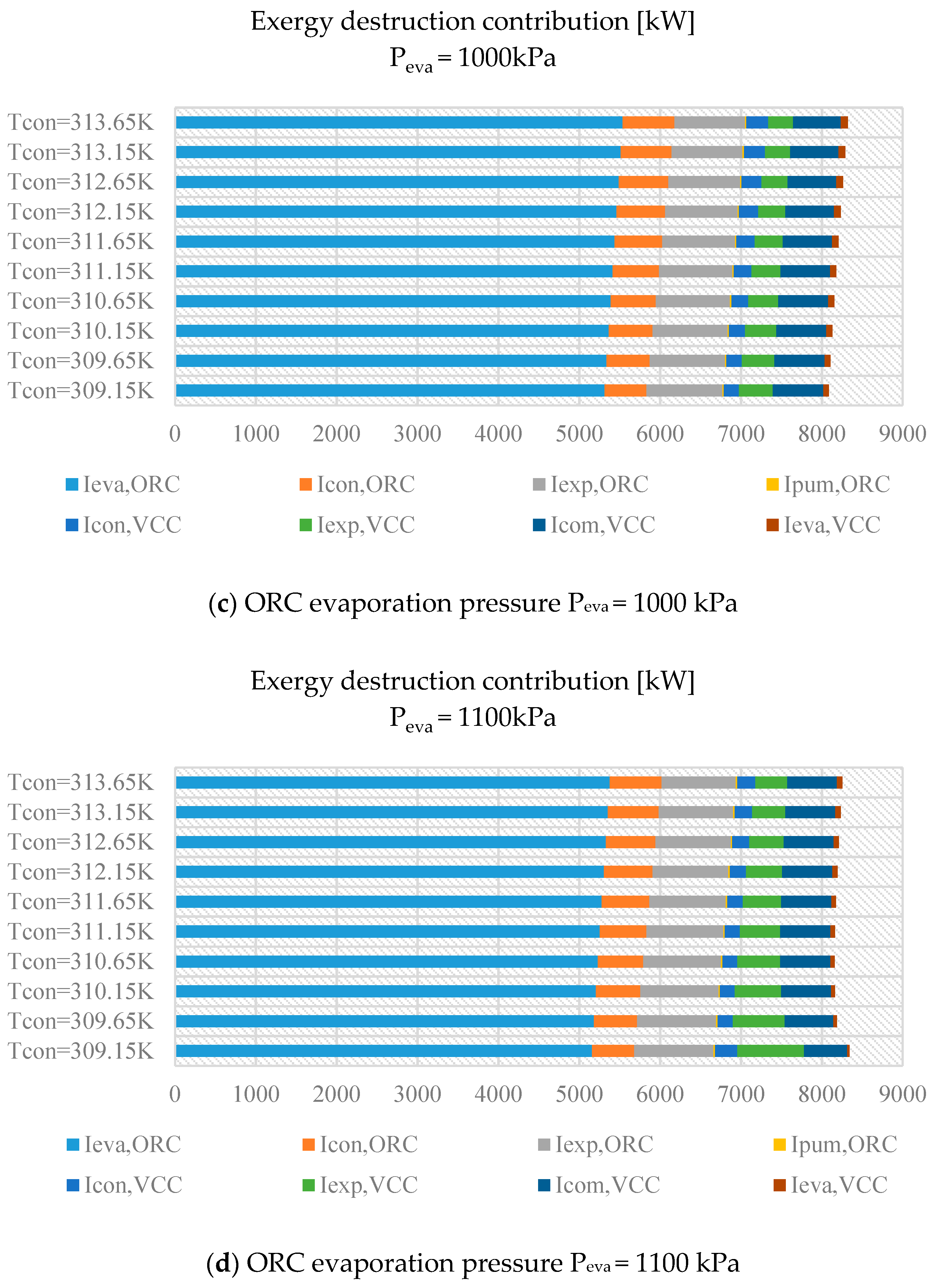
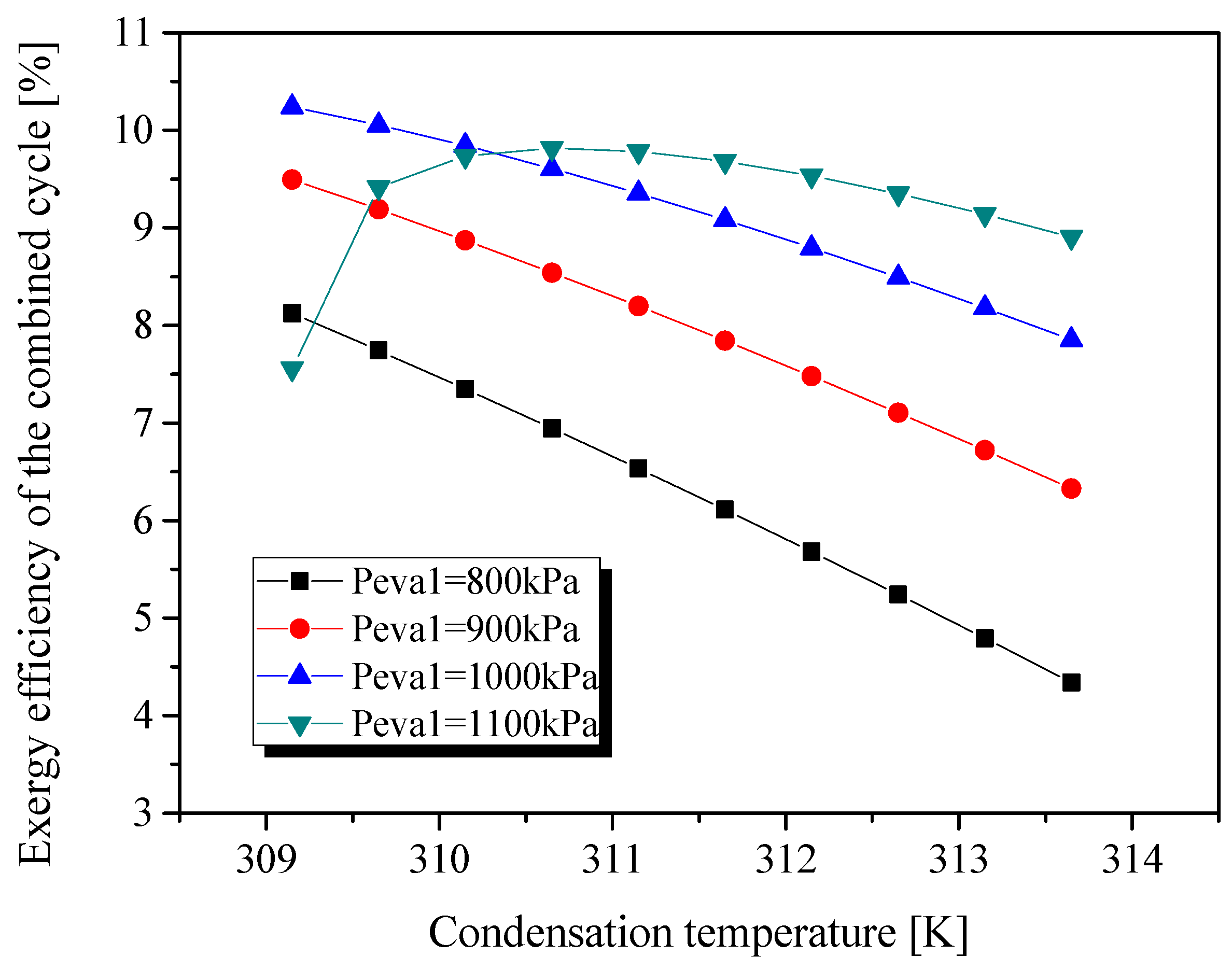
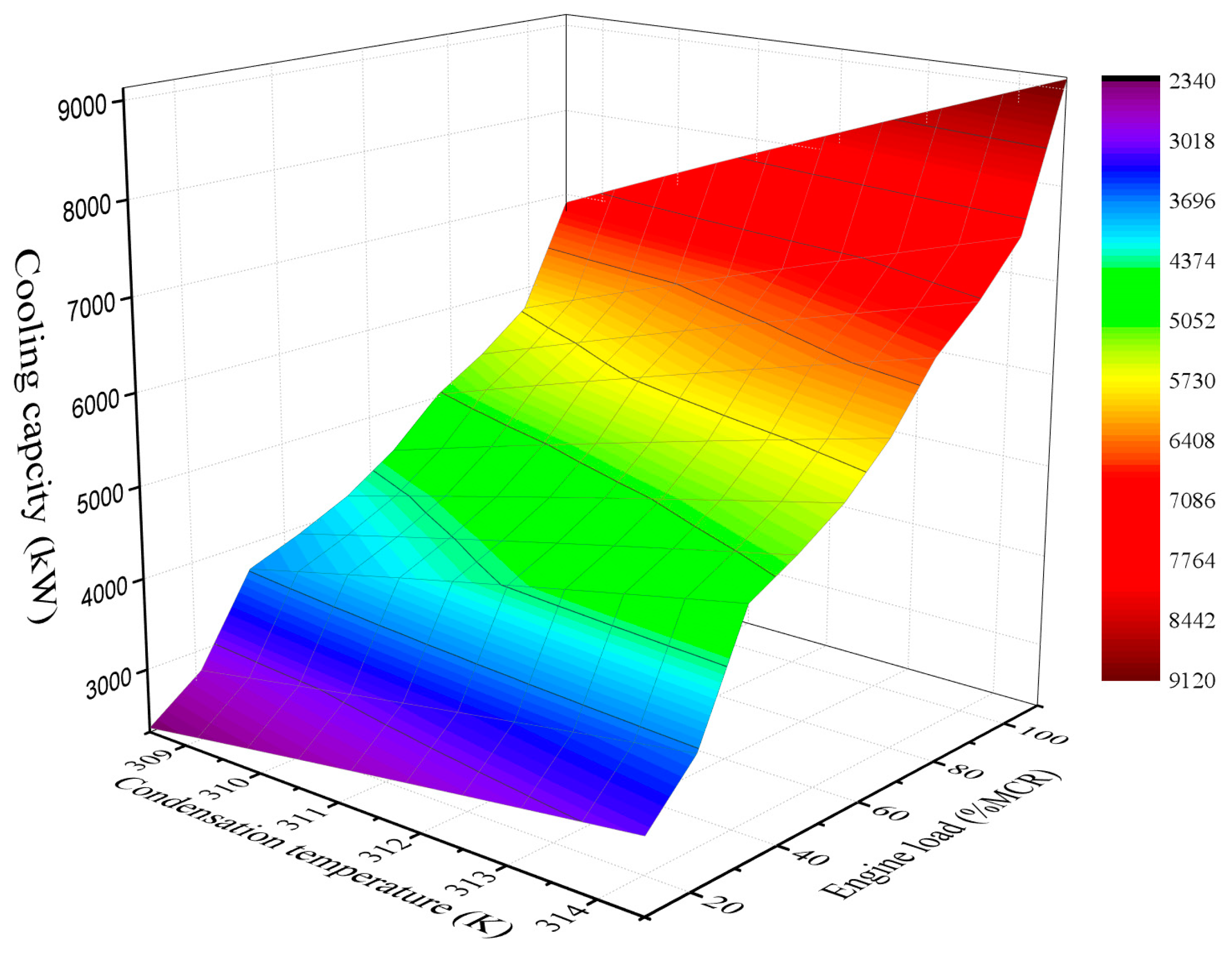
3. Results
3.1. Belt Drive as the Transmission Unit
3.2. Sharing a Common Shaft
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nomenclature | |
| IC | Internal combustion |
| ECCS | Electricity-cooling combined system |
| MCR | Contract maximum continuous rating |
| COP | Coefficient of performance |
| EER | Energy efficiency ratio |
| HFO | Heavy fuel oil |
| PPTD | Pinch point temperature difference |
| ORC | Organic Rankine cycle |
| SRC | Steam Rankine cycle |
| VCC | Vapour compression cycle |
| WHR | Waste heat recovery |
| Symbols | |
| E | Exergy (kW) |
| h | Specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) |
| I | Exergy destruction |
| m | Mass flow rate (kg/s) |
| Q | Heat (kW) |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| W | Power (kW) |
| η | Efficiency |
| Subscript | |
| cond | Condenser |
| exp | Expander |
| exh | Exhaust gas |
| com | Compressor |
| eva | Evaporator |
| ex | Exergy |
| in | Input |
| is | Isentropic process |
| f1 | Working fluid in ORC |
| f2 | Working fluid in VCC |
| pump | Fluid pump |
| out | Output |
| w | Water |
| 0 | Reference environment |
References
- UNEP. Green Economy in a Blue World; Synthesis Report; The WordFish Center Working Papers: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tsitsilonis, K.M.; Theotokatos, G. A novel systematic methodology for ship propulsion engines energy management. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 212–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Liang, Y.; Wei, H.; Tian, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L. A review of waste heat recovery on two-stroke IC engine aboard ships. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidini, G.; di Maria, F.; Generosi, M. Micro-cogeneration system for a small passenger vessel operating in a nature reserve. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, W.K.; Yeh, R.H.; Hong, J.M. Theoretical analysis of cogeneration system for ships. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, G.R.; Hallegraeff, G.M.; Sutton, C. Novel ballast water heating technique offers cost-effective treatment to reduce the risk of global transport of harmful marine organisms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 191, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Theotokatos, G.; Livanos, G. Exhaust gas waste heat recovery in marine propulsion plants. In Sustainable Maritime Transportation and Exploitation of Sea Resources; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 663–671. [Google Scholar]
- Theotokatos, G.; Livanos, G. Techno-Economical analysis of single pressure exhaust gas waste heat recovery systems in marine propulsion plants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2013, 227, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altosole, M.; Laviola, M.; Trucco, A.; Sabattini, A. Waste heat recovery systems from marine diesel engines: Comparison between new design and retrofitting solutions. In Maritime Technology and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 735–742. [Google Scholar]
- Benvenuto, G.; Trucco, A.; Campora, U. Optimization of waste heat recovery from the exhaust gas of marine diesel engines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2014, 230, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.C. Waste heat recovery of organic Rankine cycle using dry fluids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2001, 42, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.V.; Pedersen, E. A review of waste heat recovery technologies for maritime applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 111, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, F.; Gabrielii, C. A feasibility analysis of waste heat recovery systems for marine applications. Energy 2015, 80, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, J.G.; Meroni, A.; Haglind, F. A comparison of organic and steam Rankine cycle power systems for waste heat recovery on large ships. Energies 2017, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Shu, G.; Tian, H.; Liang, X.; Wei, H.; Liu, L. Analysis of an electricity–cooling cogeneration system based on RC–ARS combined cycle aboard ship. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Shu, G.; Tian, H.; Wei, H.; Liang, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Theoretical analysis of a novel electricity–cooling cogeneration system (ECCS) based on cascade use of waste heat of marine engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Shu, G.; Tian, H.; Sun, Z. Investigation of a cascade waste heat recovery system based on coupling of steam Rankine cycle and NH3-H2O absorption refrigeration cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 166, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lior, N. Methodology for thermal design of novel combined refrigeration/power binary fluid systems. Int. J. Refrig. 2007, 30, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouraghaie, M.; Atashkari, K.; Besarati, S.M.; Nariman-Zadeh, N. Thermodynamic performance optimization of a combined power/cooling cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkaya, G.; Vasquez, P.R.; Goswami, D.Y.; Stefanakos, E.; Rahman, M.M. Analysis of a combined power and cooling cycle for low-grade heat sources. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 35, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigmore, D.; Barber, R. Cooling with the Sun’s heat design consideration and test data for a Rankine cycle prototype. Sol. Energy 1975, 17, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peterson, R.; Harada, K.; Miller, E.; Ingram-Goble, R.; Fisher, L.; Yih, J.; Ward, C. Performance of a combined organic Rankine cycle and vapor compression cycle for heat activated cooling. Energy 2011, 36, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peterson, R.; Herron, T. Design study of configurations on system COP for a combined ORC (organic Rankine cycle) and VCC (vapor compression cycle). Energy 2011, 36, 4809–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, E. Working fluids for solar, Rankine-cycle cooling systems. Energy 1980, 5, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, E. Optimum working fluids for solar powered Rankine cycle cooling of buildings. Sol. Energy 1980, 25, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aphornratana, S.; Sriveerakul, T. Analysis of a combined Rankine-vapor-compression refrigeration cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H. Performance analysis and working fluid selection for geothermal energy-powered organic Rankine-vapor compression air conditioning. Geotherm. Energy 2013, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.B.; Li, H.S.; Wang, L.B. Performance analysis and working fluids selection of solar powered organic Rankine-vapor compression ice maker. Sol. Energy 2013, 95, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H. Working fluids selection for fishing boats waste heat powered organic Rankine-vapor compression ice maker. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 50, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancardi, F.R.; Sitler, J.W.; Melikian, G. Development and test of solar Rankine cycle heating and cooling systems. Int. J. Refrig. 1982, 5, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demierre, J.; Henchoz, S.; Favrat, D. Prototype of a thermally driven heat pump based on integrated Organic Rankine Cycles (ORC). Energy 2012, 41, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demierre, J.; Favrat, D.; Schiffmann, J.; Wegele, J. Experimental investigation of a Thermally Driven Heat Pump based on a double Organic Rankine Cycle and an oil-free Compressor-Turbine Unit. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 44, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Cai, L.; Yan, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X. Power management strategy for a parallel hybrid-power gas engine heat pump system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, B.; Shi, W. Energy-saving analysis of a hybrid power-driven heat pump system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Al-Tameemi, M.; Yu, Z. Investigation of a gas-fuelled water heater based on combined power and heat pump cycles. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 1476–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Bian, X.; Qian, W.; Pan, M.; Ban, Z.; Yu, Z. Theoretical analysis of a regenerative supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle/organic Rankine cycle dual loop for waste heat recovery of a diesel/natural gas dual-fuel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 197, 111845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships-Updated 2000 Study on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Ships Phase 1 Report; MEPC 58/INF. 6; International Maritime Organization (IMO): London, UK, 2008.
- Technical File for Hyundai-Man B&W 12K98MC-C Mk6; Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.: Ulsan, Korea, 2006.
- Poling, B.E.; Prausnitz, J.M.; O’Connell, J.P. The Properties of Gases and Liquids; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, G.; Liu, L.; Tian, H.; Wei, H.; Liang, Y. Analysis of regenerative dual-loop organic Rankine cycles (DORCs) used in engine waste heat recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, J.; Yu, G.; Liang, Y.; Tian, H.; Shu, G.; Markides, C.N. Organic Rankine cycle systems for engine waste-heat recovery: Heat exchanger design in space-constrained applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 111968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
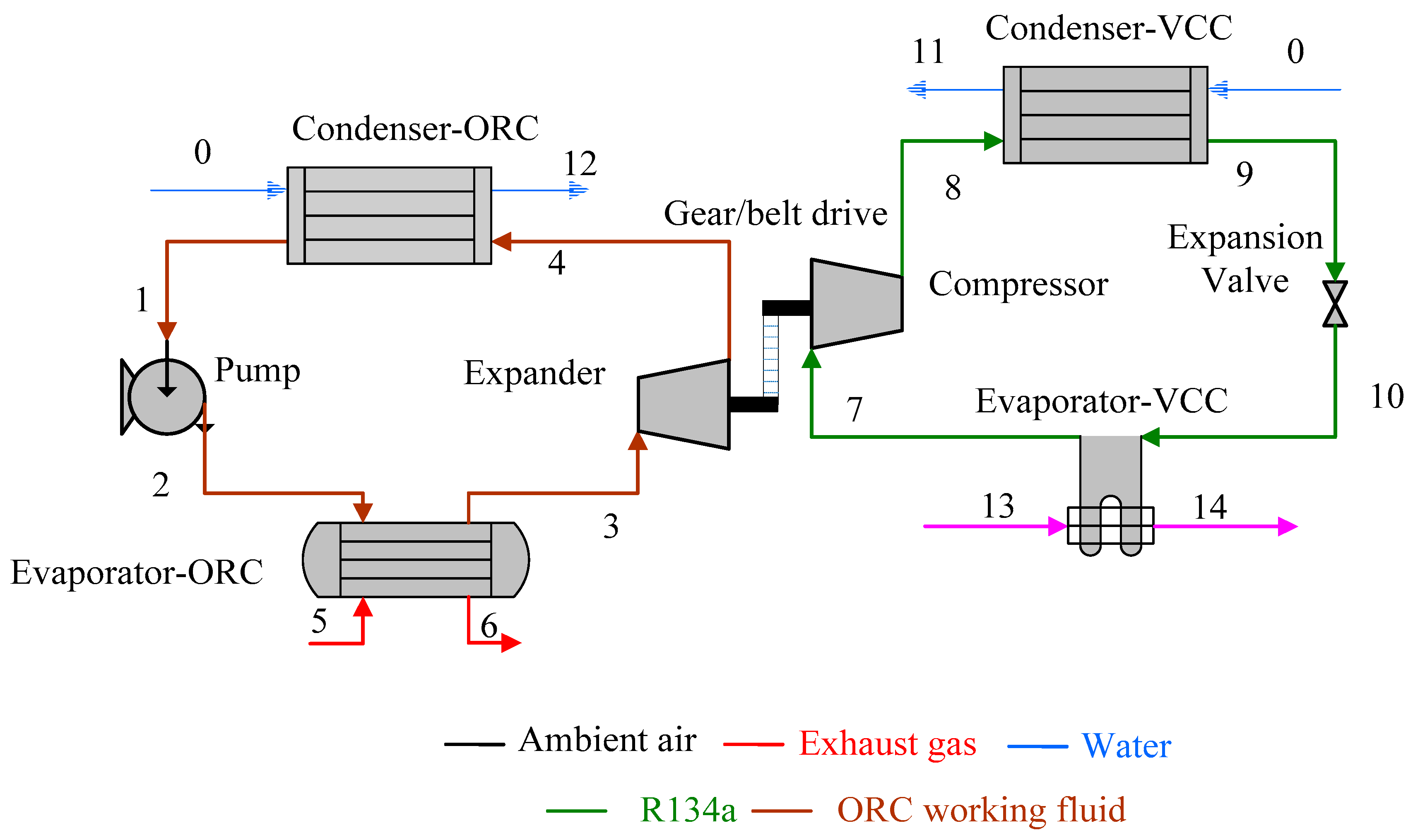
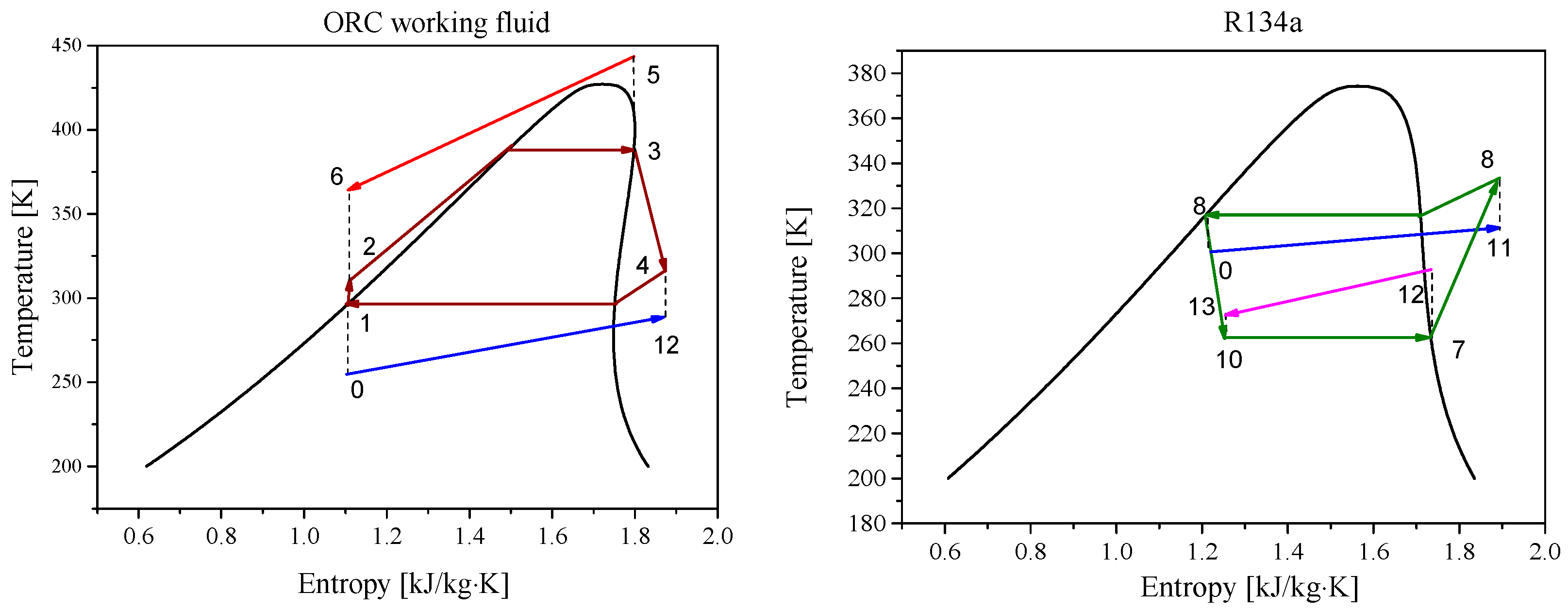
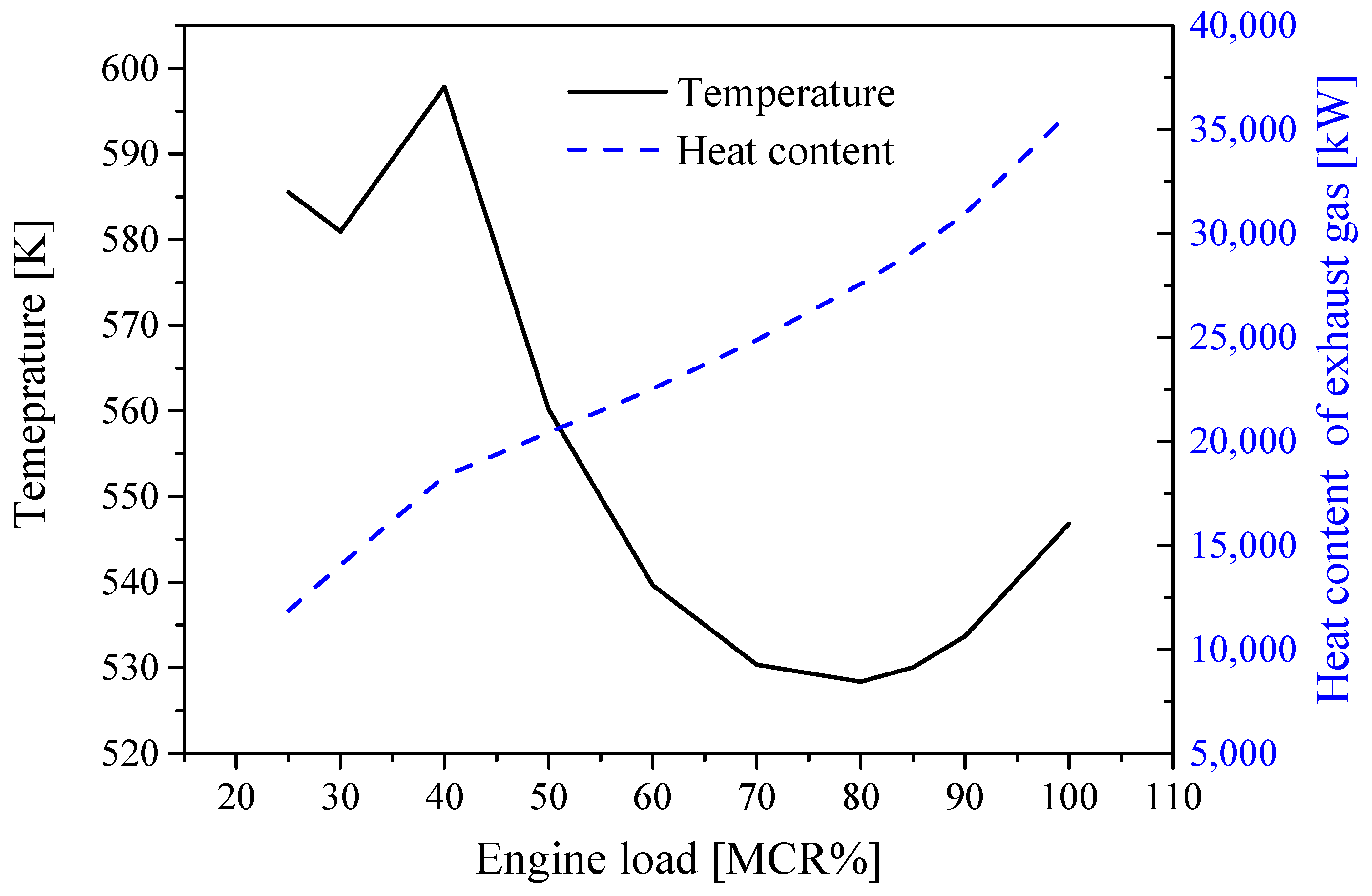
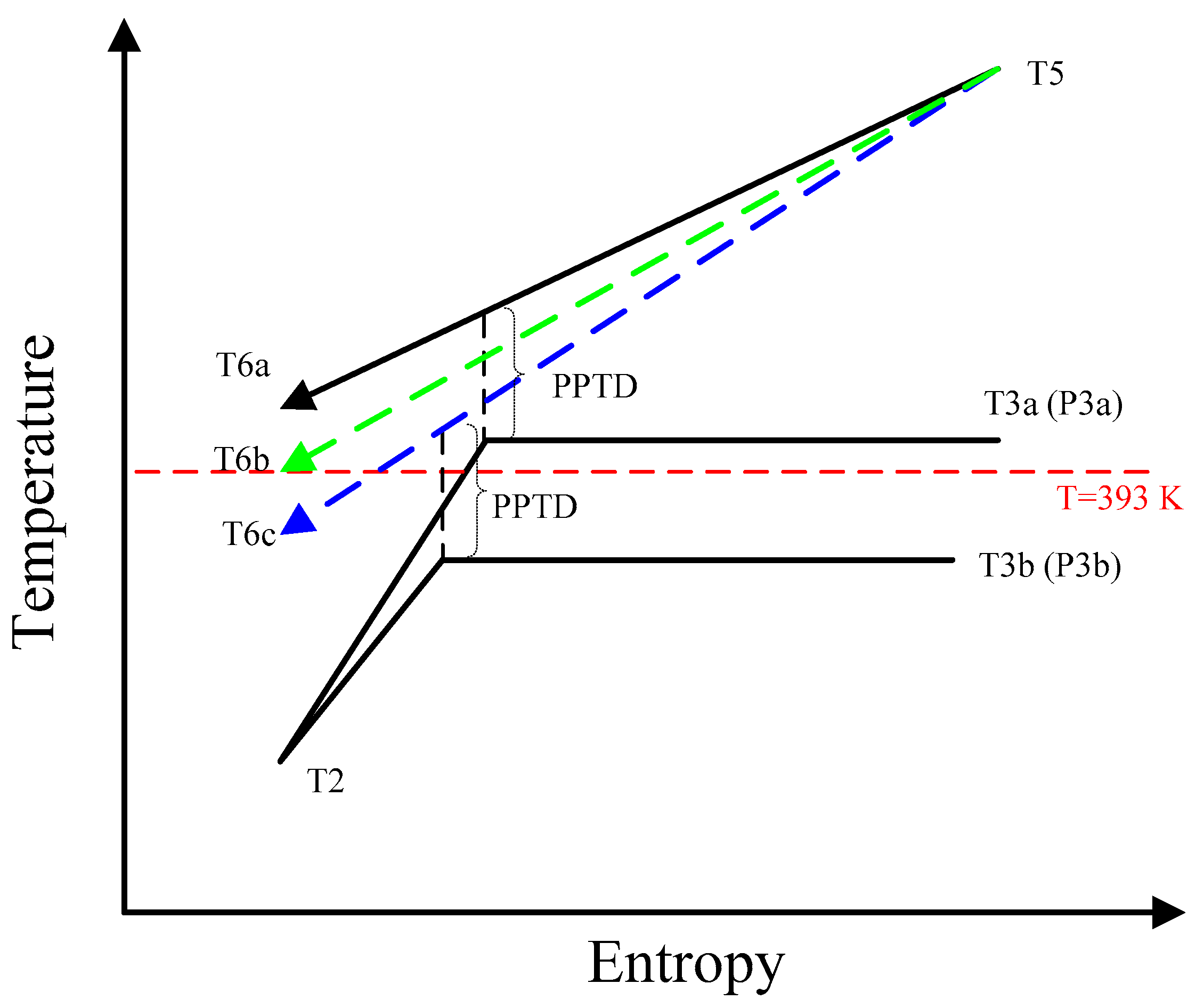

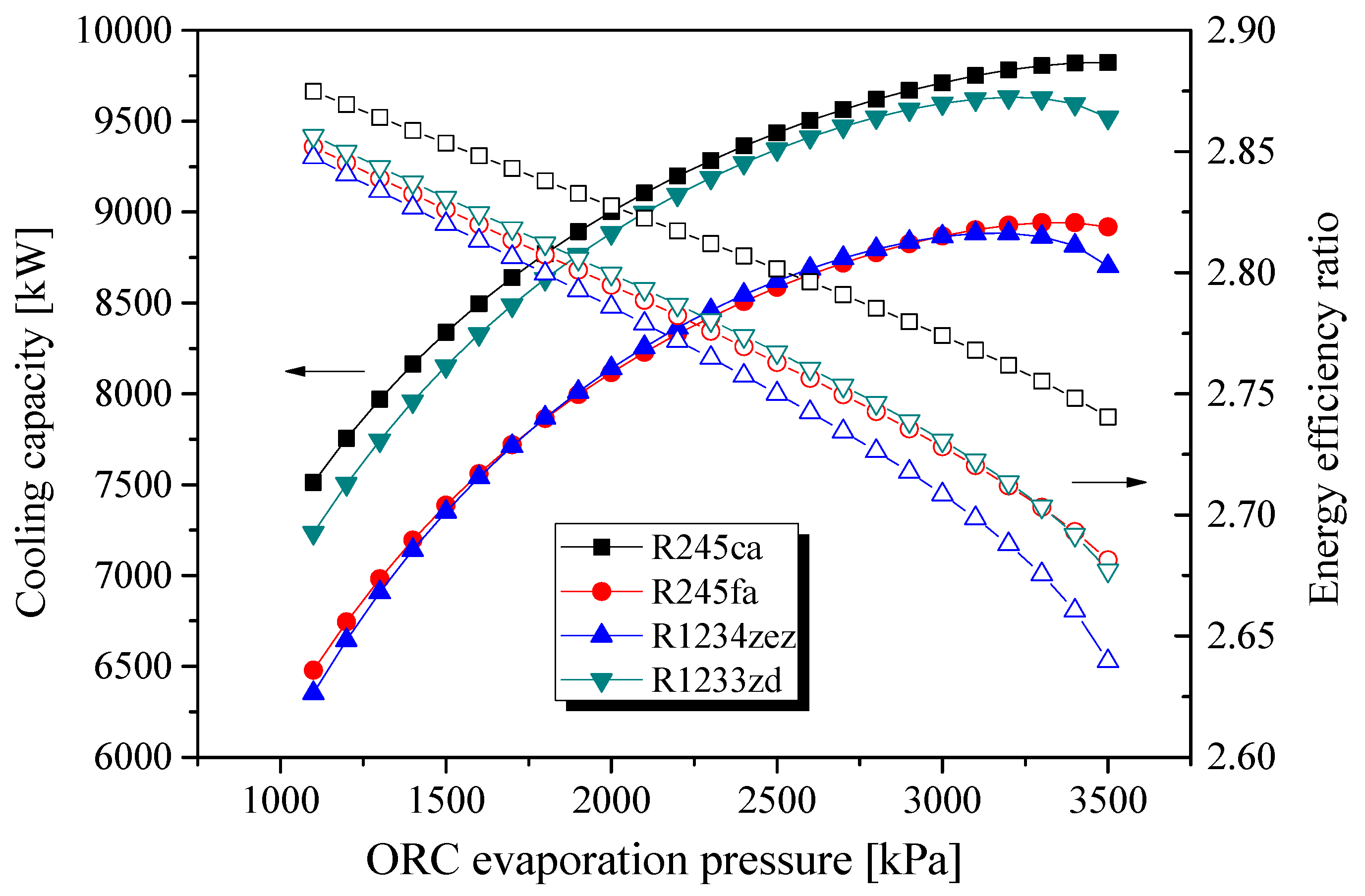
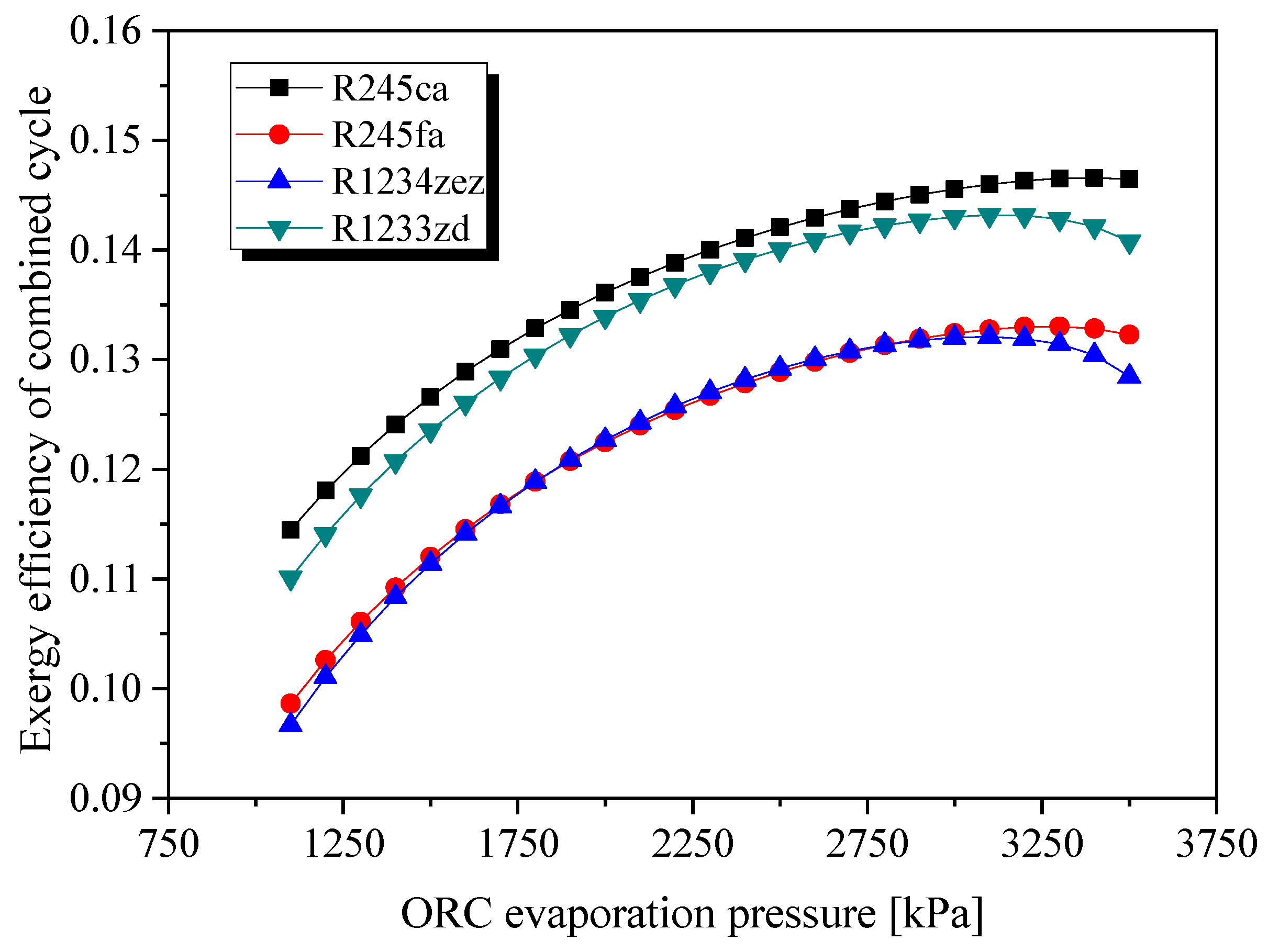
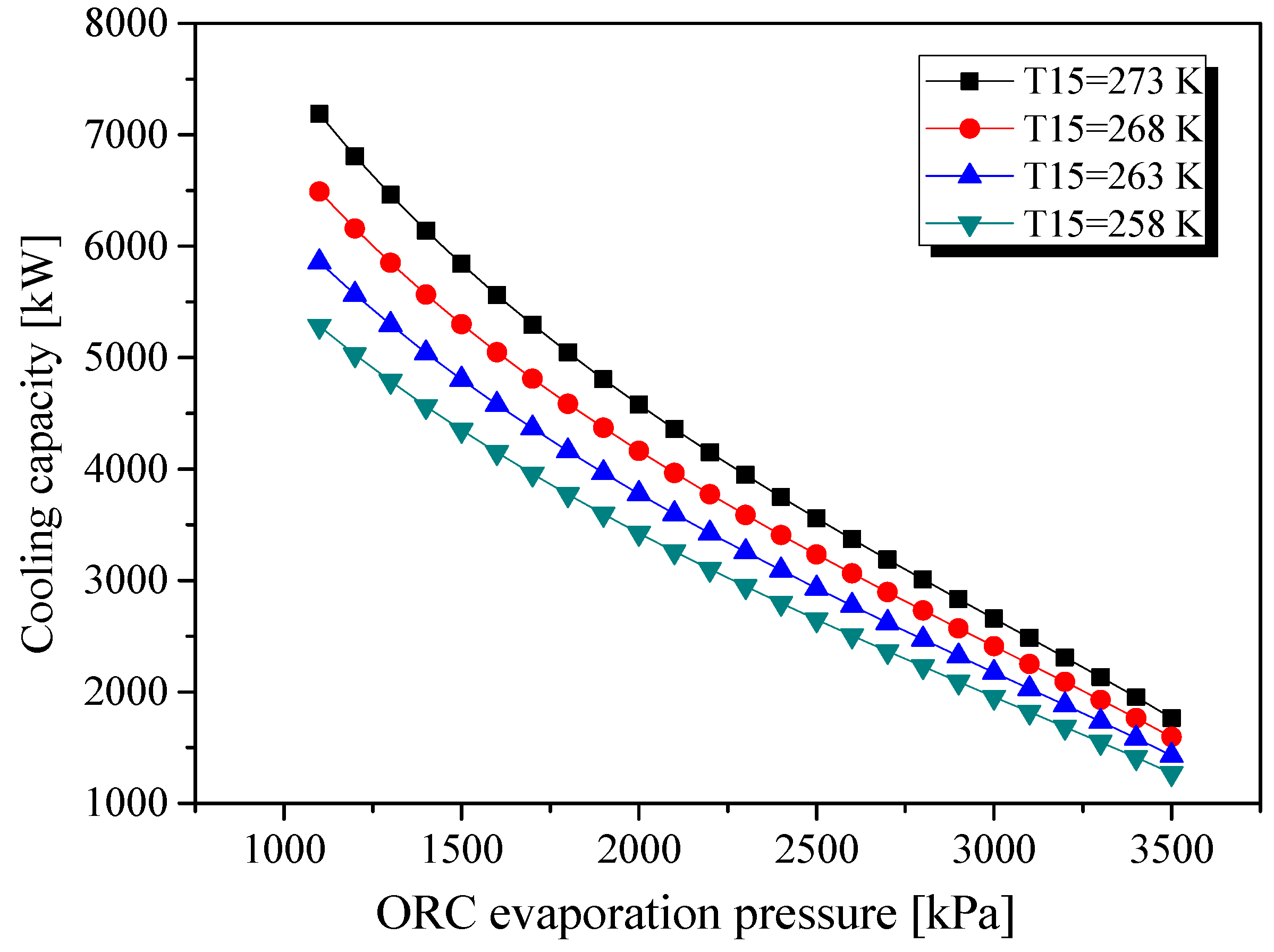

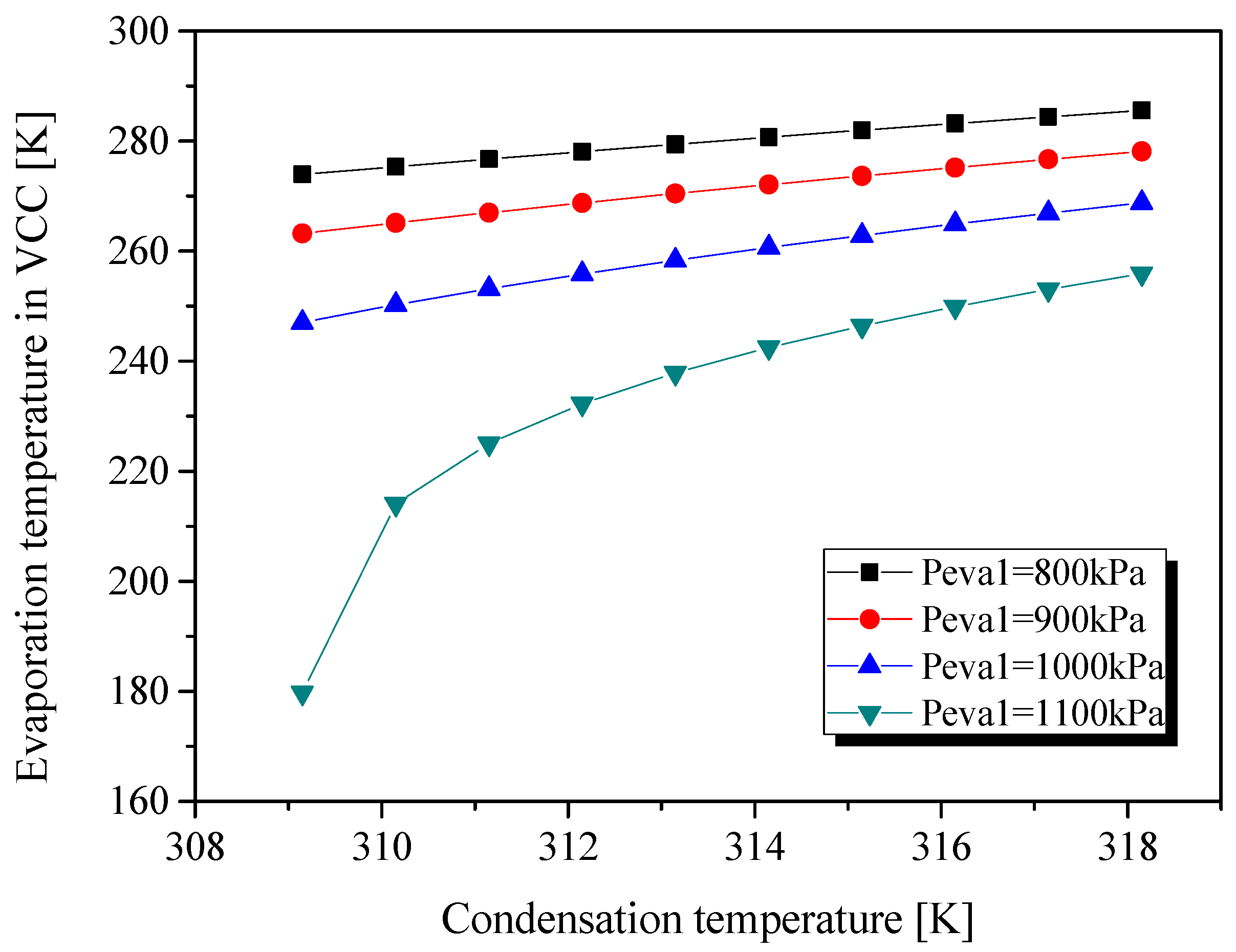
| Parameters | Belt Drive | Common Shaft |
|---|---|---|
| ORC working fluid | R245ca | R1233zd |
| VCC refrigerant | R134a | R134a |
| Cooling capacity at 263K [kW] | 9823 | 6902 |
| ORC evaporation pressure [kPa] | 3500 | 900 |
| Energy efficient ratio (EER) | 2.74 | 3.06 |
| Power output of expander [kW] | 3584 | 2180 |
| Total exergy destruction [kW] | 7482 | 8132 |
| ORC thermal efficiency [%] | 13.79 | 9.10 |
| Exergy efficiency [%] | 13.10 | 9.50 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, W. A Waste Heat-Driven Cooling System Based on Combined Organic Rankine and Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycles. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204242
Liang Y, Yu Z, Li W. A Waste Heat-Driven Cooling System Based on Combined Organic Rankine and Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycles. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Youcai, Zhibin Yu, and Wenguang Li. 2019. "A Waste Heat-Driven Cooling System Based on Combined Organic Rankine and Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycles" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204242
APA StyleLiang, Y., Yu, Z., & Li, W. (2019). A Waste Heat-Driven Cooling System Based on Combined Organic Rankine and Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycles. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204242




