Featured Application
This work can contribute to the knowledge on the behavior of tungsten in the soil in relation to its potential transfer into the food chain through plant uptake. The results are aimed to bring the attention of the legislator to this element, which is completely neglected in environmental legislation.
Abstract
Tungsten is largely used in high-tech and military industries. Soils are increasingly enriched in this element, and its transfer in the food chain is an issue of great interest. This study evaluated the influence of soil characteristics on tungsten uptake by Zea mays grown on three soils, spiked with increasing tungsten concentrations. The soils, classified as Histosol, Vertisol, and Fluvisol, are characteristic of the Mediterranean area. The uptake of the element by Zea mays was strictly dependent on the soil characteristics. As the pH of soils increases, tungsten concentrations in the roots and shoots of the plants increased. Also, humic substances showed a great influence on tungsten uptake, which decreased with increasing organic matter of soils. Tungsten uptake by Zea mays can be described by a Freundlich-like equation. This soil-to-plant transfer model may be useful in promoting environmental regulations on the hazards of this element in the environment.
1. Introduction
Tungsten (W) is a metal characterized by a very low abundance in the Earth’s crust, and thus occurs in soils in small concentrations of less than 3 mg kg−1 [1]. Tungsten occurs naturally in several minerals such as wolframite (Fe,Mn)WO4, hübnerite MnWO4, ferberite FeWO4, and scheelite (CaWO4). It is used in a variety of industrial activities for the production of high-tech components [2] due to its high melting point and resistance to corrosion.
Tungsten has also been used in several military applications as a substitute for the dangerous depleted uranium [1,3]. The most important use of tungsten is in the production of tungsten/nylon bullets as alternatives to lead-based munitions [4]. Soils are an important sink and source of tungsten in the environment as a result of the transport of dust deriving from erosion processes. These last have been recognized as one of the most important contributions to the dispersion of tungsten into the environment [1].
In soil, tungstate is the most stable form of the element. This oxyanion is chemically similar to molybdate, however, while molybdenum is an essential element [5], tungsten is not an essential micronutrient, and it has been historically regarded as inert in the soil environment and classified as nontoxic for human health [6].
However, several ecotoxicological studies have discovered that under certain environmental conditions, tungsten compounds can be solubilized and enter the biogeochemical cycles [7,8]. Occupational studies on workers’ exposure in industry where tungsten is used have revealed several adverse health effects [9]. The presence of tungsten in the atmosphere has been particularly studied in Nevada, due to the possible link between tungsten in the atmosphere and cases of childhood leukemia [10,11].
Knowledge regarding the effects of tungsten in the soil, on its transfer in the food chain, and thus on human health is still incomplete [1]. In some cases, tungsten has been found to be nontoxic and substantially inert in the soil [12], whereas in other studies, very negative hypotheses have been put forward on the possible action of tungsten in the formation of neoplasms in animal cells [7]. The growing interest in this element is further highlighted by several studies on the impact of W on soil microorganisms. Several works have shown that under certain conditions, the presence of tungsten increases the microbial biomass [13]. Conversely, in other cases, negative impacts on microbial activity have been verified [14].
The increase in the industrial and military use of tungsten has become of interest due to its potential entry into the food chain following uptake by agricultural crops. Moreover, in agricultural soils tungsten is also added to fertilizers [15], and may be present in sewage sludge due to its presence in many household products [16]. Many plants such as oats, radishes, and lettuce are able to grow in soil with high tungsten concentrations [17] and can accumulate significant quantities of the metal also due to its similarity with molybdenum [14]. At high concentrations, tungsten has been reported to decrease root elongation in Pisum sativum and Gossypium hirsutum [18,19,20]. High concentrations of tungsten in plants have been reported for species growing on the soils of abandoned mine [21,22,23]. Near tungsten mines, its transfer from soil to rice has been reported as a possible health risk via the food chain [24]. In general, the tungsten content in roots is higher than that in the aerial parts of plants [25,26].
Studies on tungsten are very lacking in Italy where the potential problems arising from this element are completely neglected. This element is not taken into consideration in any environmental legislation, nor in the regulations that define the quality of fertilizers to be used in agriculture. It therefore seems no longer unpostponable to study the behavior of this element in Italian soils with a view to protecting the environment and human health.
The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of different soil characteristics pH, organic matter (O.M.), and texture on tungsten uptake by Zea mays, and to provide a simple model to evaluate the uptake of increasing tungsten concentration in soil. Zea mays was selected due to its relevant production in the Mediterranean area, which highlights the growing interest in this crop. In Italy, the average production for over a decade has been ~9.5 t ha−1, which is higher than the mean European production. The experiment was carried out at a greenhouse scale by growing the plants on three agricultural soils characteristic of Mediterranean areas spiked with increasing concentrations of sodium tungstate. The concentrations were chosen to be close to natural soil values conditions and to take into account potential anthropogenic contamination, which can reach 2000 mg/kg in particular areas [24]. The chosen range of concentrations can be considered environmentally significant due to the increase in electronic waste, which is a feature of all industrialized countries [14]. Obtained results show that soil properties regulate tungsten plants uptake, which increases with increasing pH and decreasing organic matter content.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soils
Samples were collected from three Italian soils, classified as Histosol (soil A), Vertisol (soil B), and Fluvisol (soil C), according to FAO classification. The soil samples were air-dried, sieved at 2 mm, and analyzed for pH [27], organic matter [28], and texture [29]. The studied soils characteristics are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the soils A, B, and C.
2.2. Experimental Soils
Increasing amounts of Na2WO4·H2O solutions were added to each soil to obtain final concentrations of 10, 30, 40, 50, and 100 mg kg−1 of tungsten.
To promote the interactions between soil and the added tungsten salt and to simulate the ageing effects, the soils were incubated at 50% maximum water holding capacity for 12 months at room temperature.
During this period, the spiked soils were maintained in loosely covered polypropylene containers. To obtain the greatest homogeneity, once a week soils were gently mixed by a shovel, and watered with deionized water once a month as necessary [30].
At the end of this period, before starting the microcosm experiments the pH of each spiked soils was determined [27] to check if there were any changes in the values of this parameter. No changes were detected.
To determine tungsten in the soil solution, deionized water was added to each spiked soil samples (1:0.5 soil/water), and after 24h of incubation, tungsten in soil solution was evaluated by centrifugation at 21,000 g for 15 min [30]. Three replicates for each concentration were carried out.
2.3. Microcosm Experiment
The experiment was carried out at a greenhouse scale with a 12h photoperiod (320 μmol m−2 s−1 photosynthetic active radiation). Microcosms were filled with 400 g of soil. Six Zea mays seeds per pot were sown. Three replicates for each concentration were carried out with controls (CT) running simultaneously. During the growing period, plants were watered daily. The whole experiment lasted 60 days. At plant harvest, the aerial parts were separated from the roots and pooled to a composite sample representative of each pot. All samples were washed with deionized water. The roots were further washed in an ultrasound bath (Branson Sonifier 250 ultrasonic processor, Branson Ultrasonics Corporation, USA) for 10 min, to eliminate any soil particles remaining on root surfaces. The dry biomass of vegetal samples was then gravimetrically determined after the samples had been dried in a ventilated oven at 60°C until a constant weight was achieved.
2.4. Tungsten Analysis in Plants and Soil
The dry plant samples were ground, homogenized, and digested with an acid mixture (HNO3 + H2O2) for tungsten determination, according to the procedure described by Poykio et al. [31] and Oburger et al. [30].
Concentrations of tungsten in spiked soils and soil solution were determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICPOES Varian AX Liberty, Milano, Italy). Due to the specific tungsten properties in soils that can lead to the formation of insoluble species, the procedure based on the addition of phosphoric acid to nitric acid developed by Dermatas et al. (2004) [32] and reported by Bednar et al. [33] was used. All chemicals used were of reagent grade.
Quality assurance and quality control were carried out by testing a standard solution every 10 samples. Because no reference plant material for tungsten is available, for quality control the procedure developed and described in detail by Oburger et al. [30] was strictly followed using Oriental Basma Tobacco Leaves, INCT-OBTL-5, as reference material. As a certified reference soil material, NIST SRM 2710 was used to control the quality of the analytical system. The detection limit for tungsten was 0.05 mg L−1. The recovery of spiked samples ranged from 95 to 101%, with an RSD of 1.84 of the mean.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using STATISTICA version 6.0 (Statsoft, Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). Treatment effects were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Differences among means were compared and a post hoc analysis of variance was performed using the Tukey Honestly Significant Difference test (p < 0.05).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biomass Production
The biomass of plants grown in the three soils with different tungsten concentrations is reported in Table 2. Shoot and root productions are considered separately.

Table 2.
Biomass production (mg dry weight) of shoot and root grown in the soils with increasing tungsten concentrations. CT is the original soil. Values are the mean ± standard deviation.
Despite the different characteristics, such as pH and organic matter content, no significant differences in biomass were observed among the three soils. At the tungsten concentrations used in this experiment, no differences in biomass production were found between the control and tungsten enriched soils. The results are in agreement with previous findings for another species, Triticum aestivum, which reported that biomass was not influenced by low tungsten concentrations in soil [34,35]. A reduction in biomass production was discovered in soils only with very high tungsten concentrations of up to 5000 mg kg−1 for Glycine max [30] and 2600 mg kg−1 for Helianthus annuus [26]. Under the experimental conditions adopted, tungsten did not show any visual toxicity effects on plants.
3.2. Tungsten Uptake by Plants
The concentration of tungsten in plants grown in the control soils (CT) was always under the limit of detection, thus the data are not reported. Considering the plants grown in the spiked soils, the uptake of tungsten was lowest in soil A and highest in soil C, with intermediate values in soil B. Data are reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Tungsten concentration in shoots and roots of Zea mays grown in the different spiked soils. Values are the mean ± standard deviation.
Considering the mean of the five concentrations (from 10 to 100 mg kg−1), the tungsten concentration in the root portions increased with respect to soil A by an average factor of 2 in soil B and of 9 in soil C, respectively.
A similar trend was found in the aerial part of the plants with an increase with respect to plants grown in soil A by an average factor of 3 and 15 in plants grown in soils B and C, respectively.
The effects of tungsten on the physiological responses of plants were not studied, unless exclusively concerning the production of biomass. There are many studies that address these aspects to which refer for further deepening [30,36]. Finally, we considered the dose–uptake relationship and the internal distribution of tungsten between the roots and shoots, which may have occurred within the time frame of this experiment. Table 3 clearly shows that the amount of tungsten in the plants differed significantly in the three soils at each tungsten concentration. Regardless of the type of soil, tungsten mainly accumulates in the roots, probably as a protective action, as tungsten does not play any essential role in the plant [37]. In fact, the translocation factor (TF), defined as the ratio between the tungsten concentration in the shoots and in roots, is always lower than 1 (Figure 1).
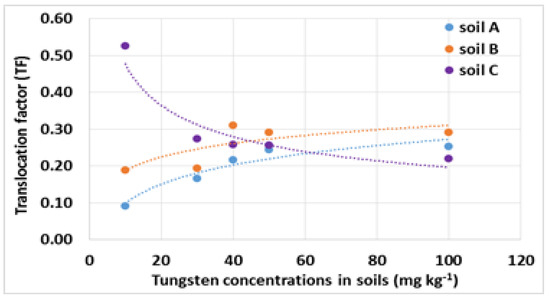
Figure 1.
Trend of translocation factor at increasing tungsten concentrations in soils.
Taken as the average at the different concentrations of tungsten in the soil, the TF values ranged from 0.19 (soil A) to 0.30 (soil C), with an intermediate value (0.25) in soil B. A different behavior of TF was observed between the three soils. It is worth noting that in soil C, as the concentration of tungsten increased, the TF decreased. Since, TF describes the passage of tungsten from the roots to the aerial part of the plants, the results obtained suggest that in the presence of high concentrations of tungsten in soils, the roots play a protective role acting as a filter and accumulating organ.
These results are in agreement with those reported for Raphanus sativus L. (radish) grown in an alkaline substrate [38]. Conversely, in soil A, as the concentration of tungsten increases, the TF increases. Soil B showed an intermediate trend; in fact, the TF increases up to a concentration of 40 mg kg−1 of tungsten added to the soil, and then decreases. The soil plant barrier concept [39] does not appear to be entirely applicable to tungsten. In fact, tungsten is not strongly held by the soil surfaces and can be absorbed by the plant roots.
3.3. Influence of Soil Characteristics on Plant Uptake
There are few studies on tungsten uptake by plants and the reported tungsten concentrations in plants are highly variable due to the differences between plant species and experimental conditions [26,30,34]. Although in hydroponic experiments, the tungsten uptake can be directly linked to the concentration of metal in solution and to specific tolerance mechanisms, the interpretation of the phytoavailability in soil is more complex since it is essentially determined by tungsten species in the soil liquid phase. It is thus fundamental to evaluate the effects of soil properties on tungsten solubility and plant uptake, in particular of soil pH, which is considered the most important parameter that determines the amount and the forms of tungsten in soil solutions [9].
Considering the different soil pH, it appears that by increasing pH, plant uptake significantly increased (Figure 2).
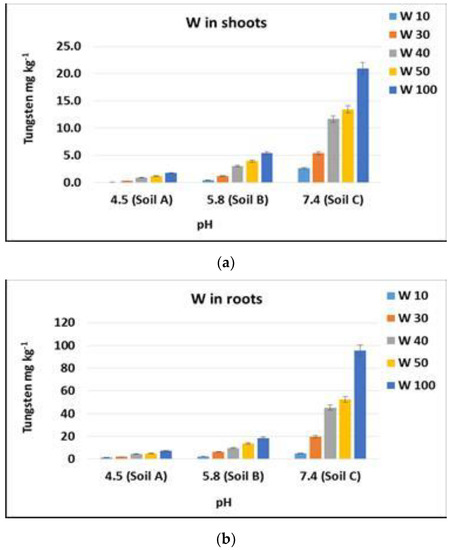
Figure 2.
Mean values of tungsten concentrations in plants in relation to pH of the different soils. Bars indicate standard deviation. (a) shoots; (b) roots.
At the highest concentration (100 mg kg−1) of tungsten in soil, in plants grown in soil C with a pH value of 7.40, the amount of tungsten in the root portion (95.5 mg kg−1) was approximately thirteen times greater than that (7.1 mg kg−1) in the roots of plants grown in soil A. The same trend was found by comparing the concentration of tungsten in the roots of plants grown in soil B (18.6 mg kg−1) and soil A (7.1 mg kg−1). In this case, the concentration increased by more than twice as the soil pH increased from 4.50 to 5.80. Finally, the concentration of tungsten in the roots of plants grown in soil C increased by 5.1 times compared to that found in the roots of plants grown in soil B (from 18.6 to 95.5 mg kg−1).
The aboveground parts of the plant behaved similarly. As the pH increased, from soil A (4.5) to soil C (7.4), the concentration of tungsten in the aerial part of the plants increased at each concentration of tungsten in the soil. This increase was evident above all at the highest tungsten concentration (100 mg kg−1), from 1.8 to 21 mg kg−1 of tungsten in the aerial part of the plants grown respectively in soils A and C, with an increase of about 12 times. In soil B, the concentration of tungsten in the aerial part of the plants was ~5.43 mg kg−1, with an increase with respect to soil A of approximately three times. In the aerial part of the plants grown in soil C, the amount of tungsten was about four times higher than that in plants from soil B.
Increasing pH promotes the deprotonation of soil surfaces, thus reducing the retention of tungstate ions in the solid phase of soil [40]. The consequent increase in tungsten in the soil solution led to an increase in bioavailability and therefore a higher uptake by the plants. The greatest uptake occurred in the Fluvisol (soil C), which is characterized by alkaline pH values and a low content of organic matter, conditions that are very common in soils of the Mediterranean area.
The organic matter is another parameter that seems to play a key role in the absorption of tungsten by plants. Figure 3 reports the uptake trend in relation to the different values of organic matter in the soils.
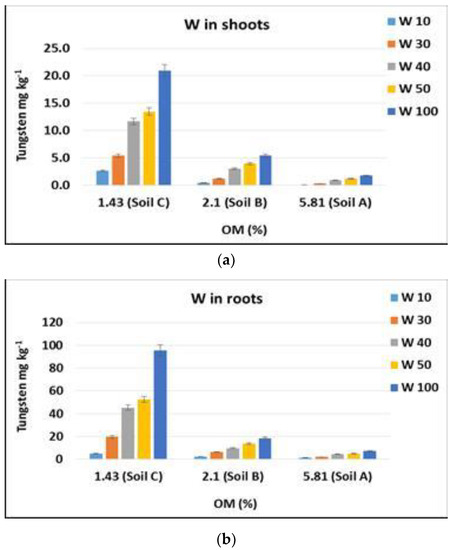
Figure 3.
Mean values of tungsten concentrations in plants in relation to organic matter (OM%) of the different soils. Bars indicate standard deviation. (a) shoots; (b) roots.
The data reported in Figure 3 show that the different organic matter content in the three soils influences the concentration of tungsten in the aerial part and in the roots of the plants. As the amount of organic matter increases, the concentration of tungsten in plant tissues decreases. The action of organic matter can be ascribed to the adsorption reactions of tungstate on humic materials [41], with the formation of stable complexes [42] that reduce the tungsten mobility and bioavailability in soil. This trend is particularly notable in soil A due to the specific characteristics of this Histosol: low pH with a high organic matter content.
Humic compounds can greatly influence the distribution of metallic elements, such as tungsten, between the solid and liquid phase of the soil. This is also in relation to the environmental variations in the soil, such as dynamic redox conditions [43], that can modify the interactions between humic compounds and the surfaces of oxides and hydroxides of iron on which the metal can be adsorbed. Similar to what was found in the case of arsenic and antimony in the soil [44,45,46], organic materials with a high binding capacity, strongly influence the adsorption of anions on variable charge minerals in soils.
The content of tungsten in plants does not seem to be linked to the texture of the soils. For example, Figure 4 reports the uptake trend in relation to the clay content of the three studied soils. The highest clay content in the Vertisol (Soil B) does not influence plant uptake. Similar trends were also obtained considering the plant tungsten concentration in relation to the silt and sand fraction of the three soils (data not reported).
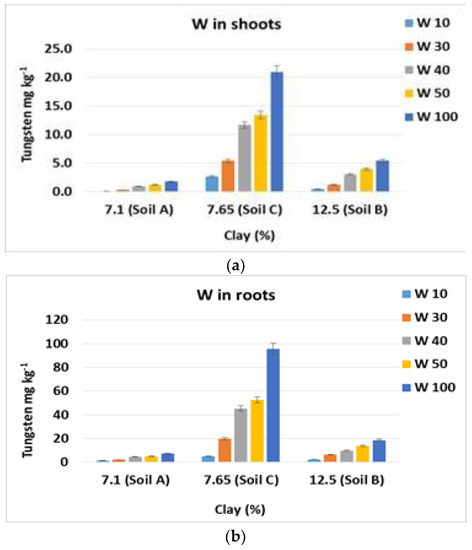
Figure 4.
Mean values of tungsten concentrations in plants in relation to clay content of the different soils. Bars indicate standard deviation. (a) shoots; (b) roots.
Another interesting aspect to tackle is the trend in plant uptake of tungsten from the soil. In the study of plant uptake from soil, there is often an assumption of linearity: the concentration of a substance in plants increases with an increasing of its soil concentrations. However, deviation from linearity has been observed in several contaminant uptake studies [47,48,49]. Plants generally take up elements more efficiently at low than at high soil concentrations, thus deviating from linearity with a decrease in uptake with increasing soil concentrations. The use of nonlinear functions to take into account this behavior has been proposed by several authors [48,50,51].
To evaluate tungsten uptake, it may be useful to estimate the increase in concentration in plants with increasing both soil concentrations and soil solution concentrations. The trend of tungsten uptake for shoots and roots was analogous in both cases, and it is reported in Figure 5, as an example, in relation to soil solution concentration.
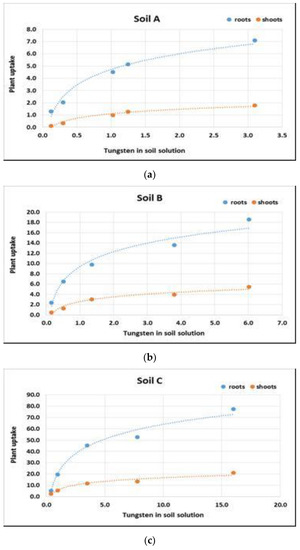
Figure 5.
Trend of tungsten uptake for shoots and roots at increasing W concentrations in soil solution. Data are expressed as mg kg−1. (a) Soil A; (b) Soil B; (c) Soil C.
Also, in this experiment, the increase in tungsten in the plants was not linearly correlated with an increase in tungsten concentration in soil. The uptake of tungsten by the plants, in relation to the concentration of the element in the soil, and in the soil solution although not far from linearity, is described more accurately by a trend that can be modeled using a Freundlich-like equation. The absorption is higher when the concentration in the soil is lower, whereas it is reduced when the concentration of an element in the soil increases.
In recent years, models of plant uptake have been proposed for organic [52,53] and inorganic [54,55] contaminants at contaminated sites to define the risk to human health.
In agricultural soils, where the concentration of potentially toxic elements is much lower, simpler models can be successfully used to provide useful information on the soil to plant transfer process. One of the models is based on the use of a Freundlich-like equation to evaluate plant uptake in the presence of increasing quantities of an element. This approach has been successfully used also in the case of contaminated soils [56].
The Freundlich-like equation (1):
where q is the tungsten concentration in plants (mg kg−1) and C is the tungsten concentration in the soil or soil solution (mg kg−1).
It is important to underline that no thermodynamic value can be attributed to the parameters of the Freundlich-like equation, which can be used exclusively as an operational tool to relate plant uptake and tungsten soil concentration. In broad terms, similarly to the Freundlich equation, K can be considered as the uptake capacity (a larger K indicates a greater uptake).
The Freundlich parameters (Table 4) can be estimated from the linearized form of the equation (2):

Table 4.
Relationship between tungsten concentration in shoots and roots and tungsten concentration in soil. Parameters of the Freundlich-like model.
By operationally using the Freundlich model parameters, we can infer that the uptake capacity increased when the value of K was increased. As expected, the results from this model confirm that the uptake always increased with increasing soil pH due to the alkaline pH of soil influencing the desorption of tungsten from soil surfaces, and its release in soil solution. The coefficient 1/n has been interpreted as an index of a plant’s ability to control metal accumulation [47]. A value of less than 1 of the coefficient 1/n is considered an index of active tungsten uptake, whereas higher values of this index suggest the reduced ability of the plant to control the tungsten uptake. The obtained data show a different behavior of this index among soils and between the roots and shoot uptake of the plants.
The correlation between the concentrations calculated by the model and measured in the shoots was high, with R2 values ranging from 0.922 (soil A) to 0.942 (soil C). Similar results were obtained for the root portion with R2 values ranging from 0.896 (soil A) to 0.944 (soil C).
The same Freundlich-like model was also applied by correlating the amount absorbed by the plants with tungsten concentration in soil solution. This amount is determined by the retention/release processes, which influence the distribution of tungsten between the solid and liquid phases, and thus regulate the amount of tungsten in the soil solution from which the plants absorb the element. The results are reported in Table 5 for shoots and roots, respectively.

Table 5.
Relationship between tungsten concentration in shoots and roots and tungsten concentration in soil solution. Parameters of the Freundlich-like model.
Also in this case, a Freundlich-like equation can be used to describe the pattern of plant uptake from soil solution with correlation coefficients higher than those of uptake vs. total content (see Table 4) with R2 values ranging from 0.961 (soil B) to 0.973 (soil C); whereas, for the root portion, R2 values range from 0.959 (soil B) to 0.988 (soil A).
The K and 1/n coefficients changed, but the trend was similar to the uptake vs. total concentration, with the highest K value in soil C, and the lowest in soil A. We have to consider that soil pH exerts a great influence on W solubility due to increased sorption under acidic conditions [57], and this parameter appears to mainly determine plant uptake.
Although speciation of tungsten in soil is of great importance [9,58], especially for the polymerization phenomena [59,60], we decided to evaluate the trend of the tungsten uptake using a model as simple as possible. This approach of course can only be considered as a preliminary step in developing mechanistic models. More experiments need to be performed by varying plant species and using soils with different characteristics to improve the modeling of tungsten uptake by plants, or to develop more complex models. Clearly, the plant uptake model and the model parameters applied in this study are not necessarily valid for different plant species and soils. For example, in the case of soils subject to seasonal variations in the oxidation–reduction conditions, it will be essential to take into consideration also the redox potential [61], which may influence the mobility of the element and therefore its transferability to plants. However, this approach is very simple and can be easily adjusted in different environmental contexts where the tungsten uptake by plants needs to be monitored.
4. Conclusions
There is still a limited understanding of the behavior of tungsten in the environment [62], both because it is a not essential element and because until recently it was considered completely inert. However, tungsten has placed among the possible emerging pollutants by EPA [63]. The present work, to our knowledge, is the only one dealing with the problem of tungsten in Italian soils. The study of this element in different types of Mediterranean soils and the potential passage in the food chain, following the transfer from the soil to the plant, is very important to focus attention on an environmental problem that is currently very undervalued. Our results highlight the importance of soil properties in determining the transfer of tungsten from the soil to plants. The obtained data show that with decreasing pH and increasing organic matter content the plant uptake decreases, due to lower tungsten concentrations in soil solution in bioavailable forms.
In this work, we have taken into consideration those characteristics of the soil that are generally considered in environmental regulations. However, knowledge of the behavior of this element in the soil requires further investigation, so as to better understand the processes that regulate its bioavailability. Among these, a role of primary importance can be played by the redox potential because the oxidizing and reducing conditions determine the behavior of trace elements in soil. Redox variations in soil and the influence of these variations on the mineralogy [61,64] is an essential aspect for future research on the geochemical behavior of tungsten, which is strictly linked to plant bioavailability.
In the last few years, several studies on tungsten in plants have revealed several toxic effects related to the Mo-enzyme inhibitor and gene expression [30,36]. However, in our experiment, the addition of increasing amounts of tungsten to the soil did not cause a biomass reduction or toxicity effects in plants. It is possible that considerable amounts of tungsten accumulate in plants, especially in alkaline conditions. Under the worst conditions, plants may be insensitive to tungsten at levels that are already toxic to animals. This phenomenon has also been detected for molybdenum in the case of forage for ruminants [65].
The low phytotoxicity of tungsten highlights the need to find appropriate models aimed at predicting the passage of tungsten from the soil to plants. We applied a Freundlich-like model for Zea mays uptake at increasing tungsten concentrations in three different Italian soils. The aim of this approach is to respond as simply as possible to the need to assess the potential effects derived from the transfer of W into the food chain, and also to enable the regulatory authorities to better define the hazards of this element in the environment. The transfer mechanism of tungsten from the soil to roots and shoots is of great interest and should be further investigated to understand how the environmental source of this element may impact on human health, which is an urgent issue that must be addressed in the near future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.P. and F.P.; Writing – original draft, G.P. and F.P.
Funding
This research received no external funding. This study was supported by the Italian National Research Council CNR.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Irene Rosellini for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Koutsospyros, A.D.; Braida, W.J.; Christodoulatos, C.; Dermatas, D.; Strigul, N.S. A review of tungsten: From environmental obscurity to scrutiny. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsospyros, A.D.; Strigul, N.S.; Braida, W.J.; Christodoulatos, C. Tungsten: Environmental pollution and health effects. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Health; Nriagu, J.O., Ed.; Elsevier: Burlington, UK, 2011; pp. 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- Clausen, J.L.; Korte, N. Environmental fate of tungsten from military use. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2009, 407, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Technical Fact Sheet-Tungsten; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Kaiser, B.N.; Gridley, K.L.; Ngaire Brady, J.; Phillips, T.; Tyerman, S.D. The role of molybdenum in agricultural plant production. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Voet, G.B.; Todorov, T.I.; Centeno, J.A.; Jonas, W.; Ives, J.; Mullick, F.G. Metals and Health: A Clinical Toxicological Perspective on Tungsten and Review of the Literature. Mil. Med. 2007, 172, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.D.R.; Lemaire, M.; Young, Y.K.; Eustache, J.H.; Guilbert, C.; Molina, M.F.; Mann, K.K. In vivo tungsten exposure alters B-cell development and increases DNA damage in murine bone marrow. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laulicht, F.; Brocato, J.; Cartularo, L.; Vaughan, J.; Wu, F.; Kluz, T.; Sun, H.; Oksuz, B.A.; Shen, S.; Peana, M.; et al. Tungsten-induced carcinogenesis in human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2015, 288, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strigul, N. Does speciation matter for tungsten ecotoxicology? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, P.R.; Ridenour, G.; Speakman, R.J.; Witten, M.L. Elevated tungsten and cobalt in airborne particulates in Fallon, Nevada: Possible implications for the childhood leukemia cluster. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, P.R.; Speakman, R.J.; Ridenour, G.; Witten, M.L. Using lichen chemistry to assess airborne tungsten and cobalt in Fallon, Nevada. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.G.; Roberts, M.J.; Harrison, P.T. Assessment of the environmental toxicity and carcinogenicity of tungsten-based shot. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringelberg, D.B.; Reynolds, C.M.; Winfield, L.E.; Inouye, L.S.; Johnson, D.R.; Bednar, A.J. Tungsten effects on microbial community structure and activity in a soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strigul, N.; Koutsospyros, A.D.; Arienti, P.; Christodoulatos, C.; Dermatas, D.; Braida, W.J. Effects of tungsten on environmental systems. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senesi, N.; Padovano, G.; Brunetti, G. Scandium, titanium, tungsten and zirconium content in commercial inorganic fertilizers and their contribution to soil. Environ. Technol. Lett. 1988, 9, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Lycken, J.; Dave, G. Sediment quality assessment of road runoff detention systems in Sweden and the potential contribution of tire wear. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 194, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, J.E.; Butler, A.D.; Heim, K.E.; Pittinger, C.A.; Lemus, R.; Staveley, J.P.; Lee, K.B.; Venezia, C.; Pardus, M.J. Toxicity of sodium tungstate to earthworm, oat, radish and lettuce. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2312–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Eleftheriou, E.P.; Rost, T.L. Effects of sodium tungstate on the ultrastructure and growth of pea (Pisum sativum) and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 63, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Panteris, E.; Eleftheriou, E.P. Tungsten affects the cortical microtubules of Pisum sativum root cells: Experiments on tungsten-molybdenum antagonism. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Panteris, E.; Eleftheriou, E.P. The fatal effect of tungsten on Pisum sativum L. root cells: Indications for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced programmed cell death. Planta 2011, 234, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratas, J.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Freitas, H.; Conde, L. Plants growing in abandoned mines of Portugal are useful for exploration of arsenic, antimony, tungsten and mine reclamation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2005, 85, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Pyatt, F.B. Bioavailability of tungsten in the vicinity of an abandoned mine in the English Lake District and some potential health implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Pyatt, F.B. Bioavailability of tungsten and associated metals in calcareous soils in the vicinity of an ancient metalliferous mine in the Corbieres area, Southwestern France. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. A 2009, 72, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Li, R.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Shao, X. Tungsten Distribution in Soil and Rice in the Vicinity of the World’s Largest and Longest-Operating Tungsten Mine in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Heilmeier, H.; Hartung, W. Abscisic acid relations of plants grown on tungsten enriched substrates. Plant Soil 2007, 301, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Inouye, L.S.; Bednar, A.J.; Clarke, J.U.; Winfield, L.E.; Boyd, R.E.; Ang, C.Y. Tungsten bioavailability and toxicity in sunflowers (Helianthus annuus). Land Contam. Reclamat. 2009, 17, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.W. Soil pH and soil acidity. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America Book Series; Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America book series; Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Klute, A., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America Book Series; Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Oburger, E.; Vergara Cid, C.; Preiner, J.; Hu, J.; Hann, S.; Wanek, W.; Richter, A. pH-Dependent Bioavailability, Speciation, and Phytotoxicity of Tungsten (W) in Soil Affect Growth and Molybdoenzyme Activity of Nodulated Soybeans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6146–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poykio, R.; Torvela, H.; Peramaki, P.; Kuokkanen, T.; Ronkkomaki, H. Comparison of dissolution methods for multielement analysis of some plant materials used as bioindicator of sulphur and heavy metal deposition determined by ICP-AES and ICPMS. Analusis 2000, 28, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermatas, D.; Braida, W.; Christodoulatos, C.; Strigul, N.; Panikov, N.; Los, M.; Larson, S. Solubility, sorption, and soil respiration effects of tungsten and tungsten alloys. Environ. Forensics 2004, 5, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednar, A.J.; Jones, W.T.; Chappell, M.A.; Johnson, D.R.; Ringelberg, D.B. A modified acid digestion procedure for extraction of tungsten from soil. Talanta 2010, 80, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Aery, N.C. Effect of tungsten on growth, biochemical constituents, molybdenum and tungsten contents in wheat. Plant Soil Environ. 2011, 57, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Aery, N.C. Effect of tungsten on growth, dry-matter production, and biochemical constituents of cowpea. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2012, 43, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamakis, I.D.S.; Panteris, E.; Eleftheriou, E.P. Tungsten toxicity in plants. Plants 2012, 1, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, R.; Nicholas, W.L. Tungsten. In Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Springer Science and Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Semhi, K.; Boutin, R.; Nallusamy, S.; Al Busaidi, W.; Al Hamdi, A.; Al Dhafri, K.; Al Busaidi, A. Impact of a Variable Tungsten Pollution on the Elemental Uptake of Two Plant Species. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G.; Chaney, R.L. Bioavailability as an issue in risk assessment and management of food cadmium: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 398, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, J.P. Modelling molybdate and tungstate adsorption to ferrihydrite. Chem. Geol. 2003, 200, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednar, A.J.; Boyd, R.E.; Jones, W.T.; McGrath, C.J.; Johnson, D.R.; Chappell, M.A.; Ringelberg, D.B. Investigations of tungsten mobility in soil using column tests. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen Tuna, G.; Braida, W. Evaluation of the adsorption of mono- and poly- tungstates onto different types of clay minerals and Pahokee peat. Soil Sediment Contamin. 2014, 23, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas Arrigo, L.K.; Mikutta, C.; Byrne, J.; Kappler, A.; Kretzschmar, R. Iron(II)-catalyzed iron atom exchange and mineralogical changes in Iron-rich organic freshwater flocs: An Iron isotope tracer study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6897–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Johnston, S.G.; Burton, E.D. Antimony and arsenic behavior during Fe(II)-induced transformation of Jarosite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4259–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Johnston, S.G.; Burton, E.D. Antimony and arsenic partitioning during Fe2+-induced transformation of jarosite under acidic conditions. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Burton, E.D.; Johnston, S.G.; Hockmann, K.; Choppala, G. Humic acid impacts antimony partitioning and speciation during iron(II)-induced ferrihydrite transformation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, M.; Wilcke, W.; Kobza, J.; Zech, W. Predicting heavy metals transfer from soil to plant: Potential use of Freundlich-type functions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.X.; Su, Y.; Monts, D.L.; Waggoner, C.A.; Plodinec, M.J. Binding, distribution, and plant uptake of mercury in a soil from Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalis, E.J.J.; Temminghoff, E.J.M.; Visser, A.; Van Riemsdijk, W.H. Metal uptake by Lolium perenne in contaminated soils using a four-step approach. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco Rodriguez, P.; Vera Tomé, F.; Lozano, J.C. About the assumption of linearity in soil-to-plant transfer factors for uranium and thorium isotopes and 226Ra. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuovinen, T.S.; Roivainen, P.; Makkonen, S.; Kolehmainen, M.; Holopainen, T.; Juutilainen, J. Soil-to-plant transfer of elements is not linear: Results for five elements relevant to radioactive waste in five boreal forest species. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantke, P.; Charles, R.; de Alencastro, L.F.; Friedrich, R.; Jolliet, O. Plant uptake of pesticides and human health: Dynamic modeling of residues in wheat and ingestion intake. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, S.; Eggen, T. Simulation of the plant uptake of organophosphates and other emerging pollutants for greenhouse experiments and field conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4018–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, M.; Escudey, M.; Chang, A.C.; Chen, W.; Arancibia-Miranda, N. Trace element uptake dynamics for maize (Zea mays L.) grown under field conditions. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Ding, Q.; Wei, D.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y. Major controlling factors and predictions for cadmium transfer from the soil into spinach plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 93, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedron, F.; Grifoni, M.; Barbafieri, M.; Petruzzelli, G.; Rosellini, I.; Franchi, E.; Bagatin, R.; Vocciante, M. Applicability of a Freundlich-Like Model for Plant Uptake at an Industrial Contaminated Site with a High Variable Arsenic Concentration. Environments 2017, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzelli, G.; Pedron, F. Tungstate adsorption onto Italian soils with different characteristics. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostick, B.C.; Sun, J.; Landis, J.D.; Clausen, J.L. Tungsten Speciation and Solubility in Munitions-Impacted Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruywagen, J.J. Protonation, oligomerization, and condensation reactions of vanadate (V), molybdate (VI). In Advances in Inorganic Chemistry; Sykes, A.G., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 127–182. [Google Scholar]
- Davantès, A.; Costa, D.; Lefèvre, G. Infrared study of (poly)tungstate ions in solution and sorbed into layered double hydroxides: Vibrational calculations and in situ analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 12356–12364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Johnston, S.G.; Burton, E.D. Iron and sulfur cycling in acid sulfate soil wetlands under dynamic redox conditions: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Vero, S.E.; Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Johannesson, K. Tungsten Contamination of Soils and Sediments: Current State of Science. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 3, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Emerging Contaminant-Tungsten. Technical Fact Sheet; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Karimian, N.; Johnston, S.G.; Burton, E.D. Acidity generation accompanying iron and sulfur transformations during drought simulation of freshwater re-flooded acid sulphate soils. Geoderma 2017, 285, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, G.A.; Brobst, R.B.; Chaney, R.L.; Kincaid, R.L.; Mcdowell, L.R.; Pierzynski, G.M.; Rubin, A.; Riper, G.V. A modified risk assessment to establish molybdenum standards for land application of biosolids. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1490–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).