Rapid Green Extractions of C-Phycocyanin from Arthrospira maxima for Functional Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Conventional Extraction for Phycobiliproteins Extraction
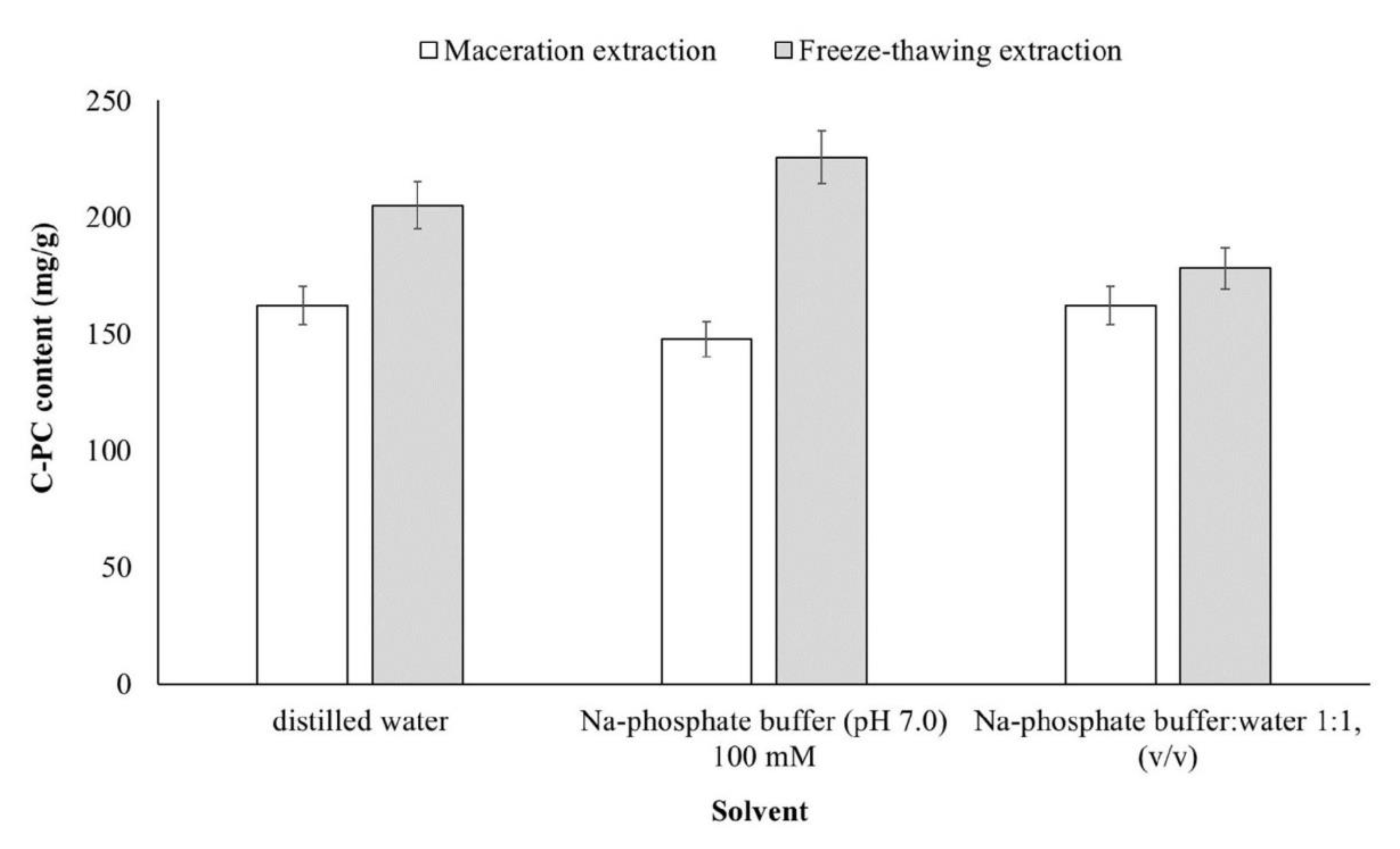
2.2.1. Maceration Extraction
2.2.2. Freeze–Thawing Extraction
2.3. Green Extraction Design for Phycobiliproteins Extraction
2.3.1. Microwave (MW) Design
2.3.2. High-Pressure Homogenization (HPH) Design
2.4. C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) Quantification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
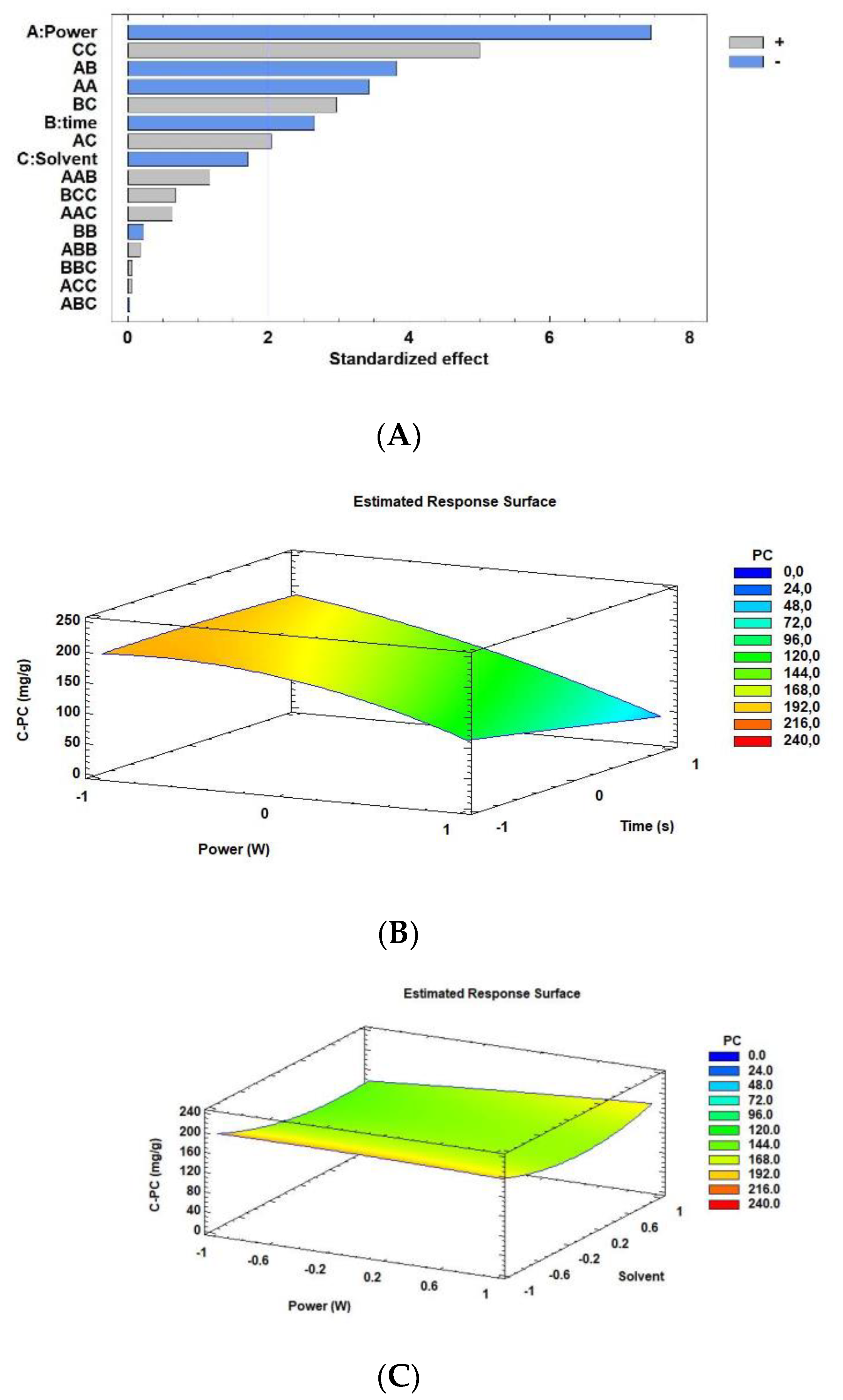
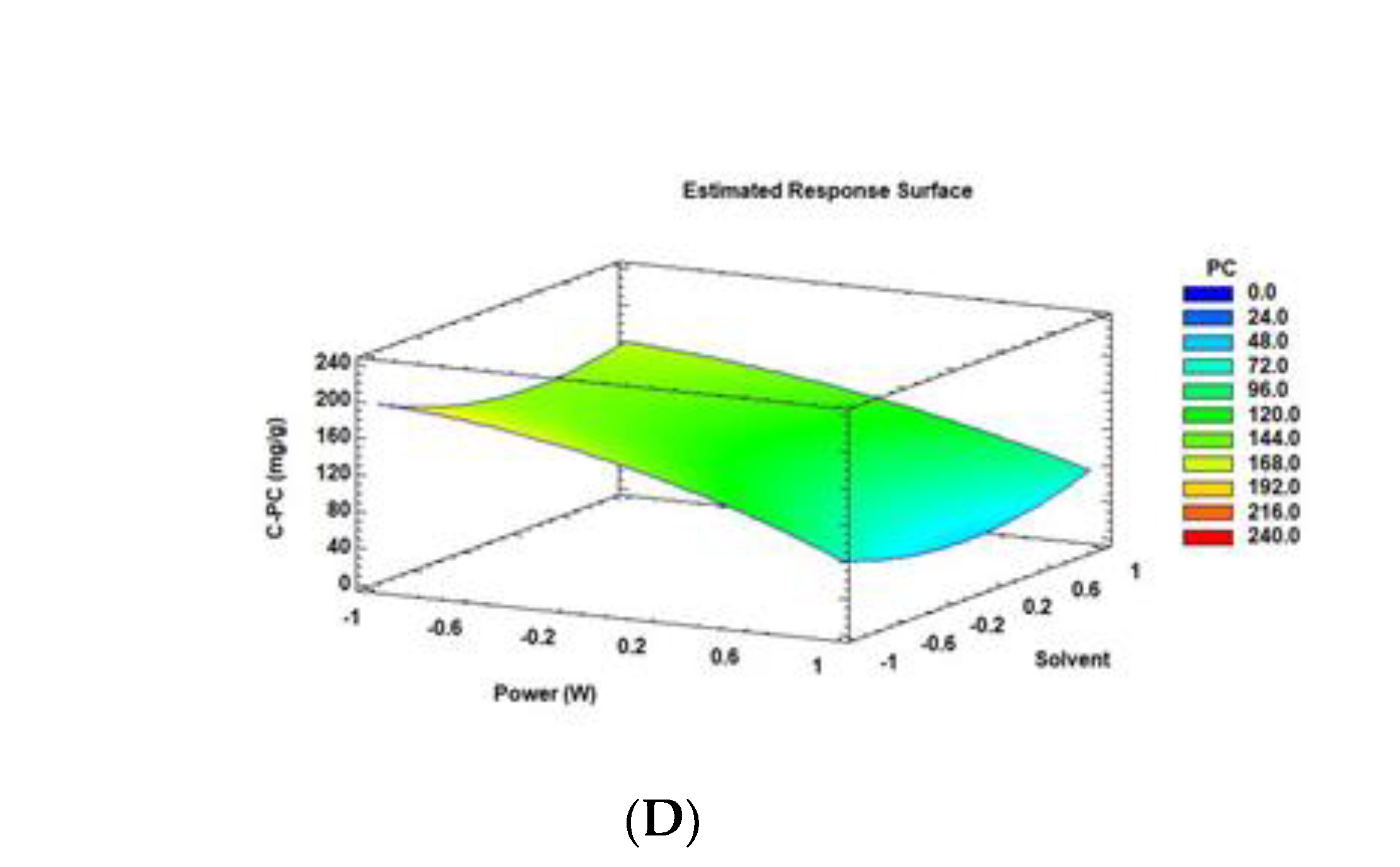
3.1. Optimization of MW Extraction Conditions for C-PC from Arthrospira Maxima
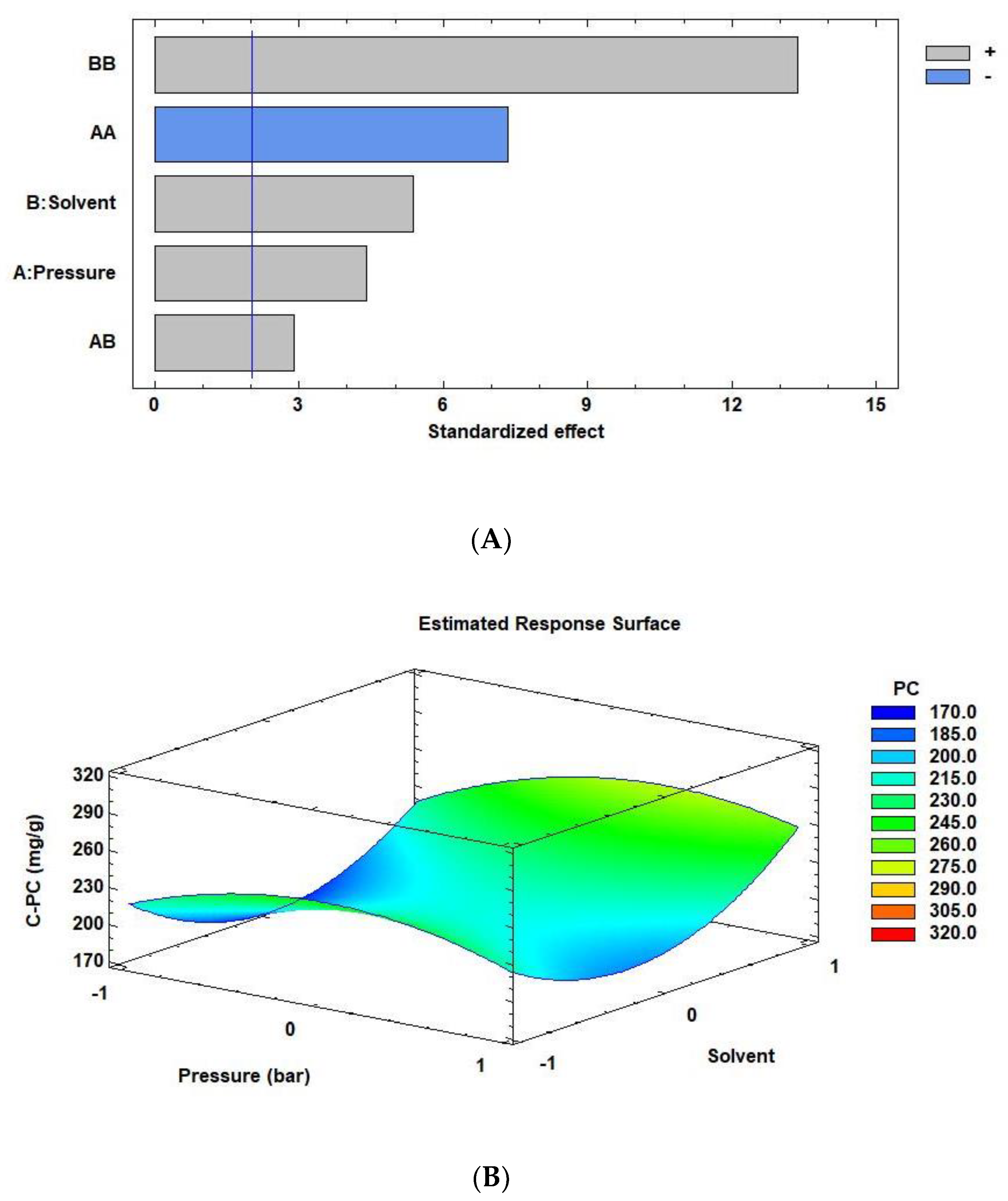
3.2. Optimization of HPH Extraction Conditions for C-PC of Arthrospira Maxima
3.3. Comparison of C-PC Content of Arthrospira Maxima between Conventional and Green Extraction Techniques
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braithwaite, M.C.; Tyagi, C.; Tomar, L.K.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. Nutraceutical-based therapeutics and formulation strategies augmenting their efficiency to complement modern medicine: An overview. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, E.; Florou-Paneri, P.; Bonos, E. Microalgae: A novel ingredient in nutrition. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibañez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Benefits of using algae as natural sources of functional ingredients. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberfroid, M.B. Global view on functional foods: European perspectives. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, S133–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, S.; Chandramohan, M. Phycobiliproteins as a commodity: Trends in applied research, patents and commercialization. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemlata, G.P.; Bano, F.; Fatma, T. Studies on anabaena sp. Nccu-9 with special reference to phycocyanin. J. Algal. Biomass Utln. 2011, 2, 30–51. [Google Scholar]
- Richa, K.V.; Kesheri, M.; Singh, G.; Sinha, R. Biotechnological potentials of phycobiliproteins. Int. J. Pharma. Bio. Sci. 2011, 2, 446–454. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.-L. Biotechnological applications of microalgae. IeJSME 2012, 6, S24–S37. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Gong, X. Promising fluorescent probes from phycobiliproteins. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2003, 9, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.T.; Puranik, P.R. C-phycocyanin production by halotolerant cyanobacteria. PHYKOS—Off. J. Phycol. Soc. India 2014, 44, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, V.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, V. Biotechnological applications of cyanobacterial phycobiliproteins. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2013, 2, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, C.C.; Sala, L.; Cerveira, G.P.; Kalil, S.J. C-phycocyanin extraction from spirulina platensis wet biomass. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuddus, M.; Singh, P.; Thomas, G.; Al-Hazimi, A. Recent developments in production and biotechnological applications of c-phycocyanin. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus Raposo, M.F.; de Morais, R.M.S.C.; de Morais, A.M.M.B. Health applications of bioactive compounds from marine microalgae. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rojas, B.; Hernández-Juárez, J.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Nutraceutical properties of phycocyanin. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 11, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A. High-value products from microalgae—Their development and commercialisation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiklahan, R.; Chirasuwan, N.; Loha, V.; Tia, S.; Bunnag, B. Stepwise extraction of high-value chemicals from arthrospira (spirulina) and an economic feasibility study. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 20, e00280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Mozafari, M. Nutritional and medical applications of spirulina microalgae. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-W.; Yang, T.-S.; Chen, M.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Eugene, I.; Wang, C.; Ho, C.-L.; Lai, Y.-J.; Yu, C.-C.; Chou, J.-C. Purification and immunomodulating activity of c-phycocyanin from spirulina platensis cultured using power plant flue gas. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, G.; Folli, C.; Visai, L.; Daglia, M.; Ferrari, D. Thermal stability improvement of blue colorant c-phycocyanin from spirulina platensis for food industry applications. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuhu, A.A. Spirulina (arthrospira): An important source of nutritional and medicinal compounds. J. Mar. Biol. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q. Environmental effects on cell composition in handbook of microalgal culture. In Biotechnology and Applied Phycology; Richmond, A., Ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sarada, R.; Pillai, M.G.; Ravishankar, G. Phycocyanin from spirulina sp: Influence of processing of biomass on phycocyanin yield, analysis of efficacy of extraction methods and stability studies on phycocyanin. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poojary, M.M.; Barba, F.J.; Aliakbarian, B.; Donsì, F.; Pataro, G.; Dias, D.A.; Juliano, P. Innovative alternative technologies to extract carotenoids from microalgae and seaweeds. Mar. drugs 2016, 14, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viskari, P.J.; Colyer, C.L. Rapid extraction of phycobiliproteins from cultured cyanobacteria samples. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 319, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.; Bogorad, L. Complementary chromatic adaptation in a filamentous blue-green alga. J. Cell Biol. 1973, 58, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juin, C.; Chérouvrier, J.-R.; Thiéry, V.; Gagez, A.-L.; Bérard, J.-B.; Joguet, N.; Kaas, R.; Cadoret, J.-P.; Picot, L. Microwave-assisted extraction of phycobiliproteins from porphyridium purpureum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İlter, I.; Akyıl, S.; Demirel, Z.; Koç, M.; Conk-Dalay, M.; Kaymak-Ertekin, F. Optimization of phycocyanin extraction from spirulina platensis using different techniques. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 70, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquet, V.; Chérouvrier, J.-R.; Farhat, F.; Thiéry, V.; Piot, J.-M.; Bérard, J.-B.; Kaas, R.; Serive, B.; Patrice, T.; Cadoret, J.-P. Study on the microalgal pigments extraction process: Performance of microwave assisted extraction. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.-H.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, G.-K. Evaluation of vacuum microwave-assisted extraction technique for the extraction of antioxidants from plant samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8867–8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.; Jeffrey, S.; Mantoura, R. Phytoplankton Pigments in Oceanography: Guidelines to Modern Methods; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Halim, R.; Harun, R.; Danquah, M.K.; Webley, P.A. Microalgal cell disruption for biofuel development. Appl. Energy 2012, 91, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carullo, D.; Abera, B.D.; Casazza, A.A.; Donsì, F.; Perego, P.; Ferrari, G.; Pataro, G. Effect of pulsed electric fields and high pressure homogenization on the aqueous extraction of intracellular compounds from the microalgae chlorella vulgaris. Algal Res. 2018, 31, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Grimi, N.; Vorobiev, E. New approaches for the use of non-conventional cell disruption technologies to extract potential food additives and nutraceuticals from microalgae. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, K.; Kar, J.R.; Singhal, R.S. Extraction of lipids from chlorella saccharophila using high-pressure homogenization followed by three phase partitioning. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, B.H.; Dumsday, G.J.; Scales, P.J.; Martin, G.J. Energy evaluation of algal cell disruption by high pressure homogenisation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarasinghe, N.; Fernando, S.; Lacey, R.; Faulkner, W.B. Algal cell rupture using high pressure homogenization as a prelude to oil extraction. Renew. Energy 2012, 48, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.Y.; Lee, H.Y. Enhancement of neuroprotective effects of spirulina platensis extract from a high-pressure homogenization process. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, B.; Kalavadia, B.; Trivedi, U.; Madamwar, D. Extraction, purification and characterization of phycocyanin from oscillatoria quadripunctulata—isolated from the rocky shores of bet-dwarka, gujarat, india. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkova, K.; Tchernov, A.; Tchorbadjieva, M.; Fournadjieva, S.; Antova, R.; Busheva, M.C. Purification of c-phycocyanin from spirulina (arthrospira) fusiformis. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 102, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, S.T.; Burkert, J.F.d.M.; Costa, J.A.V.; Burkert, C.A.V.; Kalil, S.J. Optimization of phycocyanin extraction from spirulina platensis using factorial design. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L.; Guevara, M.; Gómez, B.; Arredondo-Vega, B.; Cortez, R.; Licet, B. Production of pigments from arthrospira maxima cultivated in photobioreactors. Revista Colombiana de Biotecnología 2017, 19, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, K.; Shukla, S.; Vennila, A.; Purushothaman, C.; Manjulekshmi, N. Cultivation of spirulina (arthrospira) platensis in low cost seawater based medium for extraction of value added pigments. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2005, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, E.W. Microalgae: Biotechnology and Microbiology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Simpore, J.; Zongo, F.; Kabore, F.; Dansou, D.; Bere, A.; Nikiema, J.-B.; Pignatelli, S.; Biondi, D.M.; Ruberto, G.; Musumeci, S. Nutrition rehabilitation of HIV-infected and HIV-negative undernourished children utilizing spirulina. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 49, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MW Extraction Conditions | C-PC Content (mg/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Power (W) | Time (s) | Solvent Type * | ||||
| 1 | −1 | (100) | −1 | (15) | −1 | (water) | 201.9 ± 5.1 |
| 2 | −1 | −1 | 0 | (Buffer) | 148.9 ± 2.0 | ||
| 3 | −1 | −1 | +1 | (Buffer:water) | 149.1 ± 5.6 | ||
| 4 | −1 | 0 | (30) | −1 | 215.0 ± 5.5 | ||
| 5 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 161.5 ± 6.9 | |||
| 6 | −1 | 0 | +1 | 165.9 ± 9.3 | |||
| 7 | −1 | +1 | (60) | −1 | 169.5 ± 3.8 | ||
| 8 | −1 | +1 | 0 | 160.9 ± 8.4 | |||
| 9 | −1 | +1 | +1 | 168.6 ± 12.2 | |||
| 10 | 0 | (200) | −1 | −1 | 192.5 ± 1.3 | ||
| 11 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 170.7 ± 7.5 | |||
| 12 | 0 | −1 | +1 | 143.8 ± 16.9 | |||
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 134.7 ± 2.6 | |||
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 121.2 ± 24.9 | |||
| 15 | 0 | 0 | +1 | 136.9 ± 1.8 | |||
| 16 | 0 | +1 | −1 | 153.0 ± 5.2 | |||
| 17 | 0 | +1 | 0 | 87.5 ± 17.4 | |||
| 18 | 0 | +1 | +1 | 172.9 ± 16.1 | |||
| 19 | +1 | (300) | −1 | −1 | 109.1 ± 12.7 | ||
| 20 | +1 | −1 | 0 | 61.8 ± 25.9 | |||
| 21 | +1 | −1 | +1 | 92.0 ± 8.1 | |||
| 22 | +1 | 0 | −1 | 85.7 ± 30.0 | |||
| 23 | +1 | 0 | 0 | 46.8 ± 14.2 | |||
| 24 | +1 | 0 | +1 | 86.9 ± 10.7 | |||
| 25 | +1 | +1 | −1 | 37.8 ± 6.6 | |||
| 26 | +1 | +1 | 0 | 35.1 ± 5.7 | |||
| 27 | +1 | +1 | +1 | 44.2 ± 2.2 | |||
| HPH Extraction Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Pressure (Bar) | Solvent * | C-PC Content (mg/g) | ||
| 1 | −1 | (800) | −1 | (Water) | 218.1 ± 10.1 |
| 2 | −1 | 0 | (Buffer) | 225.9 ± 0.4 | |
| 3 | −1 | +1 | (Buffer:water) | 179.3 ± 1.1 | |
| 4 | −0.5 | (1000) | −1 | 224.0 ± 3.3 | |
| 5 | −0.5 | 0 | 233.7 ± 5.6 | ||
| 6 | −0.5 | +1 | 203.4 ± 6.9 | ||
| 7 | 0 | (1200) | −1 | 252.5 ± 4.1 | |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 268.8 ± 6.4 | ||
| 9 | 0 | +1 | 212.3 ± 9.3 | ||
| 10 | +0.5 | (1400) | −1 | 249.1 ± 6.1 | |
| 11 | +0.5 | 0 | 291.9 ± 6.7 | ||
| 12 | +0.5 | +1 | 210.3 ± 1.2 | ||
| 13 | +1 | (1600) | −1 | 224.3 ± 6.4 | |
| 14 | +1 | 0 | 257.4 ± 7.4 | ||
| 15 | +1 | +1 | 177.9 ± 5.9 | ||
| C-PC Content (mg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Terms of the Model | Estimate | p-Value |
| Constant | 120.021 | |
| A:Power | −51.8069 | 0.0000 * |
| B:time | −18.4825 | 0.0100 * |
| C:solvent | −11.8465 | 0.0938 |
| AA Power × power | −18.512 | 0.0011 * |
| AB Power × time | −14.5478 | 0.0003 * |
| AC Power × solvent | 7.76572 | 0.0459 * |
| BB time × time | −1.20219 | 0.8243 |
| BC time × solvent | 11.3066 | 0.0043 * |
| CC solvent × solvent | 26.9978 | 0.0000 * |
| AAB Power × power × time | 0.0 | 0.2485 |
| AAC Power × power × solvent | 0.0 | 0.5327 |
| ABB Power × time × time | 1.15228 | 0.8621 |
| ACC Power × solvent × solvent | 0.338278 | 0.9803 |
| BBC Time × time × solvent | 0.0 | 0.9593 |
| BCC Time × solvent × solvent | 4.42314 | 0.9513 |
| ABC Power × time × solvent | 12.1269 | 0.5056 |
| Statistics for goodness of fit of the model | ||
| R2 | 0.84615 | |
| RSD | 22.885 | |
| P | 0.4008 | |
| RRSD (%) | 3.00351 | |
| C-PC Content (mg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Terms of the Model | Estimated | p-Value |
| constant | 211.26 | |
| A Pressure | 10.3651 | 0.0001 * |
| B Solvent | 10.9577 | 0.0000 * |
| AA Pressure × Pressure | −29.2046 | 0.0000 * |
| AB Pressure × solvent | 8.37285 | 0.0061 * |
| BB Solvent × solvent | 47.2129 | 0.0000 * |
| Statistics for goodness of fit of the model | ||
| R2 | 0.881058 | |
| RSD | 11.1752 | |
| P | 0.4979 | |
| RRSD (%) | −7.51706 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Domínguez, M.C.; Jáuregui, M.; Medina, E.; Jaime, C.; Cerezal, P. Rapid Green Extractions of C-Phycocyanin from Arthrospira maxima for Functional Applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9101987
Ruiz-Domínguez MC, Jáuregui M, Medina E, Jaime C, Cerezal P. Rapid Green Extractions of C-Phycocyanin from Arthrospira maxima for Functional Applications. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(10):1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9101987
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Domínguez, Mari Carmen, Marjorie Jáuregui, Elena Medina, Carolina Jaime, and Pedro Cerezal. 2019. "Rapid Green Extractions of C-Phycocyanin from Arthrospira maxima for Functional Applications" Applied Sciences 9, no. 10: 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9101987
APA StyleRuiz-Domínguez, M. C., Jáuregui, M., Medina, E., Jaime, C., & Cerezal, P. (2019). Rapid Green Extractions of C-Phycocyanin from Arthrospira maxima for Functional Applications. Applied Sciences, 9(10), 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9101987





