A Novel Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Method for Maneuvering Targets Based on Modified Chirp Fourier Transform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
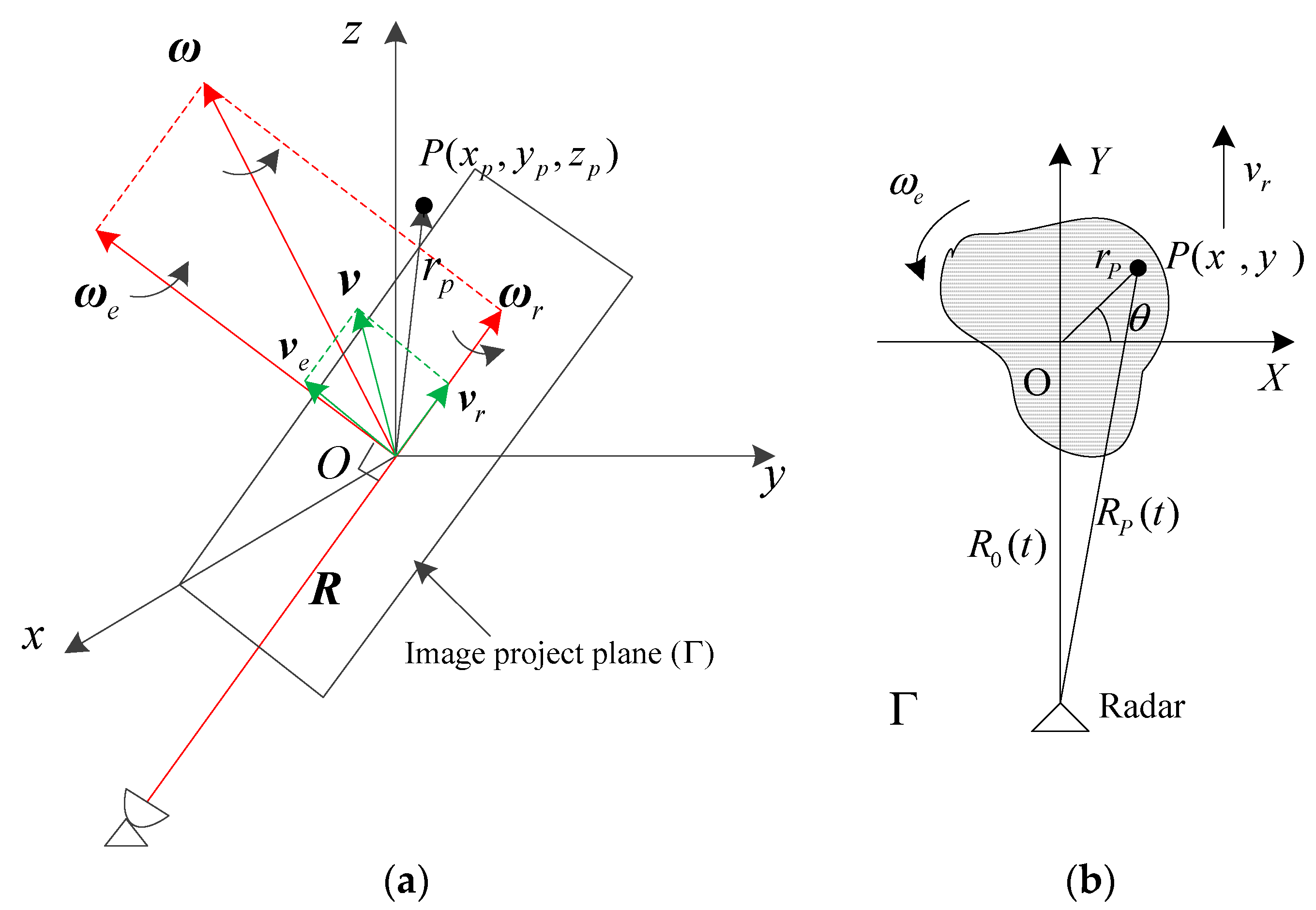
2. ISAR Imaging Model of Maneuvering Targets
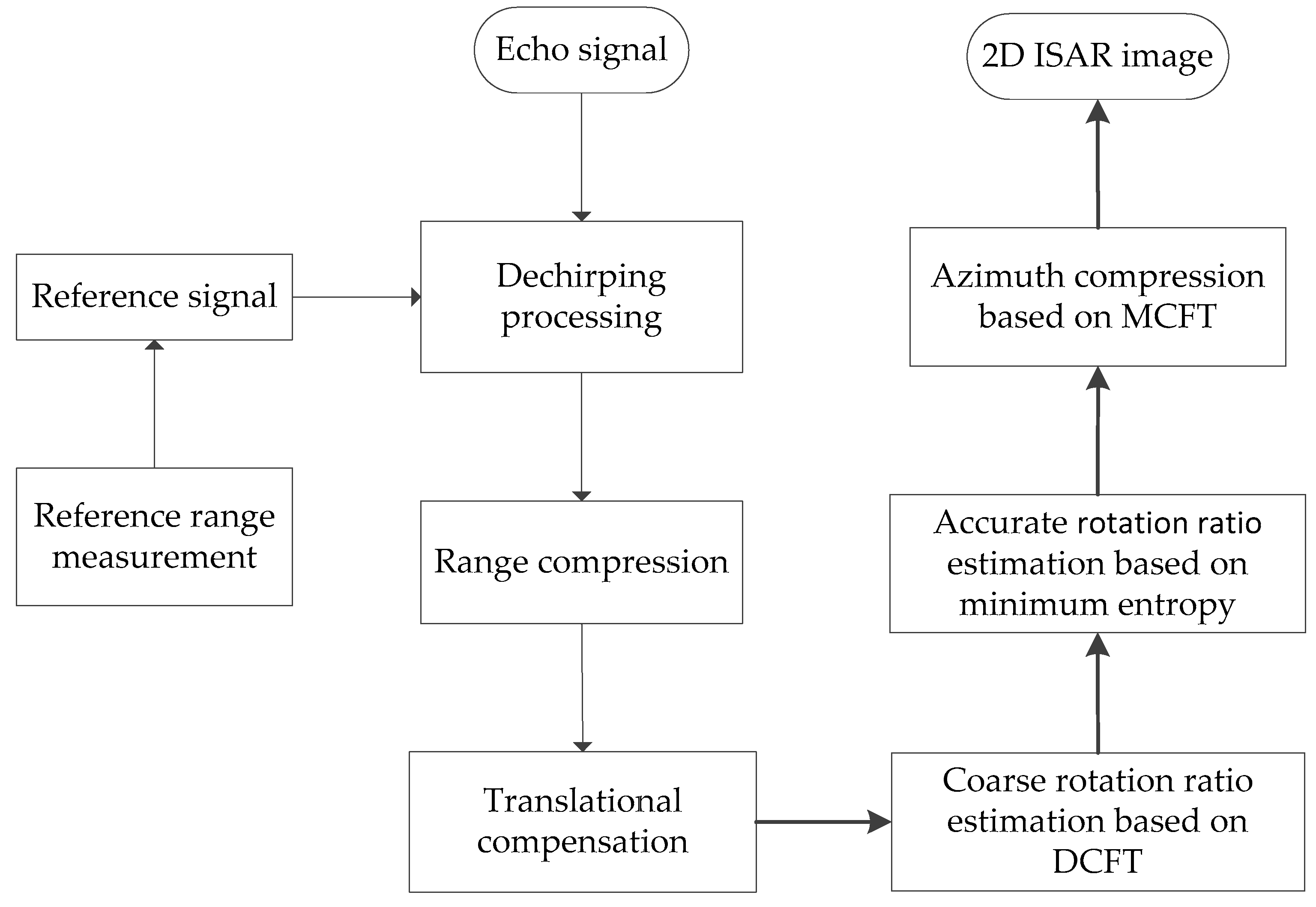
3. Imaging Algorithm Based on Modified Chirp Fourier Transform
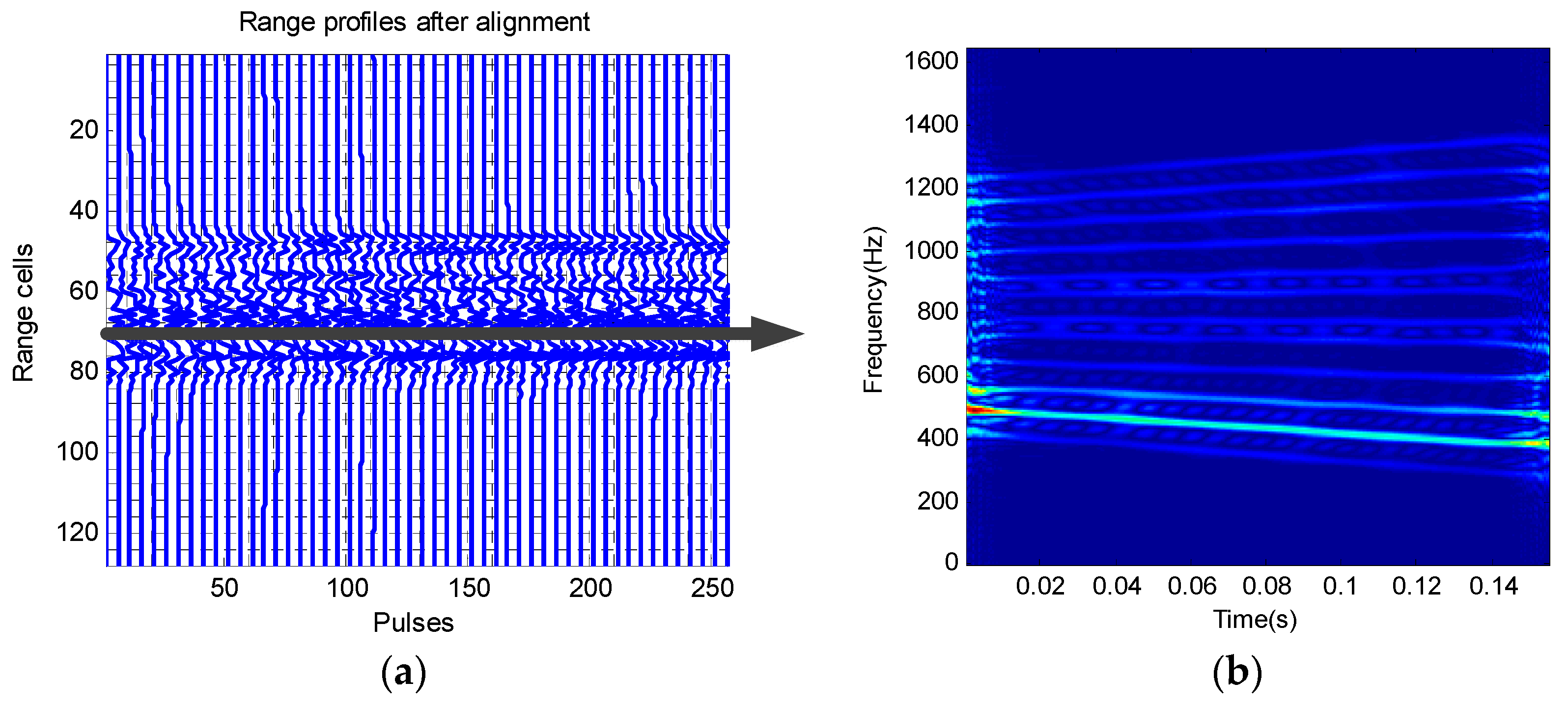
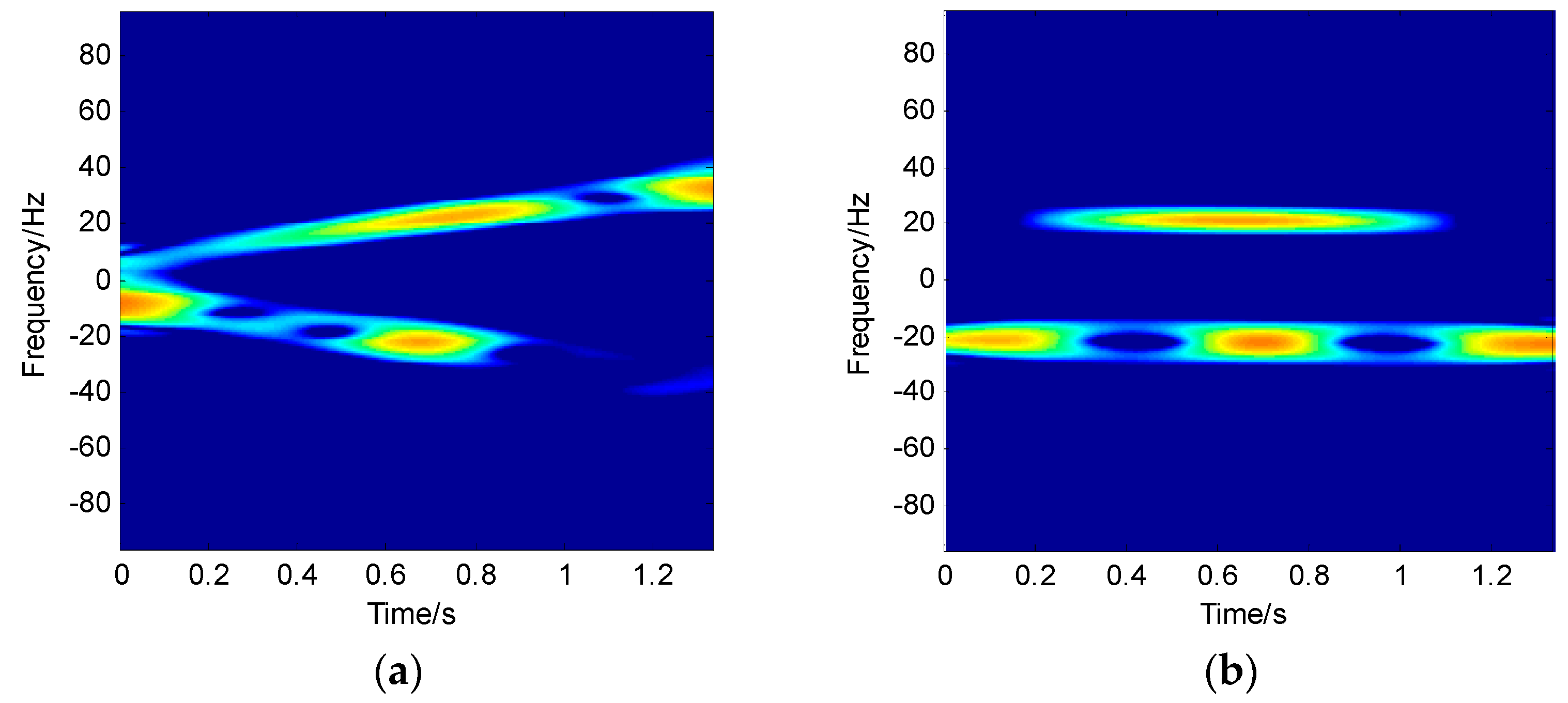
3.1. Azimuth Fast Compression Based on MCFT
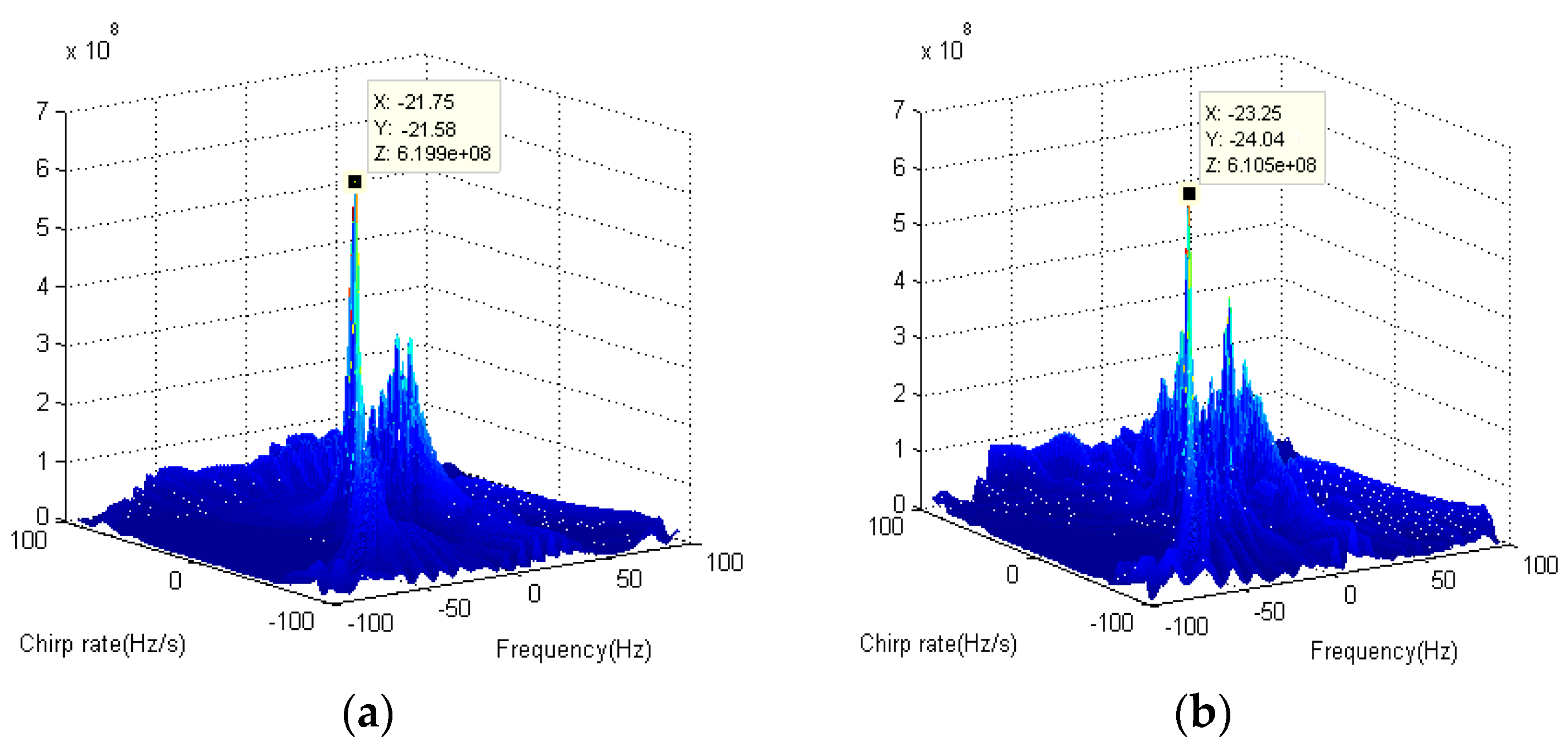
3.2. Coarse Rotation Ratio Estimation Based on DCFT
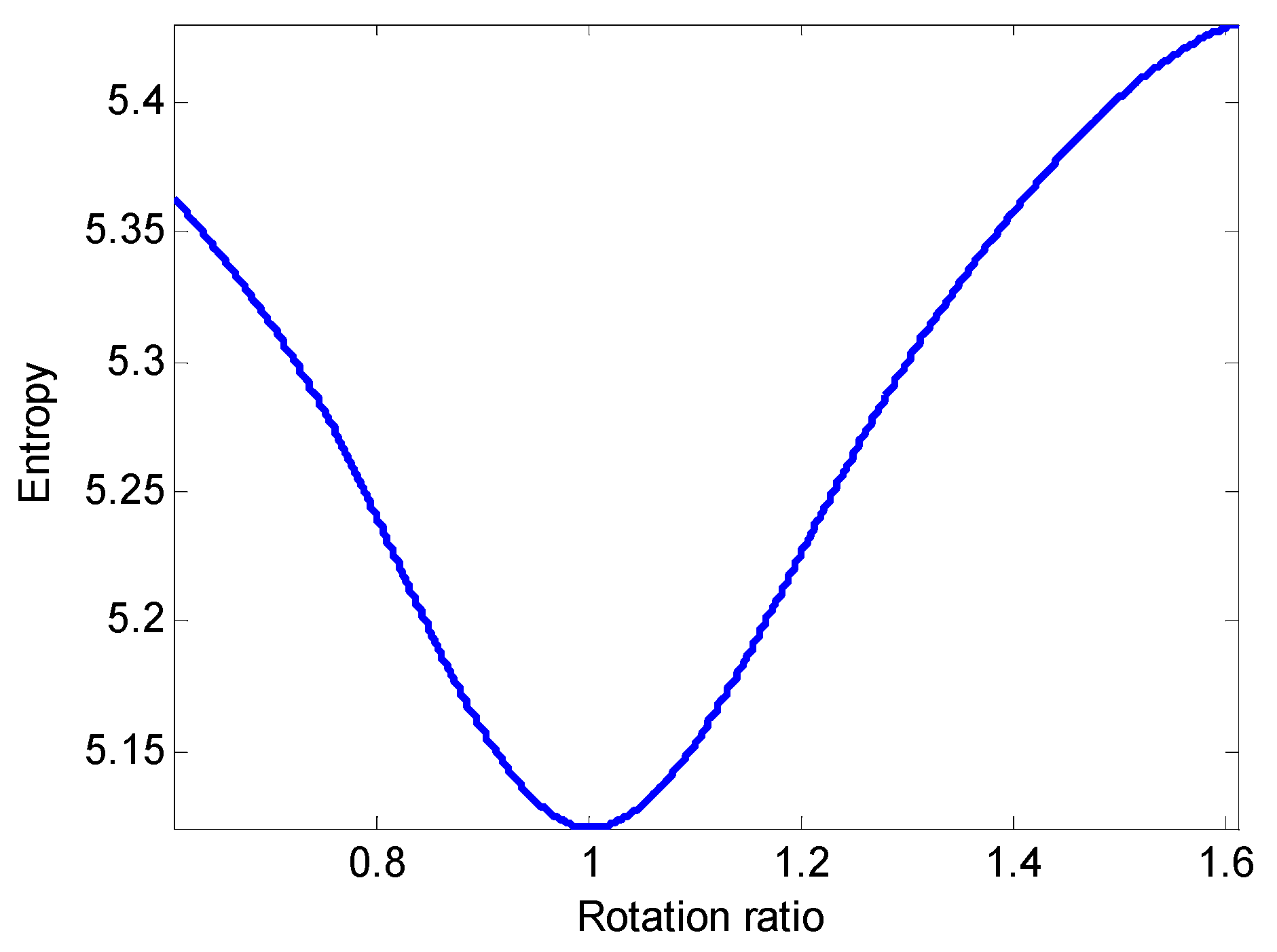
3.3. Accurate Rotation Ratio Estimation Based on Minimum Entropy
- (1)
- Input the radar echo signal;
- (2)
- Generate reference signal by measured reference range;
- (3)
- Perform dechirping processing for the echo signal and reference signal;
- (4)
- Range compression and translational compensation for the signal after dechirping;
- (5)
- Coarse rotation ratio estimation based on DCFT in Section 3.2;
- (6)
- Accurate rotation ratio estimation based on minimum entropy in Section 3.3;
- (7)
- Azimuth compression based on MCFT in Section 3.1;
- (8)
- Output the two-dimensional (2D) ISAR image.
4. Simulation Experiment
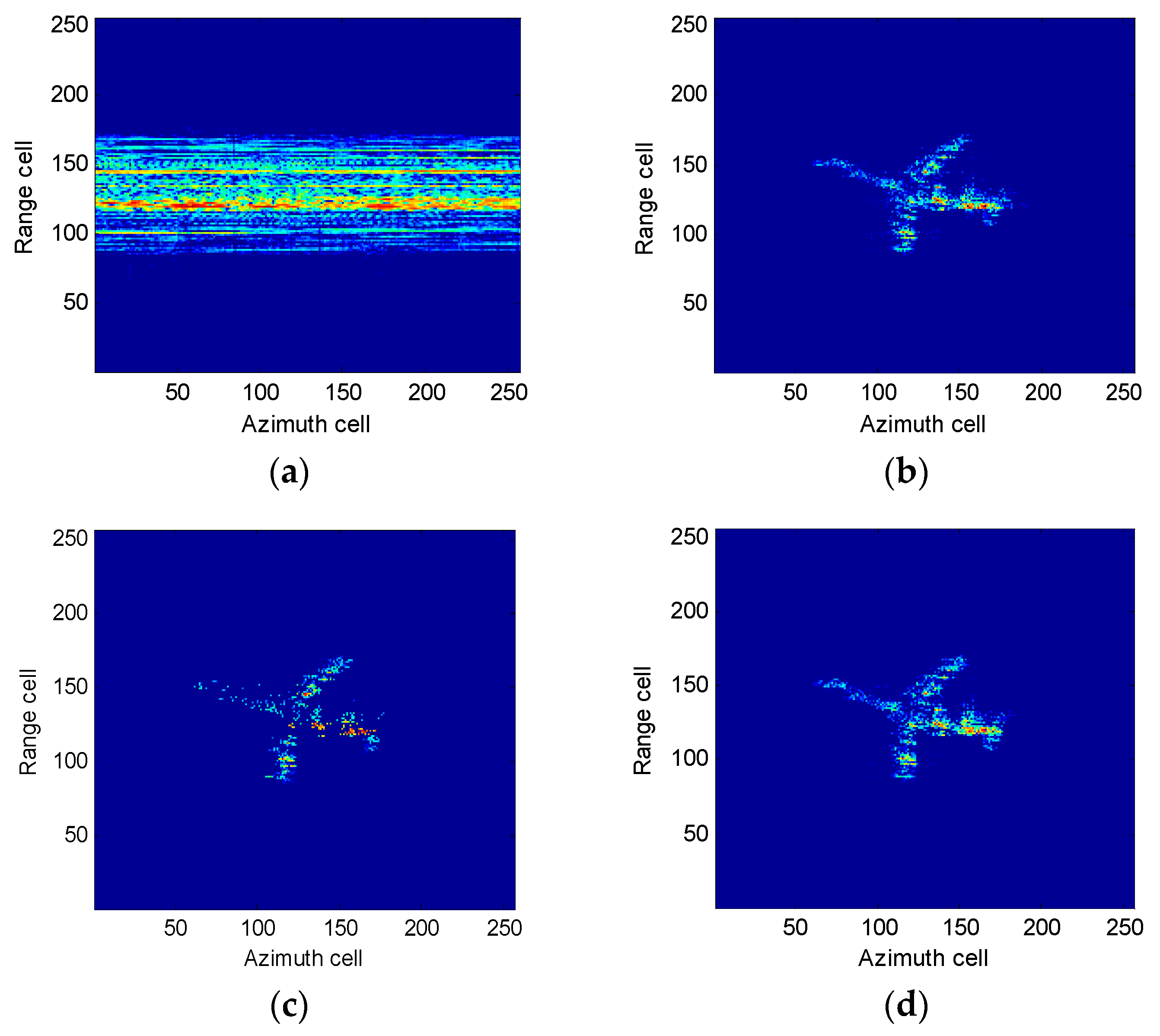
4.1. Simulation Results
4.2. Experimental Results
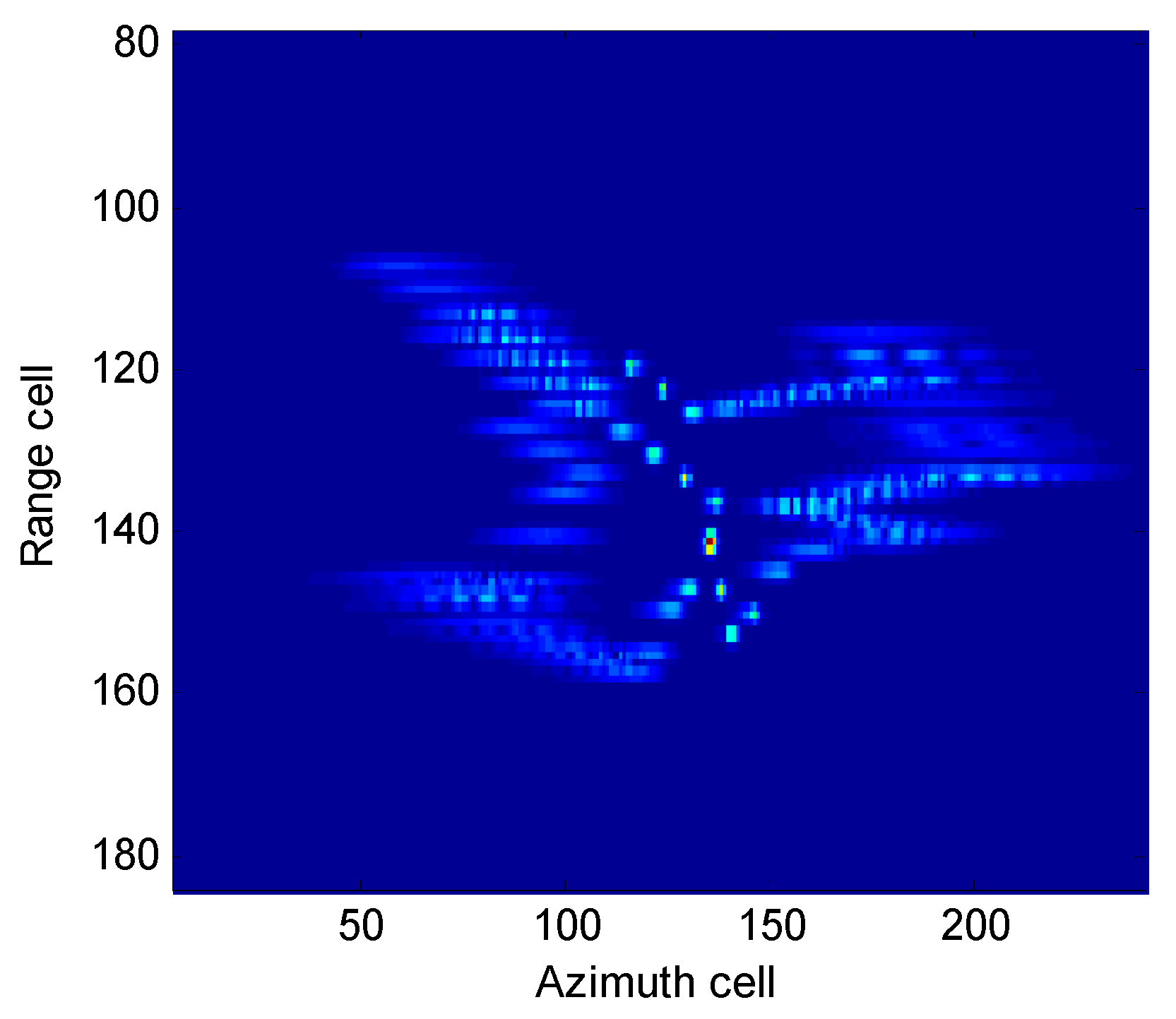
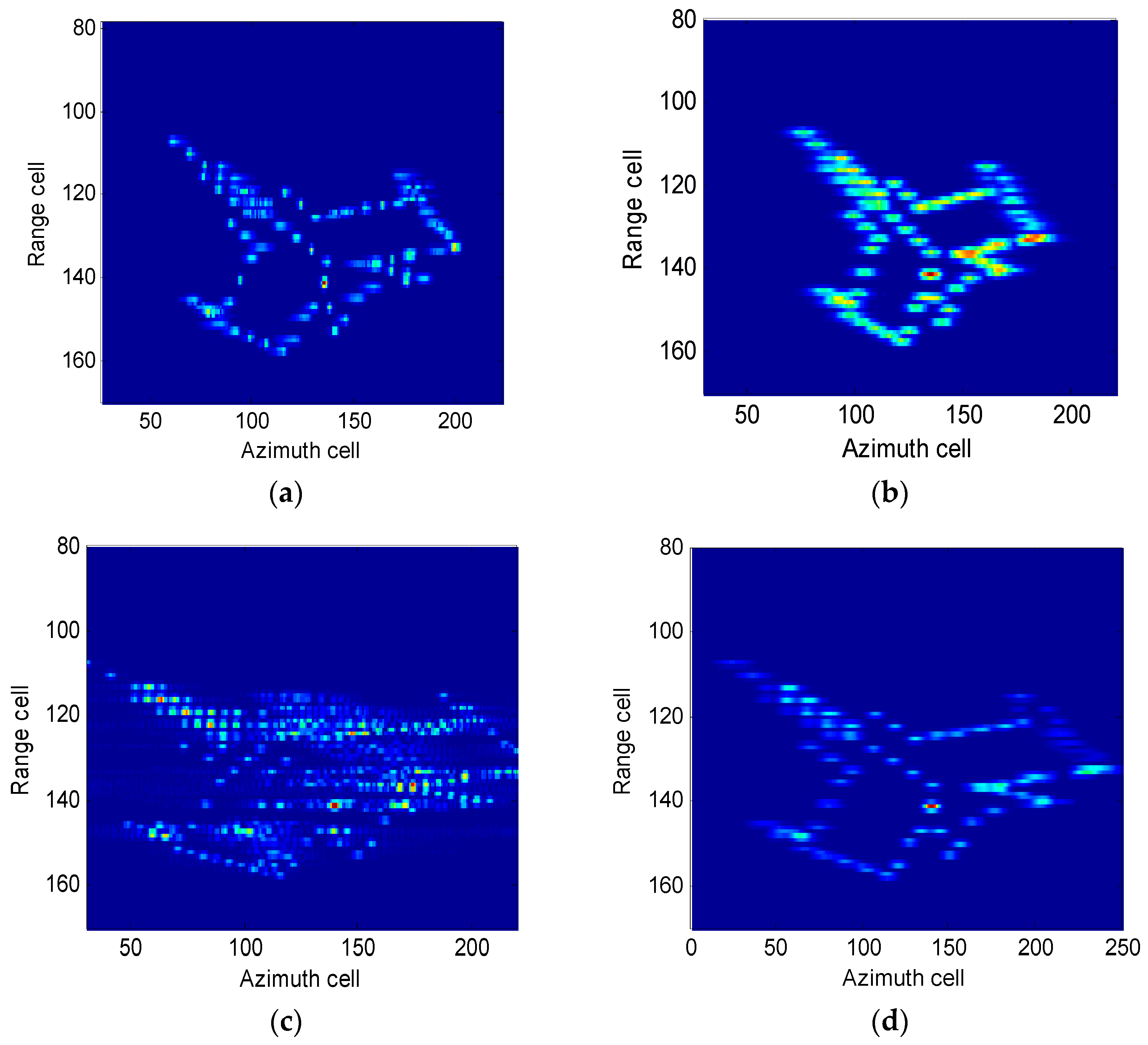
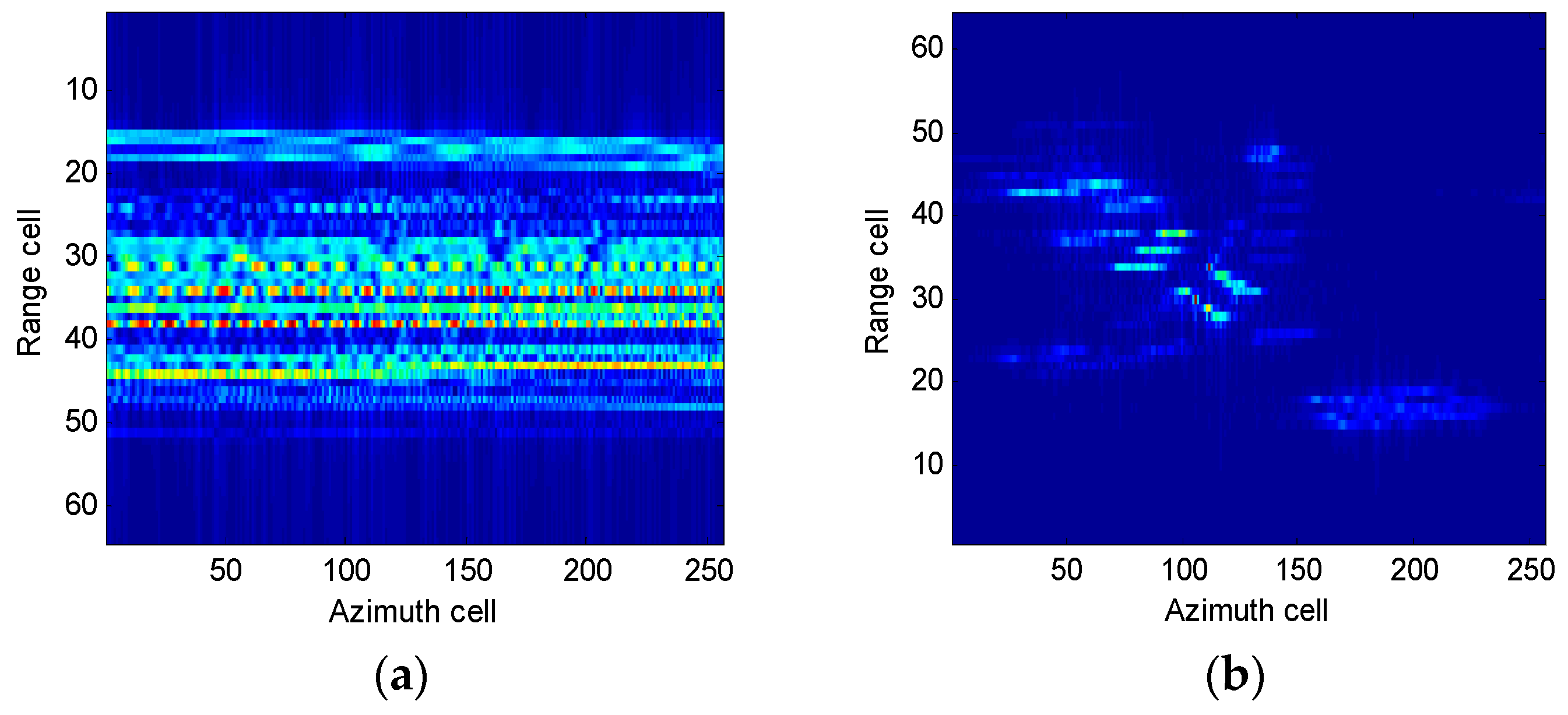
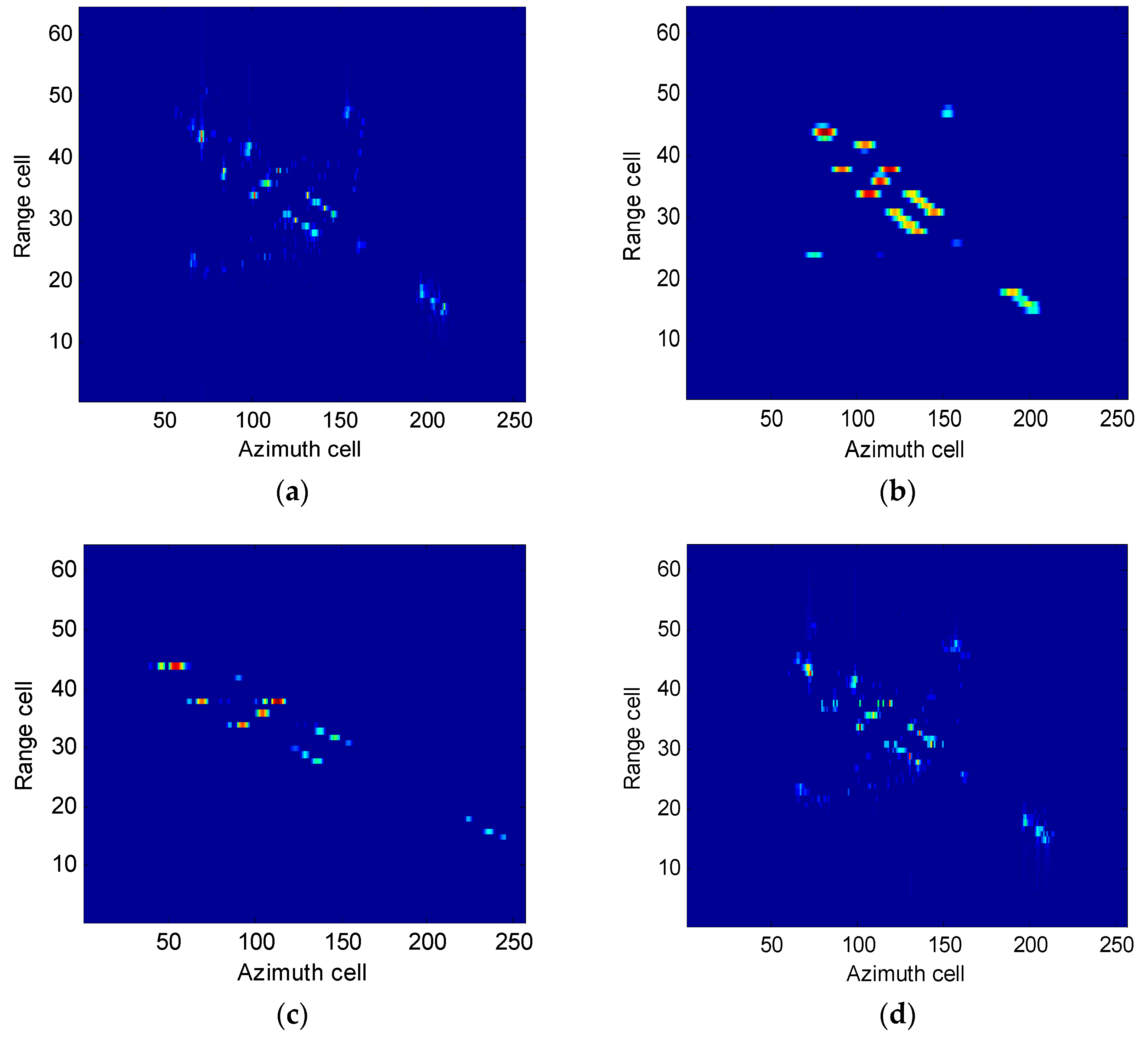
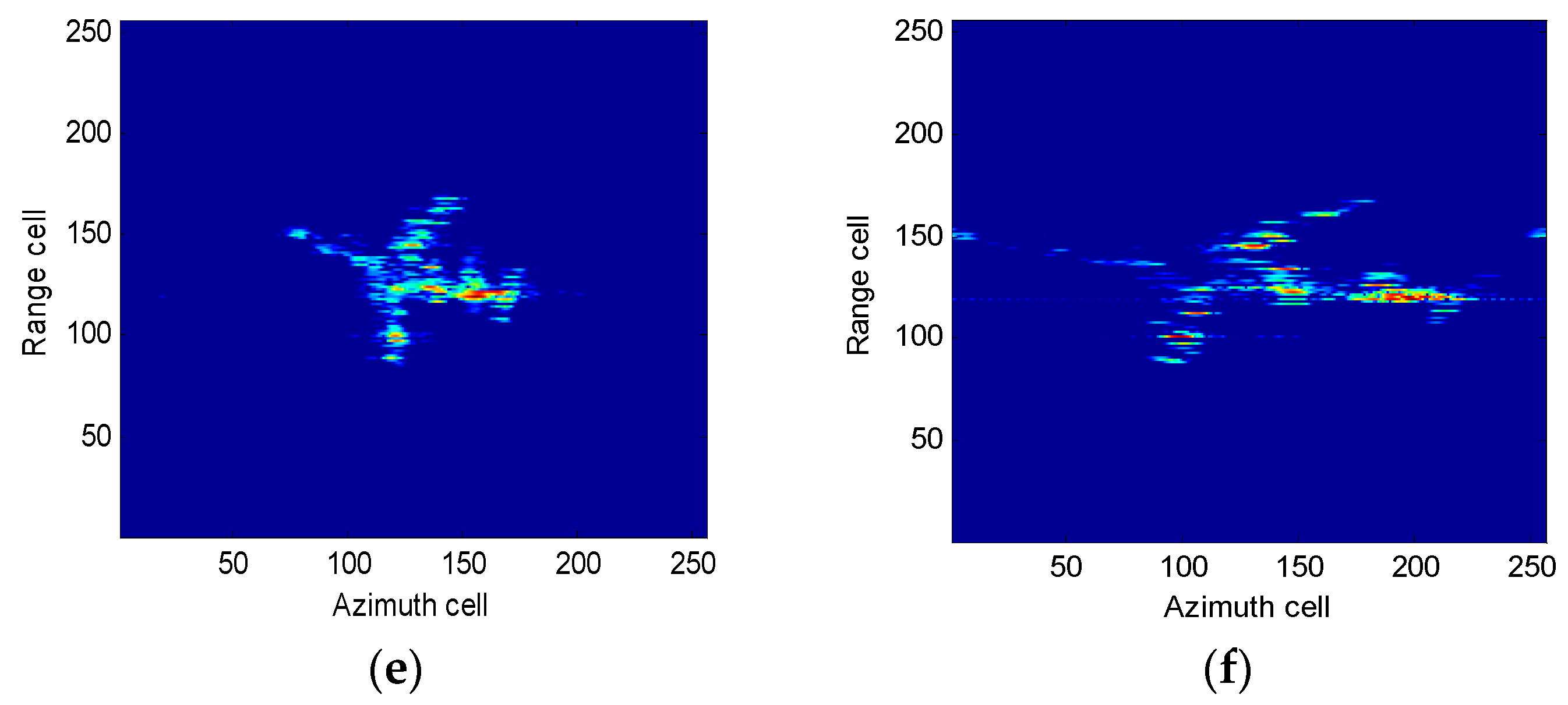
4.2.1. Boeing-727 Imaging Results
4.2.2. Yak-42 Imaging Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, H.; Wu, Y.; Jia, X. Novel ISAR imaging algorithm for maneuvering targets based on a modified keystone transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, A.; Minchev, C. ISAR geometry, signal model, and image processing algorithms. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.C.; Martorella, M. Introduction to ISAR imaging. In Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Principles, Algorithms and Applications; SciTech Publishing: Edison, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xing, M.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, J.; Li, Y.; Bao, Z. Novel range profile synthesis algorithm for linearly stepped-frequency modulated inversed synthetic aperture radar imaging of remote manoeuvring target. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.Q.; Xia, X.G. ISAR 2-D imaging of uniformly rotating targets via matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ling, H.; Chen, V.C. ISAR motion compensation via adaptive joint time-frequency technique. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.L.; Xing, M.D.; Wan, C.R.; Zhang, S. ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets based on the range centroid Doppler technique. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.C. ISAR imaging of maneuvering target based on the L-Class of fourth-order complex-lag PWVD. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Wang, G.Y.; Luo, L. Range-instantaneous Doppler imaging in ISAR. ACTA Electron. Sin. 1998, 26, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.C.; Wang, X.S.; Wang, G.Y. Scaled radon-Wigner transform imaging and scaling of maneuvering target. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.W.; Hu, J.M.; Li, X. ISAR imaging of uniformly accelerative rotating targets based on chirp-Fourier transform. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2011, 33, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wei, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, H.; Li, X. ISAR Imaging of targets with complex motion based on discrete chirp Fourier transform for cubic chirps. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4201–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Bao, Z. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of maneuvering targets based on chirplet decomposition. Opt. Eng. 1999, 38, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.C. ISAR imaging of a ship target using product high order matched-phase transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, R.; Xing, M.D.; Bao, Z. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of ship target with complex motion. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2008, 2, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.C. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of maneuvering target based on the product generalized cubic phase function. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.N.; Xiang, J.B. Parametric inverse synthetic aperture radar manoeuvring target motion compensation based on particle swarm optimiser. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, C.; Fornaro, G.; Braca, P.; Martorella, M. Fast and Accurate ISAR Focusing Based on a Doppler Parameter Estimation Algorithm. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, S.; Wu, W.; Hu, P.; Chen, Z. Adaptive ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets based on a modified Fourier transform. Sensors 2018, 18, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, Y. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of targets with complex motion based on cubic Chirplet decomposition. LET Signal Process. 2015, 9, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W. Distributed ISAR Subimage Fusion of Nonuniform Rotating Target Based on Matching Fourier Transform. Sensors 2018, 18, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xu, S.; Hu, P.; Zou, J.; Chen, Z. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging of Targets with Complex Motion based on Optimized Non-Uniform Rotation Transform. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiu, L.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Y. An Inverse Synthetic Aperture Ladar Imaging Algorithm of Maneuvering Target Based on Integral Cubic Phase Function-Fractional Fourier Transform. Electronics 2018, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Tao, M.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z. Adaptive Translational Motion Compensation Method for ISAR Imaging Under Low SNR Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5146–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhan, M.; Liu, H.; Liao, Y.; Liao, G. A Robust Translational Motion Compensation Method for ISAR Imaging Based on Keystone Transform and Fractional Fourier Transform under Low SNR Environment. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Grenier, D.; Delisle, G.Y.; Fang, D.G. Translational motion compensation in ISAR image processing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1995, 4, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Sun, H.B.; Wang, S.L.; Liu, G.S. Comments on discrete chirp-Fourier transform and its application to chirp rate estimation [with reply]. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 3115–3116. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, Y. ISAR Imaging Based on Frequency Modulated Fourier Transform in Low SNR Environment. J. Proj. Rockets Missiles Guid. 2017, 2, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.B. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of ship targets with complex motion based on match Fourier transform for cubic chirps mode. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2013, 7, 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, P.; Xia, X. Two modified discrete chirp Fourier transform schemes. Sci. China 2001, 44, 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, Z. Keystone transform and MDCFT-based detection and parameter estimation for maneuvering weak targets. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2013, 34, 855–863. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.L. Parameter estimation of multi-component chirp signals based on discrete chirp Fourier transform and population Monte Carlo. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 9, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Ding, X.; Zhou, H. Optimization method based extreme learning machine for classification. Neurocomputing 2010, 74, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 169–199. [Google Scholar]
- Yonel, B.; Mason, E.; Yazici, B. Deep Learning for Passive Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alakkari, S.; Jamil, K.; Alhumaidi, S. Range only target localization in multi-static passive radar system: A gradient descent approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 Signal Processing Symposium (SPSympo), Debe, Poland, 10–12 June 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.C. Doppler signatures of radar backscattering from objects with micro-motions. IET Signal Process. 2008, 2, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B727S.mat. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/10/4/593/s1 (accessed on 12 October 2018).
- Wang, Y.; Kang, J.; Jiang, Y.C. ISAR imaging of maneuvering target based on the local polynomial Wigner distribution and integrated high order ambiguity function for cubic phase signal model. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2971–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
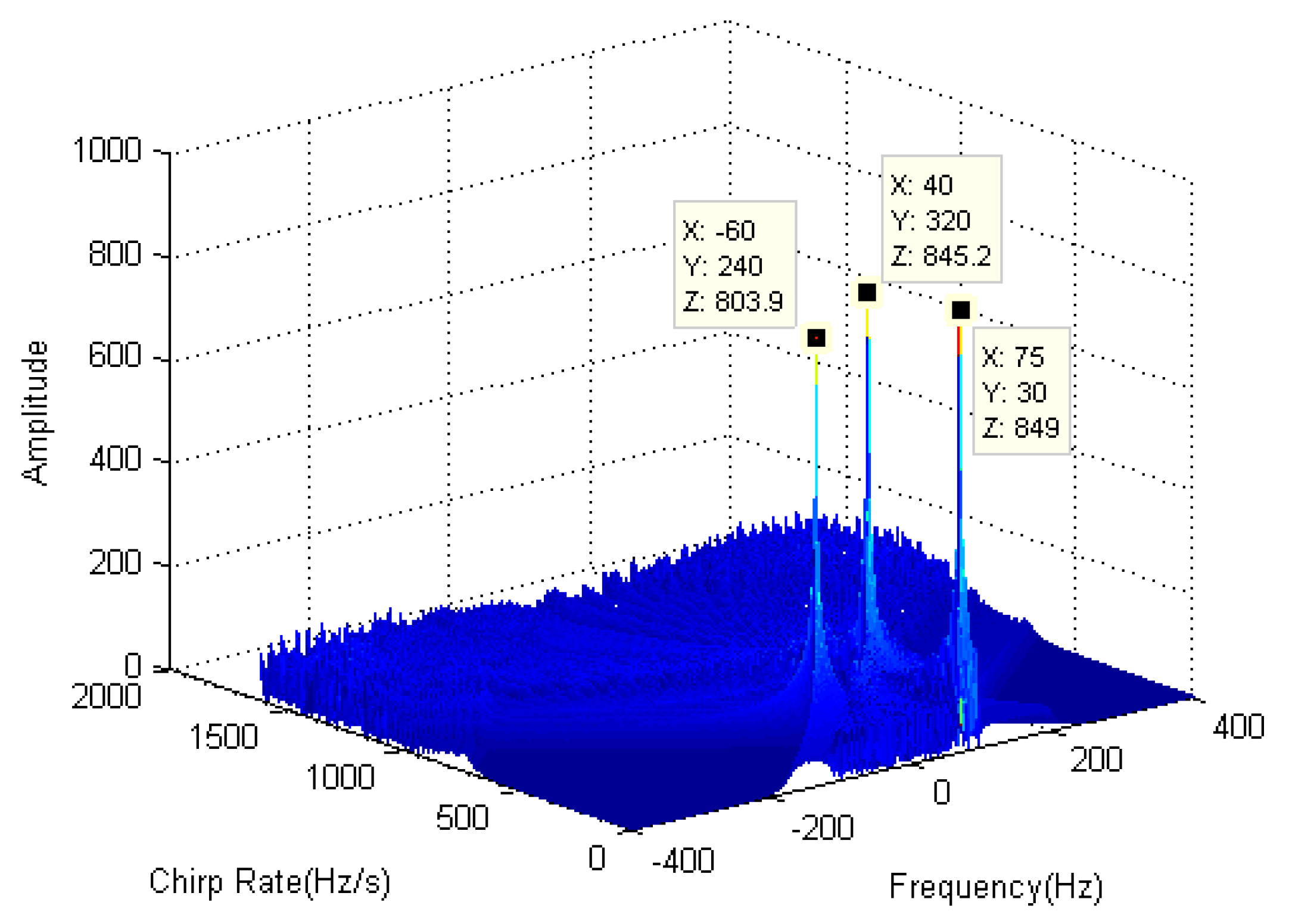





| Parameter | Estimated Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 320 | 40 | 320 | ||
| 1 | 75 | 30 | 75 | 30 | ||
| 1 | −60 | 240 | −60 | 240 |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| wavelength (m) | 0.05 | pulse number | 256 |
| carrier frequency (Ghz) | 6 | sampling frequency (MHz) | 10 |
| signal bandwidth (MHz) | 400 | processing time (s) | 1.28 |
| pulse width (ms) | 25.6 | Target angular velocity (rad/s) | 0.05 |
| PRF (Hz) | 200 | Target angular acceleration (rad/s2) | 0.05 |
| range sampling number | 256 |
| Range Cell | 113th | 122th | 128th | 133th | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Hz/s) | −21.58 | −24.04 | 36.34 | −8.66 | - |
| (Hz) | −21.75 | −23.25 | 35.97 | −10.8 | - |
| 0.992 | 1.034 | 1.010 | 0.802 | 0.960 |
| Imaging Algorithm | RD | RWT | STFT | WVD | SPWVD | MCFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image entropy | 7.4181 | 6.8982 | 7.1582 | 6.9537 | 6.7750 | 5.122 |
| Contrast ratio | 4.7893 | 6.9965 | 5.8101 | 5.7753 | 6.3976 | 10.5882 |
| Running time (s) | 0.5126 | 57.9541 | 2.8543 | 40.6241 | 179.3857 | 3.2347 |
| Imaging Algorithm | RD | STFT | SPWVD | RWT | MCFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image entropy | 6.5821 | 6.1303 | 4.9231 | 5.5312 | 4.5851 |
| Contrast ratio | 2.4918 | 2.7934 | 6.5815 | 7.7614 | 9.1270 |
| Running time (s) | 0.0015 | 0.6861 | 7.3798 | 32.1524 | 1.5768 |
| Imaging Algorithm | RD | STFT | SPWVD | RWT | MCFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image entropy | 6.0291 | 6.1303 | 4.7586 | 5.7942 | 4.9807 |
| Contrast ratio | 4.7072 | 2.7934 | 12.5733 | 7.9916 | 14.7757 |
| Running time (s) | 0.0012 | 2.8561 | 36.7251 | 15.7137 | 1.4107 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiu, L.; Zhao, H.; Sun, Y. A Novel Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Method for Maneuvering Targets Based on Modified Chirp Fourier Transform. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122443
Lv Y, Wang Y, Wu Y, Wang H, Qiu L, Zhao H, Sun Y. A Novel Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Method for Maneuvering Targets Based on Modified Chirp Fourier Transform. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122443
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yakun, Yongping Wang, Yanhong Wu, Hongyan Wang, Lei Qiu, Hongzhong Zhao, and Yang Sun. 2018. "A Novel Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Method for Maneuvering Targets Based on Modified Chirp Fourier Transform" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122443
APA StyleLv, Y., Wang, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, H., Qiu, L., Zhao, H., & Sun, Y. (2018). A Novel Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Method for Maneuvering Targets Based on Modified Chirp Fourier Transform. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122443





