Desert and Sonic Ecosystems: Incorporating Environmental Factors within Site-Responsive Sonic Art
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Overview of Garden Ecologies
2. Background
2.1. Sound and the Environment
2.2. Ecological Systems in Sound
2.3. Responsiveness to Site
3. Methodology
3.1. Surveying the Site
- which aspects of the environment could be used structurally or compositionally?
- what in the environment is moving, could make sound through movement, or is already audible?
- which elements of the environment are static, and which are dynamic/changing?
- which aspects are consistent/inconsistent?
3.2. Re-Sounding Material
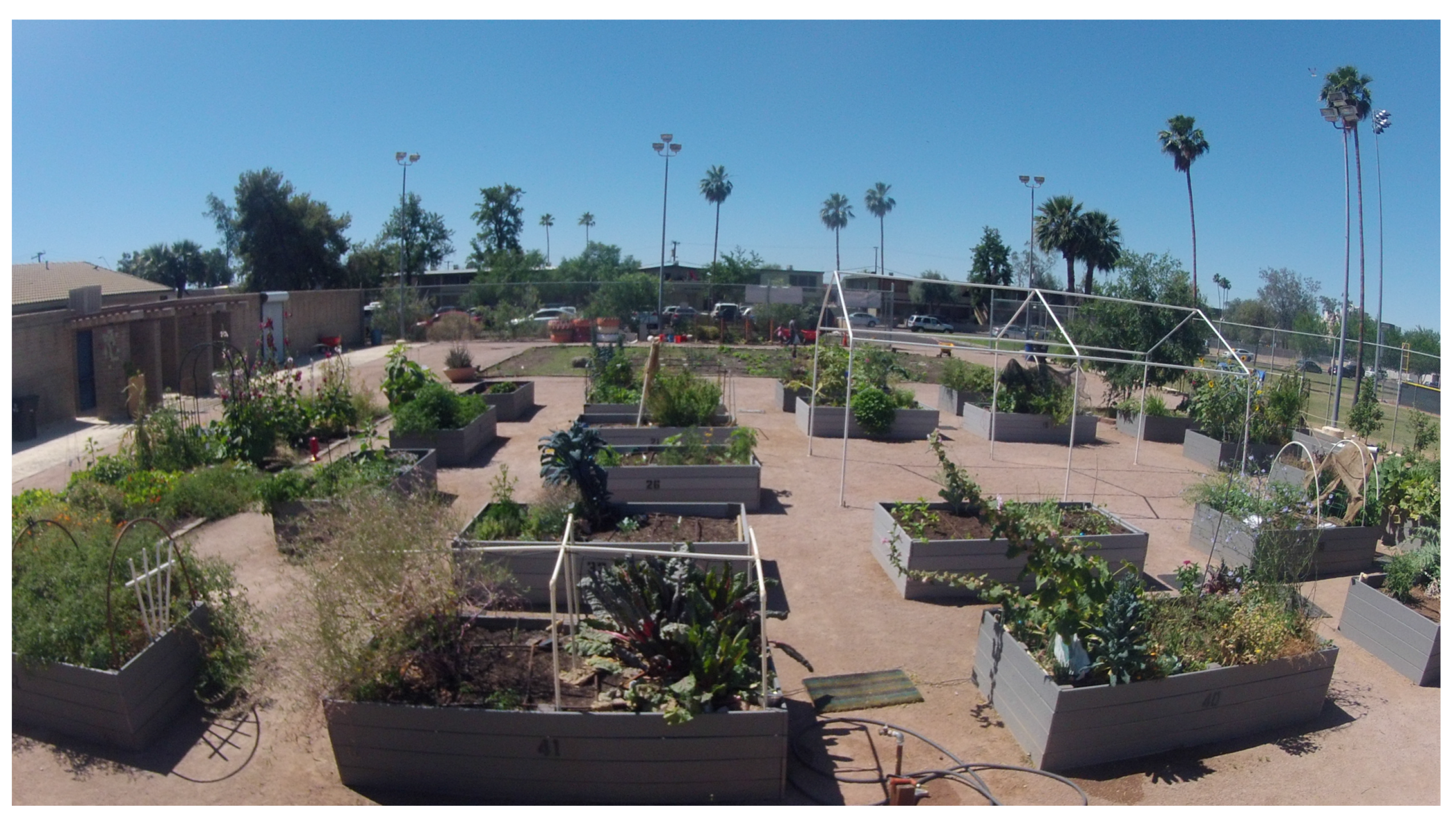
3.3. Ecological Garden-Raised Beds
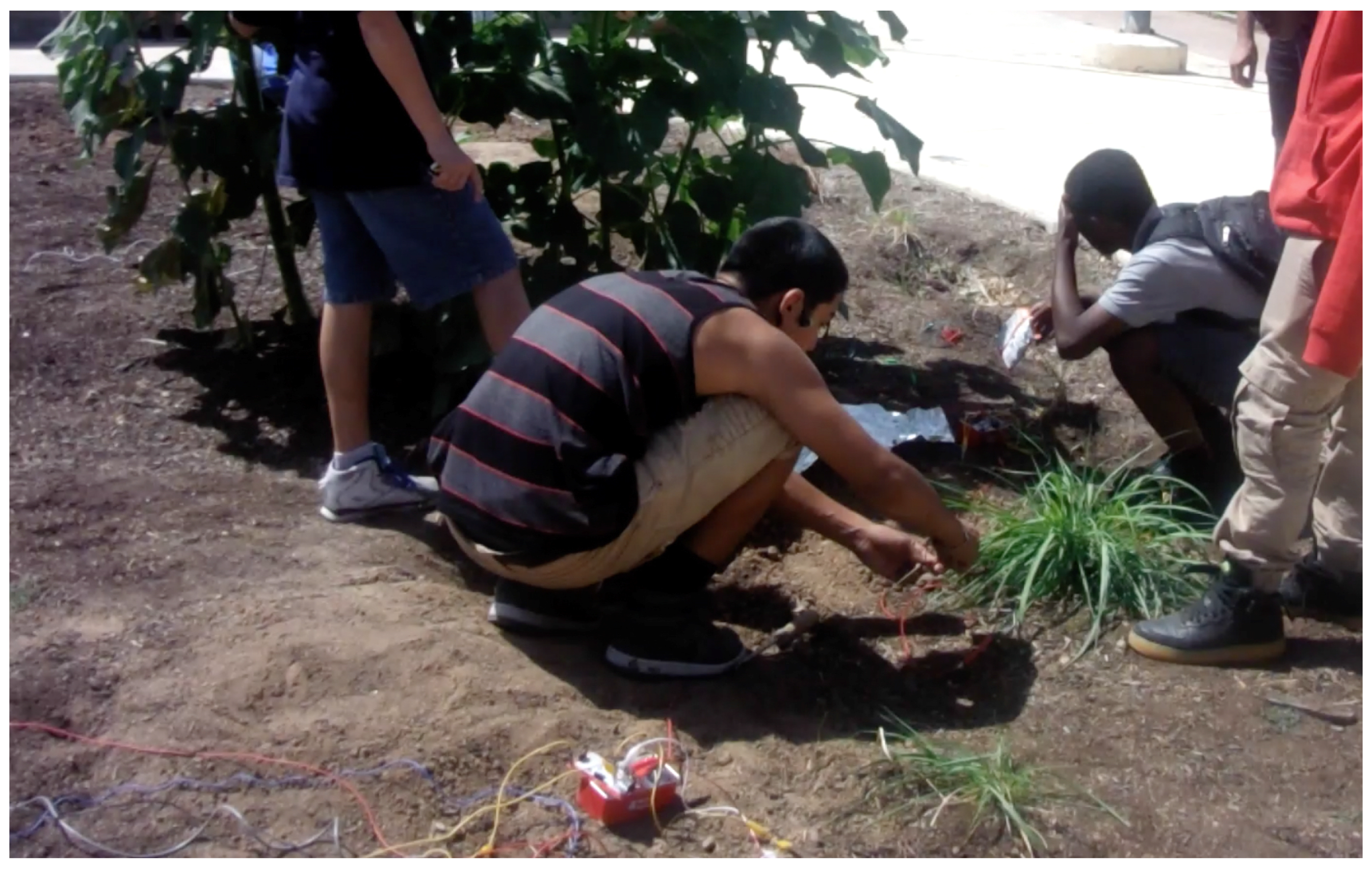
3.3.1. Environmental Sensing
3.3.2. Composed Relations
3.4. Highlighting Acoustic Phenomena-Tires
3.5. Historical Narratives
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSP | digital signal processing |
| DMI | digital musical instrument |
| HCI | human–computer interaction |
| TCAA | Tempe Community Action Agency |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| C4DM | Centre for Digital Music |
| Pd | Pure Data |
| CdS | cadmium sulphide |
References
- Hayes, L. From Site-Specific to Site-Responsive: Sound Art Performances as Participatory Milieu. In Organised Sound; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; Volume 22, pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Maturana, H.R.; Varela, F.J. Autopoiesis and Cognition: The Realization of the Living; Reidel, D., Ed.; Boston Studies in the Philosophy of Science; Springer: Dordecht, The Netherlands, 1980; Volume 42. [Google Scholar]
- Westerkamp, H. Linking Soundscape Composition and Acoustic Ecology. In Organised Sound; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; Volume 7, pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- López, F. Profound Listening and Environmental Sound Matter. In Audio Culture: Readings of Modern Music; Continuum International Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsomichalis, M. On Soundscapes, Phonography and Environmental Sound Art. J. Sonic Stud. 2013, 4. Available online: http://journal.sonicstudies.org/vol04/nr01/a05 (accessed on 11 January 2018).
- Truax, B. Handbook for Acoustic Ecology; World Soundscape Project; Aesthetic Research Centre: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Barclay, L. Sonic Ecologies: Exploring the Agency of Soundscapes in Ecological Crisis. In Soundscape: The Journal of Acoustic Ecology; WFAE: Charlotte, NC, USA, 2013; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Barclay, L. Acoustic Ecology in UNESCO Biosphere Reserves–Barclay & Gifford. In International Journal of UNESCO Biosphere Reserves; VIU Press: Nanaimo, BC, Canada, 2017; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sueur, J.; Farina, A.; Gasc, A.; Pieretti, N.; Pavoine, S. Acoustic Indices for Biodiversity Assessment and Landscape Investigation. In Acta Acustica United with Acustica; Hirzel, S., Ed.; Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2014; Volume 100, pp. 772–781. [Google Scholar]
- Ingold, T. Against Soundscape. In Autumn LEaves: Sound and the Environment in Artistic Practice; Carlyle, A., Ed.; Double Entendre: Paris, France, 2007; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Blacking, J. How Musical Is Man? University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA; London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, G.; Moon, B.; Hoffman, R.R. Making Sense of Sensemaking 1: Alternative Perspectives. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2006, 21, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, S. Performance Ecosystems: Ecological Approaches to Musical Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2007 Electroacoustic Music Studies Network, Leicester, UK, 12–15 June 2007; EMS: Leicester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Green, O. Pondering Value in the Performance Ecosystem. eContact! 2008, 10, 197–213. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, T. Towards a Relational Understanding of the Performance Ecosystem. In Organised Sound; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 16, pp. 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio, A. Sound is the Interface: From Interactive to Ecosystemic Signal Processing. In Organised Sound; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Malloch, J.; Birnbaum, D.; Sinyor, E.; Wanderley, M.M. Towards a New Conceptual Framework for Digital Musical Instruments. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–20 September 2006; pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio, A. Using PD for Live Interactions in Sound. An Exploratory Approach. In Proceedings of the 4th International Linux Audio Conference, Karlsruhe, Germany, 27–30 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sanfilippo, D.; Di Scipio, A. Environment-Mediated Coupling of Autonomous Sound-Generating Systems in Live Performance: An Overview of the Machine Milieu Project. In Proceedings of the 14th Sound and Music Computing Conference, Espoo, Finland, 5–8 July 2017; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sanfilippo, D.; Valle, A. Feedback Systems: An Analytical Framework. In Computer Music Journal; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 37, pp. 12–27. [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk, J. Experimental Music Since 1970; Bloomsbury: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kaye, N. Site-Specific Art: Performance, Place and Documentation; Routledge: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- LaBelle, B. Background Noise, Second Edition: Perspectives on Sound Art; Bloomsbury Academic: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, M. One Place after Another: Notes on Site Specificity. In October; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; Volume 80, pp. 85–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rydarowski, A.; Samanci, O.; Mazalek, A. Murmur: Kinetic Relief Sculpture, Multi-Sensory Display, Listening Machine. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tangible, Embedded and Embodied Interaction, Bonn, Germany, 18–20 February 2008; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Misawa, D. Transparent Sculpture: An Embodied Auditory Interface for Sound Sculpture. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Tangible, Embedded and Embodied Interaction, Barcelona, Spain, 10–13 February 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 389–390. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, B. The Violin, The River, and Me: Artistic Research and Environmental Epistemology in balancing string and Devil’s Water 1, Two Recent Environmental Sound Art Projects. HZ J. 2013, 18. Available online: http://www.hz-journal.org/n18/hogg.html (accessed on 11 January 2018).
- Tempe Comunity Action Agency. 2017. Available online: http://tempeaction.org/about-us/ (accessed on 18 December 2017).
- Stirling, C. Sound Art/Street Life: Tracing the Social and Political Effects of Sound Installations in London. J. Sonic Stud. 2015, 11. Available online: https://www.researchcatalogue.net/view/234018/234019 (accessed on 11 January 2018).
- Oliveros, P. Deep Listening: A Composer’s Sound Practice; iUniverse: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Willow, D. Ambient Sites: Making Tangible the Subtle, Ephemeral and Seemingly Silent. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Cambridge, MA, USA, 25–27 January 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Droumeva, M.; Antle, A.; Wakkary, R. Exploring Ambient Sound Techniques in the Design of Responsive Environments for Children. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Tangible, Embedded and Embodied Interaction, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 15–17 February 2007; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Schiettecatte, B.; Vanderdonckt, J. AudioCubes: a Distributed Cube Tangible Interface based on Interaction Range for Sound Design. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tangible, Embedded and Embodied Interaction, Bonn, Germany, 18–20 February 2008; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, L. Sound, Electronics, and Music: A Radical and Hopeful Experiment in Early Music Education. In Computer Music Journal; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Voluem 41, pp. 36–49. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, A. Bela: An Embedded Platform for Low-Latency Feedback Control of Sound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 3618. [Google Scholar]
- Collective, B.M.; Shaw, D. Makey Makey: Improvising Tangible and Nature-Based User Interfaces. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Tangible, Embedded and Embodied Interaction, Kingston, ON, Canada, 19–22 February 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 367–370. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, T. On Sonic Art; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, G.; Bin, A.; Jack, R.H.; Heinrichs, C.; McPherson, A.P. Making High-Performance Embedded Instruments with Bela and Pure Data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Live Interfaces, Brighton, UK, 29 June–3 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Augoyard, J.F. Sonic Experience: A Guide to Everyday Sounds; McGill-Queens Press: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cinti, L. The Sensorial Invisibility of Plants: An Interdisciplinary Inquiry through Bio Art and Plant Neurobiology. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London (University of London), London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
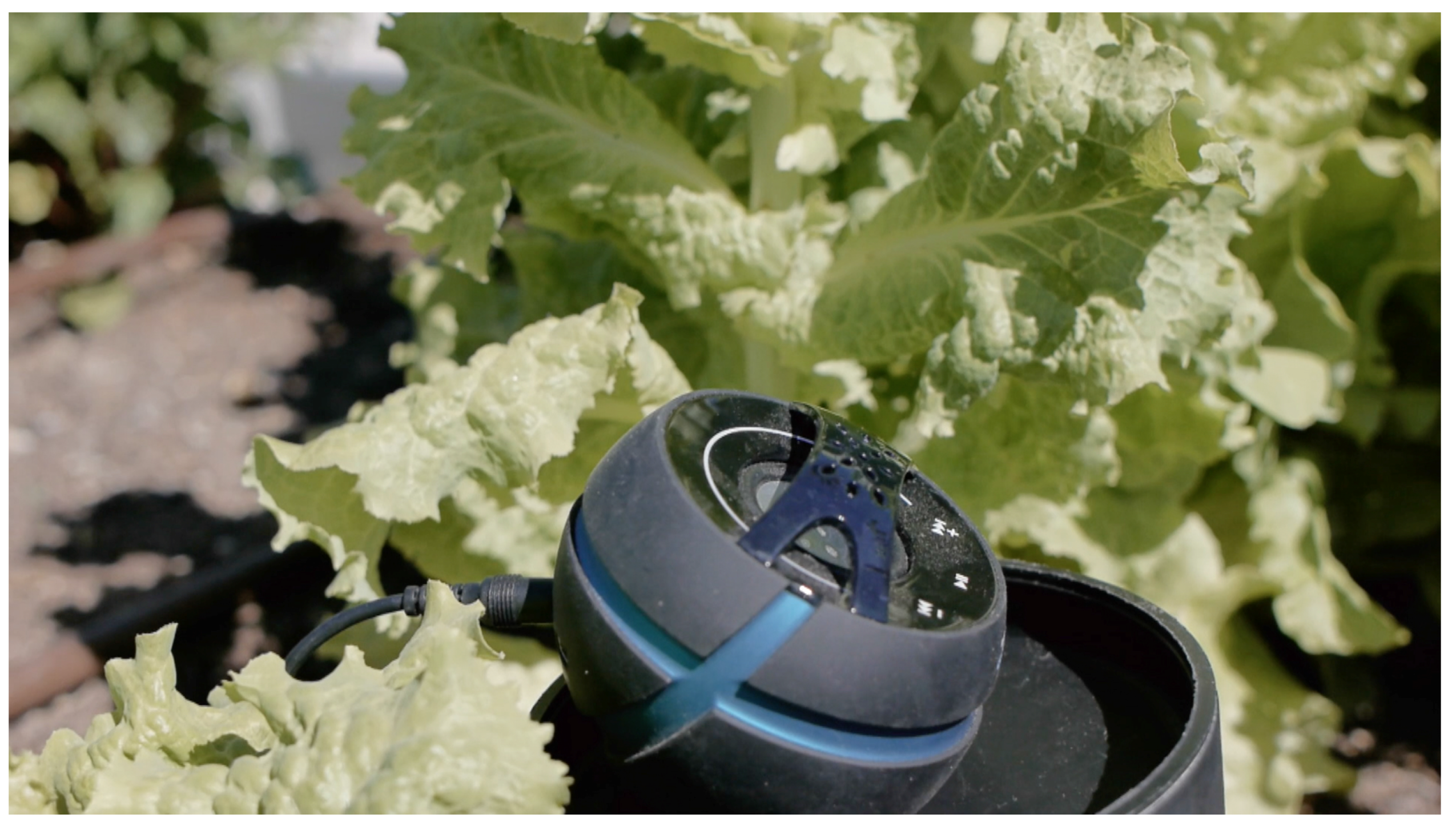
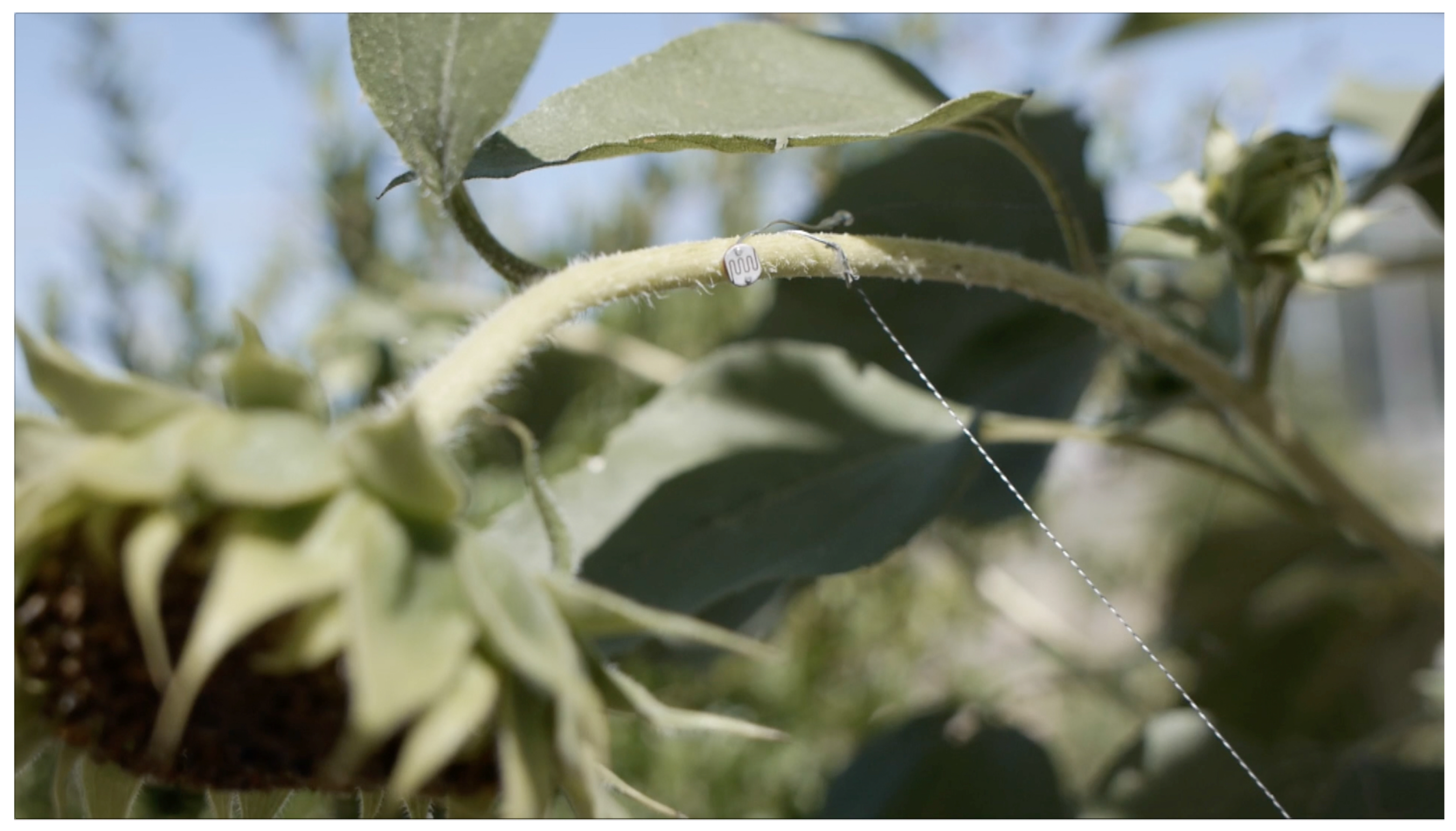




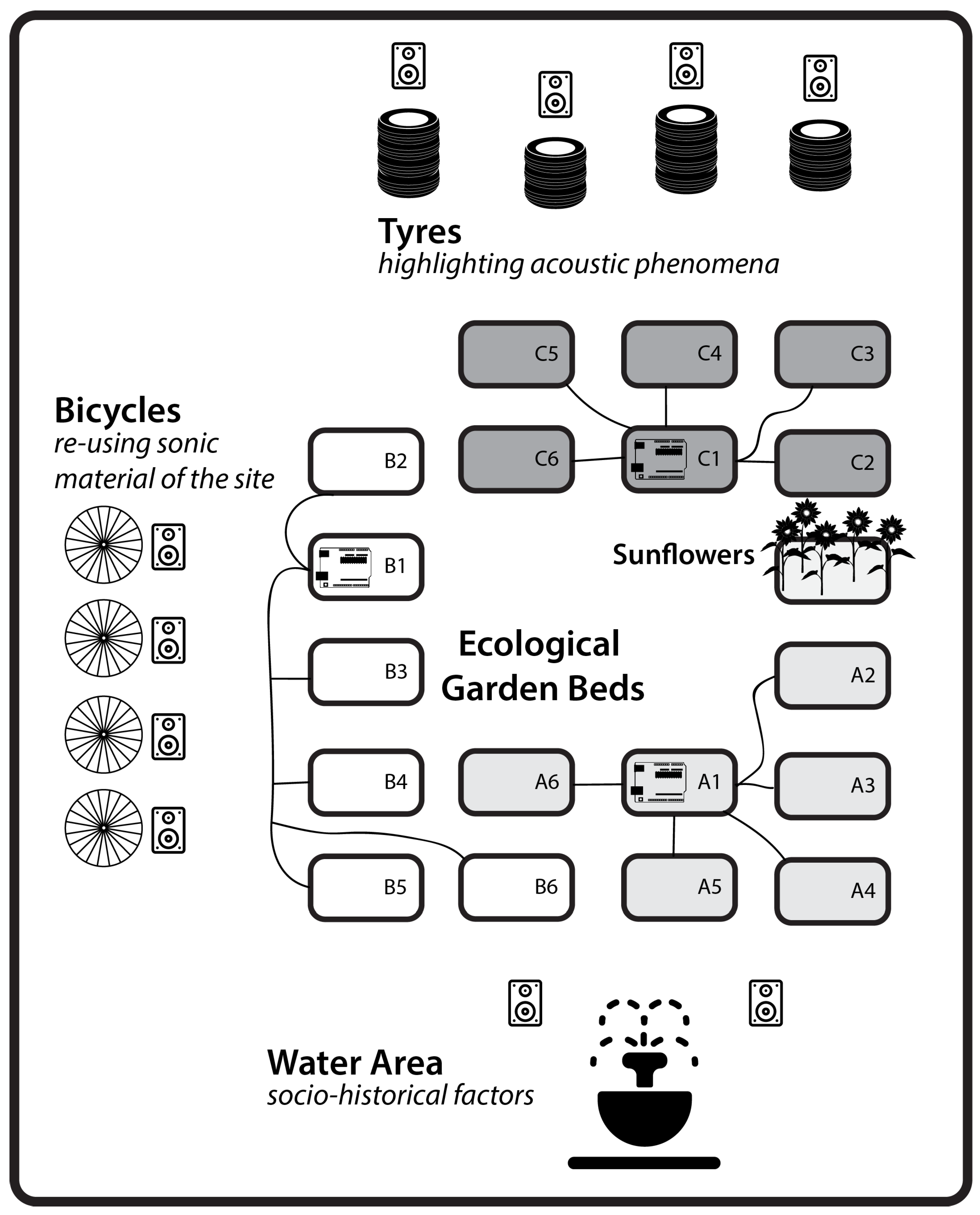
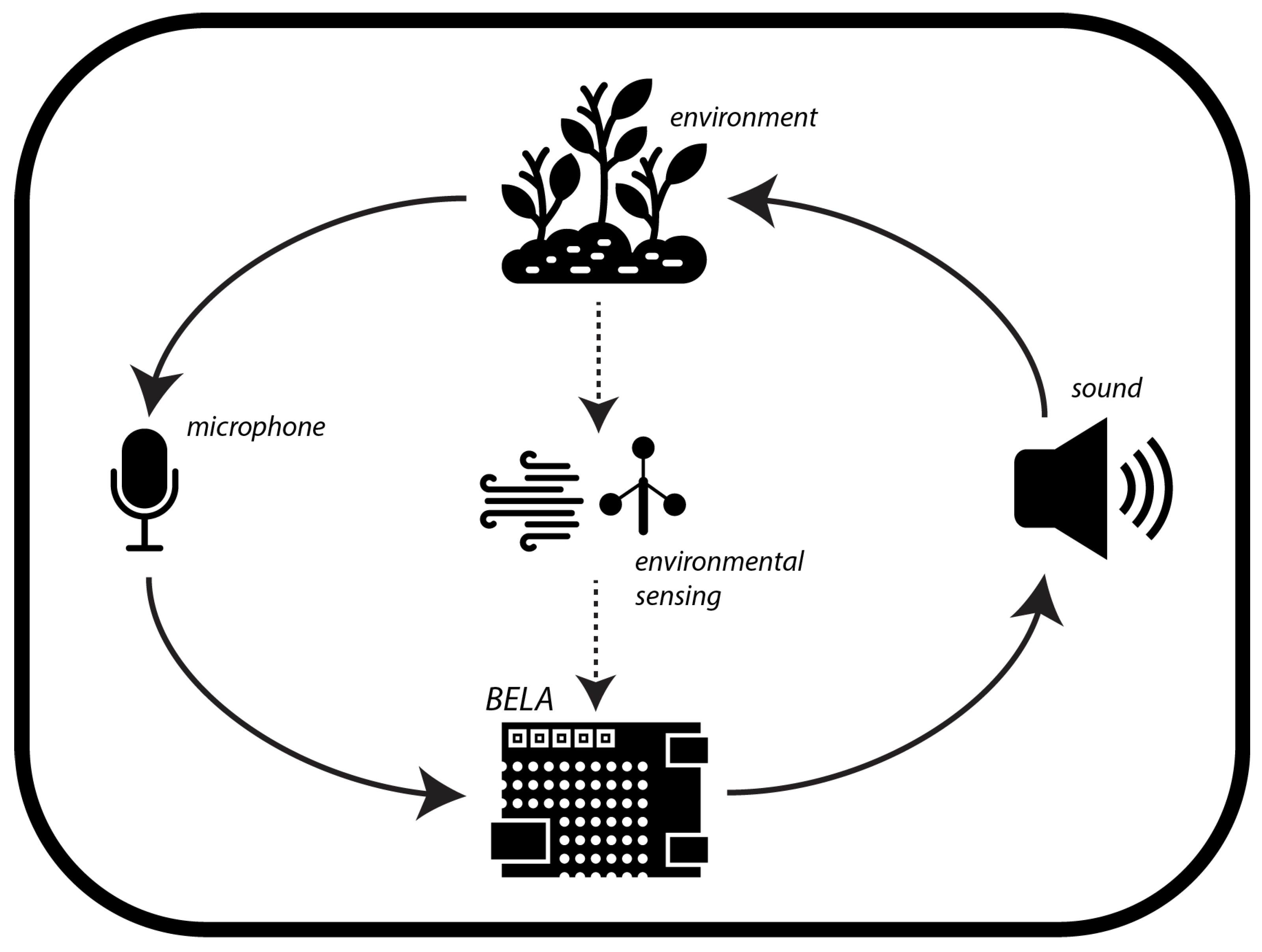


| Equipment | Description | Bed Location |
|---|---|---|
| Mighty Dwarf | portable 10 W speaker | A1, B1 |
| Minirig | portable 15 W speaker | C1, B5 |
| X-Mini | low-cost 2.5 W portable speaker | all remaining beds |
| Zoom H1 audio recorder | used for powered X-Y stereo microphones | A1, B1, C1 |
| LOLLETTE anemometer | wind speed sensor | B1 |
| Adafruit accelerometer | used to detect movement | B1 |
| cadmium sulphide (CdS) photoresistor | used to detect movement via fluctuations in light | A1 |
| Sonbest temperature/humidity sensor | used to detect slow changes in soil state | C1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayes, L.; Stein, J. Desert and Sonic Ecosystems: Incorporating Environmental Factors within Site-Responsive Sonic Art. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010111
Hayes L, Stein J. Desert and Sonic Ecosystems: Incorporating Environmental Factors within Site-Responsive Sonic Art. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010111
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayes, Lauren, and Julian Stein. 2018. "Desert and Sonic Ecosystems: Incorporating Environmental Factors within Site-Responsive Sonic Art" Applied Sciences 8, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010111
APA StyleHayes, L., & Stein, J. (2018). Desert and Sonic Ecosystems: Incorporating Environmental Factors within Site-Responsive Sonic Art. Applied Sciences, 8(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010111





