On the Link between Diesel Spray Asymmetry and Off-Axis Needle Displacement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reference Nozzle and Off-Axis Configuration of the Needle
2.2. Off-Axis Displacement of the Needle
2.3. Modeling Approach
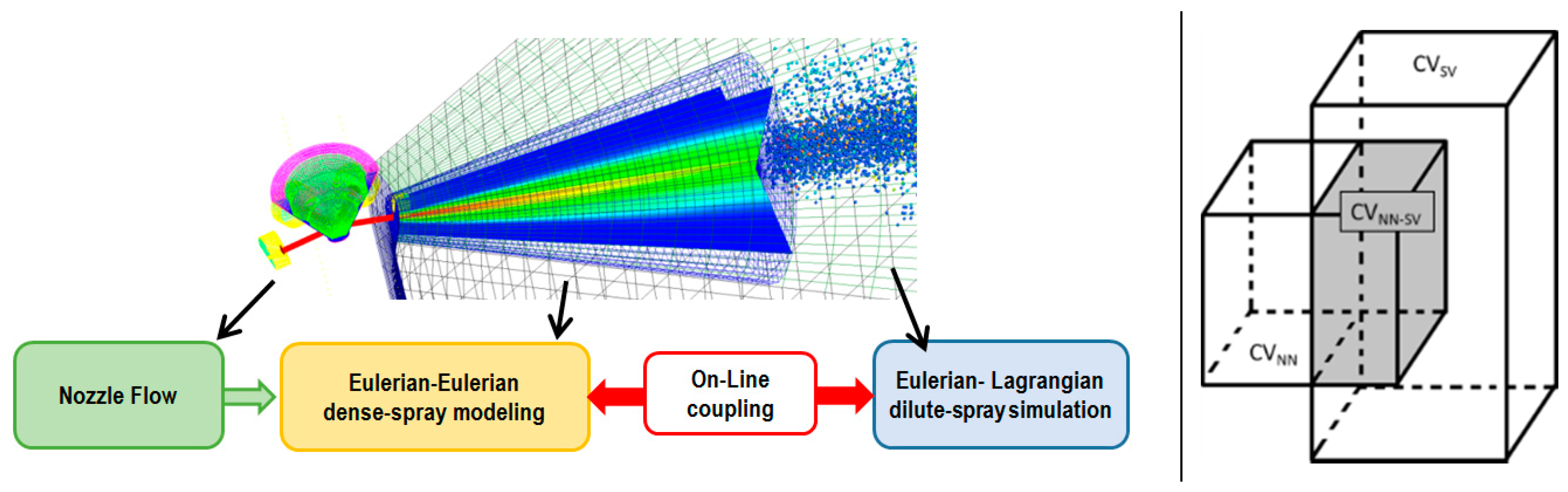
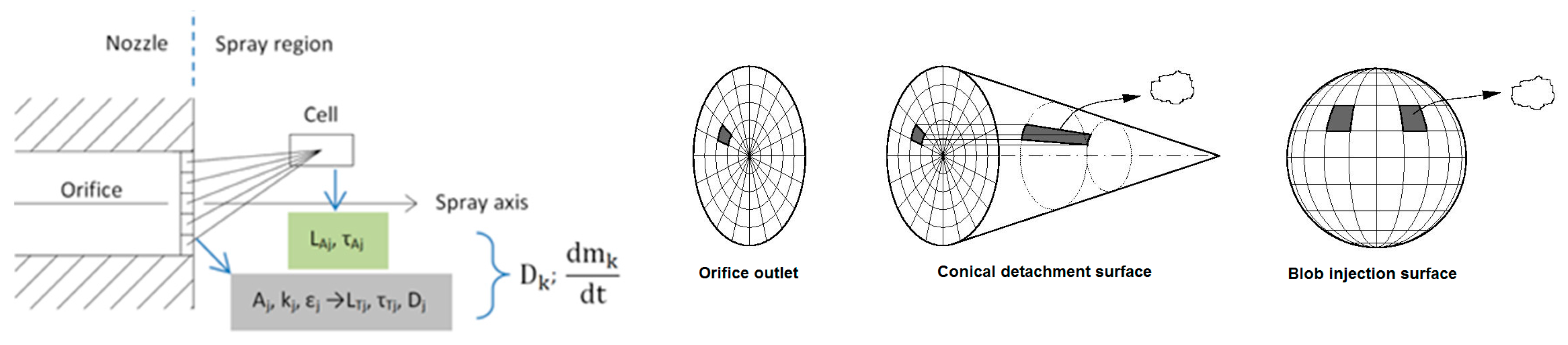
2.3.1. Coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian Spray Simulation
2.3.2. Near Nozzle Eulerian Spray Modeling
2.4. Primary Break-Up
2.4.1. Core Injection Approach under Nozzle Flow Local Information
2.4.2. Lagrangian Spray Modeling
2.5. Multiphase Nozzle Flow Modeling
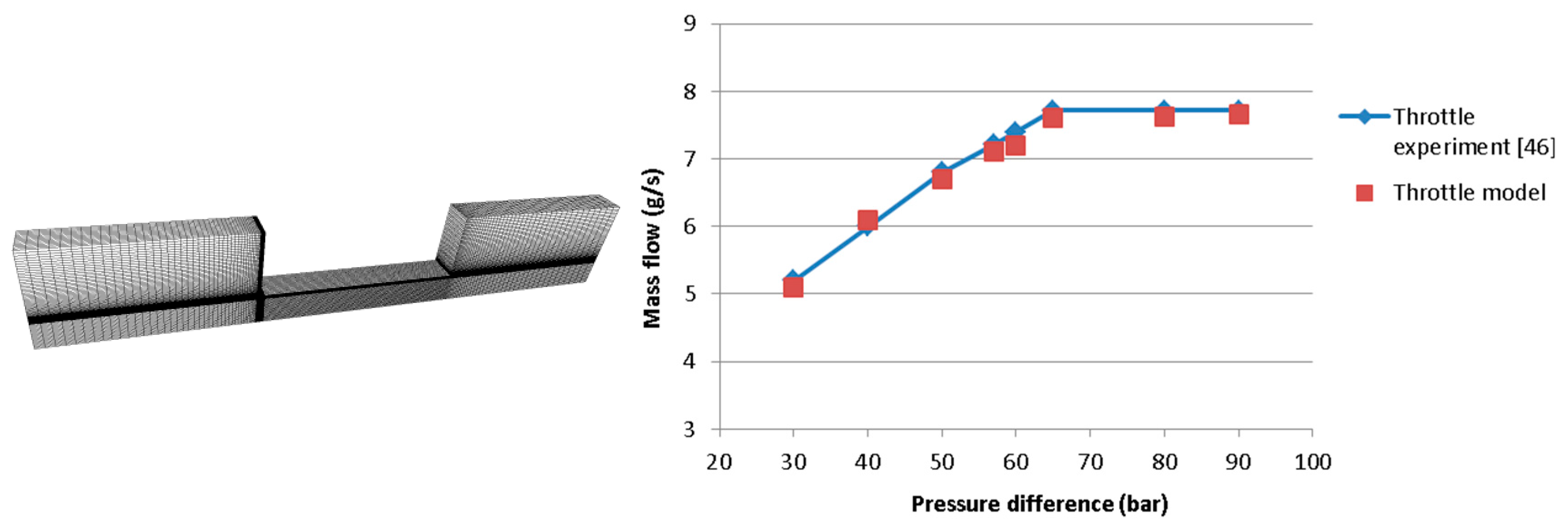
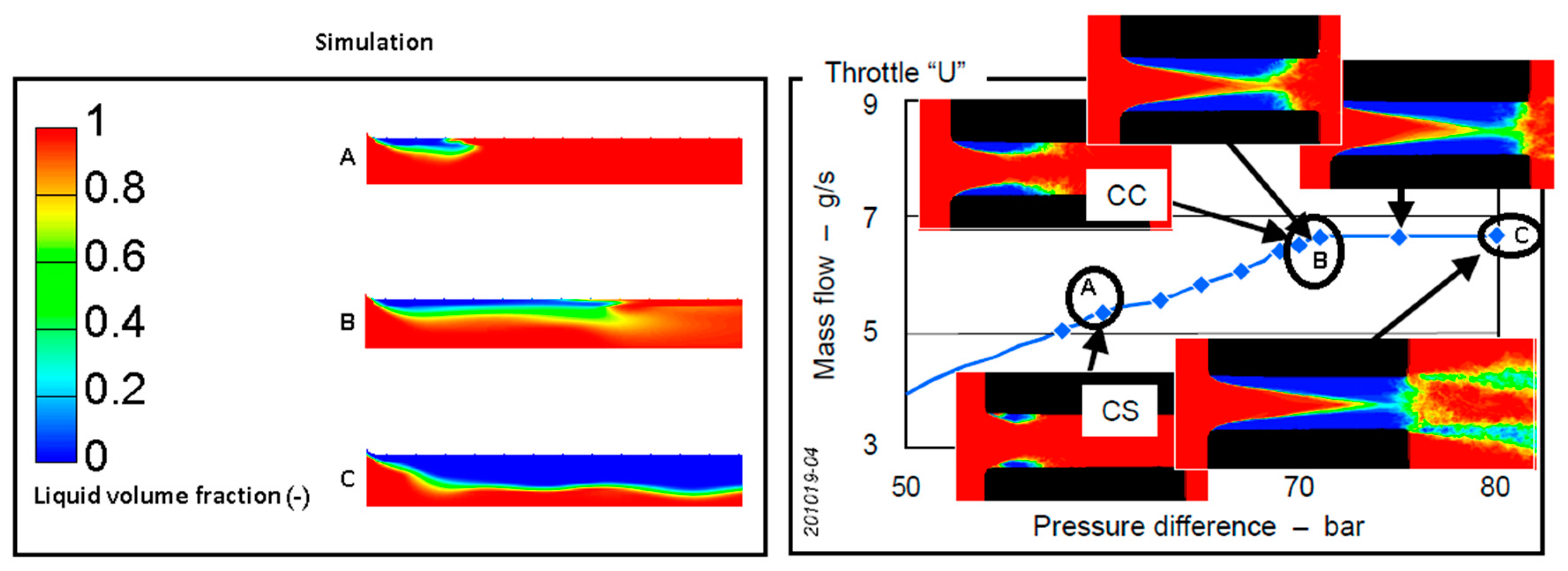
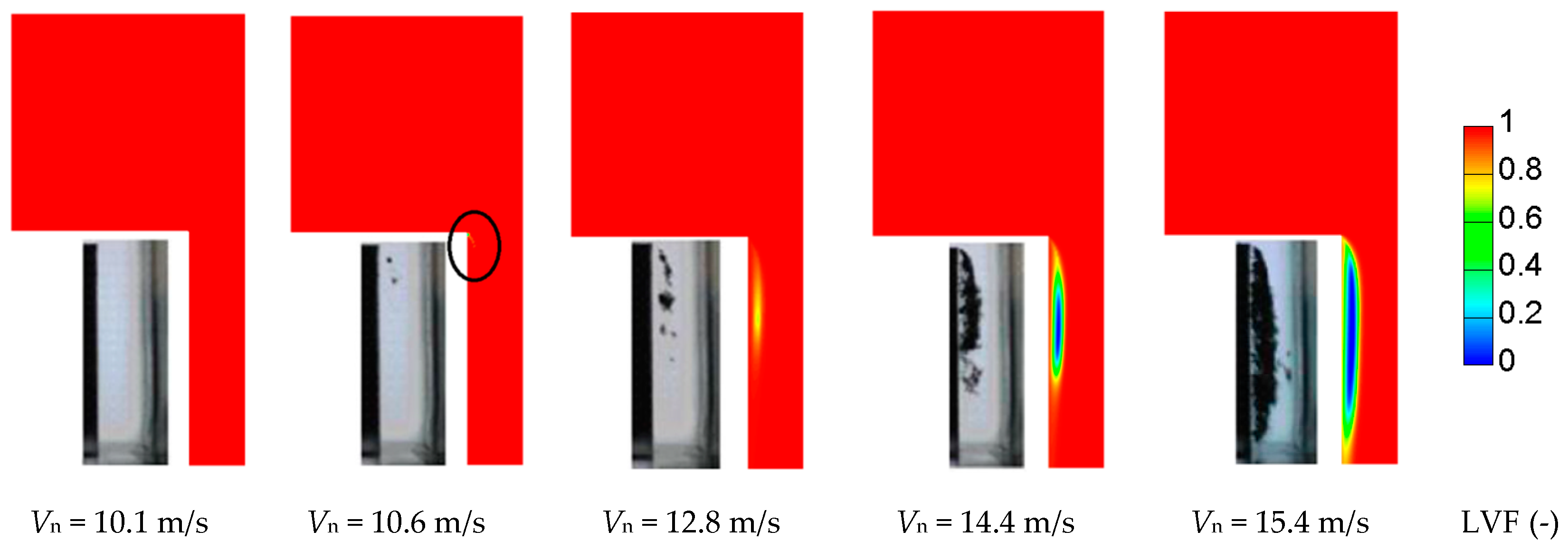
2.6. Cavitation Model Assessment
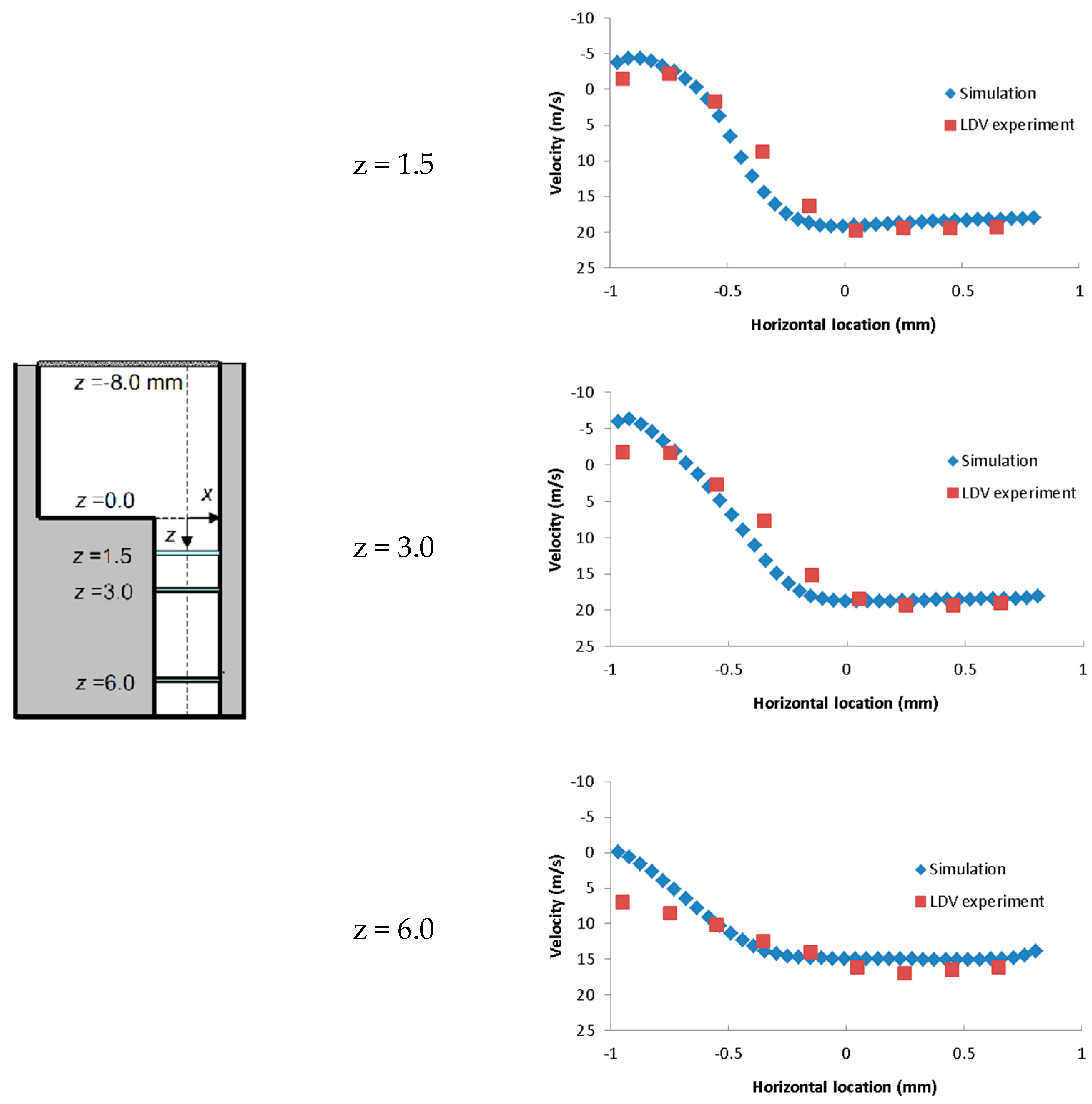
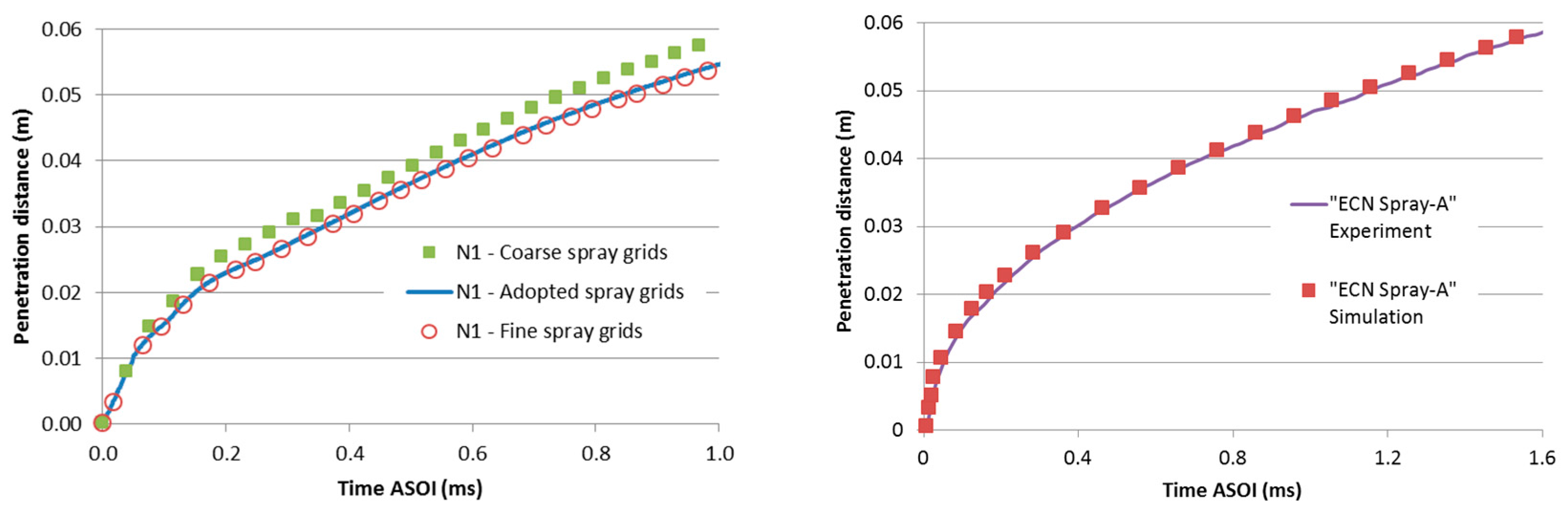
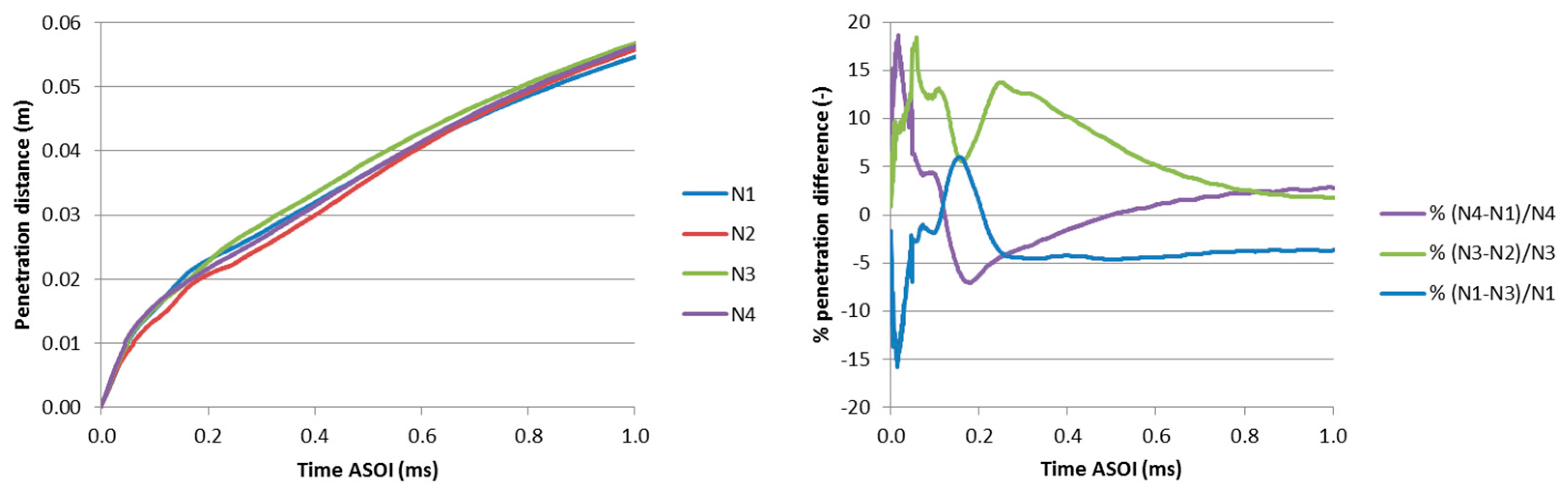
2.7. Grid Sensitivity Tests and Spray Model Assessment
2.8. Non-Dimensional Coefficients
3. Results
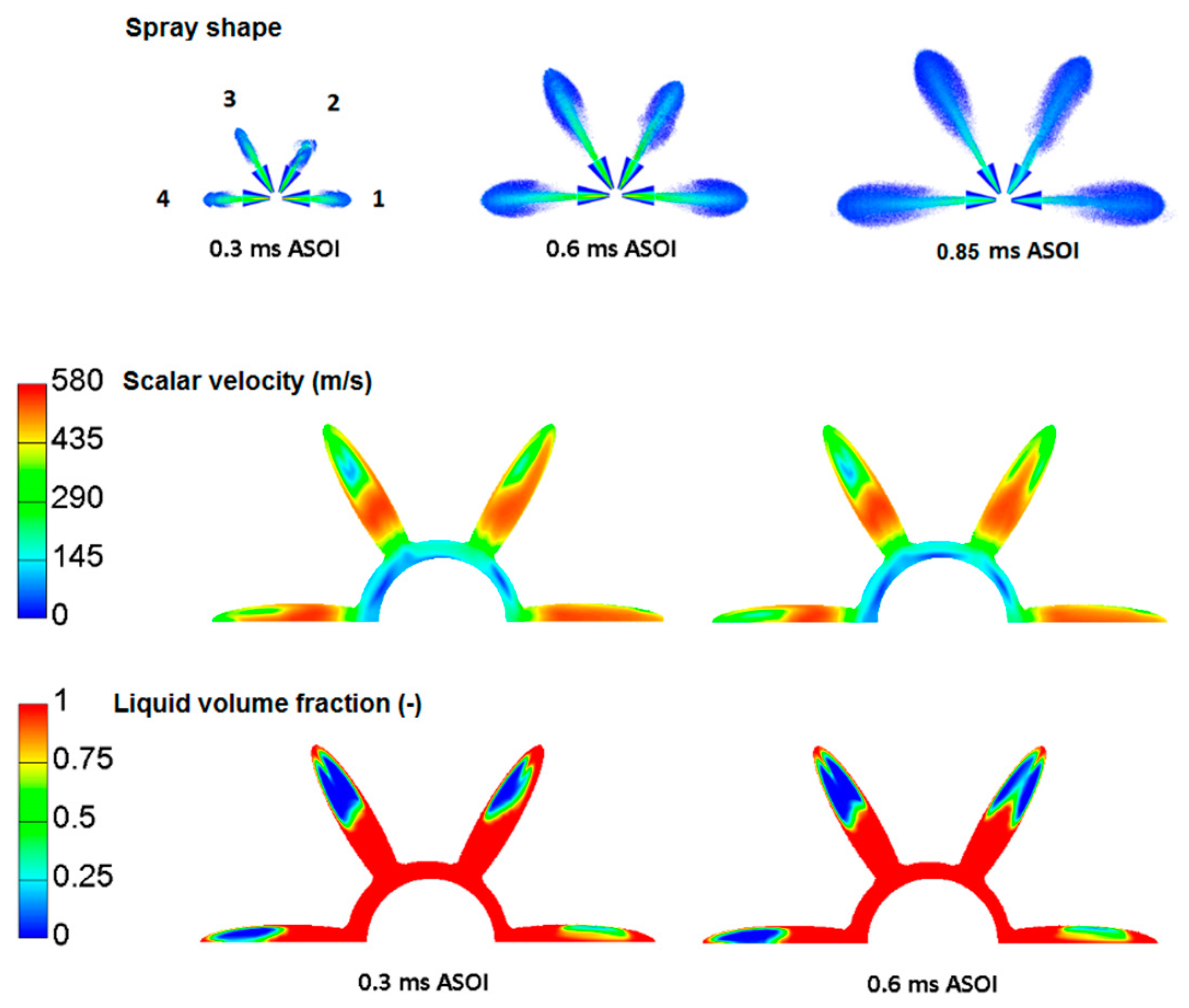
3.1. Hole-to-Hole Difference on Spray Penetration
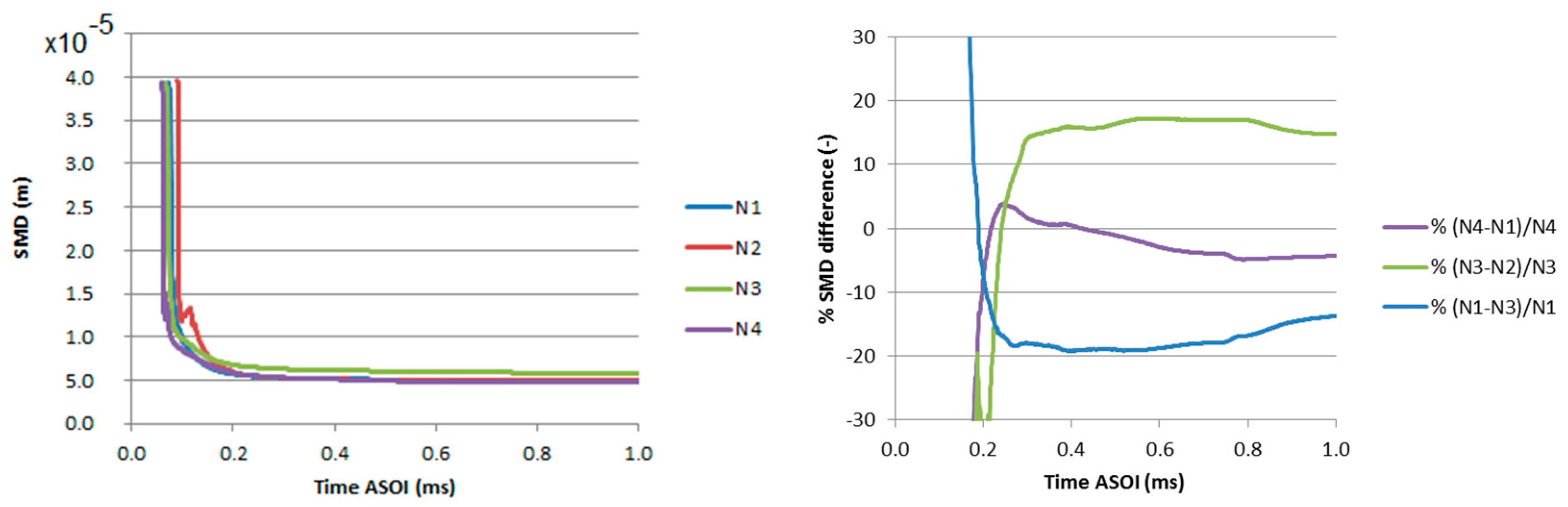
3.2. Hole-to-Hole Differences for Spray Sauter Mean Diameter (SMD)
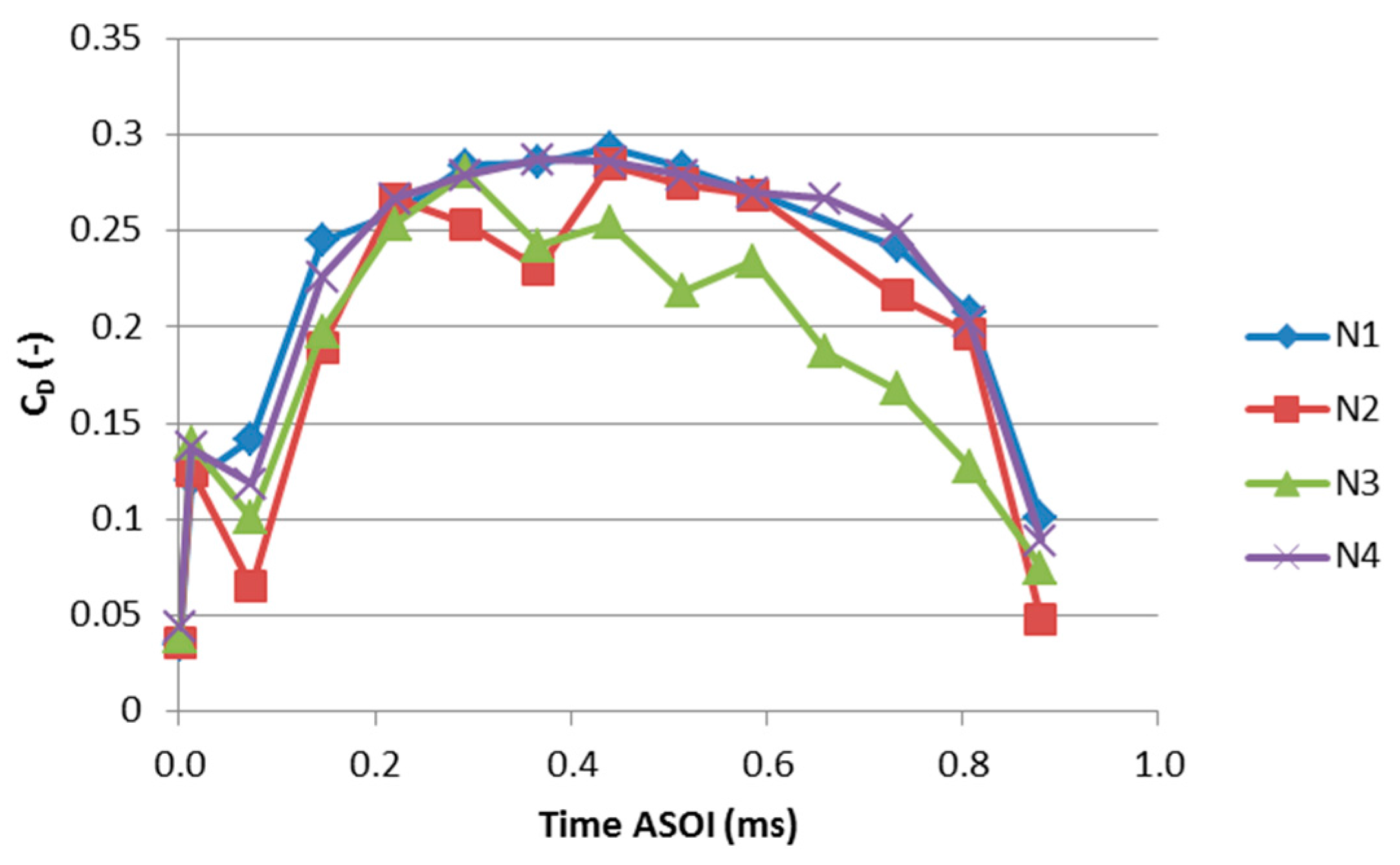
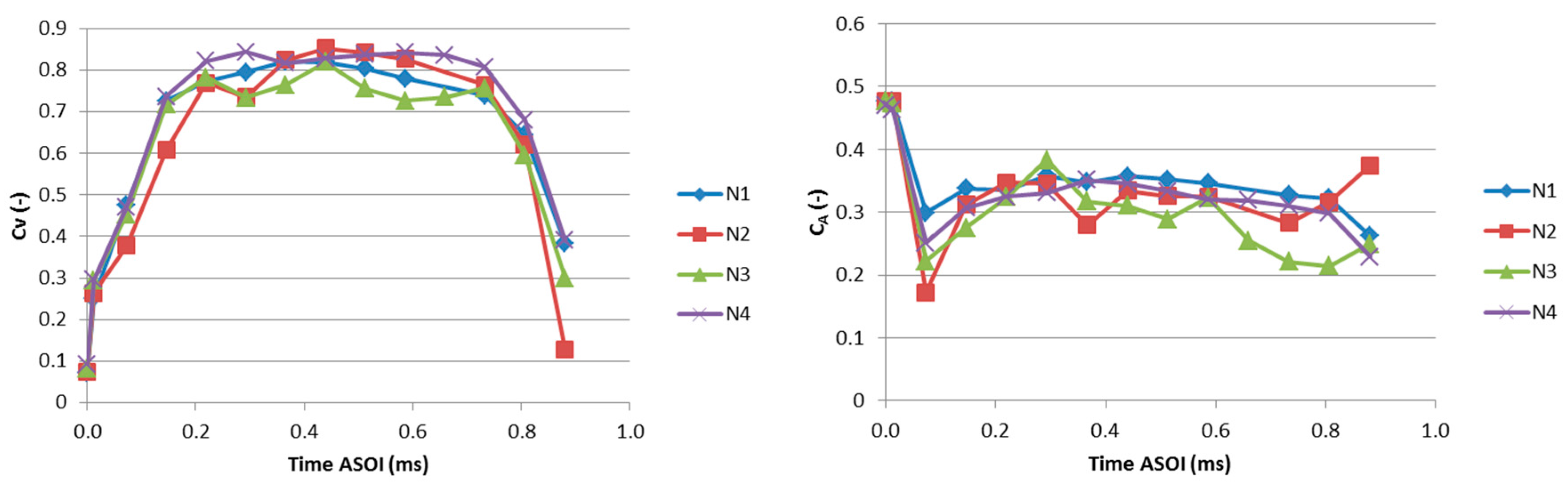
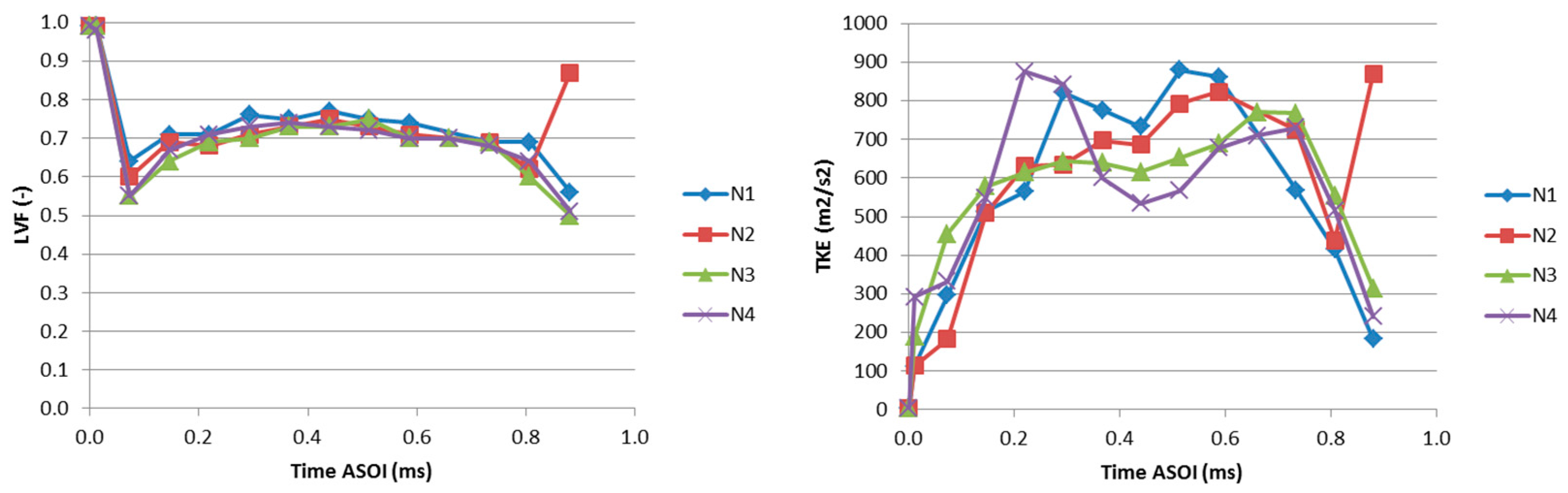
3.3. Flow Features at the Outlet of the Holes
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Roman | Description (Unit) |
| k,l | Eulerian class index |
| pressure gradient (Pa/m) | |
| f | body force vector (N/m3) |
| h | specific enthalpy (J/kg) |
| Mk,l | momentum exchange term between phase k and l (N/m3) |
| Hk,l | heat flux vector (W/m2) |
| t | time (s) |
| dt | calculation time step |
| WF | weighting factor |
| v | velocity vector (m/s) |
| Greek | Description (Unit) |
| α | volume fraction (–) |
| θ | enthalpy volumetric source (W/kg) |
| ρ | density (kg/m3) |
| τ | shear stress tensor (N/m2) |
| Гk,l | mass exchange term between phase k and l (kg/(m3 s)) |
| ε | turbulence dissipation rate (m2/s3) |
| Subscripts | Description |
| k | phase index |
| ex | extensive property |
| in | intensive property |
| NN | near nozzle |
| SV | spray volume |
| Superscripts | Description |
| t | turbulent index |
| Abbreviations | Description |
| ASOI | after start of injection |
| 3D-CFD | three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics |
| CV | control volume |
| DDM | discrete droplet method |
| RANS | Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes |
| SMD | Sauter mean diameter |
| VCO | valve covered orifice |
| LVF | liquid volume fraction |
References
- Stan, C. Direct Injection Systems for Spark-Ignition and Compression-Ignition Engines; Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE): Troy, MI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Eagle, W.E.; Musculus, M.P.B. Cinema-Stereo Imaging of Fuel Dribble after the End of Injection in an Optical Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine. In Proceedings of the Thiesel Conference on Thermo and Fluid Dynamic Processes in Direct Injection Engines, Valencia, Spain, 9–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Crua, C.; Heikal, M.R.; Gold, M.R. Microscopic imaging of the initial stage of diesel spray formation. Fuel 2015, 157, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiji, M.; Goldsworthy, L.; Brandner, P.A.; Garaniya, V.; Hield, P. Analysis of diesel spray dynamics using a compressible Eulerian/VOF/LES model and microscopic shadowgraphy. Fuel 2017, 188, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.; Aleiferis, P. Numerical Modelling of the in-Nozzle Flow of a Diesel Injector with Moving Needle during and after the End of a Full Injection Event. SAE Int. J. Eng. 2015, 8, 2285–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, V.; Payri, R.; Salvador, F.J.; Plazas, A.H. Study of the influence of nozzle seat type on injection rate and spray behavior. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2005, 219, 677–689. [Google Scholar]
- Salvador, F.J.; Carreres, M.; Jaramillo, D.; Martínez-López, J. Comparison of microsac and VCO diesel injector nozzles in terms of internal nozzle flow characteristics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, A.; Zhou, Q.; Xue, F.; Luo, F. Comparative study of flow characteristics within asymmetric multi hole VCO and SAC nozzles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 132, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiatti, G.; Chiavola, O.; Recco, E.; Palmieri, F. Soot Particles Experimental Characterization during Cold Start of a Micro Car Engine. Energy Proced. 2016, 101, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, W.E.; Musculus, M.P.B. Image-Based Correlation of Engine Operating Parameters with Occurrence and Duration of Diesel Fuel Injector Dribble. In Proceedings of the Oral Communication at SAE World Congress 2015, Detroit, MI, USA, 21–23 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mitroglou, N.; Gavaises, M.; Arcoumanis, D. Spray Stability from VCO and a New Diesel Nozzle Design Concept; Fuel Systems for IC Engines; IMechE: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chiatti, G.; Chiavola, O.; Palmieri, F. Diesel Nozzle Flow Investigation in Non-Radial Multi Hole Geometry, ASME Paper 5556. In Proceedings of the 2014 Internal Combustion Engine Division Fall Technical Conference, Columbus, IN, USA, 19–22 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, C.; Kang, J. Diesel Spray Development of VCO Nozzles for High Pressure Direct-Injection. SAE Tech. Pap. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Risi, A.; Colangelo, G.; Laforgia, D. An Experimental Study of High-Pressure Nozzles in Consideration of Hole-To-Hole Spray Abnormalities. SAE Tech. Pap. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Hiratsuka, M.; Goda, Y.; Kanaike, S.; Ohsawa, K. Experimental and Numerical Investigation about Internal Cavitating Flow and Primary Atomization of a Large-scaled VCO Diesel Injector with Eccentric Needle. In Proceedings of the ILASS-Europe, Brno, Czech Republic, 6–9 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fezzaa, K.; Lee, W.K.; Cheong, S.; Powell, C.F.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Lai, M.C. High Pressure Diesel Injection Studied by Time-Resolved X-ray Phase Contrast Imaging; ICES2006 ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Battistoni, M.; Xue, Q.; Som, S.; Pomraning, E. Effect of Off-Axis Needle Motion on Internal Nozzle and Near Exit Flow in a Multi-Hole Diesel Injector. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, F. The Influence of Actual Layout and Off-Axis Needle Stroke on Diesel Nozzle Flow under Ballistic Needle Displacement. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2013, 135, 101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Luo, F.; Cui, H.; Moro, A.; Zhou, L. Numerical analyses of transient flow characteristics within each nozzle hole of an asymmetric diesel injector. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 104, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, F.J.; Martínez-López, J.; Romero, J.-V.; Roselló, M.-D. Study of the influence of the needle eccentricity on the internal flow in diesel injector nozzles by computational fluid dynamics calculations. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2014, 91, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Battistoni, M.; Powell, C.F.; Longman, D.E.; Quan, S.P.; Pomraning, E.; Senecal, P.K.; Schmidt, D.P.; Som, S. An Eulerian CFD model and X-ray radiography for coupled nozzle flow and spray in internal combustion engines. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 70, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payri, R.; Viera, J.P.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Szymkowicz, P.G. The effect of nozzle geometry over the evaporative spray formation for three different fuels. Fuel 2017, 188, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranović, Z.; Edelbauer, W.; Vujanović, M.; Duić, N. Modelling of spray and combustion processes by using the Eulerian multiphase approach and detailed chemical kinetics. Fuel 2017, 191, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FIRE Rev.14.2. User’s Guide, Solver Manual. Eulerian Multiphase Manual, Spray Manual; AVL List: Graz, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- LMS Imagine. Lab. AMESim Manuals. In Technical Bulletins and Libraries; Release 14; Steris Life Sciences: Mentor, OH, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, W. The Fuel Rate Indicator: A New Measuring Instrument for Display of the Characteristics of Individual Injection. SAE Tech. Pap. 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J. Studio e Modellazione del Comportamento Meccanico-Idraulico di Polverizzatori di Elettroiniettori Diesel Common-Rail. Master’s Thesis, Roma TRE University, Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Manin, J.; Kastengren, A.; Payri, R. Understanding the acoustic oscillations observed in the injection rate of a common-rail direct injection diesel injector. J. Energy Power Eng. 2012, 134, 122801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desantes, J.M.; García-Oliver, J.M.; Pastor, J.M.; Pandal, A.; Baldwin, E.; Schmidt, D.P. Coupled/decoupled spray simulation comparison of the ECN spray a condition with the σ-Y Eulerian atomization model. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2016, 80, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandal, A.; Pastor, J.M.; García-Oliver, J.M.; Baldwin, E.; Schmidt, D.P. A consistent, scalable model for Eulerian spray modeling. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2016, 83, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, A.; Burluka, A.A.; Borghi, R. Development of an Eulerian model for the “atomization” of a liquid jet. At. Sprays 2001, 11, 619–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokkeel, G.; Barbeau, B.; Borghi, R. A 3D Eulerian model to improve the primary breakup of atomizing jet. SAE 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoulin, F.X. Coupling vaporization model with the Eulerian–Lagrangian Spray Atomization (ELSA) model in diesel engine conditions. SAE Tech. Pap. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Reitz, R.D.; Diwakar, R.; Lippert, A.M. An Eulerian–Lagrangian spray and atomization model with improved turbulence modeling. At. Sprays 2009, 19, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyas, S.; Gil, A.; Margot, X.; Khuong-Anh, D.; Ravet, F. Evaluation of the Eulerian–Lagrangian Spray Atomization (ELSA) model in spray simulations: 2D cases. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 57, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, C. Validation of a 1D spray model for simulation of mixture formation in direct injection Diesel engines. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Edelbauer, W.; Suzzi, D.; Sampl, P.; Tatschl, R.; Krueger, C.; Weigand, B. New concept for on-line coupling of 3D Eulerian and Lagrangian spray approaches in engine simulations. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Liquid Atomisation and Spray Systems, Kyoto, Japan, 27 August–1 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Edelbauer, W. Coupling of 3D Eulerian and Lagrangian spray approaches in industrial combustion engine simulations. J. Energy Power Eng. 2014, 8, 190–200. [Google Scholar]
- Vujanović, M.; Petranović, Z.; Edelbauer, W.; Duić, N. Modelling spray and combustion processes in diesel engine by using the coupled Eulerian–Eulerian and Eulerian–Lagrangian method. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 125, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.A.; Passman, S.L. Theory of Multicomponent Fluids; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, M.A.; Reitz, R.D. Modeling the Effects of Fuel Spray Characteristics on Diesel Engine Combustion and Emissions. SAE Tech. Pap. 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, P.J.; Bracco, F.V. Modelling of Drop Interactions in Thick Sprays and a Comparison with Experiments; IMechE: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Sekoguchi, K. Liquid Velocity Distribution in Two-Phase Bubble Flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1975, 2, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.M.; Greif, D. Progress in modeling injector cavitating flows with a multi-fluid method. In Proceedings of the ASME 2006 2nd Joint US-European Fluids Engineering Summer Meeting Collocated with the 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering, Miami, FL, USA, 17–20 July 2006; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Von Berg, E.; Edelbauer, W.; Alajbegovic, A.; Tatschl, R.; Volmajer, M.; Kegl, B.; Ganippa, L.C. Coupled simulations of nozzle flow, primary fuel jet breakup, and spray formation. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2005, 127, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winklhofer, E.; Kull, E.; Kelz, E.; Morozov, A. Comprehensive hydraulic and flow field documentation in model throttle experiments under cavitation conditions. In Proceedings of the ILASS-Europe Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 2–6 September 2001; pp. 574–579. [Google Scholar]
- Sou, A.; Biçer, B.; Tomiyama, A. Numerical simulation of incipient cavitation flow in a nozzle of fuel injector. Comput. Fluids 2014, 103, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, F.J.; Romero, J.V.; Roselló, M.D.; Martínez-López, J. Validation of a code for modeling cavitation phenomena in Diesel injector nozzles. Math. Comput. Model. 2010, 52, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Som, S.; Aggarwal, S.K.; El-Hannouny, E.M.; Longman, D.E. Investigation of nozzle flow and cavitation characteristics in a diesel injector. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2010, 132, 042802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spray-A Characterization Data, Engine Combustion Network. Available online: https://ecn.sandia.gov/ecn-data-search/ (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- Naber, J.; Siebers, D. Effects of Gas Density and Vaporization on Penetration and Dispersion of Diesel Sprays. SAE Tech. Pap. 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
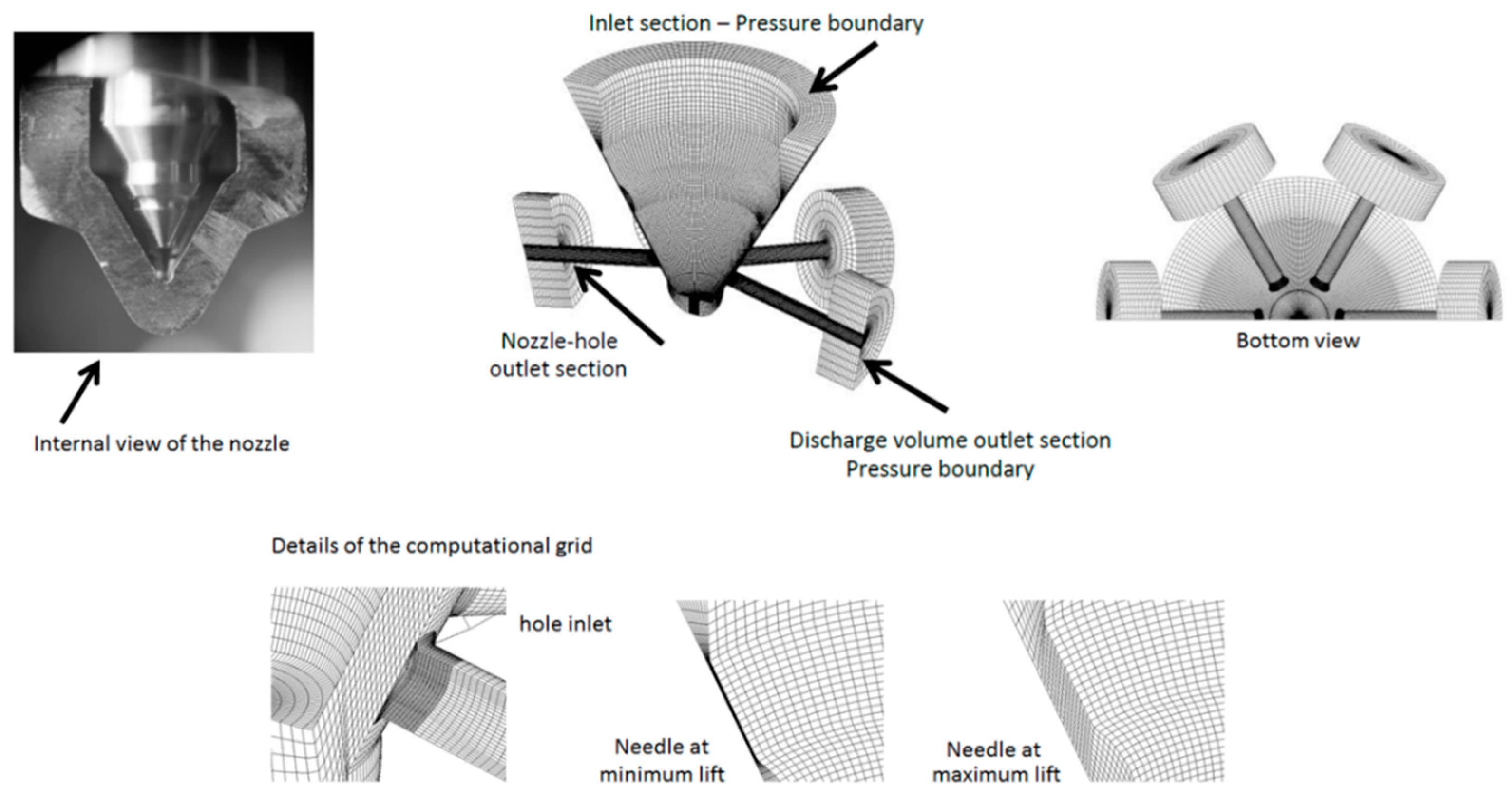
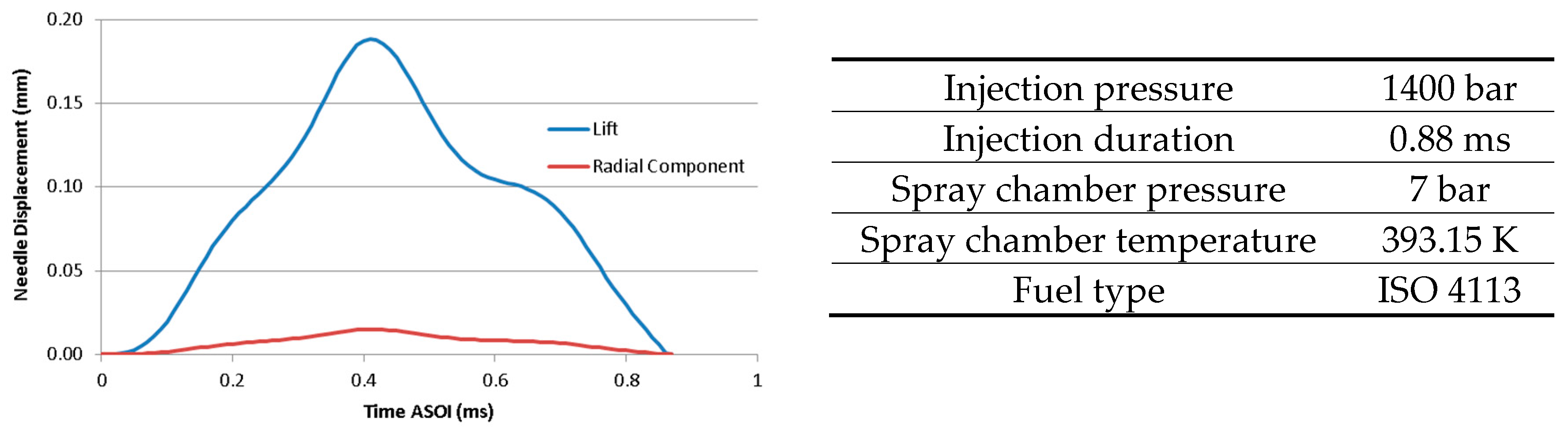
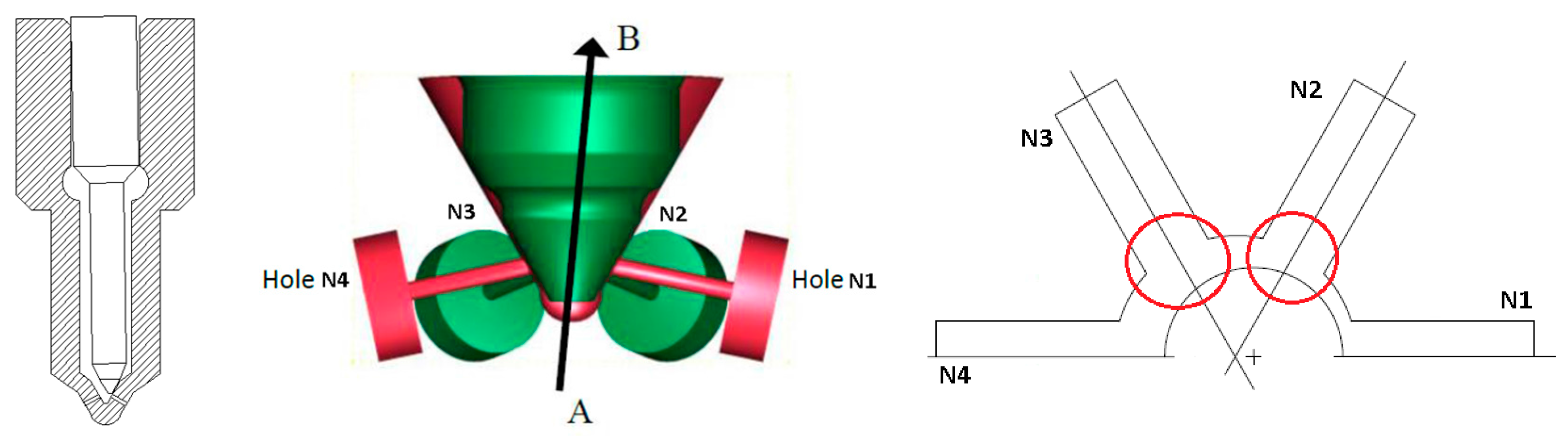

| Nozzle Layout | |
|---|---|
| Nozzle type | VCO 1 |
| Number of nozzle holes | 6 |
| Hole diameter (mm) | 0.175 |
| Length to diameter ratio | 5.7 |
| Hole plane angle (deg) | 156 |
| Conditions | Cavitation Start (A) | Critical Cavitation (B) | Super Cavitation (C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | Model | Experiment | Model | Experiment | Model | |
| Pressure difference (bar) | 57.0 | 57.0 | 65.0 | 65.0 | 80 | 80 |
| Mass flow (g/s) | 7.21 | 7.1 | 7.72 | 7.60 | 7.72 | 7.63 |
| Injector Nozzle | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| mesh type | min cell number | max cell number | adopted cell number |
| Hexahedral-structured | 195,500 | 3,800,000 | 490,000 |
| Mass flow rate % difference during refinement tests | 7.4% more | 1.6% less | reference case |
| Near nozzle region | |||
| mesh type | min cell number | max cell number | adopted cell number |
| Hexahedral-structured | 11,760 | 687,000 | 94,080 |
| Spray volume | |||
| mesh type | min cell number | max cell number | adopted cell number |
| Hexahedral-structured | 54,230 | 372,000 | 105,984 |
| Rail Pressure (MPa) | Ambient Pressure (MPa) | Ambient Temperature (K) | Nozzle Number | Fluid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 6 | 900 | 210677 | N-C12-H26 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiatti, G.; Chiavola, O.; Frezzolini, P.; Palmieri, F. On the Link between Diesel Spray Asymmetry and Off-Axis Needle Displacement. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040375
Chiatti G, Chiavola O, Frezzolini P, Palmieri F. On the Link between Diesel Spray Asymmetry and Off-Axis Needle Displacement. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(4):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040375
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiatti, Giancarlo, Ornella Chiavola, Pierluigi Frezzolini, and Fulvio Palmieri. 2017. "On the Link between Diesel Spray Asymmetry and Off-Axis Needle Displacement" Applied Sciences 7, no. 4: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040375
APA StyleChiatti, G., Chiavola, O., Frezzolini, P., & Palmieri, F. (2017). On the Link between Diesel Spray Asymmetry and Off-Axis Needle Displacement. Applied Sciences, 7(4), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7040375









