Status of the High Average Power Diode-Pumped Solid State Laser Development at HiLASE
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HiLASE Centre

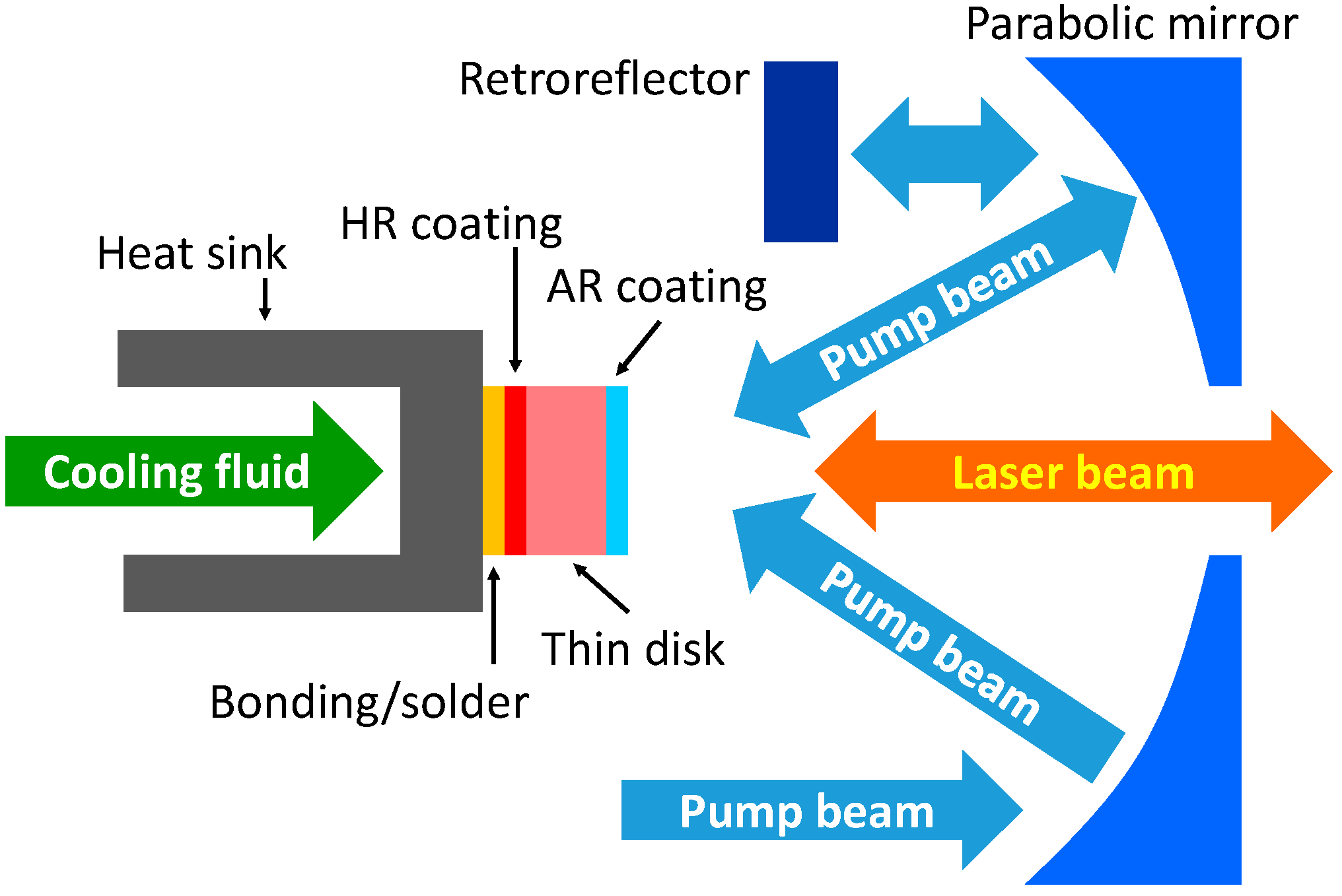
3. Kilowatt-Class Picosecond Thin-Disk Lasers
Improvements of Thin Disk Laser Operations at HiLASE
4. High Average Power Short-Pulse Thin Disk Lasers at HiLASE
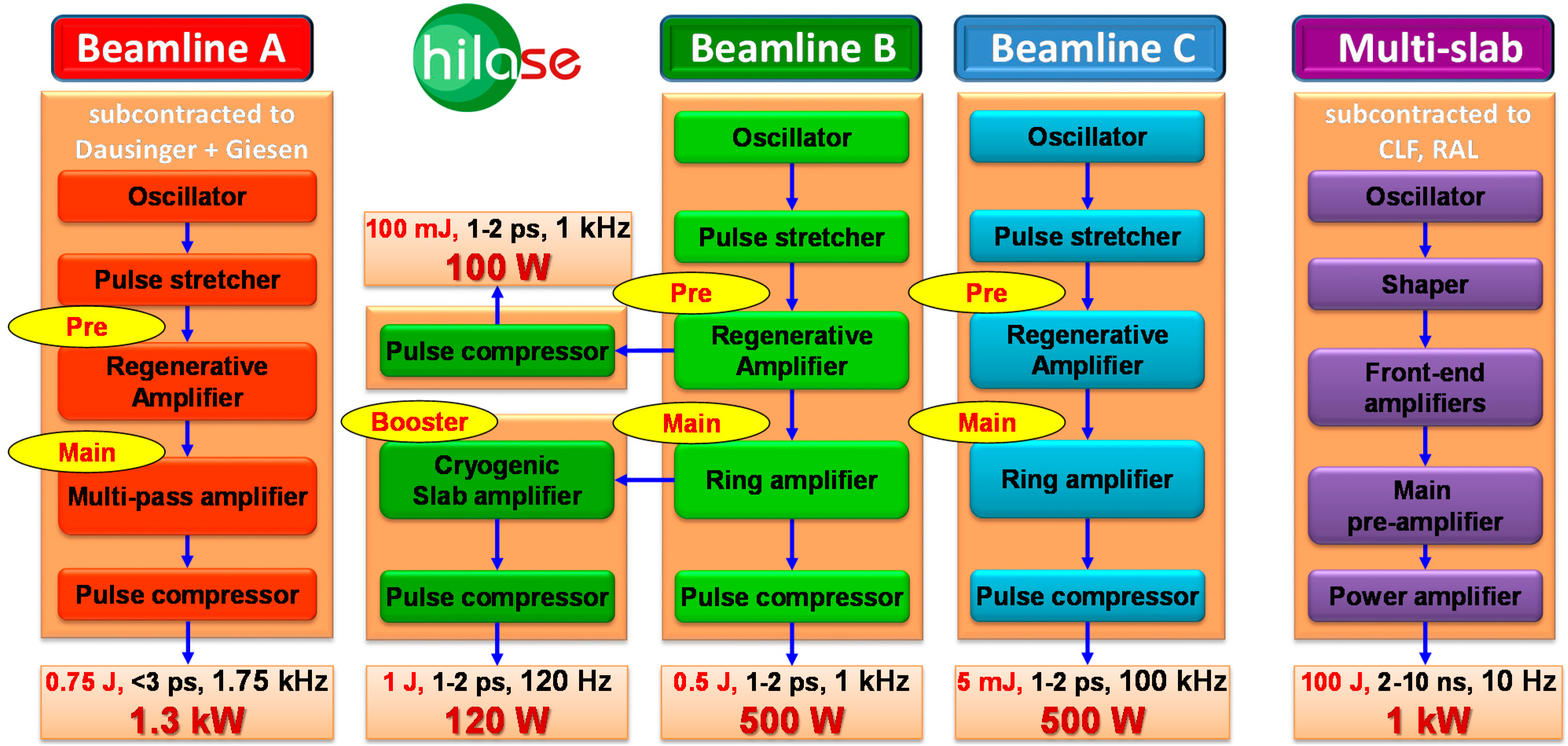
4.1. Beamline A
4.2. Beamline B

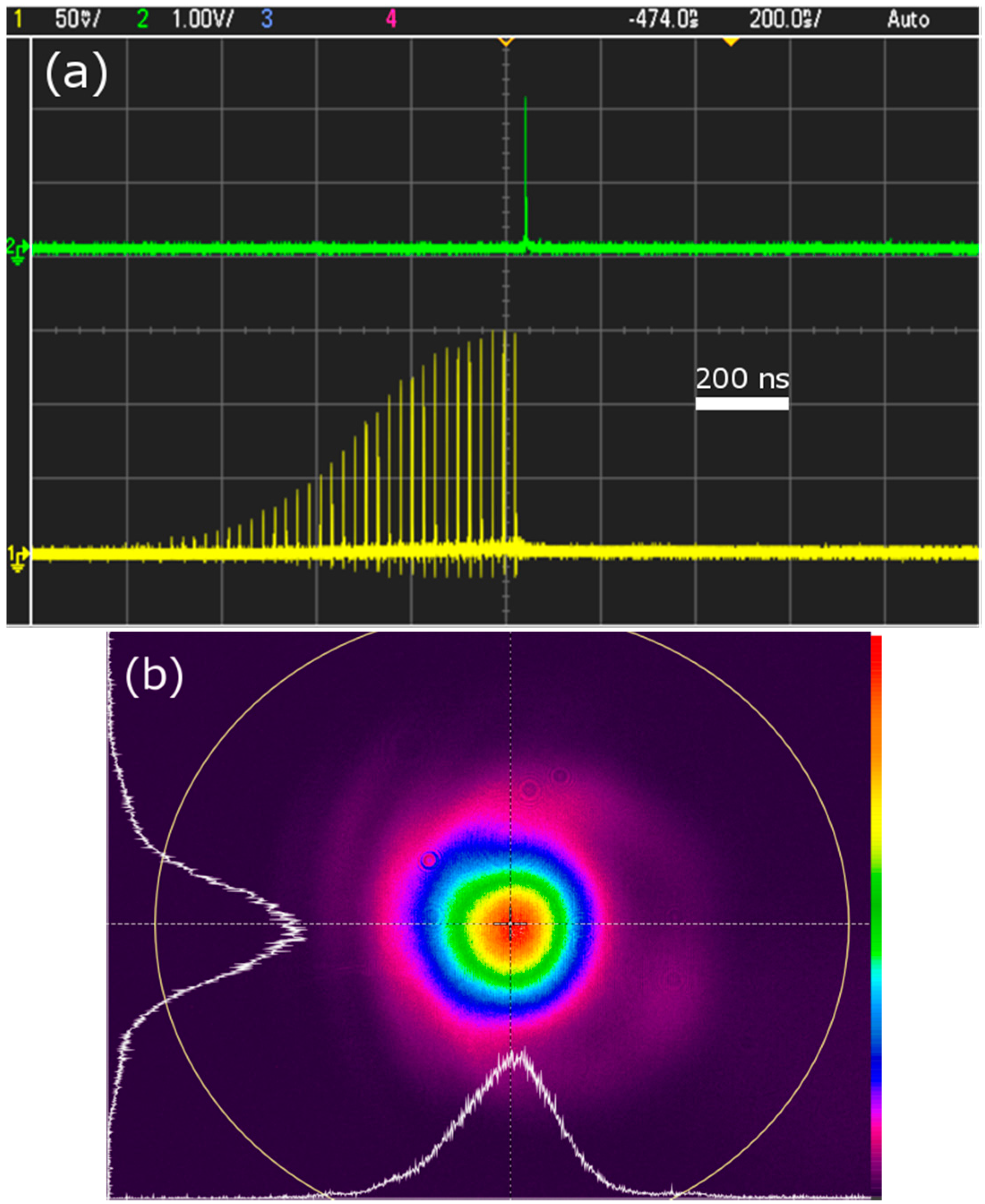
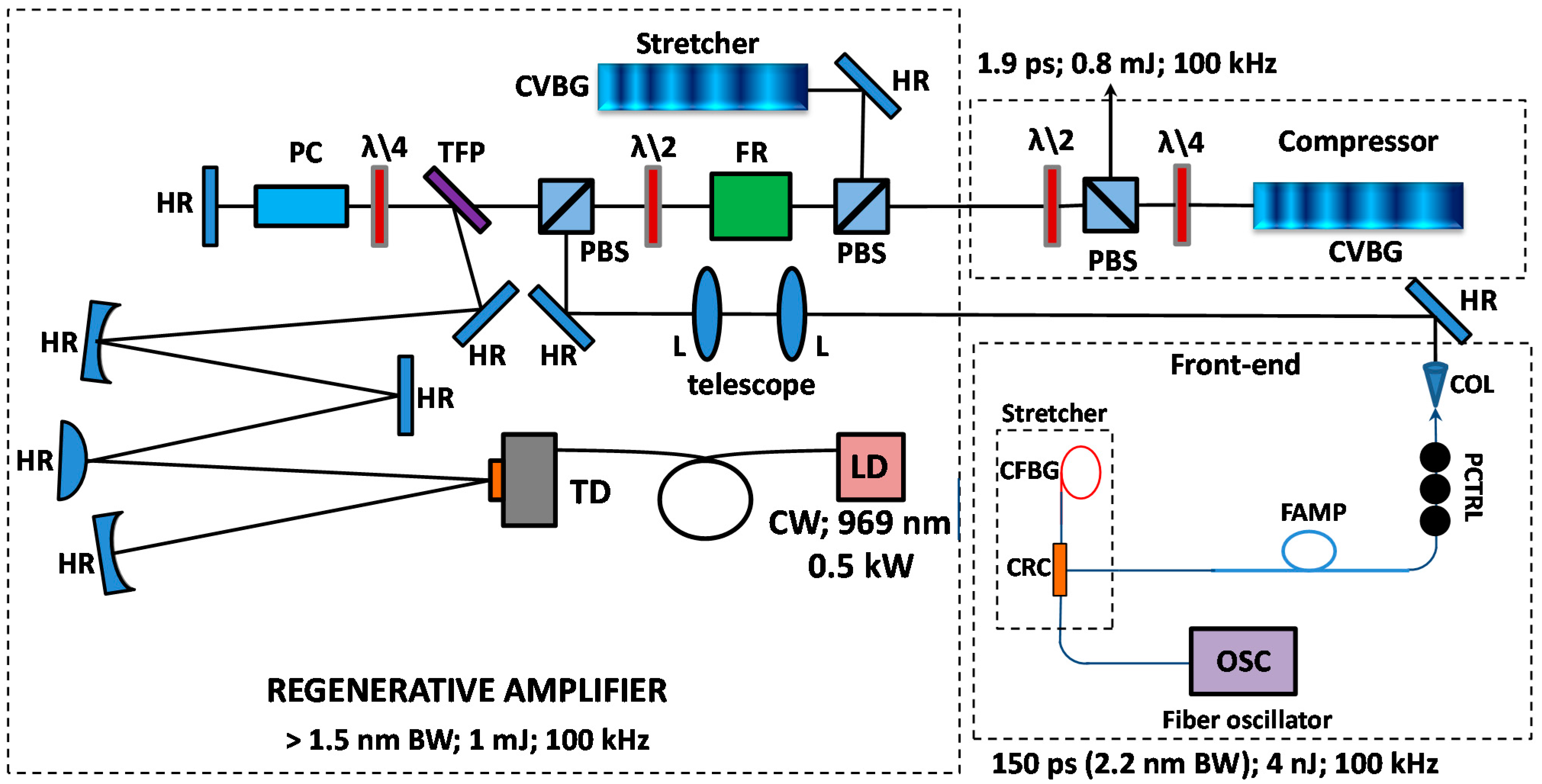
4.3. Beamline C
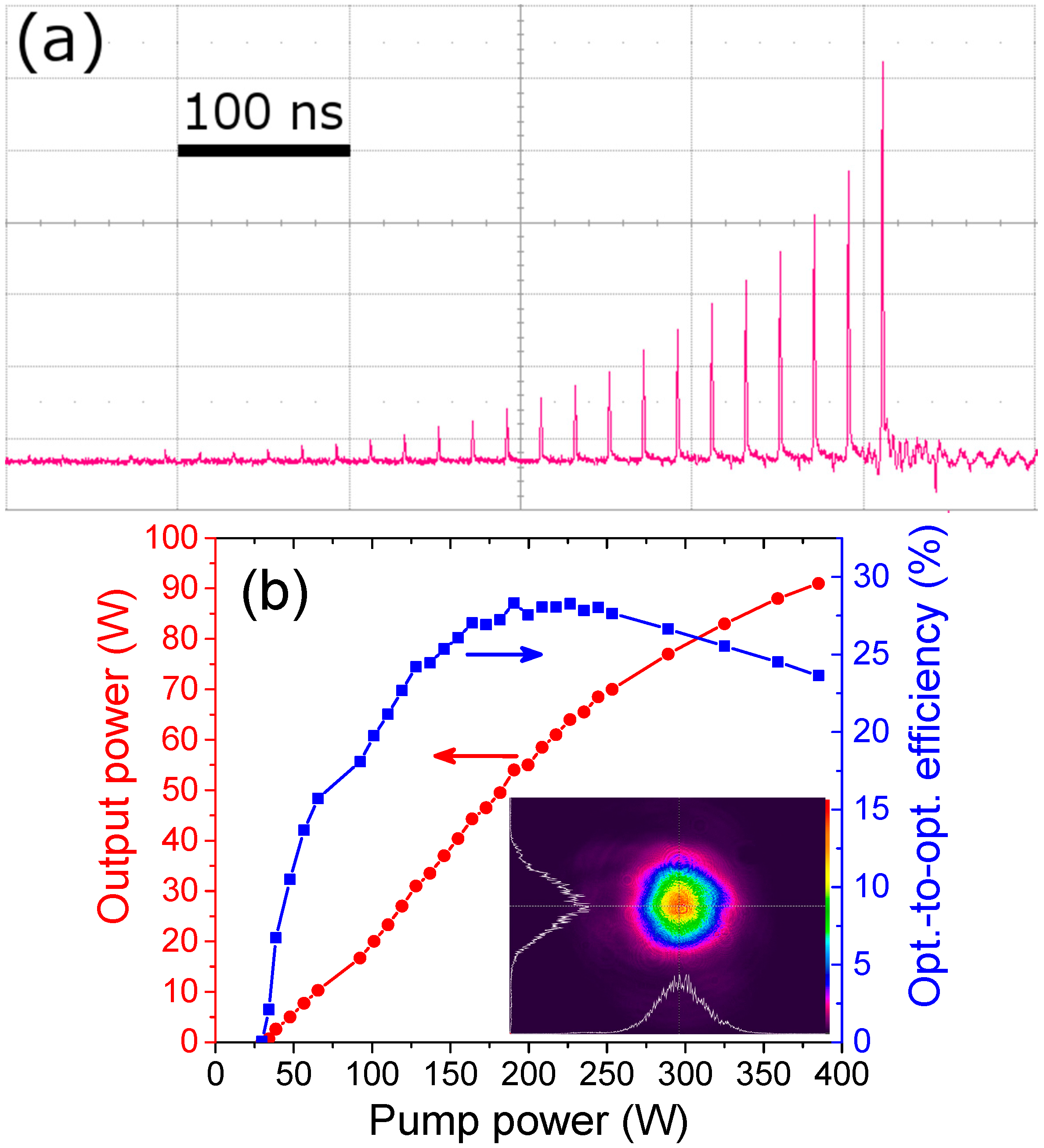

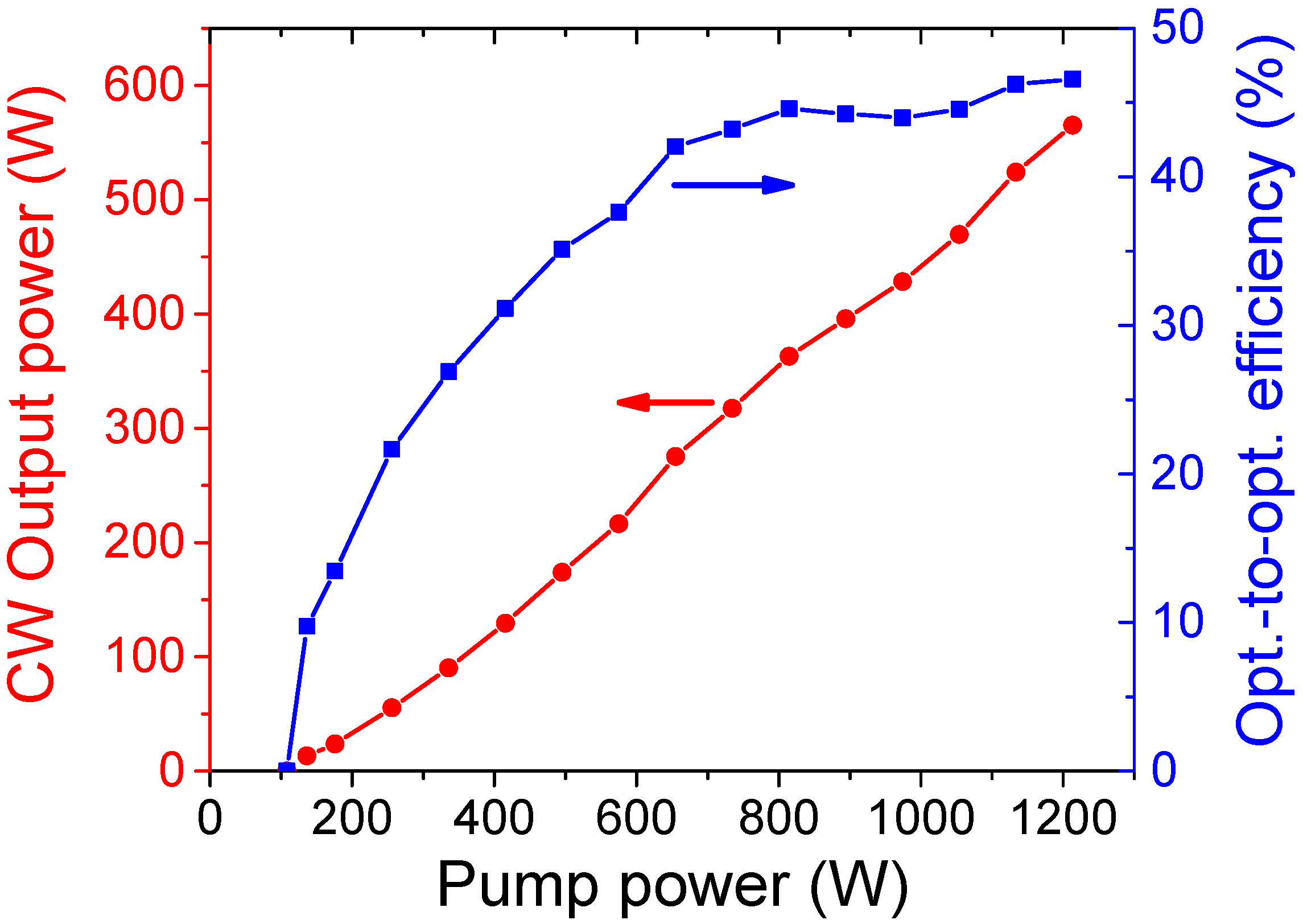
4.3.1. Second and Fourth Harmonic Generation
4.3.2. Mid-IR Generation
4.4. Fiber Oscillator and Front-End

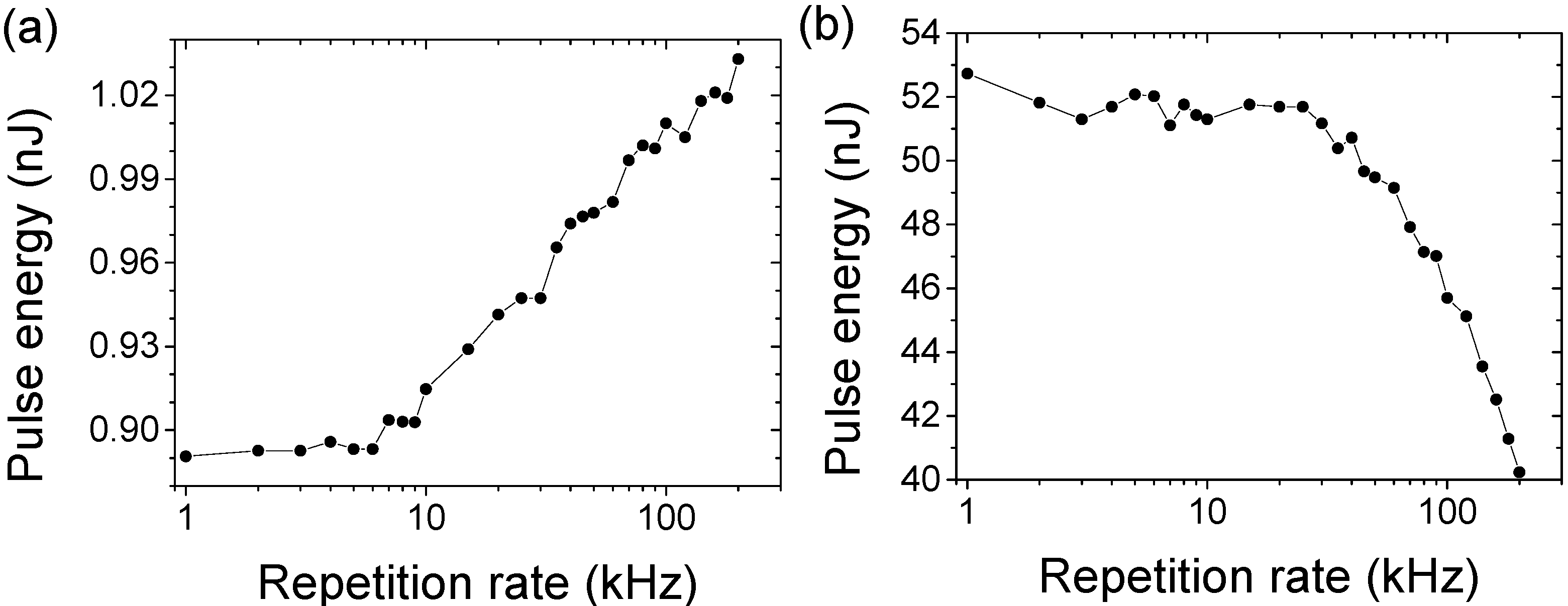
4.5. Frequency-Stabilized Oscillator
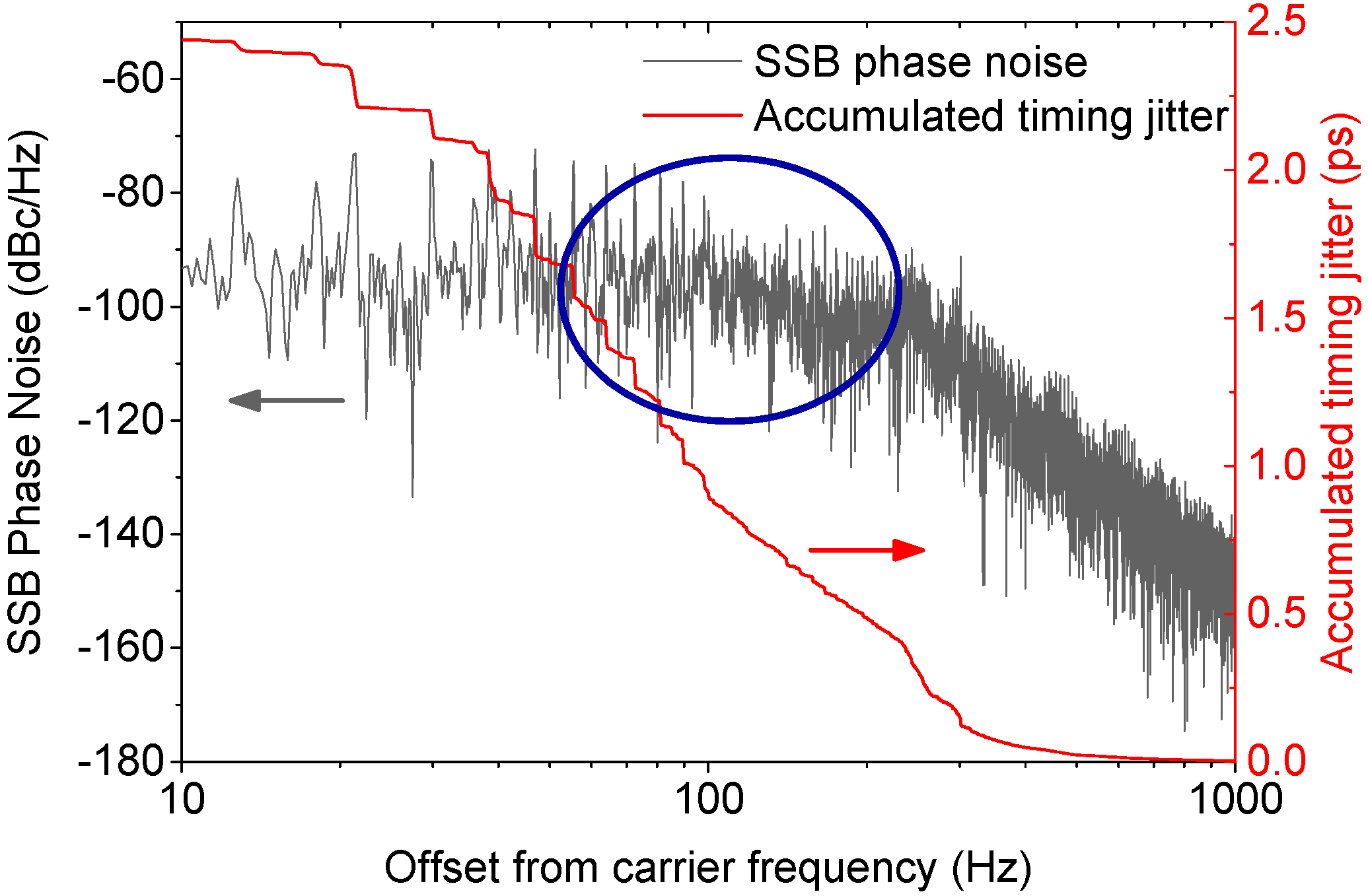
5. Advanced Tools for High Average Power Laser Developments
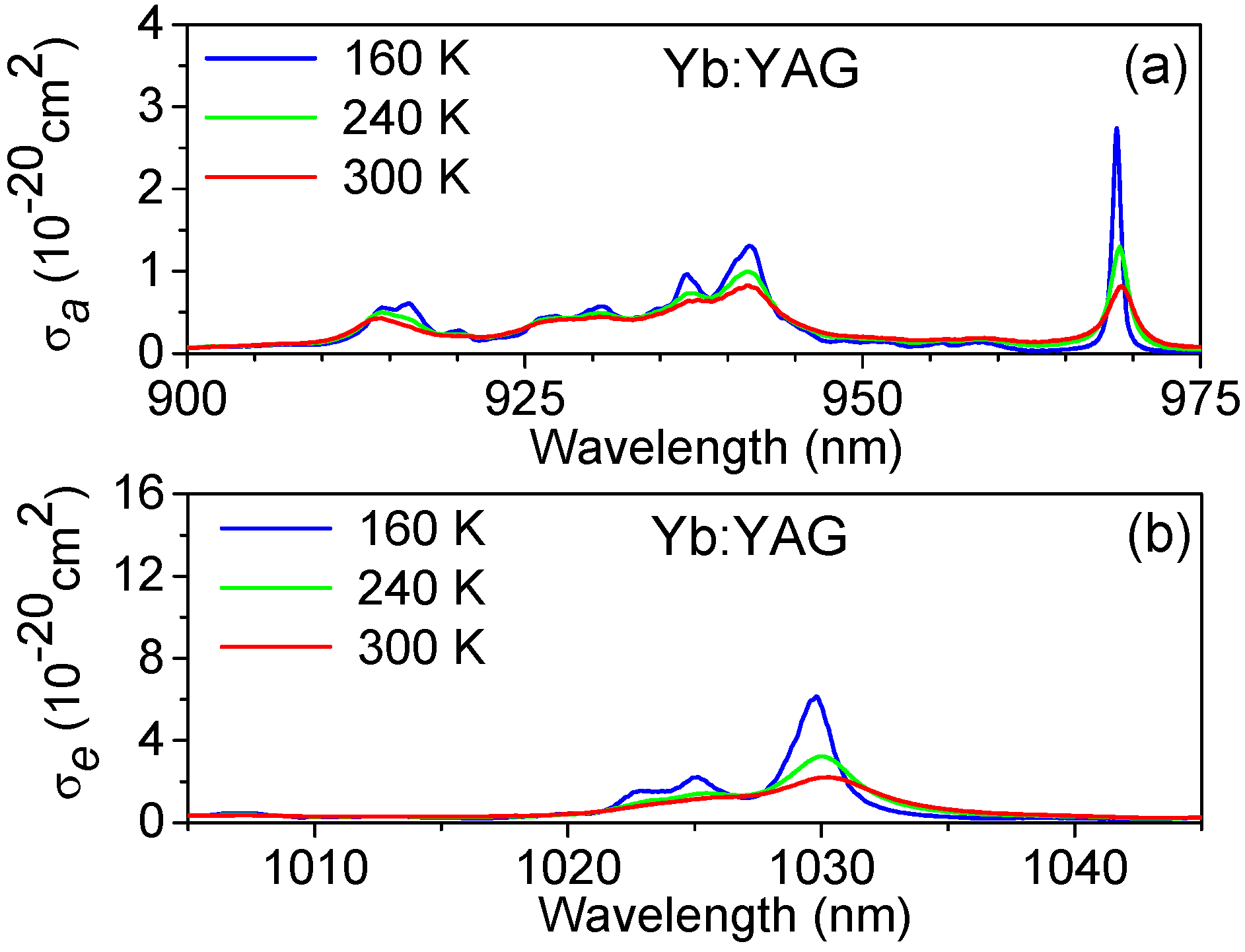
5.1. High Resolution Spectroscopy of Yb-Doped Materials
5.2. In Situ Thin Disk Deformation Measurements


5.3. Single-Shot M2 Measurement

6. Multi-Slab Laser Amplifier
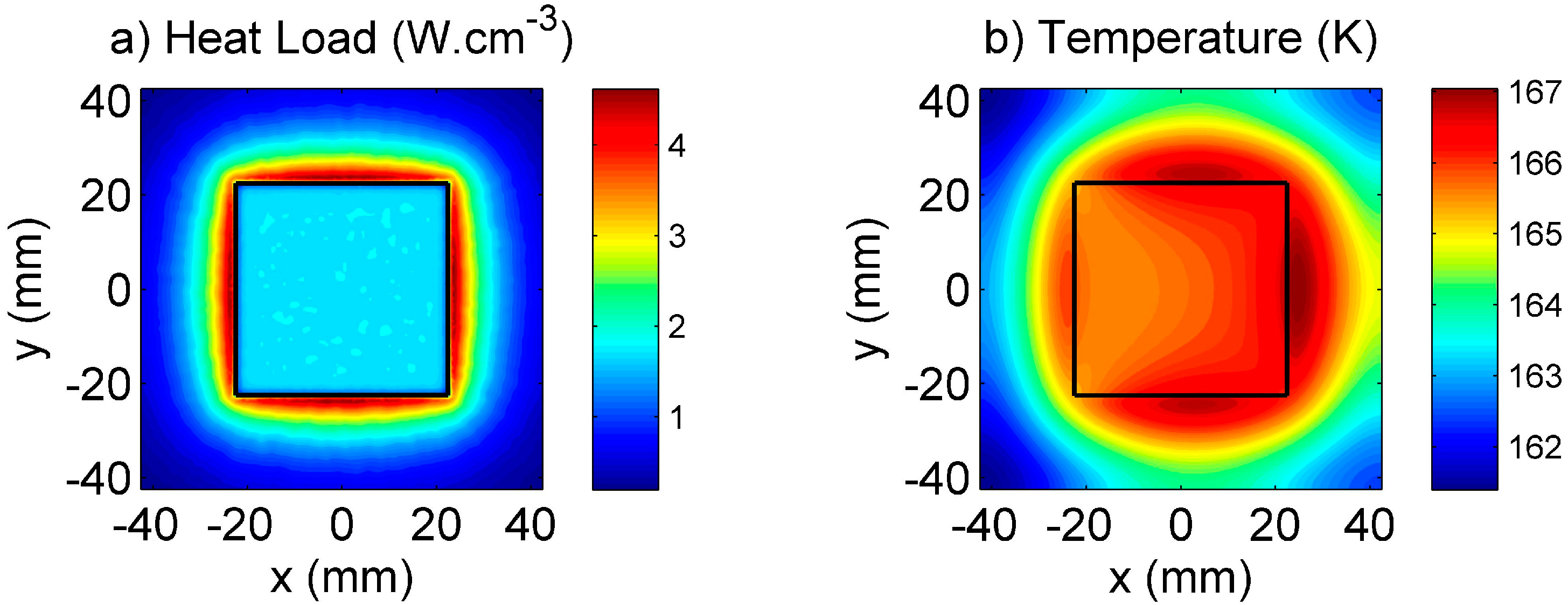
6.1. Numerical Modelling of Laser Amplifiers
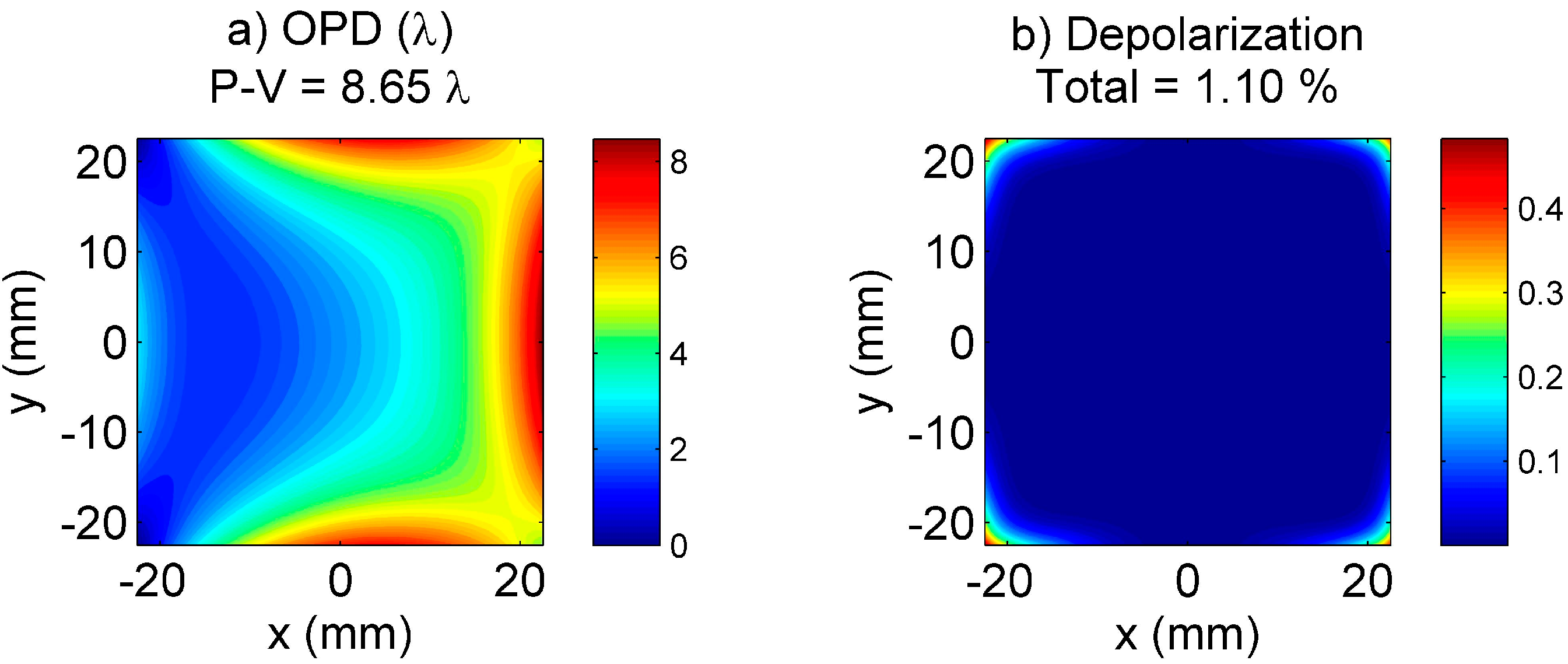

6.2. Wavefront Correction by a Deformable Mirror

7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strickland, D.; Mourou, G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 1985, 56, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koechner, W. Solid-State Laser Engineering; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 1, p. 750. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ripin, D.; Ochoa, J.; Fan, T. Measurement of thermo-optic properties of Y3Al5O12, Lu3Al5O12, YAIO3, LiYF4, LiLuF4, BaY2F8, KGd(WO4)2, and KY(WO4)2 laser crystals in the 80–300 K temperature range. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Ripin, D.; Aggarwal, R.; Ochoa, J.; Chann, B.; Tilleman, M.; Spitzberg, J. Cryogenic Yb3+-doped solid-state lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2007, 13, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D.; Miller, D.; Ripin, D.; Fan, T. Cryogenic Yb3+-doped materials for pulsed solid-state laser applications. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, J.; Jambunathan, V.; Hein, J.; Seifert, R.; Loeser, M.; Siebold, M.; Schramm, U.; Sikocinski, P.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T.; et al. Spectroscopic characterization of Yb3+-doped laser materials at cryogenic temperatures. Appl. Phys. B 2014, 116, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambunathan, V.; Koerner, J.; Sikocinski, P.; Divoky, M.; Sawicka, M.; Lucianetti, A.; Hein, J.; Mocek, T. Spectroscopic characterization of various Yb3+ doped laser materials at cryogenic temperatures for the development of high energy class diode pumped solid state lasers. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Prague, Czech Republic, 15–17 April 2013; Volume 8780, pp. 87800G-1–87800G-9.
- Eidam, T.; Hanf, S.; Seise, E.; Andersen, T.; Gabler, T.; Wirth, C.; Schreiber, T.; Limpert, J.; Tunnermann, A. Femtosecond fiber CPA system emitting 830 W average output power. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesen, A.; Hugel, H.; Voss, A.; Wittig, K.; Brauch, U.; Opower, H. Scalable concept for diode-pumped high-power solid-state lasers. Appl. Phys. B 1994, 58, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Loosen, P.; Poprawe, R. Optical amplifier arrangement for a solid state laser. U.S. Patent 6,654,163 B1, 25 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Russbueldt, P.; Mans, T.; Rotarius, G.; Weitenberg, J.; Hoffmann, H.; Poprawe, R. 400 W Yb:YAG Innoslab fs-amplifier. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 12230–12245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, M.; Keppler, S.; Bodefeld, R.; Kessler, A.; Liebetrau, H.; Korner, J.; Hellwing, M.; Schorcht, F.; Jackel, O.; Savert, A.; et al. High-intensity, high-contrast laser pulses generated from the fully diode-pumped Yb:glass laser system POLARIS. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan, B.; Curtis, A.; Wernsing, K.; Furch, F.; Luther, B.; Rocca, J. Development of High Energy Diode-Pumped Thick-Disk Yb:YAG Chirped-Pulse-Amplification Lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2012, 48, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, B.; Wernsing, K.; Curtis, A.; Furch, F.; Luther, B.; Patel, D.; Menoni, C.; Rocca, J. Demonstration of a 100 Hz repetition rate gain-saturated diode-pumped table-top soft x-ray laser. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3624–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves-Novo, T.; Albach, D.; Vincent, B.; Arzakantsyan, M.; Chanteloup, J. 14 J/2 Hz Yb3+:YAG diode pumped solid state laser chain. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandt, C.; Klingebiel, S.; Keppler, S.; Hornung, M.; Loeser, M.; Siebold, M.; Skrobol, C.; Kessel, A.; Trushin, S.; Major, Z.; et al. Development of a Joule-class Yb:YAG amplifier and its implementation in a CPA system generating 1 TW pulses. Laser Photonics Rev. 2014, 8, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divoky, M.; Tokita, S.; Hwang, S.; Kawashima, T.; Kan, H.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T.; Kawanaka, J. 1-J operation of monolithic composite ceramics with Yb:YAG thin layers: Multi-TRAM at 10-Hz repetition rate and prospects for 100-Hz operation. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayramian, A.; Aceves, S.; Anklam, T.; Baker, K.; Bliss, E.; Boley, C.; Bullington, A.; Caird, J.; Chen, D.; Deri, R.; et al. Compact, Efficient Laser Systems Required for Laser Inertial Fusion Energy. Fusion Sci. Technol. 2011, 60, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertel, K.; Banerjee, S.; Mason, P.D.; Phillips, P.J.; Greenhalgh, R.J.S.; Hernandez-Gomez, C.; Collier, J.L. DiPOLE: A scalable laser architecture for pumping multi-Hz PW systems. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Prague, Czech Republic, 15–17 April 2013; Volume 8780, pp. 87801W-1–87801W-5.
- Sawicka, M.; Divoky, M.; Novak, J.; Lucianetti, A.; Rus, B.; Mocek, T. Modeling of amplified spontaneous emission, heat deposition, and energy extraction in cryogenically cooled multislab Yb3+:YAG laser amplifier for the HiLASE Project. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2012, 29, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, O.; Lucianetti, A.; Divoky, M.; Sawicka, M.; Mocek, T. Optimization of Wavefront Distortions and Thermal-Stress Induced Birefringence in a Cryogenically-Cooled Multislab Laser Amplifier. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2013, 49, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELI-Extreme Light Infrastructure. Available online: http://www.eli-laser.eu (accessed on 31 July 2015).
- The HiPER Project. Available online: http://www.hiper-laser.org (accessed on 31 July 2015).
- Kuang, Z.; Perrie, W.; Edwardson, S.; Fearon, E.; Dearden, G. Ultrafast laser parallel microdrilling using multiple annular beams generated by a spatial light modulator. J. Phys. D 2014, 47, 115501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyla, M.; Miura, T.; Smrz, M.; Severova, P.; Novak, O.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. 50-mJ, 1-kHz Yb:YAG thin-disk regenerative amplifier with 969-nm pulsed pumping. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–4 February 2014; Volume 8959, pp. 89590S-1–89590S-6.
- Cummins, T.; Otsuka, T.; Yugami, N.; Jiang, W.; Endo, A.; Li, B.; O’Gorman, C.; Dunne, P.; Sokell, E.; O’Sullivan, G.; et al. Optimizing conversion efficiency and reducing ion energy in a laser-produced Gd plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 061118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, C.; Wiedenmann, M.; Negel, J.; Loescher, A.; Onuseit, V.; Weber, R.; Ahmed, M.; Graf, T. High-quality processing of CFRP with a 1.1-kW picosecond laser. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 119, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, A.; Speiser, J. Fifteen years of work on thin-disk lasers: Results and scaling laws. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2007, 13, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichelt, B.; Voss, A.; Ahmed, M.; Graf, T. Enhanced performance of thin-disk lasers by pumping into the zero-phonon line. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3045–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.; Cone, R.; Sun, Y.; Equall, R. Yb:YAG absorption at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2005, 11, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrz, M.; Miura, T.; Chyla, M.; Nagisetty, S.; Novak, O.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Suppression of nonlinear phonon relaxation in Yb:YAG thin disk via zero phonon line pumping. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4919–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambunathan, V.; Miura, T.; Tesnohlidkova, L.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Efficient laser performance of a cryogenic Yb:YAG laser pumped by fiber coupled 940 and 969 nm laser diodes. Laser Phys. Lett. 2015, 12, 015002-1–015002-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyla, M.; Miura, T.; Smrz, M.; Jelinkova, H.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Optimization of beam quality and optical-to-optical efficiency of Yb:YAG thin-disk regenerative amplifier by pulsed pumping. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Chyla, M.; Smrz, M.; Nagisetty, S.S.; Severova, P.; Novak, O.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. In-situ optical phase distortion measurement of Yb:YAG thin disk in high average power regenerative amplifier. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–7 February 2013; Volume 8603, pp. 860303-1–860303-8.
- Muzik, J.; Chyla, M.; Nagisetty, S.S.; Miura, T.; Mann, K.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Precise curvature measurement of Yb:YAG thin disk. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Liberec, Czech Republic, 7–10 October 2014; Volume 9442, pp. 94420X-1–94420X-6.
- Chyla, M.; Nagisetty, S.S.; Severova, P.; Miura, T.; Mann, K.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Time-resolved deformation measurement of Yb:YAG thin disk using wavefront sensor. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 February 2015; Volume 9343, pp. 93431E-1–93431E-7.
- Larionov, M.; Neuhaus, J. Regenerative thin disk amplifier with a pulse energy of 120 mJ at 1 kHz. In Advanced Solid State Lasers; Optical Society of America: Shanghai, China, 2014; p. ATh2A.51. [Google Scholar]
- Yanovsky, V.; Felix, C.; Mourou, G. Why ring regenerative amplification (regen)? Appl. Phys. B 2002, 74, S181–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrž, M.; Chyla, M.; Novák, O.; Miura, T.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Amplification of picosecond pulses to 100 W by an Yb:YAG thin-disk with CVBG compressor. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Prague, Czech Republic, 14–15 April 2015; Volume 9513, pp. 951304-1–951304-7.
- Painchaud, Y.; Paquet, C.; Guy, M. Optical Tunable Dispersion Compensators based on Thermally Tuned Fiber Bragg Gratings. Opt. Photonics News 2007, 18, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turčičová, H.; Novák, O.; Smrž, M.; Miura, T.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Picosesond pulses in deep ultraviolet produced by a 100 kHz solid-state thin disk laser. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Prague, Czech Republic, 14–15 April 2015; Volume 9513, pp. 95130V-1–95130V-6.
- Popmintchev, T.; Chen, M.; Popmintchev, D.; Arpin, P.; Brown, S.; Alisauskas, S.; Andriukaitis, G.; Balciunas, T.; Mucke, O.; Pugzlys, A.; et al. Bright Coherent Ultrahigh Harmonics in the keV X-ray Regime from Mid-Infrared Femtosecond Lasers. Science 2012, 336, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta, E.; Soong, K.; England, R.; Colby, E.; Wu, Z.; Montazeri, B.; McGuinness, C.; McNeur, J.; Leedle, K.; Walz, D.; et al. Demonstration of electron acceleration in a laser-driven dielectric microstructure. Nature 2013, 503, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, N.; Mailis, S.; Bulgakova, N.; Sazio, P.; Day, T.; Sparks, J.; Cheng, H.; Badding, J.; Peacock, A. Extreme electronic bandgap modification in laser-crystallized silicon optical fibres. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, O.; Miura, T.; Smrz, M.; Huynh, J.; Severova, P.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Tunable mid-IR parametric conversion system pumped by a high-average-power picosecond Yb:YAG thin-disk laser. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Brussels, Belgium, 14–17 April 2014; Volume 9135, pp. 91350I-1–91350I-7.
- Novák, O.; Smrž, M.; Miura, T.; Turčičová, H.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Continuous-wave seeded mid-IR parametric system pumped by the high-average-power picosecond Yb:YAG thin-disk laser. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Prague, Czech Republic, 13–15 April 2015; Volume 9503, pp. 95030W-1–95030W-10.
- Chong, A.; Buckley, J.; Renninger, W.; Wise, F. All-normal-dispersion femtosecond fiber laser. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 10095–10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Měsíček, J.; Linnemann, J.; Smrž, M.; Miura, T.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Timing jitter measurement and stabilization of a mode-locked ytterbium fiber laser. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Prague, Czech Republic, 14–15 April 2015; Volume 9513, pp. 95130B-1–95130B-7.
- Jambunathan, V.; Horackova, L.; Miura, T.; Sulc, J.; Jelinkova, H.; Endo, A.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Spectroscopic and lasing characteristics of Yb:YGAG ceramic at cryogenic temperatures. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambunathan, V.; Horackova, L.; Navratil, P.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Narrow-band zero-phonon-line pumped efficient cryogenic Yb:YAG laser. In Proceedings of the CLEO/Europe 2015-European Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Munich, Germany, 21–25 June 2015.
- Sulc, J.; Jelinkova, H.; Jambunathan, V.; Miura, T.; Endo, A.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Wavelength tunability of laser based on Yb-doped YGAG ceramics. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 February 2015; Volume 9342, pp. 93421T-1–93421T-9.
- Cortes, R.; Villagomez, R.; Coello, V.; Lopez, R. Laser beam quality factor (M2) measured by distorted fresnel zone plates. Rev. Mex. Fis. 2008, 54, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldakova, J.V.; Kudryashov, A.V.; Zavalova, V.Y.; Cherezova, T.Y. Beam quality measurements with Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor and M2-sensor: Comparison of two methods. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Jose, CA, USA, 22–24 June 2007; Volume 6452, pp. 645207-1–645207-5.
- Jorge, K.C.; Riva, R.; Silveira Rodrigues, N.A.; Destro, M.G. Real-time measurement of laser beam quality factor (M2) by imaging transverse scattered light. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Jose, CA, USA, 22–24 June 2007; Volume 6452, pp. 645215-1–645215-10.
- Nagisetty, S.S.; Miura, T.; Smrz, M.; Kubecek, V.; Endo, A.; Mocek, T. Single shot M2 measurement for near infrared high energy laser pulses. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 February 2015; Volume 9343, pp. 93431F-1–93431F-8.
- Mason, P.D.; Banerjee, S.; Ertel, K.; Phillips, P.J.; Butcher, T.J.; Smith, J.M.; de Vido, M.; Tomlinson, S.; Chekhlov, O.; Shaikh, W.; et al. DiPOLE100: A 100 J, 10 Hz DPSSL using cryogenic gas cooled Yb:YAG multi slab amplifier technology. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Prague, Czech Republic, 14–15 April 2015; Volume 9513, pp. 951302-1–951302-9.
- Slezak, O.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Efficient ASE Management in Disk Laser Amplifiers with Variable Absorbing Clads. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2014, 50, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, O.; Yasuhara, R.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Wavelength dependence of magneto-optic properties of terbium gallium garnet ceramics. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 13641–13647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divoky, M.; Smrz, M.; Chyla, M.; Sikocinski, P.; Severova, P.; Novak, O.; Huynh, J.; Nagisetty, S.S.; Miura, T.; Pilař, J.; et al. Overview of the HiLASE project: High average power pulsed DPSSL systems for research and industry. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, e14 11–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucianetti, A.; Sawicka, M.; Slezak, O.; Divoky, M.; Pilar, J.; Jambunathan, V.; Bonora, S.; Antipenkov, R.; Mocek, T. Design of a kJ-class HiLASE laser as a driver for inertial fusion energy. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, e13 11–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divoky, M.; Sikocinski, P.; Pilar, J.; Lucianetti, A.; Sawicka, M.; Slezak, O.; Mocek, T. Design of high-energy-class cryogenically cooled Yb3+:YAG multislab laser system with low wavefront distortion. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 064201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilar, J.; Slezak, O.; Sikocinski, P.; Divoky, M.; Sawicka, M.; Bonora, S.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T.; Jelinkova, H. Design and optimization of an adaptive optics system for a high-average-power multi-slab laser (HiLASE). Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 3255–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilar, J.; Bonora, S.; Slezak, O.; Sawicka-Chyla, M.; Divoky, M.; Phillips, J.; Smith, J.; Ertel, K.; Collier, J.; Jelinkova, H.; et al. Adaptive optics system for HiLASE high average-power multi-slab laser system. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Adaptive Optics for Industry and Medicine, Padova, Italy, 15–19 June 2015; pp. 197–200.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novák, O.; Miura, T.; Smrž, M.; Chyla, M.; Nagisetty, S.S.; Mužík, J.; Linnemann, J.; Turčičová, H.; Jambunathan, V.; Slezák, O.; et al. Status of the High Average Power Diode-Pumped Solid State Laser Development at HiLASE. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 637-665. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040637
Novák O, Miura T, Smrž M, Chyla M, Nagisetty SS, Mužík J, Linnemann J, Turčičová H, Jambunathan V, Slezák O, et al. Status of the High Average Power Diode-Pumped Solid State Laser Development at HiLASE. Applied Sciences. 2015; 5(4):637-665. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040637
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovák, Ondřej, Taisuke Miura, Martin Smrž, Michal Chyla, Siva Sankar Nagisetty, Jiří Mužík, Jens Linnemann, Hana Turčičová, Venkatesan Jambunathan, Ondřej Slezák, and et al. 2015. "Status of the High Average Power Diode-Pumped Solid State Laser Development at HiLASE" Applied Sciences 5, no. 4: 637-665. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040637
APA StyleNovák, O., Miura, T., Smrž, M., Chyla, M., Nagisetty, S. S., Mužík, J., Linnemann, J., Turčičová, H., Jambunathan, V., Slezák, O., Sawicka-Chyla, M., Pilař, J., Bonora, S., Divoký, M., Měsíček, J., Pranovich, A., Sikocinski, P., Huynh, J., Severová, P., ... Mocek, T. (2015). Status of the High Average Power Diode-Pumped Solid State Laser Development at HiLASE. Applied Sciences, 5(4), 637-665. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5040637






