Enhancing Continuous Sign Language Recognition via Spatio-Temporal Multi-Scale Deformable Correlation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Continuous Sign Language Recognition
2.2. Deformable Neural Net Module
3. Methods
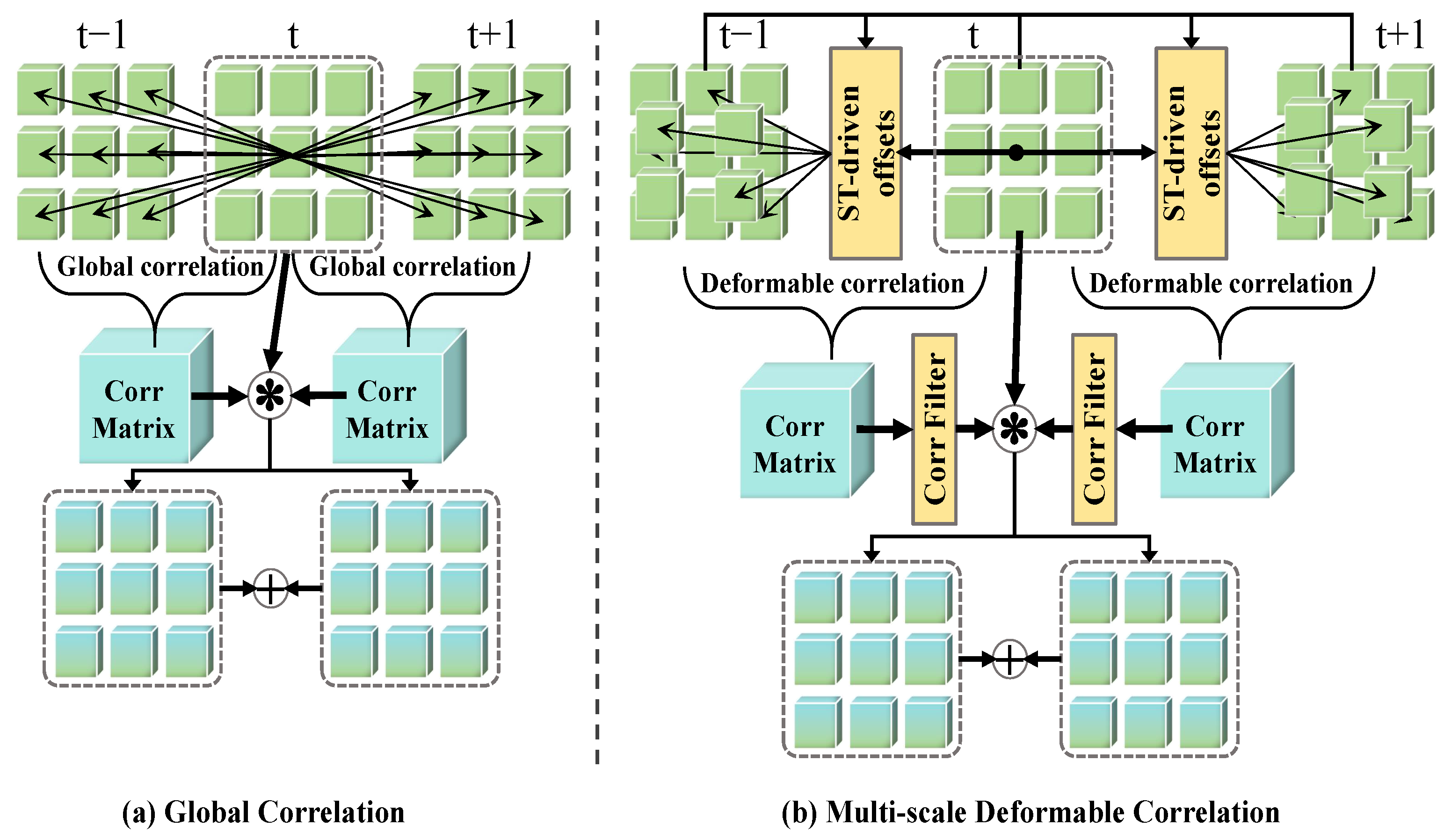
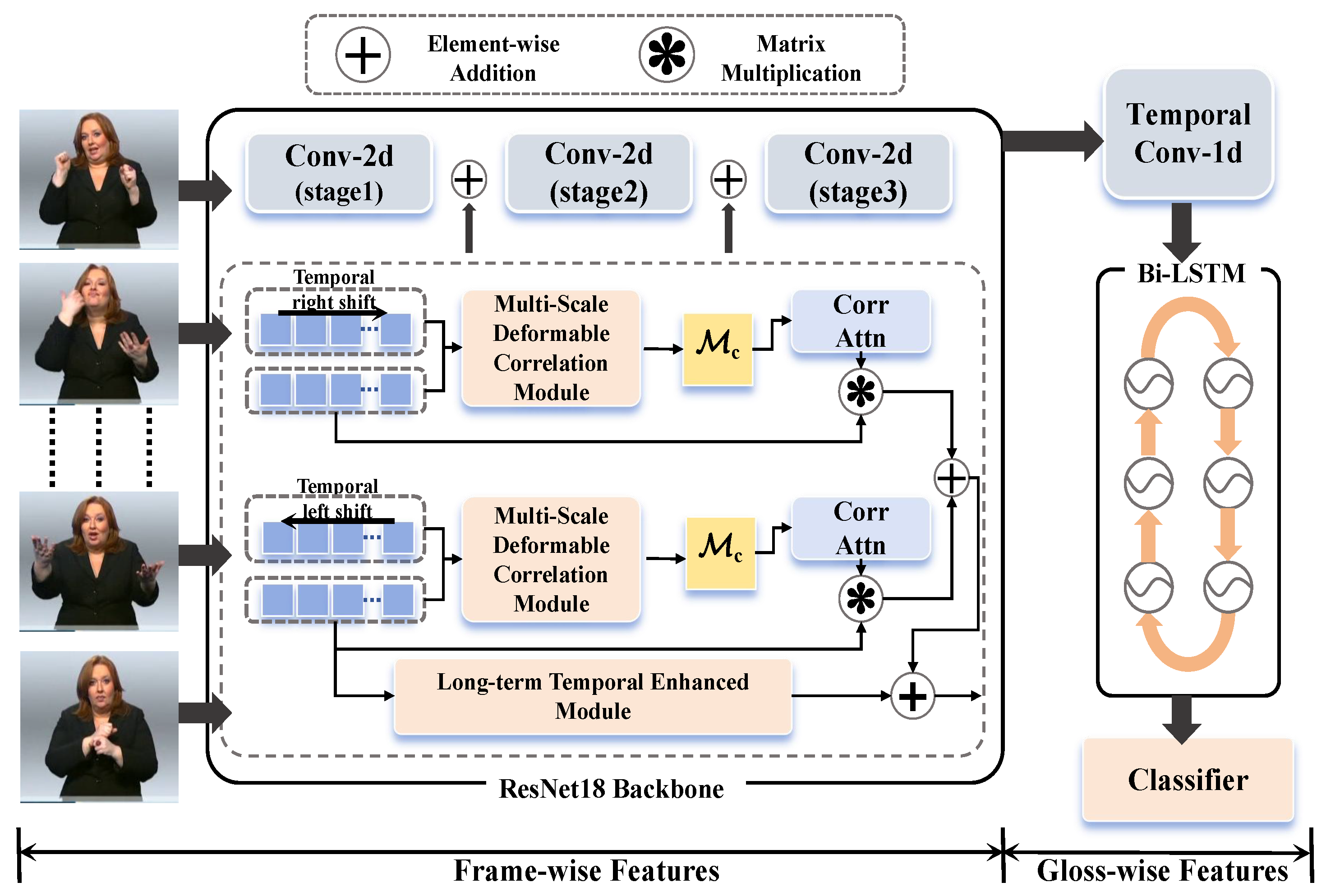
3.1. Method Overview and Motivation
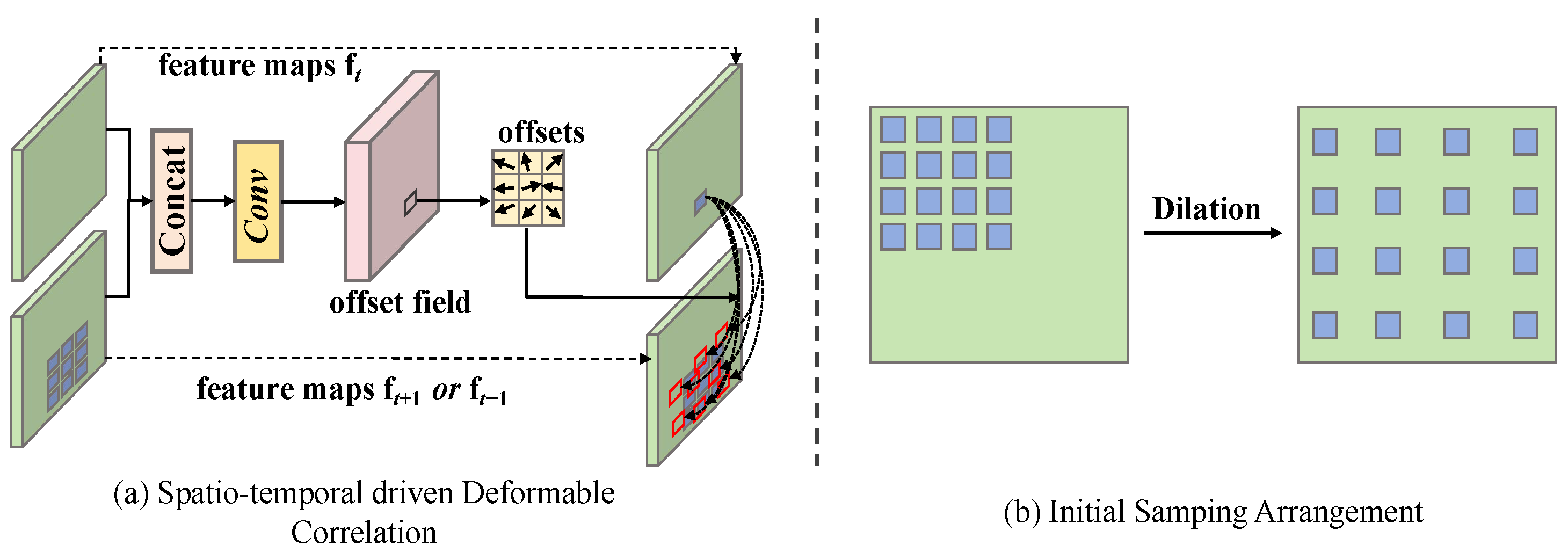
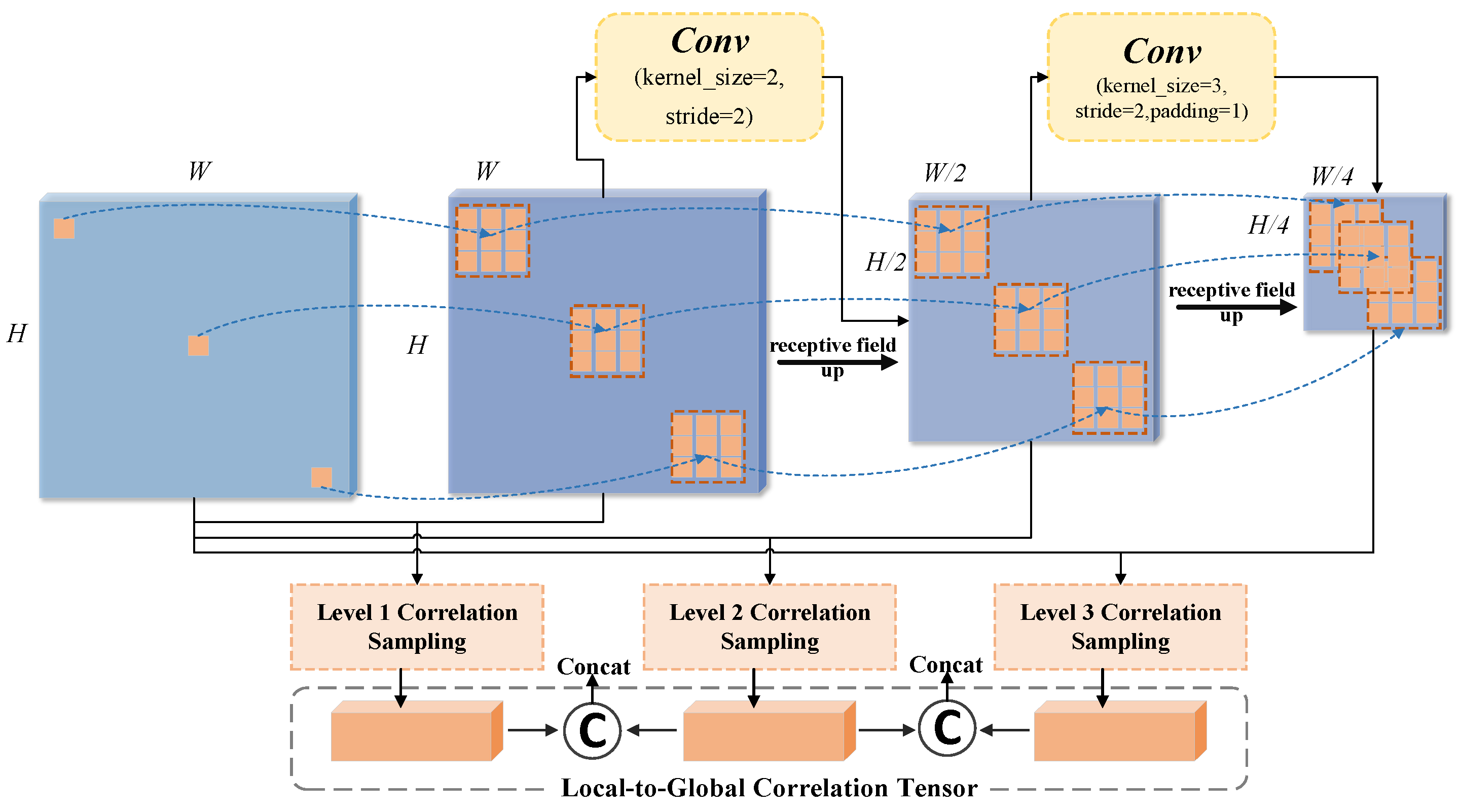
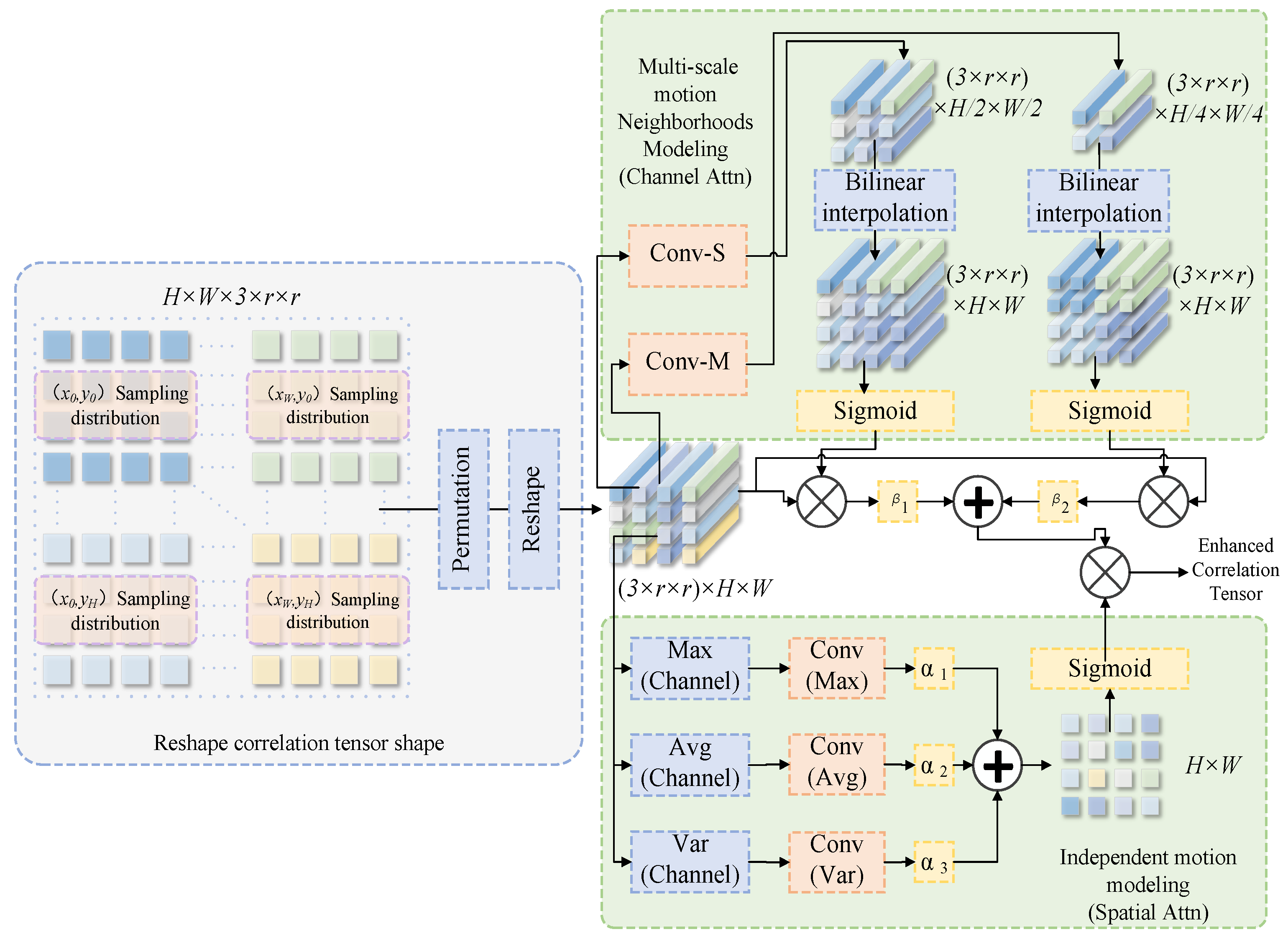
3.2. Deformable Correlation Module Based on Motion Prior
| Algorithm 1: Deformable correlation sampling kernel (pseudo code) |
 |
3.3. Correlation Matrix Filter
3.4. Temporal Affine Transformation
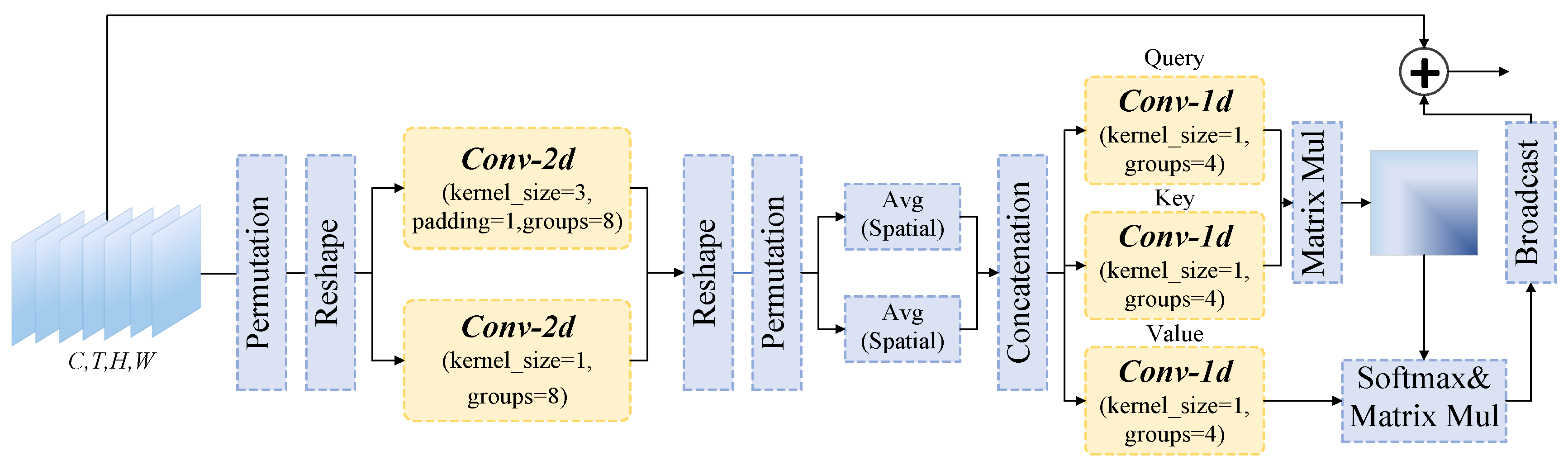
3.5. Long-Term Temporal Enhanced Module Based on Spatial Aggregation
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Training Details
4.3. Evaluation Metric
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.6. Visualization Analysis
4.7. Qualitative Analysis
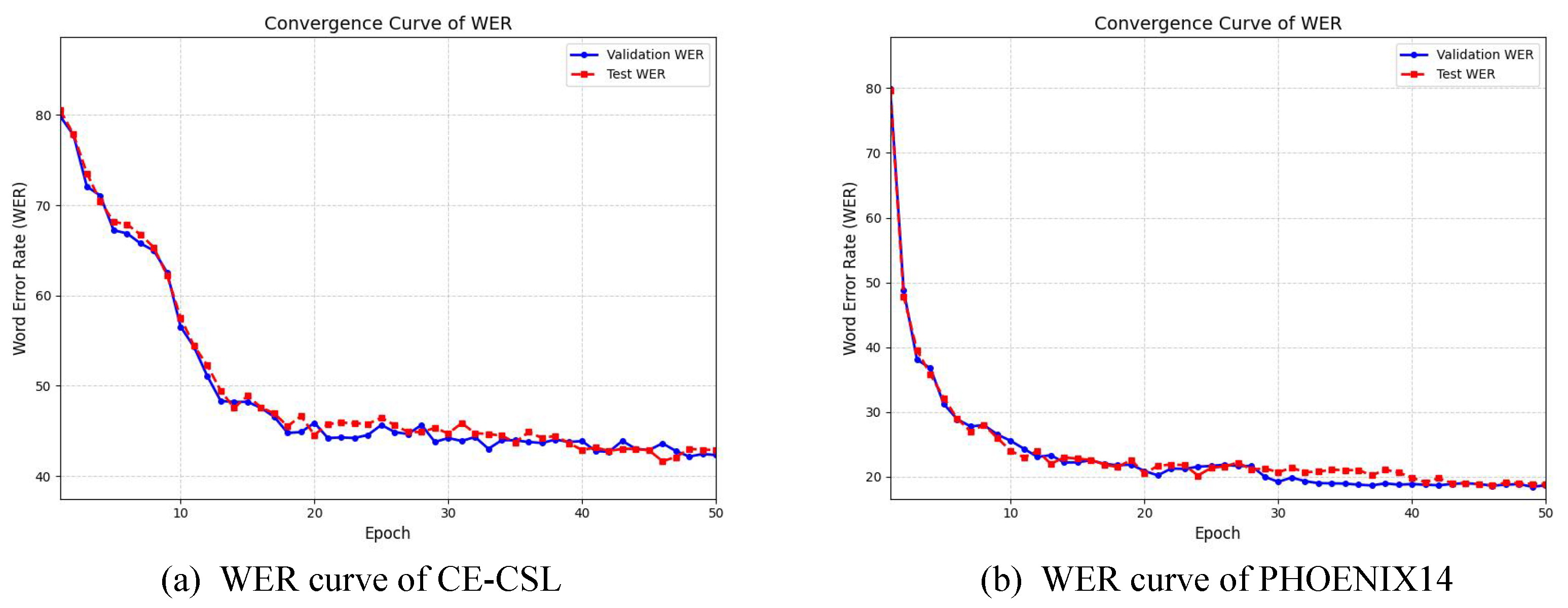
4.8. Converge Analysis
5. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aloysius, N.; Geetha, M. Understanding vision-based continuous sign language recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 22177–22209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C. Recurrent convolutional neural networks for continuous sign language recognition by staged optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7361–7369. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Hu, L. Rethinking the temporal downsampling paradigm for continuous sign language recognition. Multimed. Syst. 2025, 31, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, L.; Xue, W. Dynamical semantic enhancement network for continuous sign language recognition. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C. A deep neural framework for continuous sign language recognition by iterative training. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Tai, Y.W. Fully convolutional networks for continuous sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXIV 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 697–714. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, A.; Min, Y.; Chen, X. Self-mutual distillation learning for continuous sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11303–11312. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition, a new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; LeCun, Y.; Paluri, M. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Gan, C.; Han, S. Tsm: Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7083–7093. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tai, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Huang, F.; Lu, T. Teinet: Towards an efficient architecture for video recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11669–11676. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, W. Continuous sign language recognition with correlation network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2529–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Firkat, E.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Hamdulla, A. Spatio-temporal mix deformable feature extractor in visual tracking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Koller, O.; Zargaran, O.; Ney, H.; Bowden, R. Deep sign: Hybrid CNN-HMM for continuous sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2016, York, UK, 19–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Koller, O.; Zargaran, S.; Ney, H. Re-sign: Re-aligned end-to-end sequence modelling with deep recurrent CNN-HMMs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4297–4305. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Li, G.; Zhao, W.; Tang, X. A coupling method of learning structured support correlation filters for visual tracking. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z. Toward robust visual tracking for UAV with adaptive spatial-temporal weighted regularization. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 8987–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiman, U.; Ahmad, T. Angle based hand gesture recognition using graph convolutional network. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2024, 35, e2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; He, M.; Liu, L.; Yu, F.; Jiang, M. Human action recognition in immersive virtual reality based on multi-scale spatio-temporal attention network. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2024, 35, e2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Gao, L.; Wan, L.; Feng, W. Multi-scale context-aware network for continuous sign language recognition. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2024, 6, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Gomez, F.; Schmidhuber, J. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Min, Y.; Hao, A.; Chai, X.; Chen, X. Visual alignment constraint for continuous sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11542–11551. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, W. Temporal lift pooling for continuous sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 511–527. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, W. Self-emphasizing network for continuous sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 854–862. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, W.; An, W.; Guo, Y. Deformable 3d convolution for video super-resolution. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ji, L.; Liu, H.; Ye, M. LGU-SLAM: Learnable Gaussian Uncertainty Matching with Deformable Correlation Sampling for Deep Visual SLAM. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.23231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, O.; Forster, J.; Ney, H. Continuous sign language recognition: Towards large vocabulary statistical recognition systems handling multiple signers. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2015, 141, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camgoz, N.C.; Hadfield, S.; Koller, O.; Ney, H.; Bowden, R. Neural sign language translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7784–7793. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, F.; Fan, J.; Gan, Q. A Chinese Continuous Sign Language Dataset Based on Complex Environments. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, F.; Gan, Q. Multiscale temporal network for continuous sign language recognition. J. Electron. Imaging 2024, 33, 023059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, W. Scalable frame resolution for efficient continuous sign language recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H. Spatial-temporal multi-cue network for continuous sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13009–13016. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, J.; Hu, K.; Hagenbuchner, M.; Tsoi, A.C.; Bennamoun, M.; Wang, Z. Sign language translation with hierarchical spatio-temporal graph neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 3367–3376. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xue, W.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, T.; Chen, S. Tb-net: Intra-and inter-video correlation learning for continuous sign language recognition. Inf. Fusion 2024, 109, 102438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Salah, A.A.; Poppe, R. Tcnet: Continuous sign language recognition from trajectories and correlated regions. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 3891–3899. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, F.; Gan, Q. Continuous sign language recognition based on motor attention mechanism and frame-level self-distillation. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2025, 36, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
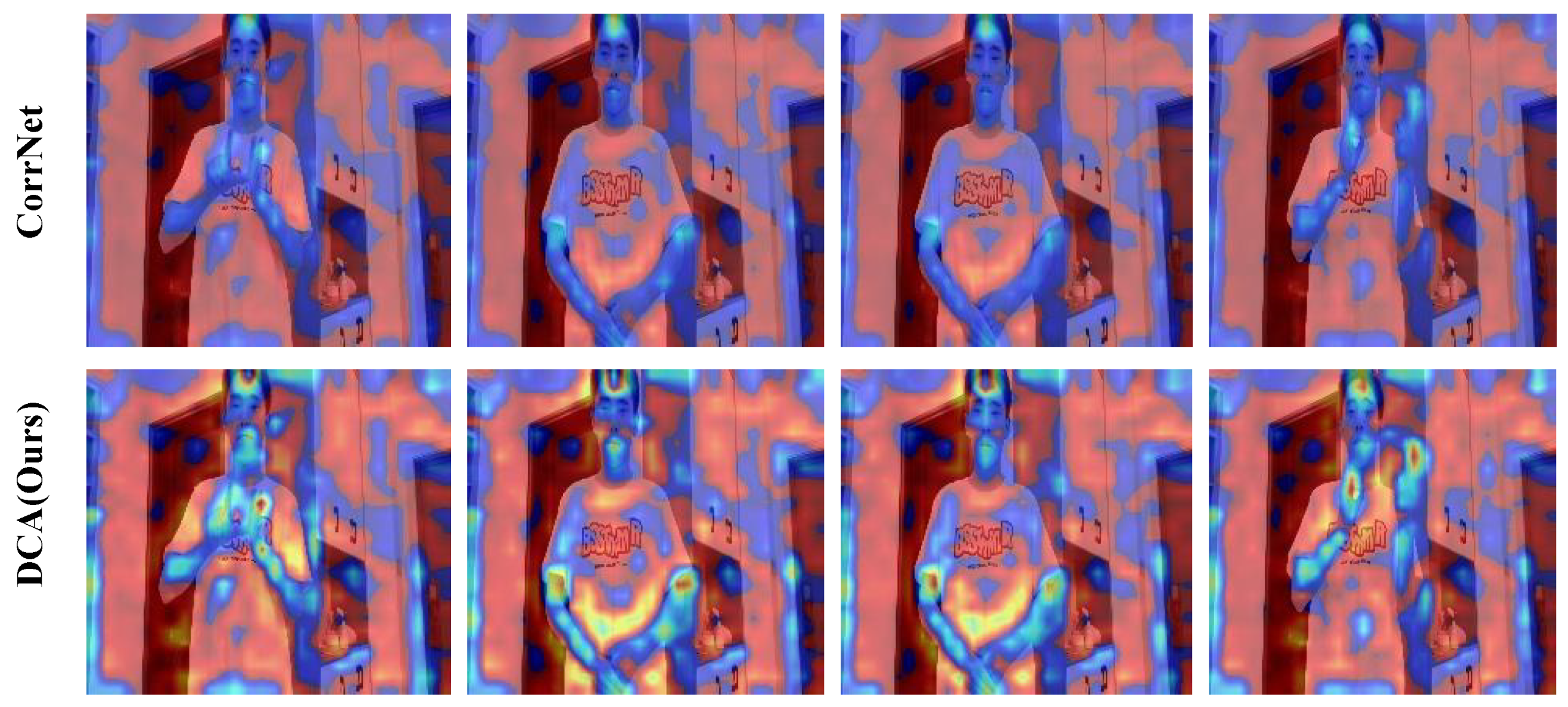
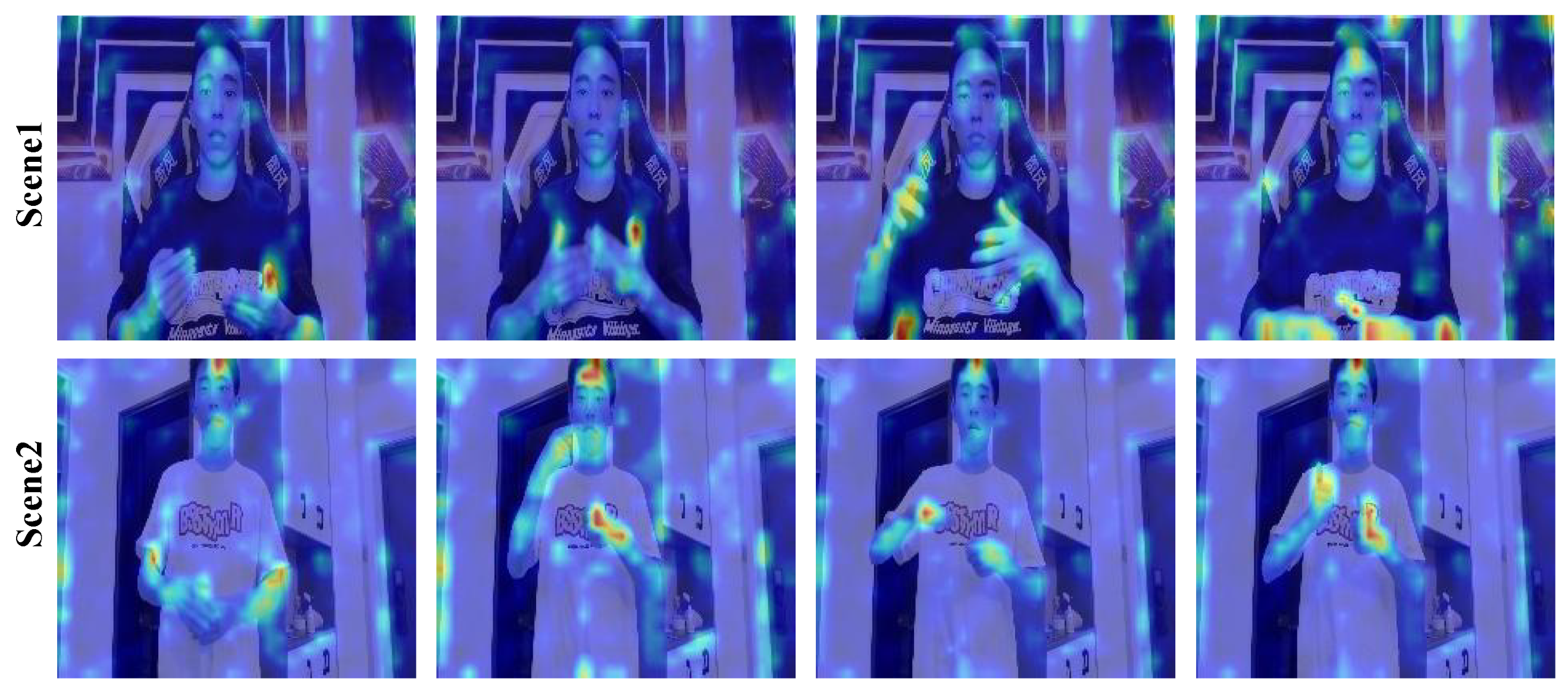
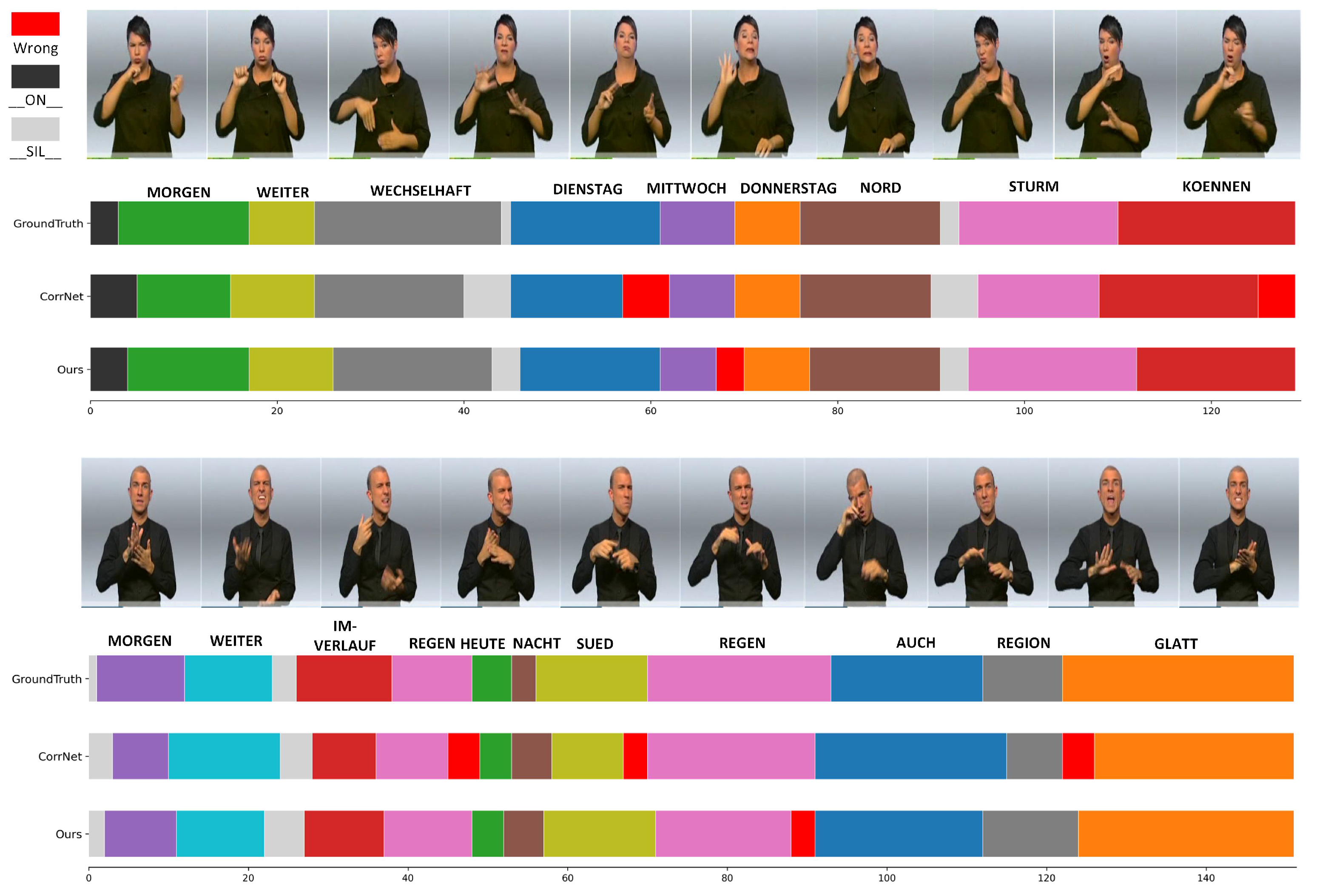



| Configuration | PHOENIX14 | CE-CSL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Val (%) | Test (%) | Val (%) | Test (%) | |
| Baseline | 19.2 | 19.3 | 47.2 | 46.5 |
| Baseline + DC | 18.5 | 18.8 | 43.9 | 43.4 |
| Baseline + CMF | 18.6 | 18.7 | 44.7 | 44.9 |
| Baseline + LTE | 18.8 | 18.9 | 46.3 | 46.1 |
| Baseline + CMF + DC + LTE | 18.4 | 18.6 | 42.1 | 41.6 |
| DC Configuration | PHOENIX14 (Test %) | CE-CSL (Test %) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 19.3 | 46.5 | |
| Sampling scale | 19.0 | 45.4 | |
| 18.8 | 45.2 | ||
| 18.7 | 44.9 | ||
| Initial sampling arrangement | w/Dilation | 19.2 | 45.9 |
| w/Motion-prior | 19.0 | 45.4 | |
| Offset generation | Element-wise addition | 19.3 | 46.2 |
| Channel-wise concat | 18.7 | 44.9 | |
| Configuration | PHOENIX14 | CE-CSL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Val (%) | Test (%) | Val (%) | Test (%) | |
| w/SA + CA | 18.6 | 18.7 | 44.7 | 44.9 |
| w/SA | 18.9 | 19.1 | 45.6 | 45.9 |
| w/CA | 18.8 | 18.9 | 45.3 | 45.7 |
| Method | FLOPs (G) | Params (K) | Latency (ms) | MEM (GiB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 15.57 | 77.66 | 40.13 | 5.1 |
| Baseline + CD | 10.22 | 68.74 | 36.86 | 3.6 |
| Baseline + CD + CMF + LTE | 12.53 | 72.42 | 39.93 | 4.3 |
| Methods | PHOENIX14 | PHOENIX14-T | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Val (%) | Test (%) | Val (%) | Test (%) | |
| VAC [24] | 21.2 | 22.3 | - | - |
| MSTNet [32] | 20.3 | 21.4 | - | - |
| SEN [26] | 19.5 | 21.0 | 19.3 | 20.7 |
| AdaSize [33] | 19.7 | 20.9 | 19.7 | 20.7 |
| STMC [34] | 21.1 | 20.7 | 19.6 | 21.0 |
| HST-GNN [35] | 19.5 | 19.8 | 20.1 | 20.3 |
| DSE [4] | 18.6 | 19.8 | 18.9 | 19.9 |
| TB-Net [36] | 18.9 | 19.6 | 18.8 | 20.0 |
| CorrNet [12] | 19.2 | 19.4 | 18.9 | 20.5 |
| TCatet [37] | 18.1 | 18.9 | 18.3 | 19.4 |
| MAM-FSD [38] | 19.2 | 18.8 | 18.2 | 19.4 |
| THNet [31] | 18.7 | 18.6 | 18.0 | 19.1 |
| DCA (Ours) | 18.4 | 18.6 | 18.3 | 18.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, C. Enhancing Continuous Sign Language Recognition via Spatio-Temporal Multi-Scale Deformable Correlation. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010124
Jiang Y, Yang D, Chen C. Enhancing Continuous Sign Language Recognition via Spatio-Temporal Multi-Scale Deformable Correlation. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(1):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010124
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yihan, Degang Yang, and Chen Chen. 2026. "Enhancing Continuous Sign Language Recognition via Spatio-Temporal Multi-Scale Deformable Correlation" Applied Sciences 16, no. 1: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010124
APA StyleJiang, Y., Yang, D., & Chen, C. (2026). Enhancing Continuous Sign Language Recognition via Spatio-Temporal Multi-Scale Deformable Correlation. Applied Sciences, 16(1), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010124






