Chemical and Radiometric Profiling of Indoor Particulate Matter in a Cultural Heritage Site: The Case of Saronno’s Sanctuary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Particulate Matter Sampling
2.2. Chemical Characterization of Particulate Matter
2.3. Radiometric Analysis and Radiological Hazard Effects Assessment
2.4. Particulate Matter Concentration Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Carbonaceous Fraction and Inorganic Soluble Ions
3.2. Heavy Metals
3.3. Radioactivity and Radiological Health Hazard
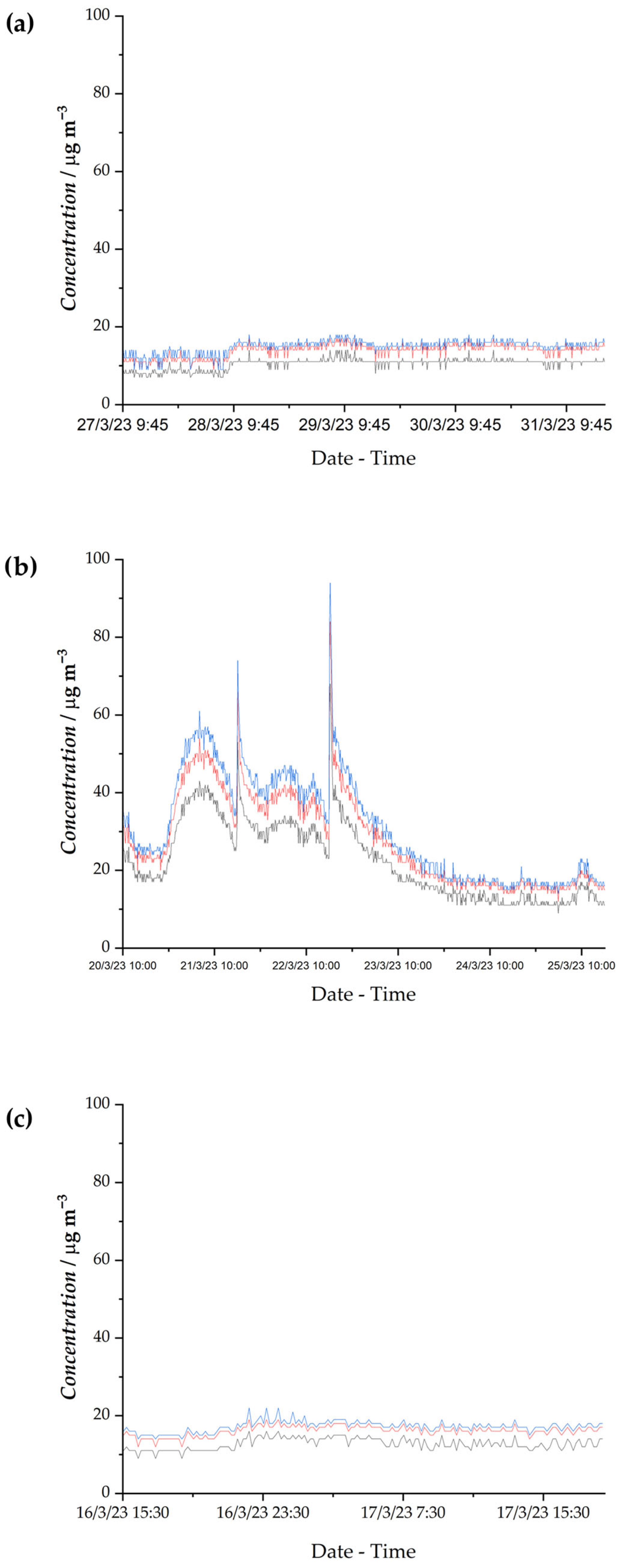
3.4. Real-Time Measurement of Particulate Matter
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Portela, N.B.; Teixeira, E.C.; Agudelo-Castañeda, D.M.; Civeira, M.d.S.; Silva, L.F.O.; Vigo, A.; Kumar, P. Indoor-Outdoor Relationships of Airborne Nanoparticles, BC and VOCs at Rural and Urban Preschools. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, G.; Ciuchini, C.; Pasini, A.; Tappa, R. Monitoring of Ambient BTX at Monterotondo (Rome) and Indoor-Outdoor Evaluation in School and Domestic Sites. J. Environ. Monit. 2002, 4, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, J.; Paciência, I.; De Oliveira Fernandes, E. Levels and Indoor-Outdoor Relationships of Size-Specific Particulate Matter in Naturally Ventilated Portuguese Schools. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health—Part A Curr. Issues 2012, 75, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensirion. Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) and Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)SGP30 TVOC and CO2eq Sensor. Version 2.0. November 2019. Available online: https://www.sensirion.com/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Brimblecombe, P.; Blades, N.; Camuffo, D.; Sturaro, G.; Valentino, A.; Gysels, K.; Van Grieken, R.; Busse, H.J.; Kim, O.; Ulrych, U.; et al. The Indoor Environment of a Modern Museum Building, The Sainsbury Centre for Visual Arts, Norwich, UK. Indoor Air 1999, 9, 146–164, ISSN 0905-6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D.; Brimblecombe, P.; Van Grieken, R.; Busse, H.-J.; Sturaro, G.; Valentino, A.; Bernardi, A.; Blades, N.; Shooter, D.; De Bock, L.; et al. Indoor Air Quality at the Correr Museum, Venice, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 236, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellini, T.; Berlangieri, C.; Dei, L.; Carretti, E.; Santini, S.; Barone, A.; Cincinelli, A. Indoor Levels of Volatile Organic Compounds at Florentine Museum Environments in Italy. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Bovè, J.; Strlic, M. Fine particulate matter in indoor cultural heritage: A literature review. Herit. Sci. 2013, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupa, G.; Rapsomanikis, S. Air Pollutant Emission Rates and Concentrations in Medieval Churches. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 60, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, M. Analysis of Indoor Air Quality in a Naturally Ventilated Church. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018; Volume 49. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.C.; Jones, T.; Bérubé, K. Combustion Particles Emitted during Church Services: Implications for Human Respiratory Health. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergomi, A.; Carrara, E.; Festa, E.; Colombi, C.; Cuccia, E.; Biffi, B.; Comite, V.; Fermo, P. Optimization and Application of Analytical Assays for the Determination of Oxidative Potential of Outdoor and Indoor Particulate Matter. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.Y.; Kim, G.D. Particulate Matter-Induced Emerging Health Effects Associated with Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, J.; Aizezi, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y. Single-Particle Decoding of Aerosol Pollutants Size-Composition Relationships: An Interpretable XGBoost-SHAP Framework with DTEWD-Enhanced SPAMS Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 500, 140397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beelen, R.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Wolf, K.; Samoli, E.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; et al. Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution on Natural-Cause Mortality: An Analysis of 22 European Cohorts within the Multicentre ESCAPE Project. Lancet 2014, 383, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.L.; Tennant, R.K.; Stewart, A.G.; Gosden, C.; Worsley, A.T.; Jones, R.; Love, J. The Evolution of Atmospheric Particulate Matter in an Urban Landscape since the Industrial Revolution. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee, Directive 2013/59/Euratom. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2013/59/oj/eng (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Matthaios, V.N.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Kang, C.M.; Vieira, C.L.Z.; Gold, D.R.; Koutrakis, P. Sources of Indoor PM2.5 Gross α and β Activities Measured in 340 Homes. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Kang, C.M.; Liu, M.; Koutrakis, P. PM2.5 Sources Affecting Particle Radioactivity in Boston, Massachusetts. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Koutrakis, P.; Li, L.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Kosheleva, A.; Zanobetti, A. Synergistic Effects of Particle Radioactivity (Gross β Activity) and Particulate Matter ≤ 2.5 Μm Aerodynamic Diameter on Cardiovascular Disease Mortality. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomberg, A.J.; Nyhan, M.M.; Bind, M.A.; Vokonas, P.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. The Role of Ambient Particle Radioactivity in Inflammation and Endothelial Function in an Elderly Cohort. Epidemiology 2020, 31, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.; Martins, M.; Liu, M.; Koutrakis, P. Measurement of the Gross Alpha Activity of the Fine Fractions of Road Dust and Near-Roadway Ambient Particle Matter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2021, 71, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergomi, A.; Comite, V.; Guglielmi, V.; Borelli, M.; Lombardi, C.A.; Bonomi, R.; Pironti, C.; Ricciardi, M.; Proto, A.; Mariani, C.; et al. Preliminary Air Quality and Microclimatic Conditions Study in the Santuario Della Beata Vergine Dei Miracoli in Saronno (VA). Molecules 2023, 28, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ANPA Agenzia Nazionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente. Guida Tecnica Sulle Misure di Radioattività Ambientali. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files/pubblicazioni/AGFTGTE0002_v2.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, Soils, and Oils; Method 3051A; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/3051a.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Italian Higher Institute for Environmental Protection and Research (ISPRA). Manual of the RESORAD Network; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2016. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files/sicurezza-nucleare-radioattivita/ManualeReteRESORAD_rev2.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Caridi, F.; Marguccio, S.; Durante, G.; Trozzo, R.; Fullone, F.; Belvedere, A.; D’Agostino, M.; Belmusto, G. Natural Radioactivity Measurements and Dosimetric Evaluations in Soil Samples with a High Content of NORM. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELSE Nuclear. ELSE ALBA/LLAB User Manual; ELSE Nuclear: Busto Arsizio, Italy, 2000; Available online: https://www.elsenuclear.com (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Caridi, F.; Testagrossa, B.; Acri, G. Elemental Composition and Natural Radioactivity of Refractory Materials. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortec. GammaVision® 8; Ortec: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ortec-online.com/-/media/ametekortec/manuals/a/a66-mnl.pdf?la=en&revision=dd63bfec-f5cd-4579-8201-e81a52f7fb78 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Caridi, F.; Messina, M.; Belvedere, A.; D’Agostino, M.; Marguccio, S.; Settineri, L.; Belmusto, G. Food Salt Characterization in Terms of Radioactivity and Metals Contamination. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACCREDIA. Available online: https://www.accredia.it/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Italy. Legislative Decree No. 101 of 2020. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2020/08/12/20G00121/sg (accessed on 28 October 2025).
- Perrino, C.; Tofful, L.; Canepari, C. Chemical characterization of indoor and outdoor fine particulate matter in an occupied apartment in Rome, Italy. Indoor Air 2015, 26, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, D.; Pinho, I.; Cerqueira, M.; Nunes, T.; Pio, C. Indoor and Outdoor Suspended Particulate Matter and Associated Carbonaceous Species at Residential Homes in Northwestern Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosa, M.; Cuccia, E.; Colombi, C. Campagna di Approfondimento Della Composizione Chimica del PM10 Nel Supersito di Varese; ARPA Lombardia: Milan, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Santo, U.; Algieri, A.; Carli, P.; Colombi, C.; Corbella, L.; Cuccia, E.; Martini, D.; Gianelle, V.; Siliprandi, G. Caratterizzazione Del PM10 in Alcune Città Lombarde. In Proceedings of the PM2020 Conference, Lecce, Italy, 14–16 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Directive 2008/50/EC of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 152, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Directive 2004/107/EC of 15 December 2004 Relating to Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, Nickel and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 23, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-003422-8. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 100F: Chemical Agents and Related Occupations; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Manousakas, M.; Furger, M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Canonaco, F.; Chen, G.; Tobler, A.; Rai, P.; Qi, L.; Tremper, A.H.; Green, D.; et al. Source Identification of the Elemental Fraction of Particulate Matter Using Size Segregated, Highly Time-Resolved Data and an Optimized Source Apportionment Approach. Atmos. Environ. X 2022, 14, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State of California, Resources Board. Initial Statement of Reasons for Rulemaking—Proposed Identification of Nickel as A Toxic Air Contaminant; Technical Support Document, Part A; State of California, Air Resources Board: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1991.
- Liang, N.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Fu, N.; Zhong, G.; Lin, X.; Mao, K.; Zhang, P.; Chang, Z.; Yang, D.; et al. A Systematic Review on Heavy Metals in Indoor Air: Occurrence, Spatial Variation, and Health Risk. Build. Environ. 2025, 269, 112357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISIN. Radioactivity Information System; ISIN: Rome, Italy, 2025; Available online: https://sinrad.isinucleare.it/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Kang, C.M.; Liu, M.; Garshick, E.; Koutrakis, P. Indoor Particle Alpha Radioactivity Origins in Occupied Homes. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, S.; Krupińska, B.; Worobiec, A.; Cevik, U.; Taskın, H.; Van Grieken, R.; Samek, L.; Wiłkojć, E. Gross Alpha and Beta Activities of Airborne Particulate Samples from Wawel Royal Castle Museum in Cracow, Poland. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 295, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
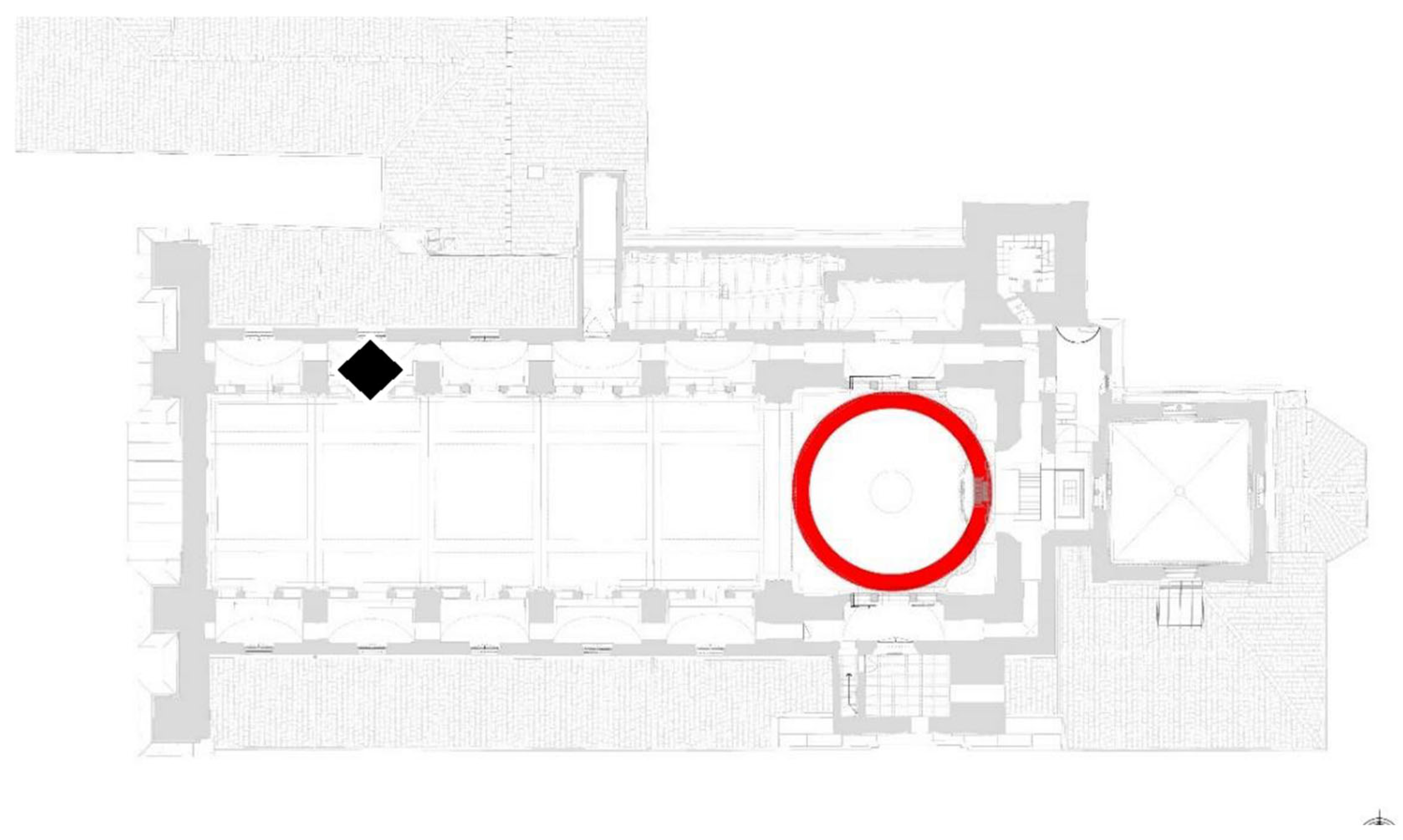
| Sample | Location | Start Date—Time | End Date—Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Milan | 18 April 2023—14:20 | 26 April 2023—12:02 |
| 2 | Saronno | 27 March 2023—09:48 | 31 March 2023—18:00 |
| 3 | Saronno | 20 March 2023—10:02 | 25 March 2023—16:00 |
| 4 | Saronno | 16 March 2023—15:31 | 17 March 2023—18:53 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| FWHM | 1.94 keV |
| Peak/Compton | 65:1 |
| εr | 37.5% (at the 1.33 MeV 60Co γ–line) |
| ΔV | −4800 V |
| ΔE | 5 keV–2 MeV |
| Sample | OC | EC | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Br− | NO2− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.12 | 0.64 | 0.51 | 0.63 | 0.39 | 0.08 | 1.06 | 0.99 | 1.70 | 2.59 | <LOD | <LOD |
| 2 | 4.93 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.27 | 0.37 | 0.11 | 1.35 | 0.98 | 1.51 | 2.14 | <LOD | <LOD |
| 3 | 10.35 | 1.36 | 0.46 | 1.37 | 0.56 | 0.09 | 0.92 | 1.95 | 5.14 | 4.46 | <LOD | <LOD |
| 4 | 11.29 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 4.20 | 4.92 | 5.47 | 5.75 | <LOD | <LOD |
| Sample | As | Cr | Cd | V | Cu | Ni | Sb | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.24 | 6.86 | 0.99 | 0.49 | 18.2 | 6.17 | 1.33 | 22.4 |
| 2 | 0.40 | 4.30 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 14.76 | 5.70 | 4.55 | 21.6 |
| 3 | 0.41 | 4.30 | 0.17 | 0.76 | 15.75 | 3.98 | 1.59 | 34.2 |
| 4 | 0.54 | 12.15 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 31.98 | 11.56 | 2.94 | 50.5 |
| Sample | αtot (mBq m−3) | βtot (mBq m−3) | 137Cs (mBq m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | <0.46 (MDC) | <0.65 (MDC) | <0.14 (MDC) |
| 2 | <2.3 (MDC) | <2.5 (MDC) | <0.16 (MDC) |
| 3 | <3.7 (MDC) | <4.1 (MDC) | <0.21 (MDC) |
| 4 | <2.1 (MDC) | <2.3 (MDC) | <1.18 (MDC) |
| Sample | PM10 | PM2.5 | PM1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 15 | 14 | 10 |
| 3 | 31 | 28 | 23 |
| 4 | 17 | 16 | 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Bergomi, A.; Caridi, F.; Spagnuolo, A.; Comite, V.; Venuti, V.; Lubritto, C.; Lombardi, C.A.; Borelli, M.; Masiello, A.; Fermo, P. Chemical and Radiometric Profiling of Indoor Particulate Matter in a Cultural Heritage Site: The Case of Saronno’s Sanctuary. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010112
Bergomi A, Caridi F, Spagnuolo A, Comite V, Venuti V, Lubritto C, Lombardi CA, Borelli M, Masiello A, Fermo P. Chemical and Radiometric Profiling of Indoor Particulate Matter in a Cultural Heritage Site: The Case of Saronno’s Sanctuary. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(1):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010112
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergomi, Andrea, Francesco Caridi, Antonio Spagnuolo, Valeria Comite, Valentina Venuti, Carmine Lubritto, Chiara Andrea Lombardi, Mattia Borelli, Antonio Masiello, and Paola Fermo. 2026. "Chemical and Radiometric Profiling of Indoor Particulate Matter in a Cultural Heritage Site: The Case of Saronno’s Sanctuary" Applied Sciences 16, no. 1: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010112
APA StyleBergomi, A., Caridi, F., Spagnuolo, A., Comite, V., Venuti, V., Lubritto, C., Lombardi, C. A., Borelli, M., Masiello, A., & Fermo, P. (2026). Chemical and Radiometric Profiling of Indoor Particulate Matter in a Cultural Heritage Site: The Case of Saronno’s Sanctuary. Applied Sciences, 16(1), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010112














