Tracking Control of a Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Integral Sliding Mode Control and a Linear Quadratic Regulator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Modeling of a TWMR System
2.1. Nonlinear Model
2.2. Linearized Model
2.3. Model with Uncertainties
- 1.
- , and the pair (, ) is controllable.
- 2.
- is unknown but upper-bounded for all .
- 3.
- is known and lies in the range space of matrix ; therefore, it is possible to write for some .
3. Design of an Integral Sliding Mode Control Law
3.1. Nominal Control Law
3.2. Discontinuous Control Law
3.3. Overall Control Law
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
4.1. System Parameters and Controller Settings
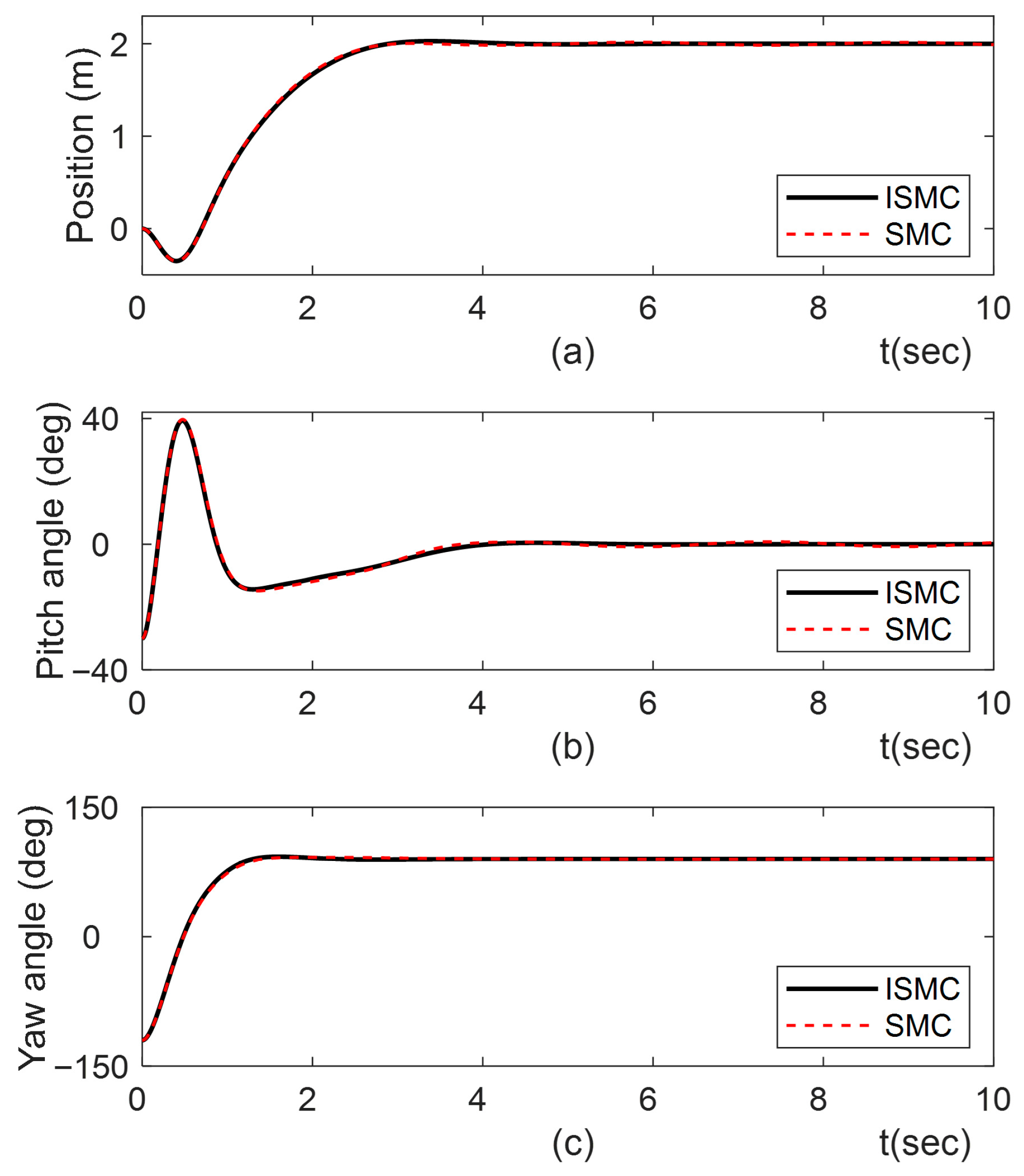
4.2. Performance Under Setpoint Changes
- Case 1: Reference and initial condition ;
- Case 2: Reference and initial condition .
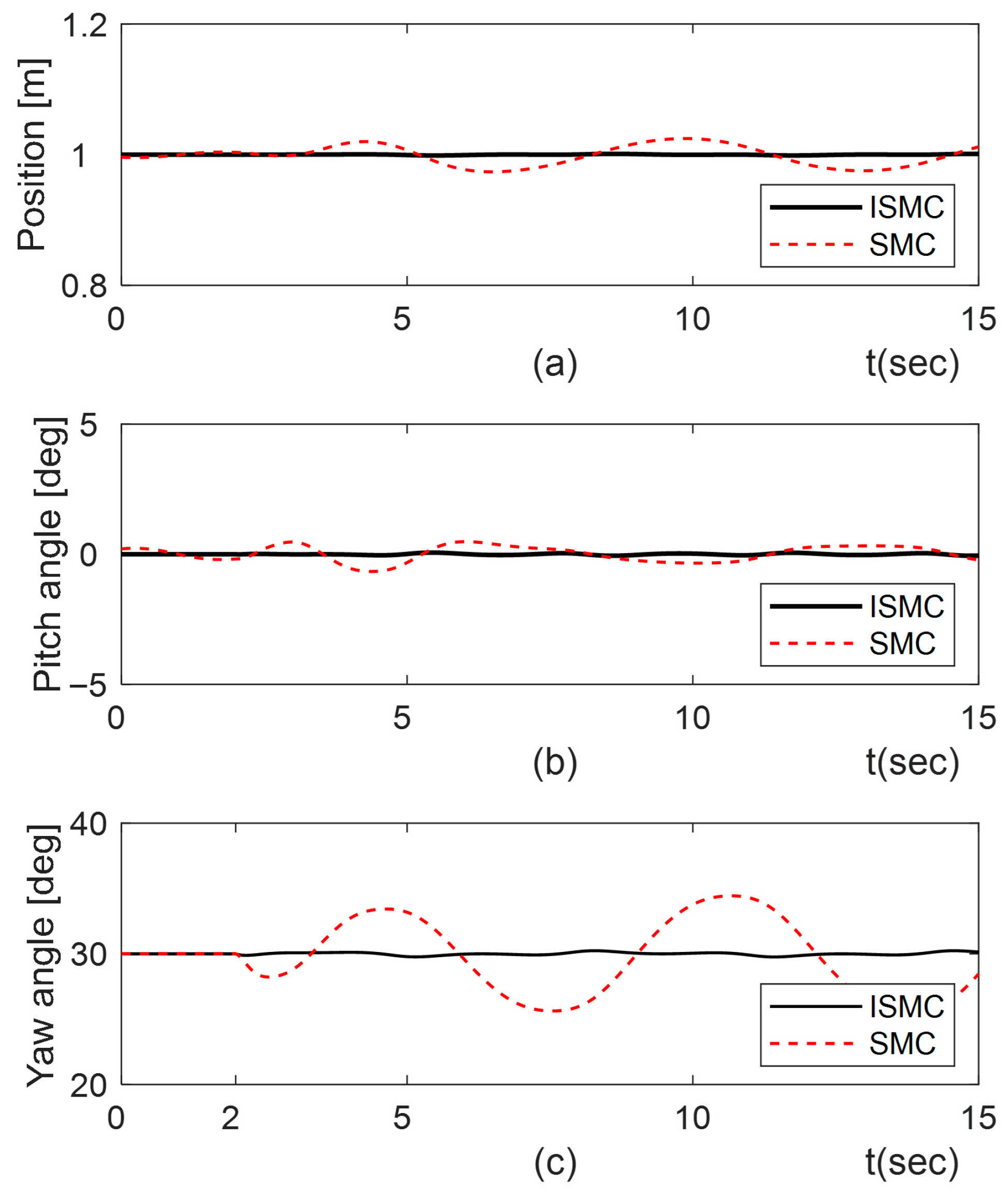
4.3. Performance Under External Disturbance
4.4. Performance Under Disturbance Plus Parameter Changes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOF | Degree of freedom |
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
| IAE | Integral Absolute Error |
| ISMC | Integral sliding mode control |
| LQG | Linear quadratic Gaussian regulator |
| LQR | Linear quadratic regulator |
| MPC | Model predictive control |
| MWMRs | Mecanum-wheeled mobile robots |
| PID | Proportional–Integral–Derivative |
| SMC | Sliding mode control |
| TWIP | Two-wheeled inverted pendulum |
| TWMR | Two-wheeled mobile robot |
References
- Hayward, R. The Tortoise and the Love-Machine: Grey Walter and the Politics of Electroencephalography. Sci. Context 2001, 14, 615–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamajuji, K.; Kawamura, T. Postural control of a monoaxial bicycle. J. Robot. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 7, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, S.J. Dynamic Modeling of a Two-wheeled Inverted Pendulum Balancing Mobile Robot. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2015, 13, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhen, L.; Feng, H. The Kinematics Model of a Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Autonomous Mobile Robot and Its Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications, Bali, Indonesia, 19–21 March 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Liu, A.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Q. Two-Wheeled Robot Platform Based on PID Control. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering (ICISCE), Zhengzhou, China, 20–22 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehpour, M.H.; Taghirad, H.D.; Moradi, H. Two PID-Based Controllers for a Tethered Segway on Dome Shaped Structures. In Proceedings of the 2018 6th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (IcRoM), Tehran, Iran, 23–25 October 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, H.H.; Aldair, A.A.; Al-Hussaibi, W.A. Robust Control Design for Two-Wheel Self-Balanced Mobile Robot. Iraqi J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023, 19, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Kwon, S.J. Nonlinear Optimal Control Design for Underactuated Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum Mobile Platform. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. Height Adaptive LQR Control of a Two-Wheel Legged Robot via Closed-Loop Frequency Identification. In Proceedings of the 2025 5th International Conference on Computer, Control and Robotics (ICCCR), Hangzhou, China, 16–18 May 2025; pp. 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Asad Rizvi, S.A.; Lin, Z. Optimal control of a two-wheeled self-balancing robot by reinforcement learning. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2021, 31, 6205–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, L. An Integrated LQR and Sliding Mode Controller for Balance and Motion Control of a Five-Link Two-Wheel Legged Robot. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems (TAROS 2025), York, UK, 20–22 August 2025; pp. 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önkol, M.; Kasnakoğlu, C. Adaptive Model Predictive Control of a Two-wheeled Robot Manipulator with Varying Mass. Meas. Control 2018, 51, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Guo, Y. Adaptive model predictive control for trajectory tracking of Mecanum mobile robots. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2019, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, V.Q.; Pham, S.H.-T.; Vu, N.T.-T. Adaptive Fuzzy Type-II Controller for Wheeled Mobile Robot with Disturbances and Wheelslips. J. Robot. 2021, 2021, 6946210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefek, A.; Pham, V.T.; Krivanek, V.; Pham, K.L. Optimization of Fuzzy Logic Controller Used for a Differential Drive Wheeled Mobile Robot. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, Z.K.; Shishavan, H.K. A New Approach for Control of Two-wheeled Mobile Robot. Univers. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 6, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozek, P.; Karavaev, Y.; Ardentov, A.A.; Yefremov, K.S. Neural network control of a wheeled mobile robot based on optimal trajectories. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420916077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Yan, X.-G.; Spurgeon, S.K.; Mao, Z. Nonlinear Sliding Mode Control of a Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot System. Int. J. Model. Identif. Control 2017, 27, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyildiz, M.; Tilki, U. Adaptive sliding mode based fault tolerant control of wheeled mobile robots. J. Control. Meas. Electron. Comput. Commun. 2023, 64, 467–483. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Nie, J.; Sun, J.; Tian, X. Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Control for Mobile Robots Based on High-Gain Observers. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4048507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmel, I.; Dimassi, H.; Hadj-Said, S.; M’Sahli, F. Adaptive Observer-Based Sliding Mode Control for a Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot under Terrain Inclination and Disturbances. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8853441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chung, K.-W. Turning Motion Control Design of a Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum Using Curvature Tracking and Optimal Control Theory. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2019, 181, 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peifeng, L.; Hong, B.; Cheng, X. Path tracking control optimization algorithm for mobile robot based on backstepping control algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1914, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, B. Design of linear multivariable continuous-time tracking. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2013, 5, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear Systems, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Bergen, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 1–734. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Sliding Mode Control Using MATLAB; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–346. [Google Scholar]
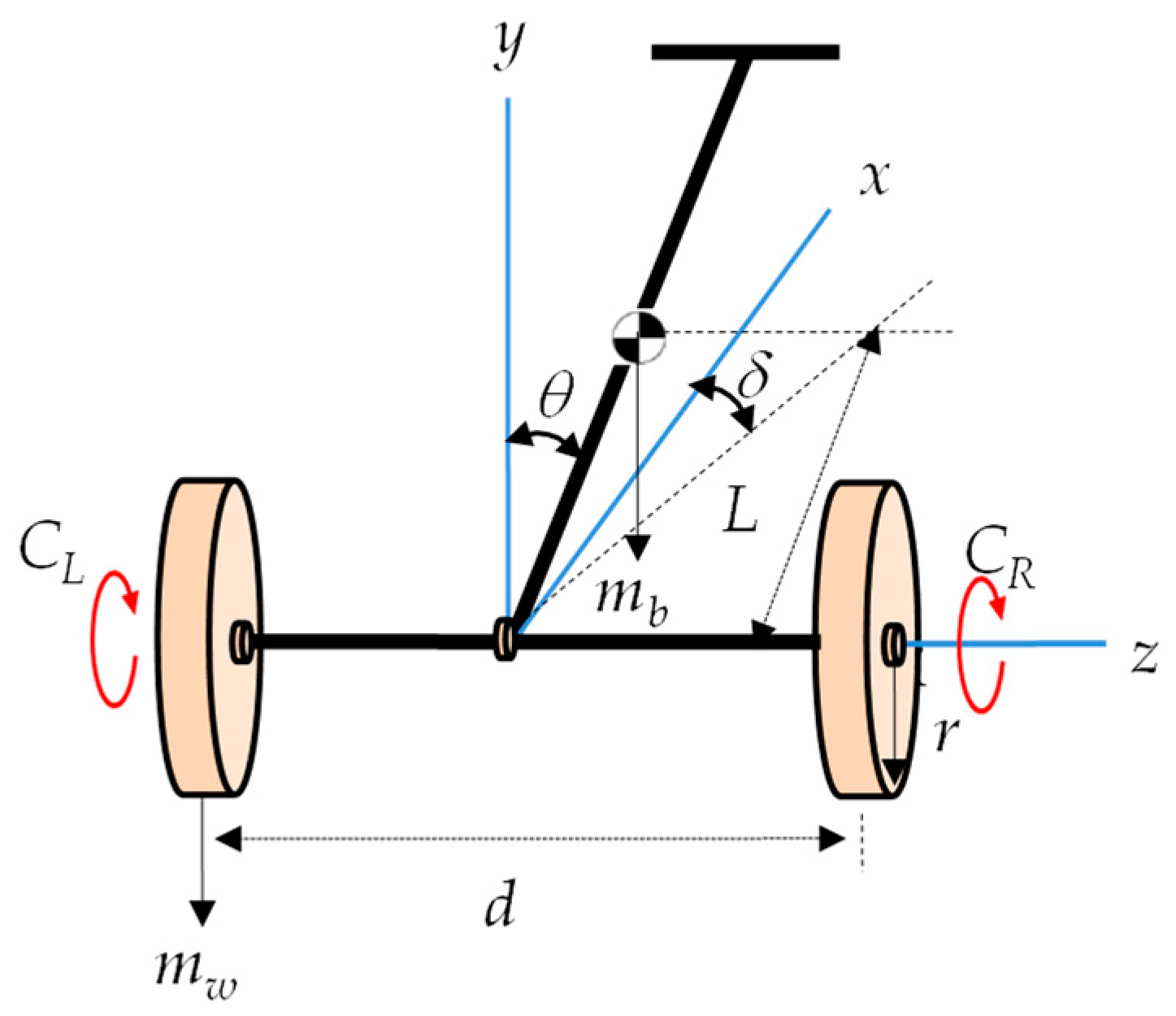


| Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass of the wheel () | 2 | kg |
| Mass of the body () | 45 | kg |
| Radius of the wheel () | 0.2032 | m |
| Distance between the center of the wheels and the TWMR’s center of gravity () | 0.135 | m |
| Distance between the contact patches of the wheels () | 0.6 | m |
| Gravity constant () | 9.81 | m/s2 |
| Moment of inertia of the pendulum body (, , ) | 1.9, 2.1, 1.6 | kg·m2 |
| Moment of inertia of the wheel for the wheel axis () | 0.02 | kg·m2 |
| Moment of inertia of the wheel for the vertical axis () | 0.04 | kg·m2 |
| Case | Output | Controller | Performance Indices | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (m) | ISMC | 4.705 | 1.187 | 2.238 | 1.557 |
| SMC | 5.508 | 1.135 | 2.952 | 1.615 | ||
| (deg) | ISMC | 0.000 | 1.640 | 2.483 | 33.389 | |
| SMC | 1.452 | 1.544 | 2.480 | 35.315 | ||
| 2 | (m) | ISMC | 1.070 | 1.387 | 2.373 | 2.965 |
| SMC | 0.881 | 1.388 | 2.379 | 2.993 | ||
| (deg) | ISMC | 0.512 | 0.747 | 1.010 | 102.72 | |
| SMC | 0.934 | 0.796 | 1.091 | 106.41 | ||
| Output | Controller | Performance Indices | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | ISMC | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| SMC | 0.026 | 0.189 | |
| (deg) | ISMC | 0.238 | 1.183 |
| SMC | 4.439 | 34.962 | |
| Output | Controller | Performance Indices | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | ISMC | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| SMC | 0.028 | 0.186 | |
| (deg) | ISMC | 0.234 | 1.158 |
| SMC | 4.429 | 35.311 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Namera, L.F.; Jin, G.-G.; So, G.; Ahn, J. Tracking Control of a Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Integral Sliding Mode Control and a Linear Quadratic Regulator. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010111
Namera LF, Jin G-G, So G, Ahn J. Tracking Control of a Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Integral Sliding Mode Control and a Linear Quadratic Regulator. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010111
Chicago/Turabian StyleNamera, Lalise Fufi, Gang-Gyoo Jin, Gunbaek So, and Jongkap Ahn. 2026. "Tracking Control of a Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Integral Sliding Mode Control and a Linear Quadratic Regulator" Applied Sciences 16, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010111
APA StyleNamera, L. F., Jin, G.-G., So, G., & Ahn, J. (2026). Tracking Control of a Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Integral Sliding Mode Control and a Linear Quadratic Regulator. Applied Sciences, 16(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010111






