Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
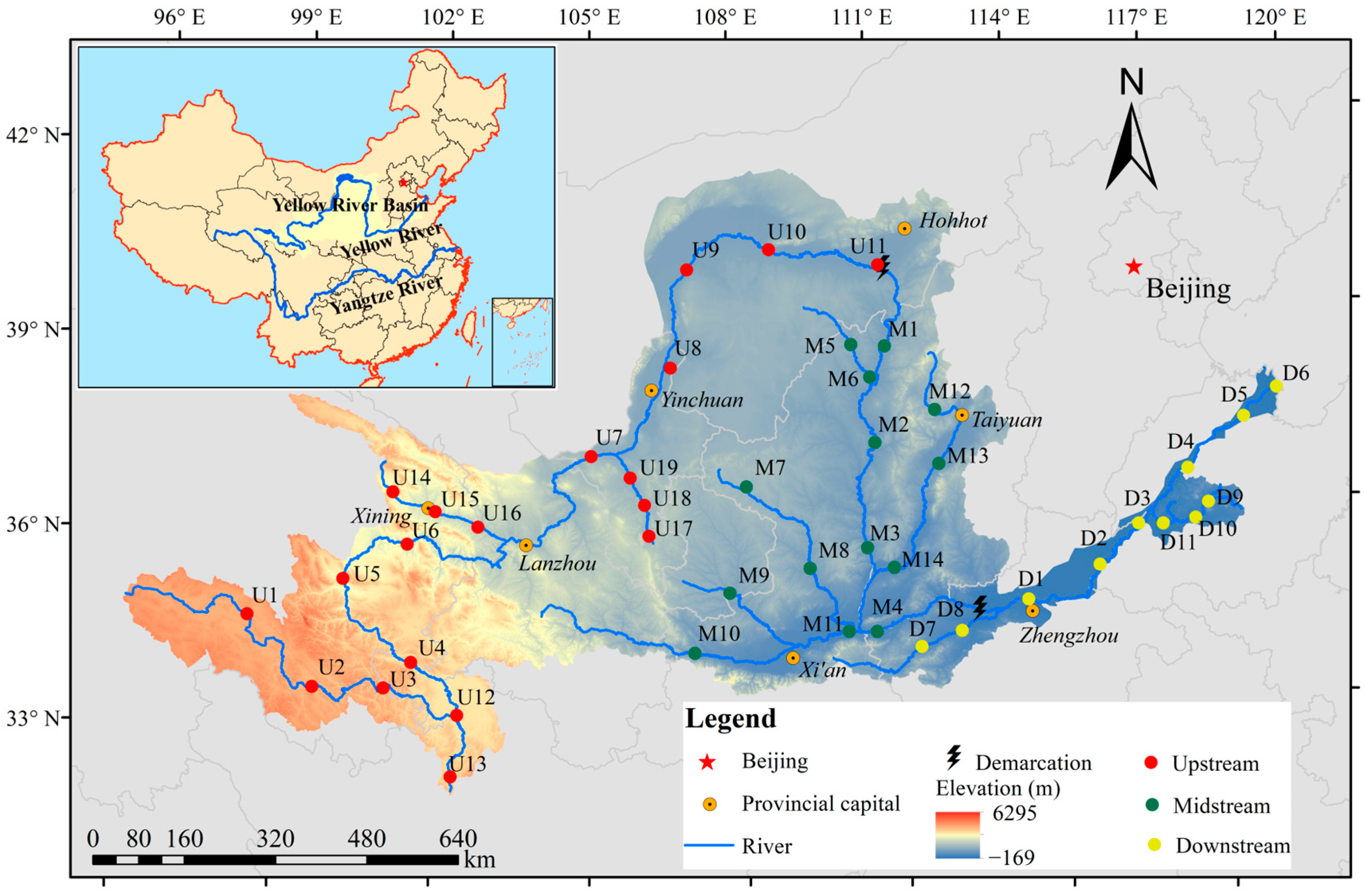
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Metal Concentration Measurement
2.3. Methods for HM Pollution Assessment
2.3.1. Pollution Index Method
2.3.2. Human Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation
2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Model
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
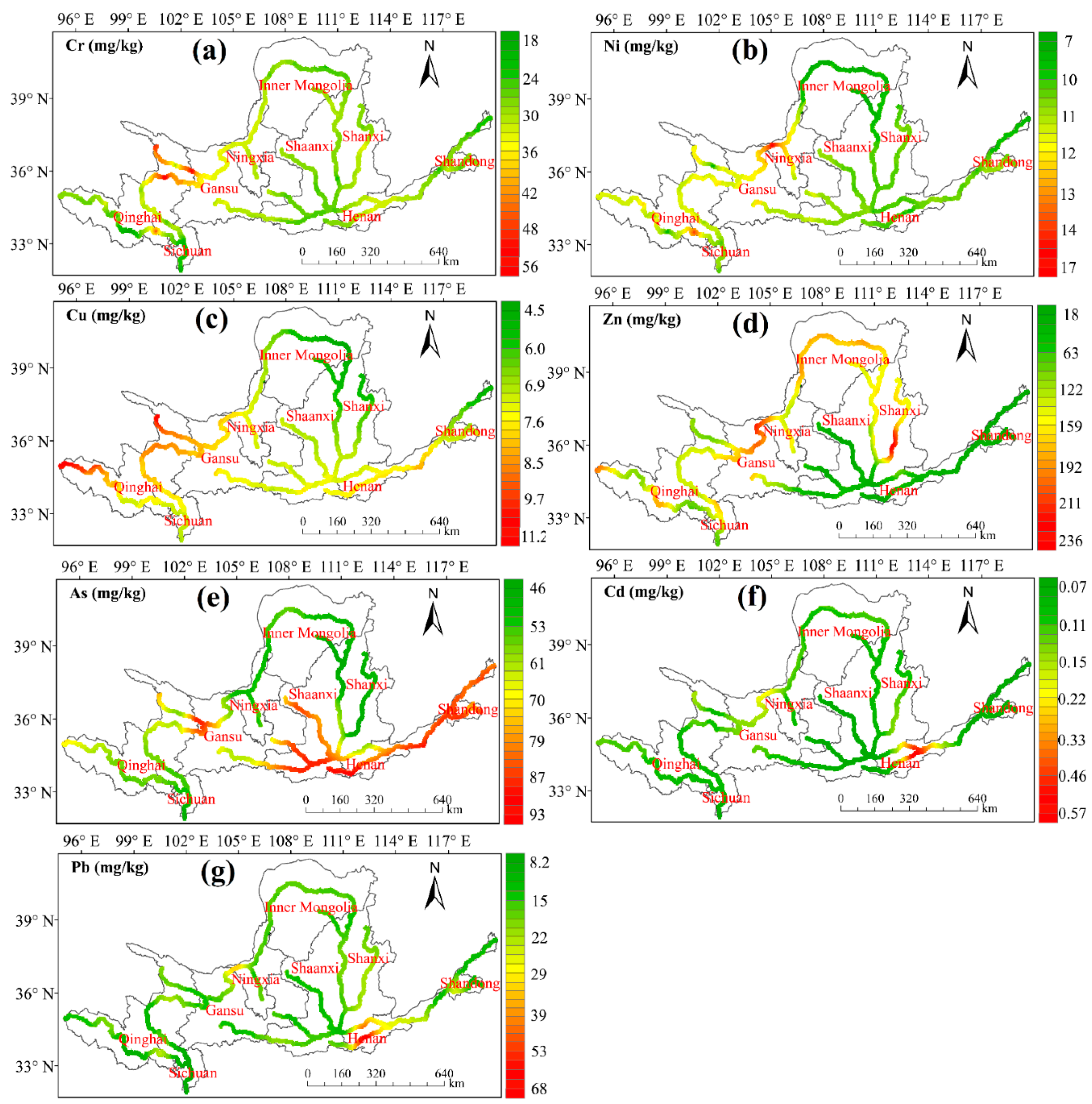
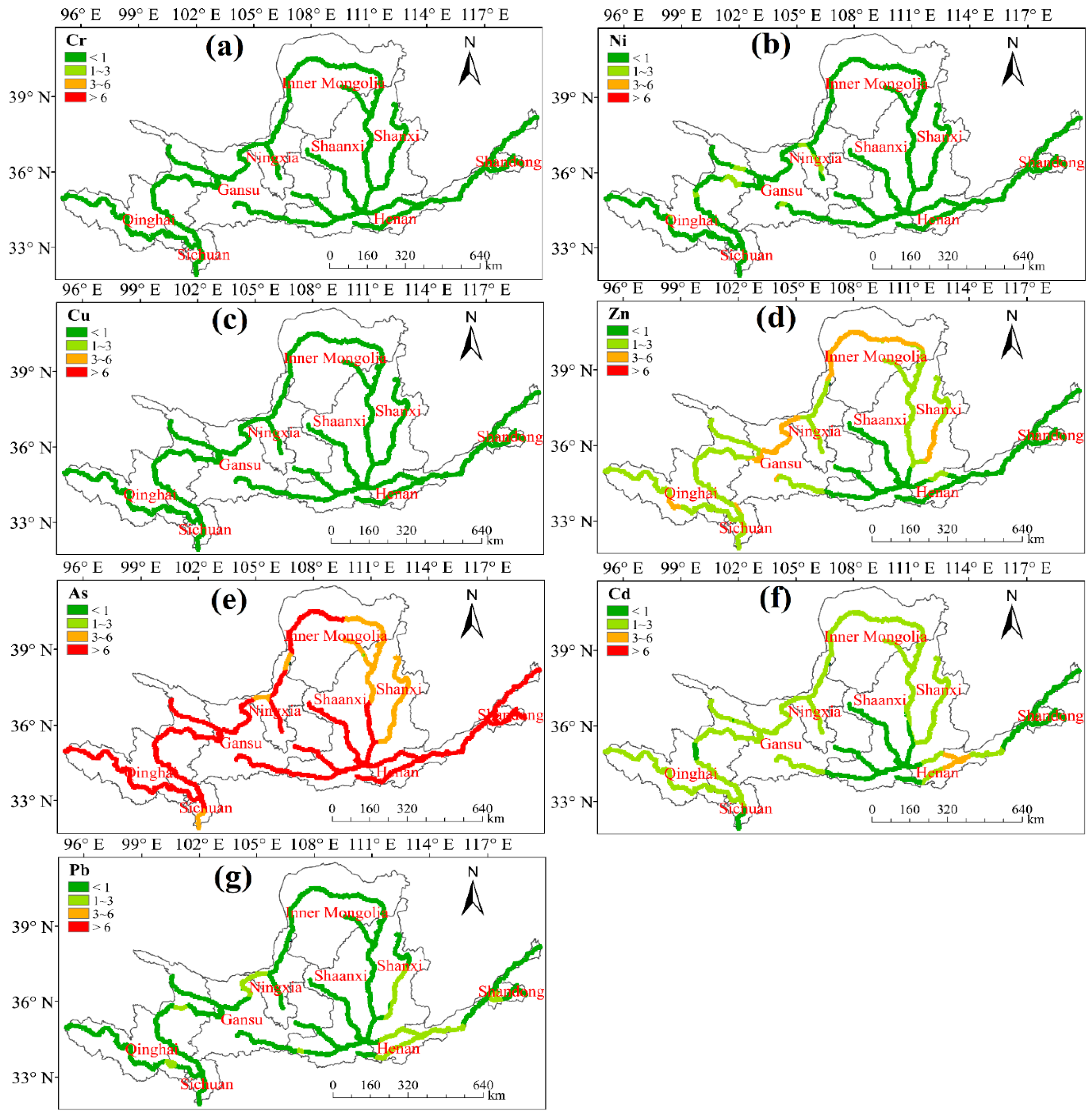
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of HMs in Sediments
3.2. Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment
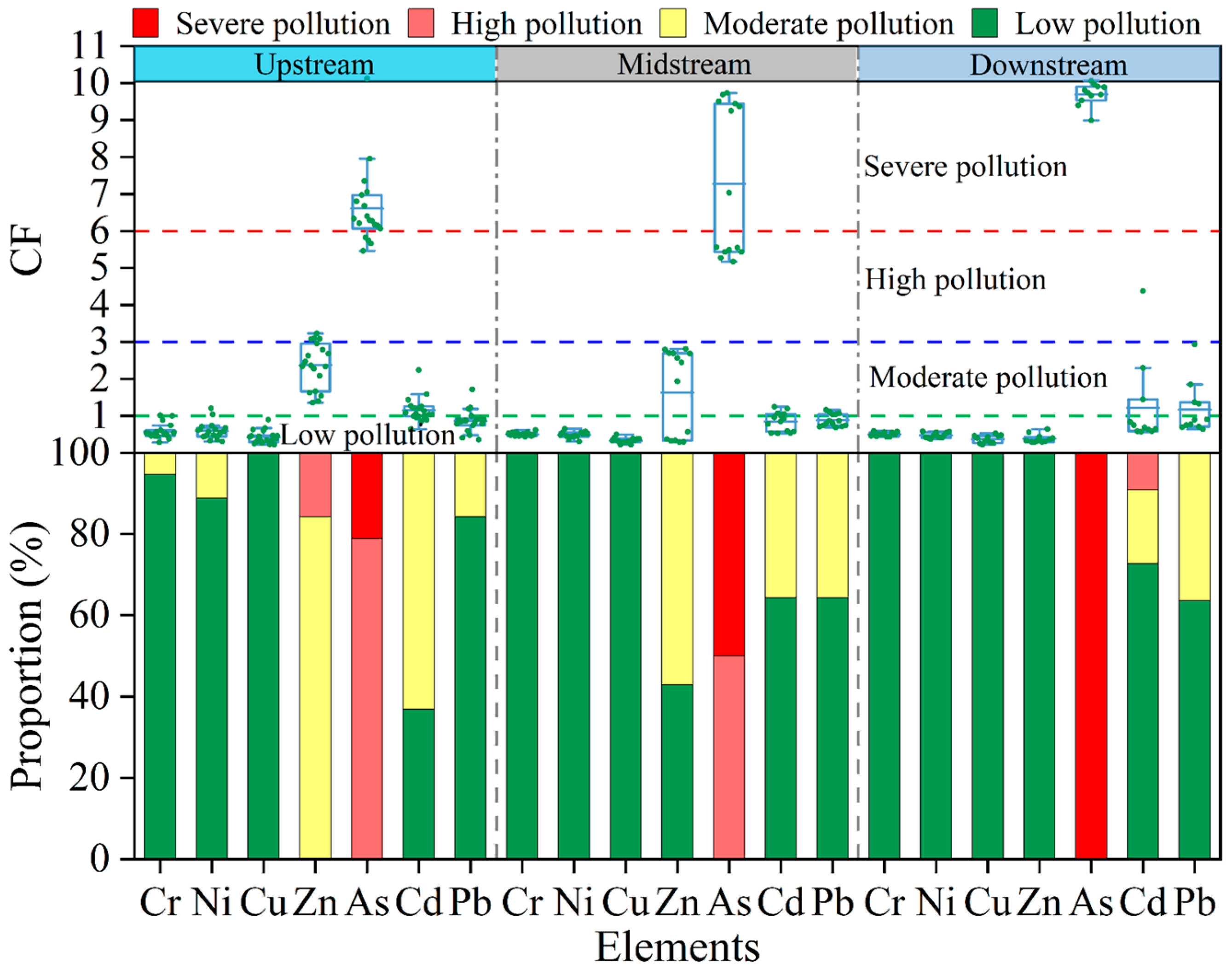
3.2.1. Contamination Factor (CF)
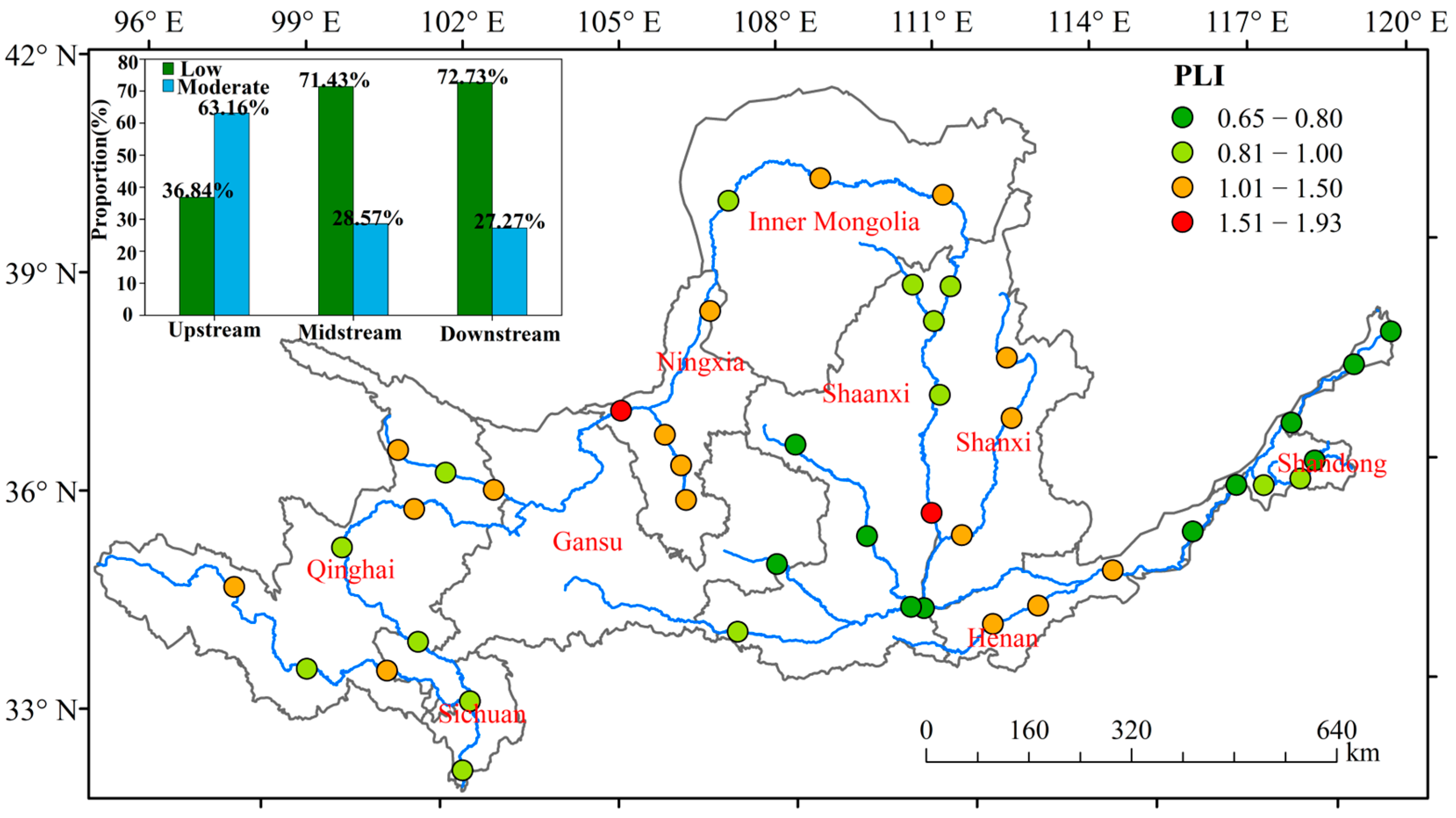
3.2.2. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
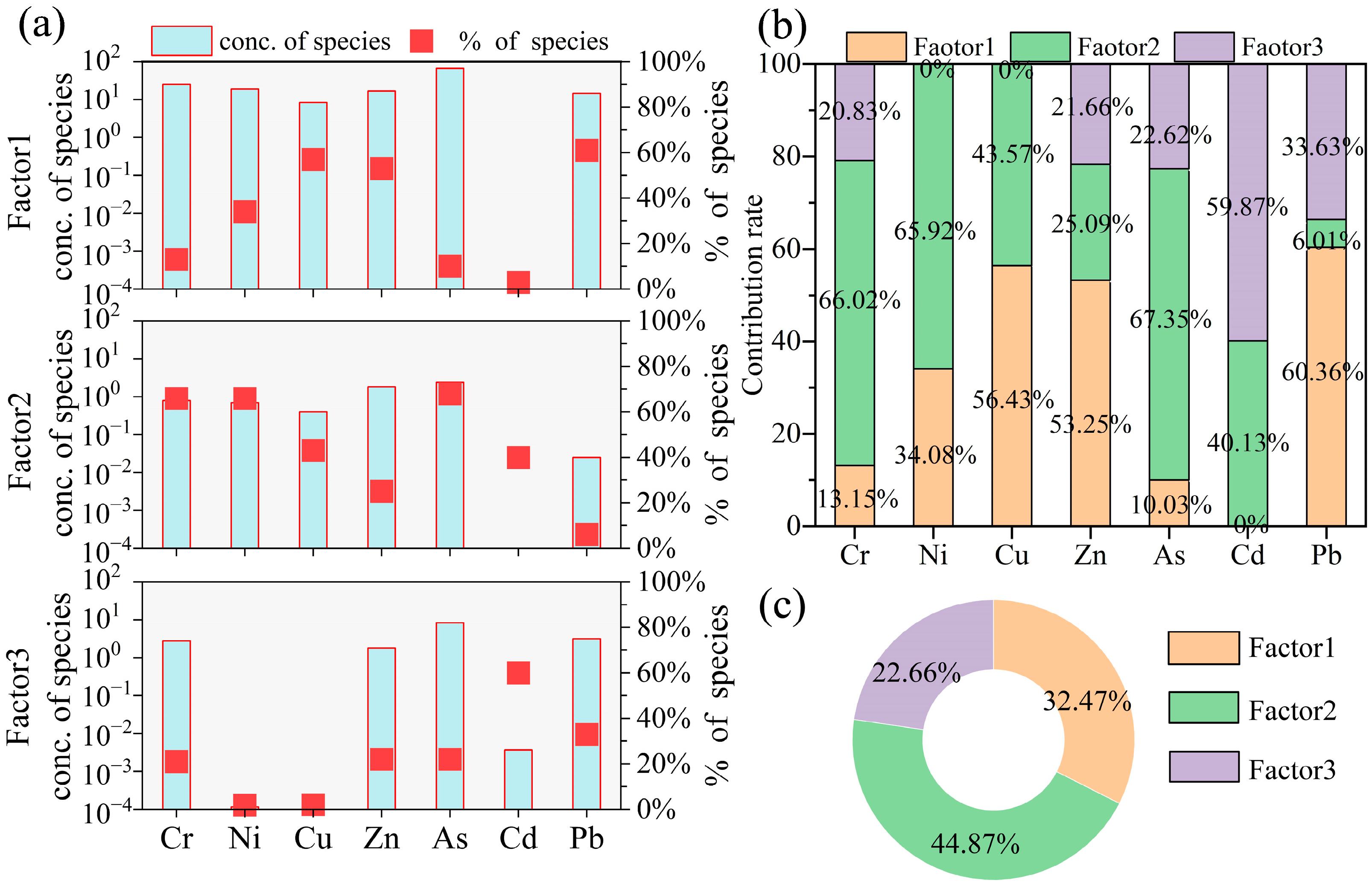
3.3. Identification of the Sources of HMs in Sediments
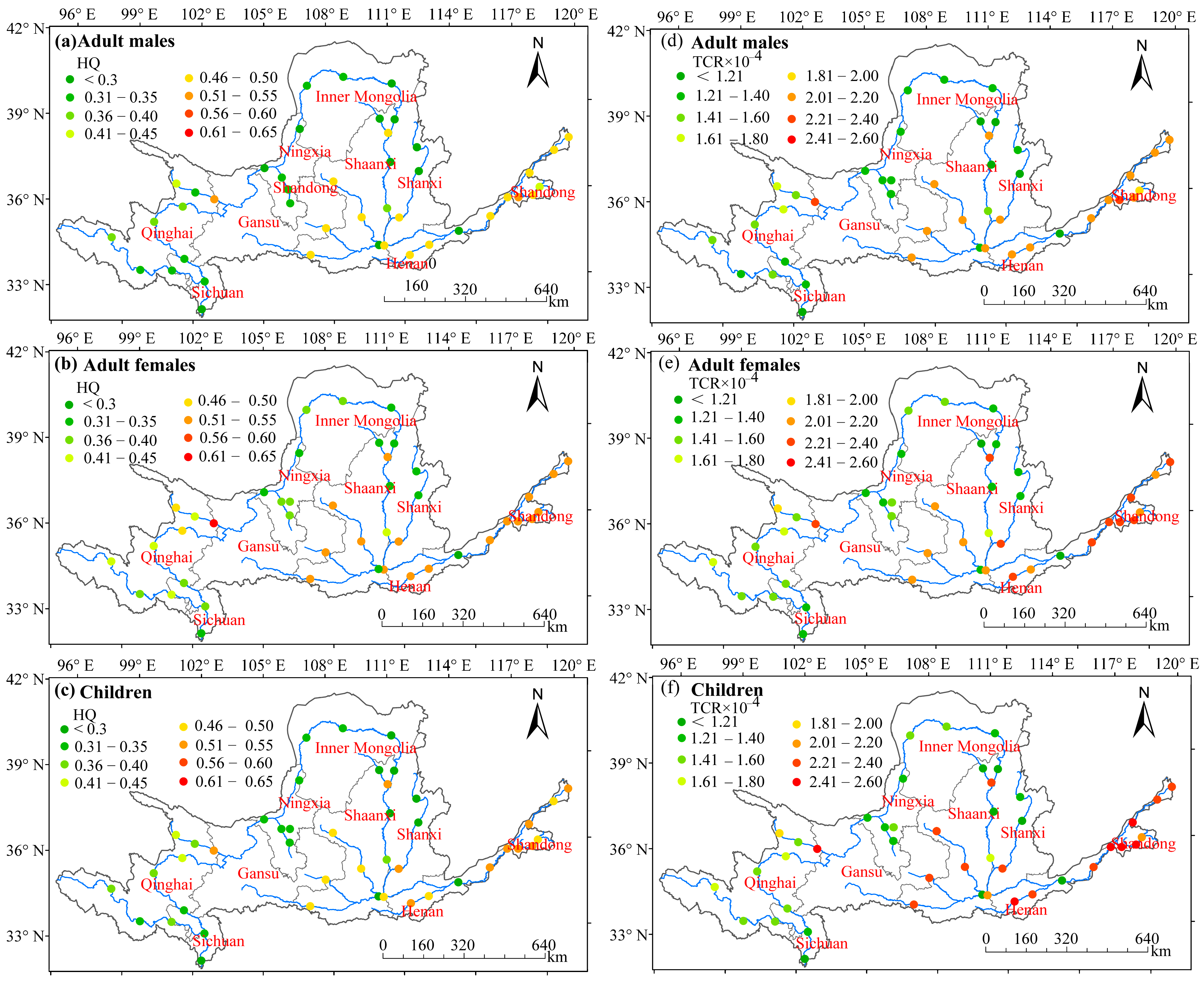
3.4. Assessment of Human Health Risks Associated with HMs
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of HMs in Sediments
4.2. Analysis of Population Health Risks and Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Fu, X.Y.; Li, G.L.; Zhang, J.M.; Li, H.B.; Xie, F.Z. Source-specific probabilistic health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of the Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakan, S.; Devic, G.; Relic, D.; Andelkovic, I.; Sakan, N.; Dordevic, D. Risk assessment of trace element contamination in river sediments in Serbia using pollution indices and statistical methods: A pilot study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6625–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.Y.; Wu, W.H.; Nel, W.; Ji, J.F. The behavior of metals/metalloids during natural weathering: A systematic study of the mono-lithological watersheds in the upper Pearl River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Wiechuła, D. Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Chen, C.T.A. Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Shahab, A.; Li, J.Y.; Xi, B.D.; Sun, X.J.; He, H.J.; Yu, G. Distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of Huixian karstwetland, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2019, 185, 109700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Wang, F.F.; Meng, F.P.; Jiang, L.; Li, G.J.; Zhou, R.G. Assessment of metal contamination in estuarine surface sediments from Dongying City, China: Use of a modified ecological risk index. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Pandey, S.D.; Gopal, K.; Misra, V. Distribution of heavy metals in sediment and water of river Gomti. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 102, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.H.; Yang, X.E.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Q.; Malik, A.; Sadeghpour, A. Heavy metal pollution risk assessments and their transportation in sediment and overlay water for the typical Chinese reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, S.; Krishnan, K.A.; Krishnakumar, A.; Maya, T.V.; Dev, V.V.; Antony, S.; Arun, V. Monitoring of heavy metal contamination in Netravati river basin: Overview of pollution indices and risk assessment. Sustain. Wat. Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.L.; Bu, X.J.; Chen, J.B.; Wu, X. Metals in Yellow River estuary sediments during the 2018 water-sediment regulation scheme period. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Q.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chen, J.; Hou, K.; Ren, W.H.; Qu, W.G.; Chen, Y. Distribution characteristics, source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yellow River, China. Catena 2022, 216, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Guo, D.; Ali, A.; Mi, S.S.; Liu, T.; Ren, C.Y.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Accumulation, ecological-health risks assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in paddy soils: A case study in Hanzhong, Shaanxi, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, P.P.; Zha, X.B.; Xu, C.Y.; Kang, S.X.; Zhou, M.M.; Nover, D.; Wang, Y.H. Overview assessment of risk evaluation and treatment technologies for heavy metal pollution of water and soil. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 379, 134043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.M.; Wang, Q.S.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Wang, S. Heavy metals in agricultural soils from a typical township in Guangdong Province, China: Occurrences and spatial distribution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Shao, J.J.; Yu, B.; Liang, Y.; Duo, B.; Fu, J.J.; Yang, R.Q.; Shi, J.B.; Jiang, G.B. Mercury isotopic compositions of mosses, conifer needles, and surface soils: Implications for mercury distribution and sources in Shergyla Mountain, Tibetan Plateau. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.H.; Duan, J.C.; Ma, Y.L.; He, K.B.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, S.X.; Huang, Y.L.; Si-Tu, S.P. Long-term trends of chemical characteristics and sources of fine particle in Foshan City, Pearl River Delta: 2008–2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Xu, C.Q.; Pan, N.H.; Lin, J.K.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Luo, H.P. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, Northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.C.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, H.L.; Martín, J.D. Bioavailability and health risk of toxic heavy metals (As, Hg, Pb and Cd) in urban soils: A Monte Carlo simulation approach. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergbusch, N.T.; Saunders, M.D.; Leonard, K.; St-Hilaire, A.; Gibson, R.B.; Jardine, T.D.; Courtenay, S.C. A systematic scoping review of the collaborative governance of environmental and cultural flows. Environ. Rev. 2025, 33, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICPR. Sediment Management in the Rhine Basin: 2020 Program Evaluation Report; International Commission for the Protection of the Rhine: Koblenz, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- EPA-823-R-24-005; Mercury Reduction Plan for the Mississippi River Basin. USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- NMCG. Heavy Metal Control in Ganga River: Annual Technical Report 2022-23; National Mission for Clean Ganga: New Delhi, India, 2023.
- Miao, C.; Ni, J.; Borthwick, A.G.L. Recent changes of water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow River basin, China. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Fu, B.J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.B.; Zhao, M.M.; Ma, J.F.; Wu, J.H.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.G.; Wang, H. Sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin: Issues and strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, C.; Lu, J.Y.; Qin, Y.H.; Mo, Y.K.; Xiao, P.J.; Liu, Y. Identification of the heavy metal pollution sources in the rhizosphere soil of farmland irrigated by the Yellow River using PMF analysis combined with multiple analysis methods-using Zhongwei city, Ningxia, as an example. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16203–16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bi, Z.L.; Yu, Y.; Shi, P.; Ren, L.J.; Shan, Z.X. The impact of land use changes and erosion process on heavy metal distribution in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.Y.; Yu, M.C.; Yuan, Q.K.; Meng, Y.; Qie, Y.K.; Shang, Z.M.; Luan, F.B.; Zhang, D.L. Spatial distribution, pollution assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in the Yellow River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.Y.; Ren, Z.P.; Li, Z.B.; Zhang, X.M.; Ma, X.N.; Li, P.; Shen, Z.Z. Evolution of the precipitation–stream runoff relationship in different precipitation scenarios in the Yellow River Basin. Urban CLim. 2023, 51, 101609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Wang, X.Q.; Dai, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, D.S.; Hu, Q.H.; Wang, W.; Xie, M.J.; Lu, Y.X.; Tian, M.; et al. Spatial variations, health risk assessment, and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in the middle Yellow River Basin of northern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2023, 252, 107275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Q.X.; Guo, J.Q.; Liu, G.N.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.Y. Spatial distribution, sediment–water partitioning, risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in the Golmud River-Dabson Salt Lake ecosystem. Environ. Res. 2025, 268, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.H.; Zhi, Y.; Xiao, Q.C.; Yu, F.; Cao, G.Z.; Xu, X.E.; Zhang, Y.S. Source-oriented health risk of heavy metals in sediments: A case study of an industrial city in China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2025, 292, 117929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.Y.; Liang, M.; Feng, B. Average Background Values of 39 Chemical Elements in Stream Sediments of China. Earth Sci. 2016, 41, 234–251. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); U.S. Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS); U.S. Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Yang, S.Y.; Liu, X.M.; Xu, J.M. New Perspectives about Health Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Polltion-Origin and Prospects of Probabilistic Risk Analysis. Acta. Pedologica Sinica. 2022, 59, 28–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Sun, J.X.; Li, X.; Geng, X.L.; Zhao, M.L.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z.Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China byusing Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.B.; Chen, S.J. Reducing uncertainty in ecological risk assessment for heavy metal contamination based on Monte Carlo-Hakanson model. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1706–1712. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G. Source apportionment and source-oriented risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of anurban river-lake system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.B.; Hu, J.; Long, Y.C.; Zhou, S.Q. Spatial distribution fractionation and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in surfacesediments from Caohai Lake, Guizhou. Acta Sci. Circums. 2021, 41, 2212–2221. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, K.M.; Jiao, L.; Tai, X.S.; Zang, F.; Cao, S.Z. Characteristics and Identification Priority Source of Heavy Metals Pollution in Farmland Soils in the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; He, P.; Qiao, G.; Huang, J.T.; Yuan, X.T.; Li, Q. Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the Subei Shoal, China: Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Dai, J.R. Factorial kriging and stepwise regression approach to identify environmental factors influencing spatial multi-scale variability of heavy metals in soils. J. Hazard Mater. 2013, 261, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, I.; Abdugheni, A.; Shi, Q.D.; Liu, S.H.; Nijat, K.; Li, H. Pollution and source identification of heavy metals in surrounding soils of eastern Junggar coalfield based on PMF model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.G.; Peng, M.; Wang, H.Y. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals at township scale in the high background of heavy metals, southwestern, China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4197–4209. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.D.; Lu, X.W.; Yang, G. Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. Catena 2012, 98, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Duan, X.J.; Wang, L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: Case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Vohra, M.S.; Onaizi, S.A. Adsorptive removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Progress of adsorbents development and their effectiveness. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Singh Sidhu, G.P.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A metaanalysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.C.; Yu, H.H.; Ye, T.R.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, G.L.; Albanese, S. Geostatistical mapping and quantitative source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in top- and sub-soils: A case of suburban area in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.D.; Lan, X.P.; Yu, F.X.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.Y.; Du, L.Y. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop system based on PMF and evolutionary game theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Lu, X.W.; Yu, B.; Fan, X.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Lei, K.; Yang, Y.F.; Zuo, L.; Rinklebe, J. Spatial distribution, risk estimation and source apportionment of potentially toxic metal(loid)s in resuspended megacity street dust. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 160, 107073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, C.X.; Fu, X.; Wu, G. Impact of coal power generation on the characteristics and risk of heavy metal pollution in nearby soil. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1787092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Bong, K.M.; Kang, T.W.; Hwang, S.H.; Na, E.H. Assessing heavy metals in surface sediments of the Seomjin River Basin, South Korea, by statistical and geochemical analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.X.; Tang, W.Z. Spatial distribution, fractionation, toxicity and risk assessment of surface sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.R.; Lu, S.Y. Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment of xinfengjiang reservoir. Environ. Eng. 2018, 36, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, F.M. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Xining Section of the Huangshui River. J. Salt Lake Res. 2017, 25, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Fan, D.J.; Li, W.R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, M.; Guo, Z.G. Enrichment of heavy metals in the inner shelf mud of the East China Sea and its indication to human activity. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 90, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Ma, X.L.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y.Z.; Chen, J.H.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.Y.; Wang, R.M.; Fang, F.; Liu, Y. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Metals in Surface Water and Sediment in the Upper Reaches of the Yellow River, China. Soil. Sediment. Contam. 2016, 25, 917–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.L.; Wang, R.L.; Huang, W.H.; Wang, W.L.; Li, X.D. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments from the Yellow River Wetland National Nature Reserve (the Sanmenxia section), China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 8586–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcik, M.; Grzegorzek, M.; Canales, F.A.; Struk-Sokolowska, J.; Kaz, B. Examination of interactions between heavy metals and benzotriazoles in rainwater runoff and snowmelt in an urban catchment in Poland. Water Resour. Ind. 2024, 31, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Guo, X.J.; Liu, J.Y. Characteristic contaminants in snowpack and snowmelt surface runoff from different functional areas in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36256–36266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Khan, A.; Zaman, R.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; Jalal, A.; Kim, K.I. Vermi- remediation impacts on growth and metals bioaccumulation in tomato irrigated with wastewater. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwizeyimana, H.; Wang, M.I.; Chen, W.P.; Khan, K. The eco-toxic effects of pesticide and heavy metal mixtures towards earthworms in soil. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 55, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.T.; Li, X.L.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.M.; Yinglan, A.; Ren, S.L. Heavy metals in the continuous river−estuary−sea system of the Yellow River Delta, China: Spatial patterns, potential sources, and influencing factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Tang, X.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Lin, L.; Zhao, L.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal distribution dynamics of heavy metals in water, sediment, and zoobenthos in mainstream sections of the middle and lower Changjiang River. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.C.; Zhi, Z.X.; Li, Z.B.; Zhuang, J.; Guo, M.J.; Fang, K.; Yi, J.; Ren, Z.P.; Gao, H.D.; Jia, L. Attribution of sediment changes and inffuencing factors of microbial communities in sediment in the Wuding River basin of the Yellow River. Catena 2025, 249, 108626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, D.J.; Bi, N.S.; Sun, X.S.; Tian, Y. Impact of water-sediment regulation on the concentration and transport of dissolved heavy metals in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.Z.; Wang, S.H.; Che, F.F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.J.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, Y.X.; Guo, H.C.; Fu, Z.H. Adsorption and desorption of heavy metals at water sediment interface based on bayesian model. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Z.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.F.; Ng, J.C.; Huang, J.Y.; Xu, Z.B.; Zhang, H. Difference analysis of organic matter-mediated heavy metal pollution in the sediments of urban water bodies. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 968, 178747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Adsorption-desorption behavior of heavy metals in aquatic environments: Influence of sediment, water and metal ionic properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, H.; Memarzadeh, M.; Asl, F.N. Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risks of heavy metals in windborne sediments from a residential area (Case study: Tabas, Iran). Aeolian Res. 2024, 70–71, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-osman, M.; Yang, F.; Massey, I.Y. Exposure routes and health effects of heavy metals on children. Biometals 2019, 32, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkoç, H.B.; Ariman, S. Contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals in coastal sediments from the Mid-Black Sea, Turkey. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, M.C.; Özkaynak, H.; Beamer, P.; Dang, W.; Hsi, H.C.; Jiang, C.B.; Chien, L.C. Mouthing activity data for children age 3 to <6 years old and fraction of hand area mouthed for children age < 6 years old in Taiwan. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filipsson, M.; Lindström, M.; Peltola, P.; Öberg, T. Exposure to contaminated sediments during recreational activities at a public bathing place. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, B.R.; Pai, B.J.; Salmataj, S.A.; Naik, N. Assessment of Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk indices of heavy metal exposure in different age groups using Monte Carlo Simulation Approach. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; Van-der-Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.C.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.H. The industrial technological spillover effect and differentiation characteristics of industrial chains in the ecological efficiency of the yellow river basin. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 477, 143856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.H.; Chin, L.; Samad, A.R.A.; Senan, M.K.A.M.; Ding, Y.M. Environmental quality, residents’ health, and economic growth in the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 4445–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Feng, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, F.; Zhao, C.G.; Yu, T.F.; Chen, W.Y. Formation of the upper reaches of the Yellow River: Provenance evidence from the strata of the Yellow River sedimentary basin. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2023, 229, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.H.; Hong, J.P. Concentration, Sources and Ecological Risk of Nutrients and Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments from Fenhe River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 95–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, K.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, B. Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin, China. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5188. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095188
Fang K, Xu G, Wang Y, Cheng Y, Li J, Chen X, Wang B. Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin, China. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):5188. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095188
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Kang, Guoce Xu, Yun Wang, Yuting Cheng, Jing Li, Xin Chen, and Bin Wang. 2025. "Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin, China" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 5188. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095188
APA StyleFang, K., Xu, G., Wang, Y., Cheng, Y., Li, J., Chen, X., & Wang, B. (2025). Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin, China. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 5188. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095188




