Fish Body Pattern Style Transfer Based on Wavelet Transformation and Gated Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
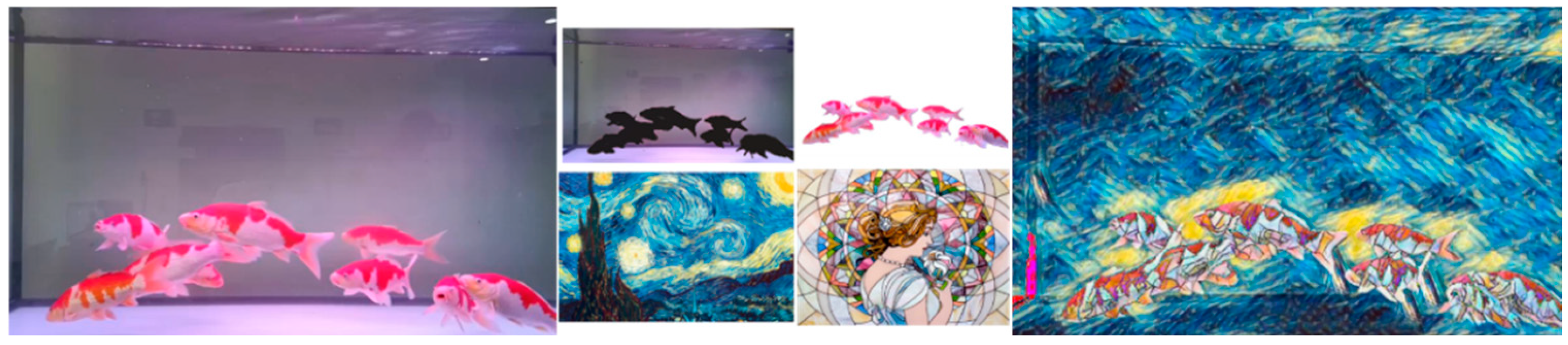
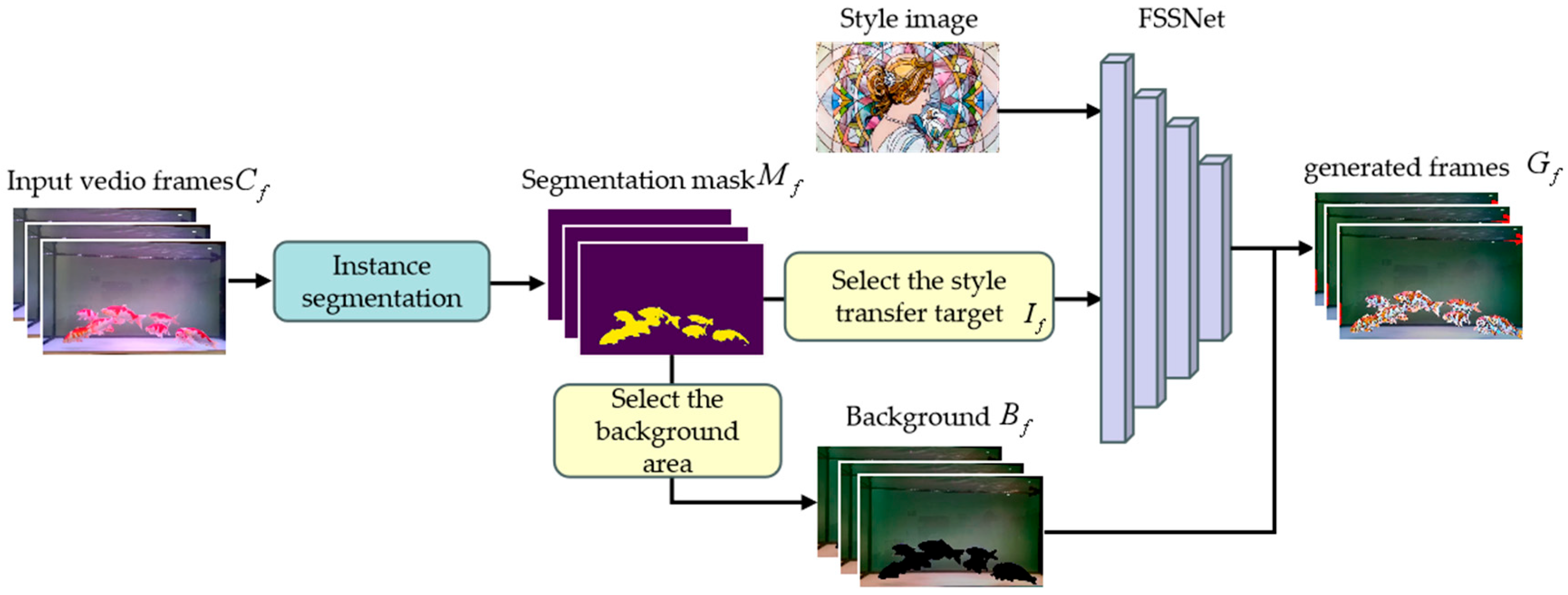
- High-precision mask-based local style transfer: We propose FSSNet, a style transfer model tailored for various ornamental fish species, optimizing the accuracy of fish body mask generation in complex underwater scenes. Using segmentation masks, we achieve fast and synchronized pattern transformations while supporting distinct style transfers for foreground fish and the background. Our model effectively adapts multiple styles, such as oil painting and blue-and-white porcelain, enhancing visual diversity.
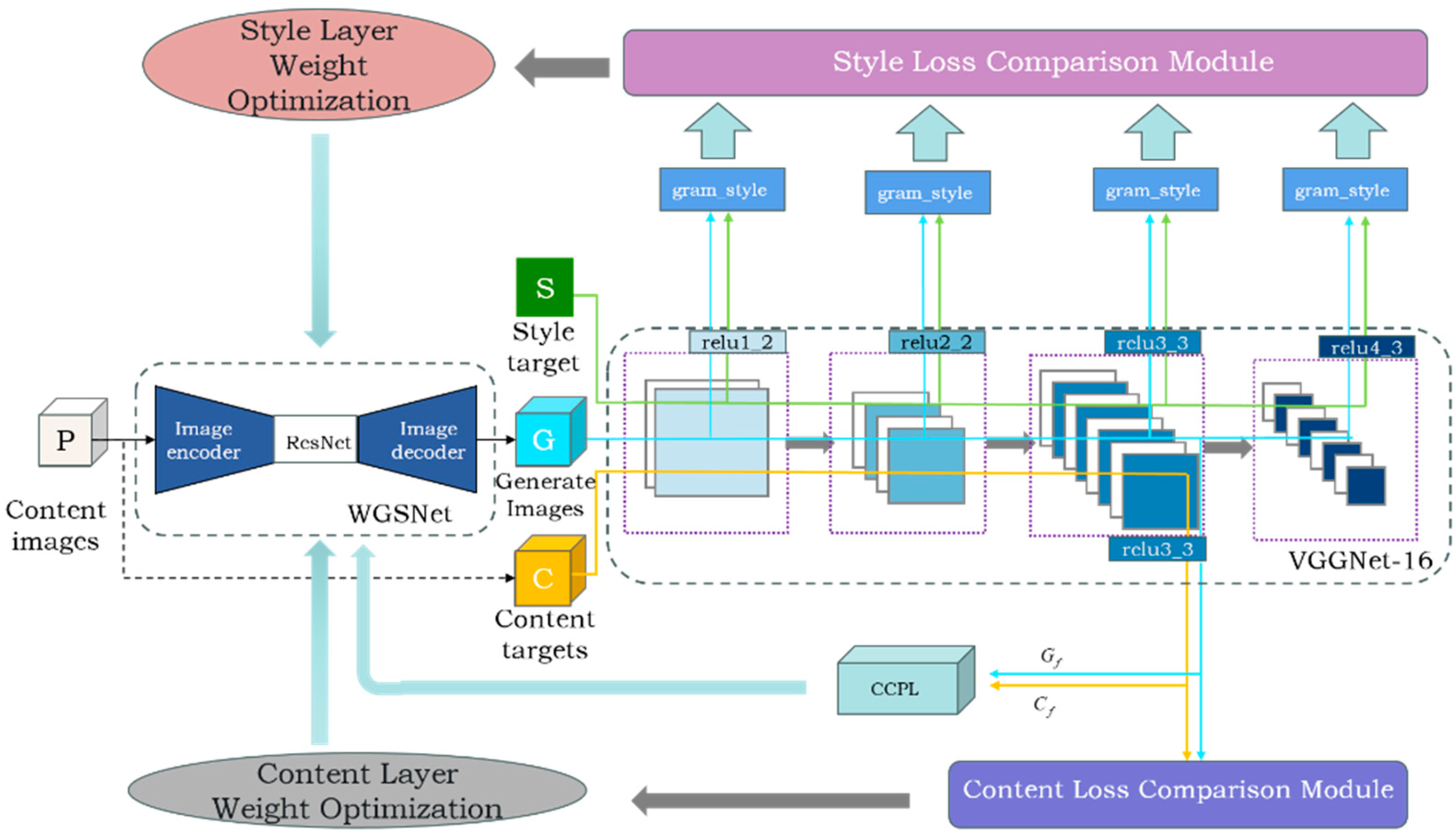
- Wavelet transform and attention-enhanced style transfer: We introduce a wavelet-gated styling network (WGSNet), which incorporates a convolutional block attention module [6] into residual networks to bolster feature matching in fish body regions. Furthermore, we employ wavelet transform functions to refine the downsampling process, effectively capturing localized image details.
- Temporal consistency optimization: To mitigate video flickering and jitter, we integrate contrastive coherence preserving loss within the perceptual loss function, significantly improving the temporal consistency of the generated frames.
2. Related Work
2.1. Instance Segmentation
2.2. Global Style Transfer
2.3. Local Style Transfer
3. Proposed System
3.1. Architecture
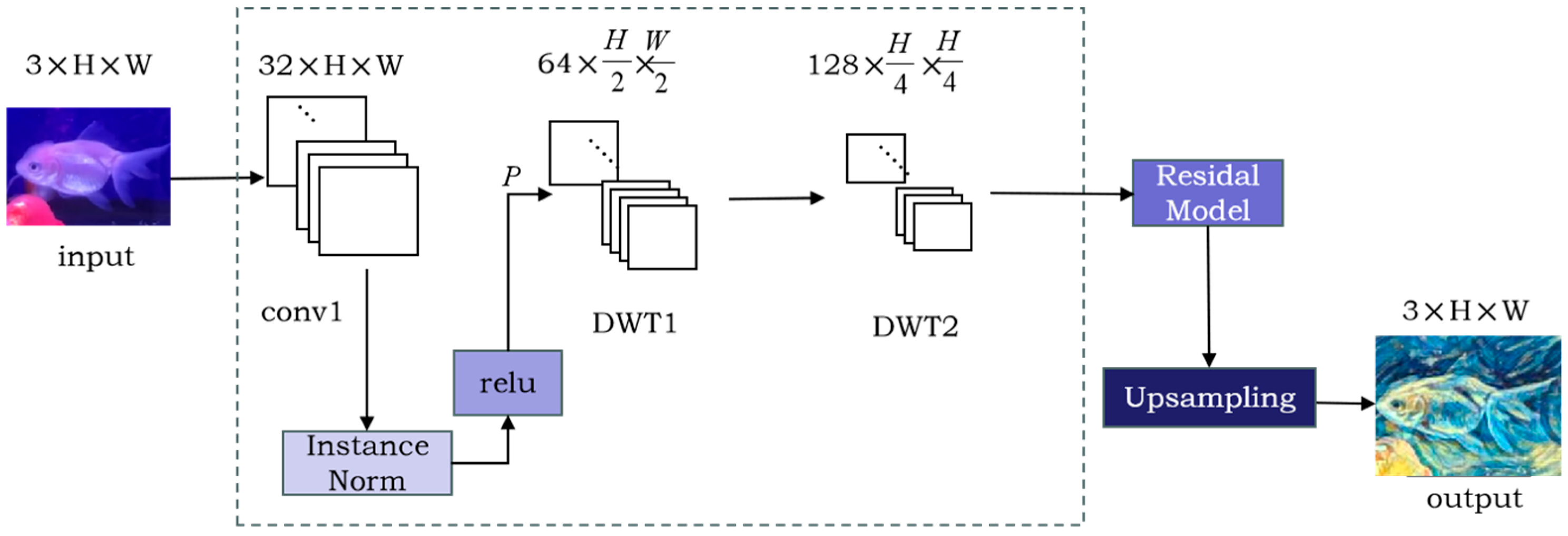
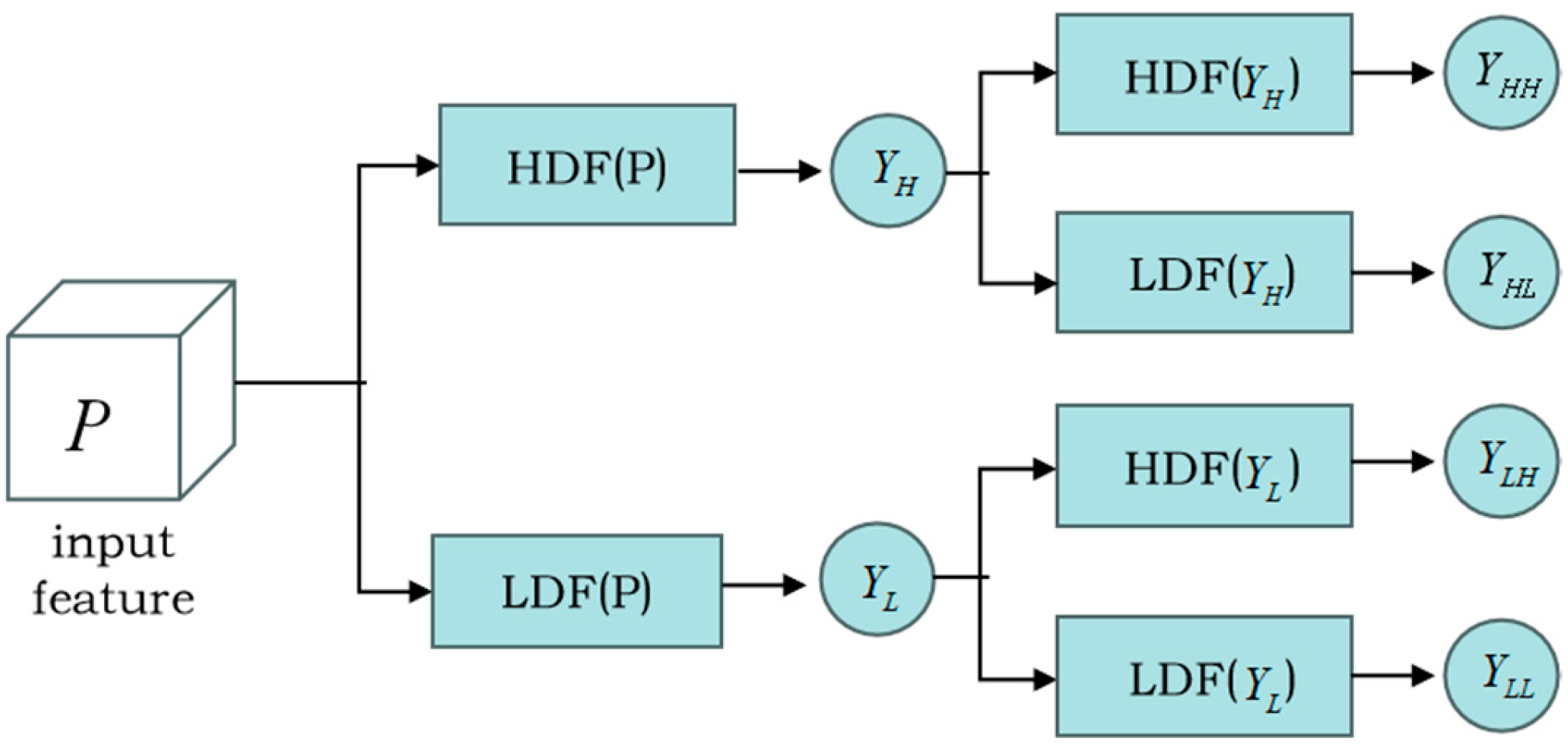
3.2. Wavelet-Gated Styling Network
3.2.1. Upsampling
3.2.2. Wavelet-Based Downsampling
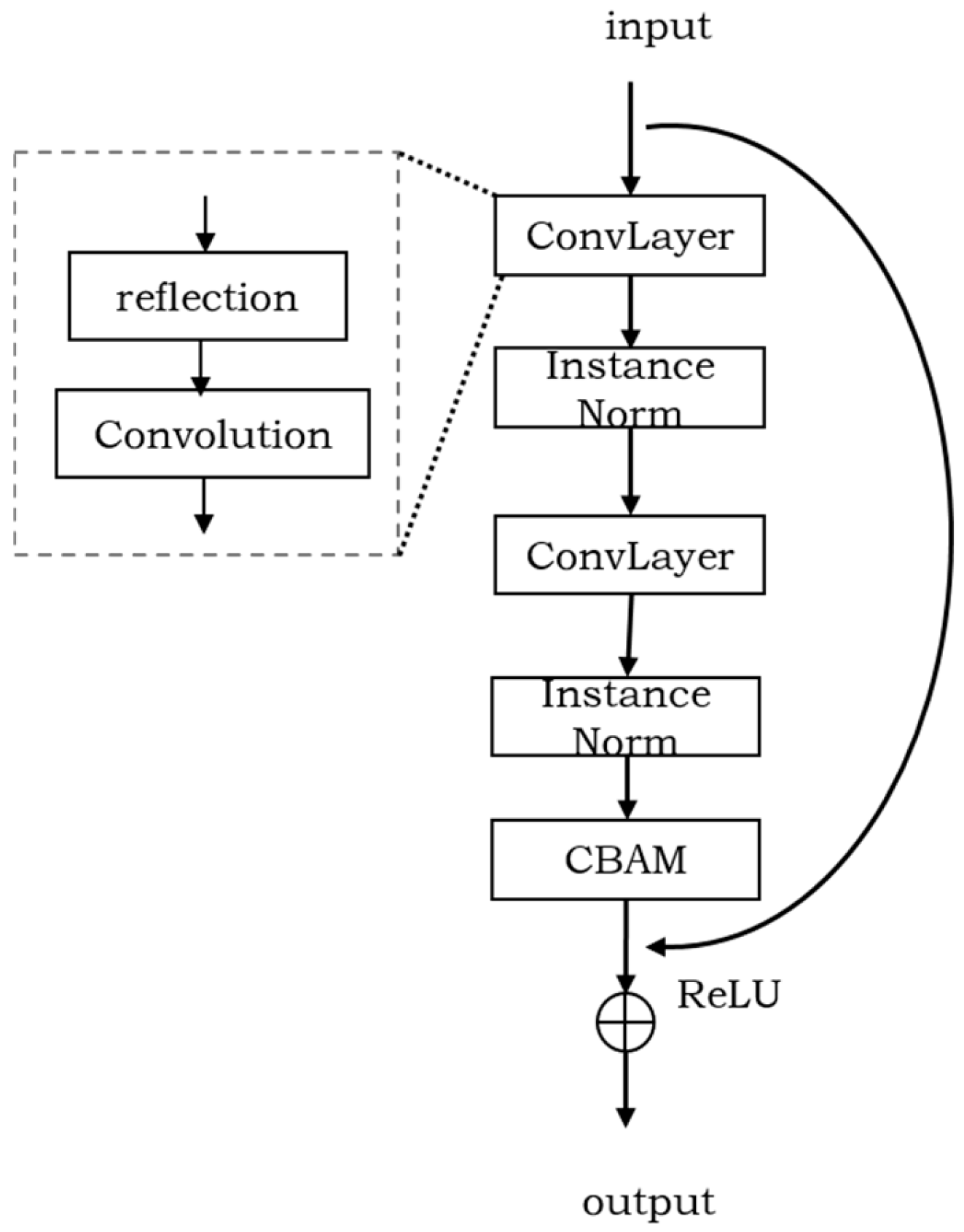
3.2.3. Residual Module with Attention Mechanism
3.3. Contrastive Coherence Preserving Loss
3.4. The Training and Loss Function
- Segmentation loss is a weighted combination of the classification loss, dice loss, and mask loss. The overall loss function is expressed as follows:where Lcls represents the cross-entropy loss, Lmask represents the binary cross-entropy loss, and Ldice represents the dice loss.
- Cross-entropy loss employs class-weighted balanced cross-entropy to address class imbalance, ensuring that the model can learn distinguishing boundaries between different classes. Dice loss enhances the modeling of segmentation region continuity, focusing on improving the boundary accuracy between foreground objects and the background, making it particularly suitable for improving segmentation quality in scenarios involving small targets or complex backgrounds. If the task prioritizes overall region accuracy, increasing the weight of the dice loss is advisable. Conversely, if pixel-level classification precision is more critical, elevating the weight of the cross-entropy loss is recommended. Mask loss is based on binary cross-entropy, focusing on refining mask predictions. Equation (8) is as follows:where N represents the number of instances, Wc denotes the class weight, yi is the ground-truth label, and Pi is the predicted probability.
- Content loss is computed by measuring the mean squared error between high-level convolutional features of the target and content images, evaluating content similarity.
- The perceptual loss function for the style transfer is expressed as follows:
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
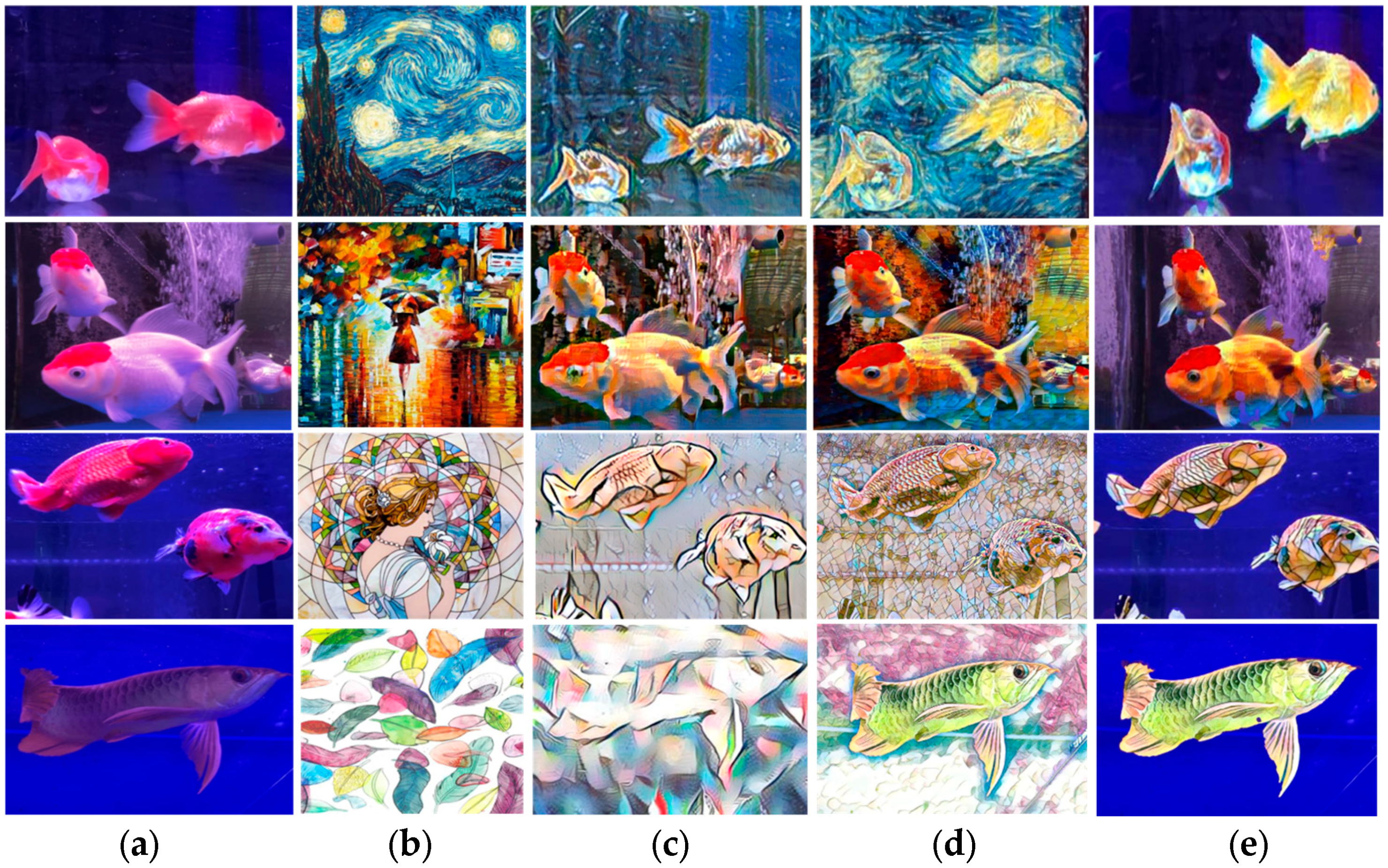
4.3. Comparison
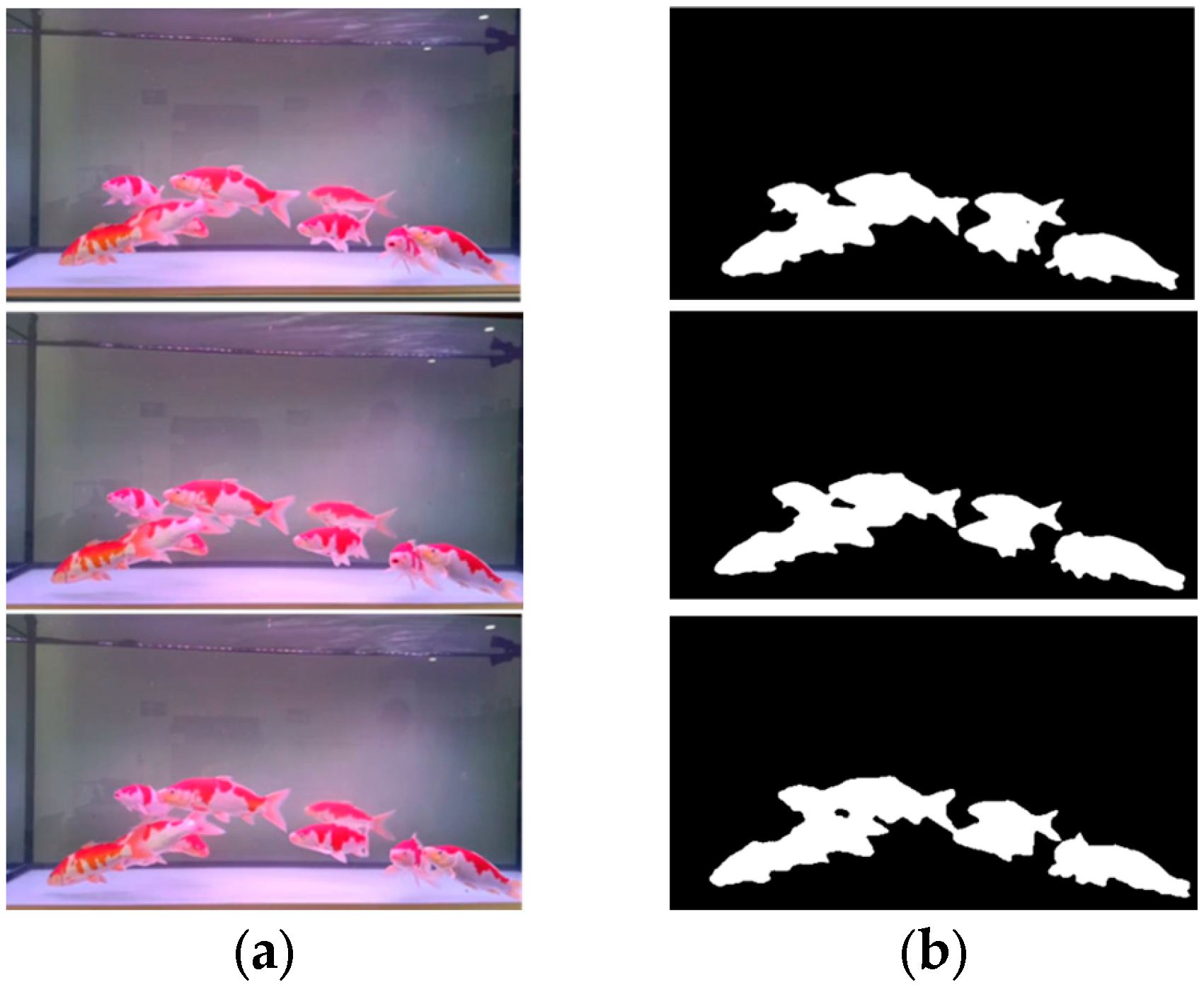
4.3.1. Fish Body Instance Segmentation
4.3.2. Quantitative Results
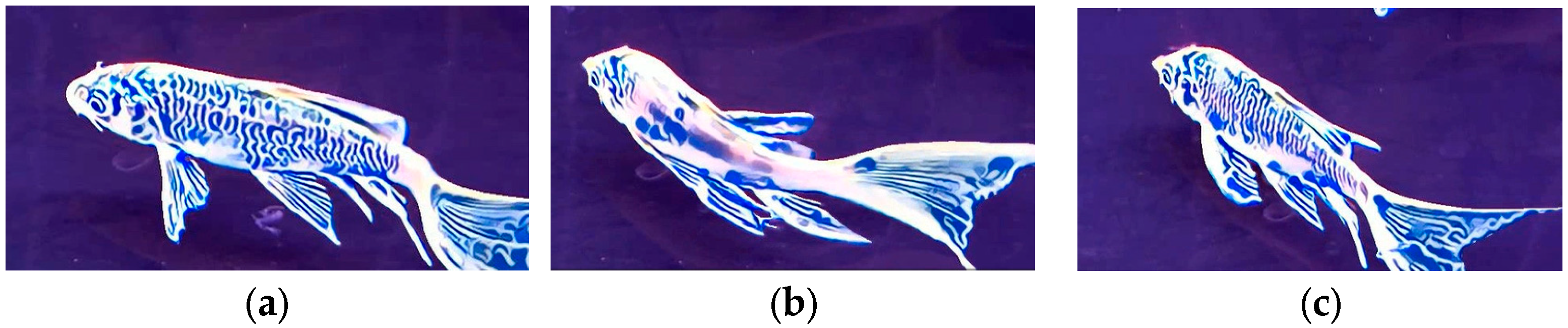
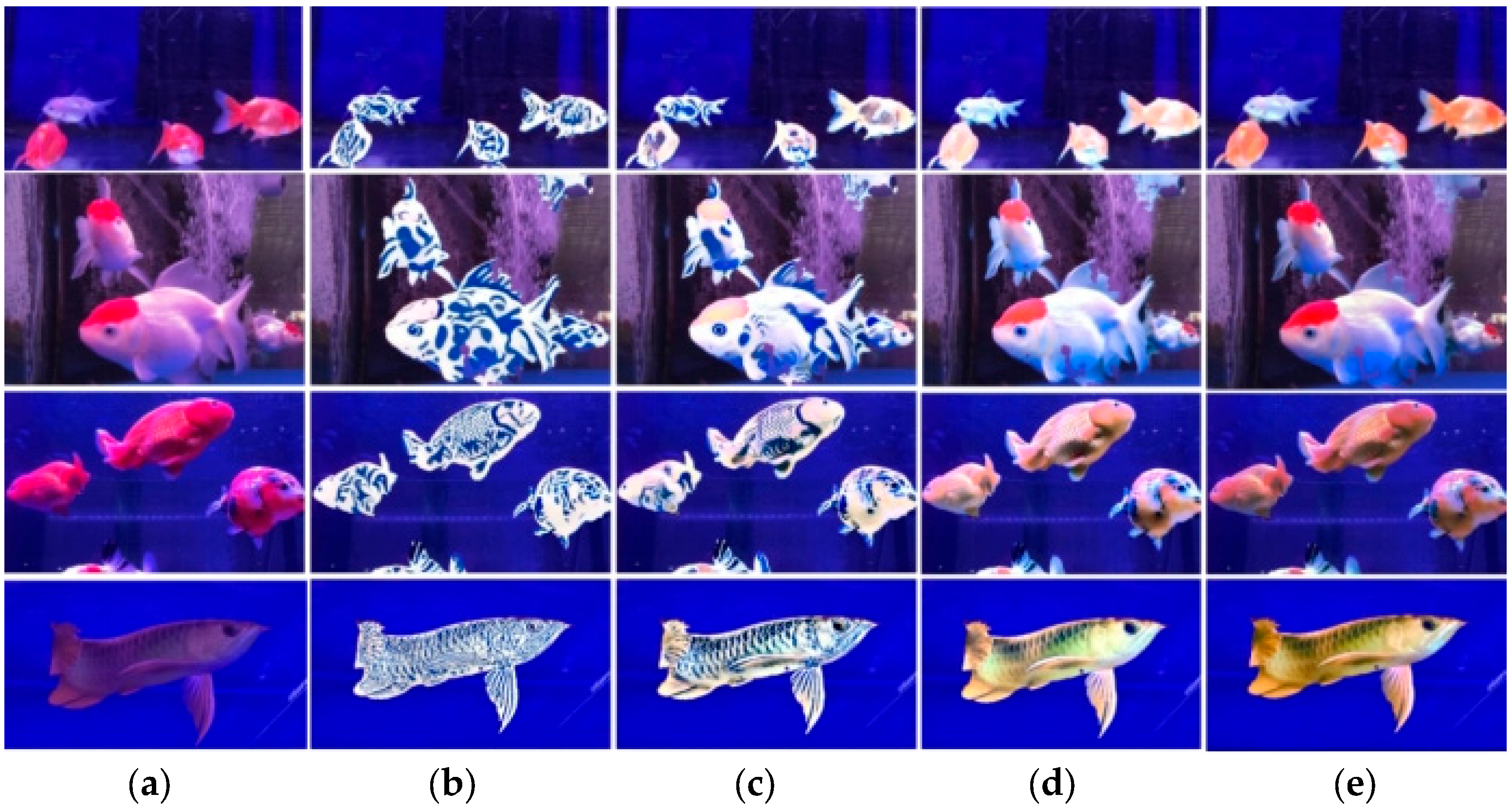
4.3.3. Qualitative Results
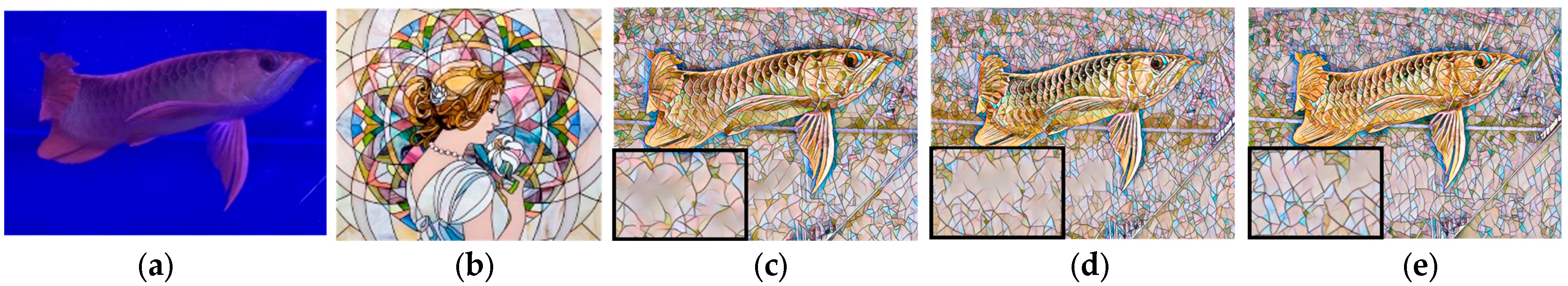
4.3.4. Ablation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, T.Q.; Schmidt, M. Fast Patch-based Style Transfer of Arbitrary Style. arXiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Jaiswal, V.; Joshi, G.; Sanjeeve, A.; Gite, S.; Kotecha, K. Neural Style Transfer: A Critical Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 131583–131613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.; Paris, S.; Shechtman, E.; Bala, K. Deep Painterly Harmonization. Comput. Graph. Forum 2018, 37, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Du, J.; Bai, X. CCPL: Contrastive Coherence Preserving Loss for Versatile Style Transfer. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of The European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. arXiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzman, L.; Vazquez, D.; Laradji, I. Class-Based Styling: Real-time Localized Style Transfer with Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.K.; Tai, Y.-W.; Tang, C.-K. Rethinking Space-Time Networks with Improved Memory Coverage for Efficient Video Object Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–14 December 2021; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 34, pp. 11781–11794. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. Aerial-BiSeNet: A real-time semantic segmentation network for high resolution aerial imagery. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Zhmoginov, A.; Sandler, M. CycleGAN, a Master of Steganography. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Belongie, S. Arbitrary Style Transfer in Real-time with Adaptive Instance Normalization. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lin, T.; He, D.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, Q.; Ding, E. AdaAttN: Revisit Attention Mechanism in Arbitrary Neural Style Transfer. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Hafner, D.; James, S.; Abbeel, P. Temporally consistent transformers for video generation. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; JMLR.org: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2023; Volume 202, pp. 39062–39098. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual Losses for Real-Time Style Transfer and Super-Resolution. arXiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liao, J.; Yuan, L.; Yu, N.; Hua, G. Coherent Online Video Style Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Kautz, J.; Yang, M.-H. Learning Linear Transformations for Fast Arbitrary Style Transfer. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.; Paris, S.; Shechtman, E.; Bala, K. Deep Photo Style Transfer. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, X. Local Style Transfer Method Based on Residual Neural Network. Prog. Laser Optoelectron. 2020, 57, 081012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2414–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; ISBN 978-0-08-052083-4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Liao, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; He, X.; Wu, X. Haar wavelet downsampling: A simple but effective downsampling module for semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 143, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, R.; He, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ge, W. ColoristaNet for Photorealistic Video Style Transfer. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruder, M.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T. Artistic Style Transfer for Videos. In Pattern Recognition, Proceedings of the 38th German Conference, GCPR 2016, Hannover, Germany, 12–15 September 2016; Rosenhahn, B., Andres, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucan, O.; Karakaya, D.; Turkan, M. A Large-Scale Dataset for Fish Segmentation and Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference (ASYU), Istanbul, Turkey, 15–17 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Kai, L.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pang, J.; Chen, K.; Loy, C.C. K-Net: Towards Unified Image Segmentation. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, R.P.K.; Liwicki, S.; Cipolla, R. Fast-SCNN: Fast Semantic Segmentation Network. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.-S.; Huang, J.-B.; Wang, O.; Shechtman, E.; Yumer, E.; Yang, M.-H. Learning Blind Video Temporal Consistency. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11219, pp. 179–195. ISBN 978-3-030-01266-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
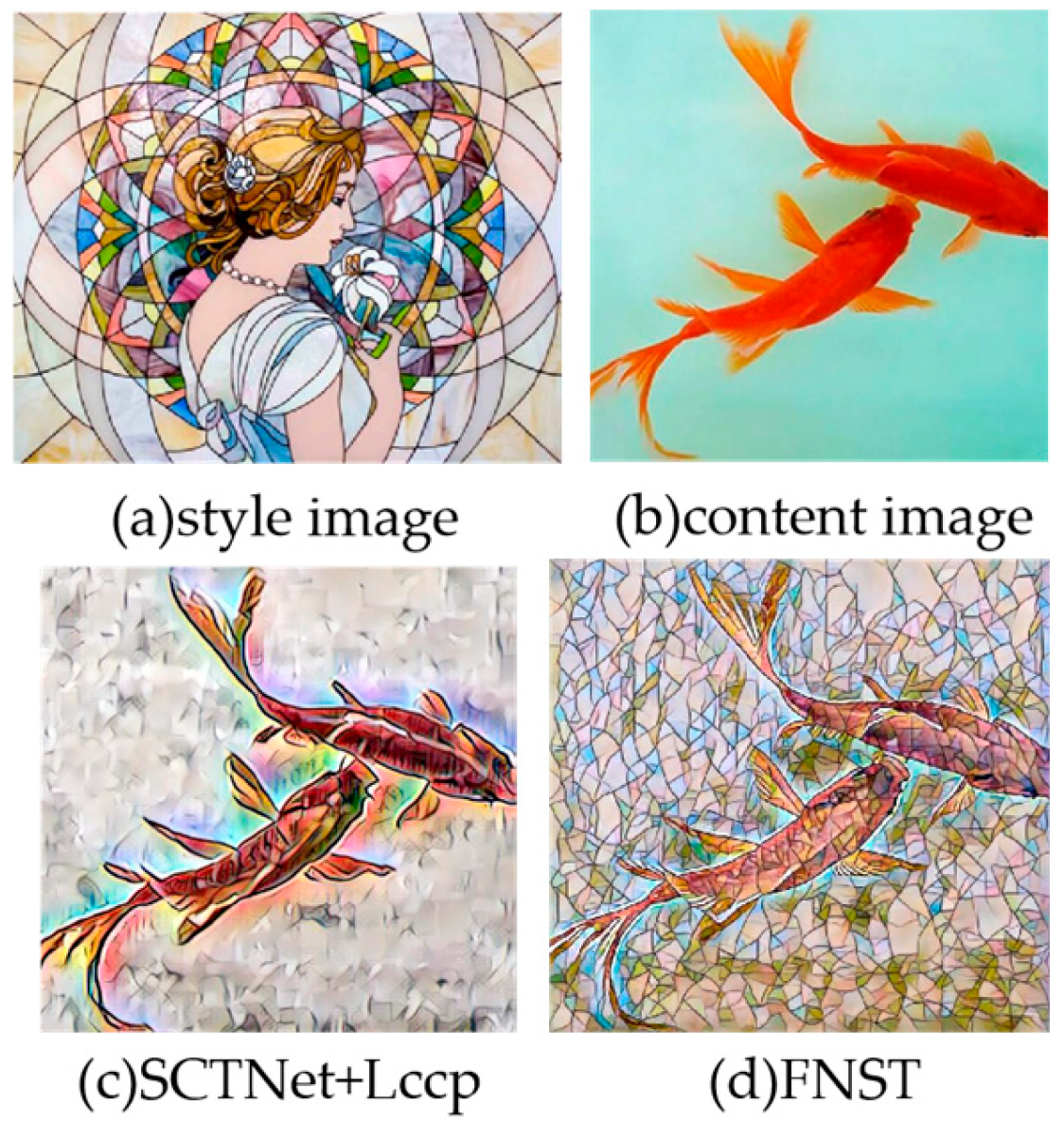




| Model | IoU ↑ | Acc ↑ | Dice ↑ | Precision ↑ | Recall ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deeplabv3+ [32] | 94.46 | 96.26 | 97.15 | 97.69 | 96.30 |
| K-Net [33] | 94.78 | 96.12 | 97.32 | 97.58 | 96.12 |
| Fast-SCNN [34] | 83.65 | 86.23 | 86.78 | 87.04 | 86.23 |
| Mask2Former [4] | 94.81 | 96.59 | 97.33 | 98.07 | 96.59 |
| Style | Index | CycleGAN [13] | AdaAttN [15] | SCTNet + Lccp [5] | FSSNet (Ours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue and white porcelain | SSIM ↑ | 0.607 | 0.620 | 0.582 | 0.632 |
| PSNR ↑ | 16.17 | 16.32 | 16.15 | 16.41 | |
| Starry night | SSIM | 0.612 | 0.641 | 0.577 | 0.653 |
| PSNR | 16.43 | 16.68 | 16.35 | 16.64 | |
| Mosaic | SSIM | 0.543 | 0.612 | 0.581 | 0.625 |
| PSNR | 16.06 | 16.44 | 16.21 | 16.53 | |
| Feathers | SSIM | 0.492 | 0.528 | 0.503 | 0.546 |
| PSNR | 15.64 | 16.29 | 15.88 | 16.38 |
| Stylized Method | User Preference | Temporal Consistency | Stylization Strength | Content Fidelity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCTNet + Lccp | 18.75 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| Global FFSNet | 25 | 25 | 18.75 | 25 |
| Local FFSNet | 25 | 31.25 | 12.5 | 18.75 |
| FFSNet with spacial control | 31.25 | 37.5 | 56.25 | 43.75 |
| Style Model | Params (M) | FLOPs (GFLOPs) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1.679 | 321,010 | 1.225 |
| Baseline + DWT | 1.628 | 310,393 | 1.200 |
| Baseline + DWT + CBAM | 1.639 | 312,155 | 1.198 |
| Video Number | FNST | WGSNet | WGSNet + Lccp |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.405 | 4.768 | 1.412 |
| 2 | 7.855 | 5.314 | 1.791 |
| 3 | 7.653 | 4.849 | 1.812 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Wang, Y. Fish Body Pattern Style Transfer Based on Wavelet Transformation and Gated Attention. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095150
Yuan H, Wang Y. Fish Body Pattern Style Transfer Based on Wavelet Transformation and Gated Attention. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095150
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Hongchun, and Yixuan Wang. 2025. "Fish Body Pattern Style Transfer Based on Wavelet Transformation and Gated Attention" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095150
APA StyleYuan, H., & Wang, Y. (2025). Fish Body Pattern Style Transfer Based on Wavelet Transformation and Gated Attention. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 5150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095150






