1. Introduction
Since the advent of the laser generator in 1960, in order to apply lasers in multiple fields, researchers have continuously explored and conducted studies to enhance the intensity and performance of lasers [
1,
2,
3,
4]. After the emergence of chirped pulse amplification technology [
5], ultrashort laser pulses have acquired the ability to generate attosecond X-rays, which has drawn significant attention and in-depth research from experts in the field of the interaction between high-energy lasers and microscopic particle-like substances. Different from femtosecond pulses that can only measure at the molecular and atomic scales, the attosecond-scale pulses brought by chirped pulse amplification technology are of great assistance in the study of high-energy electrons.
The motion process undergone by high-energy electrons in a strong laser field exhibits relativistic features [
6]. In nonlinear Thomson scattering (NTS) under this condition, parameters like the beam waist radius, pulse width, initial phase and polarization state of the incident laser pulse, along with the electron’s initial speed, initial trajectory orientation, and starting coordinates, all lead to considerable regular variations in the motion trajectory and radiation characteristics of the electron.
In recent years, NTS in the interaction between high-energy lasers and high-energy electrons has garnered numerous theoretical and experimental investigations [
7]. Numerous studies have presented the characteristics of electron trajectories, spectral radiation characteristics, spatial radiation characteristics, etc., in the interaction between high-energy laser pulses and electrons.
Salamin and Faisal et al. examined that the beam waist radius of attosecond-pulse high-energy lasers would exert a certain influence on the pulse shape and monochromaticity of the lasers [
8]. Yu et al. [
9] and Zhang et al. [
10] investigated the impact of pulse width and beam waist radius on the electron radiation distribution in the interaction between high-energy lasers and electrons in nonlinear Thomson scattering. Chen et al. experimentally verified the theoretical predictions regarding the relativistic Thomson scattering of high-energy lasers and electrons [
11].
Nevertheless, a large number of studies are concerned with nonlinear inverse Thomson scattering (NITS) radiation, and the X-rays produced by the mentioned methods are generally parallel to the optical axis [
12,
13,
14,
15]. The intense radiation produced backward renders it challenging to install radiation detection instruments oriented in this direction for measurement, thereby causing certain difficulties in the practical application of these research findings. Meanwhile, it is necessary to utilize off-axis electrons within the range of radiation power to prevent damage to the lens caused by ray radiation [
16,
17].
In this paper, we establish a model of the cross-collision between a tightly focused linearly polarized pulsed laser and a single relativistic electron within the framework of classical nonlinear Thomson scattering, generating observable transverse X-ray pulses. Through this mode of cross-collision, the nonlinear cross Thomson scattering (NCTS) radiation resulting from the cross-collision of electrons and laser beams can be generated. The beam waist radius of the pulsed laser is regarded as the control variable to investigate the trajectory of the electron, the spatial distribution of radiation, the temporal characteristics, and the spectrum characteristics. In the context of tight focusing, the electron is subject to certain spatial constraints during the interaction process in the spatial range. Therefore, in order to make the experiment more effective and rigorous, it is also necessary to control the parameter of the delay time of the laser pulse emission for research.
To further optimize the experimental design, the influence of the laser pulse’s arrival timing is examined systematically. This approach ensures that this study accounts for potential variations in electron behavior due to changes in the temporal characteristics of the laser pulse, thereby providing more robust and reliable results.
Based on the experimental results, it can be observed that the beam waist radius influences the oscillation direction of the electron trajectory and the deflection exit angle, and the delay time plays a crucial role in the deflection direction of the electron. Simultaneously, with the beam waist radius increasing, the spatial radiation distribution of the electrons exhibits a comet-shaped pattern, and the power peak approaches the z-axis. Regarding the time distribution, it presents the symmetrical three-peak structure. The spectrum reveals the property of transitioning from a supercontinuum to a multi-peak state spectrum as the beam waist radius enlarges, and the phenomenon of the interchange between the main peak and the secondary peak is also witnessed. These accomplishments offer novel insights for the study of the cross-collision between high-energy electrons and tightly focused linearly polarized laser pulses, and exert a certain facilitating effect on the advancement of medical treatment and the field of optical physics.
2. Materials and Methods
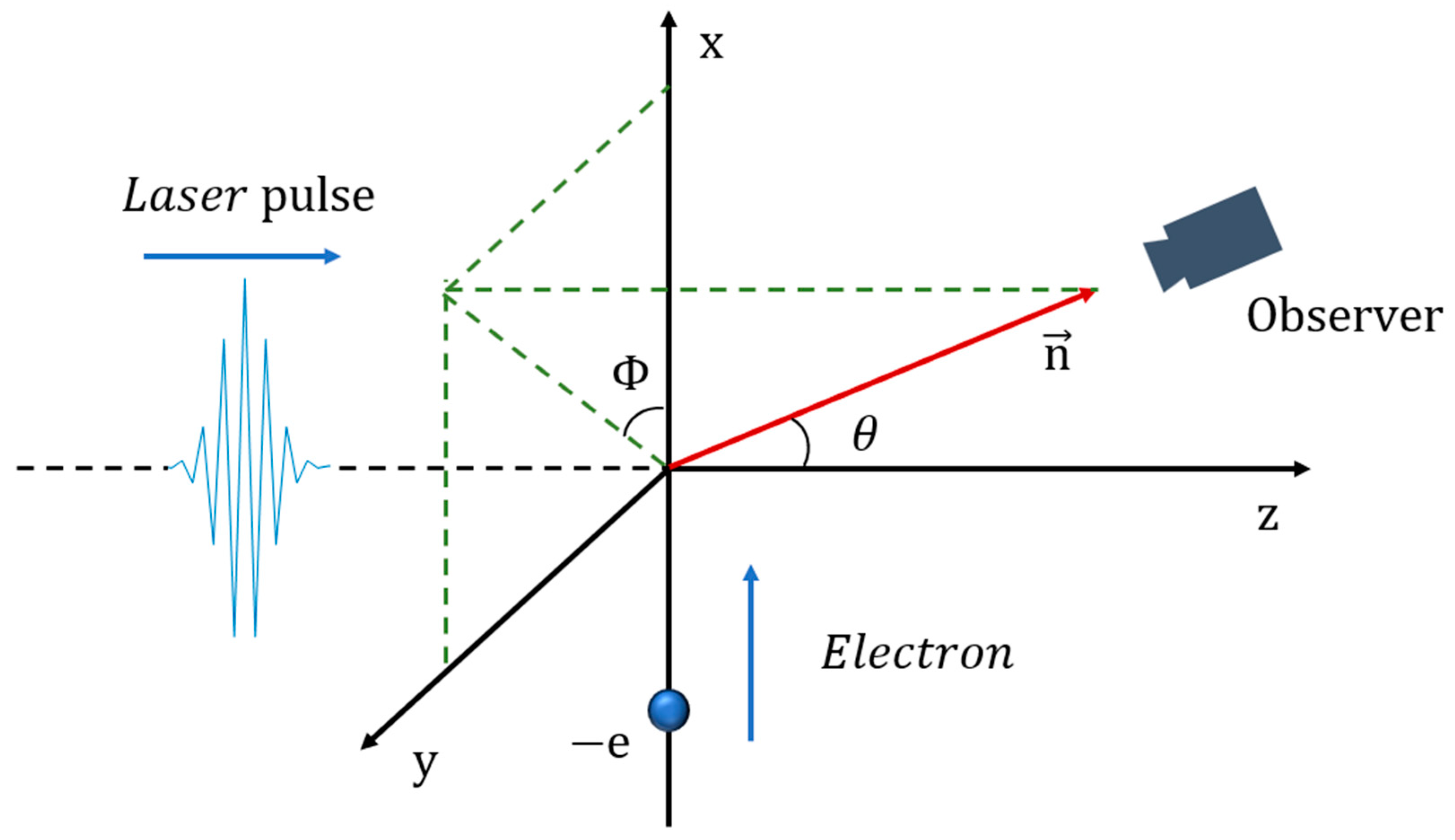
The cross-collision scenario of a linearly polarized laser pulse with an electron under relativistic conditions is depicted in
Figure 1. A linearly polarized high-energy intense laser with a wavelength λ of 1 μm and parallel to the z-axis is incident along the +z direction. Considering the existence of the NTS effect of the linearly polarized intense laser pulse in the plasma, the paraxial approximation is no longer valid for tightly focused laser beams. Hence, it is necessary to take into account the higher-order field effects [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. By establishing a mathematical model, the beam is modeled as a linearly polarized vector potential along the +x axis. The specific electric field components can be expressed as [
23]:
Likewise, the magnetic field components can also be derived and expressed as:
,
, and
, where
is equal to
. In this model, the beam is approximated as a cylinder, where each cross-section along the optical axis is a circle, and the radius
is determined by
and the Rayleigh length
. The sole position where the laser can remain at its strongest state is at the focal point. At the focal point, the radius of the laser is the minimum and its intensity is the maximum.
represents the diffraction angle,
represents the pulse width,
, and the duration of the laser is equal to
.
Herein, the phase of the laser pulse can be expressed as , where represents the phase of the plane wave, and represents a constant phase. , which is related to the curvature of the wavefront. The Gouy phase , indicating that during the process where z increases from to , the Gaussian pulse undergoes a total phase change of .
Regarding the motion of the electron, it can be described by the Lorentz equation and the electron energy function. We can describe the motion of the electron using the Lorentz equation and the electron energy function. The formulas are presented as follows:
Among them, represents the energy of the electron, where the definition is given by the Lorentz factor . In this expression, represents the rest mass of the electron, c represents the velocity of light, and represents the velocity of the electron. The momentum of the electron is expressed as .
In the physical model of
Figure 1, the incident laser emitted along the +z-axis will undergo cross-collision with the electrons. The initial coordinates of the electrons are set as
, and by setting
and
as 0, the coordinates can be simplified to
. The velocity is represented as
. Utilizing the 4–5th order Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg method (RKF45) and performing numerical simulation computations in MATLAB R2020a, the specific variations in the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of the electrons before and after the collision can be acquired.
The time-varying electromagnetic field produced by the moving electron can be deduced using the Liénard–Wiechert potentials. The use of polar coordinates makes it easier to describe the radiation situation in terms of unit angles. Here, the direction vector is defined as
, where
represents the azimuth angle and
represents the polar angle. The following formula is used to calculate the radiation power per unit solid angle:
Herein, is the normalized radiation power, is the displacement distance of the electron on the x-axis, the observation vector represents the observation direction, and the subscript delay time is a condition that must be employed in the equation calculation. Among them, R is the straight-line distance from the observation point to the interaction point between the intense laser and the electron, and this distance should be sufficiently large.
The radiated energy is normalized to
per unit angular frequency and per unit azimuth angle, which can be represented by the following equation:
Among them, denotes the order of the radiated harmonic, where is the scattering angular frequency.
Equations (11) and (12) are used to calculate the spatiotemporal distribution and spectrum of the nonlinear cross Thomson scattering (NCTS).
3. Results
In this section, we shall investigate and analyze the relationship between the radiation characteristics of NTS arising from the cross-collision of a linearly polarized Gaussian intense laser with an electron and the beam waist radius of the laser. The initial position of the electron is on the negative half-axis of the x-axis and it moves in the +x-axis direction. The Gaussian linearly polarized intense laser is incident along the direction of the +z-axis and collides with the high-energy electron at the origin of the Cartesian coordinate system, giving rise to radiation. In this paper, the electric field vector of the laser oscillates along the x-axis, and thus the polarization plane of the linearly polarized laser is the XOZ plane.
Gaussian pulse lasers present distinct characteristics under varying beam waist radii
. To investigate the impact of the beam waist radius on NTS, it is requisite to rationally set other parameters of the laser pulse and the electron. This paper is grounded in classical electrodynamics, and the parameters configured are required to fall within a rational range [
24]. When necessary, the recoil correction in quantum mechanics needs to be taken into account; namely, Thomson scattering transforms into Compton scattering [
25]. In this paper, the parameters set hereinafter only comply with classical dynamics. We configure the parameters of the incident linearly polarized intense laser pulse as follows: the normalized laser intensity
, the pulse width
= 3
, the initial phase
= 0, and the wavelength
= 1 μm. For the convenience of studying and depicting the phenomenon, it is necessary to set the interaction point where the linearly polarized Gaussian intense laser pulse and the electron cross and collide at the origin. The electron’s normalized initial energy is set to γ = 10, indicating that its initial velocity is nearly equivalent to the speed of light. Under the condition that the initial position of the electron remains invariant, the emission time of the linearly polarized Gaussian pulse is adjusted. A delay time
is introduced. Either an excessively long or overly short delay time will result in the electron being unable to encounter and collide with the laser pulse. When
= 3.26 fs, the electron precisely undergoes collision at the trailing edge of the Gaussian pulse. The electron precisely undergoes collision at the front edge of the Gaussian pulse when
= 6.74 fs.
3.1. The Electron Deflection Trajectory in a Gaussian Pulse
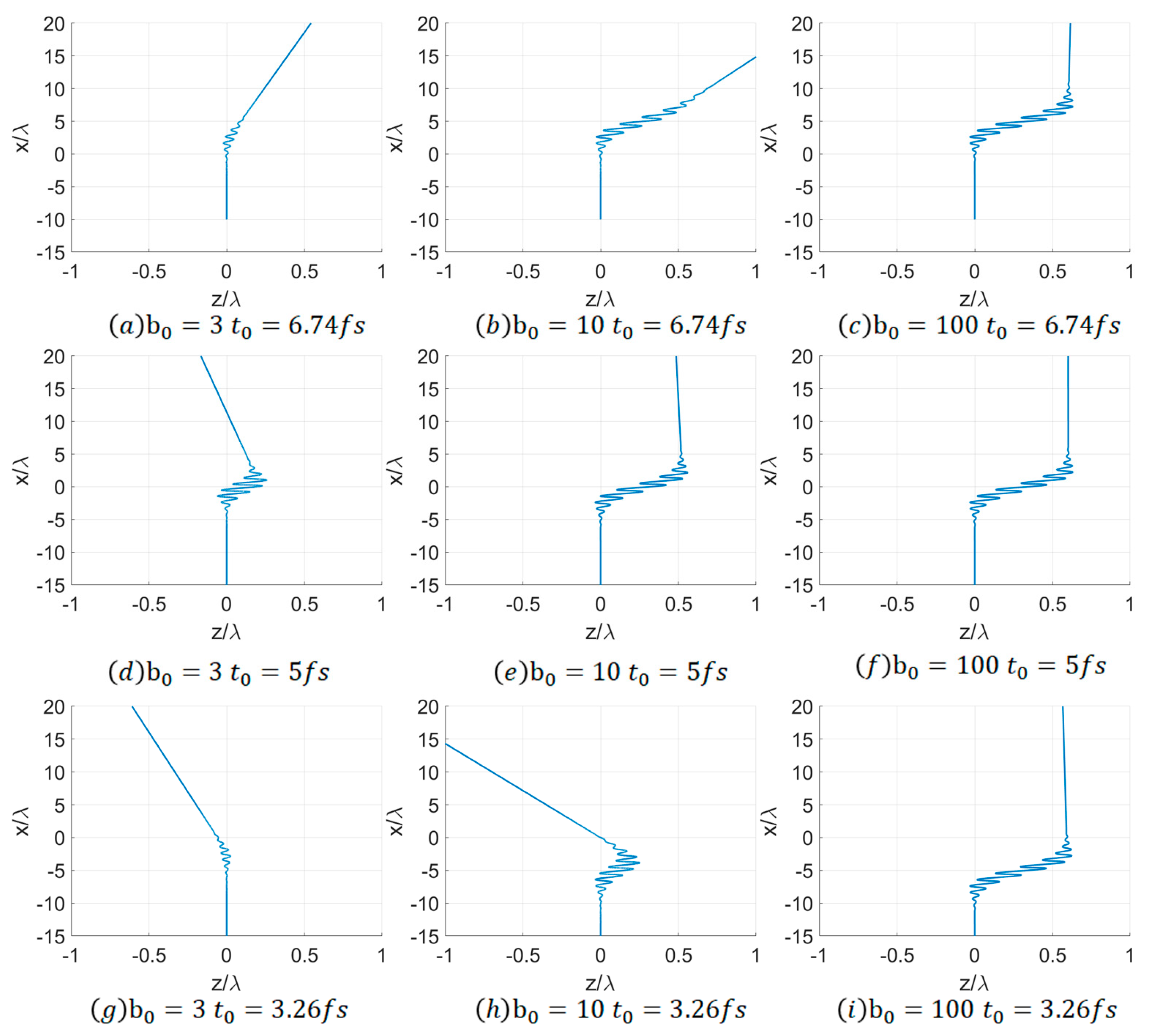
Theoretical analysis indicates that in order to investigate the influence of the beam waist radius of the Gaussian pulse on the electron collision trajectory, it is necessary to determine the relative maximum delay time of electron radiation. It can be concluded from
Figure 2 that the radiation generated by the electron is the maximum when
= 5 fs.
To study the electron trajectory, it is necessary to divide and decompose the electron movement stage. In the incident stage, the electron moves uniformly and linearly from -x-axis to +x-axis, and the Gaussian pulse moves uniformly and linearly from -z-axis to +z-axis. The two cross and collide around the origin of the Cartesian coordinate system. In the oscillation and distortion stage, the electron is subjected to the action of the linearly polarized Gaussian pulse and continuously performs oscillation motion in a single plane. Within the oscillation plane, the amplitude of the electron’s movement initially rises and subsequently decreases. In the exit stage, the electron exits the influence range of the Gaussian pulse and is no longer affected by the electromagnetic field. The exit direction is biased towards the positive half-axis of the x-axis, and there is also a certain deviation in the positive and negative half-axes of the z-axis.
Even when electrons interact with Gaussian pulses of the identical beam waist radius, variations in the delay time of laser emission will give rise to distinct trajectory characteristics. This is because the velocity of electrons is extremely high, approximating the speed of light. The movement of electrons within the Gaussian pulse only undergoes a very brief period and is only influenced at a particular section of the Gaussian pulse.
Regulating the emission delay time and the beam waist radius of the Gaussian pulse enables the acquisition of some distinct patterns. When the delay time of the Gaussian pulse is set at = 5 fs, the electron radiation reaches its maximum, and the interaction between the electron and the laser is the most vigorous.
Overall, the increase in beam waist radius will cause the movement time of electrons within the Gaussian pulse to increase, leading to a reduction in the electron emission angle. For the convenience of researching the impact of on the electron trajectory, the delay time of the laser is supposed be set initially. Subsequently, the influence of is investigated under various delay times.
As depicted in
Figure 2a–c, when a relatively large delay time of
= 6.74 fs is set, the moving electron will collide with the falling edge of the Gaussian pulse and interact therewith. Irrespective of
, the electron always exits in the direction of +z-axis. As
increases, the oscillation trajectory of the electron within the pulse becomes longer. Within the tight focusing regime, the increase in
gives rise to a more pronounced increase in the oscillation trajectory. Nevertheless, in the non-tight focusing case, the length of the electron’s oscillation trajectory undergoes hardly any change. Concurrently, in the tight focusing scenario, the deflection angle of the electron upon exit is greater. This is because a larger beam waist radius leads to a longer interaction duration of the electron with the pulse, thereby generating a longer oscillation trajectory. Additionally, it can be discerned that in the non-tight focusing case, the deflection angle of the electron’s exit is smaller, and the incident and exit directions of the electron are relatively proximate. This is because, in the non-tight focusing situation, the Gaussian pulse has a larger interaction range with the electron, and the electron moves within the pulse for a longer period, experiencing a more balanced positive and negative deflection from the laser pulse.
As illustrated in
Figure 2d–f, when a medium delay time of
= 5 fs is set, the moving electron will precisely strike the center of the Gaussian pulse and interact with it. Regardless of
, the electron always exits along the negative z-axis. At this juncture, the electron radiation attains its maximum. Furthermore, the length of the electron’s oscillation trajectory augments with the increase in
. Under this delay time, the exit angle of the electron is relatively similar to the incident angle.
As presented in
Figure 2g–i, when a relatively small delay time of
= 3.26 fs is set, the moving electron will collide with the leading edge of the Gaussian pulse and engage in interaction with it. Regardless of
, the electron always exits along the negative z-axis. The phenomenon and principle regarding the oscillation distance of the electron’s trajectory and the smaller deflection angle of the electron in the non-tight focusing case are in accordance with the delay time
= 6.74 fs.
3.2. Spatial and Angular Distribution
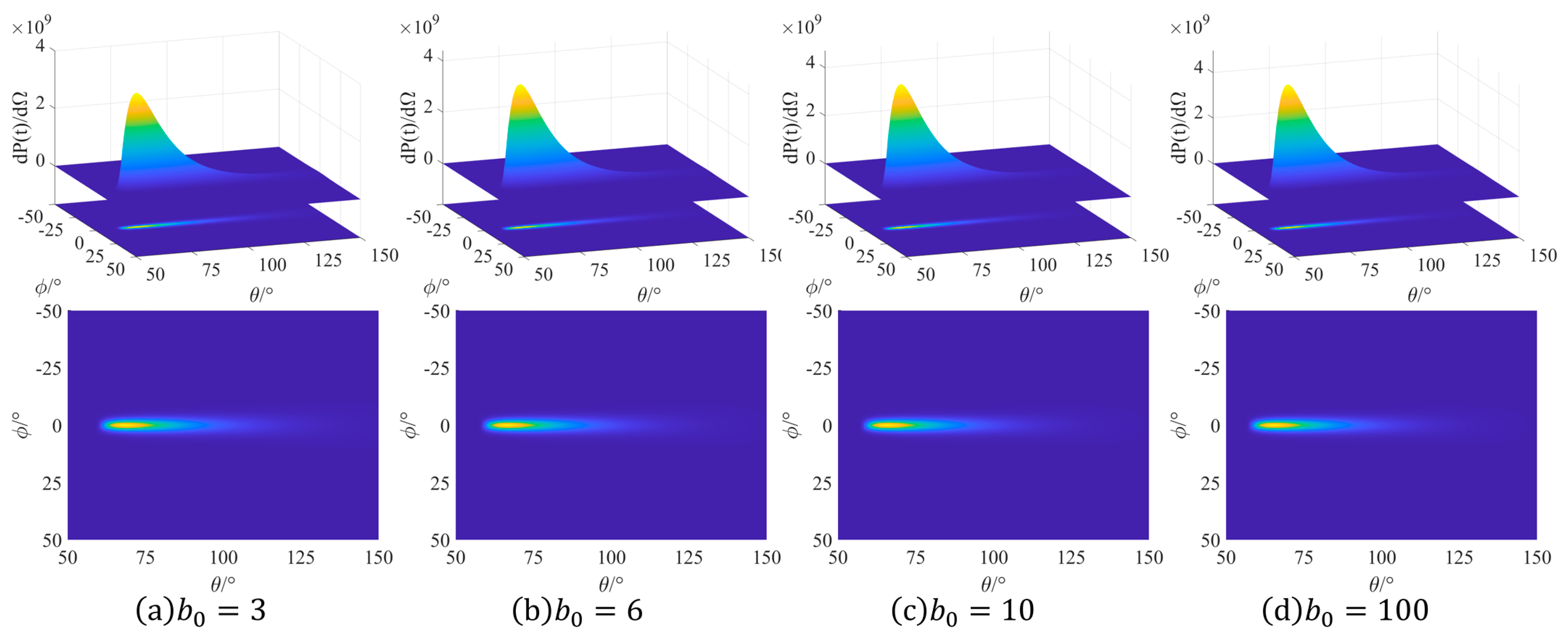
The laser delay time was set at 5 fs to maximize the electron radiation power. To investigate the characteristics of the angular and the spatial distribution of electron radiation, we have plotted the normalized radiation power distribution of the interaction between the electron and the pulse at a 5 fs delay time. As obtained from
Figure 3, the radiation spectrum exhibits a comet-like shape, and the peak of the radiation power is located at the head of the comet.
It can be observed from
Figure 3 that with the increase in
, the peak power of electron radiation will increase. Since the extent of the increase in the peak value of the electron radiation power with the increase in the beam waist radius is significantly reduced when
, especially when
, we have provided
Figure 4 to clearly demonstrate the variation of the peak power value and its corresponding polar angle value with
. The relationship of radiation power is as follows [
26]:
Among them,
represents the electron energy, and
denotes the acceleration of the electron in the z-axis direction. Then, the peak of spatial radiation can be expressed as [
25]:
When the z-axis velocity of the electrons attains its maximum, namely when the z-axis acceleration assumes a minimum value, the spatial radiation attains its peak. By observing
Figure 5, the peak value of the electrons’ velocity in the z-axis direction does not undergo a substantial change. However, as the
increases, the variation period of the electrons’ z-axis velocity, namely the number of action cycles, keeps on increasing. The electron and the laser pulse will interact for multiple cycles, and the radiation will be superimposed multiple times throughout the entire process. As
increases, the number of superimposed radiation cycles keeps rising, and the total radiation peak keeps escalating. When
increases to the non-tightly focused state, the total radiation peak remains nearly invariant.
The radiation distribution characteristics of electrons can be contemplated from two aspects: the polar angle
and the azimuth angle
. It can be deduced from
Figure 3 that the power radiation of electrons is concentrated in the part where
= 0. When
deviates from 0, regardless of the value of the polar angle
, the electron power radiation will rapidly decay to 0. This is because the oscillation direction of the linearly polarized pulsed laser is in the XOZ plane, and the oscillation of electrons after colliding with it also occurs in the XOZ plane. Consequently, the electron radiation is concentrated in the XOZ plane.
Simultaneously, observe
in
Figure 3. The radiation of electron power is primarily concentrated within the polar angle
range from 60° to 90°. Under the circumstance of tight focusing, as
increases, the
at which the electron power radiation reaches its maximum gradually diminishes. The variation rule of the peak of electron power radiation with respect to
can be derived from
Figure 4. When the laser pulse is in a non-tightly focused situation, the
at which the maximum power occurs remains essentially invariant.
Examine
Figure 3 and
Figure 5 and conduct an analysis of the peak shift phenomenon in terms of the velocity and acceleration of electron movement. It can be derived from
Figure 5 that there exists a phenomenon of periodic and sudden reduction in the velocity of the electron in the x-direction. This leads to a sudden decrease in the deflection velocity of the electron towards the +x-axis during the oscillatory motion after their collision with the laser pulse. This is because the intensity of the tightly focused laser beam at the focal point is higher, resulting in more vigorous electron movement and more concentrated radiation in the forward position. As the
keeps increasing, the laser intensity at the focal point decreases, and the maximum radiation polar angle
in the spatial distribution correspondingly reduces.
In practical applications, the electron radiation can be focused in the z-axis direction through an appropriate increase in the radius of the beam waist .
3.3. Temporal Distribution
To acquire the temporal distribution characteristics of electron radiation, observations should be conducted in the direction of the maximum radiation power. As depicted in
Figure 6, the main peak is essentially located approximately at 50 fs. Simultaneously, two secondary peaks symmetrically distributed at positions approximately 0.5 fs on either side of the main peak can be observed. This exhibits a “mountain-shaped” symmetrical three-peak structure relative to the main peak. When
is extremely small, the height of the secondary peaks will be very low or even vanish directly. This indicates that at this stage, the majority of the electron radiation power is concentrated on a single central pulse, which can be considered as a separate ultrashort attosecond pulse. Concurrently, it can be observed that when the radius of the tight focusing beam waist is large until it reaches non-tight focusing, the heights of the two secondary peaks, that is, the radiation intensity, are relatively high compared to the main peak. This implies that the radiation power of the central pulse is not substantial, and the energy is more dispersed, making it infeasible to consider it as a single ultrashort attosecond pulse.
It is noteworthy that as the beam waist radius keeps increasing, the height difference between the two secondary peaks will correspondingly decrease. When is larger than or equal to 7, the heights of the two secondary peaks are essentially equal. Overall, the height of the secondary peaks increases relatively as becomes larger. The greater the beam waist radius is, the longer the period of the largest electron trajectory in the center will be. A longer trajectory implies a stronger interaction, resulting in stronger radiation. Consequently, the heights of both the secondary peak and the main peak will grow. This is because the increase in will lead to a longer interaction time between the electron and the linearly polarized Gaussian pulse, strengthening the deflection influence of the laser on the electron, and eventually the electron will diverge from the direction of maximum power radiation at a later time.
As the focus varies from tight to non-tight, the height of the main peak will continuously increase. This is because as increases, the duration during which electrons interact with the linearly polarized Gaussian pulse will be longer, and the corresponding total radiation intensity will increase accordingly.
In order to observe the double-peak structure of the main peak of the temporal spectrum more clearly [
27], we present the magnified graphs of these time spectra. As depicted in
Figure 6, it can be discovered that the energy of the two main peaks is relatively high, reaching the order of
.
In reality, as depicted in
Figure 7, the three-peak structure is multi-peak, except that the other peaks are extremely tiny. When observing the electron trajectory, each oscillation of the electron gives rise to a peak (actually two peaks that are very close to each other). The amplitudes generated by the three oscillation trajectories in the center are significantly greater than those of the other oscillation trajectories [
27].
3.4. Radiation Spectrum
This section explores the characteristics of the radiation spectrum concerning the beam waist radius in the direction of maximum radiation.
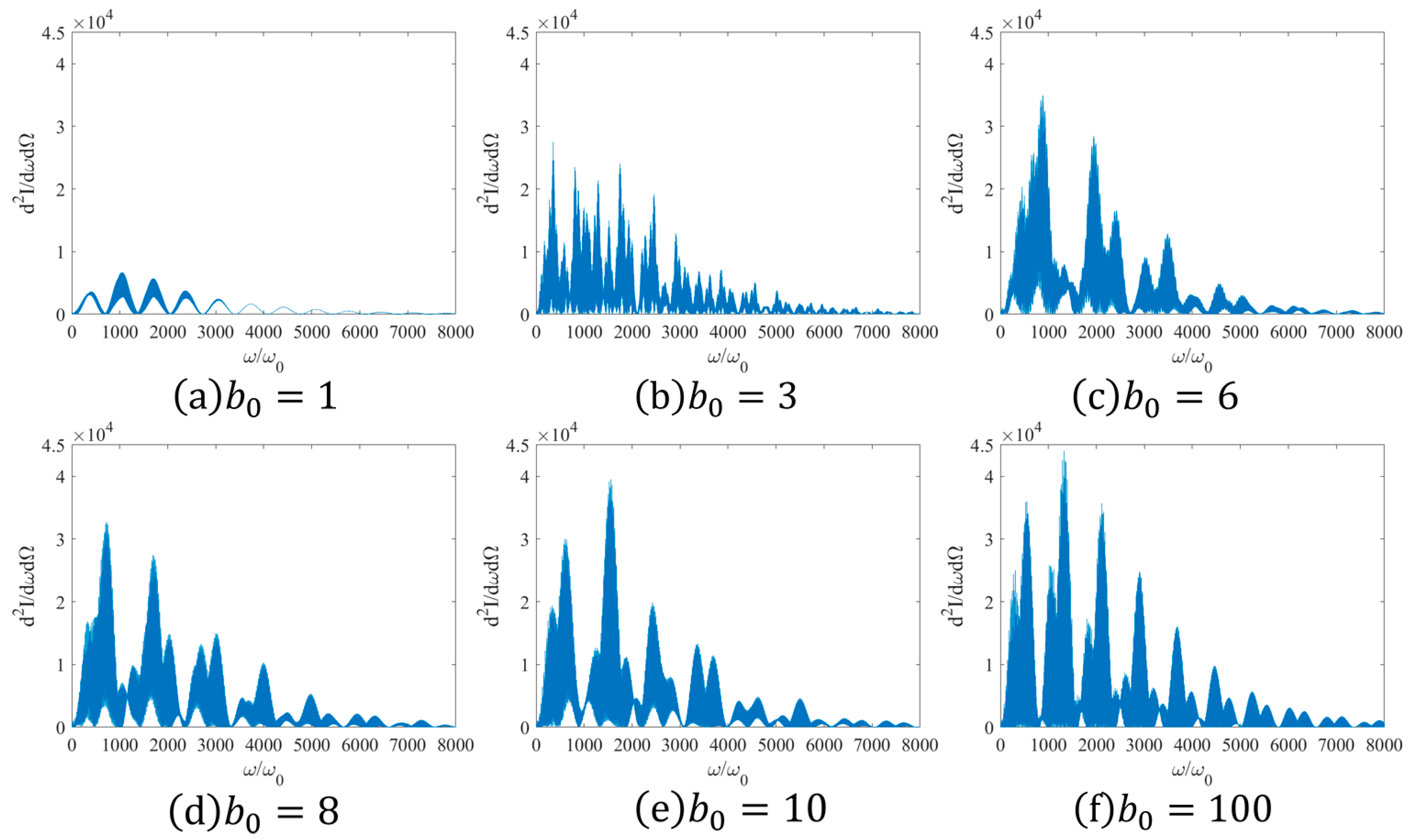
Under the circumstance of tight focusing, as increases, the normalized maximum spectral intensity grows from 7000 to 40,000. When increases to 5 and thereafter until the Gaussian pulse is in a non-tight focusing state, the normalized maximum spectral intensity remains essentially stable. This is because with the increase of the beam waist radius , the electron is exposed to a more complete period of the Gaussian laser pulse, and the longer the interaction time, the greater the spectral intensity. After reaches 5, the effect of prolonging the interaction time between the electron and the pulsed laser diminishes, the interaction time remains largely unchanged, and thus the maximum spectral intensity does not increase significantly.
From
Figure 8, it can be discerned that as the waist radius increments continuously from 1 to 100, the beam transitions from tight focusing to non-tight focusing, and a marked reduction in the number of high-order harmonics within the spectrum can be observed. When
is within 7, the cut-off frequency is approximately 1000
. Subsequently, the cut-off frequency undergoes a marginal increase with the escalating waist radius. Irrespective of the variations in the waist radius, the width of the spectrum persists at 8000
.
When lies between 2 and 4, the spectrum manifests typical supercontinuum characteristics, corresponding to an ultrashort pulse in temporal terms. This is attributed to the fact that at this juncture, is exceedingly small, and the interaction duration between the linearly polarized Gaussian pulse laser and the electron is extremely short, rendering the non-periodic nature of electron motion more pronounced, thereby giving rise to the traits of a supercontinuum.
A distinct transition mode emerges when ranges from 5 to 6. During the process of the increase in the beam waist radius, the variation of the intensity distribution of the laser field in the direction perpendicular to the propagation becomes more gradual. The time evolution of the electron acceleration shifts from non-periodic oscillation to periodic oscillation, and the modulation effect of the relativistic effect on the electron radiation is intensified. Ultimately, this results in the transformation of the supercontinuum spectrum into a multi-peak state spectrum.
When
falls within the range of 7 to 10 or even up to 100, a particular phenomenon emerges. A reciprocal relationship is witnessed between the intensities of the main peak and the secondary peak. The interchange of the primary and secondary peaks in the spectrum can be accounted for based on the time spectrum. As depicted in
Figure 6, the height of the secondary peak evidently increases with the augmentation of
, and the relative height with respect to the primary peak conspicuously decreases. This leads to the accumulation rate of the secondary peak value in the spectrum exceeding that of the primary peak value. Ultimately, the interchange of the primary and secondary peaks in the spectrum is realized when
= 9. The corresponding modification is indicated with a green shade in line 369 of the article. This implies that under the condition of tight focusing, appropriately increasing the waist radius
enables the attainment of rays with higher frequencies and greater energies. Correspondingly, appropriately reducing
facilitates the concentration of ray energy in the lower frequency segment. Currently, to enhance the radiation intensity of the rays, reliance is mainly placed on increasing
and
, which results in a certain degree of energy wastage. Through the approach of increasing the waist radius
investigated in this paper, the radiation intensity of the rays can be enhanced concurrently while minimizing a portion of the energy waste.
4. Conclusions
Through numerical simulation, this paper investigates the impact of the beam waist radius of a linearly polarized Gaussian laser pulse on the spatial distribution, temporal characteristics, and frequency domain characteristics of radiation under the condition of relativistic electron-laser cross-collision. Concurrently, we also compare the dissimilarities and similarities of the outcomes produced by tightly focused and non-tightly focused laser beams.
It has been discovered through experimental studies that the interaction duration between the relativistic electron and the linearly polarized Gaussian laser pulse can be extended by increasing the beam waist radius. Under diverse delay emission times, it induces the electron to exhibit distinct oscillation motion trajectories and exit angles.
Simultaneously, the spatial distribution of NCTS in this experimentation presents a comet-like shape, with the peak of electron radiation power concentrated at the head of the comet. The larger the beam waist radius, the closer the direction of the peak radiation power approaches the z-axis. This implies that increasing the beam waist radius can control the principal radiation direction of the rays generated by the collision, concentrating them in the z-axis direction of the laser emission and reducing waste by making the energy more concentrated.
Subsequently, this paper also examines the temporal distribution characteristics in the direction of the maximum radiation power. The temporal distribution manifests a symmetrical three-peak structure, and the two secondary peaks escalate with the increase of the beam waist radius, ultimately attaining approximately half the height of the main peak.
Ultimately, regarding the temporal distribution characteristics in the direction of the maximum radiation power, the spectrum transitions from a supercontinuum to a multi-peak state as the beam waist radius increases. We innovatively identified a transformation mode of the spectrum: under the tight focusing condition, as the beam waist radius expands, the main peak and the secondary peak of the spectrum interchange. Currently, the primary means to increase the radiation power of the rays is to increase and , which leads to energy dissipation. By appropriately increasing the beam waist radius through the method presented in this article, rays with higher frequencies and greater energies can be obtained, and energy waste can be mitigated.
The aforementioned research achievements enrich the experimental experience of nonlinear Thomson scattering theory and offer novel concepts for the study of the cross-collision between high-energy electrons and tightly focused linearly polarized laser pulses. This research contributes to generating stable and high-quality X-rays under relativistic conditions and facilitating the design of the next generation of ultra-short high-energy ray generators.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T.; Methodology, J.S. and Y.T.; Software, J.S. and Y.T.; Validation, J.L., Y.L. and Y.T.; Formal analysis, J.L. and Y.L.; Investigation, J.S. and Z.Y.; Resources, J.S. and J.L.; Data curation, J.S.; Writing—original draft, J.S.; Writing—review & editing, J.S., Y.L. and Y.T.; Visualization, J.S. and J.L.; Supervision, Y.L. and Y.T.; Project administration, J.S., Z.Y. and G.Y.; Funding acquisition, G.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 10947170/A05 and 11104291, the Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province under Grant No. 10KJB140006, the Natural Sciences Foundation of Shanghai under Grant No. 11ZR1441300, the Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications under Grant No. NY221098, and sponsored by the Jiangsu Qing Lan Project and STITP Project under Grant No. CXXZD2024158.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article: The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Perry, M.D.; Mourou, G. Terawatt to petawatt subpicosecond lasers. Science 1994, 264, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.C.; Tian, X.Q. Efficient split-lanczos propagator for strong-field ionization of atoms. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 26832–26843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozák, M. All-optical scheme for generation of isolated attosecond electron pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 203202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, M.; Stocchi, F.; Costa, G.; Curcio, A.; Del Giorno, M.; Pompili, R.; Cacciotti, L.; Di Pirro, G.; Dompè, V.; Verra, L.; et al. Overview and Recent Developments of the Frascati Laser for Acceleration and Multidisciplinary Experiments Laser Facility at SPARC_LAB. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, D.; Mourou, G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Commun. 1985, 55, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, I.; Álvarez-Estrada, R.F.; Roso, L.; Castejón, F.; Guasp, J. Nonlinear relativistic electron Thomson Scattering for laser radiation with orbital angular momentum. J. Phys. Commun. 2020, 4, 065010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y. Analysis of the Effect of Pulse Width on Nonlinear Thomson Scattering from an Applied Magnetic Field. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamin, Y.I.; Faisal, F.H.M. Harmonic generation by superintense light scattering from relativistic electrons. Phys. Rev. A 1996, 54, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Lin, H.; Gu, Z.; Li, K.; Tian, Y. Analysis of the beam waist on spatial emission characteristics from an electron driven by intense linearly polarized laser pulses. Laser Phys. 2020, 30, 045301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Tian, Y. Analysis of the pulse widths on radiation properties from an electron driven by intense elliptically polarized laser. Appl. Phys. B 2023, 129, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Maksimchuk, A.; Umstadter, D. Experimental observation of relativistic nonlinear Thomson scattering. Nature 1998, 396, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Cha, Y.H.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, D. Temporal and spatial characterization of harmonics structures of relativistic nonlinear Thomson scattering. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Ren, S.; Tian, Y. Quasi-monochromatic spectral emission characteristics from electron collision with tightly focused laser pulses. Laser Phys. 2021, 31, 035401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cai, Y.; Tian, Y. Spectral shape of quasi-monochromatic radiation from electron colliding with tightly focused laser pulses. Laser Phys. 2021, 31, 065403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Gong, X.; Tian, Y. Zeptosecond-Yoctosecond Pulses Generated by Nonlinear Inverse Thomson Scattering: Modulation and Spatiotemporal Properties. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingyu, Y.; Yubo, W.; Youwei, T. Ultrashort and high-collimation X/γ-rays generated by nonlinear inverse Thomson scattering between off-axis electrons and circularly polarized intense laser pulses. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 27723–27734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, Y. Spatial radiation features of the off-axis collision between a relativistic electron and a tightly focused linearly polarized laser. Laser Phys. Lett. 2023, 20, 045301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.; Marklund, M.; Holkundkar, A.R. Focusing effects in laser-electron Thomson scattering. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 2016, 19, 094701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esarey, E.; Ride, S.K.; Sprangle, P. Nonlinear Thomson scattering of intense laser pulses from beams and plasmas. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, T.G. Radiation reaction in electron–beam interactions with high-intensity lasers. Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 2020, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravets, Y.; Noble, A.; Jaroszynski, D. Radiation reaction effects on the interaction of an electron with an intense laser pulse. Phys. Rev. E—Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2013, 88, 011201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, A.D. Exact solution of the Landau-Lifshitz equation in a plane wave. Lett. Math. Phys. 2008, 83, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamin, Y.I.; Keitel, C.H. Electron acceleration by a tightly focused laser beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 095005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarachik, E.S.; Schappert, G.T. Classical theory of the scattering of intense laser radiation by free electrons. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 1, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.S.; Kibble, T.W.B. Interaction of intense laser beams with electrons. Phys. Rev. 1964, 133, A705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Generation of atto-zeptosecond X-rays through cross-collision between relativistic electron and tightly focused intense laser pulse. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 181, 111719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Cha, Y.H.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, D. Relativistic nonlinear Thomson scattering as attosecond x-ray source. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 026502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).