Machine Learning-Based Smartphone Grip Posture Image Recognition and Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Preprocessing Techniques for Hand Recognition
2.2. Classification Model
2.3. Ensemble Methods
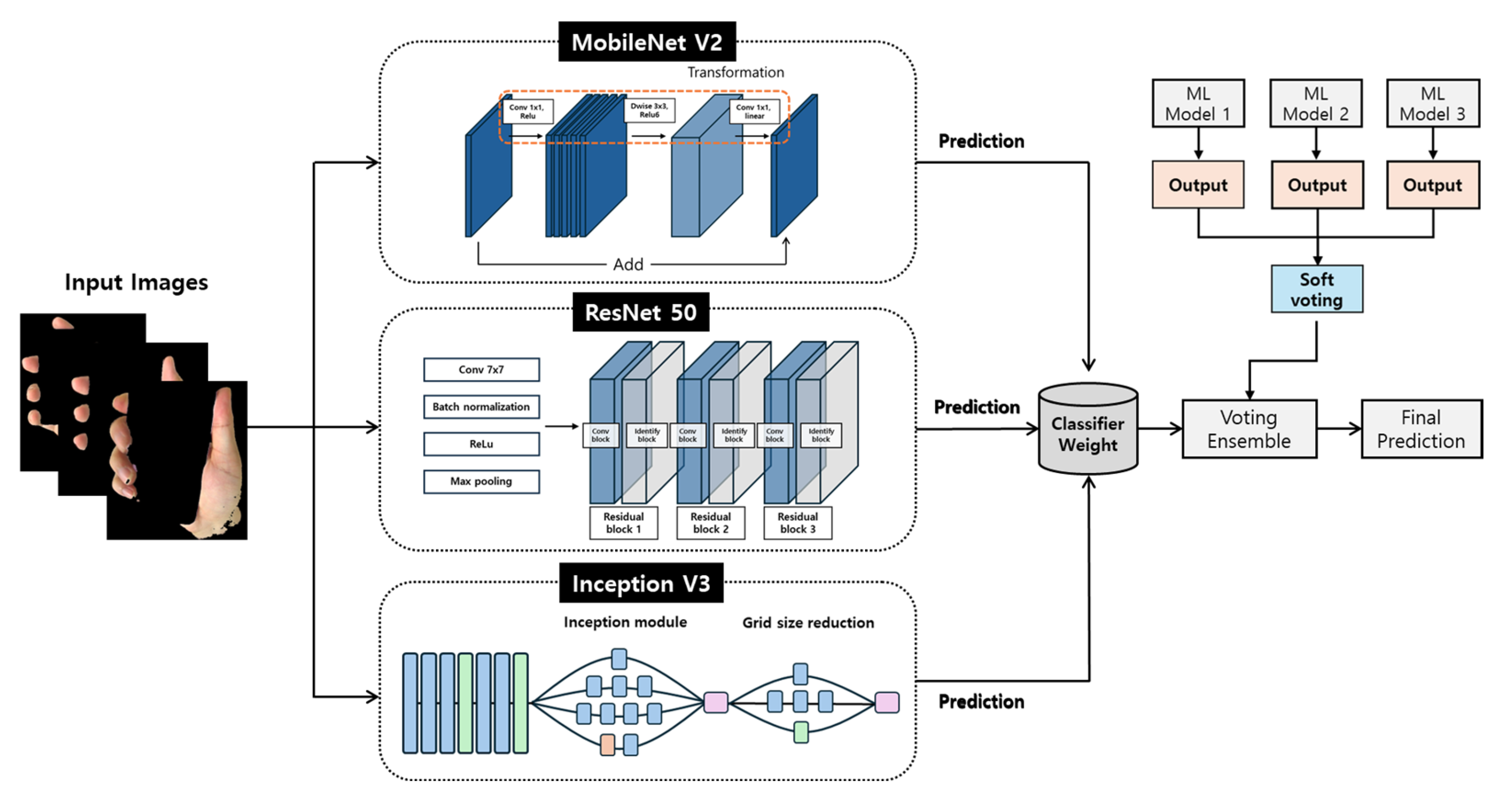
3. Methods
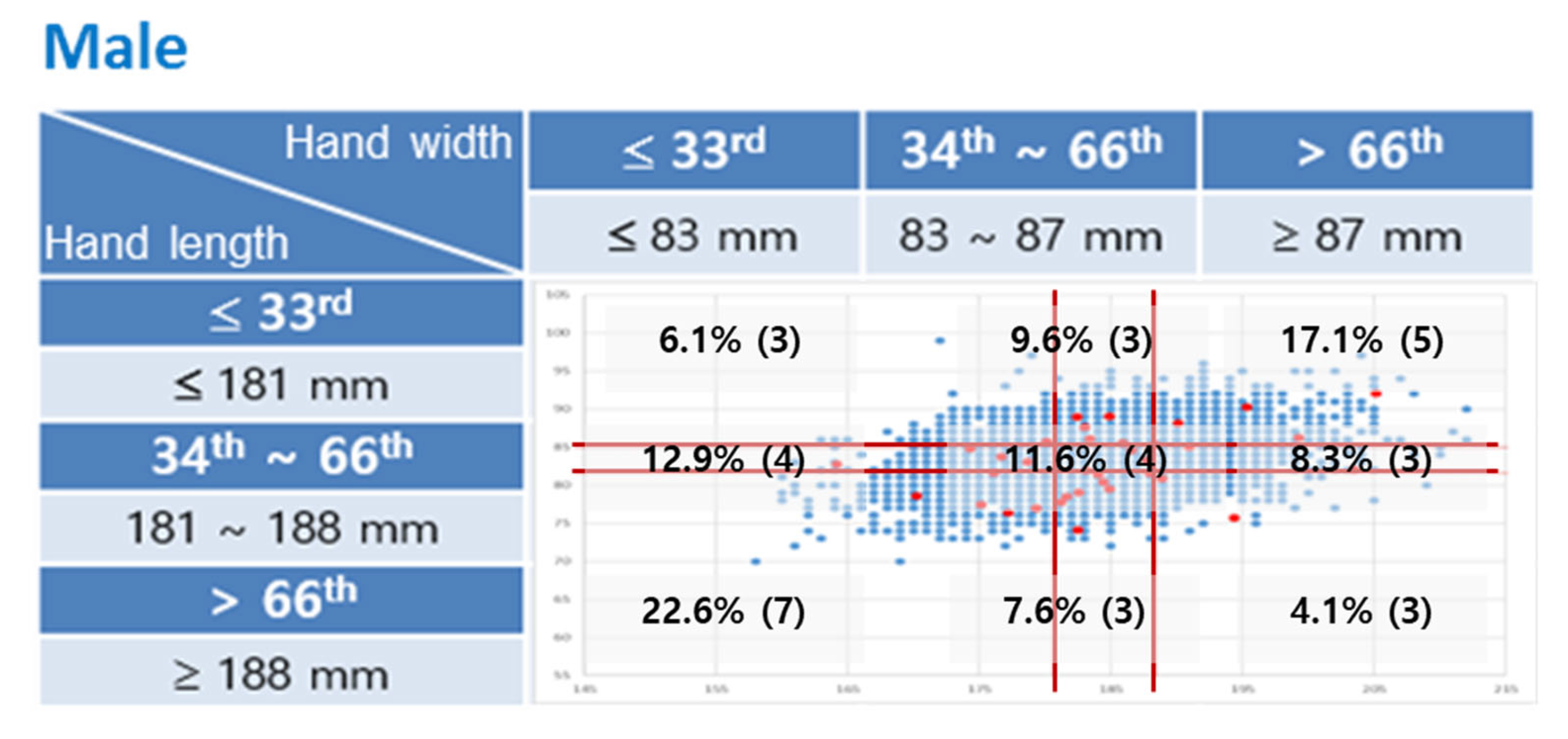
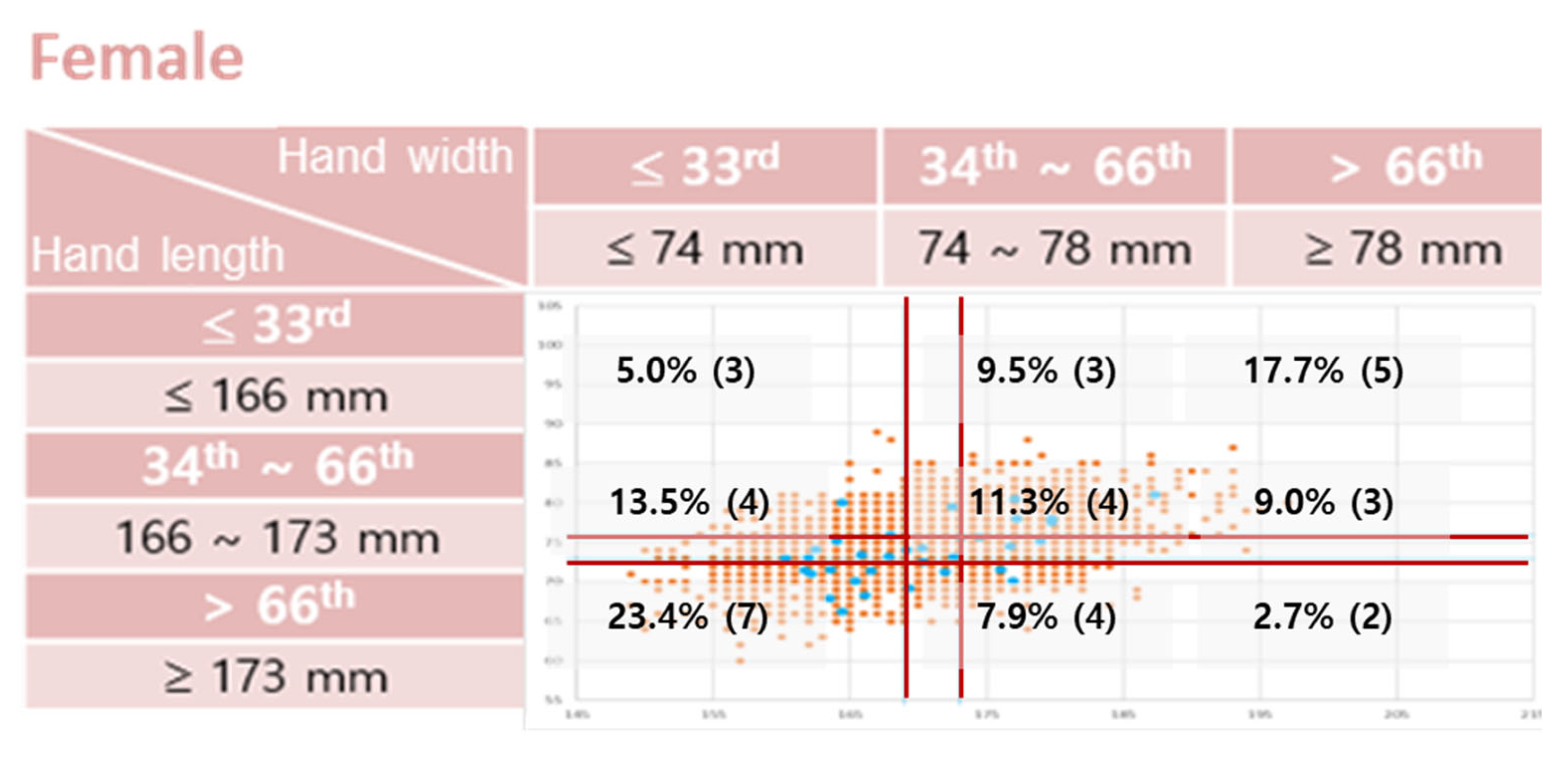
3.1. Participants
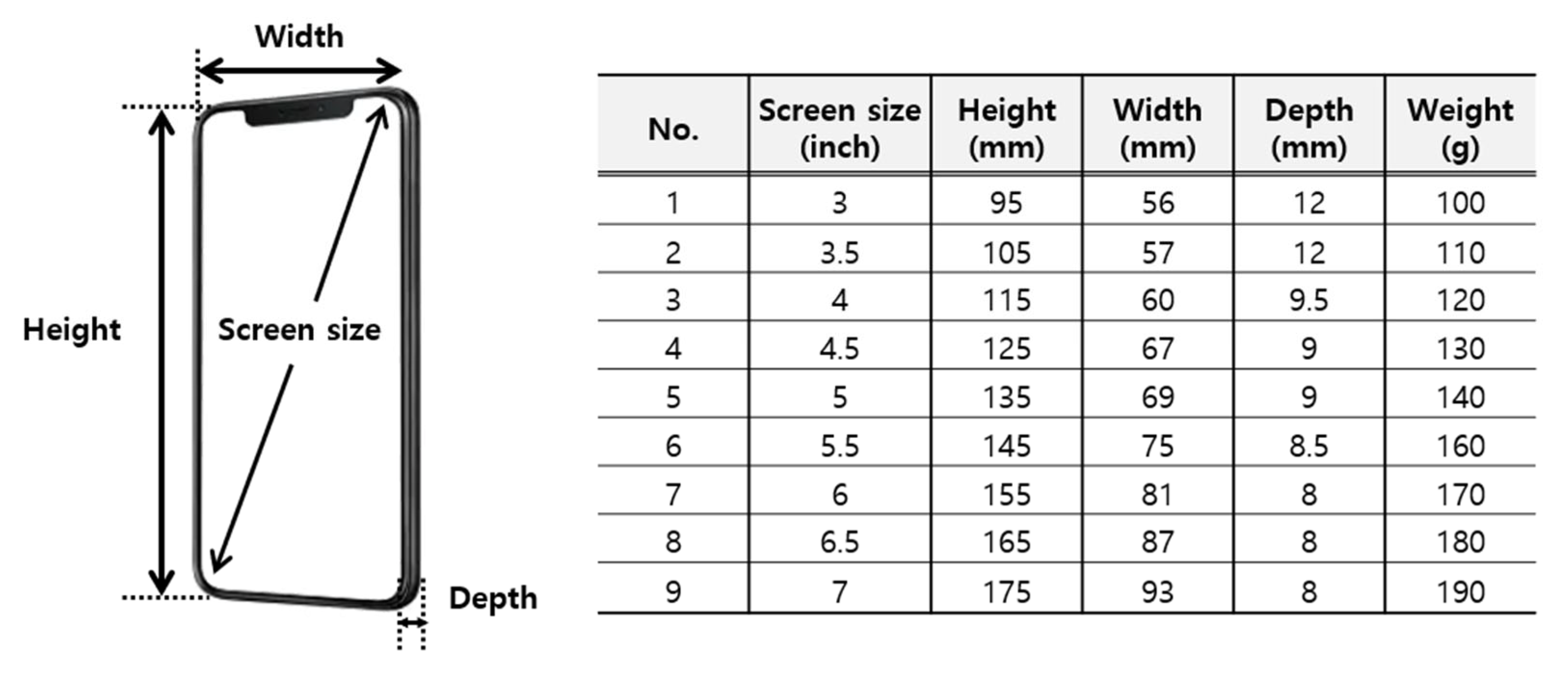
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Experiment Procedure
3.4. Grip Posture Classification
3.5. Dataset
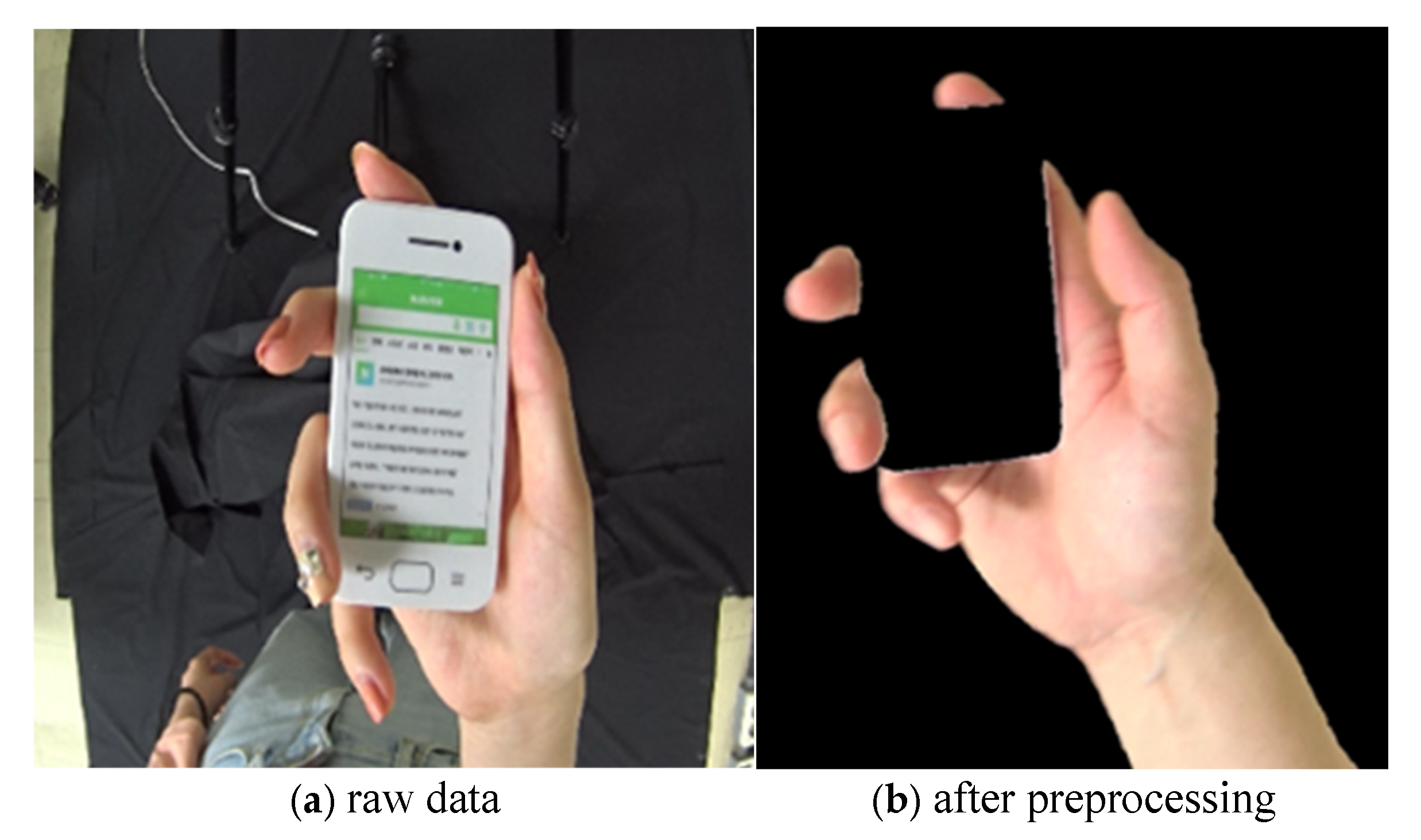
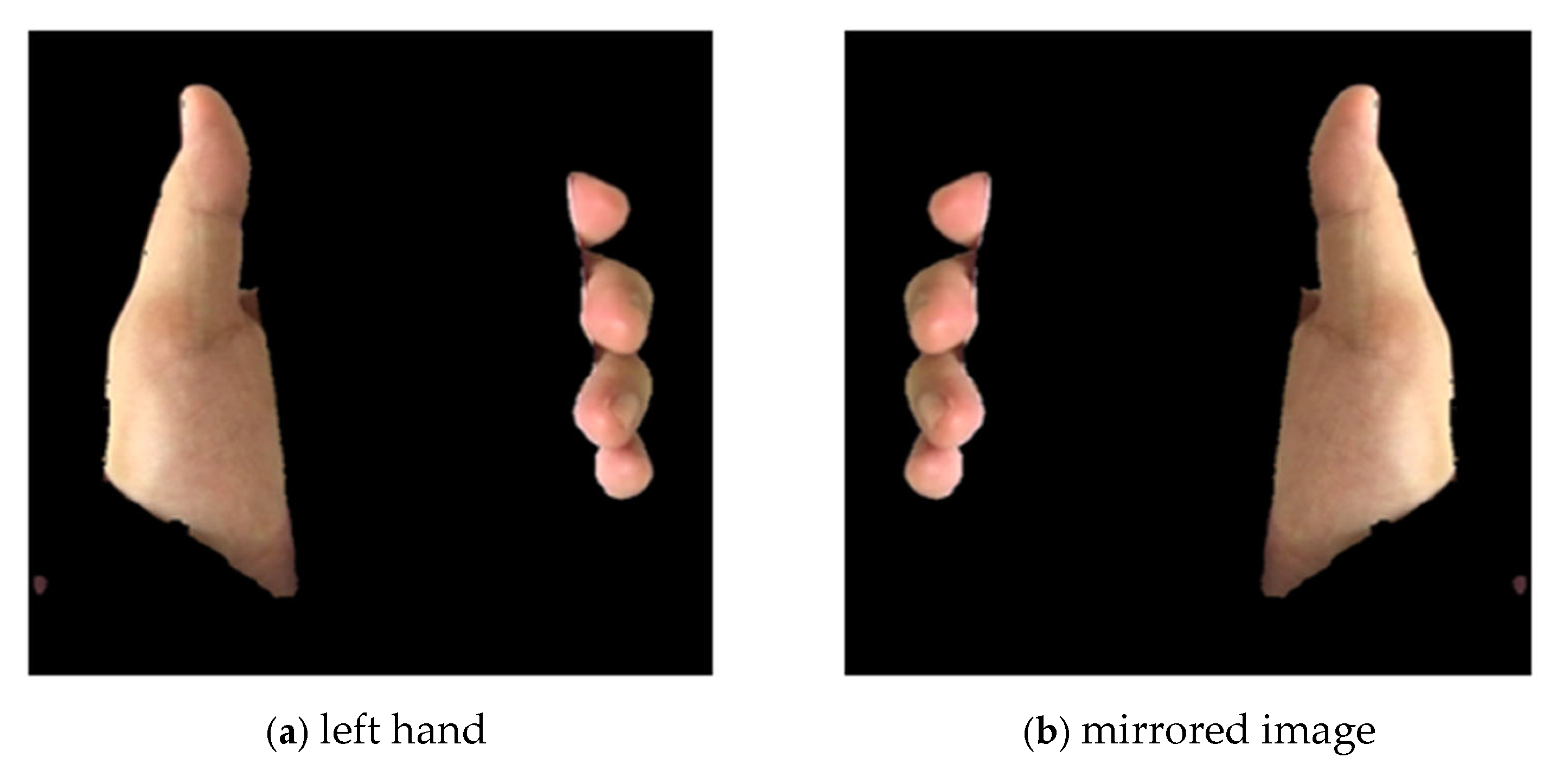
3.6. Preprocessing
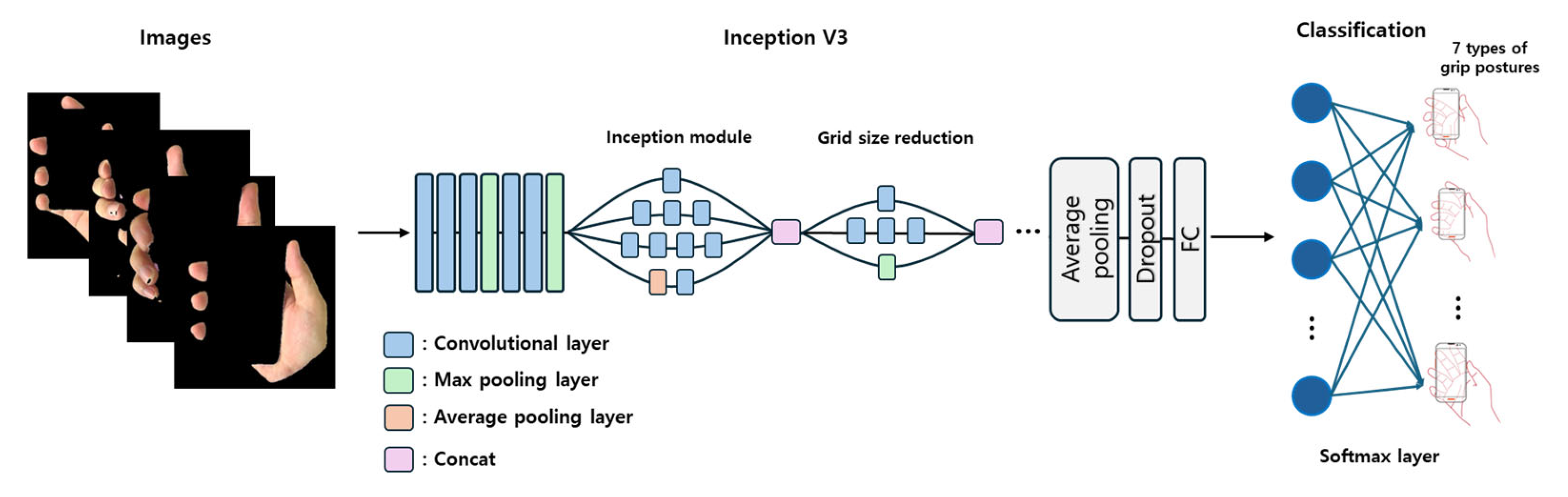
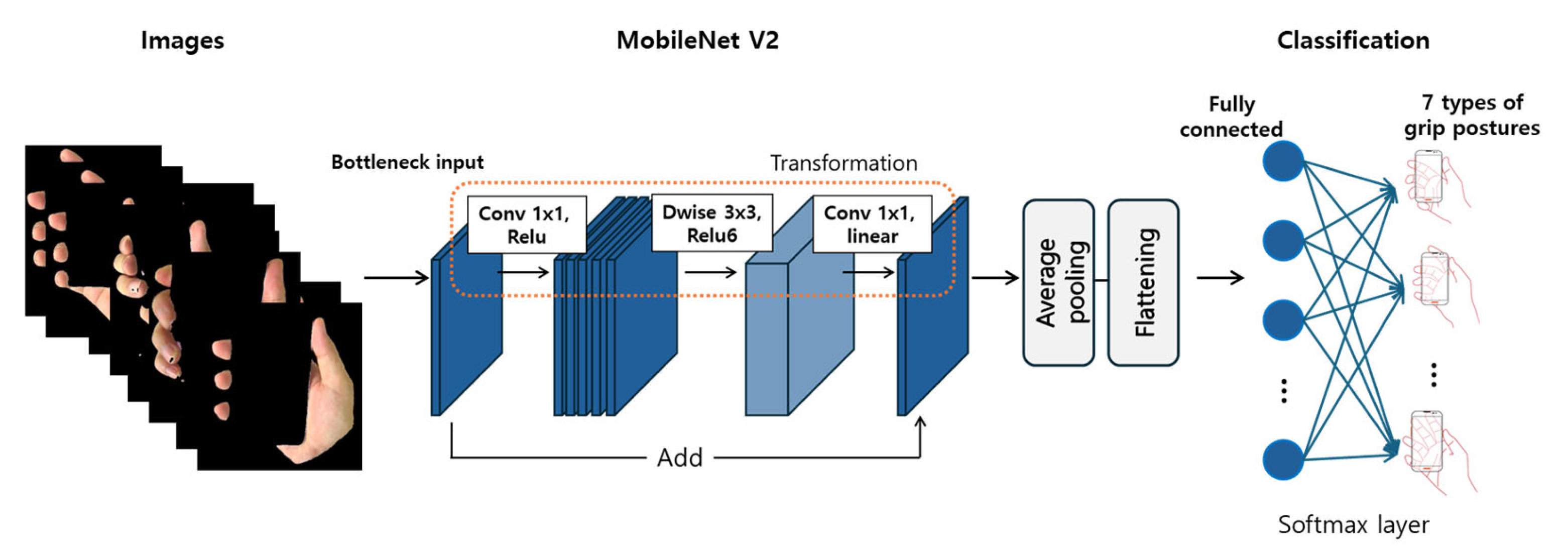
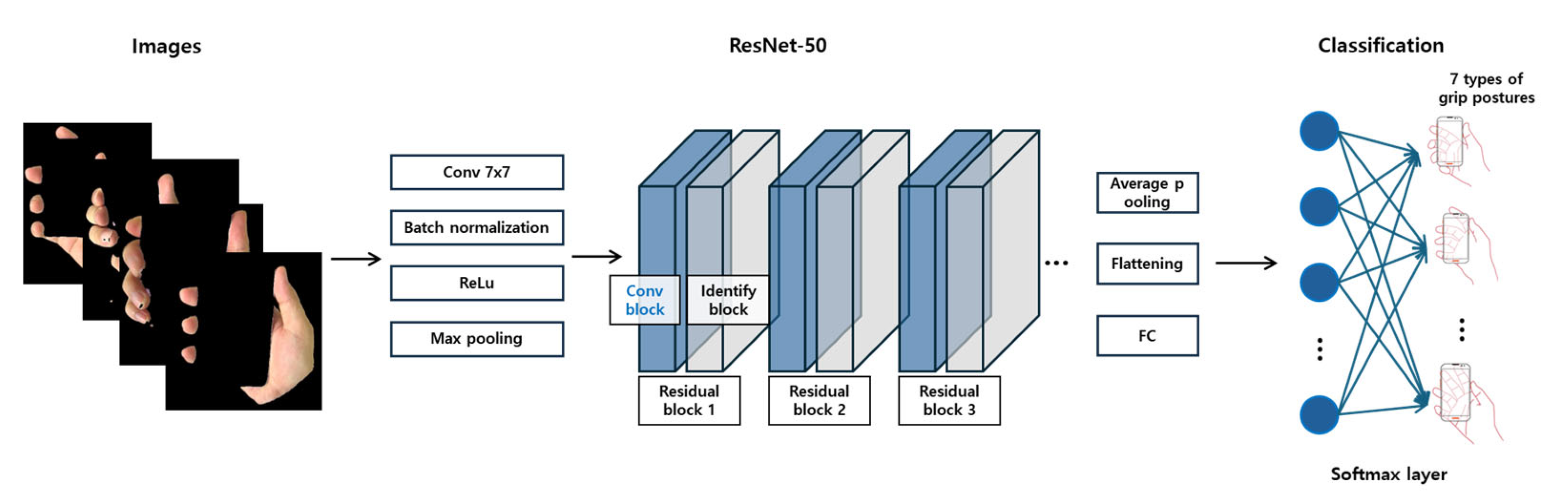
3.7. Model Architectures
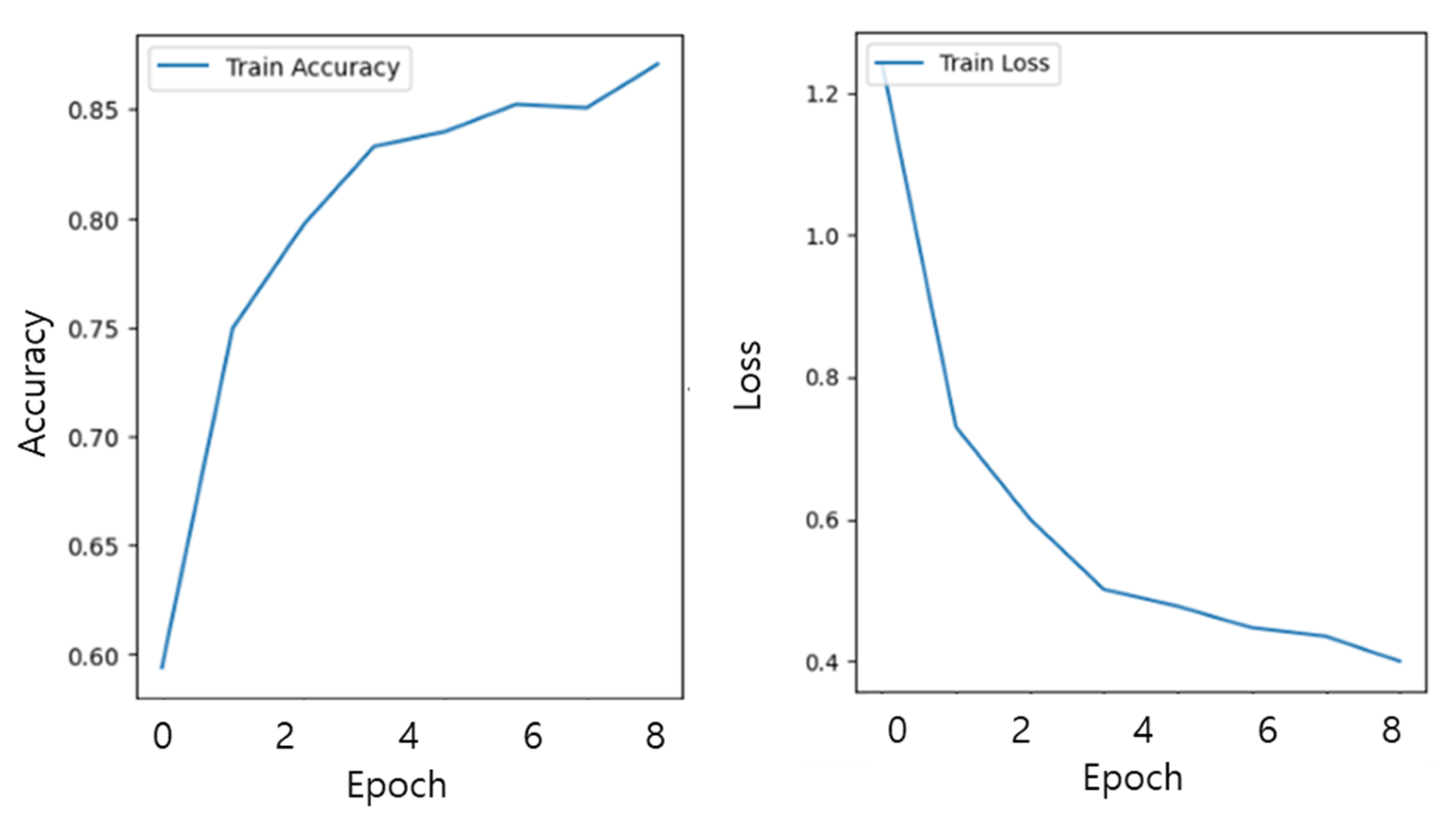
3.8. Training/Test Setup
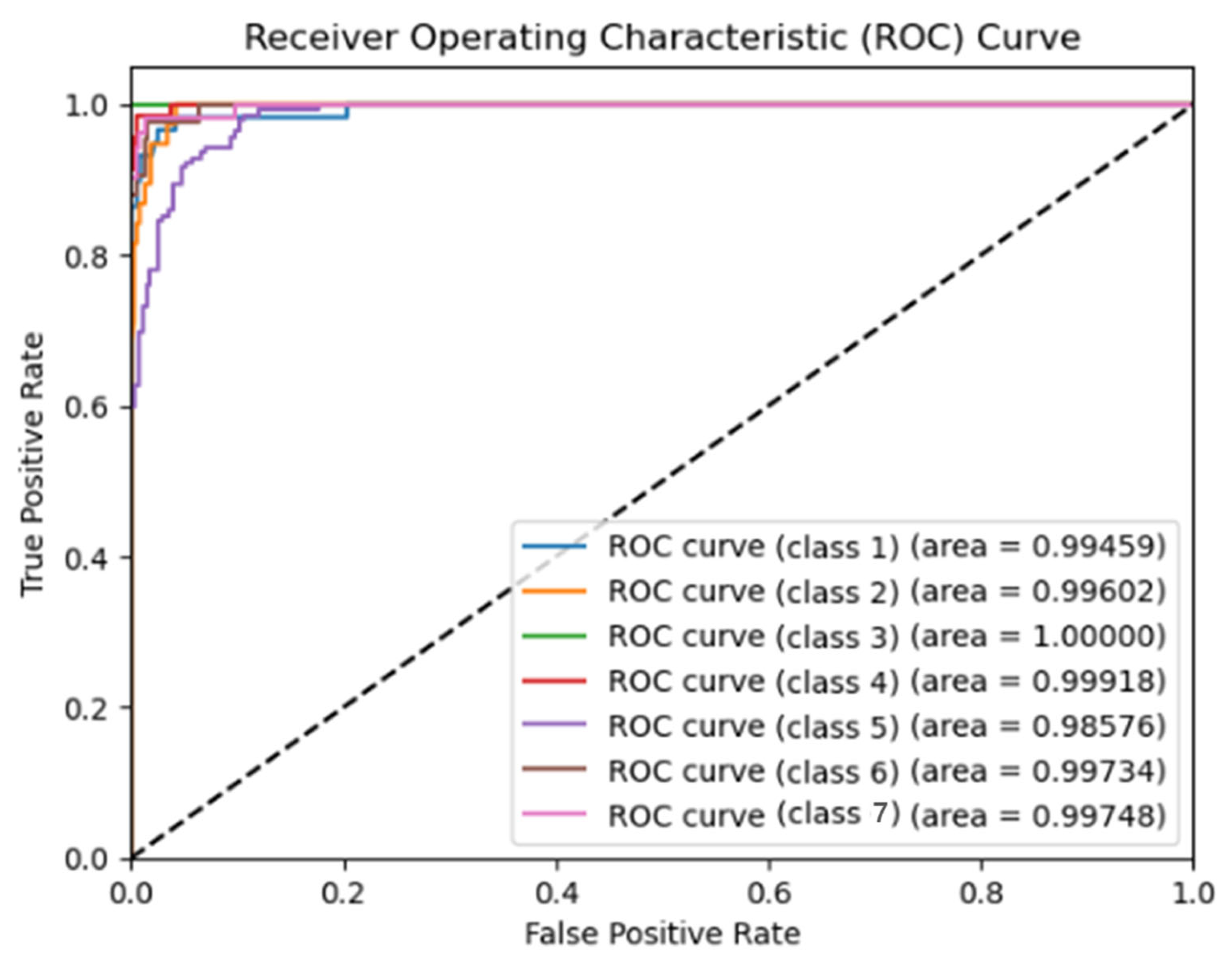
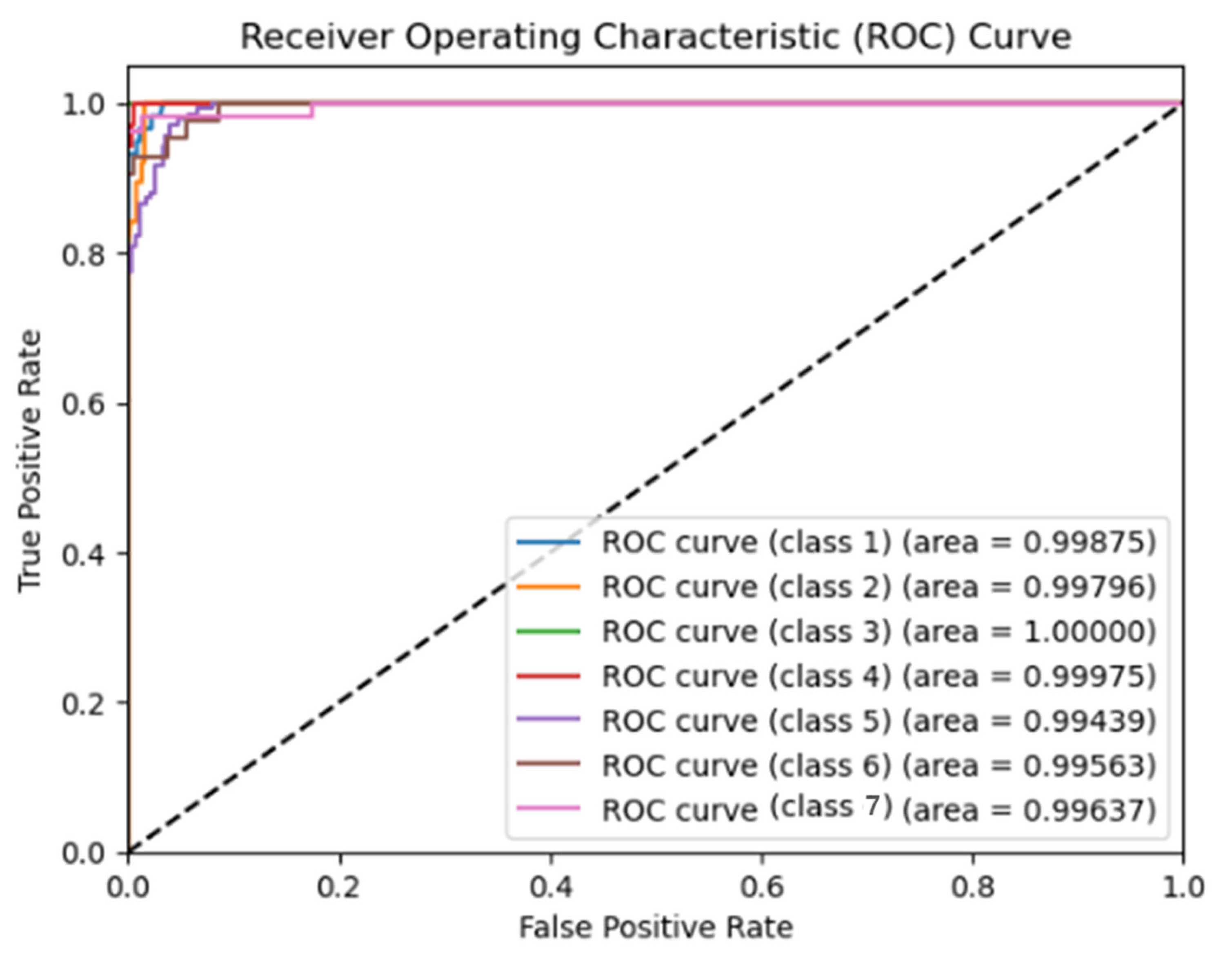
3.9. Model Evaluation
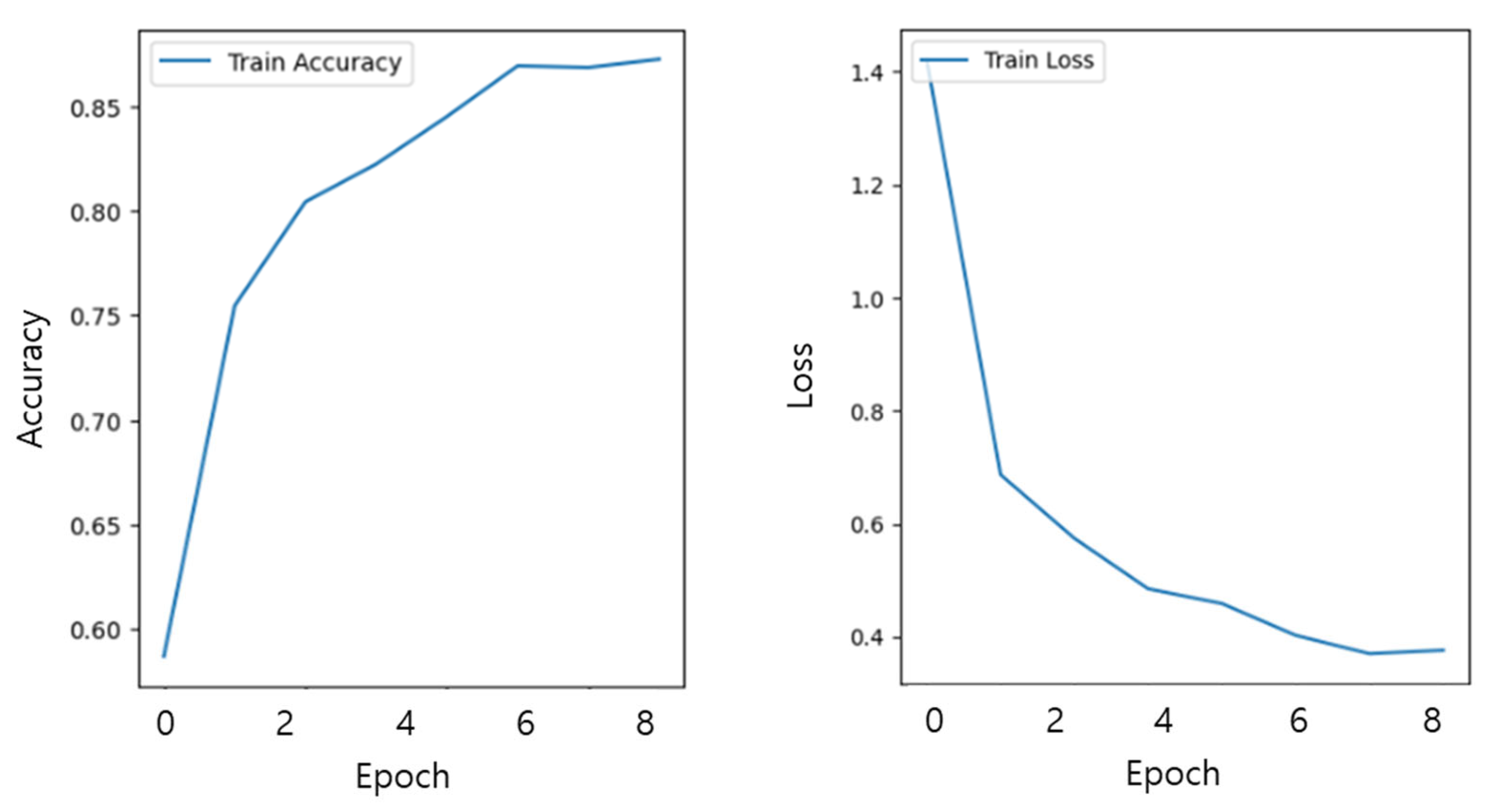
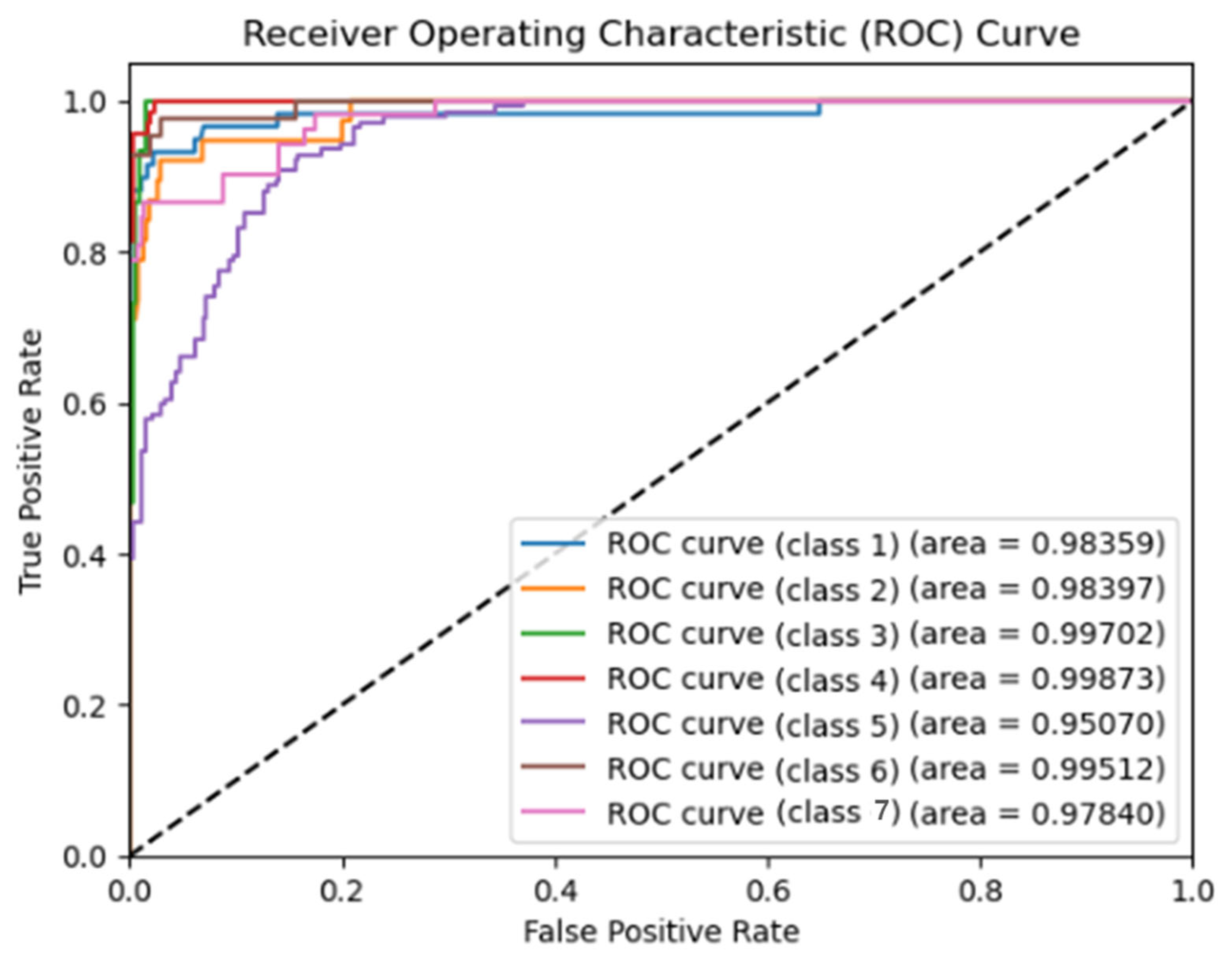
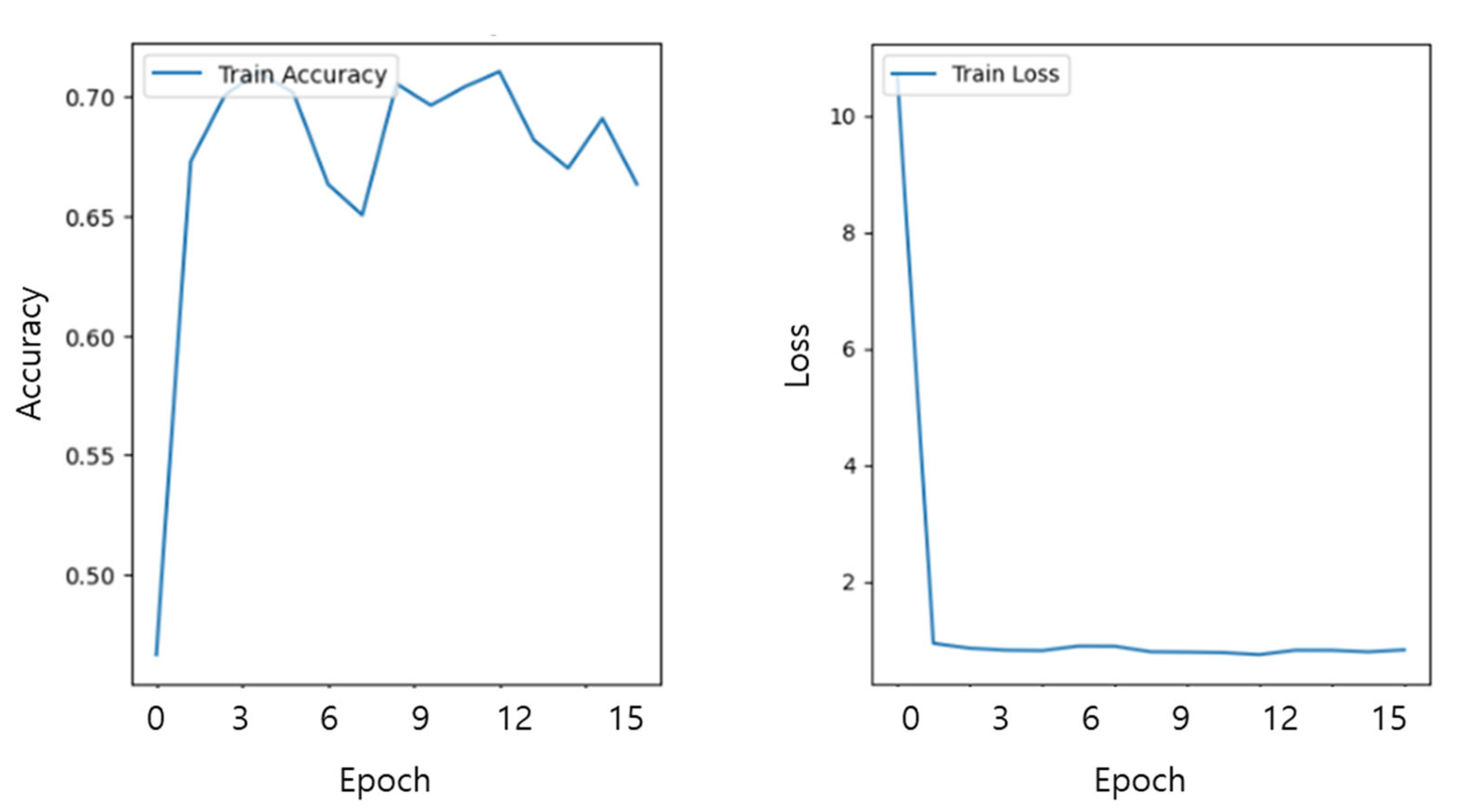
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, Y.; Yang, X.; Park, J.; Lee, W.; You, H. Effects of Smartphone Size and Hand Size on Grip Posture in One-Handed Hard Key Operations. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wobbrock, J.; Myers, B.; Aung, H. The Performance of Hand Postures in Front- and Back-of-Device Interaction for mobile computing. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2008, 66, 857–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finneran, A.; O’Sullivan, L. Effects of Grip Type and Wrist Posture on Forearm EMG Activity, Endurance Time and Movement Accuracy. Int. J. Ind. Ergonom. 2013, 43, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cha, M.; Hwangbo, H.; Mo, S.; Ji, G. Smartphone Form Factors: Effects of Width and Bottom Bezel on Touch Performance, Workload, and Physical Demand. Appl. Ergon. 2018, 67, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietrys, D.; Gerg, M.; Dropkin, J.; Gold, J. Mobile Input Device Type, Texting Style and Screen Size Influence Upper Extremity and Trapezius Muscle Activity, and Cervical Posture While Texting. Appl. Ergon. 2015, 50, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, M.B.; Asakawa, D.S.; Jindrich, D.L.; Dennerlein, J.T. Two-Handed Grip on a Mobile Phone Affords Greater Thumb Motor Performance, Decreased Variability, and a More Extended Thumb Posture Than a One-Handed Grip. Appl. Ergon. 2016, 52, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, A.K.; Bederson, B.B.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Understanding One-Handed Use of Mobile Devices. In Handbook of Research on User Interface Design and Evaluation for Mobile Technology; Lumsden, J., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 86–101. ISBN 978-159-904-871-0. [Google Scholar]
- Coleca, F.; State, A.; Klement, S.; Barth, E.; Martinetz, T. Self-Organizing Maps for Hand and Full Body Tracking. Neurocomputing 2015, 147, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, P.; Laux, S.; Purdack, D.; Müller, P.N.; Göbel, S. Give Me a Sign: Using Data Gloves for Static Hand-Shape Recognition. Sensors 2023, 23, 9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haria, A.; Subramanian, A.; Asokkumar, N.; Poddar, S.; Nayak, J.S. Hand Gesture Recognition for Human Computer Interaction. Procedia. Comput. Sci. 2017, 115, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, A.; Rani, R.; Dev, A.; Sharma, A. Hand Gesture Detection Using Convexity Hull and Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning, Computer Systems and Security (MLCSS), Bhubaneswar, India, 5–6 August 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.X.; Hameed, N.; Clos, J.; Hasan, M.M. A Framework of Ensemble CNN Models for Real-Time Sign Language Translation. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Software, Knowledge, Information Management and Applications (SKIMA), Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2–4 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Nigam, S.; Shamoon, M.; Sakshi, D.; Choudhury, T. A Complete Study of Methodology of Hand Gesture Recognition System for Smart Homes. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Amity Global Institute, Singapore, 12–14 December 2019; Niranjan, S.K., Rana, A., Khurana, H., Eds.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Dua, M.; Shakshi; Singla, R.; Raj, S.; Jangra, A. Deep CNN Models-Based Ensemble Approach to Driver Drowsiness Detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 33, 3155–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, V.H.; Rhee, E.J. A High-Accuracy Model Average Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks for Classification of Cloud Image Patches on Small Datasets. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnuaim, A.; Zakariah, M.; Hatamleh, W.A.; Tarazi, H.; Tripathi, V.; Amoatey, E.T. Human-Computer Interaction with Hand Gesture Recognition Using ResNet and MobileNet. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 8777355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Ou, Y.; Jiang, G.; Xie, Q.; Xu, Y. Hand Tracking and Pose Recognition via Depth and Color Information. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Guangzhou, China, 11–14 December 2012; pp. 1104–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, R.L.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.; Jain, A.K. Face Detection in Color Images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 24, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, R.F.; Chairunnisa, T.; Gunawan, D.; Pasha, M.F.; Budiarto, R. Hand Gestures Recognition with Improved Skin Color Segmentation in Human-Computer Interaction Applications. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2019, 97, 727–739. [Google Scholar]
- Yörük, E.; Konukoğlu, E.; Sankur, B.; Darbon, J. Shape-Based Hand Recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Fu, Y. Contour Model-Based Hand-Gesture Recognition Using the Kinect Sensor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2014, 24, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnen, D.; Zafrulla, Z. Towards Robust Cross-User Hand Tracking and Shape Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1235–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, D.; Bhuyan, M.K. Hand Detection by Two-Level Segmentation with Double-Tracking and Gesture Recognition Using Deep-Features. Sens. Imaging 2022, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Xu, K.; Ding, X. Approach to hand posture recognition based on hand shape features for human–robot interaction. Complex. Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 2825–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, H.; Al Mudawi, N.A.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Alazeb, A.; Alabdullah, B.I.; Alonazi, M.; Park, J. Hand Gesture Recognition for Characters Understanding Using Convex Hull Landmarks and Geometric Features. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 82065–82078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, C.; Chen, A.P.S.; Christanto, H.J. Deep Learning for Highly Accurate Hand Recognition Based on Yolov7 Model. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–29 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Luo, Z.; Xu, H. Recognition of Pear Leaf Disease Under Complex Background Based on DBPNet and Modified MobilenetV2. IET Image Process. 2023, 17, 3055–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Luo, X. A New Image Recognition Combining Transfer Learning Algorithm and MobileNet V2 Model for Palm Vein Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Frontiers Technology of Information and Computer (ICFTIC), Qingdao, China, 2–4 December 2022; pp. 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Dabwan, B.A.; Jadhav, M.E.; Al Yami, M.; Hassan, E.A.; Almula, S.M.; Ali, Y.A. Classifying Hand Gestures for People with Disabilities Utilizing the MobileNetV2 Model. In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Innovative Sustainable Technologies for Energy, Mechatronics, and Smart Systems (ISTEMS), Dehradun, India, 26–27 April 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Doma, G.; Miriyala, T. Object Detection Using ResNet50. Int. J. Creat. Res. Thoughts 2024, 12, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, M.E.; Salman, Y.B.; Genc, E. Person Identification by Using ResNet on Hand Images. In Proceedings of the 2024 24th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 29 October–1 November 2024; pp. 1345–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. Practice of Gesture Recognition Based on Resnet50. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1574, 012154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Amin, S.U.; Fayaz, M.; Seo, S. An Efficient and Robust Hand Gesture Recognition System of Sign Language Employing Finetuned Inception-V3 and EfficientNet-B0 Network. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 46, 3509–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsh, B.; Laskar, R.H.; Karsh, R.K. mIV3Net: Modified inception V3 network for hand gesture recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 10587–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusha, S.B.; Samyama Gunjal, G.H.; Manjushree, N.S. Static Hand Gesture Prediction Using Inception V3. In Cognitive Science and Technology, Proceedings of the International Conference on Cognitive and Intelligent Computing, Hyderabad, India, 11–12 December 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yu, Z.; Cao, W.; Shi, Y.; Ma, Q. A Survey on Ensemble Learning. Front. Comput. Sci. 2019, 14, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H. Ensemble Methods: Foundations and Algorithms; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, A.; Mishra, T.K.; Dash, R. A Novel Hand Gesture Detection and Recognition System Based on Ensemble-Based Convolutional Neural Network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 40043–40066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewe, E.L.R.; Lee, C.P.; Kwek, L.C.; Lim, K.M. Hand Gesture Recognition via Lightweight VGG16 and Ensemble Classifier. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Shin, J.; Yun, K.S. Soft Voting-based Ensemble Model for Bengali Sign Gesture Recognition. Ann. Emerg. Technol. Comput. 2022, 6, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, H.G. Advanced Threat Detection Using Soft and Hard Voting Techniques in Ensemble Learning. J. Robot. Control. 2024, 5, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Size Korea Report on the Fifth Survey of Korean Anthropometry. Available online: http://sizekorea.kats.go.kr/ (accessed on 2 May 2013).
- Oldfield, R.C. The Assessment and Analysis of Handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilleas, M.; Eleni, D.; Paris-Alexandros, K.; Minas, D. Real-Time Detection of Suspicious Objects in Public Areas Using Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 21st Pan-Hellenic Conference on Informatics, Larissa, Greece, 28–30 September 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Harini, V.; Prahelika, V.; Sneka, I.; Ebenezer, P.A. Hand Gesture Recognition Using OpenCv and Python. In New Trends in Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing; Smys, S., Iliyasu, A.M., Bestak, R., Shi, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1711–1719. [Google Scholar]
- OpenCV Team. Open Source Computer Vision Library. Available online: http://opencv.org/ (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Shiqiang, Y.; Dan, Q.; Peilei, L. Research on Hand Recognition Method Based on Markov Random Field. Procedia. Eng. 2017, 174, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.Y.; Chung, Y.L.; Tsai, W.F. An Efficient Hand Gesture Recognition System Based on Deep CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 13–15 February 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 853–858. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartl, H.; Sauter, D.; Schenk, C.; Atik, C.; Buettner, R. Vision-Based Hand Gesture Recognition for Human-Computer Interaction Using MobileNetV2. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 45th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Madrid, Spain, 12–16 July 2021; Chan, W.K., Ed.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1667–1674. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, K.; Zhou, C.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Y. MobileNetV2 Model for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Information Technology and Computer Application (ITCA), Guangzhou, China, 18–20 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnuaim, A.A.; Zakariah, M.; Shashidhar, C.; Hatamleh, W.A.; Tarazi, H.; Shukla, P.K.; Ratna, R. Speaker Gender Recognition Based on Deep Neural Networks and ResNet50. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 4444388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Long, H.; Zhao, K.; Yu, X.; Zeng, C.; Duan, J.; et al. Fundus Image Classification Using Inception V3 and ResNet-50 for the Early Diagnostics of Fundus Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1126780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Fan, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, C.; Li, D.; Hong, Y.; Wang, Y. Research on the Practical Classification and Privacy Protection of CT Images of Parotid Tumors Based on ResNet50 Model. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1576, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnin, N.; Sumi, T.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Andersson, K. Early Detection of Parkinson’s Disease from Micrographic Static Hand Drawings. In Proceedings of the Brain Informatics 2021, Virtual Event, 17–19 September 2021; Mahmud, M., Kaiser, M.S., Vassanelli, S., Dai, Q., Zhong, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 433–447. [Google Scholar]
- Afroze, T.; Akther, S.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Hossain, E.; Hossain, M.S.; Andersson, K. Glaucoma Detection Using Inception Convolutional Neural Network V3. In Proceedings of the Applied Intelligence and Informatics 2021, Nottingham, UK, 30–31 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tebaldi, C.; Knutti, R. The Use of the Multi-Model Ensemble in Probabilistic Climate Projections. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2007, 365, 2053–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, Z.C.; Elkan, C.; Naryanaswamy, B. Optimal Thresholding of Classifiers to Maximize F1 Measure. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases European Conference, ECML PKDD 2014, Nancy, France, 15–19 September 2014; pp. 225–239. [Google Scholar]
- Paumgartner, D.; Losa, G.; Weibel, E.R. Resolution Effect on the Stereological Estimation of Surface and Volume and its Interpretation in terms of Fractal Dimensions. J. Microsc. 1981, 121, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattaraj, R.; Khan, S.; Roy, D.G.; Bepari, B.; Bhaumik, S. Vision-Based Human Grasp Reconstruction Inspired by Hand Postural Synergies. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 70, 702–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Li, H. A Face Detection Method Based on Skin Color Features and AdaBoost Algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1748, 042015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariefwan, M.R.M.; Diyasa, I.G.S.M.; Hindrayani, K.M. InceptionV3, ResNet50, ResNet18 and MobileNetV2 Performance Comparison on Face Recognition Classification. Literasi Nusant. 2023, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Pei, Y. Innovative Design of Aging-Friendly Household Cleaning Products from the Perspective of Ergonomics. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (HCII 2023), Copenhagen, Denmark, 23–28 July 2023; pp. 295–312. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, F.; Liu, J. Low-frequency Background Estimation and Noise Separation from High-frequency for Background and Noise Subtraction. Appl. Opt. 2024, 63, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottha, B.R.T.N.; Penumacha, N.K.; Gadde, H.V. Smart Traffic Management System using Background Subtraction. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Expert Clouds and Applications (ICOECA), Bengaluru, India, 18–19 April 2024; pp. 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Grip Posture Name | Grip Posture Image | Number of Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L2-B1-R1-K1 |  | 511 |
| 2 | L2-R1-K2 |  | 279 |
| 3 | L2-T1-B1-R1 | 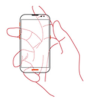 | 120 |
| 4 | L3-B1-R1 |  | 556 |
| 5 | L3-R1-K1 | 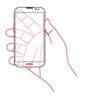 | 981 |
| 6 | L3-R1-T1 |  | 311 |
| 7 | L4-R1 | 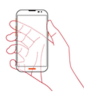 | 520 |
| Total | 3278 | ||
| Grip Posture | Accuracy (%) | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1: L2-B1-R1-K1 | 93.2 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.93 |
| Class 2: L2-R1-K2 | 76.3 | 0.97 | 0.73 | 0.85 |
| Class 3: L2-T1-B1-R1 | 80.0 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.89 |
| Class 4: L3-B1-R1 | 98.5 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
| Class 5: L3-R1-K1 | 94.3 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| Class 6: L3-R1-T1 | 90.5 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| Class 7: L4-R1 | 96.2 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| Grip Posture | Accuracy (%) | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1: L2-B1-R1-K1 | 93.2 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| Class 2: L2-R1-K2 | 84.2 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.88 |
| Class 3: L2-T1-B1-R1 | 93.3 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.97 |
| Class 4: L3-B1-R1 | 100 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.99 |
| Class 5: L3-R1-K1 | 94.4 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| Class 6: L3-R1-T1 | 92.9 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| Class 7: L4-R1 | 96.2 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| Grip Posture | Accuracy (%) | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1: L2-B1-R1-K1 | 89.8 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| Class 2: L2-R1-K2 | 52.6 | 0.87 | 0.53 | 0.66 |
| Class 3: L2-T1-B1-R1 | 60.0 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.72 |
| Class 4: L3-B1-R1 | 97.1 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| Class 5: L3-R1-K1 | 89.4 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.82 |
| Class 6: L3-R1-T1 | 88.1 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.94 |
| Class 7: L4-R1 | 86.5 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.83 |
| Grip Posture | Accuracy (%) | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1: L2-B1-R1-K1 | 93.2 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| Class 2: L2-R1-K2 | 97.3 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.95 |
| Class 3: L2-T1-B1-R1 | 100 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Class 4: L3-B1-R1 | 98.6 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Class 5: L3-R1-K1 | 95.1 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| Class 6: L3-R1-T1 | 92.9 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| Class 7: L4-R1 | 98.1 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, D.; Cui, X.; Lee, Y.; Choi, Y.; Murugan, A.S.; Kim, E.; You, H. Machine Learning-Based Smartphone Grip Posture Image Recognition and Classification. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095020
Kwon D, Cui X, Lee Y, Choi Y, Murugan AS, Kim E, You H. Machine Learning-Based Smartphone Grip Posture Image Recognition and Classification. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095020
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Dohoon, Xin Cui, Yejin Lee, Younggeun Choi, Aditya Subramani Murugan, Eunsik Kim, and Heecheon You. 2025. "Machine Learning-Based Smartphone Grip Posture Image Recognition and Classification" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095020
APA StyleKwon, D., Cui, X., Lee, Y., Choi, Y., Murugan, A. S., Kim, E., & You, H. (2025). Machine Learning-Based Smartphone Grip Posture Image Recognition and Classification. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15095020