Design of Cislunar Navigation Constellation via Orbits with a Resonant Period
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamental Theory
2.1. Circular Restricted Three-Body Problem
2.2. Earth–Moon System’s Periodic Orbit Database Generation
- DROs [22]: DROs are planar periodic orbits in the lunar vicinity, which are symmetric around the X-axis of the Earth–Moon rotating frame. These orbit families are generated through natural parameter continuation methods. They have an initial x-direction amplitude of 1000 km, which is continued along +X with step size .
- Lyapunov and orbits: Lyapunov orbits constitute planar periodic trajectories near the collinear libration points that maintain X-axis symmetry in the Earth–Moon rotating frame. Their families are similarly constructed via natural parameter continuation. They have the same parameters as DROs but these continue along −X for L1/L3.
- Halo and Vertical orbits: Halo orbit families and vertical orbit families represent non-planar periodic solutions near collinear libration points, exhibiting symmetry about the XZ-plane. These are extended via Ref. [23]’s method, starting from z-direction amplitudes of 1000 km. The normalized continuation step size for x/z-directions at each collinear point is .
2.3. Navigation Performance Modeling
2.4. Target Area Definition and Gridding
- Cuboidal grids are typically applied to global spatial domains (e.g., the entire Earth–Moon system).
- Spherical grids are suited for local regions (e.g., near the Earth or the Moon).
3. Design Methodology
3.1. Orbital Library Preprocessing
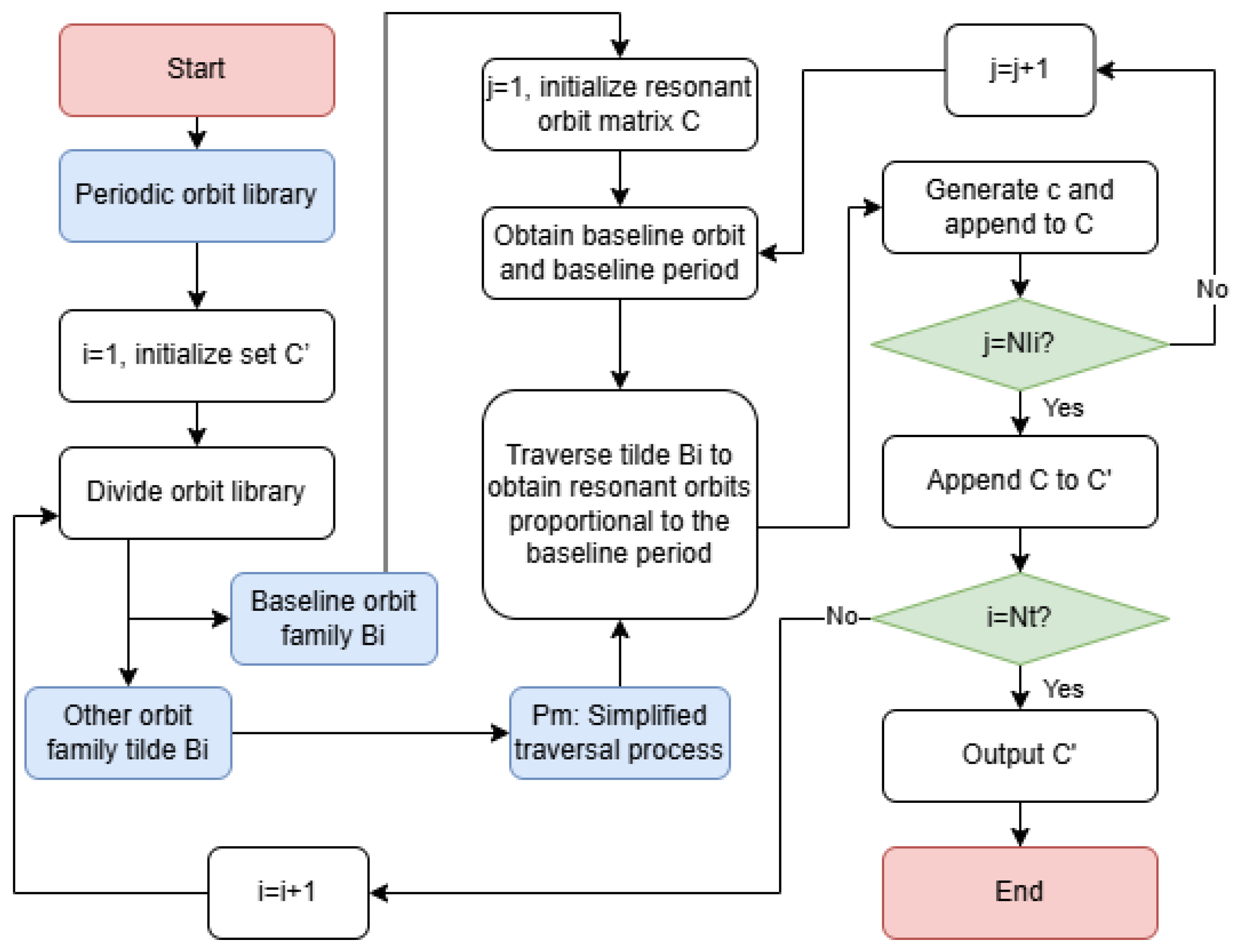
3.2. Resonant Combination Generation and Merging
- Resonance multiple f.
- Period ratio vector (storing periods proportional to ).
- Orbit combination matrix (recording parameters and type identifiers of resonant orbits). Each row vector in represents a resonant orbit.
- Initialize the resonance multiple by setting . Initialize the period ratio vector , with its first element as . Initialize the orbital combination matrix . Let m represent the row index of . When , the first row vector records the baseline orbit; then, .
- Extract the last element from the period ratio vector and compare it with the maximum period in the working orbit library. If , increment the resonance multiple f by 1 and append a new element to .
- Repeat 2 until . Remove the last element from , thereby obtaining all resonant periods in that are proportional to , and record them in the vector .
- To search for all resonant orbits, iterate through . Denote the orbit family index within .
- Retrieve the current orbit family . Extract the period column vector from the last column of . From , obtain the s-th row vector , which represents the characteristic period vector of the current orbit family.
- Iterate through . Let the resonance period index be , such that the current resonance period is .
- Determine if lies within the range specified by . If is not satisfied, cannot be found in the s-th orbit family. Proceed by incrementing s () and jump to 5 to iterate through the next orbit family until ; then, proceed to 8. If is satisfied, compute the period deviation vector .Retrieve the index of the minimum value in ,Extract the corresponding row vector from and append it to the orbital combination matrix by incrementing m()Increment k () to obtain the next . Repeat 7 until k exceeds the number of elements in . Increment s (). If , proceed to 8. Otherwise, return to 5 to iterate through the next orbit family.
- At this stage, the orbital combination matrix , containing all orbits resonant with , is obtained. Since the constructed resonant constellation in this study serves as a navigation constellation, which requires at least four satellites for positioning and navigation services, if the number of rows in is less than four, discard the current . Otherwise, record the current and its corresponding matrix in the set .
3.3. Resonant Constellation Generation and Merging
4. Simulation Analysis
4.1. Resonant Constellation Configuration Analysis for Distinct Regions
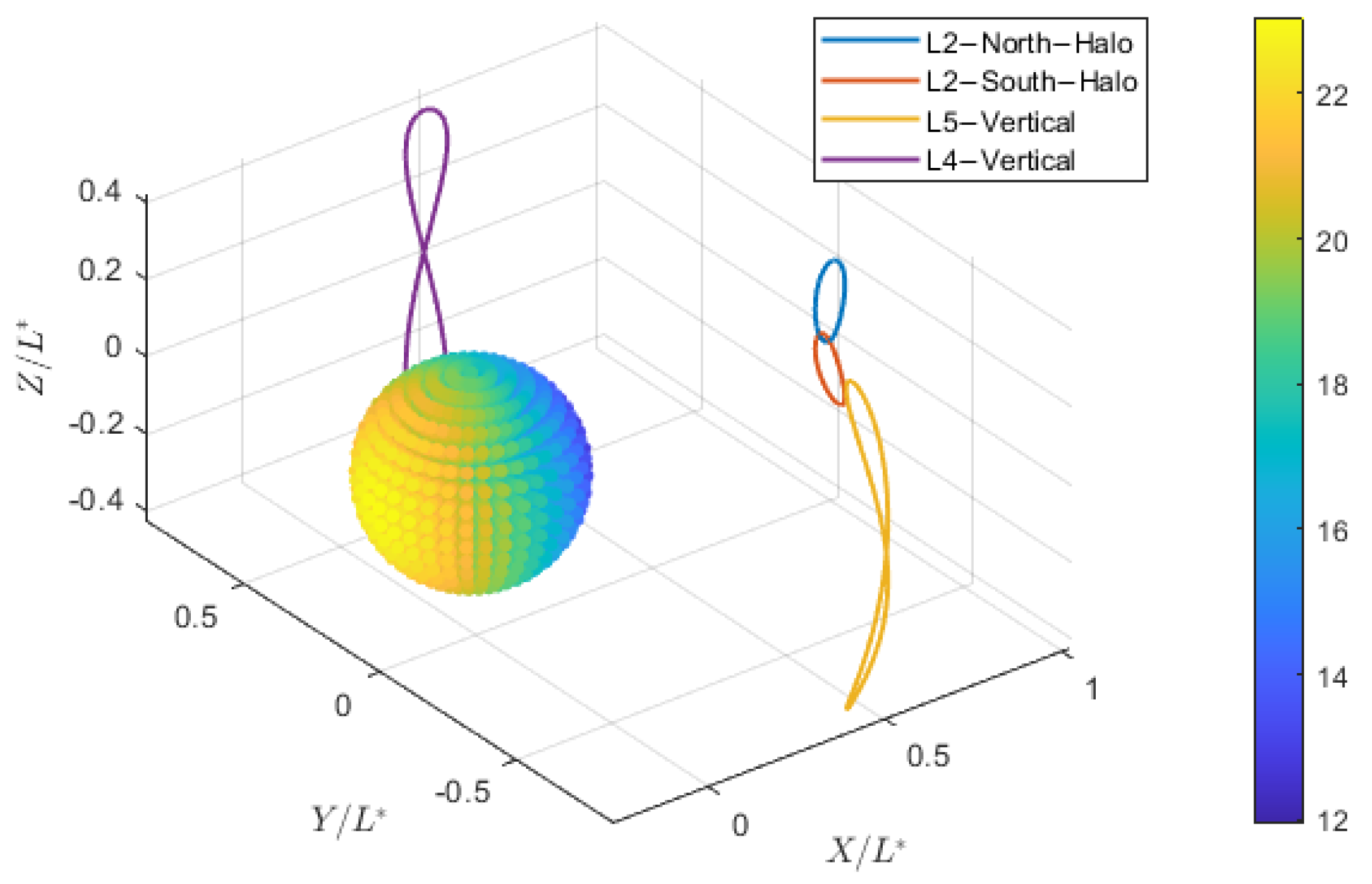
4.1.1. Near-Earth Region
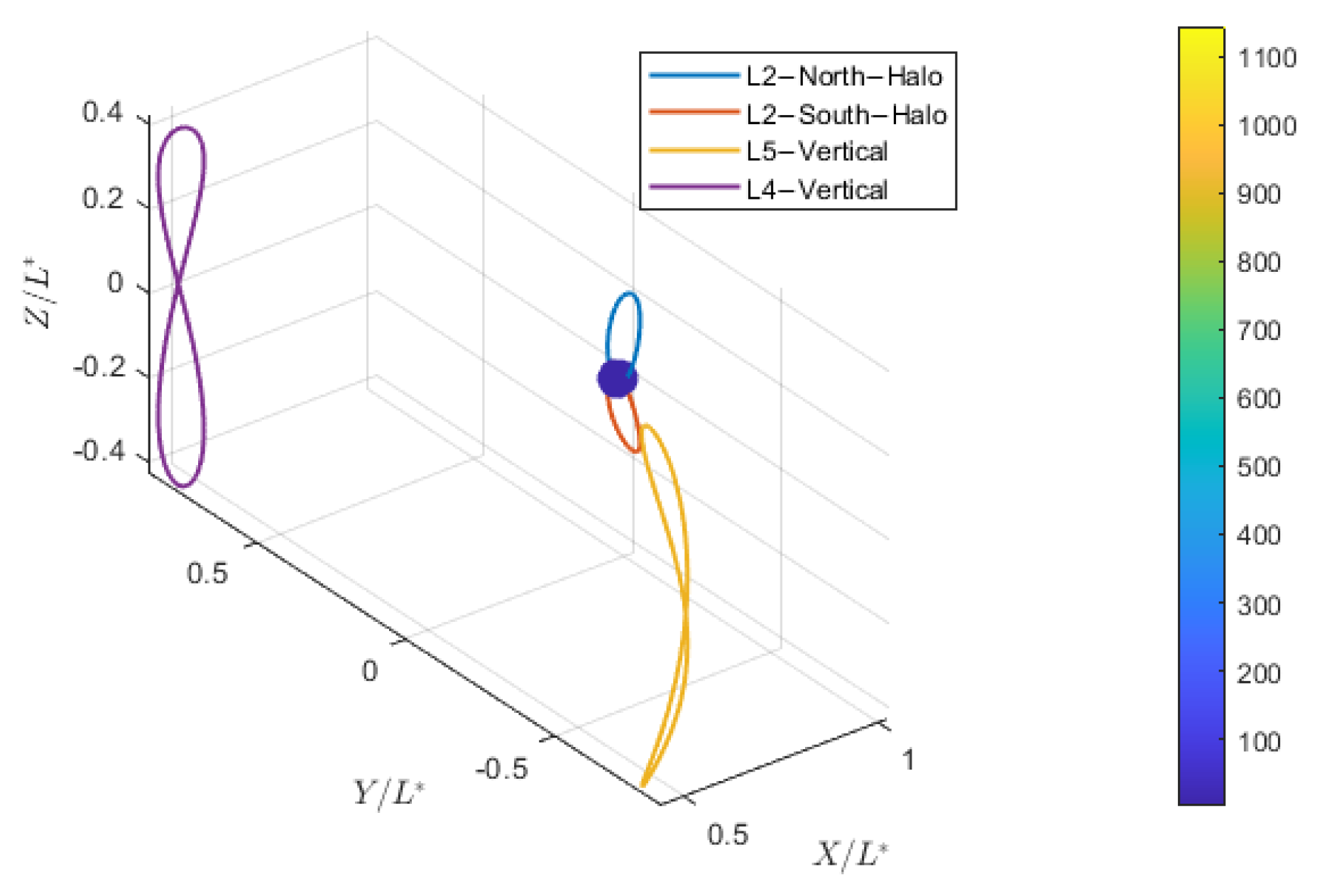
4.1.2. Lunar Region
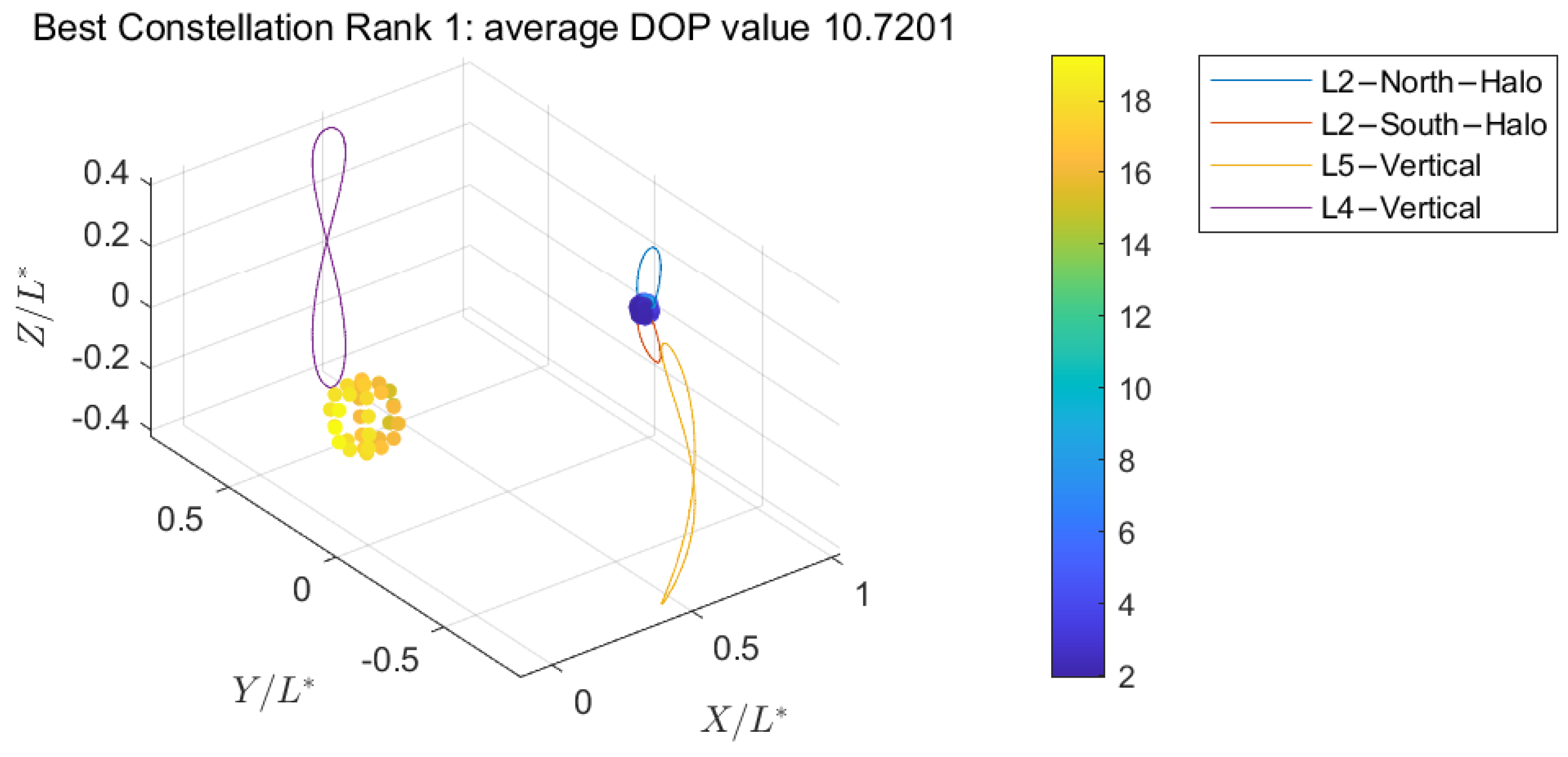
4.1.3. Combined Region
4.2. DOP Value Distribution Analysis of Resonant Constellations
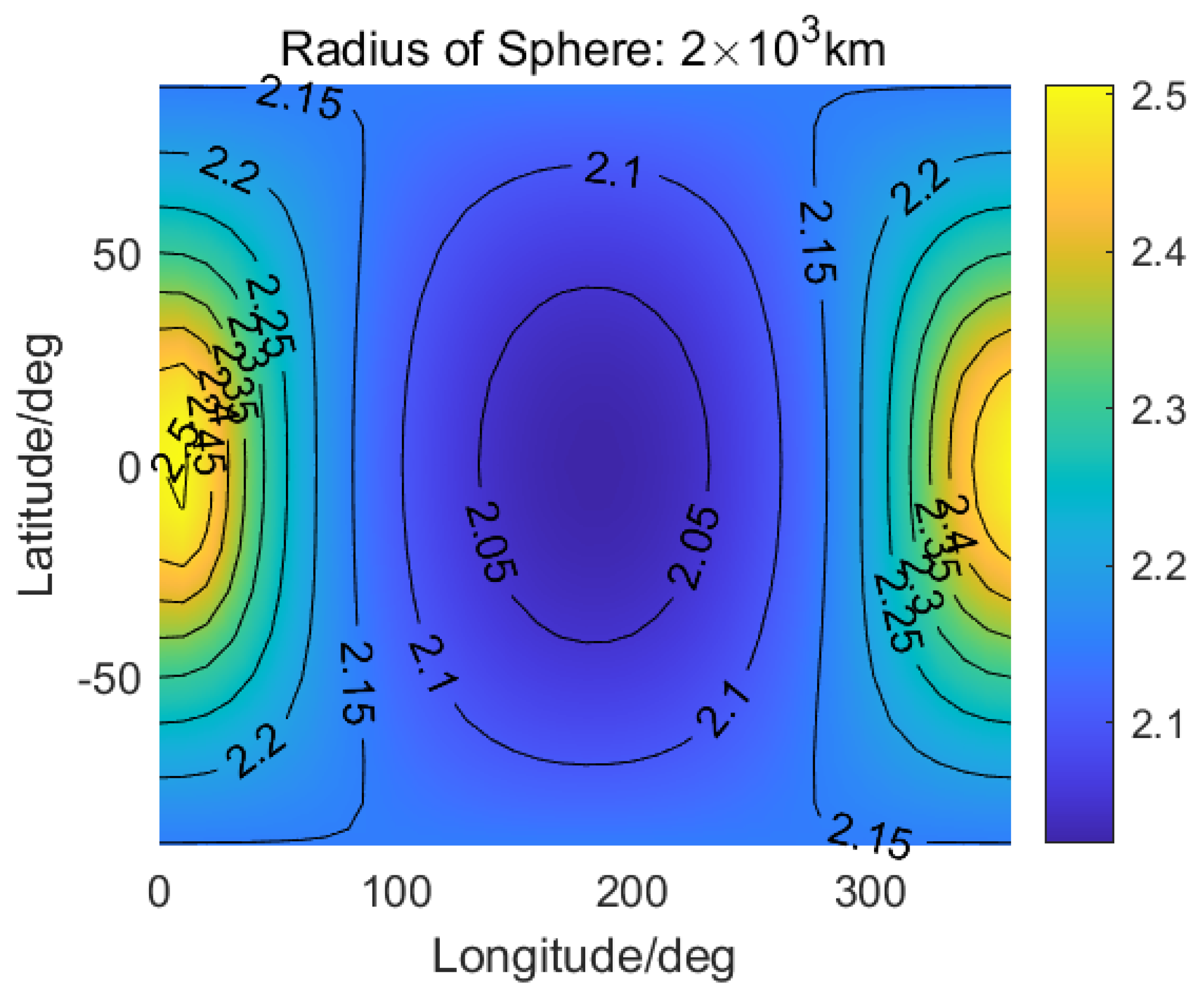
4.2.1. Performance Distribution Analysis in the Near-Earth Region
- Longitude was defined within the Earth–Moon rotating frame, with its origin set at the intersection line of the X-Z plane and the spherical surface. This line is bisected by the spherical poles, and the longitude origin corresponds to the positive X-axis direction.
- Latitude originated from the lunar orbital plane (i.e., the “White Circle” plane), with the positive direction pointing toward the spherical north pole.
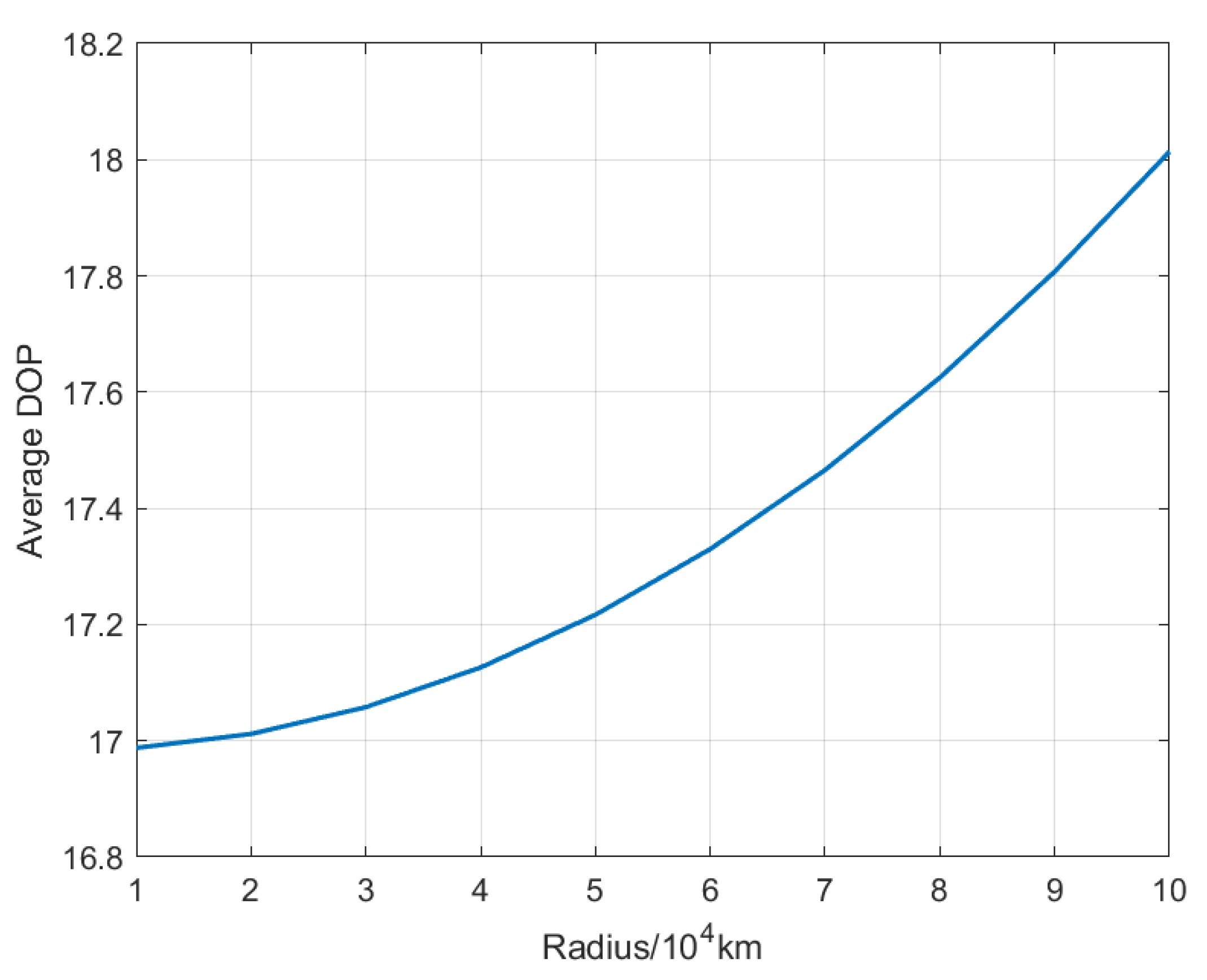
4.2.2. Performance Distribution Analysis in the Lunar Region
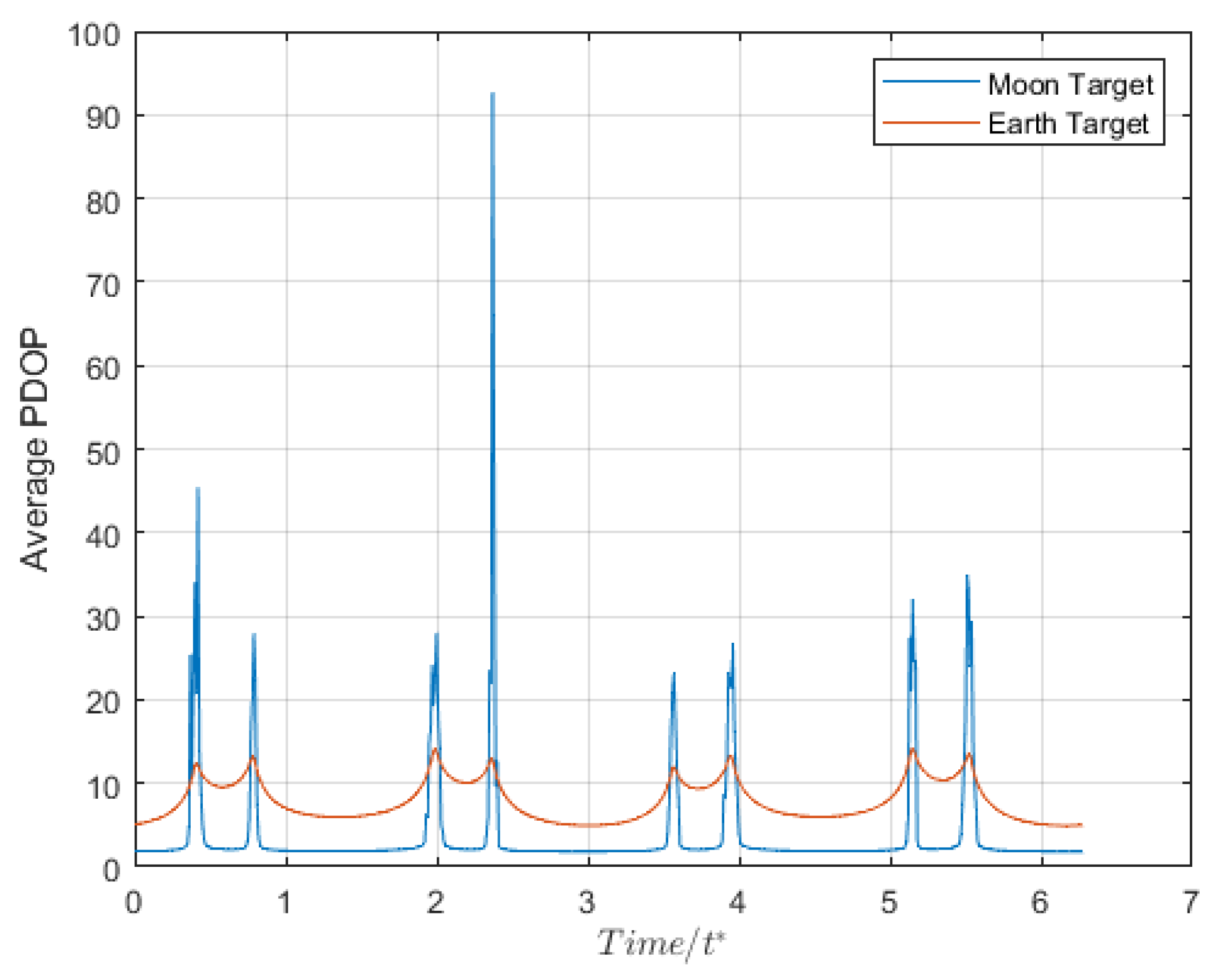
4.2.3. Time-Varying Pattern Analysis
5. Conclusions
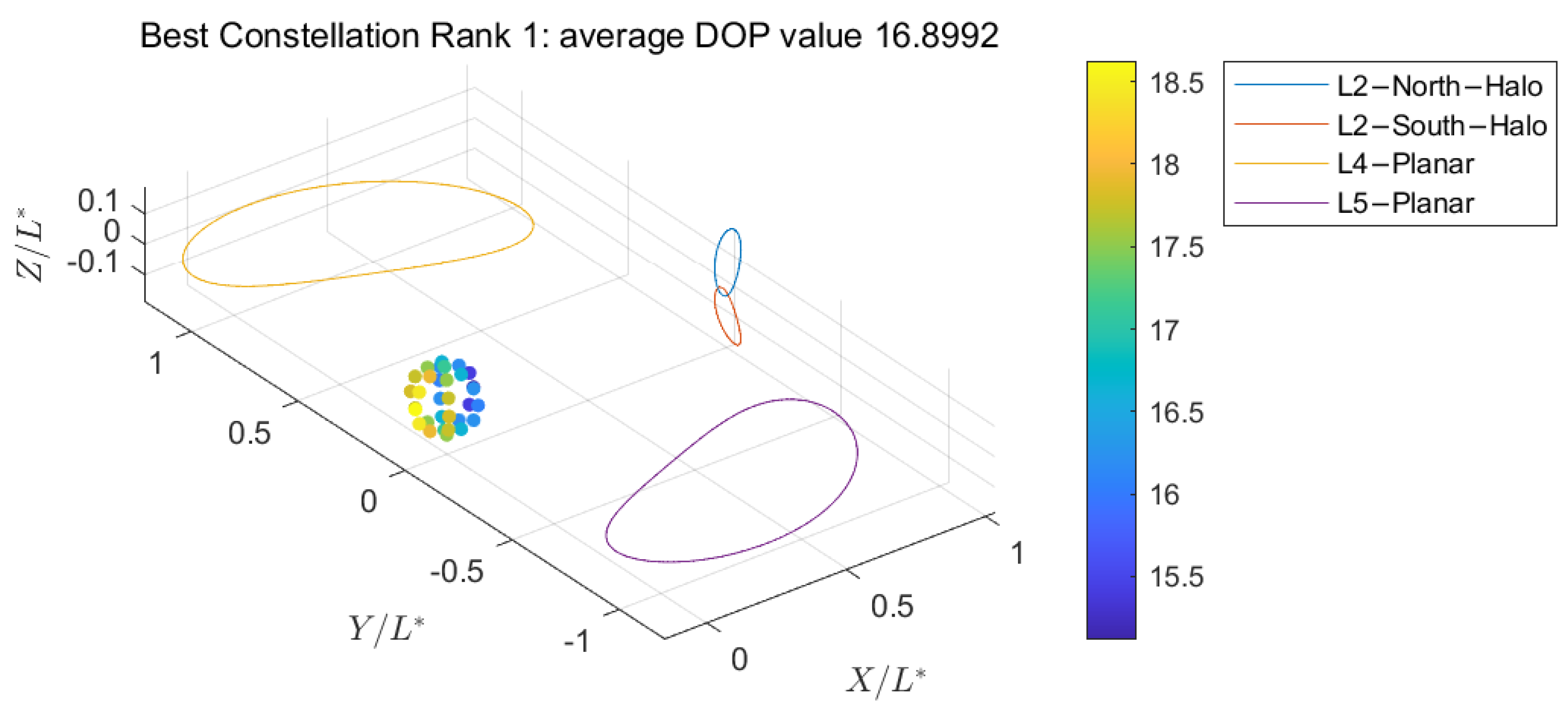
- For near-Earth regions, constellations combining L2 southern/northern NRHOs with homologous periodic orbits at L4/L5 points exhibit optimal performance.
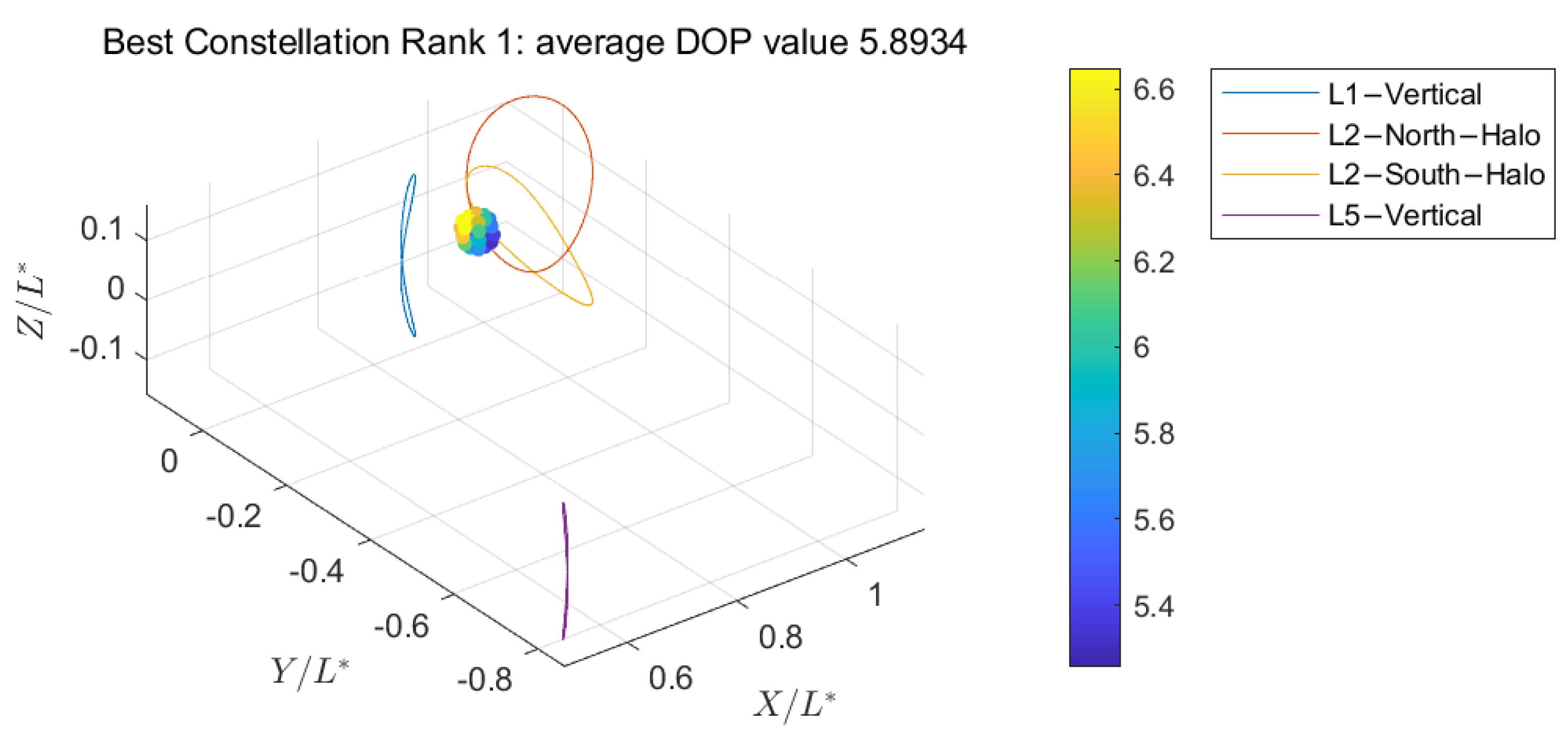
- Lunar-proximity regions achieve optimal navigation with constellations composed of L1 vertical orbits, L2 southern/northern NRHO orbits, and L4 vertical orbits.
- The combined region shares the optimal configuration with the near-Earth case.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, L.; Ma, T.; Lv, B.; Fu, Z.; Xue, C.; Zou, Y. Research of lunar water-ice and exploration for china’s future lunar water-ice exploration. Space Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 0026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Qiao, D.; Macdonald, M. Relative orbit determination using only intersatellite range measurements. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2019, 42, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Shen, M.; Wang, P.; Xin, X. Initial orbit determination of some cislunar orbits based on short-arc optical observations. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, T. Asteroid approaching orbit optimization considering optical navigation observability. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 5165–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Huo, Z.; Meng, L.; Huang, J. Near-earth asteroid surveillance constellation in the sun-venus three-body system. Space Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, D.; Cui, P. Analysis of two-impulse capture trajectories into halo orbits of Sun–Mars system. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2014, 37, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Jia, F.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. A review of orbital mechanics for space-based gravitational wave observatories. Space Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 0015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiao, D.; Circi, C. Mars high orbit capture using manifolds in the sun–Mars system. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2020, 43, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiao, D.; Li, P. Bounded trajectory design and self-adaptive maintenance control near non-synchronized binary systems comprised of small irregular bodies. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 152, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, P.; Fu, S.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, W. Requirement-Oriented TT&C Method for Satellite Based on BDS-3 Short-Message Communication System. Space Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 0038. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Macdonald, M.; Qiao, D. Fully decentralized cooperative navigation for spacecraft constellations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, R.W. The Control and Use of Libration-Point Satellites; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, J.R.; Folta, D.; Moreau, M.; Quinn, D. Libration point navigation concepts supporting the vision for space exploration. In Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, Providence, RI, USA, 16–19 August 2004; p. 4747. [Google Scholar]
- Romagnoli, D.; Circi, C. Lissajous trajectories for lunar global positioning and communication systems. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 2010, 107, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circi, C.; Romagnoli, D.; Fumenti, F. Halo orbit dynamics and properties for a lunar global positioning system design. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 3511–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, S. A new constellation configuration scheme for communicating architecture in cislunar space. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 864950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.H.; Chen, Q.F. Outline design and performance analysis of navigation constellation near earth-moon libration point. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63, 248402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, B. A universe light house—Candidate architectures of the libration point satellite navigation system. J. Navig. 2014, 67, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Bai, X. Natural deep space satellite constellation in the Earth-Moon elliptic system. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 153, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, J.C.; Neto, A.G.S.; Fernandes, S.S.; de Moraes, R.V.; Terra, M.O. Artificial satellites orbits in 2: 1 resonance: GPS constellation. Acta Astronaut. 2012, 81, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Shimizu, S.; Yoshikawa, S.; Ho, K. Satellite constellation pattern optimization for complex regional coverage. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2020, 57, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H. Midcourse correction of Earth-Moon distant retrograde orbit transfer trajectories based on high-order state transition tensors. Astrodynamics 2023, 7, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebow, D. Generating Periodic Orbits in the Circular Restricted Three-Body Problem with Applications to Lunar South Pole Coverage. MSAA Thesis, School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2006; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vutukuri, S. Spacecraft Trajectory Design Techniques Using Resonant Orbits. Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jorba, A.; Masdemont, J. Dynamics in the center manifold of the collinear points of the restricted three body problem. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1999, 132, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cheng, Y.; Qiao, D.; Huo, Z. An adaptive surrogate model-based fast planning for swarm safe migration along halo orbit. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 194, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, W.; Qiao, D.; Li, X. Effect of orbital shadow at an Earth-Moon Lagrange point on relay communication mission. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, D.; Meng, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Cui, H. Performance of BDS-3: Satellite visibility and dilution of precision. Gps Solut. 2019, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, O.S.; Connolly, J.W.; Welch, B.W.; Carpenter, J.R.; Ely, T.A.; Berry, K. Dilution of precision-based lunar navigation assessment for dynamic position fixing. In Proceedings of the 2006 National Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, Monterey, CA, USA, 18–20 January 2006; pp. 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Marzullo, A. Constellation Optimization. Doctoral Dissertation, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yarlagadda, R.; Ali, I.; Al-Dhahir, N.; Hershey, J. Gps gdop metric. IEE Proc.-Radar Sonar Navig. 2000, 147, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type Num | Position | Type | Code | Minimum Period/ | Maximum Period/ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Moon | DRO | DRO | 2.7261 | 5.9373 |
| 2 | L1 | Lyapunov | L1L | 2.6930 | 7.4280 |
| 3 | North Halo | L1NH | 1.8037 | 2.7875 | |
| 4 | South Halo | L1SH | 1.8037 | 2.7875 | |
| 5 | Vertical | L1V | 2.7695 | 5.6891 | |
| 6 | L2 | Lyapunov | L2L | 3.3735 | 6.1671 |
| 7 | North Halo | L2NH | 1.3739 | 3.4155 | |
| 8 | South Halo | L2SH | 1.3739 | 3.4155 | |
| 9 | Vertical | L2V | 3.5177 | 5.7857 | |
| 10 | L3 | Lyapunov | L3L | 6.2184 | 6.2272 |
| 11 | North Halo | L3NH | 6.2356 | 6.2391 | |
| 12 | South Halo | L3SH | 6.2356 | 6.2391 | |
| 13 | Vertical | L3V | 6.2499 | 6.2502 | |
| 14 | L4 | Planar | L4P | 6.2832 | 6.2869 |
| 15 | Vertical | L4V | 6.5391 | 6.5827 | |
| 16 | L5 | Planar | L5P | 6.2832 | 6.2869 |
| 17 | Vertical | L5V | 6.5391 | 6.5827 |
| Rank | Resonant Configuration | Baseline Period | Resonance Ratio | Mean DOP | DOP SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L2NH-L2SH-L4P-L5P | 1.5715 | 1:1:4:4 | 16.90 | 3.14 |
| 2 | L2NH-L2SH-L4V-L5V | 1.5715 | 1:1:4:4 | 17.00 | 3.19 |
| 3 | L1NH-L1SH-L4V-L5V | 2.0947 | 1:1:3:3 | 22.01 | 3.98 |
| 4 | L1NH-L1SH-L4P-L5P | 2.1812 | 1:1:3:3 | 24.12 | 5.01 |
| 5 | L1NH-L2SH-L5V-L4V | 2.0947 | 1:1:3:3 | 22.30 | 21.70 |
| Rank | Resonant Configuration | Baseline Period | Resonance Ratio | Mean DOP | DOP SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L1V-L2NH-L2SH-L4V | 3.1417 | 1:1:1:2 | 5.89 | 2.07 |
| 2 | L1V-L2NH-L2SH-L5V | 3.1417 | 1:1:1:2 | 5.89 | 2.66 |
| 3 | L1V-L2NH-L2SH-DRO | 2.7695 | 1:1:1:1 | 10.65 | 4.57 |
| 4 | L1V-L2NH-L1NH-L1SH | 2.7695 | 1:1:1:1 | 8.46 | 13.80 |
| 5 | L1L-L2L-L4P-L5P | 3.2693 | 2:3:4:4 | 15.38 | 2.62 |
| Rank | Resonant Configuration | Baseline Period | Resonance Ratio | Mean DOP | DOP SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L2NH-L2SH-L4V-L5V | 1.5715 | 1:1:4:4 | 10.72 | 24.53 |
| 2 | L2NH-L2SH-L4P-L5P | 1.6352 | 1:1:4:4 | 10.86 | 27.70 |
| 3 | L2SH-L1NH-L4V-L5V | 2.0946 | 1:1:3:3 | 15.20 | 50.58 |
| 4 | L2SH-L1NH-L4P-L5P | 2.1801 | 1:1:3:3 | 16.84 | 92.86 |
| 5 | L2NH-L1SH-L4P-L4P | 2.1801 | 1:1:3:3 | 16.84 | 92.86 |
| Type Code | X | Y | Z | VX | VY | VZ | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2NH | 1.026597 | 0 | 0.18507 | 0 | −0.1130 | 0 | 1.57146 |
| L2SH | 1.026597 | 0 | −0.1851 | 0 | −0.1130 | 0 | 1.57146 |
| L4V | 0.509526 | 0.85287 | 0.00225 | 0.07968 | −0.0487 | 0.4244 | 6.28584 |
| L5V | 0.508670 | −0.8534 | 0.00225 | −0.0806 | −0.0467 | 0.4243 | 6.28584 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, P.; Han, H.; Huo, Z.; Yang, Z. Design of Cislunar Navigation Constellation via Orbits with a Resonant Period. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094998
He J, Chen X, Tian P, Han H, Huo Z, Yang Z. Design of Cislunar Navigation Constellation via Orbits with a Resonant Period. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094998
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jiaxin, Xialan Chen, Peng Tian, Hongwei Han, Zimin Huo, and Zhihao Yang. 2025. "Design of Cislunar Navigation Constellation via Orbits with a Resonant Period" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094998
APA StyleHe, J., Chen, X., Tian, P., Han, H., Huo, Z., & Yang, Z. (2025). Design of Cislunar Navigation Constellation via Orbits with a Resonant Period. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094998






