Smart Buildings and Digital Twin to Monitoring the Efficiency and Wellness of Working Environments: A Case Study on IoT Integration and Data-Driven Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.2. Research Objective
2. Methodology
- Manage IoT data in real time and store it in dedicated DBs;
- Real-time data visualization using three-dimensional models;
- Application of machine learning models to the data for its interpretation, prediction and processing of aggregated metrics on dashboards optimized for human–computer interaction;
- Implementations on physical elements based on collected data;
- Maintenance and management of infrastructure with appropriate security standards at different levels of access;
- Use of open data to share information with external databases (maintaining security levels).
2.1. Functional Requirements
- Analysis and forecasting of the power consumption of the main equipment that make up the case study:
- monitoring of electrical consumers using smart plugs to analyze instantaneous and average power (W), status (on-off) and time of use (min);
- monitoring the consumption of electric actuators (door and window movement) in terms of instantaneous power (W), status (on-off) and time of use (min);
- monitoring of general electrical consumption of utilities, lighting, air conditioning;
- Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) monitoring and forecasting:
- analysis and prediction of air quality using dedicated sensors (tVOC, PM2.5, PM10, temperature, relative humidity, CO2) to obtain complex data (IAQ and CO2 limit UNI EN ISO 16000 [36]);
- analysis and prediction of thermal comfort using dedicated sensors (temperature, relative humidity) to obtain complex data (PMV, PPD);
- analysis and prediction of lighting comfort using dedicated sensors (luminosity);
- control of window opening (open/closed);
- Analysis of presence through dedicated sensors (presence). Possibility of counting people (number) using computer vision with dedicated cameras;
- Interoperability of communication protocols (MQTT, HTTP, etc.) and use of common standards (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Zigbee, etc.) with the possibility of external access to data [37];
- Data management on dedicated infrastructure;
- Data visualization through aggregated metrics.
2.2. System Requirements
- Communication protocols used:
- MQTT for environmental sensors;
- HTTP for environmental sensors and video streams;
- Modbus for energy meters;
- OPC UA as an alternative to the previous points [38].
- Communication networks:
- IP over Wi-Fi (WLAN) for environmental sensors and actuators;
- IP over LAN for electricity meters and weather controllers.
- Data centralizers:
- Mosquito MQTT Broker Service;
- Schneider EcoStruxure for power-meter.
- Data platform:
- NodeRed;
- data processing using custom software ML techniques (Python 3.13, JavaScript ES 15);
- Power BI dashboard for integrated data presentation based on functional requirements;
- 3D model visualization with metadata.
- Database (long-term storage of 3 years or 1 Tb of data):
- PostgreSQL;
- InfluxDB;
- SQLlite.
- Linux data server and local processing and virtualization with GPU video processing capability:
- Multicore CPU with at least 8 cores, 16 threads, 2.2 ghz;
- 1Tb storage;
- CUDA hardware GPU with 12 gb RAM for AI algorithm processing and video stream display;
- 64 gb RAM;
- PSU with uninterruptible power supply.
- Machine learning systems based on open source and commercial libraries with potential use of dedicated data processing software (e.g., KNIME 4.18);
- Sensor accuracy based on devices on the market for home automation;
- Multi-user access from the DT platform based on concepts inherited from ISO 27000 [39] in order to guarantee at least one user and one administrator level.
2.3. Key Performance Indicators
- Monitoring and forecasting of electrical and thermal consumption at the integrated level of the rooms and of each element connected to the system (W, kWh, time);
- Monitoring and prediction of indoor air quality (IAQ, CO2, time) and thermal comfort (PMD, PVM, time);
- Monitor and predict occupancy (people/time);
- Optimization of thermal comfort, air quality and noise reduction by creating specific algorithms for the movement of windows and doors;
- Reducing energy consumption and noise and improving indoor air quality and environmental comfort through the creation of dedicated algorithms for space utilization proposals;
- Real-time monitoring through data visualization via 3D models and dashboards;
- Data storage for 3 years;
- Maintaining data security through authentication systems for multi-user access to the platform;
- Maintenance of system interoperability through the use of standard communication protocols (MQTT, HTTP, API, REST, ONVIF, etc.).
2.4. Validation Matrix
3. System Development
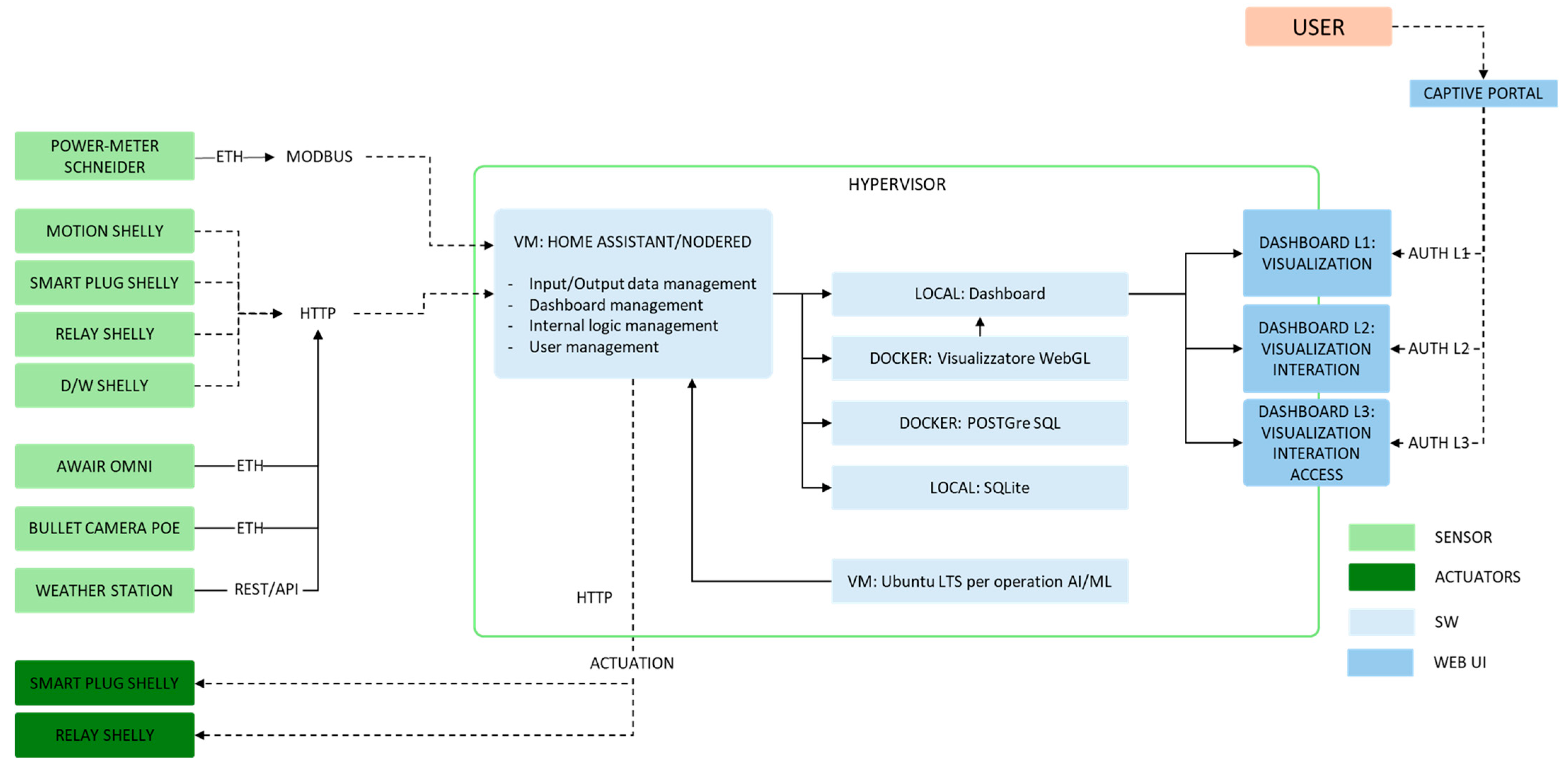
3.1. Software Architecture
3.2. Communication Protocols
3.3. Data Platform
- Node-RED: a platform developed by IBM, now open source, based on JavaScript Node.js for event and peripheral management, it supports workflow through nodes and offers great flexibility [40].
- Open Hab, an event and peripheral management platform developed by IntelliJ, based on Java, has a web-based approach to event creation and management. The platform supports over 200 different OEMs through the use of bindings. Built-in support for application management [41].
- Open Remote, a Java-based platform that provides a web-based approach to creating and managing peripherals. App-based management support possible [42].
- Home Assistant, platform developed in Python (https://www.python.org/), combined with a web-based approach, with support for agnostic hardware from any vendor, and support for management via integrated app [43].
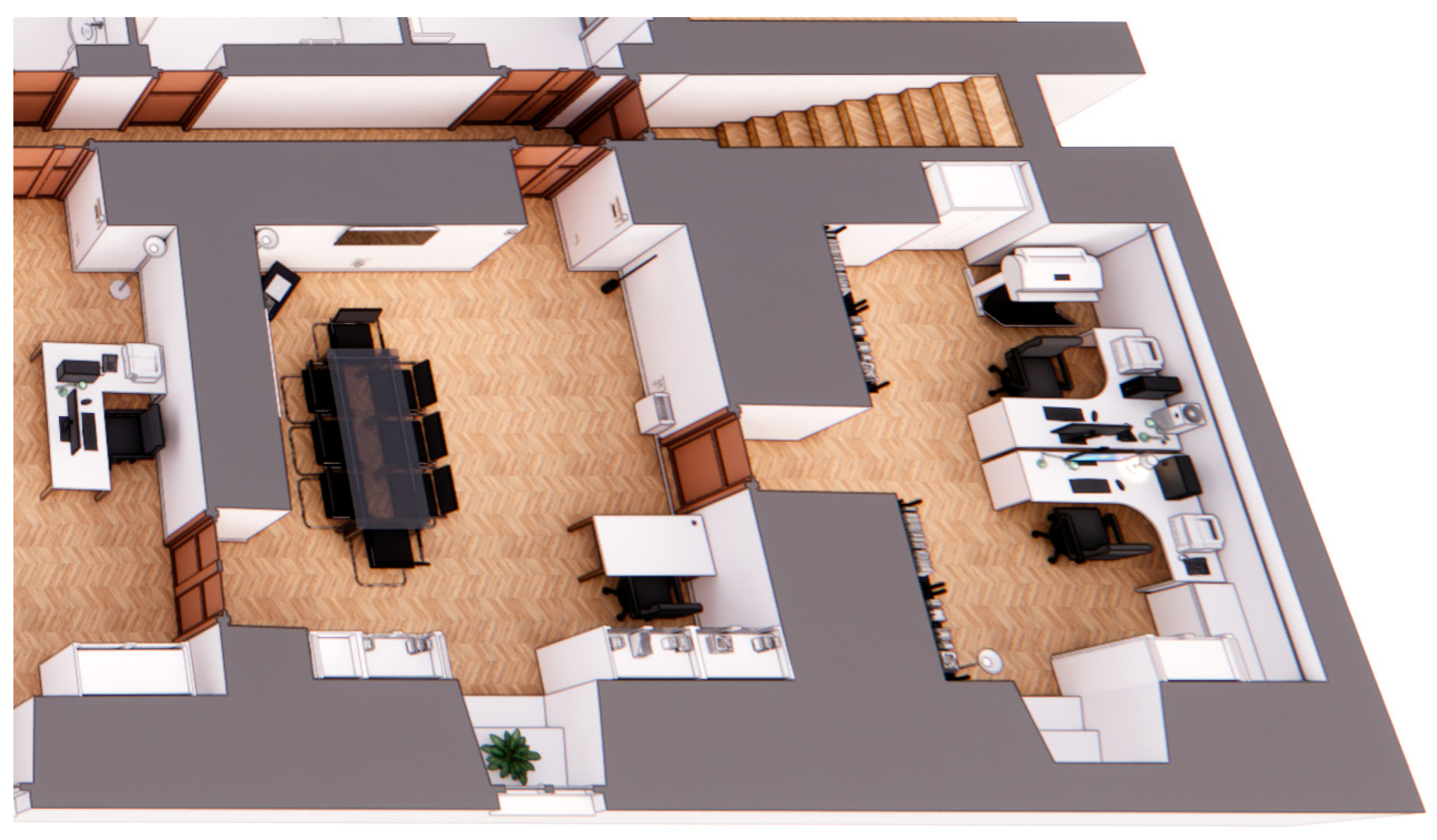
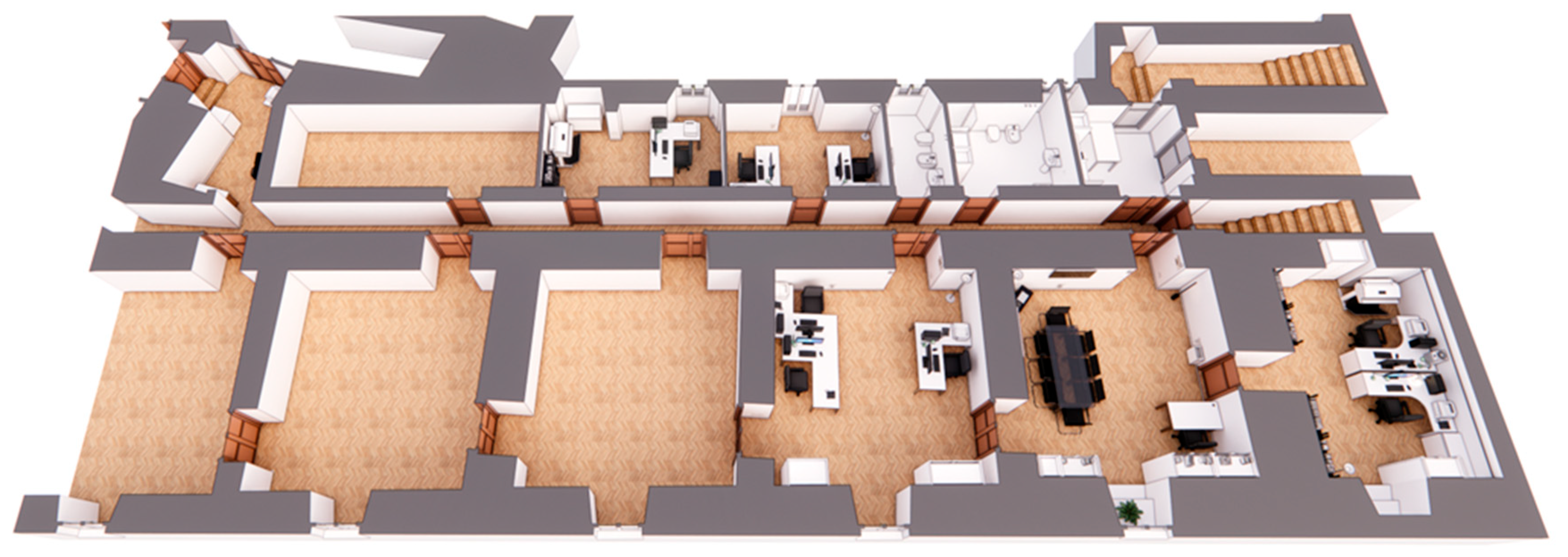
4. Case Study
- Energy management and efficiency;
- Indoor air quality control;
- Predictive maintenance;
- Management and optimization of office space.
- In individual offices, the main challenge lies in the customization of environmental comfort conditions. Occupants may have individual preferences in terms of parameters such as temperature, lighting and ventilation. The DT must therefore implement advanced predictive models to optimize the adjustment of these parameters while maintaining a balance between user satisfaction and energy consumption reduction. Machine learning systems, based on historical data analysis, can be used to identify individual preference patterns and dynamically adapt the operation of systems.
- Open space offices have very different operational dynamics, with occupancy levels that can vary significantly throughout the day. In this context, it is necessary to implement strategies that balance the thermal and lighting comfort of several people at the same time. Computational models based on thermal and lighting simulations can be integrated into the DT to optimize the distribution of energy resources. In addition, the use of distributed sensors allows the system to monitor changes in occupancy in real time and adjust system settings for optimal energy efficiency.
- Service environments, such as buvette, present a particular challenge in terms of intermittent use. In these spaces, peaks in occupancy occur at short intervals, requiring dynamic management of lighting and air conditioning systems. The DT can use presence detection algorithms and occupancy prediction models to activate systems only when necessary, minimizing energy waste. At the same time, the analysis of the collected data allows the detection of any anomalies in the operation of the systems and the planning of proactive maintenance interventions.
- In the printing area, the main critical issue is the discontinuous use of electronic equipment such as printers and copiers and the management of air pollutants produced by these devices. These include ultra-fine particles, nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can have a negative impact on indoor air quality. DT needs to integrate pollutant dispersion models and advanced ventilation strategies, possibly supported by the use of high-efficiency filters and air cleaners. Continuous monitoring of equipment status allows the identification of inefficient usage conditions or potential failures, promoting predictive maintenance, optimizing energy consumption and minimizing operational downtime.
4.1. Electricity Consumption Sensors
4.2. Motion Sensors
4.3. IAQ Sensors
4.4. IEQ Sensors
4.5. Lighting Sensors
4.6. Actuators
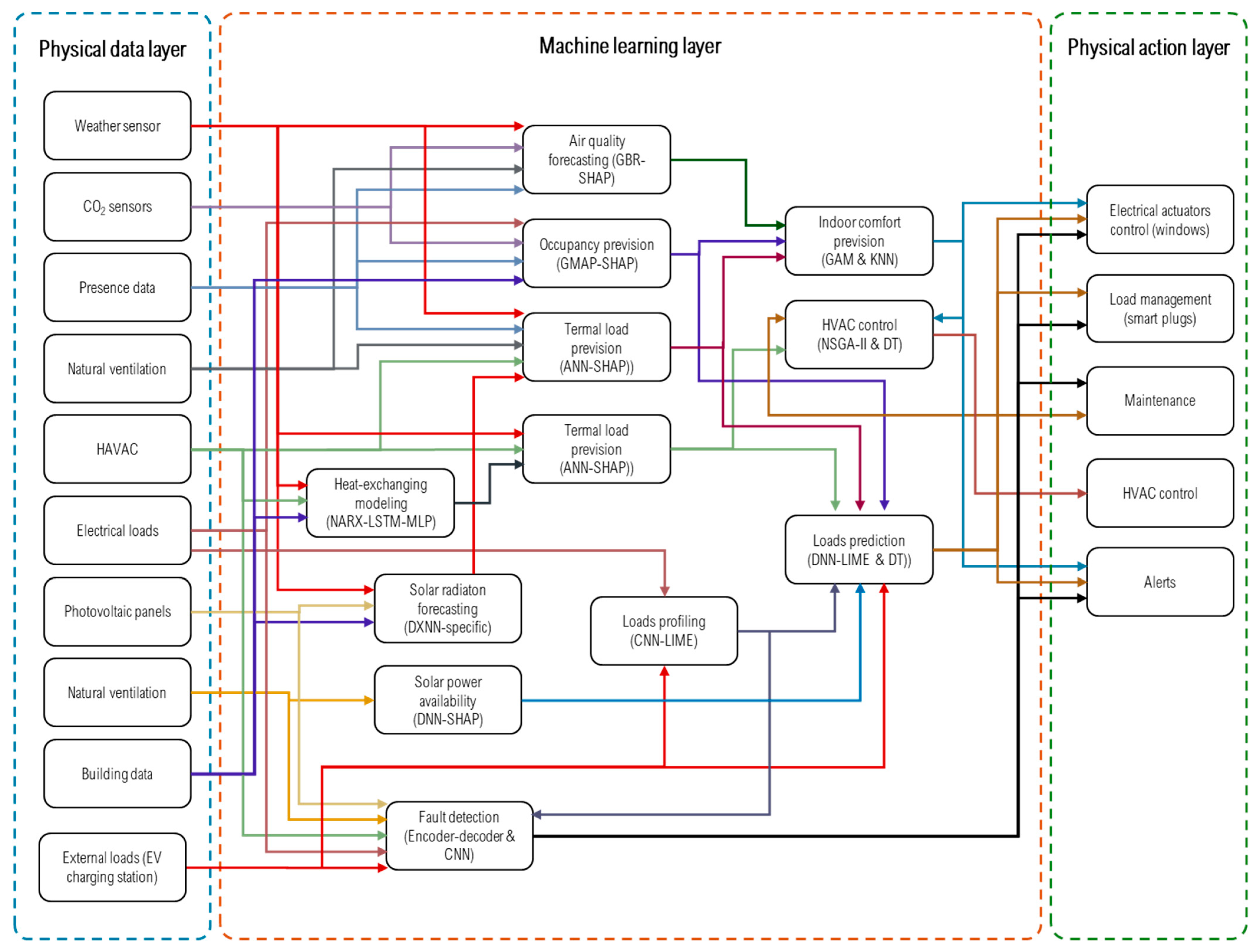
5. Machine Learning Algorithms
- Air quality can be assessed using a Gradient Boosting Regression (GBR) model in conjunction with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP). This model can act both as a classifier—categorizing air quality as poor, fair or good—and as a regressor to estimate predicted values. The GBR-SHAP model is applicable to both indoor and outdoor air quality assessments and can be used as an input to comfort estimation and load prediction models, especially when integrated with a ventilation system model. For natural ventilation prediction, a Deep Q-Network (DQN) model can be used to analyze the impact of window openings on air quality, particularly in scenarios where elevated outdoor particulate matter (PM) concentrations are expected. The use of SHAP allows users to interpret the model predictions and gain insight into the expected air quality conditions in the coming hours. In addition, the input data can be supplemented with information from local weather services to improve forecast accuracy.
- Thermal loads contribute significantly to the overall energy consumption of a building. ML techniques can be used to assess the impact of external environmental conditions on total heat loss and to evaluate potential interventions to improve building insulation. For thermal load modelling, an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) combined with Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) can be used to improve the interpretability of the results [46]. In high natural ventilation scenarios, such as Near Zero Energy Buildings (NZEBs), it is possible to isolate and quantify the contribution of natural ventilation to thermal loads using an ANN model with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) [47]. Identifying the most influential factors affecting thermal loads allows the detection of critical inefficiencies that should be addressed to improve the overall energy performance of the building. The thermal load prediction model uses input data related to weather conditions, occupancy levels, natural ventilation rates, HVAC system operation, and building geometries and materials. The output of the model can then be used as input for electrical power supply models and air quality prediction models.
- The aim of this model is to evaluate the indoor thermal comfort of a building. Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) have been identified as particularly suitable for thermal comfort prediction tasks [48]. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) and Decision Tree models can be used to generate warnings and provide recommendations to users and stakeholders. It is important to note that thermal comfort is subject to regulatory standards, as described in EN ISO 7730. Therefore, it is recommended to include empirical rules to ensure that the model keeps comfort levels within an acceptable range. The model takes data from air quality forecasting, occupancy forecasting and thermal load forecasting as input. Generated outputs include real-time alerts, activation of building electrical actuators (e.g., automated window opening), and data transfer to the HVAC control model for further optimization.
- Load profiling is essential to understand the devices connected to an electrical network and to detect potential faults in the system. To address this task, a machine learning model based on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) has been proposed, complemented with Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME) to improve the interpretability of the CNN model [49]. The implementation of a load profiling model is also valuable for detecting fraudulent energy consumption and identifying malicious users, as demonstrated by Wang et al. [50]. In addition, accurate load profiling is a critical requirement for decision makers involved in building energy management and optimization. The model uses data input from electrical loads (e.g., HVAC systems, lifts) and external loads (e.g., electric vehicle charging stations). The generated energy profiles serve as input for subsequent load forecasting models, enabling more efficient energy management.
- Load prediction is a fundamental objective of any energy monitoring system using machine learning techniques. Numerous studies in literature have explored different methodological approaches to address this challenge. As a reference, Geyer et al. proposed a DNN model enhanced with LIME for improved interpretability [51]. In addition, other researchers have developed alerts and recommendations based on decision tree models [52]. The ability to interpret load predictions is a critical requirement for stakeholders as it enables effective management of the energy system, identification of dominant loads, and the development of comprehensive energy reports to assess the energy classification of a building. This model uses data input from the HVAC efficiency prediction model, load profile prediction, solar energy prediction, thermal load prediction and occupancy prediction. The model’s output includes real-time alerts, actuator controls and maintenance recommendations, enabling optimal energy management and operational efficiency.
6. Results
6.1. Air Quality Forecasting
6.2. Thermal Comfort
- -
- Temperature: indoor temperatures should be maintained between 18 °C and 22 °C during winter and between 23 °C and 26 °C during summer. These temperature ranges have been determined to enhance comfort and efficiency while minimising health risks associated with extreme cold or heat exposure. The same ranges are considered optimal for most individuals based on the Perceived Mean Vote (PMV) model;
- -
- Humidity: the relative humidity should be maintained between 50% and 80% to prevent excessively dry air, which can lead to respiratory issues, and to inhibit the growth of pathogens and allergens.
- -
- Thermal comfort and energy efficiency: maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels is directly linked to occupant thermal comfort. By ensuring appropriate indoor environmental conditions that minimize the reliance on energy-intensive systems (such as heating and air conditioning units), significant energy savings can be achieved.
- -
- Data-driven operational decisions: the collection of real-time environmental data from temperature and humidity sensors enables informed decision-making regarding energy usage optimization. For instance, real-time monitoring allows for the dynamic adjustment of lighting and electronic devices, which contribute to indoor heat generation. By strategically managing these systems, comfortable conditions can be maintained while minimizing energy consumption.
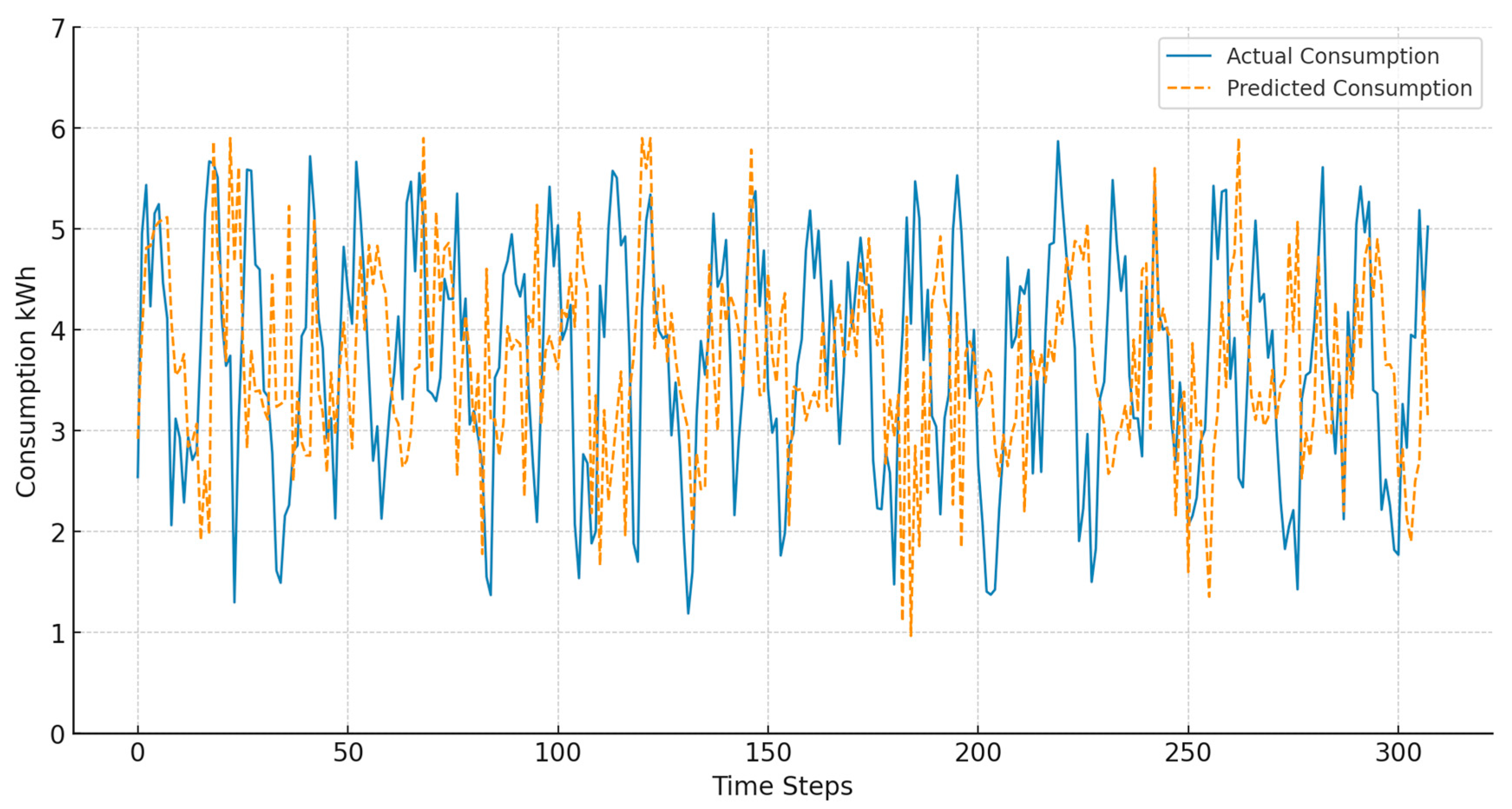
6.3. Power Consumption
6.4. Data Preparation and Training
- Data loading and cleanup: the dataset was initially retrieved from the database. Preliminary processing steps, such as interpolating missing values, were applied to maintain data integrity and ensure that the model is trained on a complete and coherent dataset.
- Temporal aggregation to hourly intervals: the original dataset, which was recorded at minute-level granularity, was resampled by computing hourly average values. This transformation reduces data complexity by minimizing short-term fluctuations while preserving broader temporal trends in energy consumption.
- Normalization: since LSTM networks and other neural architectures are scale-sensitive, power consumption values were normalized to a {0,1} range using the MinMaxScaler algorithm. This normalization step is crucial to enhance the stability and efficiency of the training process.
- Sequence generation: the LSTM model requires sequential input data to identify temporal dependencies. A sliding window method was applied, converting the dataset into a supervised learning problem, where a fixed number of past time steps are used to predict future values.
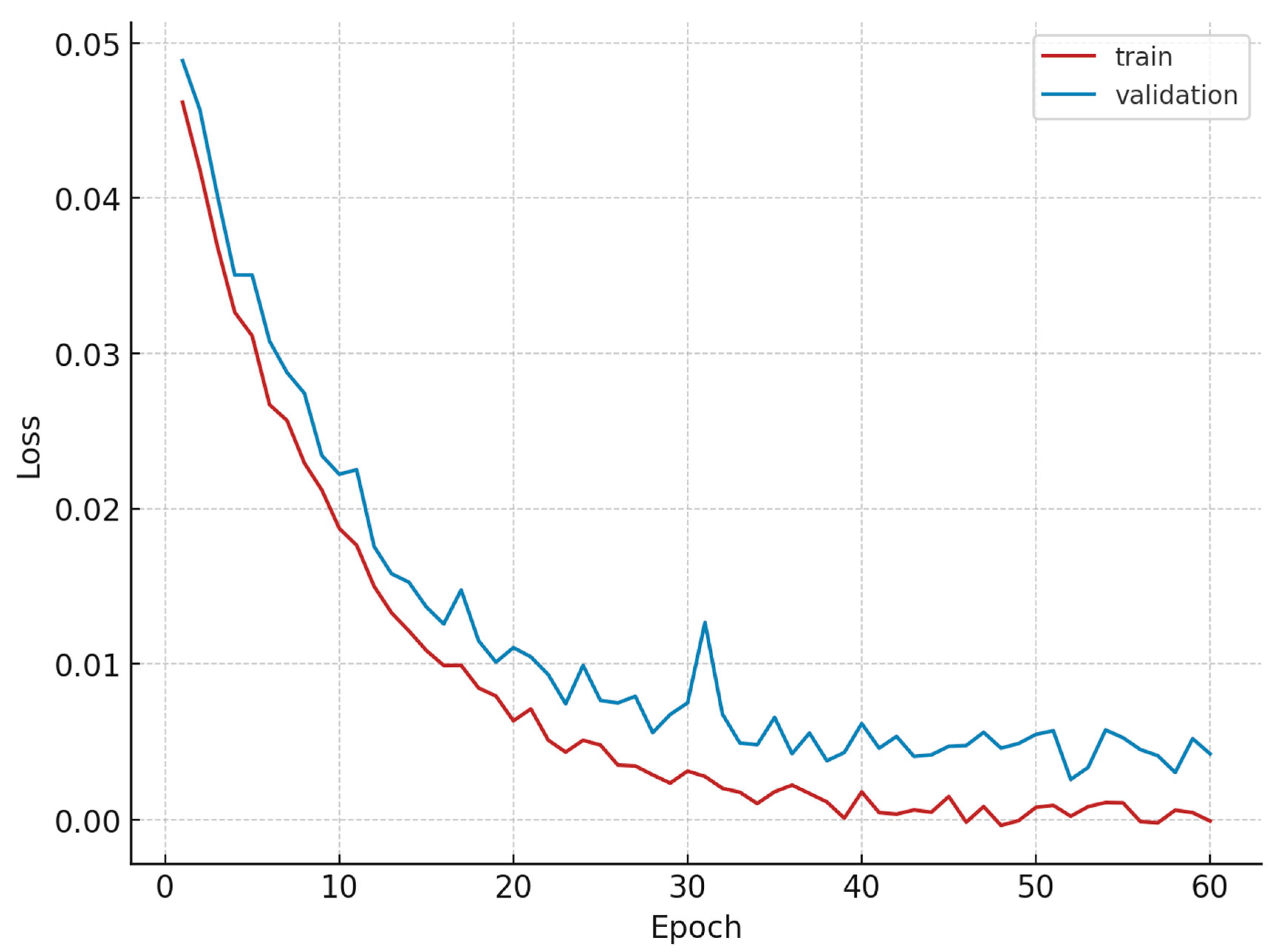
- Model architecture: the LSTM model was designed to capture both short-term and long-term correlations in the data. Additionally, dropout layers were incorporated into the architecture to mitigate overfitting, by randomly omitting units during training, thus enhancing the model’s generalization ability.
- Training and validation: the model was trained using the preprocessed time-series sequences, with a portion of the dataset reserved for validation purposes. This validation process ensured that overfitting was monitored and prevented. The training convergence curve is illustrated in Figure 8.
- Post-training evaluation: the trained model was evaluated using real-time data to assess its predictive accuracy. The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) obtained was 0.04, indicating a high level of accuracy in forecasting energy consumption trends.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| BIM | Building Information Modeling |
| BMS | Building Management System |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| CUDA | Compute Unified Device Architecture |
| DBs | Databases |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network |
| DT | Digital Twin |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
| IAQ | Indoor Air Quality |
| IEQ | Indoor Environmental Quality |
| InfluxDB | Time-Series Database |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| KNIME | Konstanz Information Miner |
| KPI | Key Performance Indicator |
| LAN | Local Area Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| Modbus | Serial communication protocol |
| MQTT | Message Queuing Telemetry Transport |
| NodeRed | Flow-based development tool for visual programming |
| ONVIF | Open Network Video Interface Forum |
| PM10 | Particulate Matter 10 |
| PM2.5 | Particulate Matter 2.5 |
| PMV | Predicted Mean Vote |
| PostgreSQL | Relational Database Management System |
| Power BI | Business Intelligence Tool by Microsoft |
| PPD | Percentage of People Dissatisfied |
| PSU | Power Supply Unit |
| REST | Representational State Transfer |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanations |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
| SQLlite | Lightweight SQL Database |
| tVOC | Total Volatile Organic Compounds |
| Wi-Fi | Wireless Fidelity |
| WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network |
References
- Vischer, J.C.; Wifi, M. The Effect of Workplace Design on Quality of Life at Work. In Handbook of Environmental Psychology and Quality of Life Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkers, A.; Yang, D.; de Vries; Baken, N. Real-Time Building Performance Monitoring using Semantic Digital Twins. In Proceedings of the LDAC2021—9th Linked Data in Architecture and Construction Workshop, Luxembourg, 11–13 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sacks, R.; Brilakis, I.; Pikas, E.; Xie, H.S.; Girolami, M. Construction with digital twin information systems. Data-Centric Eng. 2020, 1, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, W.; Wagner, A.; Schweiker, M.; Mahdavi, A.; Day, J.; Kjærgaard, M.B.; Carlucci, S.; Dong, B.; Tahmasebi, F.; Yan, D.; et al. Introducing IEA EBC annex 79: Key challenges and opportunities in the field of occupant-centric building design and operation. Build. Environ. 2020, 178, 106738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, J. Editorial Special Issue on Human Interaction with the Built Environment. Build. Environ. 2022, 228, 109879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, A.; Parisio, A.; Todd, R.; Forsyth, A. Model Predictive Control for optimizing the flexibility of sustainable energy assets: An experimental case study. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 129, 106822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnaola-Gonzalez, I.; Díez, F. Integrating Building and IoT data in Demand Response solutions. In Proceedings of the 7th Linked Data in Architecture and Construction Workshop (LDAC 2019), Lisbon, Portugal, 19–21 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Maturo, A.; Vallianos, C.; Buonomano, A.; Athienitis, A. Model predictive control for energy flexibility of a building coupled with advanced solar and energy storage technologies. In Proceedings of the SDEWES 2022, 17th Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems, Paphos, Cyprus, 6–10 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Al Horr, Y.; Arif, M.; Katafygiotou, M.; Mazroei, A.; Kaushik, A.; Elsarrag, E. Impact of indoor environmental quality on occupant well-being and comfort: A review of the literature. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2016, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.; Gunay, B.; Miller, C.; Hahn, J.; Ouf, M.M.; Lee, S.; Hobson, B.W.; Abuimara, T.; Bandurski, K.; André, M.; et al. Ten questions concerning occupant-centric control and operations. Build. Environ. 2023, 242, 110518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.; Elmansoury, O.; Yaagoubi, R. Dynamic Predicted Mean Vote: An IoT-BIM integrated approach for indoor thermal comfort optimization. Autom. Constr. 2021, 129, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yu, X.; Liang, Q.; Yu, P.; Xie, Z.; Xia, L.; Qin, M. Intelligent Monitoring and Visualization System for High Building Nighttime Utilization Based on Image Processing. Sensors 2024, 24, 6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, T.-W.; Mui, K.-W.; Wong, L.-T.; Chan, A.C.-Y.; Chan, R.C.-W. Real-Time Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) Monitoring Using an IoT-Based Wireless Sensing Network. Sensors 2024, 24, 6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Zhao, Y. Optimizing energy consumption in smart buildings: A model for efficient energy management and renewable integration. Energy Build. 2024, 323, 114754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.N.; Bensaali, F.; Himeur, Y.; Dimitrakopoulos, G.; Varlamis, I. Enhancing building sustainability: A Digital Twin approach to energy efficiency and occupancy monitoring. Energy Build. 2025, 328, 115151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrokapnidis, D.; Katsigarakis, K.; Pauwels, P.; Petrova, E.; Korolija, I.; Rovas, D. A linked-data paradigm for the integration of static and dynamic building data in digital twins. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM International Conference on Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Cities, and Transportation, Coimbra, Portugal, 17–18 November 2021; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, S.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Najafi, M.; Rahimian, F.; Park, C.; Lee, D. Digital twin applications for overcoming construction supply chain challenges. Autom. Constr. 2024, 167, 105679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, G.B. Digital Twin Research in the AECO-FM Industry. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 40, 102730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshood, T.D.; Rotimi, J.O.B.; Shahzad, W.; Bamgbade, J.A. Infrastructure digital twin technology: A new paradigm for future construction industry. Technol. Soc. 2024, 77, 102519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Chong, A.; Miller, C. Personal thermal comfort models using digital twins: Preference prediction with BIM-extracted spatial–temporal proximity data from Build2Vec. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.; Pan, Z. Intelligent control of building fire protection system using digital twins and semantic web technologies. Autom. Constr. 2023, 147, 104728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruttini, A.; Hagedorn, P.; Cleve, F.; Getuli, V.; Capone, P.; König, M. A Semantic Digital Twin Prototype for Workplace Performance Assessment. In CONVR 2023—Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Construction Applications of Virtual Reality; Firenze University Press: Florence, Italia, 2023; pp. 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, P.; Shou, W.; Sadick, A.M. Digital Twin-driven approach to improving energy efficiency of indoor lighting based on computer vision and dynamic BIM. Energy Build. 2022, 270, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polter, M.; Scherer, R.J. Management of BIM-based digital twins in multimodels. In ECPPM 2022—eWork and eBusiness in Architecture, Engineering and Construction 2022; CRC Press: London, UK, 2023; pp. 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BuildingSMART, Industry Foundation Classes (IFC). Available online: https://www.buildingsmart.org/standards/bsi-standards/industry-foundation-classes/ (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- BuildingSMART Data Dictionary (bSDD). Available online: https://www.buildingsmart.org/users/services/buildingsmart-data-dictionary/ (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Kifouche, A.; Baudoin, G.; Hamouche, R.; Kocik, R. Generic sensor network for building monitoring: Design, issues, and methodology. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Wireless Sensors (ICWiSe), Miri, Malaysia, 13–14 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Lee, G.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.; Jeon, K. Automated generation of a model view definition from an information delivery manual using idmXSD and buildingSMART data dictionary. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 54, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Ramos, A.; Pina, E.; Váz, P.; Silva, J.; Abbasi, M. Smart Building Control: An Android Application for Enhanced Monitoring and Management in the Internet of Things Era. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 238, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakalis, D.; Hellwig, R.T.; Schweiker, M.; Gauthier, S. Challenges and opportunities of Internet-of-Things in occupant-centric building operations: Towards a life cycle assessment framework. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 65, 101383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasiev, V.; Pătru, G.C.; Rosner, D.; Sava, G.; Necula, H.; Badea, A. Enhancing environmental and energy monitoring of residential buildings through IoT. Autom. Constr. 2021, 126, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngonidzashe, M.B.; Tuncay, E. A simple Node-RED implementation for digital twins in the area of manufacturing. Trends Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2023, 8, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.; Leonardi, L.; Testa, G.; Bello, L.L. PrioMQTT: A prioritized version of the MQTT protocol. Comput. Commun. 2024, 220, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicari, S.; Rizzardi, A.; Coen-Porisini, A. Security&privacy issues and challenges in NoSQL databases. Comput. Netw. 2022, 206, 108828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digital Twin Consortium, Home Page. Available online: https://www.digitaltwinconsortium.org/ (accessed on 7 November 2024).
- UNI EN ISO 16000; Aria Interna. UNI: Rome, Italy, 2016.
- Padma, B.; Erukala, S.B. End-to-end communication protocol in IoT-enabled ZigBee network: Investigation and performance analysis. Internet Things 2023, 22, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korodi, A.; Nițulescu, I.-V.; Fülöp, A.-A.; Vesa, V.-C.; Demian, P.; Braneci, R.-A.; Popescu, D. Integration of Legacy Industrial Equipment in a Building-Management System Industry 5.0 Scenario. Electronics 2024, 13, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC 27000; Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) Family of Standard. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Borissova, D.I.; Danev, V.K.; Rashevski, M.B.; Garvanov, I.G.; Yoshinov, R.D.; Garvanova, M.Z. Using IoT for Automated Heating of a Smart Home by Means of OpenHAB Software Platform. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwiringiyimana, M.M.; Nandagopal, G.; Guan, Y.; Vinkovič, S.; Kölsch, J.; Heinz, C. IoT Platforms. In IoT Platforms, Use Cases, Privacy, and Business Models: With Hands-on Examples Based on the VICINITY Platform; Zivkovic, C., Guan, Y., Grimm, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovsky, R.; Kucera, E.; Haffner, O.; Rosinova, D. Proposal of Digital Twin Platform Based on 3D Rendering and IIoT Principles Using Virtual/Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 2020 Cybernetics & Informatics (K&I), Velke Karlovice, Czech Republic, 29 January–1 February 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragupathi, C.; Prakash, R. Forecasting energy consumption using enhanced LSTM. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2452, 050006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNI EN ISO 7730:2006; Ergonomia degli ambienti termici. UNI: Rome, Italy, 2016.
- UNI EN 12464-1; Illuminazione dei Luoghi di Lavoro. UNI: Rome, Italy, 2021.
- Di Natale, L.; Svetozarevic, B.; Heer, P.; Jones, C.N. Physically Consistent Neural Networks for building thermal modeling: Theory and analysis. Appl. Energy 2022, 325, 119806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, D.Y. Comparative analysis on predictability of natural ventilation rate based on machine learning algorithms. Build. Environ. 2021, 195, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I. A comparative sensitivity analysis of human thermal comfort indices with generalized additive models. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 1605–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wastensteiner, J.; Michael Weiss, T.; Haag, F.; Hopf, K. Explainable AI for tailored electricity consumption feedback–An experimental evaluation of visualizations experimental evaluation of visualizations. In ECIS 2021 Proceedings; Association for Information Systems (AIS): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Lin, B. Interpreting the neural network model for HVAC system energy data mining. Build. Environ. 2022, 209, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, P.; Singh, M.M.; Chen, X. Explainable AI for engineering design: A unified approach of systems engineering and component-based deep learning demonstrated by energy-efficient building design. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollo Neto, M.; Silva Montanhani, M.E.; Gobbo de Freitas Bueno, L.; Harada, E.d.S.; Florentino Pereira, D. Data Mining Generating Decision Trees to Alert System Against Death and Losses in Egg Production. Int. J. Innov. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 1946-6; Ventilazione e climatizzazione. Deutsches Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 2019.
- Piras, G.; Muzi, F.; Tiburcio, V.A. Enhancing Space Management through Digital Twin: A Case Study of the Lazio Region Headquarters. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, S.; Cumo, F.; Marzo, R.; Muzi, F. Digital Construction Strategy for Project Management Optimization in a Building Renovation Site: Machine Learning and Big Data Analysis. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Objectives | KPI | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| ||
| ||
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
| ||
|
|
|
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| Meeting Room | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Rif. Model | Description | qt. | Function | Primary Use | Secondar Use | Unit Cost |
| smart meter | Shelly | Status measurement and implementation of window opening/closing | 1 | sensor/ actuator | IAQ | - | €53.00 |
| actuator for double-blade clamping | GEZE RWA K 600 G | Automatic window opening | 1 | actuator | IAQ | - | €300.00 |
| smart meter for switch panel | Shelly | Monitoring of electrical consumption of indoor air conditioning units | 1 | sensor/ actuator | energy management | - | €53.00 |
| electric box with manual switch | Bticino | Control on/off of indoor air conditioning units | 1 | actuator | energy management | - | - |
| smart plug | Shelly | Electricity consumption monitoring and control of devices (TV, lamp. purifier) | 3 | sensor/ actuator | IAQ | - | €19.14 |
| air purifier | Xiaomi | Air quality control | 1 | actuator | IAQ | - | €150.00 |
| motion sensor | Shelly | Presence detection | 1 | sensor | space management | energy management | €45.19 |
| CO2, T, HR | Ampel | Environmental quality monitoring | 2 | sensor | IAQ | IEQ; energy management | €100.00 |
| camera | TBD | Presence counting with integrated computer vision | 1 | sensor | space management | energy management | |
| touch sensor | Shelly Door/Window | Window opening/closing status detector | 1 | sensor | energy management | security management | €24.80 |
| Total €883.41 | |||||||
| Individual Office | |||||||
| Type | Rif. Model | Description | qt. | Function | Primary Use | Secondar Use | Unit Cost |
| smart meter for switch panel | Shelly | Electrical consumption monitoring of indoor air conditioning units | 1 | sensors/ actuator | energy management | €53.00 | |
| electric box with manual switch | Bticino | On/off control of indoor air conditioning units | 1 | actuator | energy management | ||
| motion sensor | Shelly | Presence detection | 1 | sensors | space management (monitoring) | energy management (cdz); | €45.19 |
| touch sensor | Shelly Door/Window | Status detector opening/closing fixtures | 1 | sensors | energy management | security management | €24.80 |
| smart plug | Shelly | Electrical consumption monitoring and device control (n.1 floor lamp) | 1 | sensors/ actuator | IAQ | €19.14 | |
| Total fixed costs €142.19 | |||||||
| smart plug | Shelly | Monitoring the power consumption of workstations | 1 | sensors | energy management | €19.14 | |
| smart plug | Shelly | Monitoring of electricity consumption and control of devices (no. 1 printer, no. 1 desk lamp) | 2 | sensors/ actuator | IAQ | €19.14 | |
| Total per station €57.42 | |||||||
| Open Space Office | |||||||
| Type | Rif. Model | Description | qt. | Function | Primary Use | Secondar Use | Unit Cost |
| smart meter for switch panel | Shelly | Electrical consumption monitoring of indoor air conditioning units | 1 | sensors/actuator | energy management | €53.00 | |
| electric box with manual switch | Bticino | On/off control of indoor air conditioning units | 1 | actuator | energy management | - | |
| motion sensor | Shelly | Presence detection | 1 | sensors | space management (monitoring) | energy management (cdz); | €45.19 |
| touch sensors | Shelly Door/Window | Status detector opening/closing fixtures | 1 | sensors | energy management | security management | €24.80 |
| smart plug | Shelly | Electrical consumption monitoring and device control (n.1 floor lamp) | 1 | sensors/actuator | IAQ | €19.14 | |
| CO2, T, HR | Ampel | Environmental quality monitoring | 2 | sensors | IAQ | IEQ; energy management | €100.00 |
| smart meter | Shelly | Measurement of window opening/closing status and implementation | 1 | sensors/actuator | IAQ | €53.00 | |
| actuator for double-blade clamping | GEZE RWA K 600G | Automatic window opening | 1 | actuator | IAQ | €695.13 | |
| Total fixed costs €695.13 | |||||||
| smart plug | Shelly | Monitoring the power consumption of workstations | 1 | sensors | Energy management | €19.14 | |
| smart plug | Shelly | Monitoring of electricity consumption and control of devices (no. 1 printer, no. 1 desk lamp) | 2 | sensors/actuator | IAQ | €19.14 | |
| Total per station €57.42 | |||||||
| Buvette | |||||||
| Type | Rif. Model | Description | qt. | Function | Primary Use | Secondar Use | Unit Cost |
| smart plug | Shelly | Monitoring of electricity consumption and control of devices (no. 1 coffee, no. 1 fridge, no. 1 microwave, no. 1 purifier) | 4 | sensors/ actuator | IAQ | - | |
| air purifier | Air quality control | 1 | actuator | IAQ | - | €150.00 | |
| motion sensor | Shelly | Presence detection | 1 | sensors | space management (monitoring) | energy management | €45.19 |
| touch sensors | Shelly Door/Window | Status detector opening/closing fixtures | 1 | sensors | energy management | security management | €24.80 |
| CO2, VOC, T, HR, PM2.5, light sensor | AWAIR Omni | Environmental quality monitoring | 1 | sensors | IAQ | IEQ; energy management | €500.00 |
| Total €796.55 | |||||||
| Services Environment | |||||||
| Type | Rif. Model | Description | qt. | Function | Primary Use | Secondar Use | Unit Cost |
| smart plug | Shelly | Monitoring of electricity consumption and control of devices (no. 1 boiler) | 1 | sensor/actuator | IAQ | €19.14 | |
| motion sensor | Shelly | Presence detection | 1 | sensor | space management (monitoring) | energy management | €45.19 |
| touch sensor | Shelly Door/Window | Status detector opening/closing fixtures | 1 | sensor | energy management | security management | €24.80 |
| Total per station €89.13 | |||||||
| Archive | |||||||
| Type | Rif. Model | Description | qt. | Function | Primary Use | Secondar Use | Unit Cost |
| smart meter for switch panel | Shelly | Monitoring of electricity consumption and control of indoor air-conditioning units | 1 | sensor/ actuator | energy management | €53.00 | |
| electric box with manual switch | Bticino | Monitoring on/off air conditioning internal unit | 1 | actuator | energy management | ||
| motion sensor | Shelly | Presence detection | 1 | sensor | space management (monitoring) | energy management | €45.19 |
| touch sensor | Shelly Door/Window | Status detector opening/closing fixtures | 1 | sensor | energy management | security management | €24.80 |
| smart plug | Shelly | Electricity consumption monitoring and device control (No. 1 floor lamp) | 1 | sensor/ actuator | IAQ | €19.14 | |
| smart plug | Shelly | Electricity consumption monitoring of workstations | 1 | sensor | energy management | €19.14 | |
| Total per station €161.27 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piras, G.; Agostinelli, S.; Muzi, F. Smart Buildings and Digital Twin to Monitoring the Efficiency and Wellness of Working Environments: A Case Study on IoT Integration and Data-Driven Management. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094939
Piras G, Agostinelli S, Muzi F. Smart Buildings and Digital Twin to Monitoring the Efficiency and Wellness of Working Environments: A Case Study on IoT Integration and Data-Driven Management. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094939
Chicago/Turabian StylePiras, Giuseppe, Sofia Agostinelli, and Francesco Muzi. 2025. "Smart Buildings and Digital Twin to Monitoring the Efficiency and Wellness of Working Environments: A Case Study on IoT Integration and Data-Driven Management" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094939
APA StylePiras, G., Agostinelli, S., & Muzi, F. (2025). Smart Buildings and Digital Twin to Monitoring the Efficiency and Wellness of Working Environments: A Case Study on IoT Integration and Data-Driven Management. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4939. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094939









