Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Mask-Improved Calcareous Sand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Laboratory Testing Program
2.1. Tested Materials
2.2. Triaxial Test
2.3. Penetration Test
3. Test Results and Analysis
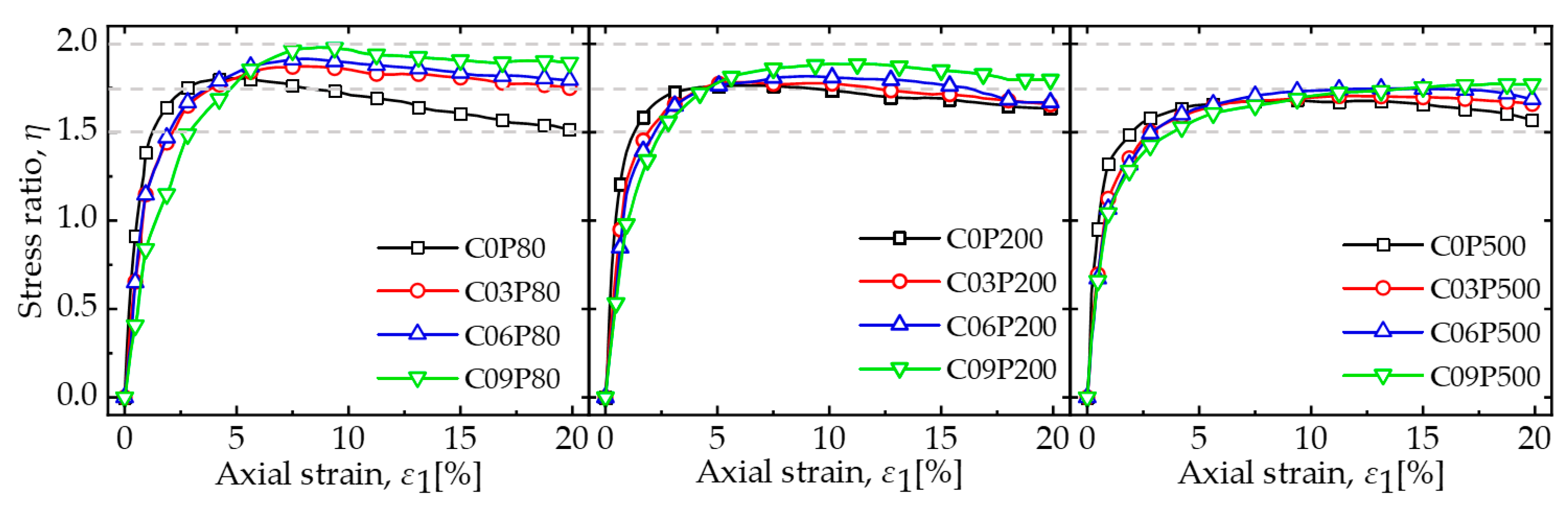
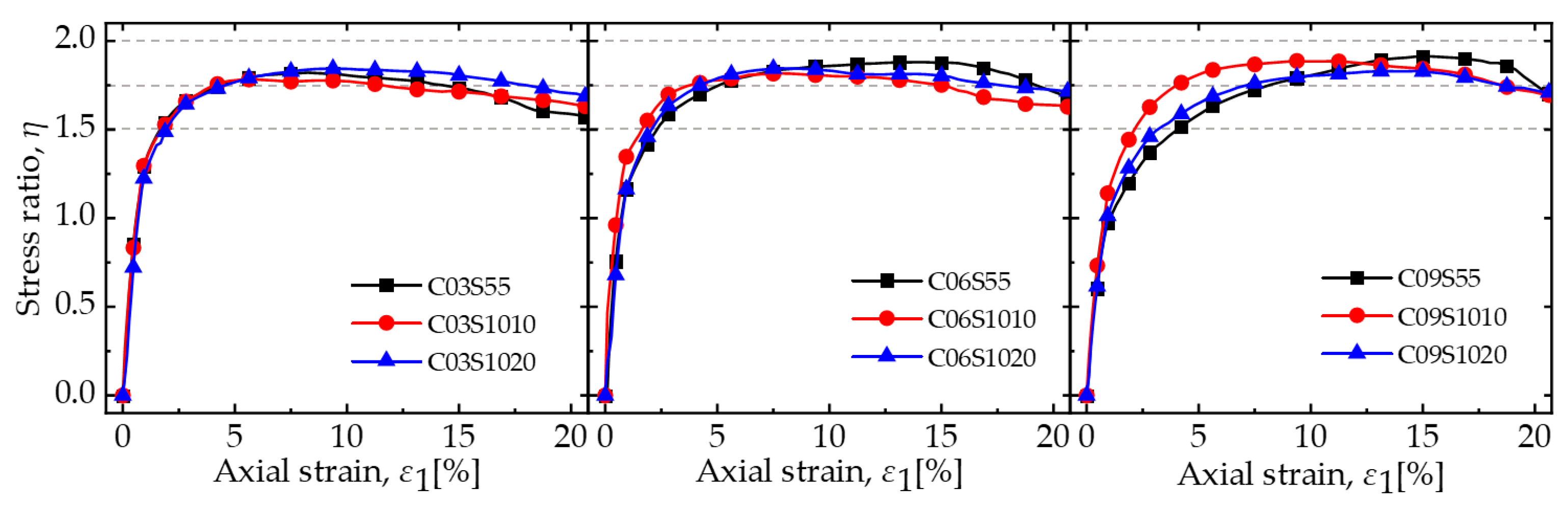
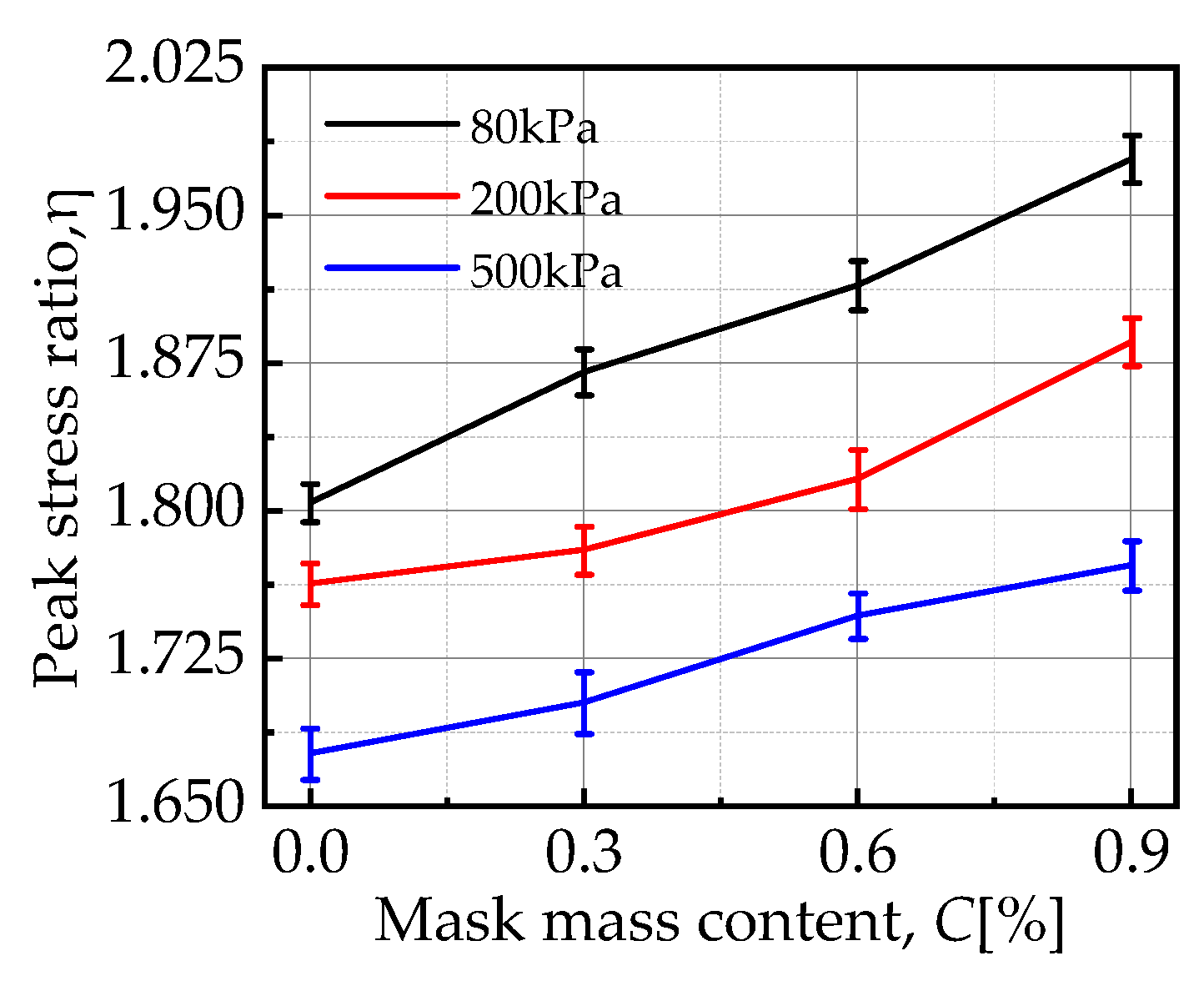
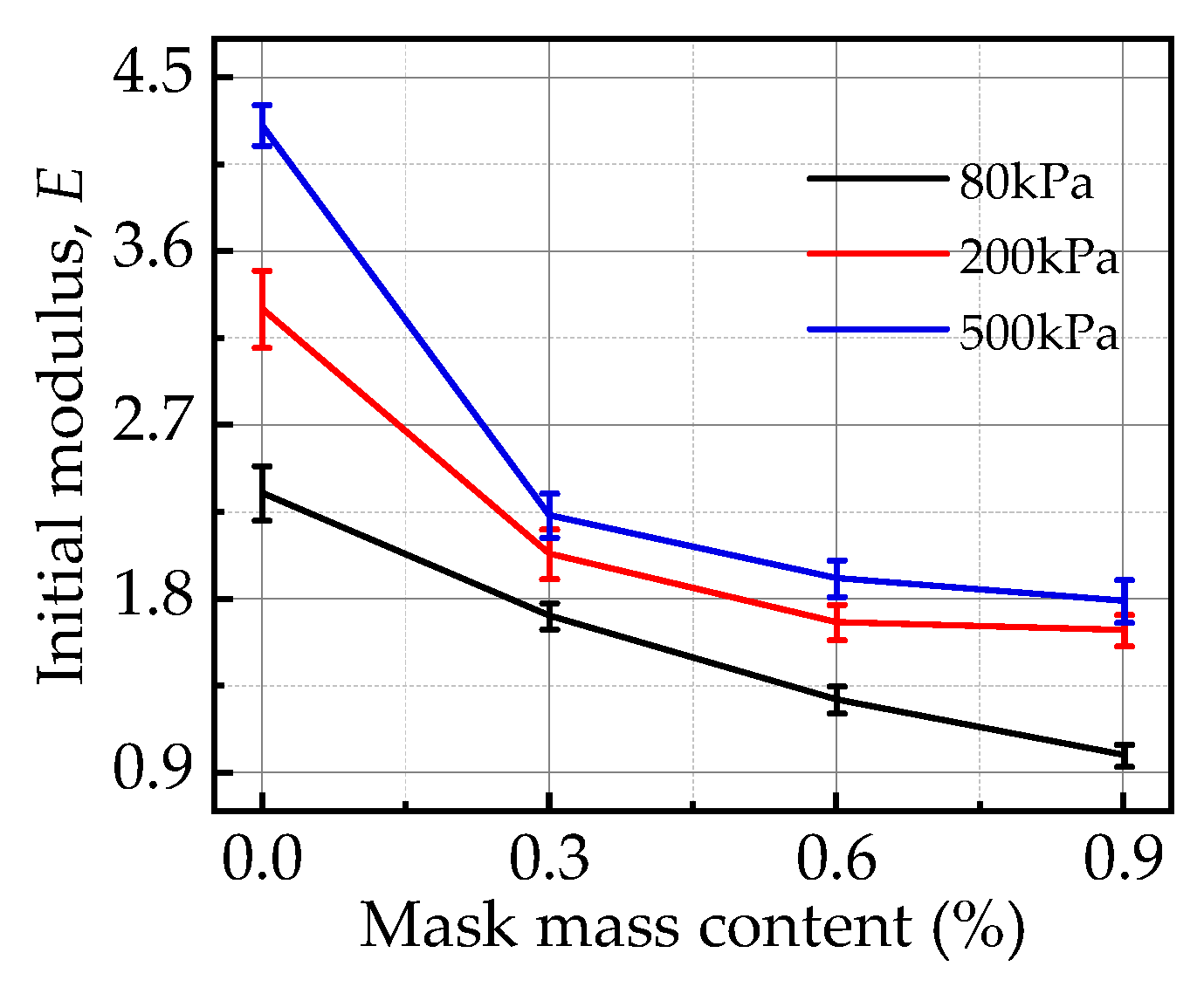
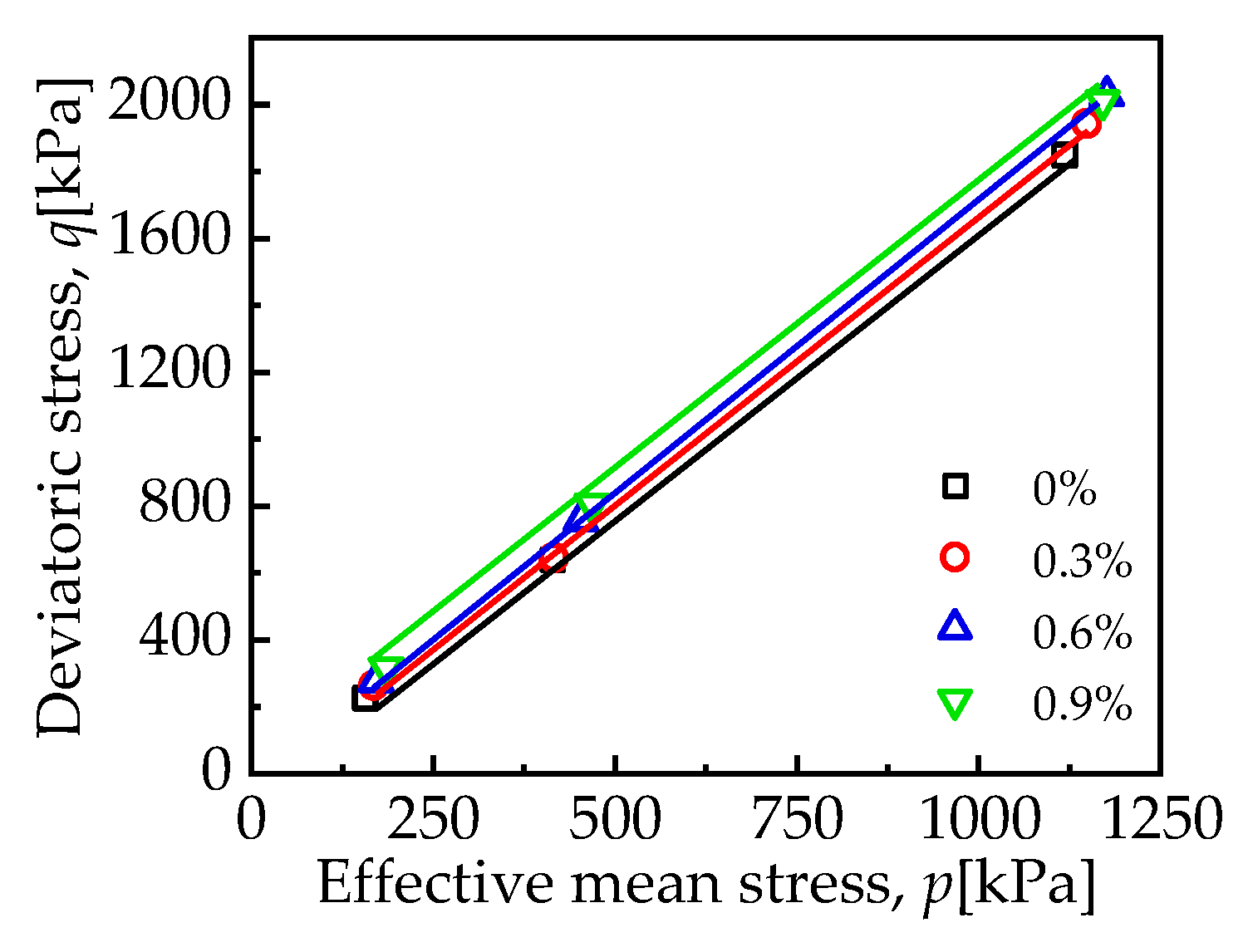
3.1. Stress–Strain Characteristics
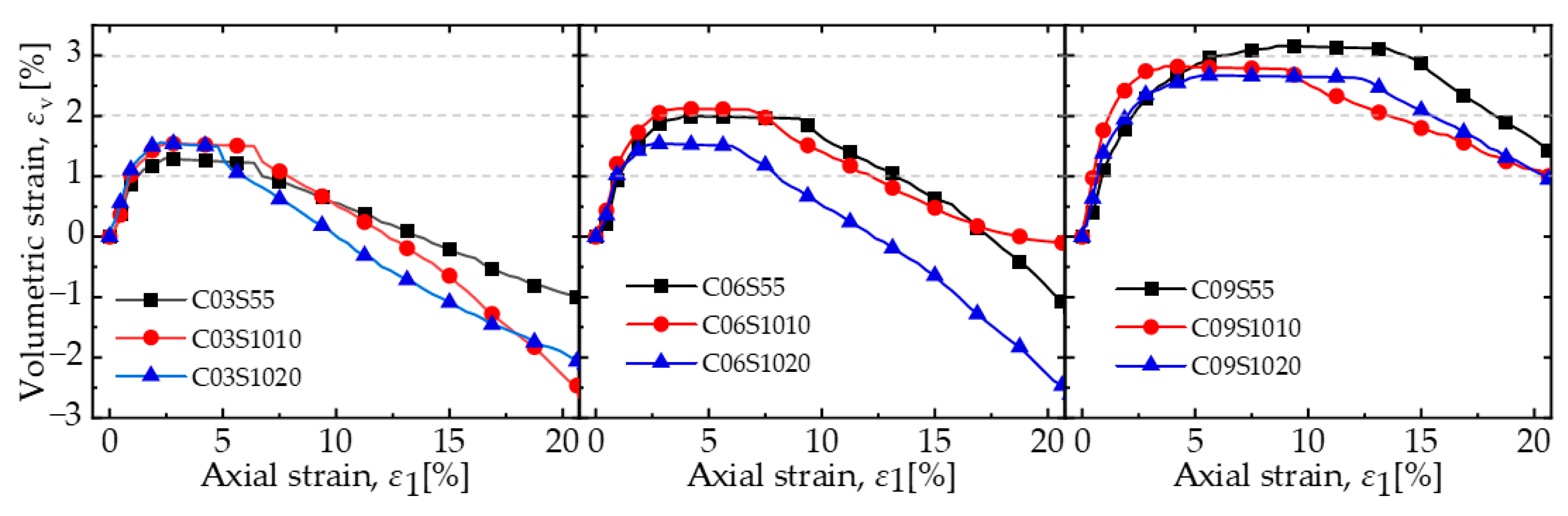
3.2. Volume Change Characteristics
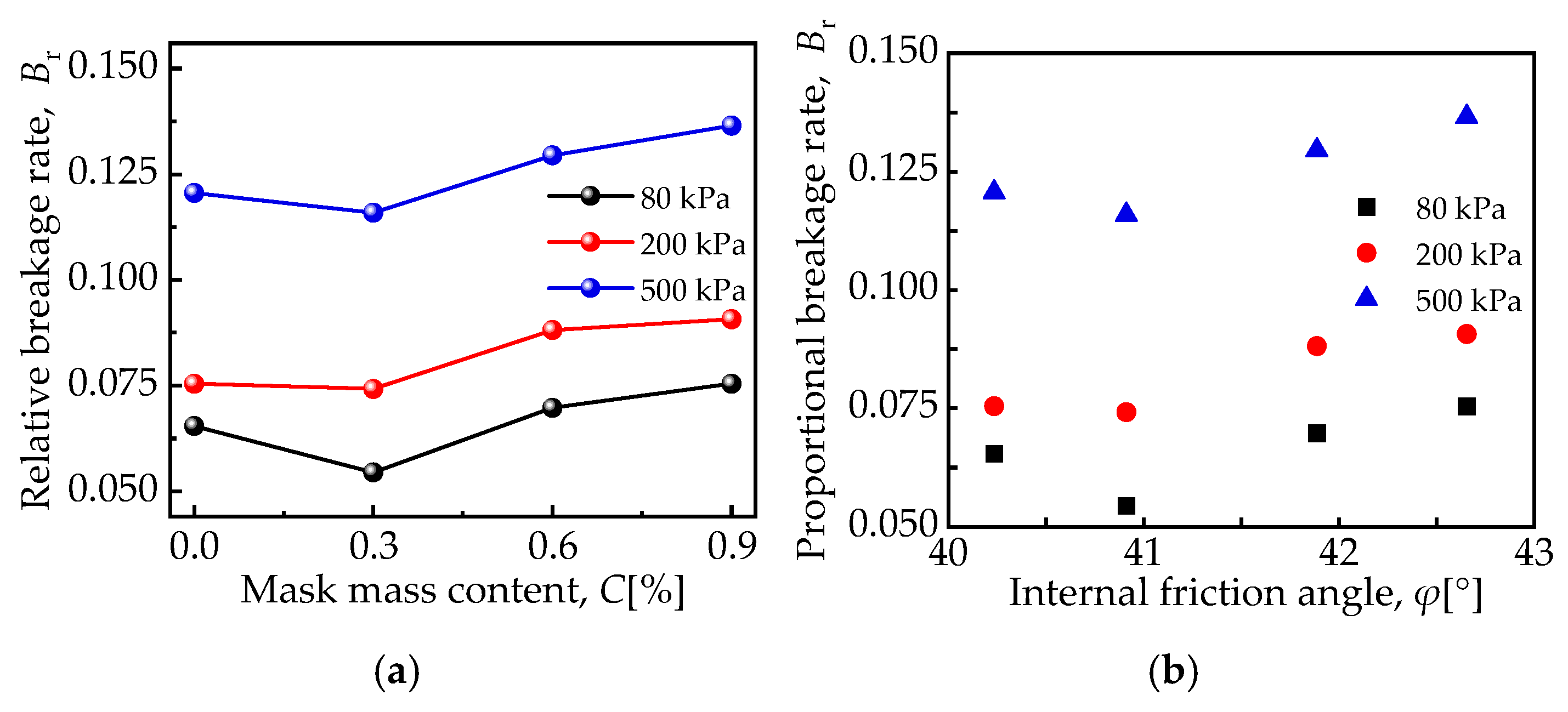
3.3. Particle Breakage Characteristics
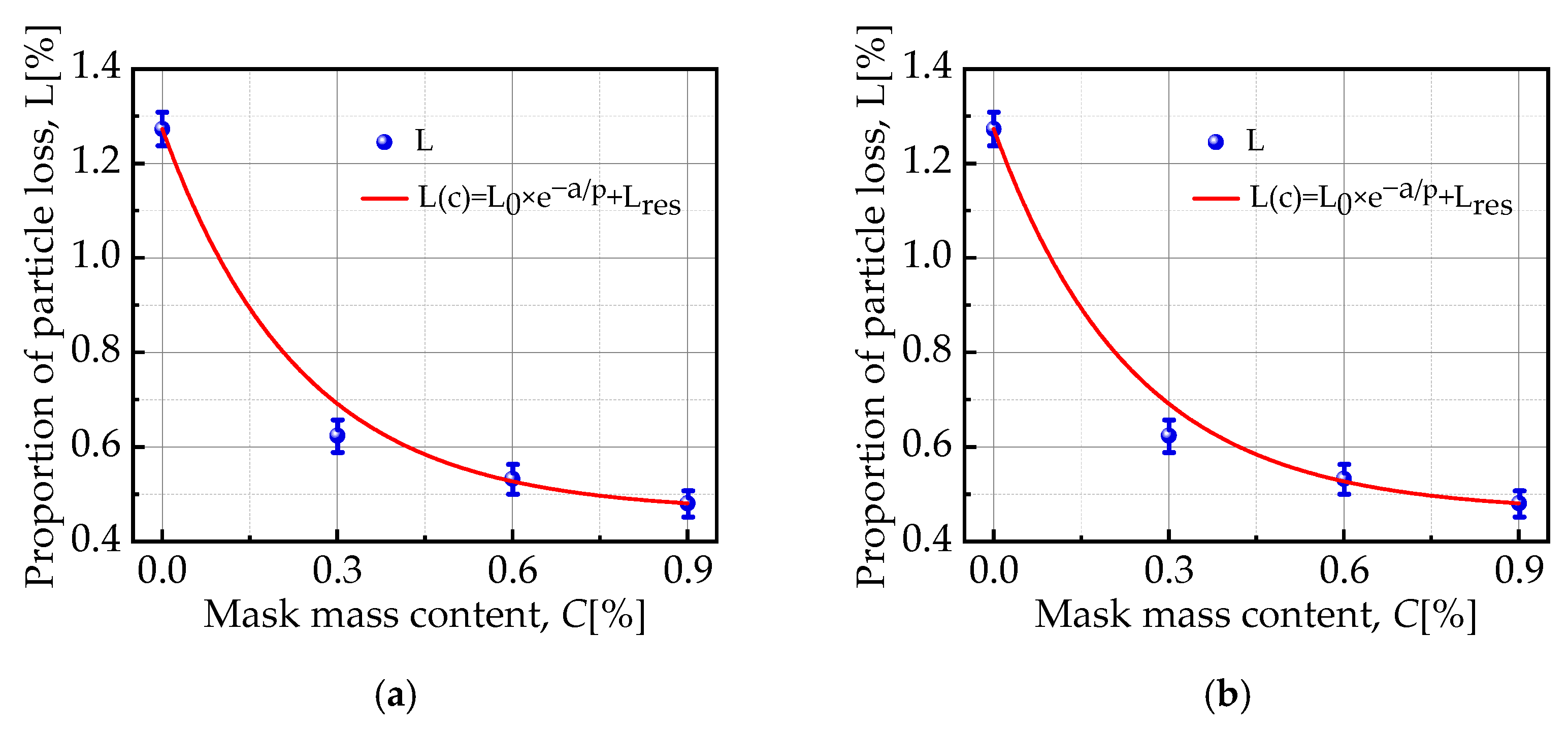
3.4. Seepage Characteristics
4. Conclusions
- (1)
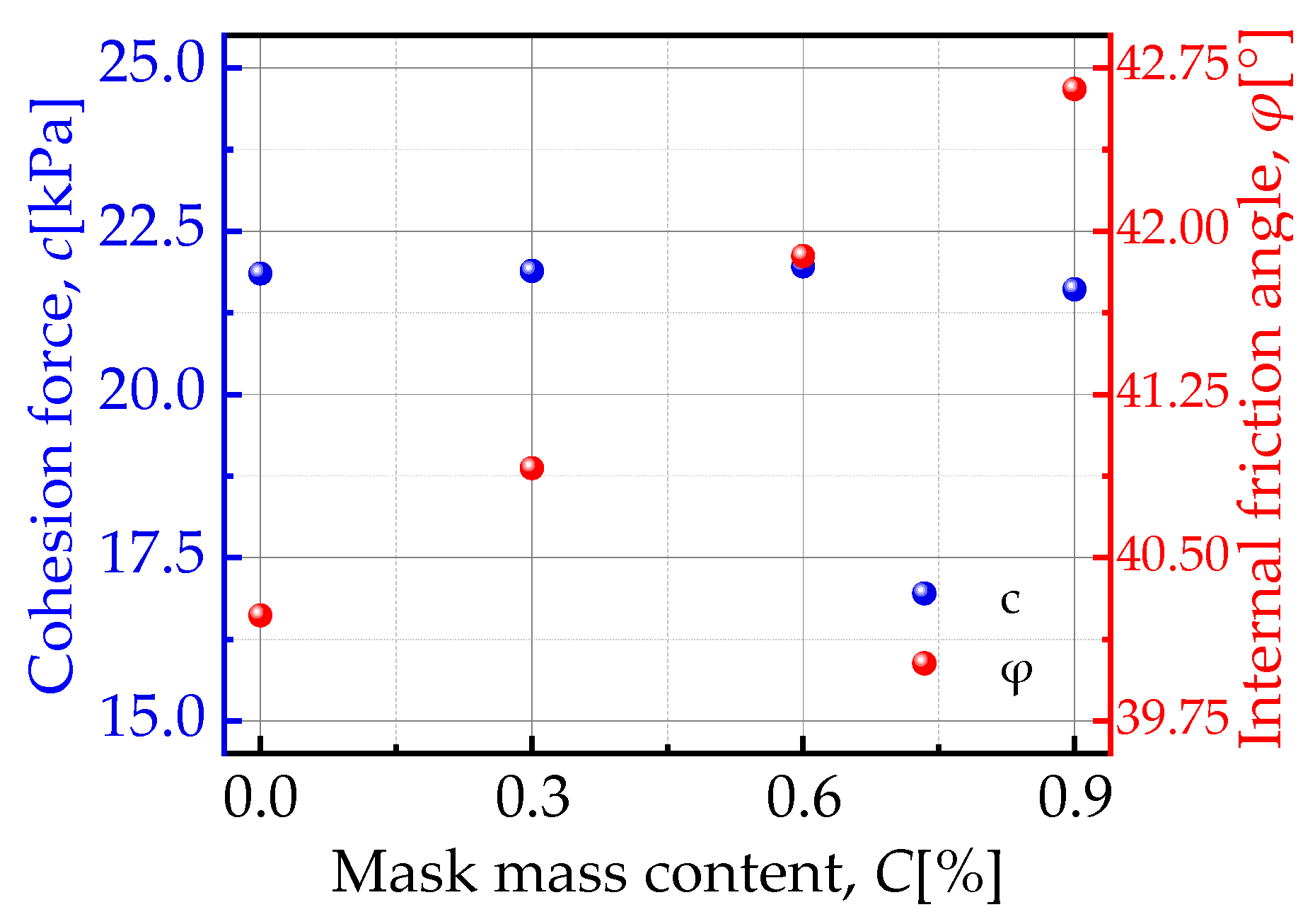
- At a low content (0.9% by mass), an increase in mask content resulted in higher peak strength, internal friction angle, and ductility of the mixture, a reduction in the initial modulus, and suppression of dilatancy. This suggests that the mask has significant potential in enhancing the bearing capacity of calcareous sand roadbeds to resist shear deformation under dynamic vehicle loading.
- (2)
- The reinforcing effect of the mask on the soil matrix arises from the high friction at the mask–calcareous sand interface, which enhances the overall strength of the mixture by restricting the movement of soil particles during deformation. However, due to the mask’s deformability, the surrounding calcareous sand undergoes rearrangement at the onset of shear, which leads to a reduction in the initial modulus of the mixture.
- (3)
- The incorporation of the mask can effectively inhibit the fragmentation of calcareous sand particles, with the optimal effect observed at a 0.3% incorporation rate. This suggests that the mask has promising potential for enhancing the long-term stability of steep-slope calcareous sand soil bodies.
- (4)
- The incorporation of the mask reduces the coefficient of permeability of calcareous sand, prevents particle loss, and, at a mask content of 0.3%, particle loss is substantially inhibited while the permeability of the specimen is only slightly reduced. In scenarios where both permeability and particle loss are critical (e.g., shallow foundations in areas with fluctuating water tables), calcareous sand particle loss is significantly reduced, thereby extending the structural lifespan.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karaivanov, A.; Lu, S.E.; Shigeoka, H.; Chen, C.; Pamplona, S. Face masks, public policies and slowing the spread of COVID-19: Evidence from Canada. J. Health Econ. 2021, 78, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.H.; Zeng, W.H.; Feng, D.L.; Lin, J.P.; Gong, X. Influence of Polypropylene Fiber on Properties of Biocemented Calcareous Sand. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2022, 59, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Liew, M.S. Tertiary recycling of plastics waste: An analysis of feedstock, chemical and biological degradation methods. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.O.; Okoffo, E.D. COVID-19 face masks: A potential source of microplastic fibers in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, K.S.; Ho, L.Y.; Lim, H.R.; Leong, H.Y.; Chew, K.W. Plastic waste associated with the COVID-19 pandemic: Crisis or oppor-tunity? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Silva, A.L.P.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Barcelo, D.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Current knowledge on the presence, bio-degradation, and toxicity of discarded face masks in the environment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaraj, S.; Ashokkumar, V.; Hariharan, S.; Manibharathi, A.; Show, P.L.; Chong, C.T.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. The COVID-19 pandemic face mask waste: A blooming threat to the marine environment. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.M.; Li, S.X.; Ahmad, I.M.; Zhang, G.Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.N.; Jiang, C.; Cui, P.; Li, D.M. Global face mask pollution: Threats to the environment and wildlife, and potential solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, D.H.G. Mechanics of fiber reinforcement in sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1983, 109, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Shen, C. Influence of Fiber Content and Length on Engineering Properties of MICP-Treated Coral Sand. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, M.P.d.S.; Pinto, C.M.T.; Carvalho, M.d.F.; Machado, S.L. Fiber reinforcement effectiveness in two different sand speci-mens. Soils Rocks 2023, 46, e2023012422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lin, S.; Meng, Q.; Liao, X.; Xu, J. Influence of different fiber types on properties of biocemented calcareous sand. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.P.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Xu, A.; Fu, X.L.; Che, C.; Tian, Z.J.; Bi, Y.Z. Recycle of discarded masks in civil Engineering: Current status and future opportunities with silane coupling agent modified discarded masks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 405, 133266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.Z.; Liu, H.; Li, X.X.; Tao, Z.; Wu, Y.J.; Shen, J.H.; Yin, M. Effect of stress path on the mechanical properties of calcareous sand. Undergr. Space 2023, 9, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.H.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Q.L.; Jia, Y.G.; Zuo, D.J.; Duan, Z.B. Three-dimensional pore characteristics and permeability properties of calcareous sand with different particle sizes. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhao, T.; Meng, Q.; Wang, X.; He, J. Experimental Evaluation of the Shear Behavior of Fiber-Reinforced Calcareous Sands. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, J.-F.; Peng, M.; Zhu, Y. Liquefaction behavior of fiber-reinforced calcareous sands in unidirectional and multi-directional simple shear tests. Geotext. Geomembr. 2022, 50, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimelahi, N.; Bayat, M.; Ajalloeian, R.; Nadi, B. Effect of woven geotextile reinforcement on mechanical behavior of calcareous sands. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Li, H.; Pan, X.H.; Yin, L.Y.; Cheng, L.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, B.; Shi, B. Coupling effect of biocementation-fiber reinforcement on mechanical behavior of calcareous sand for ocean engineering. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shen, S.-L.; Arulrajah, A.; Wu, H.-N.; Hou, D.-W.; Xu, Y.-S. Laboratory evaluation on the effectiveness of polypropylene fibers on the strength of fiber-reinforced and cement-stabilized Shanghai soft clay. Geotext. Geomembr. 2015, 43, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, S.; Najjar, S.S.; Freiha, F. Shear Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Sands. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. En-Gineering 2010, 136, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D4254; Standard Test Method for Minimum Index Density and Unit Weight of Soils and Calculation of Relative Density. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006.
- ASTM D7181; Standard Test Method for Determining the (In-plane) Flow Rate per Unit Width and Hydraulic Transmissivity of a Geosynthetic Using a Constant Head. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Zeng, Y.W.; Shi, X.S.; Zhao, J.D.; Bian, X.; Liu, J.Y. Estimation of compression behavior of granular soils considering initial density effect based on equivalent concept. Acta Geotech. 2025, 20, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Gu, J.X.; Zhou, J.R.; Li, B. Mechanical behavior and particle breakage of calcareous sand in triaxial test. Mar. Geo-Phys. Res. 2023, 44, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Xiao, Y.J.; Chen, X.B.; Liu, B.H.; Yin, Z.Y. Investigating the effects of non-uniformity of mixing on the shear behavior of soft-rigid mixtures with DEM. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 176, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2434; Standard Test Method for Permeability of Granular Soils (Constant Head). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Romero, C.M.; Páez, M.S.; Puchana, M.J. Effect of temperature on the volumetric and viscometric properties of polyols in aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Li, T.F.; Zhao, Y.M.; Chen, X.B.; Zhang, Q.L. Microstructure evolution of coarse-grained soil fillers during subgrade com-paction-operation period based on CT technology. Transp. Geotech. 2024, 47, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Jitsangiam, P.; Wang, X. DEM investigation of macro- and micro-mechanical properties of rigid-grain and soft-chip mixtures. Particuology 2021, 55, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Zhou, G.M. Investigating the compaction and the mechanical behaviors of coal gangue as subgrade filler and constructing highway subgrade in practice. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Gao, W.H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Tang, X.Y. Degradation-induced evolution of particle roundness and its effect on the shear behaviour of railway ballast. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 24, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Yin, Z.-Y.; Liang, Z. DEM modeling of large-scale triaxial test of rock clasts considering realistic particle shapes and flexible membrane boundary. Eng. Geol. 2020, 279, 105871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkness, J.; Zervos, A.; Le Pen, L.; Aingaran, S.; Powrie, W. Discrete element simulation of railway ballast: Modelling cell pressure effects in triaxial tests. Granul. Matter 2016, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.S.; Nie, J.Y.; Zhao, J.D.; Gao, Y.F. A homogenization equation for the small strain stiffness of gap-graded granular materials. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 121, 103440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.X.; Su, D.; Lin, X.T. A theoretical model for trapdoor tests considering the interaction of soil arches. Acta Geotech. 2025, 20, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.S.; Zhao, J. Practical estimation of compression behavior of clayey/silty sands using equivalent void-ratio concept. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q. Discrete element modeling of instability mechanisms of unbound permeable aggregate base materials in triaxial compression. Materials 2022, 15, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ghorbani, J.; Zhang, C. Stress overshooting solution for soil plasticity models. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 152, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, X.; Yin, Z.Y. DEM-based study on the mechanical behaviors of sand-rubber mixture in critical state. Con-Struction Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, Z.Y.; Cui, Y.J.; Liu, K.; Yin, J.-H. An elasto-plastic model of unsaturated soil with an explicit degree of satura-tion-dependent CSL. Eng. Geol. 2019, 260, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Indraratna, B.; Heitor, A.; Vinod, J.S. Closure to “Effect of Rubber Crumbs on the Cyclic Behavior of Steel Furnace Slag and Coal Wash Mixtures” by Yujie Qi, Buddhima Indraratna, Ana Heitor, and Jayan S. Vinod. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2018, 144, 04017107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.S.; Yin, Z.Y. Modeling Stress-Dilatancy for Sand under Compression and Extension Loading Conditions. J. Eng. Mech.-Asce 2010, 136, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.R.; Chen, J.X.; Lei, W.; Peng, W. Effect of drainage conditions during triaxial shearing on particle breakage, deformation, and strength properties of calcareous sand. Rock Soil Mech. 2024, 45, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.H.; Ding, Z.; Sun, Y.F.; Chen, W.Y.; Xia, T.D. Cumulative deformations and particle breakage in calcareous sand subjected to drained high-cyclic loading: Experimental investigation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 161, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Lei, M.; Huang, L. Effects of void morphology on fracturing characteristics of porous rock through a finite-discrete element method. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 104, 104684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, J. A Review of Advanced Soil Moisture Monitoring Techniques for Slope Stability Assessment. Water 2025, 17, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.V.; Fernandez, L.A. Assessment of Fabric Masks as Alternatives to Standard Surgical Masks in Terms of Particle Filtration Efficiency. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cey, E.E.; Rudolph, D.L. Field study of macropore flow processes using tension infiltration of a dye tracer in partially saturated soils. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mask Mass Content (%) | 0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. density (g/cm3) | 1.56 | 1.50 | 1.44 | 1.41 |
| Min. density (g/cm3) | 1.35 | 1.27 | 1.19 | 1.13 |
| Specimen Name | Mask Mass Content (%) | Pressurization (kPa) | Pre-Shear Pore Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0P80 | 0 | 80 | 0.879 |
| C0P200 | 200 | ||
| C0P500 | 500 | ||
| C03P80 | 0.3 | 80 | 0.945 |
| C03P200 | 200 | ||
| C03P500 | 500 | ||
| C06P80 | 0.6 | 80 | 1.020 |
| C06P200 | 200 | ||
| C06P500 | 500 | ||
| C09P80 | 0.9 | 80 | 1.065 |
| C09P200 | 200 | ||
| C09P500 | 500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Mask-Improved Calcareous Sand. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094888
Zhang L, Sun Z, Liu B, Zhang Z, Zhang J. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Mask-Improved Calcareous Sand. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094888
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Longwen, Zhuoyi Sun, Baohua Liu, Zongtang Zhang, and Junqi Zhang. 2025. "Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Mask-Improved Calcareous Sand" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094888
APA StyleZhang, L., Sun, Z., Liu, B., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, J. (2025). Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Mask-Improved Calcareous Sand. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4888. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094888







