Abstract
The generation of High-Dynamic-Range (HDR) images is essential for capturing details at various brightness levels, but current reconstruction methods, using deep learning techniques, often require significant computational resources, limiting their applicability on devices with moderate resources. In this context, this paper presents a lightweight architecture for reconstructing HDR images from three Low-Dynamic-Range inputs. The proposed model is based on Generative Adversarial Networks and replaces traditional convolutions with depthwise separable convolutions, reducing the number of parameters while maintaining high visual quality and minimizing luminance artifacts. The evaluation of the proposal is conducted through quantitative, qualitative, and computational cost analyses based on the number of parameters and FLOPs. Regarding the qualitative analysis, a comparison between the models was performed using samples that present reconstruction challenges. The proposed model achieves a PSNR- of 43.51 dB and SSIM- of 0.9917, achieving competitive quality metrics comparable to HDR-GAN while reducing the computational cost by 6× in FLOPs and 7× in the number of parameters, using approximately half the GPU memory consumption, demonstrating an effective balance between visual fidelity and efficiency.
1. Introduction
High-Dynamic-Range (HDR) images have been the subject of study by researchers, as they represent one of the most promising approaches to enhancing the visual experience of the observer in areas such as image processing, computer vision, virtual reality, the video game industry, photography, and videography [1]. The main advancements that have established this research topic as a key area of investigation include the development of HDR displays, which have demonstrated the ability to visualize colors and luminance ranges close to those of the real scene for the generation of this type of image, currently achieved through specialized cameras [2,3,4].
HDR images are capable of capturing most color and light information from real-world scenes, unlike Low-Dynamic-Range (LDR) images, which are limited by the dynamic range in scene exposure, resulting in information loss in overexposed and underexposed areas [5]. An alternative for generating HDR images involves rendering tools, widely used in virtual environments, especially in the gaming industry [3]. Other alternatives related to HDR image reconstruction include multi-exposure fusion, where for static scenes only the fusion of exposures is performed, while for dynamic scenes it is also necessary to perform alignment with a reference image. Additionally, with the implementation of deep learning techniques, methods for HDR reconstruction from a single exposure have emerged, eliminating the need for image alignment or fusion [3,6].
However, traditional HDR image reconstruction methods such as those of Debevec et al. [7] have encountered challenges in generating high-quality HDR images when there is movement in the scene, due to occlusion of certain areas and misalignment between the images. In Figure 1, the reconstruction performed using this traditional method from three inputs with motion is illustrated [7]. It becomes possible to observe that traditional methods can generate images that exhibit artifacts such as ghosts and blurs, which are characterized as the partial appearance of an element that was in motion, either due to the camera or the time interval between the input images. Ghosts are related to large movements, while blurs are related to minor movements [8,9].

Figure 1.
Reconstruction of image 010 from Kalantari et al.’s dataset [10] using Debevec et al.’s [7] method.
As a way to solve the problems of image fusion, several studies have implemented the use of deep learning techniques, both for the image alignment problem and for the generation of missing information. Among these techniques, those based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) [11] stand out, where architectures such as HDR-cGAN [12] and GlowGan [13] were developed for HDR image reconstruction from a single exposure, and MEF-GAN [14], UPHDR-GAN [15], and HDR-GAN [16] for HDR image reconstruction from multiple exposures, demonstrating excellent results. In Figure 2, the reconstruction of a sample using HDR-GAN is presented. GANs consist of a generator model that produces samples and a discriminator model that evaluates and determines whether these samples are real or generated. During training, these models compete with each other, and this dynamic results in an enhanced ability to create realistic data. Due to this, GANs are widely used in applications such as image synthesis and visual restoration [17].

Figure 2.
Reconstruction of image 010 from Kalantari et al.’s dataset [10] using HDR-GAN [16].
Excellent performance is provided for HDR reconstruction through the implementation of deep learning techniques, which is why many studies have investigated the use of these techniques to reduce the computational cost required for their execution [18]. Among the alternatives developed to improve computational cost, depthwise separable convolution [19] stands out. It replaces standard convolution by separating spatial-wise and channel-wise computation steps, emerging as a solution to optimize neural networks by reducing computational costs and the number of parameters compared to traditional convolutions. Since then, the use of depthwise separable convolution in the development of neural networks has been applied in various architectures, such as MobileNet [20] for object detection, SynthNet [21] for image synthesis, SwiftSRGAN [22] for super-resolution, Chen et al. [23] for fabric defect detection, and Guo et al. [24] for stereo-matching, among others. These architectures have demonstrated the efficiency of the approach in developing lightweight models while maintaining competitive performance.
In this context, this paper presents an optimized version of the HDR-GAN architecture [16], a well-established and purely convolutional model, in which it is proposed to replace standard convolution with depthwise separable convolution. Although depthwise separable convolution has already been used in other models, this research is the first to specifically optimize an existing HDR reconstruction model to evaluate the efficiency and computational cost reduction of this modification. This innovative approach aims to significantly reduce the computational cost of the HDR image reconstruction process from multiple exposures with motion, offering a unique contribution by demonstrating the practical benefits of this optimization on an already established model. The Kalantari dataset [10] is used for training the model and for the experiments conducted. In addition to the Kalantari dataset, the HDR-Eye [25], Sen [26], Tursun [27], and Tel [28] datasets are also utilized in the experiments. To evaluate the proposed model, quantitative analyses are performed using the metrics PSNR, PSNR, PSNR, SSIM, SSIM, SSIM, HDR-VDP2, HDR-VDP3, and IL-NIQE, and the computational cost is assessed based on the number of parameters and FLOPs. Additionally, a qualitative analysis is conducted with selected samples, performing visual comparisons regarding HDR image reconstruction, verifying the fusion and alignment capabilities.
In summary, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- Optimization of the HDR-GAN architecture using depthwise separable convolution, significantly reducing computational cost while maintaining high-quality HDR reconstruction.
- Thorough quantitative and qualitative evaluation of the proposed model, demonstrating the efficiency and effectiveness of the optimization on multiple datasets.
- Extensive comparative experiments with other methods, showing the ability of the proposed model to handle motion and alignment challenges in multi-exposure HDR reconstruction, while achieving a balance between performance and computational efficiency.
This paper is organized as follows: The literature review is presented in Section 2. The methods used, as well as the proposed approach, are described in Section 2.2. The dataset, metrics, and results of the conducted experiments are highlighted in Section 3.3. The conclusion and future work are outlined in Section 5.
2. Related Work
In the literature, there are approaches and research compositions that report the use of traditional methods and deep learning-based methods for HDR image reconstruction. Some of these studies are described in detail in this section.
2.1. Traditional Methods
The main HDR image reconstruction algorithms in this category, referring to methods that do not use deep learning techniques, were mostly developed for static scenes, proposing different weighting functions. Kirk and Andersen [29] derive a variance penalizer as the optimal weighting function, using a simplified camera noise model that estimates temporal noise. Granados et al. [30] extend the work of Kirk and Andersen by using a more complex camera noise model, estimating both temporal and spatial noise. These methods have proven to be robust and accurate for reconstructing radiance maps for static scenes.
Considering scenes with motion, the algorithms follow two main approaches. The first develops techniques for removing misaligned pixels, as performed by Khan et al. [31], who modified the weights of the HDR image fusion based on the probability of a pixel being static. Raman and Chaudhuri [32] used segmentation algorithms to detect regions with motion, outperforming previous methods. However, these methods often discard textures due to the occlusion of certain areas caused by object motion. Meanwhile, the second approach performs the alignment of the input images relative to a reference image. Examples include the works of Tomaszewska and Mantiuk [33], who used scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) keypoints to compute a homography and align the images, and Sen et al. [26], who employed a Patch-Based method that optimizes alignment and merging simultaneously.
2.2. Deep Learning Methods
The initial approaches to HDR image reconstruction using deep learning techniques were proposed to overcome the limitations of traditional methods. Kalantari et al. [10] employed optical flow to align the images relative to the reference image. The authors followed an approach similar to that used in Sen et al. [26], using a convolutional neural network (CNN) to perform the image merging, establishing an initial milestone in the application of deep learning for HDR image reconstruction. As a result, in recent years, various classes of models have been utilized to perform this task.
GAN-based models have stood out in HDR image reconstruction, both for reconstruction from a single exposure and for reconstruction from multiple exposures. The models that stand out in reconstruction from a single exposure are HDR-cGAN [12] and GlowGAN [13]. HDR-cGAN uses the HDR-REAL and HDR-SYNTH datasets and performs image reconstruction from an architecture based on a conditional GAN [34]; this model uses a pipeline based on three steps, linearization, which estimates the inverse camera function by transferring ldr to the linear domain, overexposure correction, which corrects over/underexposed regions, and refinement, which deals with remaining errors. Meanwhile, GlowGAN combines the structure of a GAN with a stochastic camera model, positioned between the generator and discriminator, enabling training with datasets containing only LDR images. Thus, both approaches treat HDR image reconstruction as an image-to-image translation problem without the need for alignment, generating artifact-free HDR images.
However, models based on HDR image reconstruction from multiple exposures achieve better results than single-exposure models [3]. For example, the MEF-GAN model [14] has a generator divided into three blocks, including a self-attention block to allow for attention-driven and long-range dependency by introducing the self-attention mechanism, a local detail block to preserve and fuse local details, and a merge block to merge features obtained by the other blocks. The model is trained with the dataset from Cai et al. [35], which includes aligned images from HDR-Eye [25], Fairchild [36], and other images collected by the authors. Additionally, the MEF-GAN model uses minimum and maximum exposure images to generate HDR images, demonstrating excellent results in the exposure merging task. On the other hand, the HDR-GAN [16] and UPHDR-GAN [15] models use three LDR images captured at different exposures with motion to generate HDR images, being trained with the Kalantari dataset [10]. Therefore, they need to perform both alignment and merging. The HDR-GAN model utilizes a multi-scale LDR encoder, reference-aligned feature fusion, and deep HDR supervision to achieve the best results. Meanwhile, the UPHDR-GAN model stands out for incorporating unlabeled data into the training process, increasing its robustness. The model achieves this by using the Min-Patch module during generator training. Both models demonstrate remarkable results for alignment and merging tasks, with a slight superiority of HDR-GAN in performance, resulting in reconstruction with superior quality compared to the other mentioned alternatives.
3. Methods
3.1. Depthwise Separable Convolution
This section is based on [37,38]. Figure 3 illustrates the process of standard convolution, which performs spatial-wise and channel-wise computation in a single step. In this process, a kernel is applied simultaneously over the height, width, and channel dimensions of the image.
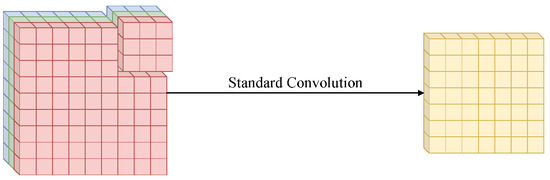
Figure 3.
Standard convolution, applying a 3 × 3 3-channel kernel to a 3 × 7 3-channel image, obtaining a 1-channel 6 × 6 output.
The number of parameters in standard convolution can be calculated using Equation (1), where and represent the kernel dimensions (height and width), is the number of input channels, and is the number of output channels.
As an alternative to standard convolution, depthwise separable convolution was proposed, dividing the process into two more efficient steps. The first step, called depthwise convolution, is represented by Figure 4. In this operation, spatial-wise computation is performed by applying a kernel separately to each channel, meaning the kernel is applied over the height and width dimensions of each channel individually.

Figure 4.
Depthwise convolution, applying a 3 × 3 kernel separately to each channel of a 3-channel 7 × 7 image, resulting in a 3-channel 6 × 6 output.
The number of parameters in depthwise convolution is calculated using Equation (2).
The second step of depthwise separable convolution is pointwise convolution, represented by Figure 5. This operation performs channel-wise computation by applying a standard convolution with a 1 × 1 kernel over the channel dimension. This allows combining the input channels to produce the desired number of output channels.

Figure 5.
Pointwise convolution, applying a 1 × 1 kernel on a 3-channel 6 × 6 image, resulting in a 1-channel 6 × 6 output.
The number of parameters in pointwise convolution is calculated using Equation (3).
In this proposal, standard convolution is replaced by depthwise separable convolution with the aim of reducing the number of parameters in the model. The total computational cost of depthwise separable convolution can be calculated using Equation (4), which sums the costs of the two steps, depthwise convolution and pointwise convolution.
The reduction in parameters can be justified by the ratio between the number of parameters in standard convolution and the number of parameters in depthwise separable convolution, as presented in Equation (5) [23]. Given that and , the ratio R demonstrates the efficiency of depthwise separable convolution compared to standard convolution.
In this way, this approach significantly reduces the computational cost, making depthwise separable convolution an efficient alternative for building lighter and faster models without compromising feature extraction capability.
3.2. Proposed Model Generator
The optimization based on depthwise separable convolution in the HDR-GAN generator blocks [16] uses not only the encoder–decoder scheme introduced by U-Net [39], but also a merging block to help with both image alignment and fusion. In order to assess the impact of these modifications, the original configurations of the other components of the HDR-GAN model were maintained, such as the loss function based on Kalantari et al.’s model [10], the Patch-GAN-based discriminator [40] with the sphere GAN loss function [41], and the pre-processing of the dataset for training.
Based on the research carried out by Niu et al. [16], where quantitative comparisons were conducted to assess the impact of different depths, the presence or absence of merging blocks and the use or not of the auxiliary upsampling path, three scales of depth, merging block and auxiliary upsampling path are used.
Thus, as illustrated in Figure 6, the proposed model receives as input three LDR images of different exposures, selects the medium exposure image as the reference, and the reconstruction process occurs through the multi-scale LDR encoder, reference-aligned feature fusion, and deep HDR supervision steps, generating the HDR image. In the multi-scale LDR encoder step, feature extraction is performed at three scales. For each input, the encoder block, represented by the blue blocks, is applied, which is a two-layer residual structure without a pooling layer, using two depthwise separable convolutions and adding them to the block input. Then, downsampling is performed, represented by the red arrows, using a depthwise separable convolution of a 3 × 3 kernel with stride 2, to move to the next scale. The reference-aligned feature fusion step merges the features extracted by scale, concatenating the results obtained by each encoder block of the same scale and processing them with the merging block, represented by the red blocks. The merging blocks have a four-layer residual structure, using four depthwise separable convolutions with a dilated factor of 2 and adding the feature corresponding to the average exposure image. Then, the deep HDR supervision step is performed from the merging block, in which the processed data are upsampled, represented by the blue arrows, and then concatenated with the data from the upper layer to serve as input for the decoder blocks, represented by the green blocks, with the same structure as the encoder block. In contrast to previous deep supervision methods [39], deep HDR supervision generates a sub-network, with a smaller number of layers and an auxiliary image output. This auxiliary upsampling path improves the quality of the output image and is used to benefit the training of the main upsampling path, composed of a larger number of layers representing the final HDR output of the network.
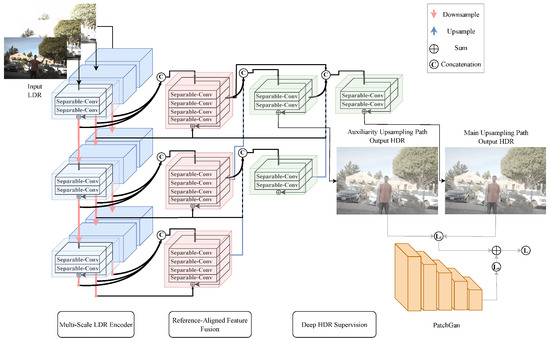
Figure 6.
Proposed model architecture.
Due to the effect of the discoloration generated by using the HDR image to calculate the supervised loss function of the generating model, as demonstrated by Kalantari et al. [10], the loss is measured from the images generated by the generating model in the tone-mapping domain, transformed from the -law function defined by Equation (6).
where represents the image in the tone-mapping domain, H is the image in the HDR domain, and is the determined compression factor.
Based on the research of Niu et al. [16], the outputs of the auxiliary upsampling path and main upsampling path of the model are used for measurement. Thus, the loss function defined in Equation (7) is used.
where represents the HDR image generated by the auxiliary upsampling path, corresponds to the HDR image generated by the main upsampling path, and is the ground truth HDR image.
3.3. Discriminator of the Proposed Model
The discriminator adopted is PatchGAN [40], which determines whether patches of are real or generated. The main benefit of this model is the low number of parameters, execution time, and the possibility of using images of any size. To perform the training, the value of N is the same as that used by the HDR-GAN model [16], consisting of using patches of from the training set, randomly cropping, rotating, and flipping the images.
To improve the geometric representation of the learned features, the adversarial loss function used is based on the Sphere GAN [41], where the discriminator is projected onto a hypersphere through inverse stereographic projection, ensuring that distances are measured on the surface of the hypersphere.
Given the discriminator , its output is mapped as a vector , which is projected to a point on the hypersphere via inverse stereographic projection, according to Equation (8).
The distance between two points projected onto the hypersphere can be measured using , defined by Equation (9).
In the context of GAN training, the adversarial loss is formulated as the distance between the features of the real and generated examples, mapped relative to a fixed reference point, the north pole of the hypersphere (), and given by Equation (10).
where is the distance of the r-th moments on the hypersphere (). Here, represents the real data (ground truth) and the Low-Dynamic-Range (LDR) input images.
Finally, the complete model is trained with a hybrid loss function calculated according to Equation (11).
where is the reconstruction loss and is the adversarial loss.
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
For model training, an NVIDIA A100 GPU with 40 GB of memory was used, employing the NVIDIA TensorFlow container (23.03-tf1-py3). The model was implemented using TensorFlow 1.15.2. The experiments were performed on a laptop equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3050 with 4 GB of memory, an Intel Core i7-12700H processor at 2.30 GHz, and 64 GB of RAM. It is worth noting that, with this GPU, the execution of the HDR-GAN model was unfeasible. However, the proposed model was executed on this hardware, evidencing its efficiency.
Training was conducted for 200,000 epochs, using batch size of eight and Adam optimizer, using and . Aiming for progressive and stable convergence of the model, the initial learning rate was for 25,000 epochs, followed by for 75,000 epochs, and for 100,000 epochs.
4.2. Dataset
In this research, the dataset from Kalantari et al. [10] is used for training and conducting the experiments. Additionally, a selection of scenes from the HDR-Eye dataset [25] is utilized for comparison between the baseline model and the proposed model. For qualitative visual comparisons of the generated results, scenes from the datasets Tursun et al. [27], Sen et al. [26], and Tel et al. [28], which contain exposures with motion, are used.
The Kalantari et al. [10] dataset consists of 74 training scenes and 15 test scenes, where each scene is composed of three LDR images with different exposures and motion between them. The HDR-Eye [25] dataset was created by combining nine bracketed images acquired with different exposures without motion. The resulting dataset comprises 46 images, encompassing a diverse range of subjects, including natural scenes (both indoor and outdoor), humans, stained glass, sculptures, historical buildings, etc. The Tursun [27] dataset contains 16 scenes, composed of nine different exposures with motion, while the Sen [26] dataset contains 8 scenes, composed of three or eight different exposures with motion, both without ground truth. The Tel et al. [28] dataset consists of 36 scenes with three different exposures with motion and ground truth.
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
To demonstrate how depthwise separable convolution contributes to reducing computational costs, the evaluation of the computational efficiency of the models will use the FLOPs (Floating Point Operations) metric, number of parameters, size of the model, inference time, and max GPU memory.
For the quantitative evaluation of the quality of the generated images, the PSNR [42] and SSIM [43] metrics are used. The PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio) metric is defined by Equation (12).
where MAX represents the maximum possible value of the signal; as the image is normalized, the value of this variable is set to 1. MSE is the mean squared error between the generated image and the reference image and is calculated using Equation (13).
where N is the total number of pixels in the image, represents the intensity of pixel i in the reference image, and is the intensity of the corresponding pixel in the reconstructed image. The difference calculates the error at each pixel, this value being squared to amplify significant deviations. The sum of these squared errors divided by N gives the mean value that quantifies the overall discrepancy between the two images.
The SSIM (Structural Similarity Index Measure) metric is defined by Equation (14).
where and are the means of the images x and y, and are the variances, is the covariance, and and are constants for numerical stabilization.
The PSNR and SSIM metrics are calculated in their linear form (), using the image in HDR format, and in their tone-mapped form (), using the transformation defined by Equation (6). Additionally, emerging approaches are used for deeper and more detailed analysis, including PSNR and SSIM in the perceptually uniform () domain [44], HDR-VDP2.2 [45,46], HDR-VDP3 [47], and IL-NIQE [48]. The IL-NIQE metric, which does not need reference images, aims to analyze the model’s generalization capacity for high-resolution, static, and moving images.
4.4. Quantitative Results
The approaches used in the comparative analysis include the traditional Patch-Based method [26], the pioneering DHDRNet model [10], Lopez-Cabrejos et al.’s model [49], a state-of-the-art Transformer-based model aiming at low computational cost, the HDR-GAN [16] used as a basis, and the proposed model. The metrics of the Patch-Based, DHDRNet, Lopez-Cabrejos et al., and HDR-GAN models come from the reference papers [10,16,18], trained using the Kalantari dataset, with the exception of Patch-Based, which does not undergo training. Regarding the number of FLOPs and the number of parameters, all values were calculated.
The performance evaluation of the models using the Kalantari dataset considers the quality metrics PSNR- and SSIM-, as well as FLOPS, number of parameters, model size, inference time, and GPU memory used, which indicate the computational cost and complexity of the architecture, presented in Table 1. The results demonstrate that the proposed model offers an excellent balance between performance and computational efficiency. Although the Lopez-Cabrejos et al. model achieves the best values in PSNR- of 44.10 and SSIM- of 0.9924, our solution presents a competitive performance of 43.51 for PSNR- and 0.9917 for SSIM-, with significant advantages in terms of computational cost, presenting a lower number of FLOPs of 0.232 T, a reduced size of 1.45 MB, a faster inference time of 0.15 s, and an efficient GPU memory consumption using a maximum of 4.5 GB. Compared to HDR-GAN, the proposed model reduces FLOPs by 6.3×, parameters by 7×, size by 7.5×, and GPU memory by half, highlighting the effectiveness of depthwise separable convolutions for a lightweight and efficient architecture ideal for resource-constrained applications.

Table 1.
Comparison of quality in relation to computational cost of models trained with Kalantari dataset.
In order to carry out a complete comparative analysis of the performance of the proposed model, calculations were performed with the other quality metrics, and the results are presented in Table 2. The results demonstrate that the proposed model, with seven times fewer parameters than HDR-GAN, maintains a competitive performance, achieving the best value in the SSIM-l metric with 0.9887 and ranking second in the PSNR- metrics with 43.17, SSIM- with 0.9902, and HDR-VDP3 with 9.24. Although the Lopez-Cabrejos et al. model presents superior performance in PSNR-l with 42.07 and HDR-VDP2 with 67.79, its evaluation being limited to only three metrics restricts the comparative analysis. Regarding HDR-GAN, the proposal shows comparable efficiency in the reconstruction of HDR images, with minimum differences of 0.03 in PSNR- and 0.0011 in SSIM-, consolidating itself as a lighter alternative that preserves visual quality, in addition to outperforming all models in the SSIM-l criterion.

Table 2.
Comparison of quality metrics used for HDR image evaluation.
To analyze the generalization capability of the proposed model in relation to HDR-GAN, an analysis was performed using the IL-NIQE metric [48] calculated from the image in the tone-mapped domain. The comparisons made with this metric use the dynamic images from the Kalantari test set [10] and a selection of thirteen high-resolution static images from HDR-Eye [25], selected by the light condition, using only three exposures (EV , EV 0, and EV +2).
Table 3 presents the results obtained from the Kalantari test set. It can be seen that the proposed model has the ability to reconstruct samples, obtaining values identical to the HDR-GAN model with IL-NIQE of 20.07. Thus, in the specific context of training with images characterized by movement and a resolution of , and considering the reduction in computational cost and number of parameters, the proposed model achieved excellent performance.

Table 3.
Comparison of IL-NIQE between the HDR-GAN and the proposed model using the Kalantari dataset.
For the selected images from the HDR-Eye set [25], the results calculated in terms of IL-NIQE are presented in Table 4. It can be seen that the proposed model outperformed the HDR-GAN model, reaching an IL-NIQE value of 24.52, demonstrating the ability to generalize and merge static images.

Table 4.
Comparison of IL-NIQE between the HDR-GAN and the proposed model using the HDR-Eye dataset.
The results obtained highlight the proposed model as an efficient and competitive solution for HDR image reconstruction. By replacing conventional convolutions with depthwise separable convolutions, it became possible to achieve a significant reduction in computational cost, evidenced by the reduction in FLOPs, without compromising the visual quality of the generated images. In addition, the model maintained a number of parameters close to those of solutions such as DHDRNet, demonstrating its efficiency. Quantitative analyses, both in traditional and HDR-specific metrics, show that the proposed model is capable of reconstructing HDR images of excellent quality, surpassing or equaling the results of the compared methods. Furthermore, tests performed with dynamic images, using the Kalantari dataset, prove its ability to reconstruct HDR images from exposures with movement. Finally, tests with the HDR-Eye dataset prove the model’s ability to generalize to different scenarios, reaffirming its potential for practical applications.
4.5. Qualitative Results
To verify the performance of the proposed model, a qualitative analysis of scenes from the datasets of Sen et al. [26], Tursun et al. [27], Tel et al. [28], and Kalantari et al. [10] was carried out, where one scene from each dataset was selected to perform the analyses with the Patch-Based [26], DHDRNet [10], HDR-GAN [16], Lopez-Cabrejos [49] models and the proposed model, respectively.
The structure of the scene presentation is composed of three different input exposures (LDRs), the image reconstructed by the proposed model, cutouts of the input regions that will be analyzed, and the comparison between the models. Therefore, Figure 7 shows an analysis of the HighChair scene from the Sen et al. dataset, chosen due to its characteristics of slight movements, as indicated in the blue rectangle, and saturated background in the red rectangle, as can be seen in Figure 7a. All models obtained excellent results in the alignment performed in the Cropped Section Figure 7b, demonstrating that the magnitude of movement in this scene was not challenging. Meanwhile, in the Cropped Section Figure 7c, all models reconstructed a smooth background, with the exception of DHDRNet [10] and Lopez-Cabrejos [49], which exhibited artifacts at the image saturation level or oversaturation.
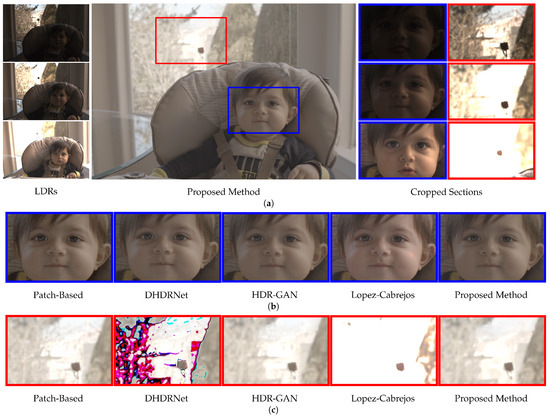

Figure 7.
Analysis of the HighChair image of the Sen et al. dataset [26], checking for short motion and a saturated background.
Figure 8 illustrates the analysis of the scene Toytrain of the Tursun et al. [27] dataset, representing low-light conditions and large movements, as shown in detail in Figure 8a. In the Cropped Section Figure 8b shown in the blue rectangle, the Patch-Based [26] model, Lopez-Cabrejos [49] model, and the proposed model presented artifacts in dark scenes, possibly due to the [10] dataset used for training, which contains mostly bright scenes [28]. This suggests that dataset diversification, including different lighting conditions, is essential for models with a low number of parameters. However, the proposed model demonstrated good performance in the reconstruction of large movements in the Cropped Section Figure 8c, highlighted by the red rectangle, while DHDRNet [10] generated light artifacts and the Lopez-Cabrejos model [49] produced a reconstruction of this region with excessive brightness, leading to loss of information.
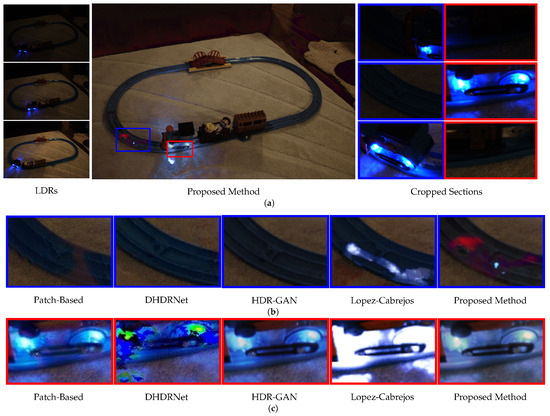
Figure 8.
Analysis ofimage Toytrain of Tursun et al. dataset [27], checking dark scene and reconstruction of objects with large motion.
Using scene 21-1 from the Tel et al. [28] dataset, presented in Figure 9, containing features of high background saturation and large movement, challenging situations are demonstrated, as can be seen in Figure 9a. In the analyzed area of the red rectangle, in the Cropped Section Figure 9b, the proposed model demonstrated a smooth background and avoided artifacts caused by movement. Unlike this, the HDR-GAN [16] model presented ghosting in this area.

Figure 9.
Analysis of image 21-1 of Tel et al. dataset [28], checking the reconstruction of an overexposed background and large motion.
Figure 10 shows scene 009 of the Kalantari et al. [10] dataset, presenting challenges related to areas occluded by the movement of objects, as indicated in the region under analysis in the blue rectangle and saturated objects in the area of the red rectangle, Figure 10a. All models had difficulties in reconstructing the Cropped Section Figure 10b, while in the Cropped Section Figure 10c, Lopez-Cabrejos [49] demonstrated the best performance in representing the shape of the building, while the proposed model managed to represent it considerably, only presenting divergence in tone.

Figure 10.
Analysis of image 009 of Kalantari et al. dataset [10], evaluating the ability to reconstruct occluded objects due to movement and the preservation of building shapes.
From the qualitative analysis, it can be observed that the proposed model excelled in the reconstruction of areas saturated by overexposure and object alignment, regardless of the magnitude of the movement analyzed, avoiding movement artifacts. In low-light scenarios, the proposed model presented limitations, with behavior similar to Patch-Based. On the other hand, the proposed model was able to reconstruct images with a higher quality than DHDRNet in different scenarios. It managed to avoid several artifacts that occurred in the Lopez-Cabrejos and HDR-GAN models, indicating that the depthwise separable convolution used in this model optimized the structure, reducing non-essential parameters, without compromising the quality of the reconstruction.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
This paper presents a lightweight architecture for HDR image reconstruction based on a GAN, using techniques to reduce the computational cost while maintaining the visual quality of the image. The training was conducted with the Kalantari dataset, and the HDR-Eye, Sen, Kalantari, Tursun, and Tel datasets were also used for the experiments. The HDR-GAN architecture was used as a basis for the proposed model, whose optimization was performed through the application of the depthwise separable convolution technique to replace standard convolution. The validation of the proposed model was performed through quantitative and qualitative analyses, comparing the results with the Patch-Based, DHDRNet, HDR-GAN, and Lopez-Cabrejos et al. reconstruction models. For the quantitative evaluation, the metrics PSNR, PSNR, PSNR, SSIM, SSIM, SSIM, HDR-VDP2, HDR-VDP3, and IL-NIQE were used. The computational cost was analyzed based on the number of parameters, FLOPs, model size, inference time, and GPU memory consumption. In the qualitative assessment, different challenges related to the magnitude of movement and saturation ratio were explored.
The results of the quantitative analyses demonstrated that the proposed model achieved competitive quantitative metrics, with a PSNR value of 43.51 dB when compared to the DHDRNet model, which has a similar computational complexity. While the Lopez-Cabrejos et al. model achieved higher scores in some metrics, with 42.07 in PSNR-l and 67.79 in HDR-VDP2, its evaluation was limited to fewer metrics. In comparison with the HDR-GAN model, the performance results in the reconstruction of the HDR image remained close. When comparing the computational cost of the models, the proposed model had a 6-fold reduction in FLOPs, a 7-fold reduction in the number of parameters, a 7.5-fold reduction in model size, with 1.45 MB versus 10.9 MB, faster inference time, with 0.15 s versus 0.19 s, and lower GPU memory consumption, with 4.5 GB versus 8.3 GB, evidencing the efficiency of the proposed model in the search for a better balance between visual quality and computational cost. In addition, the proposed method achieved remarkable values in the SSIM metrics with 0.9917 and SSIM with 0.9887, surpassing the other evaluated models. Using a selection of images from Kalantari and HDR-Eye, the proposed method achieved the highest IL-NIQE value of 24.52, proving its ability in the reconstruction of HDR images from exposures with movement and the ability of the model to generalize to different scenarios. Regarding the qualitative analysis, the proposed method presented adequate behavior, highlighting the reconstruction of areas saturated by overexposure and object alignment.
The results obtained and presented in this paper highlight the potential of the proposed model and indicate several promising paths for future research in the development of more efficient and generalizable architectures for HDR image reconstruction. These include the development of a proprietary generative model, due to the visible margin of improvement in the quality of HDR image reconstruction, particularly in metrics where the Lopez-Cabrejos et al. model showed superior performance, performance of statistical significance analysis, and the use of a training dataset with a greater variety of scenarios in terms of luminosity, motion magnitude, and saturation ratio, which should be addressed in future work. Additional optimization of inference time could also be explored to further improve the model’s practical applicability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.d.S.F., T.P. and A.B.A.; methodology, G.d.S.F.; software, G.d.S.F.; validation, G.d.S.F., T.P. and A.B.A.; formal analysis, G.d.S.F.; investigation, G.d.S.F., T.P. and A.B.A.; resources, A.B.A.; data curation, G.d.S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, G.d.S.F. and T.P.; writing—review and editing, G.d.S.F., T.P. and A.B.A.; visualization, G.d.S.F.; supervision, A.B.A.; project administration, T.P. and A.B.A.; funding acquisition, A.B.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the PAVIC Laboratory, which benefited from SUFRAMA fiscal incentives under Brazilian Law No. 8387/1991.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support from the PAVIC Laboratory (Pesquisa Aplicada em Visão e Inteligência Computacional) at the University of Acre, Brazil.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Johnson, A.K. High dynamic range imaging—A review. Int. J. Image Process. (IJIP) 2015, 9, 198. [Google Scholar]
- Seetzen, H.; Heidrich, W.; Stuerzlinger, W.; Ward, G.; Whitehead, L.; Trentacoste, M.; Ghosh, A.; Vorozcovs, A. High dynamic range display systems. In Seminal Graphics Papers: Pushing the Boundaries; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2, pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yoon, K.J. Deep learning for hdr imaging: State-of-the-art and future trends. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 8874–8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, G.; Rani, P. A review on high-dynamic-range imaging with its technique. Int. J. Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitard, R.; Pourazad, M.T.; Nasiopoulos, P.; Slevinsky, J. Demystifying high-dynamic-range technology: A new evolution in digital media. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2015, 4, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Multi-exposure image fusion techniques: A comprehensive review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debevec, P.E.; Malik, J. Recovering high dynamic range radiance maps from photographs. In Seminal Graphics Papers: Pushing the Boundaries; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2, pp. 643–652. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar, K.R.; Agrawal, S.; Singh, D.K.; Ashwath, B.; Babu, R.V. Towards practical and efficient high-resolution HDR deghosting with CNN. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXI 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 497–513. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Gallo, O.; Pulli, K.; Sun, X. HDR deghosting: How to deal with saturation? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on coMputer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 1163–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantari, N.K.; Ramamoorthi, R. Deep High Dynamic Range Imaging of Dynamic Scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH 2017) 2017, 36, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; NIPS: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. NIPS’14. Volume 2, pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Raipurkar, P.; Pal, R.; Raman, S. HDR-cGAN: Single LDR to HDR image translation using conditional GAN. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing, Virtual Event, 20–22 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Serrano, A.; Pan, X.; Chen, B.; Seidel, H.P.; Theobalt, C.; Myszkowski, K.; Leimkuehler, T. GlowGAN: Unsupervised Learning of HDR Images from LDR Images in the Wild. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2211.12352. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.P. MEF-GAN: Multi-Exposure Image Fusion via Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7203–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zeng, B.; Liu, S. Uphdr-gan: Generative adversarial network for high dynamic range imaging with unpaired data. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 7532–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Guo, W.; Lau, R.W. Hdr-gan: Hdr image reconstruction from multi-exposed ldr images with large motions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3885–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; KS, U.R.; Naik, S.M.; Panja, M.; Manvitha, B. Ten years of generative adversarial nets (GANs): A survey of the state-of-the-art. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2024, 5, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tel, S.; Heyrman, B.; Ginhac, D. Cen-hdr: Computationally efficient neural network for real-time high dynamic range imaging. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 378–394. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- V, A.; Kiran, A.G. SynthNet: A skip connected depthwise separable neural network for Novel View Synthesis of solid objects. Results Eng. 2022, 13, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.S.; Krishnan, K.S. SwiftSRGAN-Rethinking super-resolution for efficient and real-time inference. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Cybernetics Technology & Applications (ICICyTA), Bandung, Indonesia, 1–2 December 2021; pp. 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Deng, X.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Z. Fabric defect detection using a one-class classification based on depthwise separable convolution autoencoder. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2023, 2562, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Kang, Y. A Lightweight Stereo Matching Neural Network Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications (ICTA), Hefei, China, 27–29 October 2023; pp. 122–123. [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto, H.; Korshunov, P.; Hanhart, P.; Ebrahimi, T. Visual attention in LDR and HDR images. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Video Processing and Quality Metrics for Consumer Electronics (VPQM), Chandler, AZ, USA, 5–6 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.; Kalantari, N.K.; Yaesoubi, M.; Darabi, S.; Goldman, D.B.; Shechtman, E. Robust patch-based hdr reconstruction of dynamic scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursun, O.T.; Akyüz, A.O.; Erdem, A.; Erdem, E. An objective deghosting quality metric for HDR images. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 35, pp. 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Tel, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Heyrman, B.; Demonceaux, C.; Timofte, R.; Ginhac, D. Alignment-free HDR Deghosting with Semantics Consistent Transformer. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, K.; Andersen, H.J. Noise Characterization of Weighting Schemes for Combination of Multiple Exposures. In Proceedings of the BMVC, Edinburgh, UK, 4–7 September 2006; Volume 3, pp. 1129–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Granados, M.; Ajdin, B.; Wand, M.; Theobalt, C.; Seidel, H.P.; Lensch, H.P. Optimal HDR reconstruction with linear digital cameras. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, E.A.; Akyuz, A.O.; Reinhard, E. Ghost removal in high dynamic range images. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Image Processing, Las Vegas, NA, USA, 26–29 June 2006; pp. 2005–2008. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, S.; Chaudhuri, S. Reconstruction of high contrast images for dynamic scenes. Vis. Comput. 2011, 27, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, A.; Mantiuk, R. Image Registration for Multi-Exposure High Dynamic Range Image Acquisition; Vaclav Skala-UNION Agency: Plzen, Czech Republic, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L. Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2049–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, M.D. The HDR photographic survey. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 5–9 November 2007; Society of Imaging Science and Technology: Springfield, VA, USA, 2007; Volume 15, pp. 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Chollet, F. Depthwise Separable Convolutions for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Rosing, T. Depthwise convolution is all you need for learning multiple visual domains. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8368–8375. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.W.; Kwon, J. Sphere generative adversarial network based on geometric moment matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4292–4301. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh-Thu, Q.; Ghanbari, M. Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, U.; Akter, M.; Uddin, M.S. Image quality assessment through FSIM, SSIM, MSE and PSNR—a comparative study. J. Comput. Commun. 2019, 7, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoué, G.; Mantiuk, R. Quality Assessment in Computer Graphics. In Visual Signal Quality Assessment: Quality of Experience (QoE); Deng, C., Ma, L., Lin, W., Ngan, K.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 243–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantiuk, R.; Kim, K.J.; Rempel, A.G.; Heidrich, W. HDR-VDP-2: A calibrated visual metric for visibility and quality predictions in all luminance conditions. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH, Hong Kong, China, 12–15 December 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwaria, M.; Mantiuk, R.K.; Da Silva, M.P.; Le Callet, P. HDR-VDP-2.2: A calibrated method for objective quality prediction of high-dynamic range and standard images. J. Electron. Imaging 2015, 24, 010501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantiuk, R.K.; Hammou, D.; Hanji, P. HDR-VDP-3: A multi-metric for predicting image differences, quality and contrast distortions in high dynamic range and regular content. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.13625. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A.C. A Feature-Enriched Completely Blind Image Quality Evaluator. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Cabrejos, J.; Paixão, T.; Alvarez, A.B.; Luque, D.B. An Efficient and Low-Complexity Transformer-Based Deep Learning Framework for High-Dynamic-Range Image Reconstruction. Sensors 2025, 25, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).