Hierarchical Modeling for Medical Visual Question Answering with Cross-Attention Fusion
Abstract
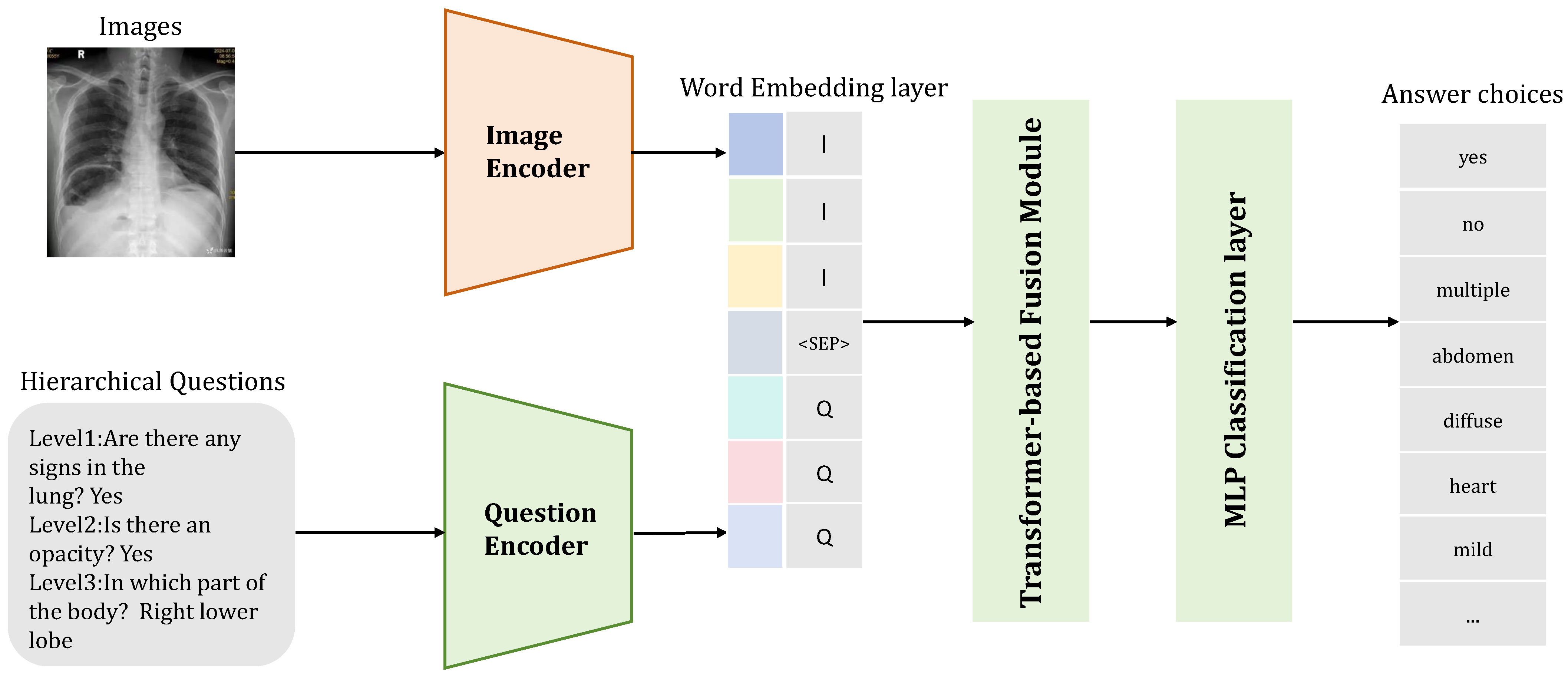
1. Introduction
- We introduce a hierarchical prompting module and hierarchical answer decoders that provide different context prompts based on varying levels of question-image sample pairs to guide the model’s attention to distinct image regions.
- We incorporate cross-attention into multi-modal feature fusion to utilize attention mechanisms for emphasizing critical components, establishing precise associations between anatomical regions and diagnostic terminology through directed alignment, and outputting a final embedding reflecting inter-modal interactions. This achieves accurate mapping between local lesions and textual terms while enhancing robustness against cross-modal noise.
- Experimental results prove that our strategy outperforms baseline methods and current state-of-the-art approaches on the Rad-Restruct [9] dataset, achieving new state-of-the-art performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Pretrained Models in Medical Visual Question Answering
2.2. Hierarchical Medical Visual Question Answering
2.3. Context Alignment Enhancements
3. Methodology
3.1. Hierarchical Prompting Module
3.2. Image Encoder
3.3. Text Encoder
3.4. Alignment Module
3.5. Hierarchical Answer Decoders
| Algorithm 1: Weighted masked cross-entropy loss |
 |
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Training and Evaluation
4.3. Baseline and SOTA
4.4. Comparative Results
4.5. Experimental Results
4.6. Ablation Experiments
4.7. Qualitative Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben Abacha, A.; Hasan, S.A.; Datla, V.V.; Demner-Fushman, D.; Müller, H. Vqa-med: Overview of the medical visual question answering task at imageclef 2019. In Proceedings of the CLEF (Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum) 2019 Working Notes, Lugano, Switzerland, 9–12 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, B.; Sun, B.; Weng, Y. Towards Visual-Prompt Temporal Answer Grounding in Instructional Video. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 8836–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, D.; Tao, Q.; Shi, D.; Haffari, G.; Wu, Q.; He, M.; Ge, Z. Medical visual question answering: A survey. Artif. Intell. Med. 2023, 143, 102611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Jiang, L.; He, X.; Pan, Y.; Cai, Y. A Weakly Supervised and Globally Explainable Learning Framework for Brain Tumor Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 5–19 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gabruseva, T.; Poplavskiy, D.; Kalinin, A. Deep learning for automatic pneumonia detection. In Proceedings of the the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 350–351. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xi, Y.; Eweje, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Bergstrom, C.; Gopaulchan, M.; Kim, T.; et al. A vision–language foundation model for precision oncology. Nature 2025, 638, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z. MedCoT: Medical Chain of Thought via Hierarchical Expert. In Proceedings of the the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; pp. 17371–17389. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Xiao, R.; Pan, Y.; Cai, Y. Accurate Explanation Model for Image Classifiers using Class Association Embedding. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 40th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 2271–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, C.; Keicher, M.; Özsoy, E.; Navab, N. Rad-restruct: A novel vqa benchmark and method for structured radiology reporting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023; pp. 409–419. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Ouyang, Z.; Qing, P.; Cheng, M.; Vosoughi, S.; Gui, J. Temporal Working Memory: Query-Guided Segment Refinement for Enhanced Multimodal Understanding. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.06020. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, X.; Cheng, M.; Barrios, W.; Jin, S. FT2TF: First-Person Statement Text-To-Talking Face Generation. In Proceedings of the the Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Tucson, AZ, USA, 28 February–4 March 2025; pp. 4821–4830. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Dai, T.; Huang, X.; Ma, F.; Xiao, J. Image Augmentation with Controlled Diffusion for Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024-2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 6175–6179. [Google Scholar]
- Eslami, S.; Meinel, C.; De Melo, G. Pubmedclip: How much does clip benefit visual question answering in the medical domain? In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EACL 2023, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2–6 May 2023; pp. 1181–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, M.; Katsantoni, M.; Köster, T.; Marks, J.; Mukherjee, J.; Staiger, D.; Ule, J.; Zavolan, M. CLIP and complementary methods. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; McAuley, J.; Lu, X.; Du, J.; Chang, E.Y.; Gentili, A.; Hsu, C.N. RadBERT: Adapting transformer-based language models to radiology. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e210258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, N.; Geras, K.J.; Shamout, F.E. MedFuse: Multi-modal fusion with clinical time-series data and chest X-ray images. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, PMLR, Durham, NC, USA, 5–6 August 2022; pp. 479–503. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, J.J.; Gayen, S.; Ben Abacha, A.; Demner-Fushman, D. A dataset of clinically generated visual questions and answers about radiology images. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Syeda-Mahmood, T.; Wong, K.C.; Gur, Y.; Wu, J.T.; Jadhav, A.; Kashyap, S.; Karargyris, A.; Pillai, A.; Sharma, A.; Syed, A.B.; et al. Chest x-ray report generation through fine-grained label learning. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Proceedings, Part II 23. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalodia, R.; Hatamizadeh, A.; Tam, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Turkbey, E.; Xu, D. Improving pneumonia localization via cross-attention on medical images and reports. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Proceedings, Part II 24. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 571–581. [Google Scholar]
- Kovaleva, O.; Shivade, C.; Kashyap, S.; Kanjaria, K.; Wu, J.; Ballah, D.; Coy, A.; Karargyris, A.; Guo, Y.; Beymer, D.B.; et al. Towards visual dialog for radiology. In Proceedings of the 19th SIGBioMed Workshop on Biomedical Language Processing, Online, 9 July 2020; pp. 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Mou, L.; Xing, E.; Xie, P. Pathvqa: 30000+ questions for medical visual question answering. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10286. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhan, L.M.; Xu, L.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.M. Slake: A semantically-labeled knowledge-enhanced dataset for medical visual question answering. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1650–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R.; Sun, L.; Xia, Y.; Qin, T.; Zhang, S.; Poon, H.; Liu, T.Y. BioGPT: Generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining. Briefings Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 19730–19742. [Google Scholar]
- Fidder, H.; Chowers, Y.; Ackerman, Z.; Pollak, R.D.; Crusius, J.B.A.; Livneh, A.; Bar-Meir, S.; Avidan, B.; Shinhar, Y. The familial Mediterranean fever (MEVF) gene as a modifier of Crohn’s disease. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol.|ACG 2005, 100, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalane, W.; Chikontwe, P.; Luna, M.; Kang, M.; Park, S.H. Context-Guided Medical Visual Question Answering. In Medical Information Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J. PubMed 2.0. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 2020, 39, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Voita, E.; Talbot, D.; Moiseev, F.; Sennrich, R.; Titov, I. Analyzing Multi-Head Self-Attention: Specialized Heads Do the Heavy Lifting, the Rest Can Be Pruned. In Proceedings of the the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 5797–5808. [Google Scholar]
- Demner-Fushman, D.; Kohli, M.D.; Rosenman, M.B.; Shooshan, S.E.; Rodriguez, L.; Antani, S.; Thoma, G.R.; McDonald, C.J. Preparing a collection of radiology examinations for distribution and retrieval. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2016, 23, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipscomb, C.E. Medical subject headings (MeSH). Bull. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2000, 88, 265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Langlotz, C. RadLex: A new method for indexing online educational materials. Radiographics 2006, 26, 1595–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Y.; Shi, H.; Ma, R.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. FedRL: A reinforcement learning federated recommender system for efficient communication using reinforcement selector and hypernet generator. ACM Trans. Recomm. Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qiu, X.; Song, S.; Chen, Z.; Huang, X.; Ma, F.; Xiao, J. Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.20439. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Dai, T.; Chen, Z.; Huang, X.; Xiao, J.; Ma, F.; Ouyang, R. Adaptive Patch Contrast for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Fan, C.; Zhou, R.; Ma, R.; Liu, Y. Personalized Consumer Federated Recommender System Using Fine-grained Transformation and Hybrid Information Sharing. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonce, B. EfficientNet. In Convolutional Neural Networks with Swift for Tensorflow: Image Recognition and Dataset Categorization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Sun, B.; Li, S.; Chen, E.; Liu, H.; Weng, Y.; Bai, Y.; Hu, M. Distinct but correct: Generating diversified and entity-revised medical response. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2024, 67, 132106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridi, L.; Chiriatti, M. GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Minds Mach. 2020, 30, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.D.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, B.X.; Do, T.; Tjiputra, E.; Tran, Q.D. Overcoming data limitation in medical visual question answering. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Proceedings, Part IV 22. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.; Nguyen, B.X.; Tjiputra, E.; Tran, M.; Tran, Q.D.; Nguyen, A. Multiple meta-model quantifying for medical visual question answering. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Proceedings, Part V 24. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, Y.; Bagal, V.; Mathew, M.; Devi, A.; Priyakumar, U.D.; Jawahar, C. Mmbert: Multimodal bert pretraining for improved medical vqa. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1033–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhan, L.M.; Wu, X.M. Contrastive pre-training and representation distillation for medical visual question answering based on radiology images. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September– 1 October 2021; Proceedings, Part II 24. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 210–220. [Google Scholar]
- Tanwani, A.K.; Barral, J.; Freedman, D. Repsnet: Combining vision with language for automated medical reports. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 714–724. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Du, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Wan, X.; Chang, T.H. Multi-modal masked autoencoders for medical vision-and-language pre-training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 679–689. [Google Scholar]
- Shavit, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Brundage, M.; Adler, S.; O’Keefe, C.; Campbell, R.; Lee, T.; Mishkin, P.; Eloundou, T.; Hickey, A.; et al. Practices for Governing Agentic AI Systems. Research Paper, OpenAI. 2023. Available online: https://cdn.openai.com/papers/practices-for-governing-agentic-ai-systems.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2025).




| Model | Acc |
|---|---|
| MEVF [43] | 66.1 |
| MMQ [44] | 67.0 |
| MM-BERT [45] | 72.0 |
| CRPD [46] | 72.7 |
| RepsNet [47] | 73.5 |
| M3AE [48] | 77.0 |
| Hi-VQA [9] | 76.3 |
| HiCA-VQA (Ours) | 79.6 |
| Model | Report Accuracy | F1 | Prec | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hi-VQA [9] | 32.6 | 31.9 | 59.9 | 34.1 |
| con-VQA [29] | 39.7 | 31.0 | 90.4 | 33.6 |
| HiCA-VQA (Ours) | 39.9 | 49.1 | 69.8 | 34.2 |
| Level | Hi-Acc | Hi-F1 | Hi-Pre | Hi-Rec | Context-Acc | Context-F1 | Context-Pre | Context-Rec | HiCA-Acc | HiCA-F1 | HiCA-Pre | HiCA-Rec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level1 | 33.6 | 64.3 | 81.0 | 64.5 | 34.7 | 67.2 | 80.7 | 61.2 | 33.7 | 68.5 | 81.1 | 64.6 |
| Level2-all | 31.0 | 71.6 | 85.2 | 72.0 | 32.9 | 71.8 | 88.9 | 70.8 | 31.0 | 78.3 | 86.0 | 72.0 |
| Level2-diseases | 48.1 | 73.5 | 83.8 | 71.3 | 52.1 | 72.8 | 89.6 | 72.7 | 48.2 | 81.1 | 84.5 | 74.1 |
| Level2-signs | 71.9 | 74.2 | 93.1 | 74.4 | 74.4 | 73.7 | 90.6 | 73.7 | 71.9 | 77.1 | 93.1 | 74.2 |
| Level2-objects | 87.4 | 67.0 | 77.1 | 67.5 | 91.4 | 67.2 | 85.0 | 68.6 | 87.7 | 84.6 | 77.5 | 67.9 |
| Level2-regions | 52.4 | 68.1 | 82.1 | 69.5 | 61.2 | 68.7 | 85.4 | 68.3 | 52.4 | 72.5 | 84.1 | 69.6 |
| Level3 | 30.2 | 4.1 | 49.9 | 6.2 | 32.5 | 3.2 | 68.7 | 4.2 | 29.6 | 29.0 | 58.5 | 7.9 |
| Method | Proposed Module | Metrics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF | CF | AL | HD | Acc | F1 | Pre | Rec | ||
| Hi-VQA [9] | (a) | ✓ | × | × | × | 32.6 | 31.7 | 70.7 | 32.1 |
| (b) | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | 33.7 | 29.5 | 80.4 | 30.7 | |
| con-VQA [29] | (a) | ✓ | × | × | × | 32.6 | 28.7 | 80.0 | 28.8 |
| (b) | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | 39.7 | 31.0 | 90.4 | 33.6 | |
| HiCA-VQA (Ours) | (a) | × | ✓ | × | × | 38.0 | 33.0 | 67.7 | 32.2 |
| (b) | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | 36.8 | 32.7 | 68.2 | 32.3 | |
| (c) | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 39.9 | 49.1 | 69.8 | 34.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Zhou, S. Hierarchical Modeling for Medical Visual Question Answering with Cross-Attention Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094712
Zhang J, Li B, Zhou S. Hierarchical Modeling for Medical Visual Question Answering with Cross-Attention Fusion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094712
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junkai, Bin Li, and Shoujun Zhou. 2025. "Hierarchical Modeling for Medical Visual Question Answering with Cross-Attention Fusion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094712
APA StyleZhang, J., Li, B., & Zhou, S. (2025). Hierarchical Modeling for Medical Visual Question Answering with Cross-Attention Fusion. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094712







