Diffusion and Consolidation of Slag-Based Geopolymer for Concrete Pavement Rehabilitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of Geopolymer Grouting Material
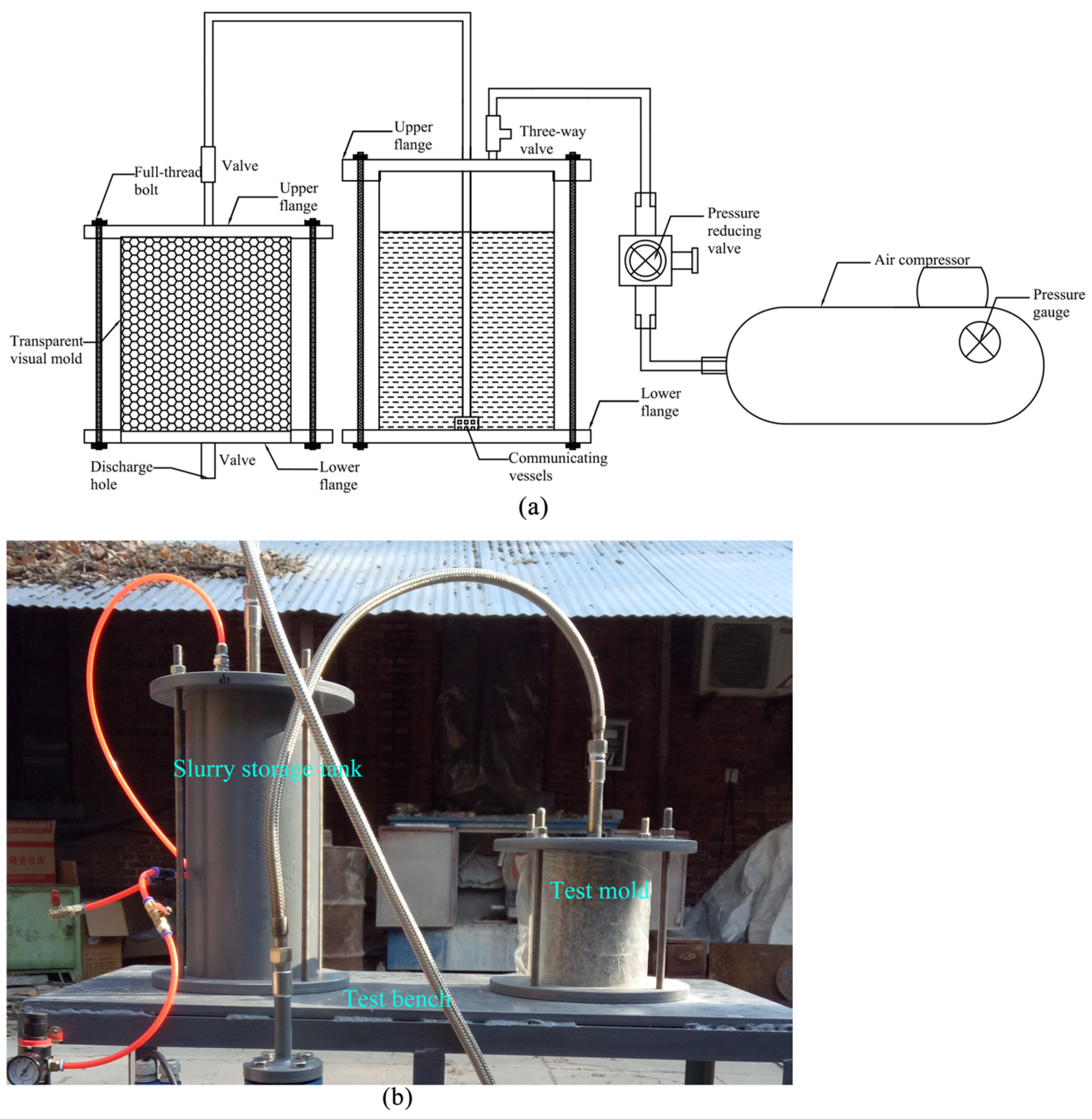
2.2. New Grouting System
2.3. Testing Methods
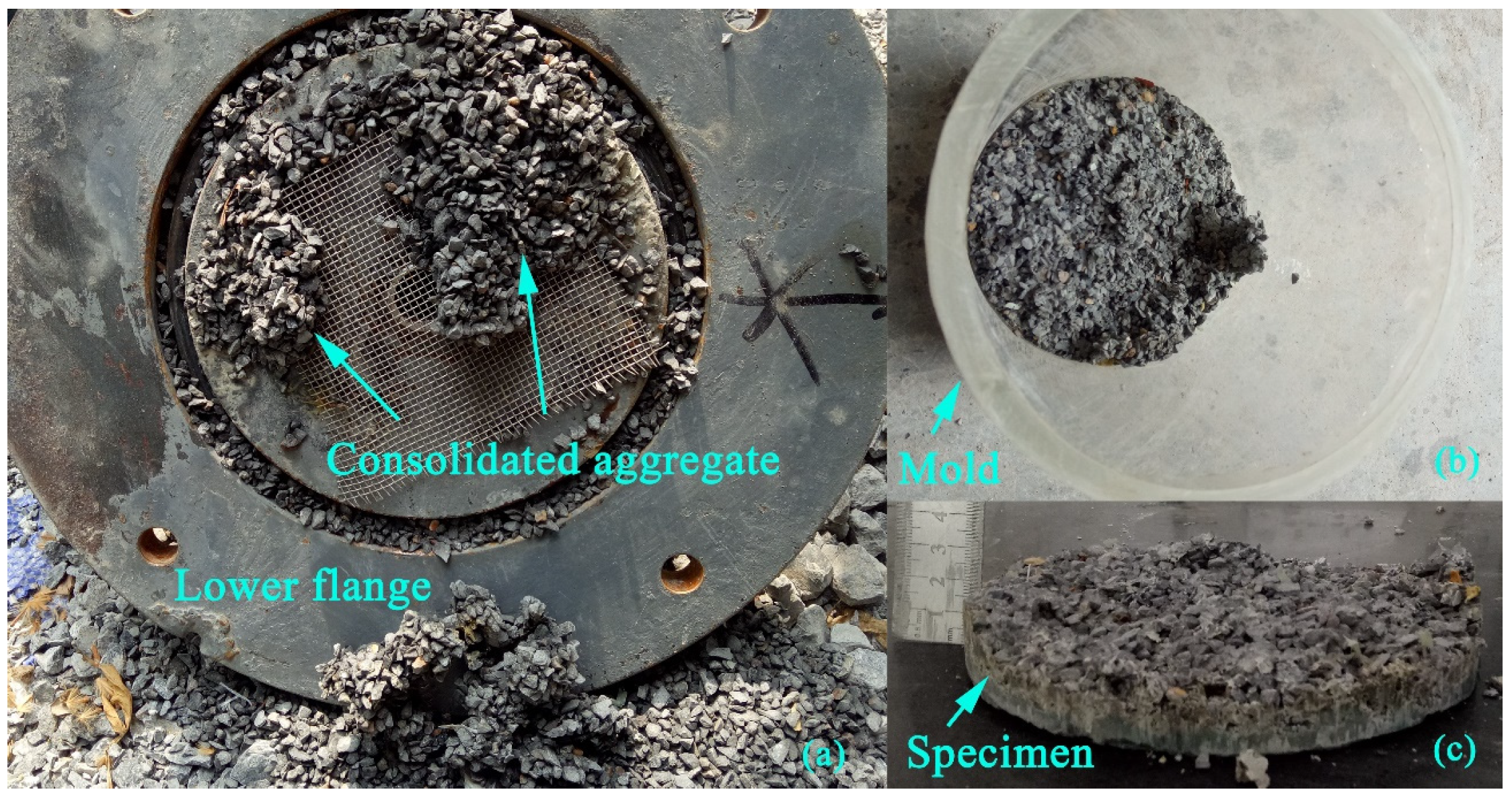
2.3.1. Indoor Grouting Test
- (1)
- Firstly, the slurry storage tank and test mold were assembled, and the aggregate was filled and compacted in layers to meet the requirements of controlling porosity.
- (2)
- The connection of pipelines between the air pump compressor, pressure reducing valve, and three-way valve were checked, so as to ensure that the slurry storage tank can be pressurized normally and the pressure reducing valve can adjust the pressure properly.
- (3)
- The geopolymer grouting slurry was prepared according to the designed water–slag ratio.
- (4)
- The slurry was poured into the storage tank, and the top flange was securely tightened to prevent leakage.
- (5)
- The air valve was opened for grouting test, and the geopolymer slurry gradually diffused in the test mold. In the test mold, when the slurry basically did not change for 1 min, the grouting valve on the top flange of the test mold was closed, and the air valve was also closed at the same time.
2.3.2. Microscopic Test of Geopolymer
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Single-Gradation 9.5–4.75 mm Grouting Test
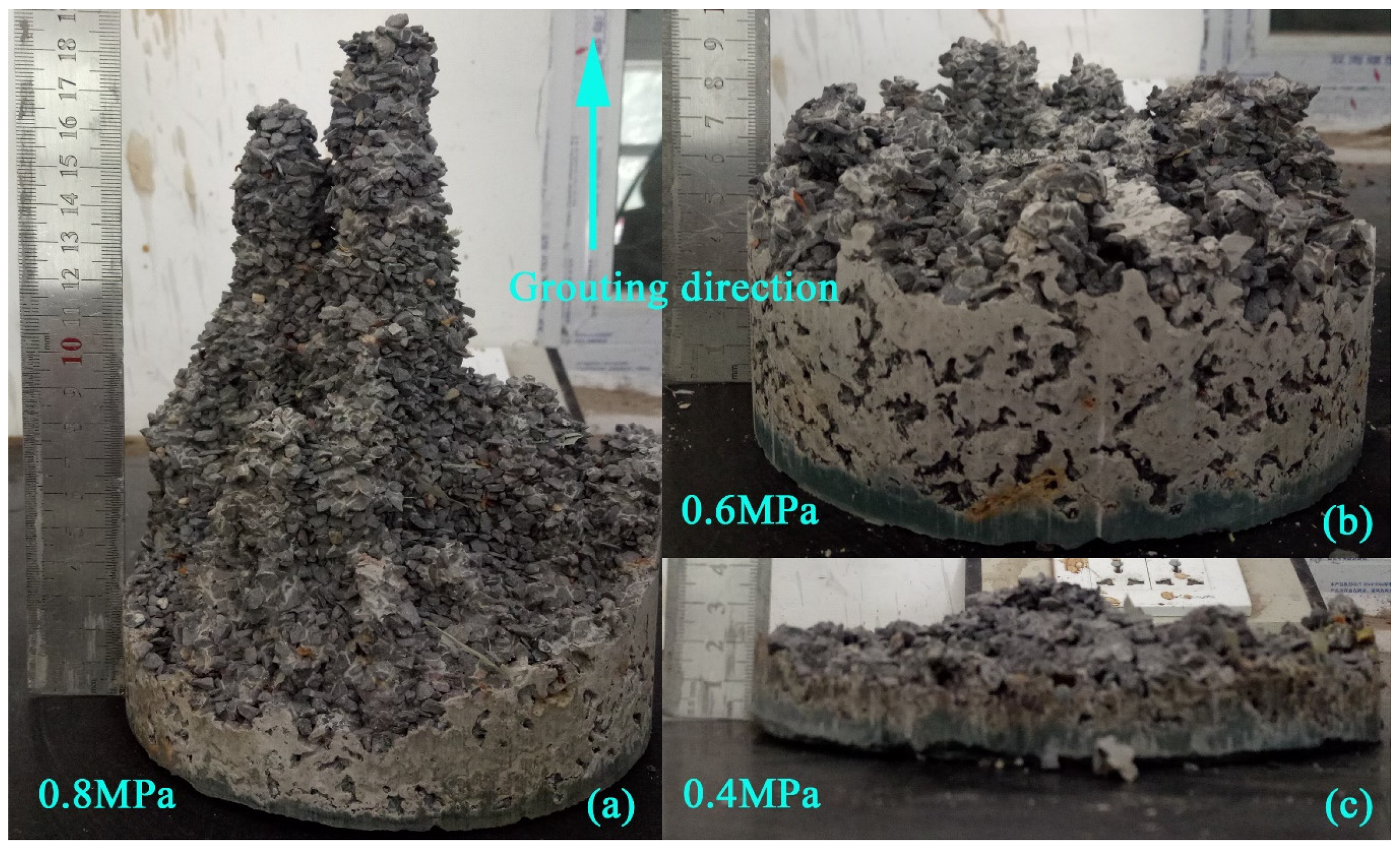
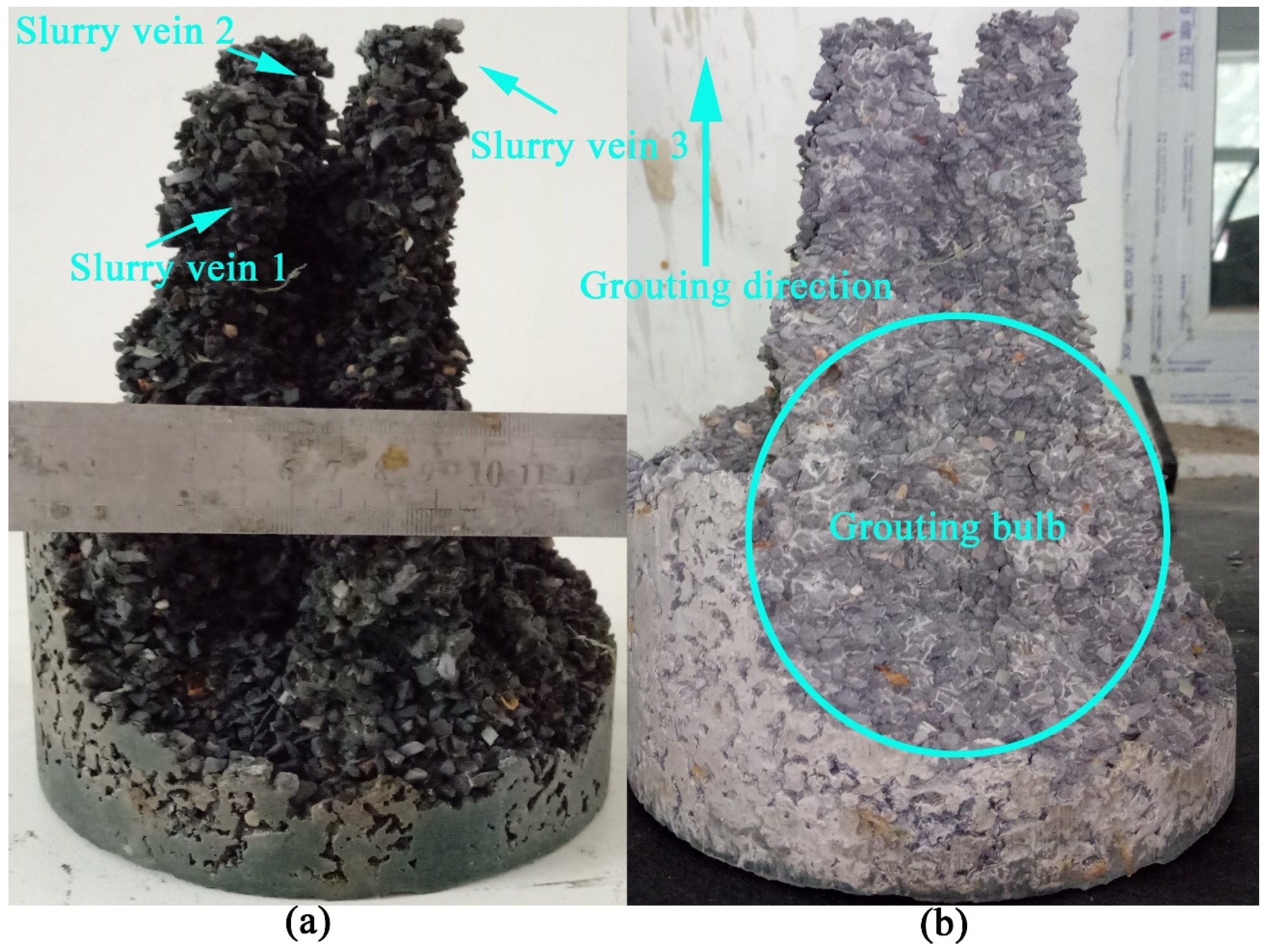
3.2. Single-Gradation 4.75–2.36 mm Grouting Test
3.3. Single-Gradation 2.36–1.18 mm Grouting Test
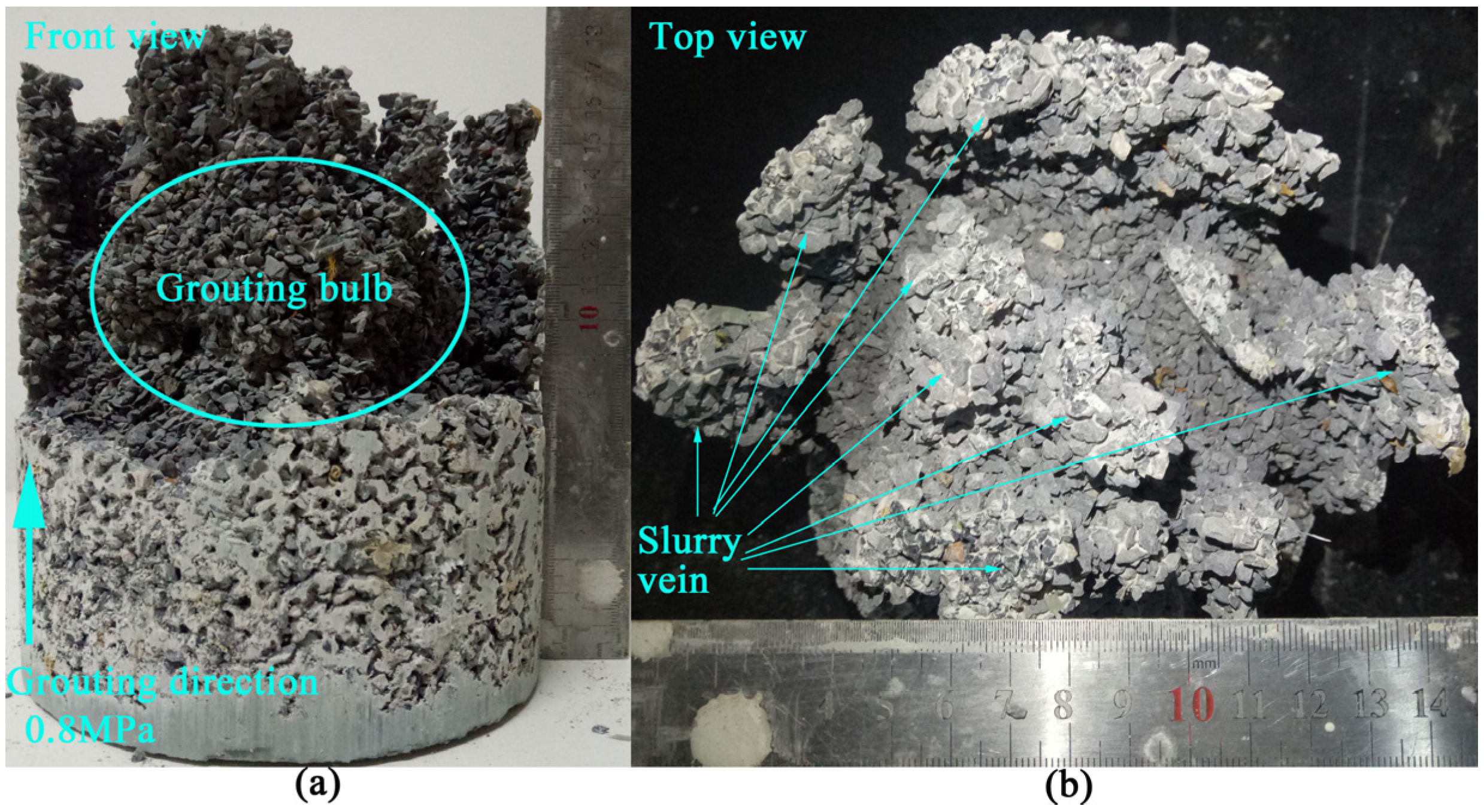
3.4. Diffusion and Consolidation Test
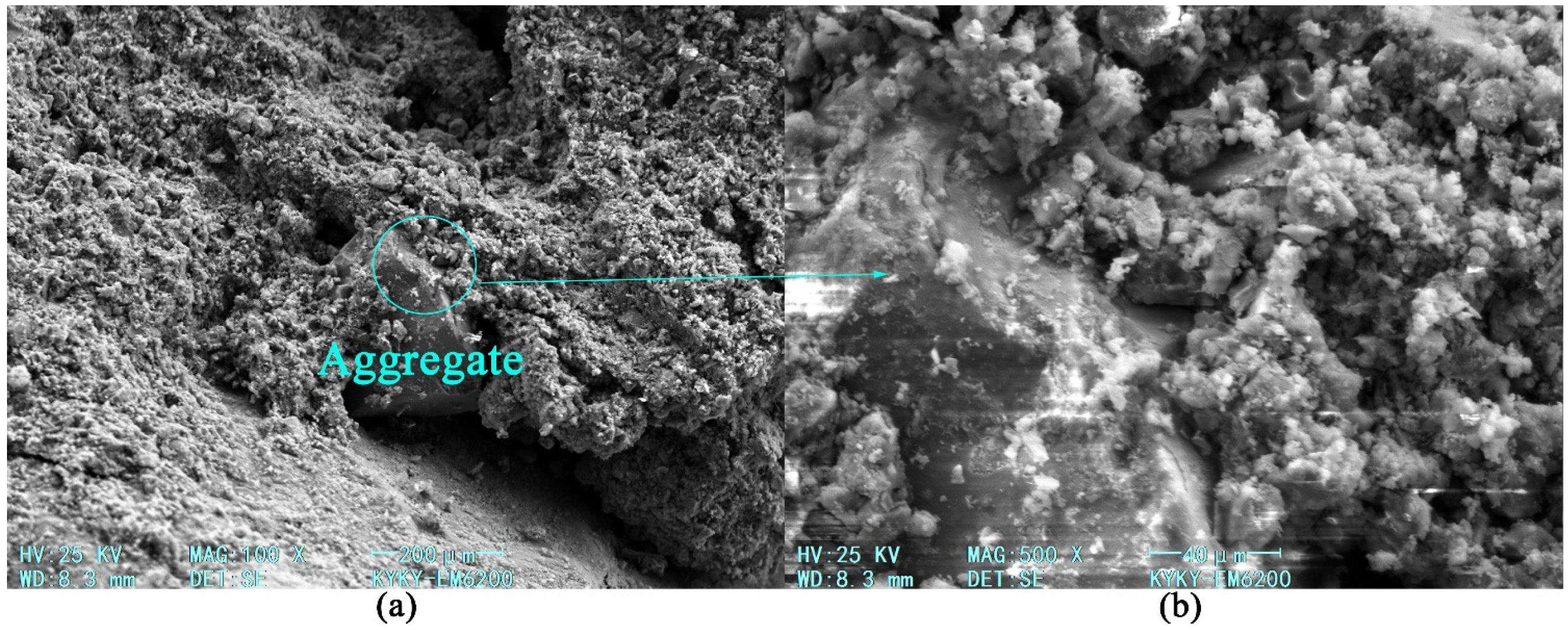
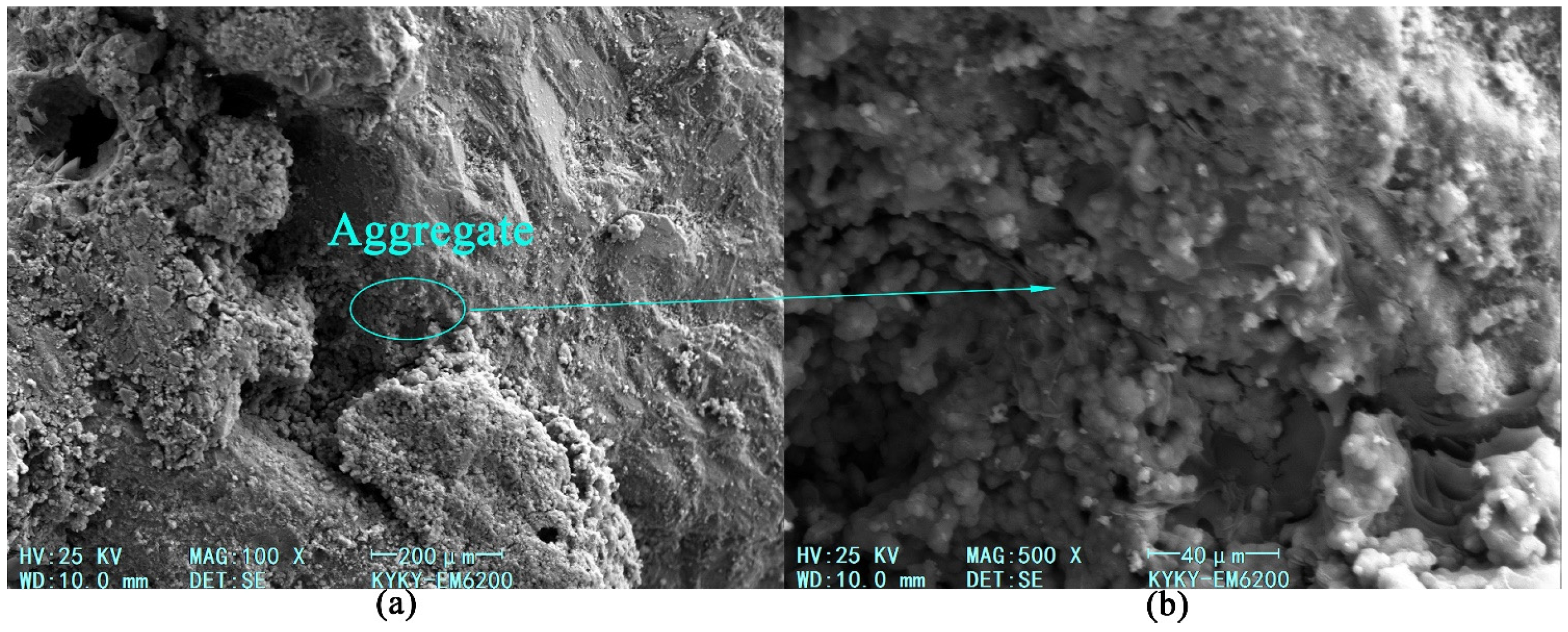
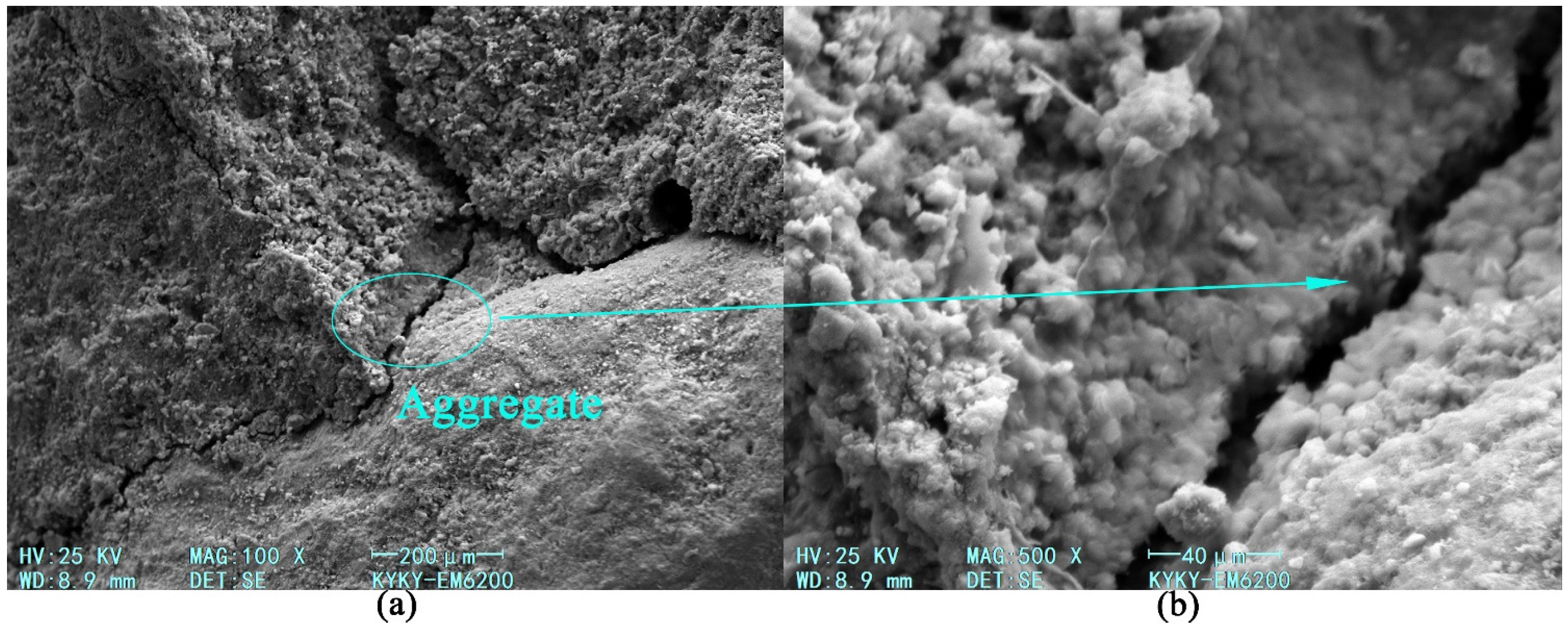
3.5. Microscopic Test
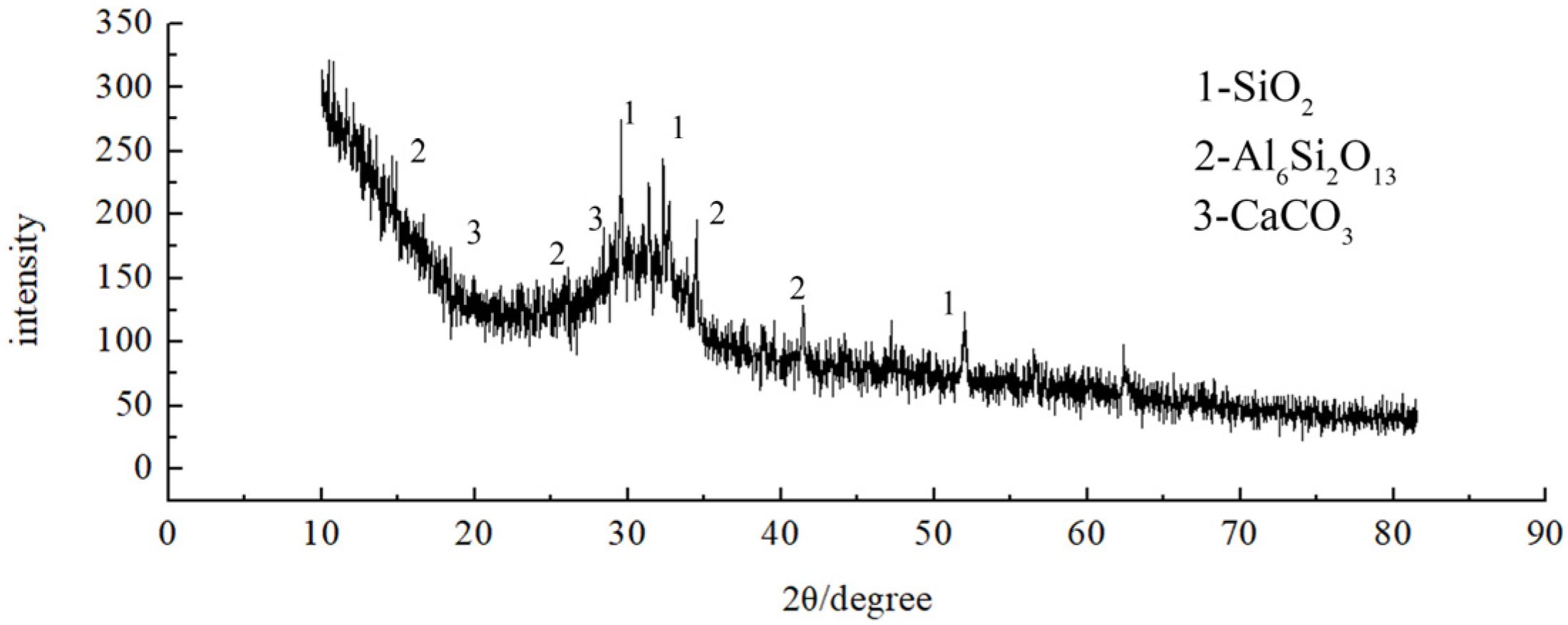
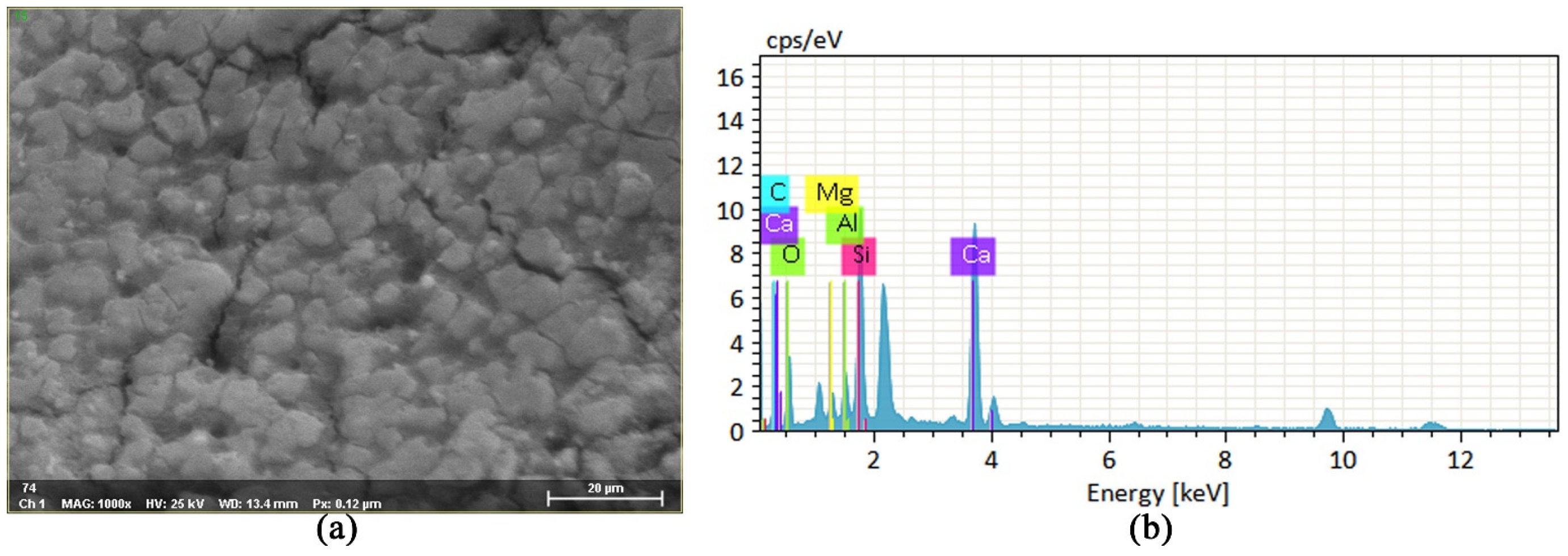
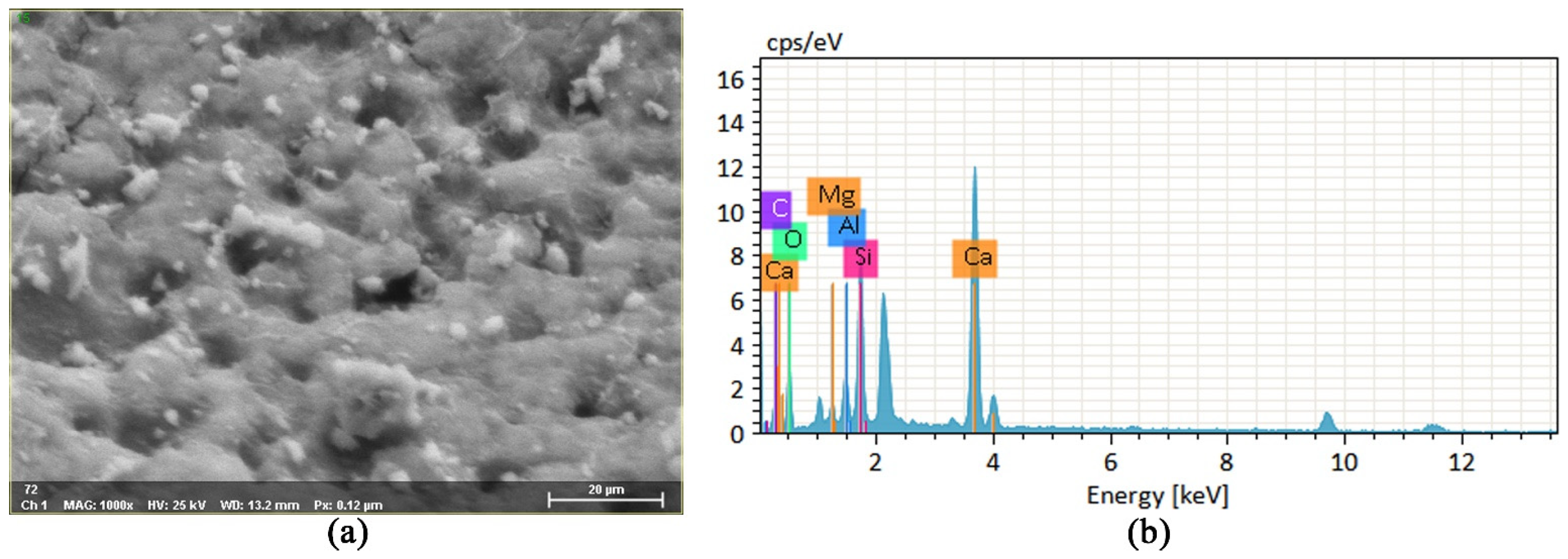
3.5.1. Microscopic Morphology and Reactants of Geopolymer Slurry
3.5.2. Microscopic Analysis of Consolidation Characteristics
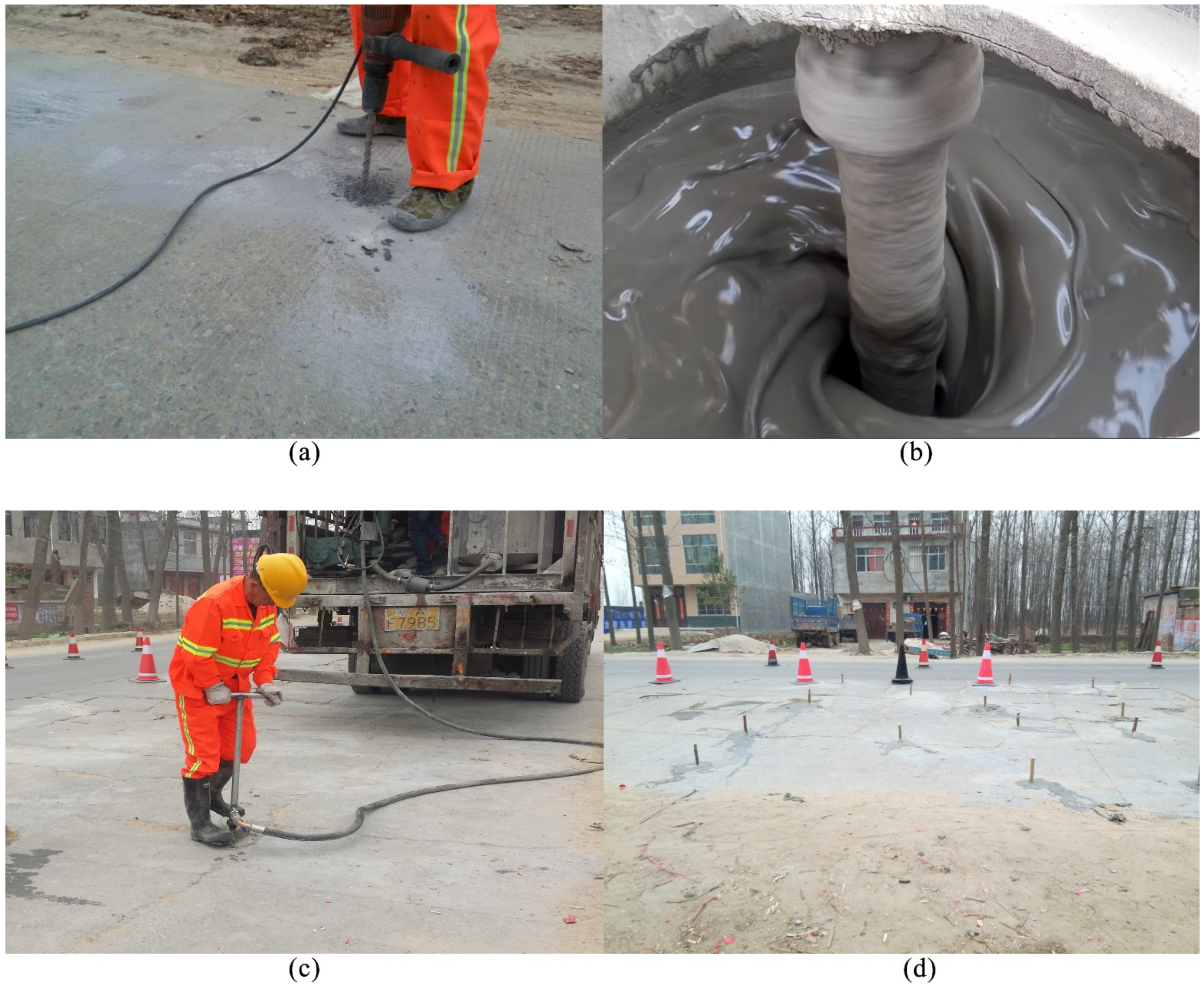
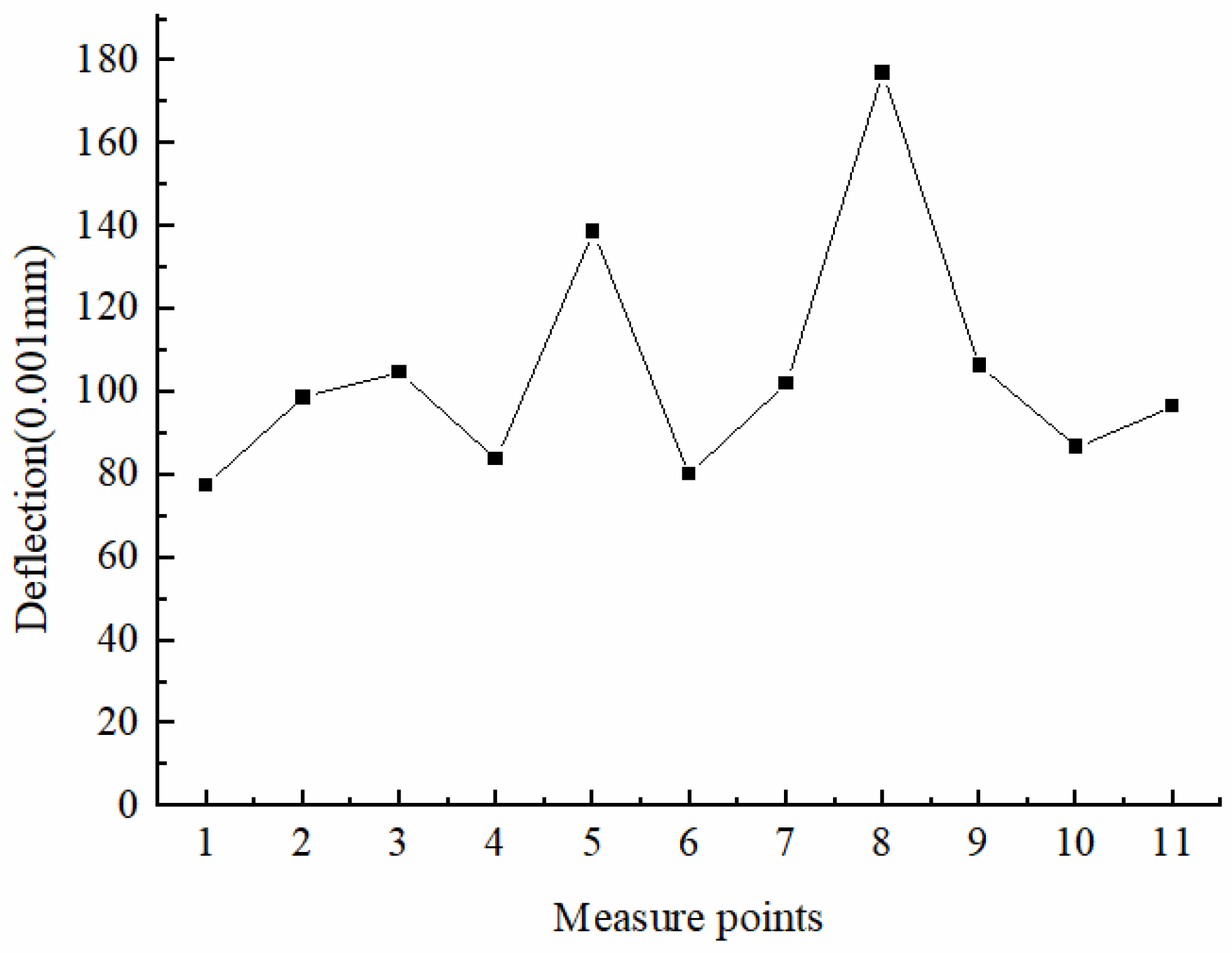
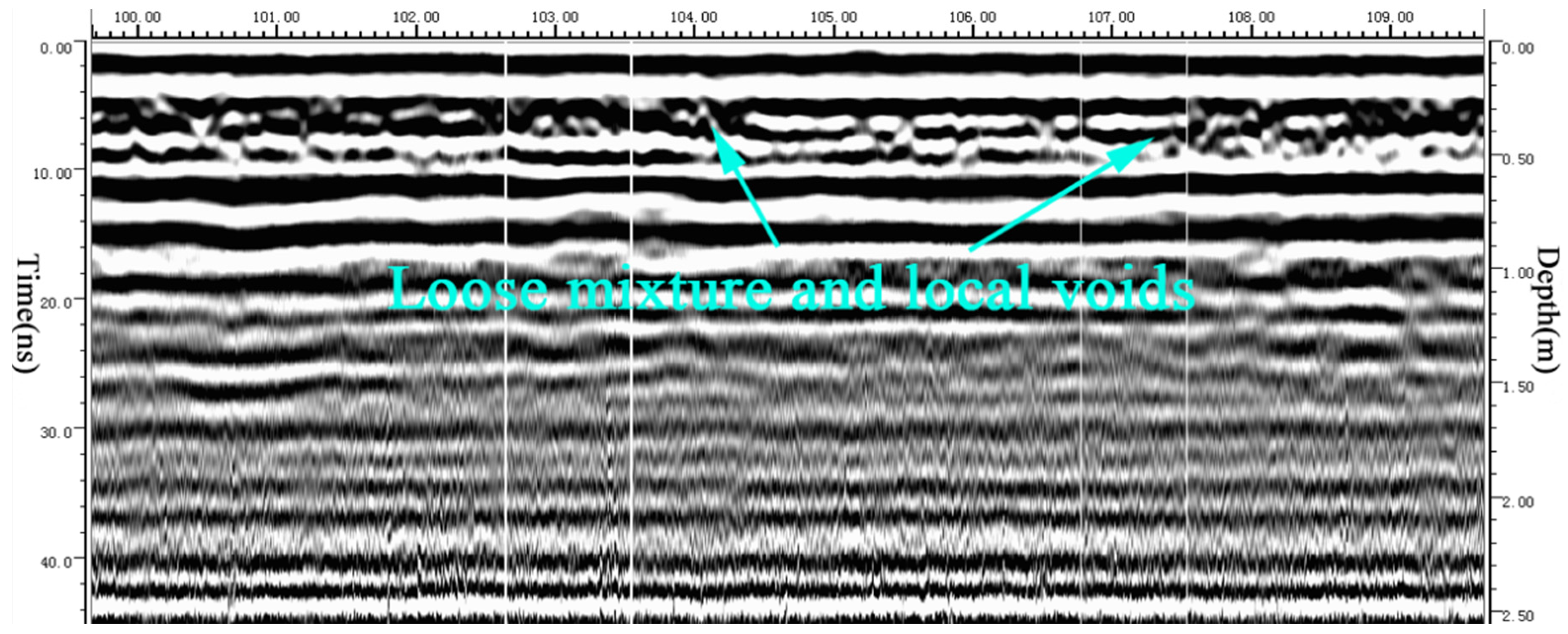
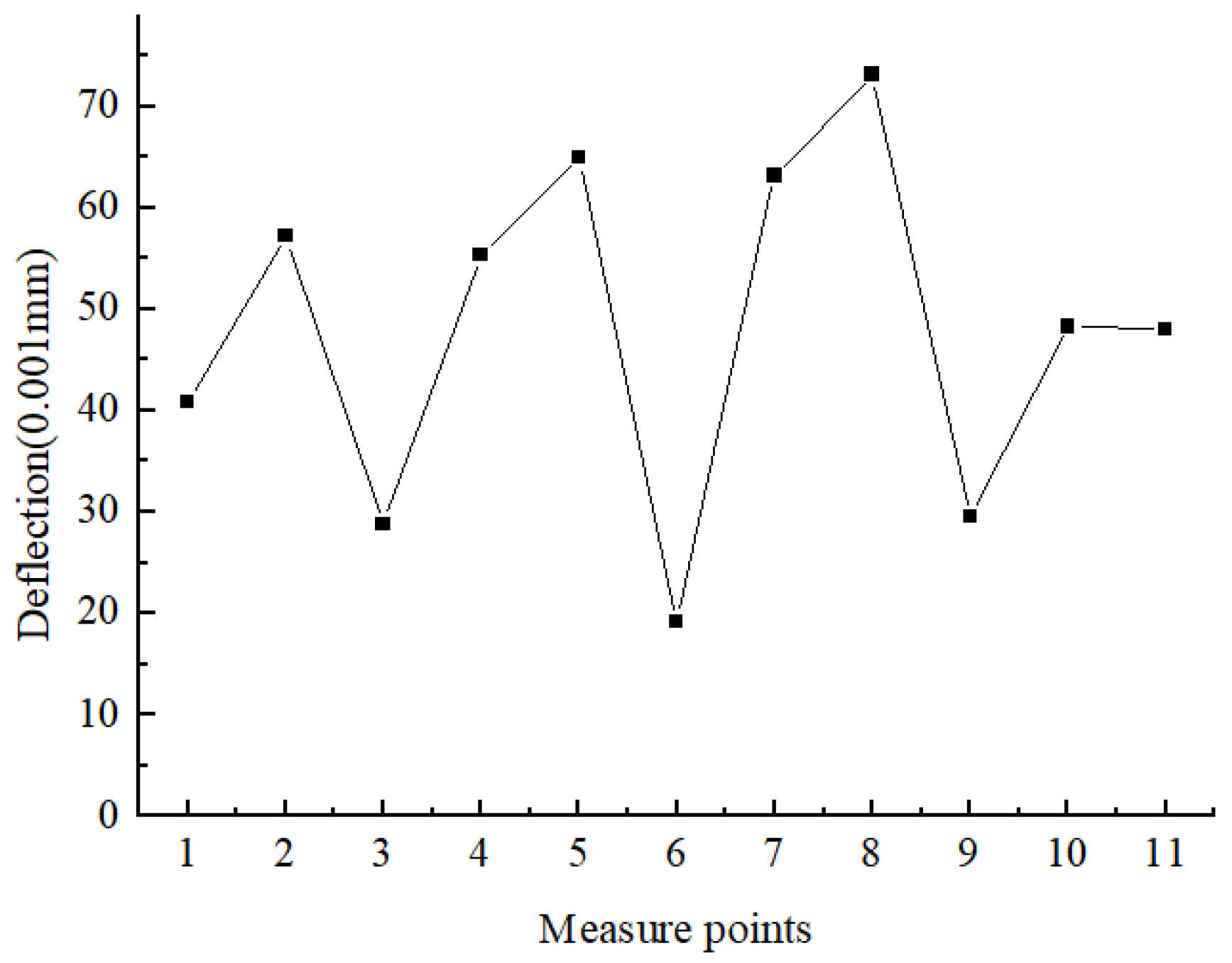
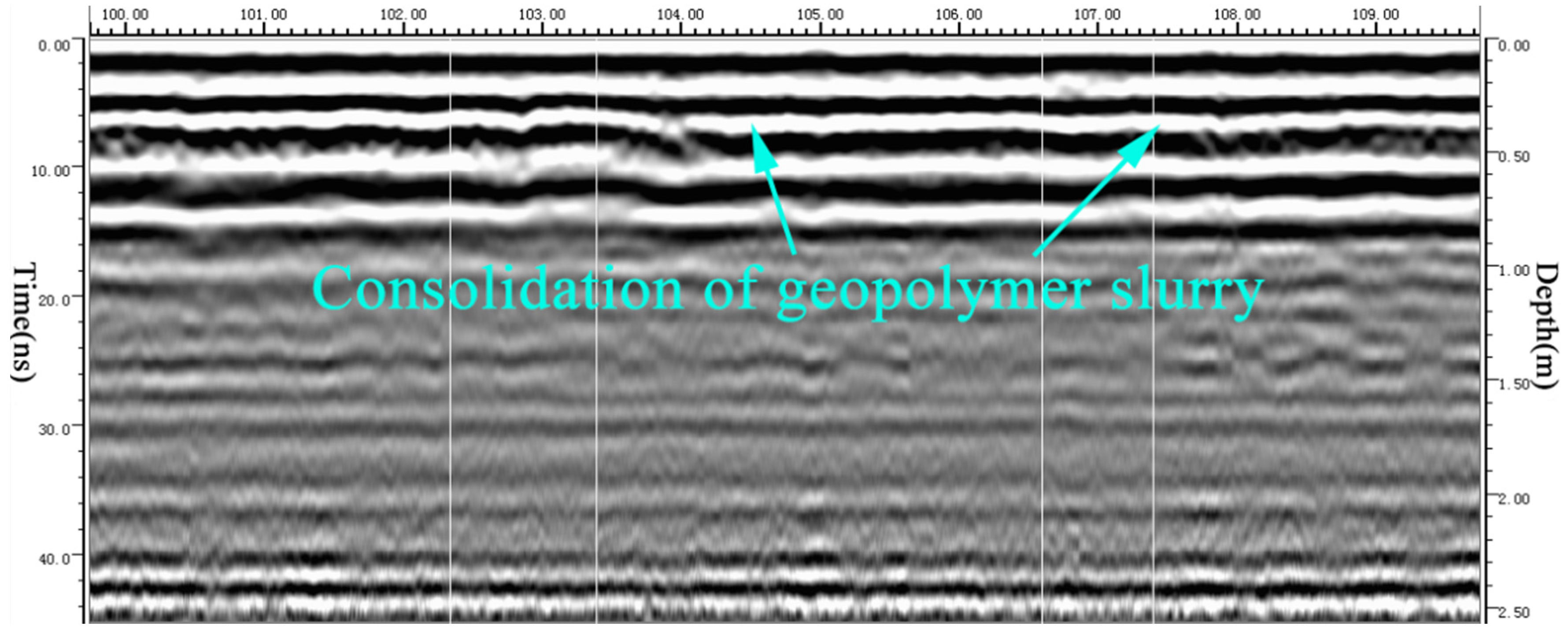
4. Practical Application
4.1. Grouting Operation
4.2. Grouting Consolidation Effect
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.J.; Zhang, Q.L.; Zhi, Z.H.; Feng, C.; Cai, Y.C.; Yue, J.C. Investigation on the fracture mechanism of homogenized micro-crack crushing technology for portland cement concrete pavement rehabilitation. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 075113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Guo, Y.; Liang, B.; Yue, J.C. A Numerical Study on the Crack Propagation of Homogenized Micro-Crack Crushing for Concrete Pavement. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, A.T.; Magee, B.; Woodward, D. A Preliminary Characterisation of Innovative Semi-Flexible Composite Pavement Comprising Geopolymer Grout and Reclaimed Asphalt Planings. Materials 2020, 13, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kang, A.H.; Wu, Z.G.; Xiao, P.; Li, B.; Lu, Y.M. Research on the Formulation and Properties of a High-Performance Geopolymer Grouting Material Based on Slag and Fly Ash. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 3437–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Q.; Yang, Z.N.; Zhang, R.R.; Li, F. Preparation, characterization and rheological analysis of eco-friendly road geopolymer grouting materials based on volcanic ash and metakaolin. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kang, A.H.; Wu, Z.G.; Xiao, P.; Gong, Y.F. Effect of high-calcium basalt fiber on the workability, mechanical properties and microstructure of slag-fly ash geopolymer grouting material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.G.; Lu, Y.M.; Kang, A.H.; Xiao, P. Optimal design of geopolymer grouting material for semi-flexible pavement based on response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.F.; Gao, Y.F.; Liu, C. Feasibility study of red mud-blast furnace slag based geopolymeric grouting material: Effect of superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 120910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güllü, H.; Agha, A.A. The rheological, fresh and strength effects of cold-bonded geopolymer made with metakaolin and slag for grouting. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 122091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; You, H.; Gao, Y.F.; Wang, C.A.; Zhang, J. Effect of ultrafine red mud on the workability and microstructure of blast furnace slag-red mud based geopolymeric grouts. Powder Technol. 2021, 392, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, K.W.; Tang, X.M. Potential using of water-soluble polymer latex modified greener road geopolymeric grouts: Its preparation, characterization and mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Z.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, C.; Jia, H.Q. Preparation of coal gangue-slag-fly ash geopolymer grouting materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 126997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, Y.J.; Li, Z.L.; Farooqi, M.U. Rheological and viscoelastic characterizations of fly ash/slag/silica fume-based geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarci, F.; Maras, M.M. Fabrication of Novel Geopolymer Grout as Repairing Material for Application in Damaged RC Beams. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 20, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Li, J.M.; Ouyang, S.Y.; Fan, B.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Hou, G.F. Preparation of the geopolymer grouting material by coal-based solid wastes for the aquiclude key strata and its application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.D.; Wu, H.B.; Wei, F.; Song, H.P.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, F.Q. Preparation, characterization, and rheological analysis of eco-friendly geopolymer grouting cementitious materials based on industrial solid wastes. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.N.; Zhou, S.Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, R.R.; Zhu, X.Y. Preparation and rheological performance analysis of volcanic ash and metakaolin based geopolymer grouting materials. Road Mater. Pavement 2023, 24, 1614–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, J.S.; Zhang, M.; Feng, B.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Fu, W.W.; Peng, H.; Lu, H.J.; et al. Effects of Steel Slag and Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum on the Properties of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Grouting Materials. J. Test. Eval. 2023, 51, 3900–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Liang, B.; Yue, J.C. Mechanical Properties of Slag-Based Geopolymer Grouting Material for Homogenized Micro-Crack Crushing Technology. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, Z.N.; Zhou, S.Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.Y.; Su, Y.J.; Niu, Q. Fly-ash-based geopolymer modified by metakaolin for greener grouting material. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Eng. Sustain. 2023, 177, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.F.; Li, Z.F.; Wang, C. Pb2+ and Cr3+ immobilization efficiency and mechanism in red-mud-based geopolymer grouts. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Feng, X.T.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Yang, C.X.; Liu, X.F. Formulation and properties of a new cleaner double liquid alkali-activated grouting material. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souayfan, F.; Rozière, E.; Loukili, A.; Justino, C. Effect of Retarders on the Reactivity and Hardening Rate of Alkali-Activated Blast Furnace Slag Grouts. Materials 2023, 16, 5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güllü, H.; Yetim, M.E.; Güllü, E.B. On the rheological, fresh and strength effects of using nano-silica added geopolymer grout for grouting columns. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 1183–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, Q.S.; Zhou, A.N.; Liu, R.T. Grouting characteristics in rock fractures with rough surfaces: Apparatus design and experimental study. Measurement 2021, 184, 109870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sang, H.M.; Liu, Q.S.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.C.; Kang, Y.S. Laboratory Study on Diffusion and Migration of Grout in Rock Mass Fracture Network. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04020242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.M.; Li, X.L.; Zhong, Y.H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, F.M. Experimental Study of Polyurethane Grout Diffusion in a Water-Bearing Fracture. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04020485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.H.; Wei, J.C.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, F.; Yin, H.Y.; Xie, D.L.; Xie, C. Quantitative permeation grouting in sand layer with consideration of grout properties and medium characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.X.; Han, L.J. Experimental Study on Grouting Seepage Characteristics of Single-Fractured Rock Masses with Different Inclination Angles under Three-Dimensional Stress. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 1491385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.X.; Gan, B.Q.; Deng, C.; Xie, Z.L.; Lu, Y.F.; Cai, Y.H. Experimental study on the effect of water-cement ratios on the diffusion behavior of sand soil grouting. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.S.; Li, Z.H.; Du, F.; Cao, Z.Z.; Wang, W.Q. Development of Grouting Test System for Rough Fissure Rock Body and Research on Slurry Diffusion Law. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, W.Q.; Ma, T.R. Study on visual simulation experiment of water-displacing grouting in fractured aquifer. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG 3420-2020; Testing Methods of Cement and Concrete for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- JTG 3432-2824; Test Methods of Aggregates for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2024.


















| Material | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | SO3 | TiO2 | FexOy | Na2O | K2O | MnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| slag | 39.46 | 26.01 | 13.24 | 8.41 | 2.25 | 1.04 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.30 |
| Particle Size (mm) | Porosity | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|
| 9.5–4.75 | 0.44 | 1.43 |
| 4.75–2.36 | 0.40 | 1.55 |
| 2.36–1.18 | 0.37 | 1.58 |
| Particle Size (mm) | Grouting Pressure (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.5–4.75 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| 4.75–2.36 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| 2.36–1.18 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Yue, J.; Liang, B. Diffusion and Consolidation of Slag-Based Geopolymer for Concrete Pavement Rehabilitation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4373. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084373
Li W, Yue J, Liang B. Diffusion and Consolidation of Slag-Based Geopolymer for Concrete Pavement Rehabilitation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4373. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084373
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenjie, Jinchao Yue, and Bin Liang. 2025. "Diffusion and Consolidation of Slag-Based Geopolymer for Concrete Pavement Rehabilitation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4373. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084373
APA StyleLi, W., Yue, J., & Liang, B. (2025). Diffusion and Consolidation of Slag-Based Geopolymer for Concrete Pavement Rehabilitation. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4373. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084373





