Urban Underground Space Geological Suitability—A Theoretical Framework, Index System, and Evaluation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
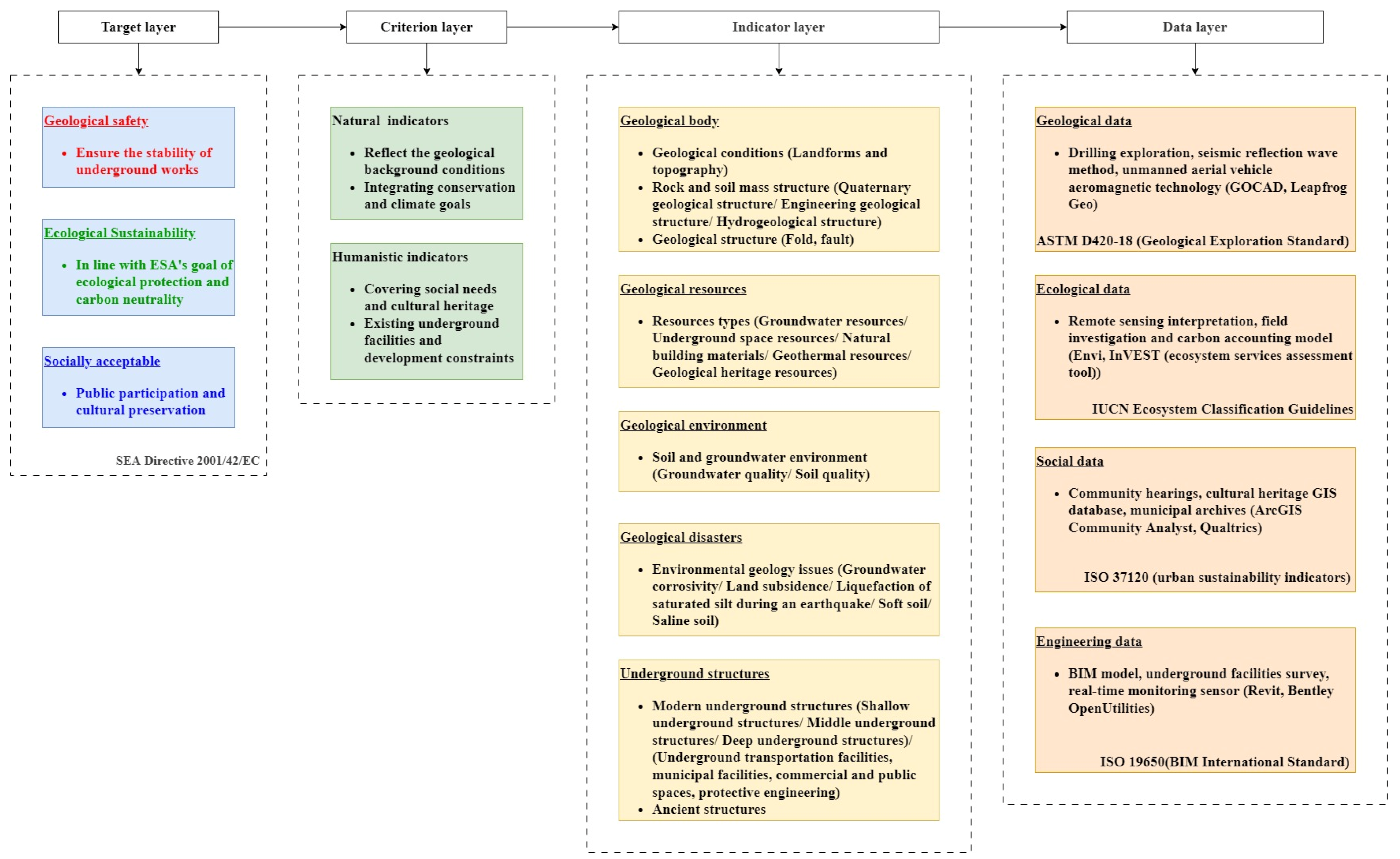
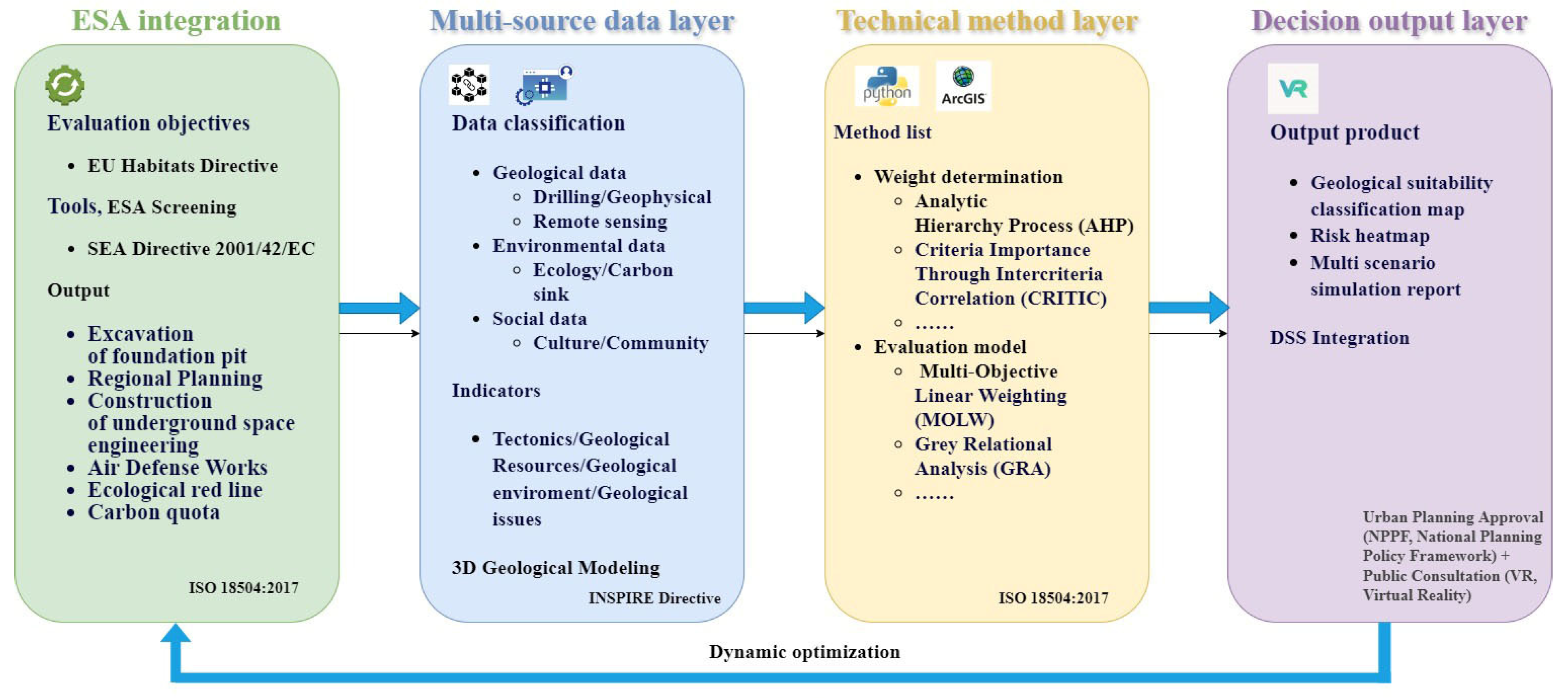
2. The Basic Frame of the Geological Suitability Evaluation of Urban Underground Space (GSEUUS)
2.1. Evaluation Objectives
2.2. Evaluation Elements
2.3. The Collaborative Mechanism Between ESA and GSEUUS
3. Evaluation Indicators
3.1. The Geological Body
3.1.1. Geological Conditions
3.1.2. Rock and Soil Structure and Geological Structure
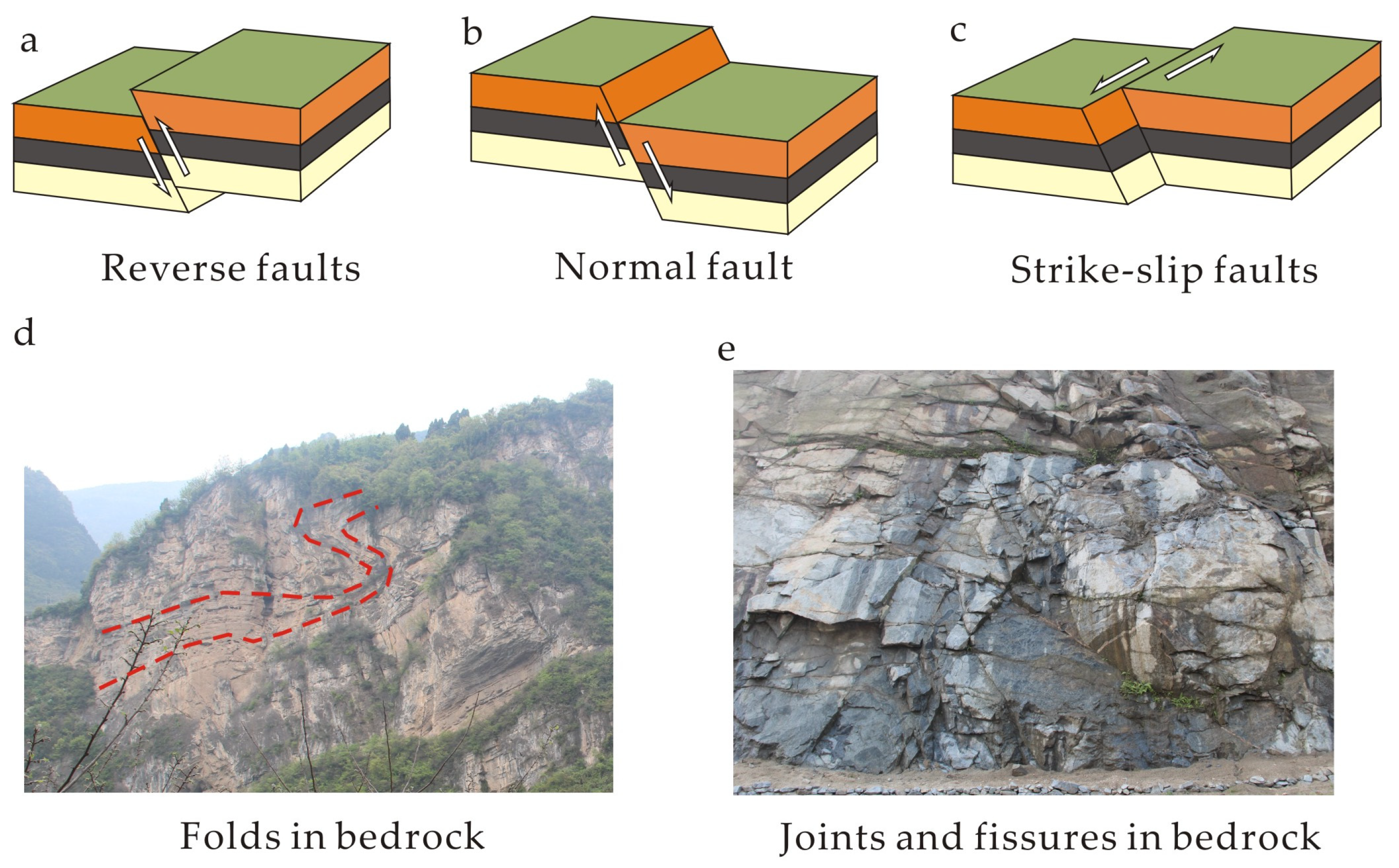
3.1.3. Geological Structure
3.2. Geological Resources
3.3. Geological Environments
3.4. Geological Disasters
3.5. Underground Structures
4. Evaluation Method
4.1. Weight Calculation Method
4.1.1. Expert Scoring Method (ESM)/Delphi
4.1.2. Analytic Hierarchy Process AHP
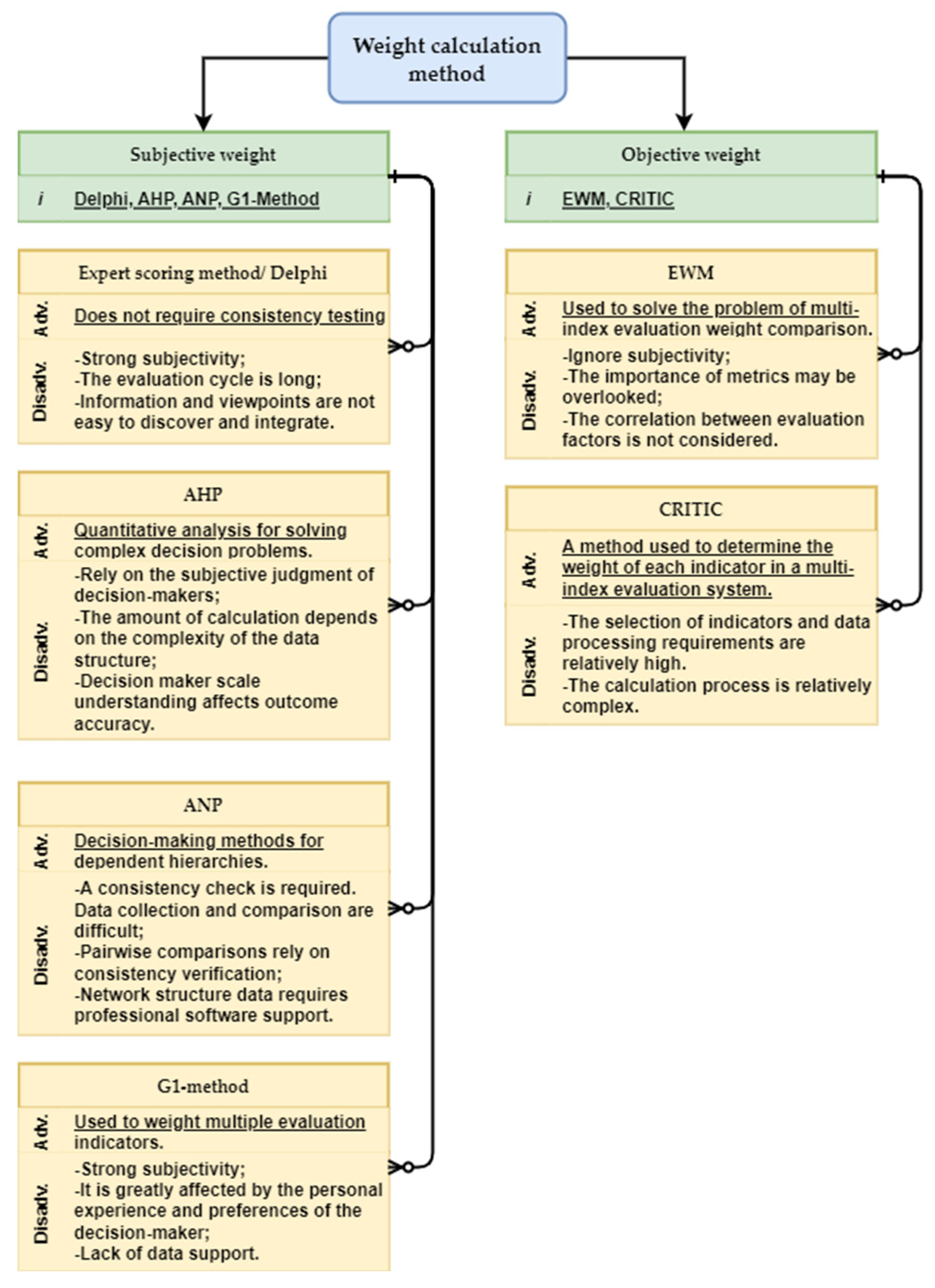

4.1.3. Analytic Network Process (ANP)
4.1.4. Order Relationship Analysis Method (G1 Method)
4.1.5. Entropy Weight Method (EWM)
4.1.6. Criteria Importance Through Intercriteria Correlation (CRITIC)
4.2. Comprehensive Evaluation and Decision Analysis
4.2.1. Multi-Objective Linear Weighting (MOLW)
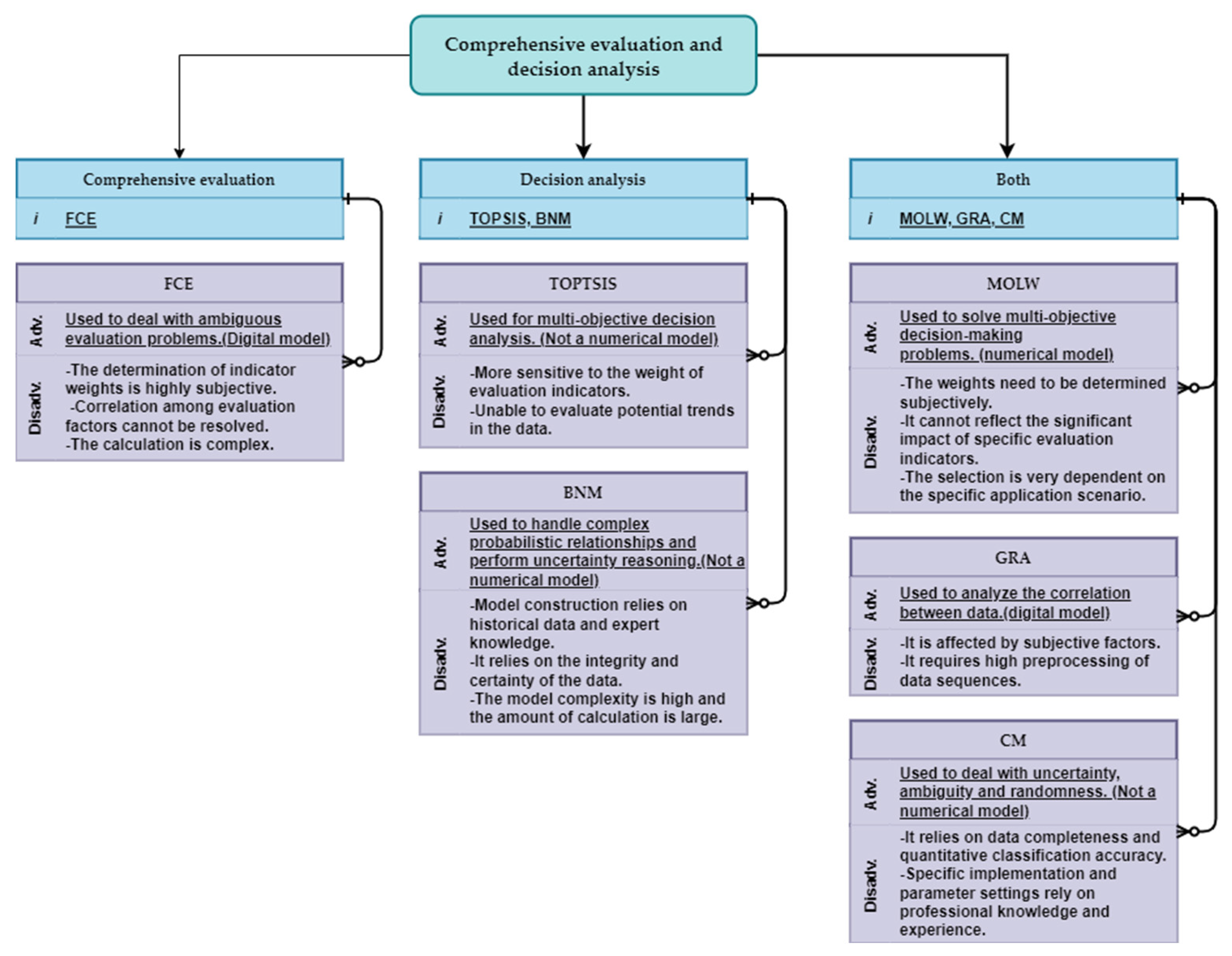
4.2.2. Grey Relational Analysis (GRA)
4.2.3. Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS)
4.2.4. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation (FCE)
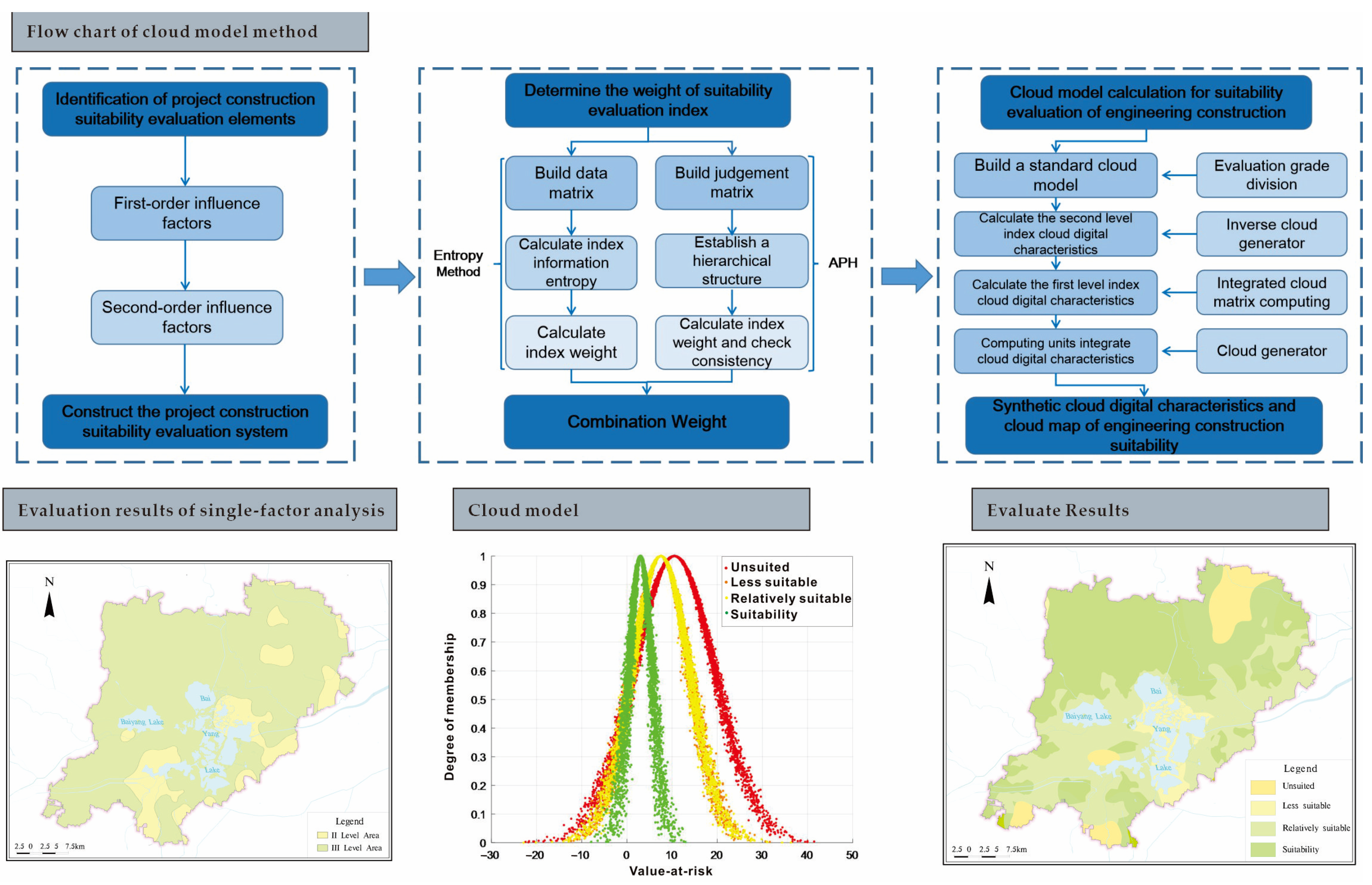
4.2.5. Cloud Model (CM)
4.2.6. Bayesian Network Model (BNM)
| Time of Publication | Author | City | Evaluation Index | Weight Evaluation | Comprehensive Evaluation and Decision Analysis | Evaluation System | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | Pu, Huang, Bi et al. [74] | Foshan City | Existing ground restrictions, the structures on the ground, engineering geological and hydrogeological conditions | EWM, G1 method | GRA | ||
| 2024 | Xu, Chen, Li et al. [135] | Sanya Central Business District | Topography, geomorphology, rock and soil properties, hydrogeological factors, geological hazards, social and economic conditions | AHP | CM, FCE | In Chinese | |
| 2024 | Li, Yang, Luo et al. [126] | Guian new area | Topography, engineering geology, environment geology, hydrogeology, water ecology, utilization of underground space, utilization of surface space | AHP, Expert scoring method (ESM) | Arcgis | In Chinese | |
| 2023 | Xu, Zhou, Zhang et al. [129] | Changsha | Socioeconomic, geological condition, and the current construction status | AHP | BNM | ||
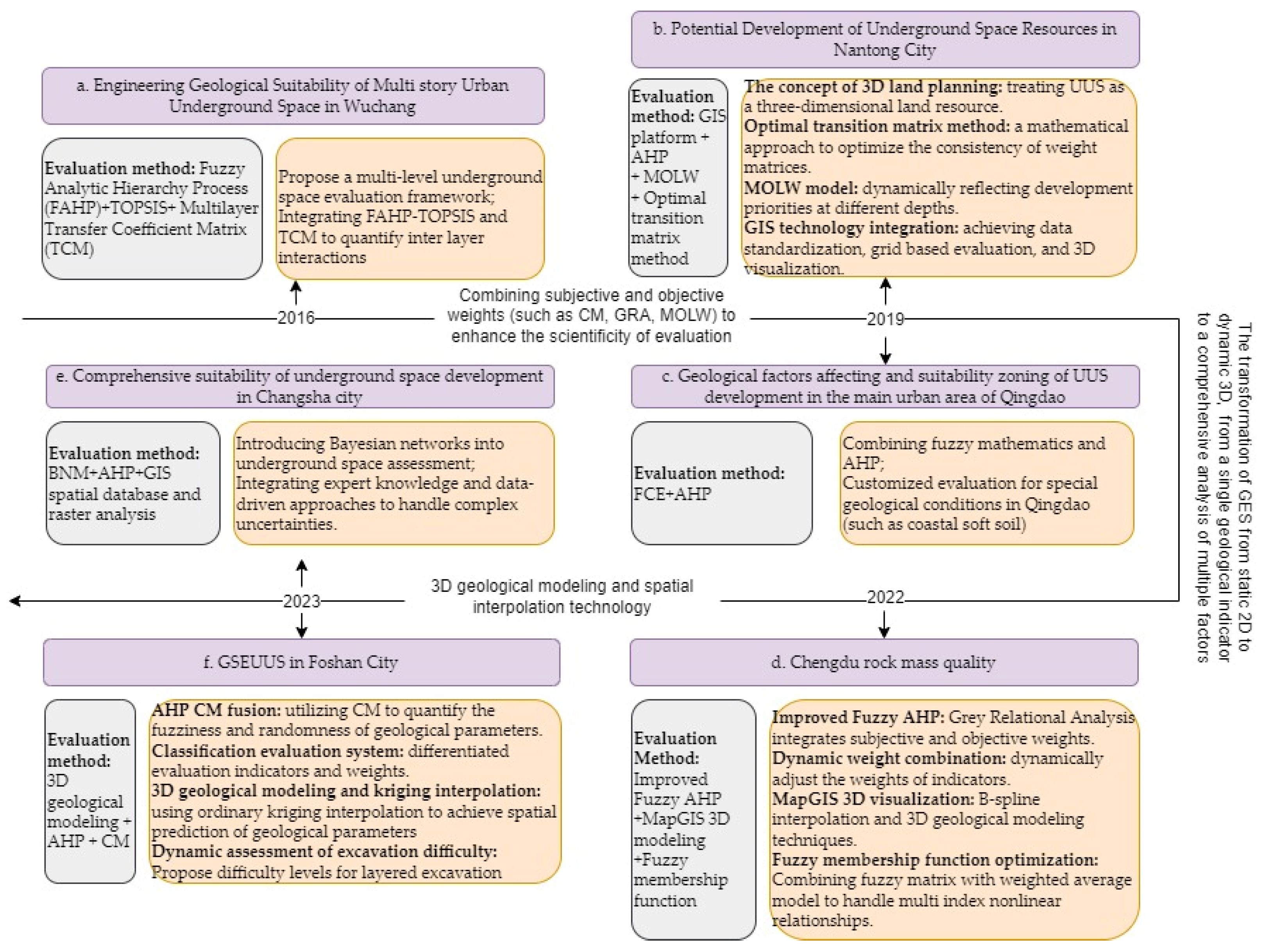
| 2023 | Deng, Pu, Huang et al. [67] | Foshan City | Engineering geological conditions, hydrogeological conditions, and the bad geological problem | AHP | CM | 3D geological modeling | |
| 2022 | Dou, Xing, Li et al. [133] | Future Sci-Tech City, Hangzhou | Topographic, geotechnical engineering properties, and hydrogeological conditions | ANP, CRITIC | The game theory(GT), GRA, TOPSIS | 3D Geomodeller software | |
| 2022 | Liu, Peng, Wu et al. [130] | Jiangbei New District of Nanjing | Characteristic value of bearing, capacity, cohesion, internal friction angle, compression modulus, water content, pore ratio, vertical permeability coefficient, horizontal permeability coefficient | EWM | GRA, Interval continuous mathematical model (ICMM) | 3D-Mine and ArcGIS | |
| 2022 | Chen, Chen, Guo et al. [142] | Nanjing | Natural conditions, ground and underground space conditions, geographical location, economic conditions, development benefits, and policy compatibility | Delphi, AHP, EWM | GIS, the multi-agent system (MAS) modelling | ||
| 2022 | Peng, Su, Chen et al. [51] | Chengdu Airport New Town | Cohesion, internal friction angle, Poisson’s ratio, saturated uniaxial compressive strength, and rock mass integrity coefficient | AHP | GRA, Super-standard multiple method (SSMM) | ||
| 2021 | Dou, Li, Xing et al. [52] | Qianjiang Newtown in Hangzhou | Topography, geotechnical engineering proper ties, hydrogeology, and spatial structure characteristics of geologic body | AHP | FCE | 3D Geomodeller software | |
| 2021 | Tan, Wang, Jiao et al. [7] | Wuhan Changjiang New Town | Topography and geomorphology, geotechnical characteristics, geological structure, hydrogeological conditions, adverse geological phenomena | AHP, EWM, CRITIC | CM, Genetic algorithm (GA) | ||
| 2021 | Zhang, Zhu, Liao et al. [143] | Luohu District, Shenzhen | Topography, hydrogeology, engineering geology, environmental geology, ground surface usage status, and underground space usage status | AHP | The most unfavorable grading method (MUGM) and the exclusive method (EM) | Artificial intervention genetic algorithm(AIGA) | |
| 2020 | Zhang, Wang, Dong et al. [9] | Xi’an | Important historical sites and cultural relics, strategic reserve, existing facility, active fault, ground fissures, land subsidence, collapsible loess, sand liquefaction, groundwater corrosion, wet land river or lake, and gravel | The negative list method (NLM) | |||
| 2020 | Kapoor, Jain and Bansal [113] | Pradesh, India | Slope, soil type, elevation, accessibility, vegetation, surface runoff, land use, aspect, groundwater table, and existing utilities | AHP, ESM | ArcGIS | ||
| 2020 | Nyimbili, Erden [36] | Istanbul | High population density, proximity to main roads, distance from existing fire stations, liquid petroleum gases, wooden building density, and distance to earthquake risk | AHP, EWM | GIS | ||
| 2020 | Ustaoglu, Aydınoglu [123] | Istanbul | Geo-physical attributes, accessibility, built-up area and infrastructure, vegetation, and green and blue amenities | AHP, EWM | GIS | ||
| 2019 | Zhou, Li, Wang et al. [106] | Nantong | Geological conditions, existing facilities and various, socio-economic factors | AHP, ESM | MOLW | GIS | |
| 2019 | Xia, Dong, He et al. [128] | Qingdao | Landform, engineering geology, hydrogeology, adverse geological processes, and human factors | AHP, ESM | FCE | In Chinese | |
| 2018 | Peng, Peng [114] | Tongren and Changzhou | Landforms, engineering geology, hydrogeology, site stability, existing subsurface construction conditions, urban location, and land use | AHP | MUGM, EM | GIS software and ArcGIS 10.2 | |
| 2017 | Aburas, Abdullah, Ramli, et al. [144] | Seremban Malaysia | Elevation, slope, soil texture, population density, land cover, distance to roads, highways, railways, powerlines, streams, industrial, residential, commercial, and educational areas | AHP | GIS | ||
| 2016 | Lu, Wu, Zhuang et al. [70] | Wuchang Railway Station | Geotechnical properties of under-layers, geological structure, geomorphology conditions, hydrogeological conditions, and adverse environmental geological problems | AHP | TOPSIS, Fuzzy set theory (FST) | ||
| 2016 | Zhu, Huang, Li et al. [30] | Changzhou | Topography and landforms, engineering geology, hydrogeology, site stability, and urban construction conditions | AHP, ESM | MUGM | the digital underground space and engineering platform | |
| 2016 | Hou, Yang, Deng et al. [11] | Foshan | Soil condition, bedrock condition, fault activity, and level | AHP, EWM | FST | 3D Voxel | |
| 2016 | Hu, Liu, Tao [134] | Ningbo | Hydrogeological conditions, engineering geological conditions, environmental geological problems, economic, and technical | AHP, ESM | FCE | In Chinese | |
| 2011 | Youssef, Pradhan [112] | Egypt | Land use/cover, geological, geomorphological, geophysical, environmental, remote sensing, and field data | AHP | GIS software |
5. Problems and Suggestions for Improvement
5.1. The Choice of Evaluation Index
5.2. Rationalization of Weights
5.3. Solve Problems at the Layer
5.4. Solve the Problem of Heterogeneity
5.5. Integration of Evaluation Results and DSS
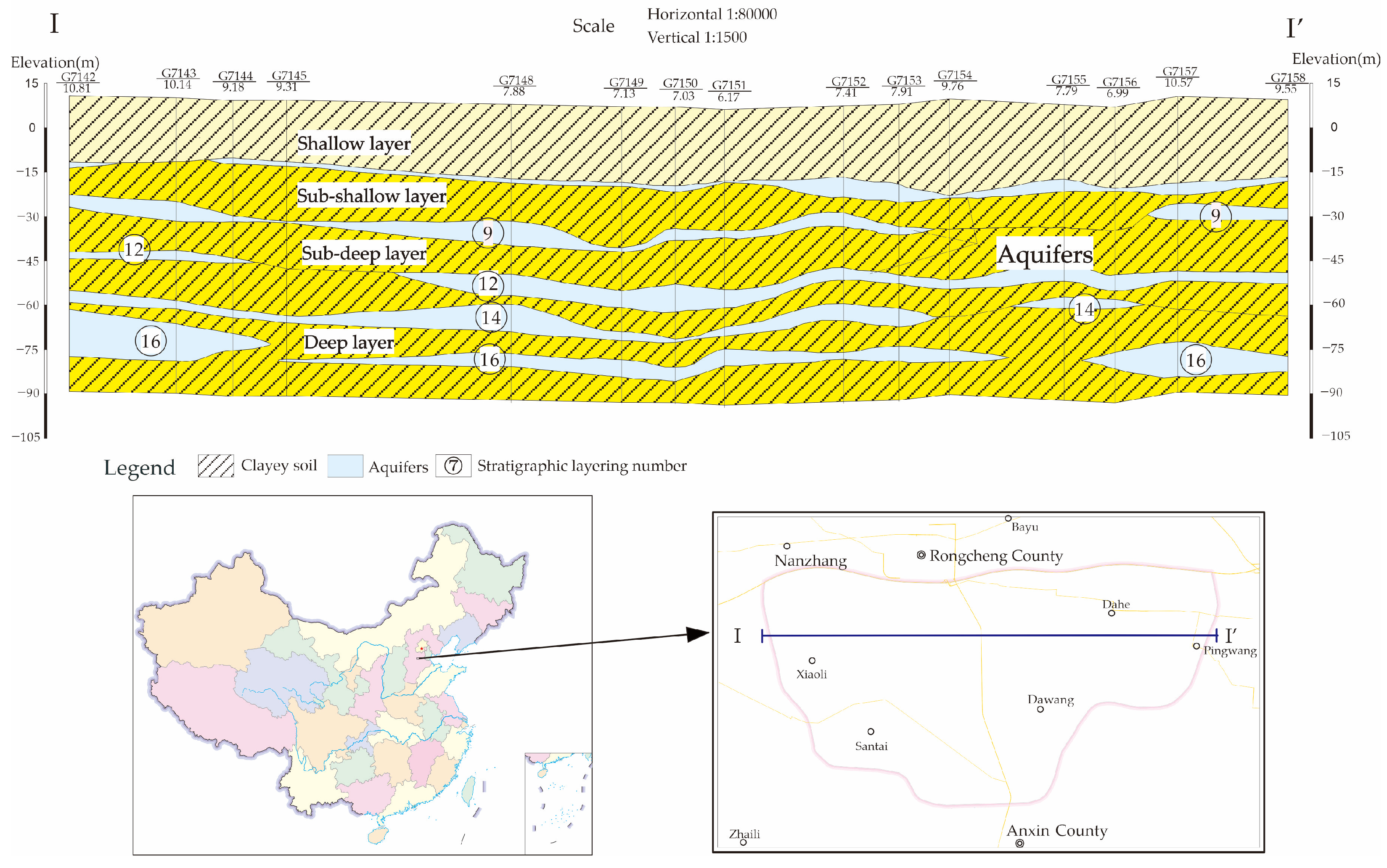
6. The Case (Xiong’an New Area, China)
6.1. The Concept of Development
6.2. Suitability Evaluation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, B.; Muñoz, P. Sharing cities and sustainable consumption and production: Towards an integrated framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 134, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Li, Z.; He, Q.C. Suitability Assessment of Multilayer Urban Underground Space Based on Entropy and CRITIC Combined Weighting Method: A Case Study in Xiong’an New Area, China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, Z.J.; Cheng, Q.W.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, P.H.; Li, M.C.; Chen, D. Quota Restrictions on Land Use for Decelerating Urban Sprawl of Mega City: A Case Study of Shanghai, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Wu, L.X.; Yang, Y. A Hybrid Weight Assignment Model for Urban Underground Space Resources Evaluation Integrated with the Weight of Time Dimension. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.; Admiraal, H.; Bobylev, N.; Parker, H.; Godard, J.-P.; Vähäaho, I.; Rogers, C.D.F.; Shi, X.D.; Hanamura, T. Sustainability issues for underground space in urban areas. Urban Des. Plan. 2012, 165, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobylev, N.; Sterling, R. Urban Underground Space: A Growing Imperative Perspectives and Current Research in Planning and Design for Underground Space Use. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Wang, J.; Jiao, Y.Y.; Ma, B.C.; He, L.L. Suitability evaluation of underground space based on finite interval cloud model and genetic algorithm combination weighting. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 108, 103743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.W.; Peng, F.L.; Yabuki, N.; Fukuda, T. Factors in the development of urban underground space surrounding metro stations: A case study of Osaka, Japan. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 91, 103009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.S.; Wang, H.Q.; Dong, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, P.P.; Zhang, G. Evaluation of urban underground space resources using a negative list method: Taking Xi’an city as an example in China. China Geol. 2020, 3, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.Y.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.X.; Xiao, H.G.; Wang, R.H. Planning urban underground space from urban emergency evacuation: A digital layout planning method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 140, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.S.; Yang, L.; Deng, D.C.; Ye, J.; Clarke, K.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhuang, W.M.; Liu, J.X.; Huang, J.C. Assessing quality of urban underground spaces by coupling 3D geological models: The case study of Foshan city, South China. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobylev, N. Mainstreaming sustainable development into a city’s Master plan: A case of Urban Underground Space use. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminska, A.; Zareba, A.; Dzikowska, A.; Kazmierczak, B.; Kutylowska, M.; Piekarska, K.; Jouhara, H.; Danielewicz, J. Bioarchitecture—A new vision of energy sustainable cities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Energy Systems and Environmental Engineering (ASEE17), Wroclaw, Poland, 2–5 July 2017; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Levinson, D.M.; Giacomin, D.; Badsey-Ellis, A. Accessibility and the choice of network investments in the London Underground. J. Transp. Land Use 2016, 9, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, I. Special Issue on Comprehensive Disaster Prevention Measures for Underground Spaces (Underground Malls, etc.). J. Disaster Res. 2016, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. Research on the Resilience Evaluation and Promotion Strategy of Urban Underground Space. Nat. Resour. Econ. China 2023, 36, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.P.; Luo, J.Z.; Zhou, Y.L. Urban Underground Space Development and Utilization and Environmental Geological Effect in Wuhan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 32, 209–214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, D.H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, W.; Long, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. Urban geophysical exploration: Case study in Chengdu International Bio-City. J. Geophys. Eng. 2023, 20, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmody, J.; Sterling, R. Underground Space Design: A Guide to Subsurface Utilization and Design for People in Underground Spaces; Van Nostrand Reinhold Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Durmisevic, S. The future of the underground space. Cities 1999, 16, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucker, J.; Allouche, E.N.; Sterling, R.L. Social Costs Associated with Trenchless Projects: Case Histories in North American and Europe. In Proceedings of the 2006 NASTT No-Dig Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 26–28 March 2006; Paper C-4-04. NASTT: Arlington, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, S.; Janssen, G. Underground spatial planning—Perspectives and current research in Germany. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, J.P. Urban underground space and benefits of going underground. In Proceedings of the World Tunnel Congress 2004 and 30th ITA General Assembly, Singapore, 22–27 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, D.V.L.; Nash, D.; Rogers, C.D.F. Sustainable utility placement via multi-utility tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 39, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.V.L.; Rogers, C.D.F. Barriers to sustainable infrastructure in urban regeneration. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Eng. Sustain. 2005, 158, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.V.L.; Jefferson, I.; Rogers, C.D.F. Assessing the sustainability of underground space usage—A toolkit for testing possible urban futures. J. Mt. Sci. 2011, 8, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Juan, A.; Pujades, E.; Vázquez-Suñè, E.; Crosetto, M.; Cuevas-González, M. Leveling vs. InSAR in urban underground construction monitoring: Pros and cons. Case of la sagrera railway station (Barcelona, Spain). Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jia, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J. Integrated TEM and GPR data interpretation for high-resolution measurement of urban underground space. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 5004409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiani, G. Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Evaluation of urban underground space resources using digitalization technologies. Undergr. Space 2016, 1, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broere, W. Urban underground space: Solving the problems of today’s cities. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanayake, P.M.; Waterman, M.K. Identifying environmental impacts of underground construction. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vähäaho, I. Underground space planning in Helsinki. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2014, 6, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, F.L. Evaluation of urban underground space based on the geological conditions: A feasibility study. New Front. Geotech. Eng. 2014, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyimbili, P.H.; Erden, T. A Hybrid Approach Integrating Entropy-AHP and GIS for Suitability Assessment of Urban Emergency Facilities. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, S.J.; Terrington, R.L.; Busby, J.; Bricker, S.; Berry, T. 3D ground-use optimisation for sustainable urban development planning: A case-study from Earls Court, London, UK. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 81, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönkä, K.; Ritola, J.; Rauhala, K. Underground space in land-use planning. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 1998, 13, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admiraal, H.; Cornaro, A. Why underground space should be included in urban planning policy–And how this will enhance an urban underground future. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Underground Engineering for Sustainable Urban Development; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therivel, R. Strategic Environmental Assessment in Action; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Walsh, F. Strategic environmental assessment: An overview. Proj. Apprais. 1992, 7, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thérivel, R.; Partidário, M.R. The Practice of Strategic Environmental Assessment; Earthscan: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, T.B. The Theory and Practice of Strategic Environmental Assessment: Towards a More Systematic Approach; Earthscan: Oxford, UK; Barcelona, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.H.; Shen, J.H.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Jin, S.; Ma, Z.; Meng, Q.H. Influence of underground space development mode on the groundwater flow field in Xiong’an new area. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, K.; Li, H.; Cui, H.; Li, X. New multi-resolution and multi-scale electromagnetic detection methods for urban underground spaces. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 159, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Wang, Y. Intelligent overall planning model of underground space based on digital twin. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, X. Grey relation analysis and multiple criteria decision analysis method model for suitability evaluation of underground space development. Eng. Geol. 2024, 338, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. The 14th Five Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China and the Long Range Objectives for 2035; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021.
- He, L.; Song, Y.; Dai, S.Z.; Durbak, K. Quantitative research on the capacity of urban underground space—The case of Shanghai, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 32, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.S.; Su, P.D.; Chen, W.Y.; Tao, H.J.; Ma, G.X.; Xia, Z.J.; Tang, B. 3D Quality Evaluation of Rock Mass in Urban Underground Space Based on Improved Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 4829–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, F.F.; Li, X.H.; Xing, H.X.; Yang, F.; Ge, W.Y. 3D geological suitability evaluation for urban underground space development—A case study of Qianjiang Newtown in Hangzhou, Eastern China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 115, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M. A detection method of urban underground geological anomalies in the United Kingdom based on feature fusion. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2022, 26, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.W.; Peng, F.L.; Wang, T.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jiang, B.N. Advances in master planning of urban underground space (UUS) in China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.W.; Peng, F.L. A GIS-based evaluation method of underground space resources for urban spatial planning: Part 1 methodology. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 74, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.X.; Peng, F.L. Evaluation of spatial performance and supply-demand ratios of urban underground space based on POI data: A case study of Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 131, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tann, L.V.D.; Sterling, R.; Zhou, Y.X.; Metje, N. Systems approaches to urban underground space planning and management—A review. Undergr. Space 2019, 5, 144–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.Y. A comparative study on urban underground space planning system between China and Japan. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.J.; Ma, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.M. Research on basic theory of urban geology. Geol. China 2020, 47, 1668–1676, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 18504:2017; Soil Quality—Sustainable Remediation. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- SEA Directive 2001/42/EC; Assessment of the Effects of Certain Plans and Programmes on the Environment. European Parliament and Council of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2001.
- Zhao, P.D. Digital Geology, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2024; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Kieu, Q.L.; Tran, D.V. Application of Geospatial Technologies in Constructing a Flash Flood Warning Model in Northern Mountainous Regions of Vietnam: A Case Study at TrinhTuong Commune, Bat Xat District, LaoCai Province; Bulletin of Geography; Physical Geography Series; Walter De Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 20, pp. 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajac, N.; Knezic, S.; Marovic, I. Decision Support System to Urban Infrastructure Maintenance Management. Organ. Technol. Manag. Constr. Int. J. 2009, 1, 72–79. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/65018 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Partidário, M.R. Strategic Environmental Assessment Better Practice Guide—Methodological Guidance for Strategic Thinking in SEA; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente e Redes Energéticas Nacionais: Lisboa, Portugal, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Huang, Q.B.; Lin, L.J.; Zhang, X.; Han, B.; Xia, Y.B.; Guo, X. Practice and application of multi-factor urban geological survey in Xiong’an New Area. North China Geol. 2022, 45, 58–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Pu, J.; Huang, Y.; Han, Q. 3D geological suitability evaluation for underground space based on the AHP-cloud model. Undergr. Space 2023, 8, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parriaux, A.; Tacher, L.; Joliquin, P. The hidden side of cities—Towards three-dimensional land planning. Energy Build. 2004, 36, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Li, X.J.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhao, S.C.; Xu, W.Y. Three-dimensional high-precision assessment of mountainous urban underground space resources: A case study in Chongqing, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 123, 104439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Wu, L.; Zhuang, X.Y.; Rabczuk, T. Quantitative assessment of engineering geological suitability for multilayer Urban Underground Space. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 59, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D420-18; Guidelines for Site Characterization Standards for Engineering Design and Construction Purposes. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ISO 37120; Sustainable Development of Communities—Indicators for City Services and Quality of Life. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO 19650; Organization and Digitization of Information about Buildings and Civil Engineering Works, Including Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Pu, J.; Huang, Y.; Bi, Y.D.; Guo, Z.; Deng, F.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, C. 3D suitability evaluation of urban underground space using a variable weight method and considering ground restrictions. Undergr. Space 2024, 19, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wan, Y.H.; Cao, C.Y.; Liu, X.Y. Innovative solutions for layout planning and implementation of a metro station and its accessory structures in mountainous cities, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 129, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.L.; Li, M.F.; Liu, Y.N.; Guo, W.H. One-dimensional constrained inversion study of TEM and application in coal goafs’ detection. Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.J.; Cao, Z.N.; Zhao, G.X.; Hu, X.Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Fan, C.S.; Huang, Z.F. Application of the high-density resistivity method in detailed exploration of superficial paleochannels in Xiong’an New Area. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2023, 47, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, H.H.; Wang, Z.S.; Fu, J.N.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q. Development of urban underground space in coastal cities in China: A review. Deep Undergr. Sci. Eng. 2023, 2, 148–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.B.; Guo, X.; Wang, B.; Han, B.; Dou, Z.X. Study on the geological origin of groundwater and soil corrosivity in Xiong’an New Area. North China Geol. 2022, 45, 69–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymen, A. Statistical models for estimating the uniaxial compressive strength and elastic modulus of rocks from different hardness test methods. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, A.; Yusoff, M.Z.; Ng, K.C. The potential influence of building optimization and passive design strategies on natural venti-lation systems in underground buildings: The state of the art. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 92, 103065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Li, C.C.; Parriaux, A.; Wu, W.B.; Li, H.Q.; Sun, L.P.; Liu, C. Multiple resources and their sustainable development in Urban Underground Space. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 9–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.P.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, T.; Li, X.L.; Wang, M.L.; Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Hou, J.; Guo, G.H.; Badal, J. The Urban Underground Space beneath the Karst Basin of Guilin, China, Revealed by Ambient Seismic Noise Tomography. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2022, 94, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Lan, H.X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Gao, X.; Li, L.P. Nonlinear dynamic failure process of tunnel-fault system in response to strong seismic event. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 64, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P.; Zhou, X.H.; Tang, L.J.; Wang, Y.B.; Lv, D.Y.; Sun, M.S.; Qu, D.M. Wrench-related folding: A case study of Bohai Sea basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Wang, G.C.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Shi, Z.M.; Zhang, H. Isotopes in groundwater (2H, 18O, 14C) revealed the climate and groundwater recharge in the Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yang, H.J.; Wang, L.W.; Han, J.B.; Hao, Q.C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, W.X.; Wang, S.B.; et al. Interaction regimes of surface water and groundwater in a hyper-arid endorheic watershed on Tibetan Plateau: Insights from multi-proxy data. J. Hydrol. 2024, 644, 132020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, O.; Yoon, Y.; Do, J. Comparative Study of the Field Performances of Pressure-Grouted Micropiles Using Gravity and Packers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Q.H.; Yu, X.L.; Ma, C.Q.; She, Z.B. Unraveling the petrological enigma of the durability and corrosion resistance of ancient Roman concrete. Adv. Earth Sci. 2024, 39, 968–986. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Shi, Z.M.; Guo, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Mao, H.R.; Liu, F.T.; Ning, H.; Liu, N.N.; Wang, G.C. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution of formation water in the continental sedimentary basin: A case study in the Qaidam Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Wang, G.C.; Shi, Z.M.; Liu, F.T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.L. Cl, Br, B, Li, and noble gases isotopes to study the origin and evolution of deep groundwater in sedimentary basins, a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1497–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Jiang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Wang, K.L.; Chen, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.T. Comprehensive evaluation of nitrogen contamination in water ecosystems of the Miyun reservoir watershed, northern China: Distribution, source apportionment and risk assessment. Env. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.B.; Wang, B.; Yang, Y.S.; Du, X.Q.; Yang, M.X. Quantitative assessment of organic mass fluxes and natural attenuation processes in a petroleum-contaminated subsurface environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.B.; Chen, G.F.; Liu, F.T.; Zhang, J.; Ning, H. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of groundwater in grassland watersheds of cold and arid regions in Xilinhot, China. Water 2024, 16, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Meng, L.S.; Liu, F.T.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Chen, S.M.; Yang, J.L.; Mao, H.R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H. Distribution, source investigation, and risk assessment of topsoil heavy metals in areas with intensive anthropogenic activities using the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model coupled with self-organizing map (SOM). Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.X.; Zheng, J.G. Engineering Geology Handbook, 5th ed.; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1219–1220. [Google Scholar]
- National Land and Resources Standardization Technical Committee (SAC-TC93TC93). Specification for Survey and Monitoring of Land Subsidence, 1st ed.; Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015; p. 16.
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for Urban Underground Space Planning (GB/T 51358-2019); China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Najafi, M.; Kim, K.O. Life-cycle-cost comparison of trenchless and conventional open-cut pipeline construction projects. In Pipeline Engineering and Construction: What’s on the Horizon? American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKim, R.A. Bidding strategies for conventional and trenchless technologies considering social costs. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1997, 24, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.; Stephenson, M.; Shaw, R. The present and future use of ‘land’ below ground. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, S302–S316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto-Perello, J.; Curiel-Esparza, J. Risks and potential hazards in utility tunnels for urban areas. In Municipal Engineer—Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Municipal Engineer; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2003; Volume 156, pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.W. Geotechnical issues for planning tunnels and underground space. In Proceedings of the International Seminar, South American Tunnelling, SAT, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 18–21 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, D.; Olaf, H. An Experimental Application of the Delphi Method to the Use of Experts. Manag. Sci. 1963, 9, 458–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hallowell, M.R.; Gambatese, J.A. Qualitative research: Application of the Delphi method to CEM research. J. Constr. Eng. Manag 2010, 136, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, T.; Gu, Q.; Xin, Y. GIS-based urban underground space resources evaluation toward three-dimensional land planning: A case study in Nantong, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 84, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 15, 234–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoni, O. Implementation of the analytical hierarchy process with VBA in ArcGIS. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.P.; Xu, Z.S.; Liu, D.L.; Cao, H.H. Application of the model based on fuzzy consistent matrix and AHP in the assessment of fire risk of subway tunnel. Procedia Eng. 2014, 71, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnaji, C.; Lee, H.W.; Karakhan, A.; Gambatese, J. Developing a decision-making framework to select safety technologies for highway construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.H.; Chen, Q.Q.; Xue, Y.G.; Su, M.X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.H.; Zhou, B.H. A new method for risk assessment of water inrush in a subsea tunnel crossing faults. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2021, 40, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.; Pradhan, B.; Tarabees, E. Integrated evaluation of urban development suitability based on remote sensing and GIS techniques: Contribution from the analytic hierarchy process. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 4, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Jain, M.; Bansal, V.K. A methodological approach for weighting factors in land suitability assessment: A tool for facilitating spatial planning. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Peng, F.L. A GIS-based evaluation method of underground space resources for urban spatial planning: Part 2 application. Tunn. Undergr Space Technol. 2018, 77, 142–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Fundamentals of the analytic network process—Dependence and feedback in decision-making with a single network. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2004, 13, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmir, M.; Zarkesh, M.M.K.; Monavari, S.M.; Jozi, S.A.; Sharifi, E. Analysis of land suitability for urban development in ahwaz County in southwestern Iran using fuzzy logic and analytic network process (ANP). Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2016, 188, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Kizil, M.; Chen, Z.W.; Chen, J.H. A new approach for selecting best development face ventilation mode based on g1-coefficient of variation method. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Meng, X.X.; Liu, Y.B.; Pang, L.F. Risk assessment of floor water inrush using entropy weight and variation coefficient model. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Huang, G.H.; Wei, S. Risk assessment of hydropower stations through an integrated fuzzy entropy-weight multiple criteria decision making method: A case study of the Xiangxi River. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 5380–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, G.Y.; Zhang, J.M. Suitability evaluation system for the shallow geothermal energy implementation in region by Entropy Weight Method and TOPSIS method. Renew. Energy 2022, 184, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.R.; Chen, X.L.; Lu, J.Z. Assessment of long and short-term flood risk using the multi-criteria analysis model with the AHP-entropy method in Poyang lake basin. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 75, 102968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheriyoun, M.; Karamouz, M.; Baghvand, A. Development of an entropy-based fuzzy eutrophication index for reservoir water quality evaluation. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ustaoglu, E.; Aydınoglu, A.C. Suitability evaluation of urban construction land in Pendik district of Istanbul, Turkey. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, E.U.; Schoner, B.; Wedley, W.C. Interpretation of criteria weights in multicriteria decision making. Comput. Ind. Eng. 1999, 37, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.B.; Guo, X.; Ma, Z.; Wang, B.; Han, B.; Zhao, C.R.; Li, H.T.; Meng, Q.H. Suitability evaluation of Xiong’an New Area engineering construction based on multi-factor grading weighted index sum method. North China Geol. 2024, 47, 63–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Luo, X.; Wang, B.H.; Shao, C.Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Le, Q.L. Suitability evaluation of Urban underground space utilization in karst area in Gui’an New District. Carsologica Sin. 2024, 43, 176–187. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Shen, L.; Liu, H. Grey relational analysis, principal component analysis and forecasting of carbon emissions based on long short-term memory in china. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.Q.; Dong, J.; He, P.; Xie, Y.J. Evaluation and suitability zoning of geological factors affecting the development and utilization of underground space in the main urban area of Qingdao. Acta Geo Sin. 2019, 93, 233–240. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Zhou, S.H.; Zhang, C.; Yang, M.H.; Jiang, M.Y. A Bayesian network model for suitability evaluation of underground space development in urban areas: The case of Changsha, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Peng, B.Q.; Wu, L.X.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Xie, B.S. Flat voxel-based modelling, assessment and visualization of urban underground space resource quality. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 113, 102984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Objective Decision Making-Methods and Applications; Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1981; p. 164. [Google Scholar]
- Alinezhad, A.; Amini, A. Sensitivity Analysis of TOPSIS Technique: The Results of Change in the Weight of One Attribute on the Final Ranking of Alternatives. J. Optim. Ind. Eng. 2011, 7, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, F.F.; Xing, H.X.; Li, X.H.; Yuan, F.; Lu, Z.T.; Li, X.L.; Ge, W.Y. 3D Geological Suitability Evaluation for Urban Underground Space Development Based on Combined Weighting and Improved TOPSIS. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 693–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.X.; Liu, G.B.; Tao, H.B. Research on evaluation suitability for the development of underground space in Ningbo city based on ArcGIS. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2016, 12, 1439–1444. Available online: http://dxkjxb.cqu.edu.cn/CN/Y2016/V12/I6/1439 (accessed on 24 April 2024). (In Chinese).
- Xu, F.F.; Chen, J.W.; Li, J.Y.; Wang SLHe, Y. Research on the application of cloud model in the suitability evaluation of the development and utilization of underground space. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2024, 31, 107–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.Y.; Shen, F.Q.; Jin, J.L. A novel multi-dimensional cloud model coupled with connection numbers theory for evaluation of slope stability. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 77, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Barker, K. Modeling infrastructure resilience using Bayesian networks: A case study of inland waterway ports. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 93, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Q.; Heinimann, H.; Han, K.; Luo, H.B.; Zhong, B.T. Evaluating resilience in urban transportation systems for sustainability: A systems-based Bayesian network model. Transport. Res. C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 121, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, L. Advantages and challenges of Bayesian networks in environmental modelling. Ecol. Model. 2007, 203, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanea, A.M.; Kurowicka, D.; Cooke, R.M.; Ababei, D.A. Mining and visualising ordinal data with non-parametric continuous BBNs. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2010, 54, 668–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landuyt, D.; Broekx, S.; D’hondt, R.; Engelen, G.; Aertsens, J.; Goethals, P.L.M. A review of Bayesian belief networks in ecosystem service modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, Z.L.; Guo, D.J.; Zhao, Z.W. Simulating spatiotemporal dynamics of urban underground space development using multi-agent system: A case study in Changzhou city, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhu, J.B.; Liao, Z.Y.; Guo, J.; Xie, H.P.; Peng, Q. An intelligent planning model for the development and utilization of urban underground space with an application to the Luohu District in Shenzhen. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 112, 103933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburas, M.M.; Abdullah, S.H.; Ramli, M.F.; Asháari, Z.H. Land suitability analysis of urban growth in Seremban Malaysia, using GIS-based analytical hierarchy process. Procedia Eng. 2017, 198, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.H.; Han, B.; Miao, J.J.; Jin, S.; Liu, H.W. Research on Suitability Evaluation of Urban Engineering Construction Based on Entropy Weight Hierarchy-Cloud Model: A Case Study in Xiongan New Area, China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyimbili, P.H.; Erden, T.; Karaman, H. Integration of GIS, AHP and TOPSIS for earthquake hazard analysis. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 1523–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Xue, W.; Shahabi, H.; Li, S.; Hong, H.; Wang, H.; Bian, H.; Zhang, S.; Pradhan, B.; et al. Modeling flood susceptibility using data-driven approaches of naïve bayes tree, alternating decision tree, and random forest methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.M.; Chen, G.J.; Xu, S.Y.; Xiao, Y. Engineering geological research on the underground space of wuhan city. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2006, 33, 29–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.Y.; Xia, Y.B.; Ma, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, H.W.; Miao, J.J.; Bai, Y.N.; Li, Z. Significance evaluation on available properties of soil mass in underground space in Xiongan New Area based on rough set theory. North China Geol. 2023, 46, 43–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhen, F.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.H. Factors influencing the development potential of urban underground space: Structural equation model approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makana, L.O.; Jefferson, I.; Hunt, D.V.L.; Rogers, C.D.F. Assessment of the future resilience of sustainable urban sub-surface environments. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Q.; Ninić, J.; Zhang, Q.B. BIM, machine learning and computer vision techniques in underground construction: Current status and future perspectives. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 108, 103677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wu, Z.X.; Zhu, J.X.; Lu, Y. Study on Calculation Method of Grid Size in the Areal Direction for Fine 3D Geological Modeling of Shallow Sediments in Urban Areas. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 35, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.M.; Zhu, L.; Liu, W.; Wen, P.; Xie, Z.Q.; Li, R.; Ji, C.H.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Y.B.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. 3D-CWC: A Method to Evaluate the Geological Suitability for Layered Development and Utilization of Urban Underground Space. Land 2025, 14, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Fan, Z.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Li, X.Z.; Zhao, P. Regional 3D geological modeling along metro lines based on stacking ensemble model. Undergr. Space 2024, 18, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Green Deal. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- The CPC Central Committee and the State Council. Master Plan for Xiongan New Area; The CPC Central Committee and the State Council: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Xiong’an New Area Administrative Committee. Special Plan for the Development and Utilization of Underground Space in Xiongan New Area (2021–2035); Xiong’an New Area Administrative Committee: Xiong’an, China, 2021.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, B.; Huang, S. Urban Underground Space Geological Suitability—A Theoretical Framework, Index System, and Evaluation Method. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4326. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084326
Tian J, Xia Y, Zhang J, Liu H, Zhang M, Gao Y, Liu J, Han B, Huang S. Urban Underground Space Geological Suitability—A Theoretical Framework, Index System, and Evaluation Method. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4326. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084326
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Ji, Yubo Xia, Jinhuan Zhang, Hongwei Liu, Mengchen Zhang, Yihang Gao, Jidong Liu, Bo Han, and Shaokang Huang. 2025. "Urban Underground Space Geological Suitability—A Theoretical Framework, Index System, and Evaluation Method" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4326. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084326
APA StyleTian, J., Xia, Y., Zhang, J., Liu, H., Zhang, M., Gao, Y., Liu, J., Han, B., & Huang, S. (2025). Urban Underground Space Geological Suitability—A Theoretical Framework, Index System, and Evaluation Method. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4326. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084326