A Data and Machine Learning-Based Approach for the Conversion of the Encounter Wave Frequency Spectrum to the Original Wave Spectrum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Methodology
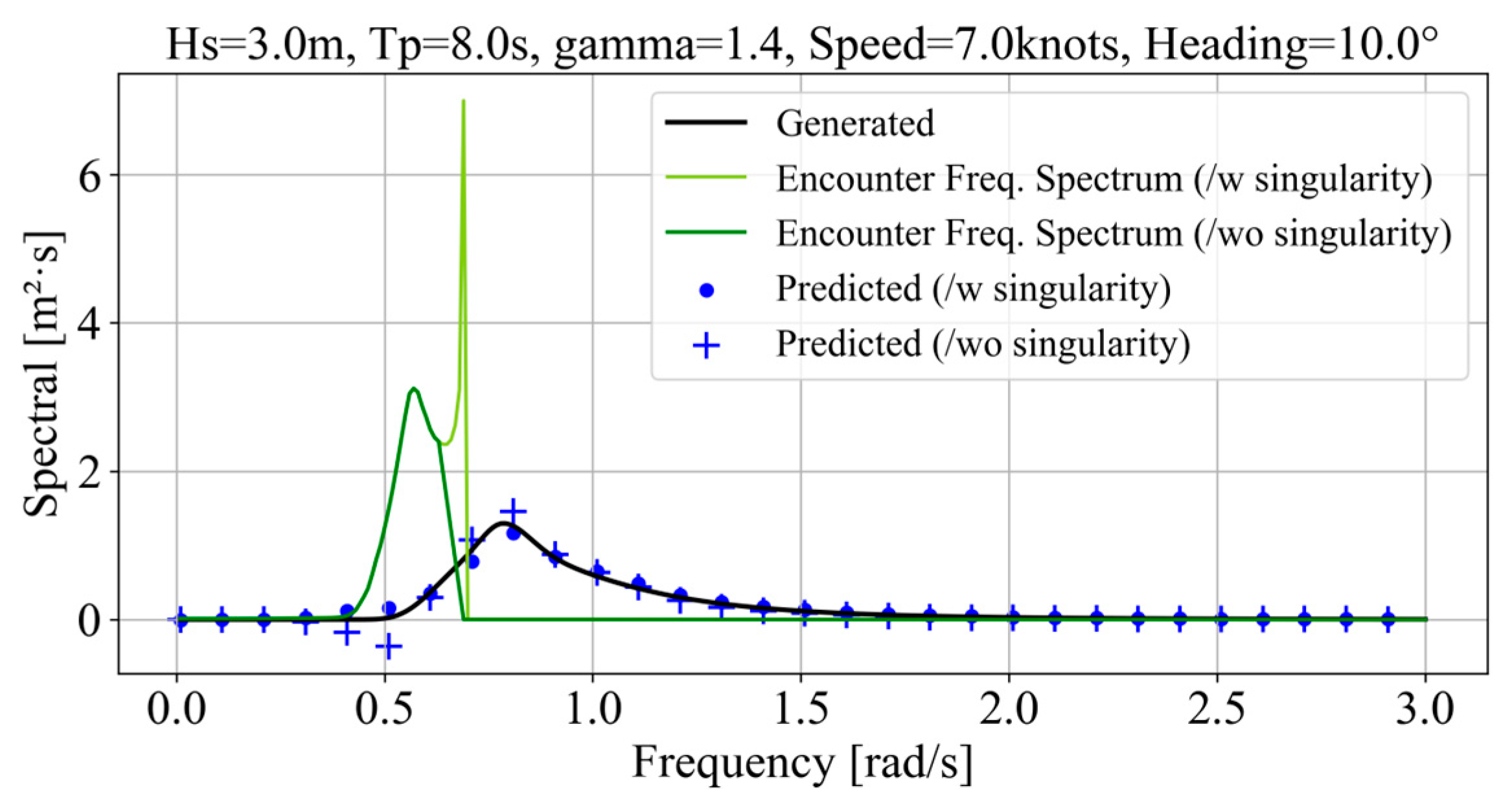
2.1. Encounter Wave Frequency and Wave-Spectrum Conversion
- Area 1:
- Area 2:
- Area 3:
2.2. Dataset Generation
2.3. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
3. Results
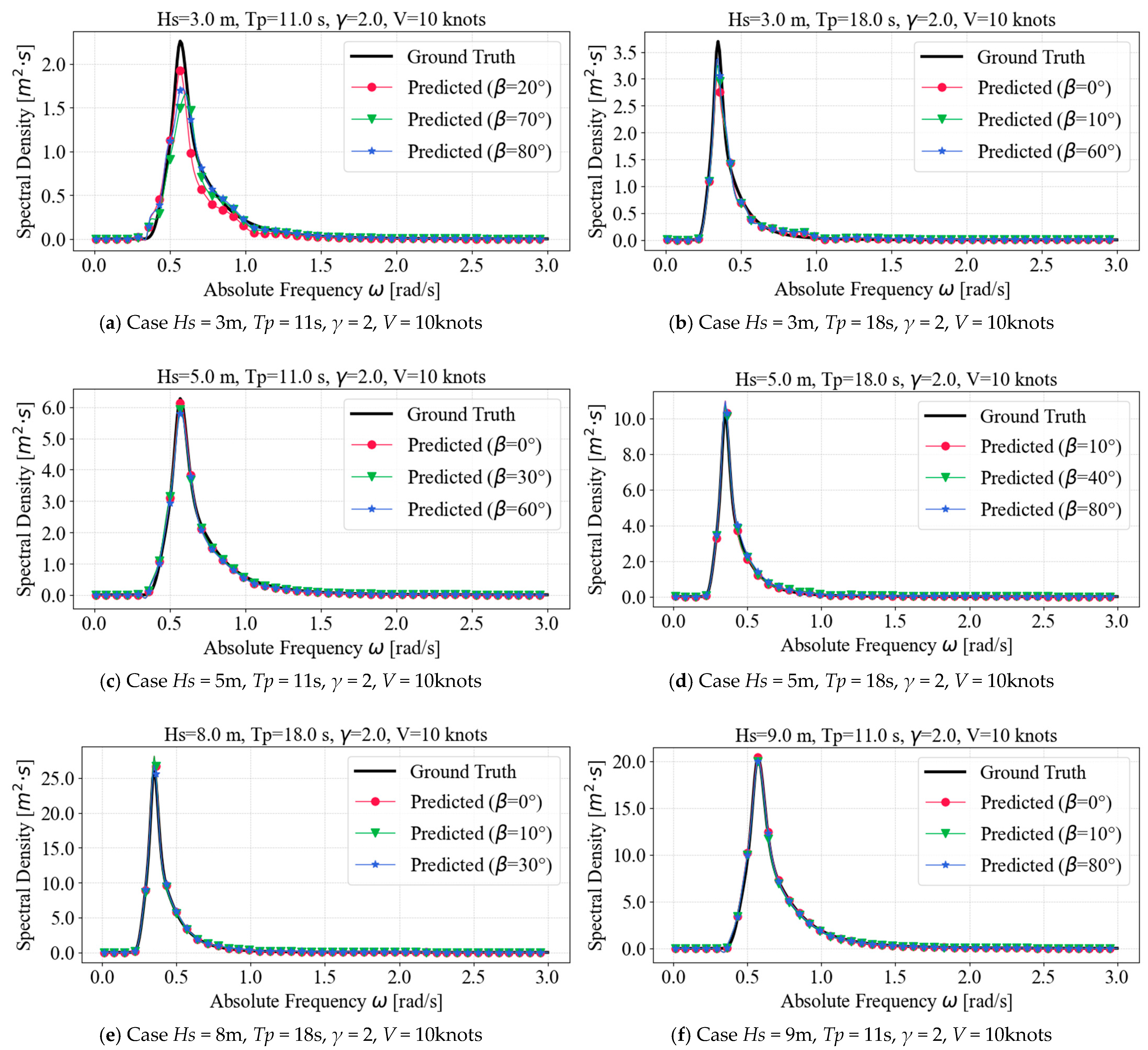
3.1. ANN Model Performance
3.2. Model Error Distribution
3.3. Bimodal Sea State
3.4. Additional Remarks
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ML | Machine Learning |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| JONSWAP | Joint North Sea Wave Project |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| NCEP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| KF | Kalman Filter |
| RAO | Response Amplitude Operator |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| RMSE | Root-Mean-Squared Error |
| NRMSE | Normalized Root-Mean-Squared Error |
| IQR | Inter-Quartile Range |
References
- Kim, S. The development of route decision-making method based on tailor-made forecast 2d wave spectra due to the operation profile of the vessel. Ocean Eng. 2020, 197, 106907. [Google Scholar]
- Vettor, R.; Soares, C.G. Development of a ship weather routing system. Ocean Eng. 2016, 123, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Caamaño, L.S.; González, M.M.; Casás, V.D. Improving the performance of a stability monitoring system by adding wave encounter frequency estimation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Leira, B.J.; Sævik, S.; Ren, Z. Onboard tuning of vessel seakeeping model parameters and sea state characteristics. Mar. Struct. 2021, 78, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natskår, A.; Moan, T.; Alvær, P.Ø. Uncertainty in forecasted environmental conditions for reliability analyses of marine operations. Ocean Eng. 2015, 108, 636–647. [Google Scholar]
- Stredulinsky, D.C.; Thornhill, E.M. Ship motion and wave radar data fusion for shipboard wave measurement. J. Ship Res. 2011, 55, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felski, A.; Zwolak, K. The ocean-going autonomous ship—Challenges and threats. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombre, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ramm-Schmidt, H.; García, J.M.V.; Malkamäki, T.; Nikolskiy, S.; Hammarberg, T.; Nuortie, H.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.H.; Särkkä, S. Sensors and AI techniques for situational awareness in autonomous ships: A review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 23, 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, T.; Ohtsu, K. Bayesian estimation of directional wave spectra based on ship motions. Control Eng. Pract. 2000, 8, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, U.D. Estimations of on-site directional wave spectra from measured ship responses. Mar. Struct. 2006, 19, 33–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Kim, M.-H. Real-time inverse estimation of ocean wave spectra from vessel-motion sensors using adaptive kalman filter. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, J.; Jin, C.; Kim, M.; Lee, D. Real-time inverse estimation of multi-directional random waves from vessel-motion sensors using Kalman filter. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114501. [Google Scholar]
- Pascoal, R.; Perera, L.P.; Soares, C.G. Estimation of directional sea spectra from ship motions in sea trials. Ocean Eng. 2017, 132, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.-S.; Jin, C.; Kim, M.; Guha, A.; Esenkov, O.E.; Ryu, S. Inverse wave estimation from measured FPSO motions through artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the SNAME Offshore Symposium, Houston, Texas, USA, 20 February 2024; p. D011S004R003. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, D.-S.; Jin, C.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, M.; Guha, A.; Gosain, G.; Ryu, S.; Ferreira, M.D.; Auburtin, E.; Minnebo, J. Inverse Ocean Wave Estimation from FPSO Motions by Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the ISOPE International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Ottawa, Canada, 19–23 June 2023; p. ISOPE-I-23-146. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, U.D.; Mittendorf, M.; Shao, Y.; Storhaug, G. Wave spectrum estimation conditioned on machine learning-based output using the wave buoy analogy. Mar. Struct. 2023, 91, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, T. Extended Bayesian estimation of directional wave spectra. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 June 2004; pp. 611–616. [Google Scholar]
- Brodtkorb, A.H.; Nielsen, U.D. Automatic sea state estimation with online trust measure based on ship response measurements. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 130, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, T. Real-time estimation of directional wave spectra using non-stationary ship motion data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, Honolulu, HI, USA, 31 May–5 June 2009; pp. 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, U.D.; Iseki, T. Estimation of Sea State Parameters From Measured Ship Responses: The Bayesian Approach With Fixed Hyperparameters. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, Shanghai, China, 6–11 June 2010; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Faltinsen, O. Sea Loads on Ships and Offshore Structures; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, U.D. Transformation of a wave energy spectrum from encounter to absolute domain when observing from an advancing ship. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 69, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, U.D. Deriving the absolute wave spectrum from an encountered distribution of wave energy spectral densities. Ocean Eng. 2018, 165, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Barnett, T.P.; Bouws, E.; Carlson, H.; Cartwright, D.E.; Enke, K.; Ewing, J.; Gienapp, A.; Hasselmann, D.; Kruseman, P. Measurements of Wind-Wave Growth and Swell Decay During the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP). “Ergänzungsheft zur Deutschen Hydrographischen Zeitschrift, Reihe A, Nr. 12.”. 1973. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/21.11116/0000-0007-DD3C-E (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- DNV. Recommended Practice DNV-RP-C205: Environmental Conditions and Environmental Loads; DNV: Høvik, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]












| JONSWAP Wave Parameter | Range of Values | Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Hs, significant wave height (m) | [1, 2, …, 9] | 1 m |
| Tp, peak period (s) | [6, 7, …, 18] | 1 s |
| γ, peak enhancement factor * | [1, 1.2, …, 3] | 0.2 |
| β, wave heading (deg) ** | [0, 10, …, 80] | 10° |
| V, forward speed (knots) | [1, 2, …, 20] | 1 m/s |
| ANN Model Parameter | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of layers | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Number of neurons (per layer) | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Activation function | ReLU | ReLU | ReLU |
| Optimizer | Adam * | Adam | Adam |
| Loss function | MSE ** | MSE | MSE |
| Input variables | |||
| Output variables | |||
| Total dataset | 21,060 **** | 231,660 | 231,660 |
| Remark | γ = 2 (fixed) | γ = range of 1–3 | γ = range of 1–3 |
| Model Optimization | R2 Score | NRMSE Mean * | Layer | Nodes | Optimizer | Loss Function | Epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v.0 | 0.984 | 0.71% | 3 | 50 | adam | MSE | 25 |
| v.0.1 | 0.985 | 0.70% | 3 | 100 | adam | MSE | 25 |
| v.0.1.1 | 0.989 | 0.54% | 3 | 100 | adam | MSE | 50 |
| v.0.2 | 0.989 | 0.52% | 3 | 150 | adam | MSE | 25 |
| v.0.2.1 | 0.987 | 0.64% | 3 | 150 | adam | MSE | 50 |
| v.0.2.2 | 0.988 | 0.54% | 3 | 150 | adam | MSE | 100 |
| v.0.3 | 0.987 | 0.60% | 3 | 200 | adam | MSE | 25 |
| v.0.3.1 | 0.991 | 0.47% | 3 | 200 | adam | MSE | 50 |
| v.0.3.2 | 0.988 | 0.64% | 3 | 200 | adam | MSE | 100 |
| v.0.3.2.1 | 0.987 | 0.56% | 2 | 200 | adam | MSE | 100 |
| v.0.3.2.2 | 0.991 | 0.47% | 4 | 200 | adam | MSE | 100 |
| v.0.3.2.3 | 0.988 | 0.56% | 5 | 200 | adam | MSE | 100 |
| v.0.3.3 | 0.991 | 0.48% | 3 | 200 | adam | MSE | 150 |
| v.0.4.2 | 0.989 | 0.54% | 3 | 300 | adam | MSE | 100 |
| ANN Model Metrics | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (Mean Absolute Error) | 0.046 | 0.052 | 0.059 |
| MSE (Mean Squared Error) | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.045 |
| RMSE (Root-Mean-Squared Error) | 0.159 | 0.159 | 0.213 |
| R Square (R2) | 0.993 | 0.993 | 0.987 |
| JONSWAP Wave Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Hs, wind sea (m) | [2.5, 3.5] |
| Hs, swell (m) | [0 *, 3, 4] |
| Tp, wind sea (s) | [5, 7] |
| Tp, swell (s) | [10, 11] |
| γ, wind sea | [1, 2] |
| γ, swell | [4, 5] |
| β (deg) | [5, 10] |
| V (knots) | [10, 40] |
| ANN Model Parameter | Model 4 |
|---|---|
| Number of layers | 3 |
| Number of neurons (per each layer) | 200 |
| Activation function | ReLu |
| Optimizer | Adam (Learning rate: 0.001) |
| Loss function | MSE (Mean Squared Error) |
| Input variables | |
| Output variables | |
| Total dataset | 384 (192 unimodal + 192 bimodal seas) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Kim, M. A Data and Machine Learning-Based Approach for the Conversion of the Encounter Wave Frequency Spectrum to the Original Wave Spectrum. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073987
Park J, Kim M. A Data and Machine Learning-Based Approach for the Conversion of the Encounter Wave Frequency Spectrum to the Original Wave Spectrum. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073987
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, JeongYong, and MooHyun Kim. 2025. "A Data and Machine Learning-Based Approach for the Conversion of the Encounter Wave Frequency Spectrum to the Original Wave Spectrum" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073987
APA StylePark, J., & Kim, M. (2025). A Data and Machine Learning-Based Approach for the Conversion of the Encounter Wave Frequency Spectrum to the Original Wave Spectrum. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073987





