Separation of Body and Surface Wave Background Noise and Passive Seismic Interferometry Based on Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
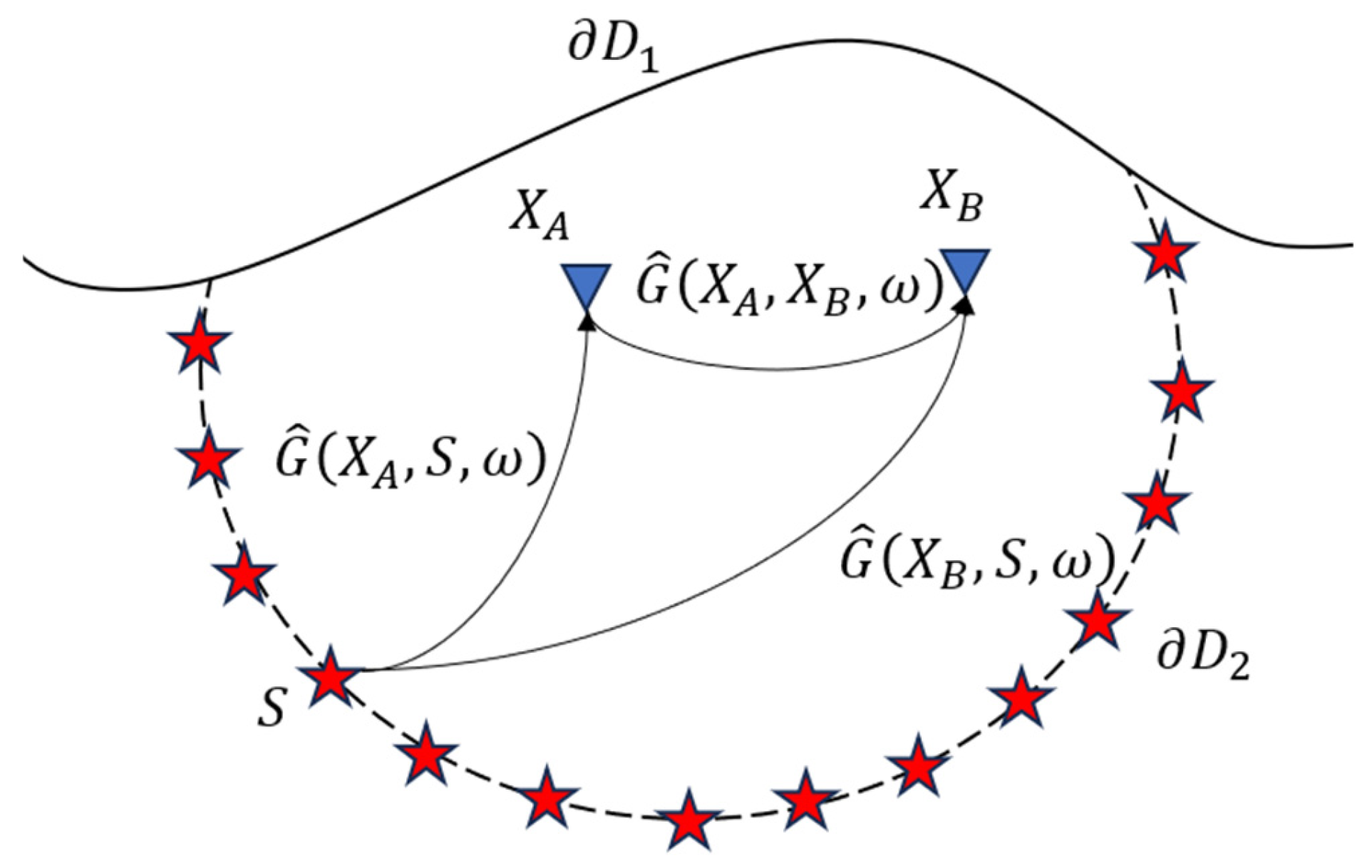
2.1. Cross-Correlation Seismic Interferometry
- Approximate the medium outside the boundary as homogeneous;
- Apply the far-field approximation, using a monopole to represent the dipole source;
- The surrounding medium parameters are assumed to undergo a uniform transformation.
2.2. Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform
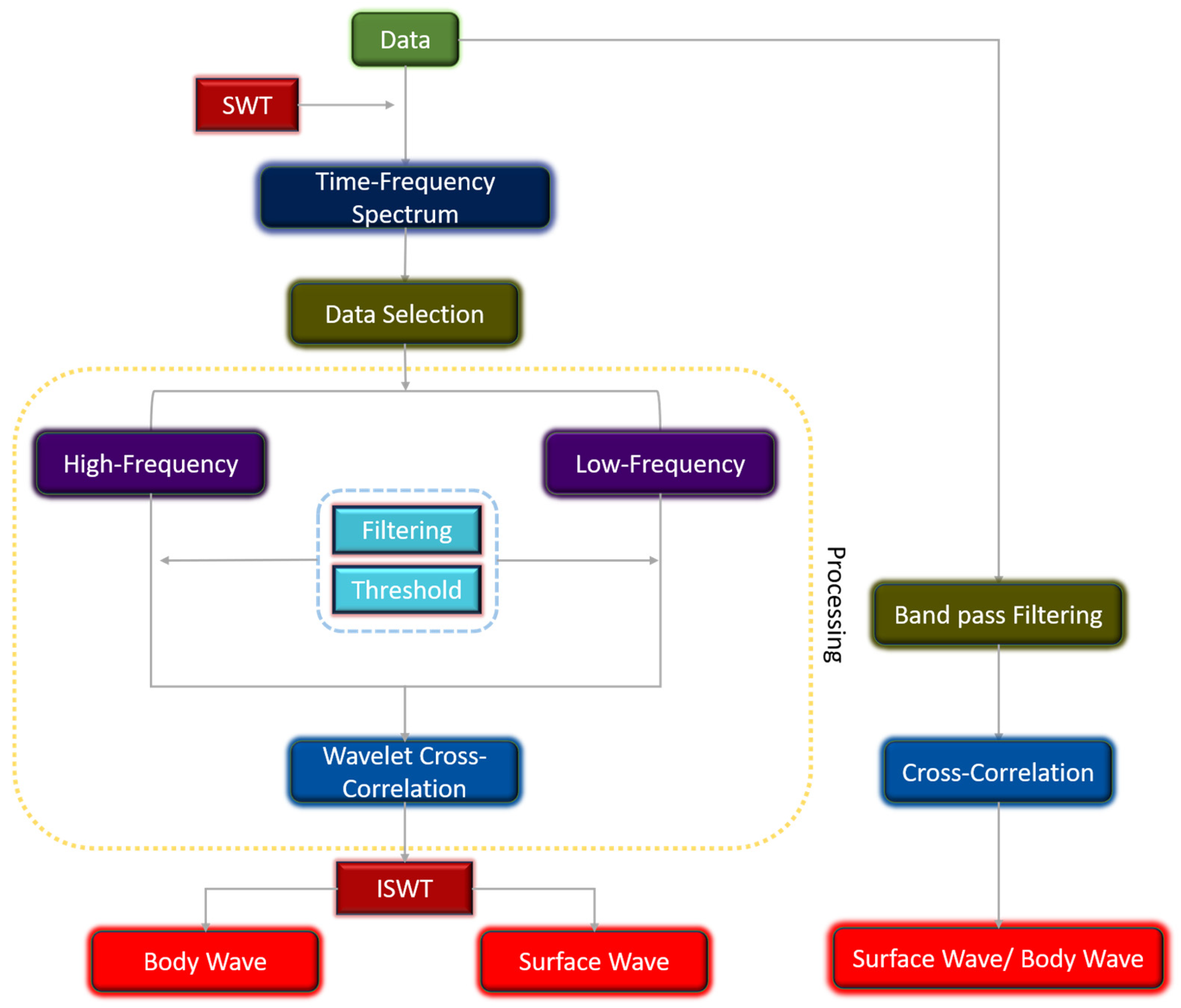
3. Method
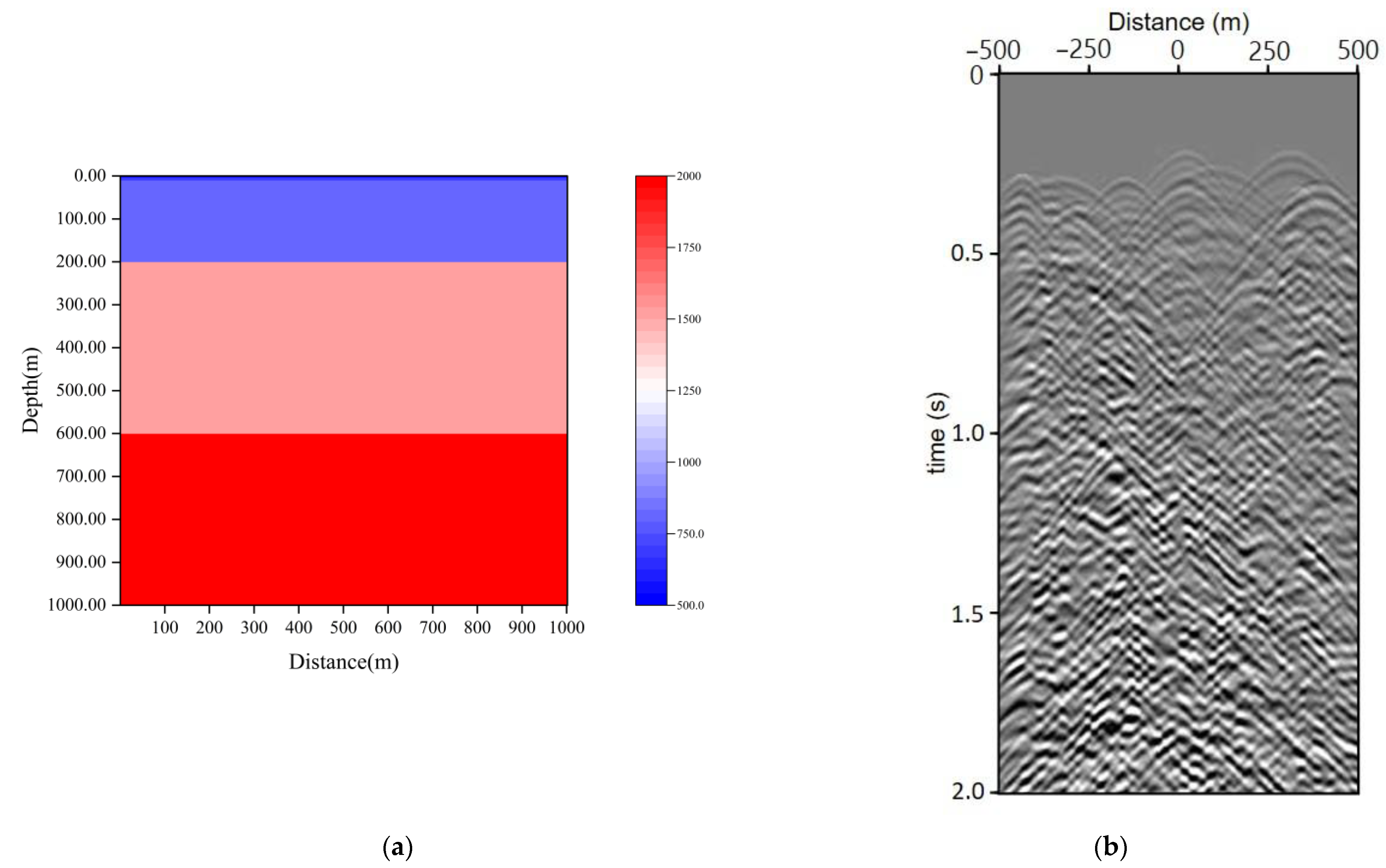
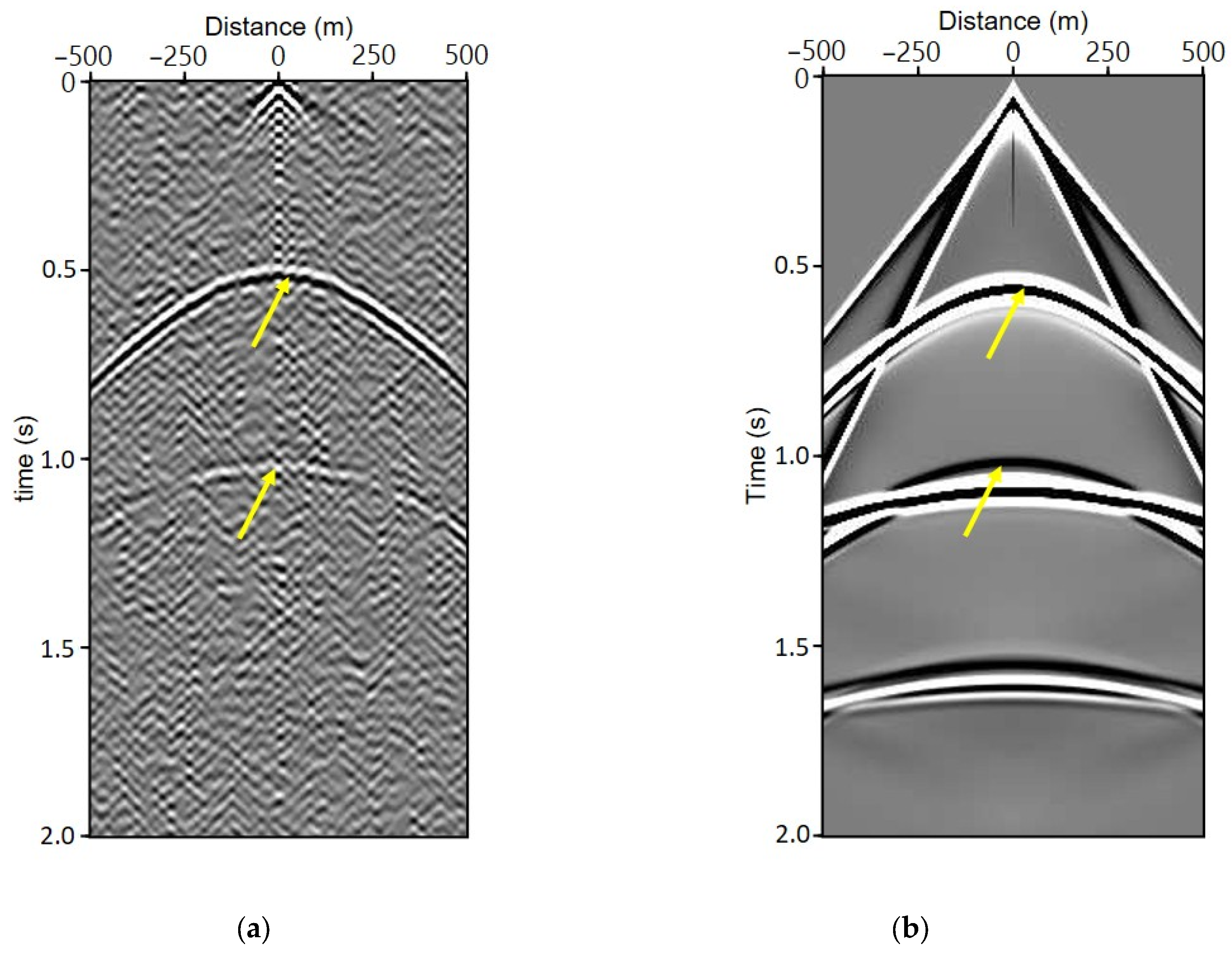
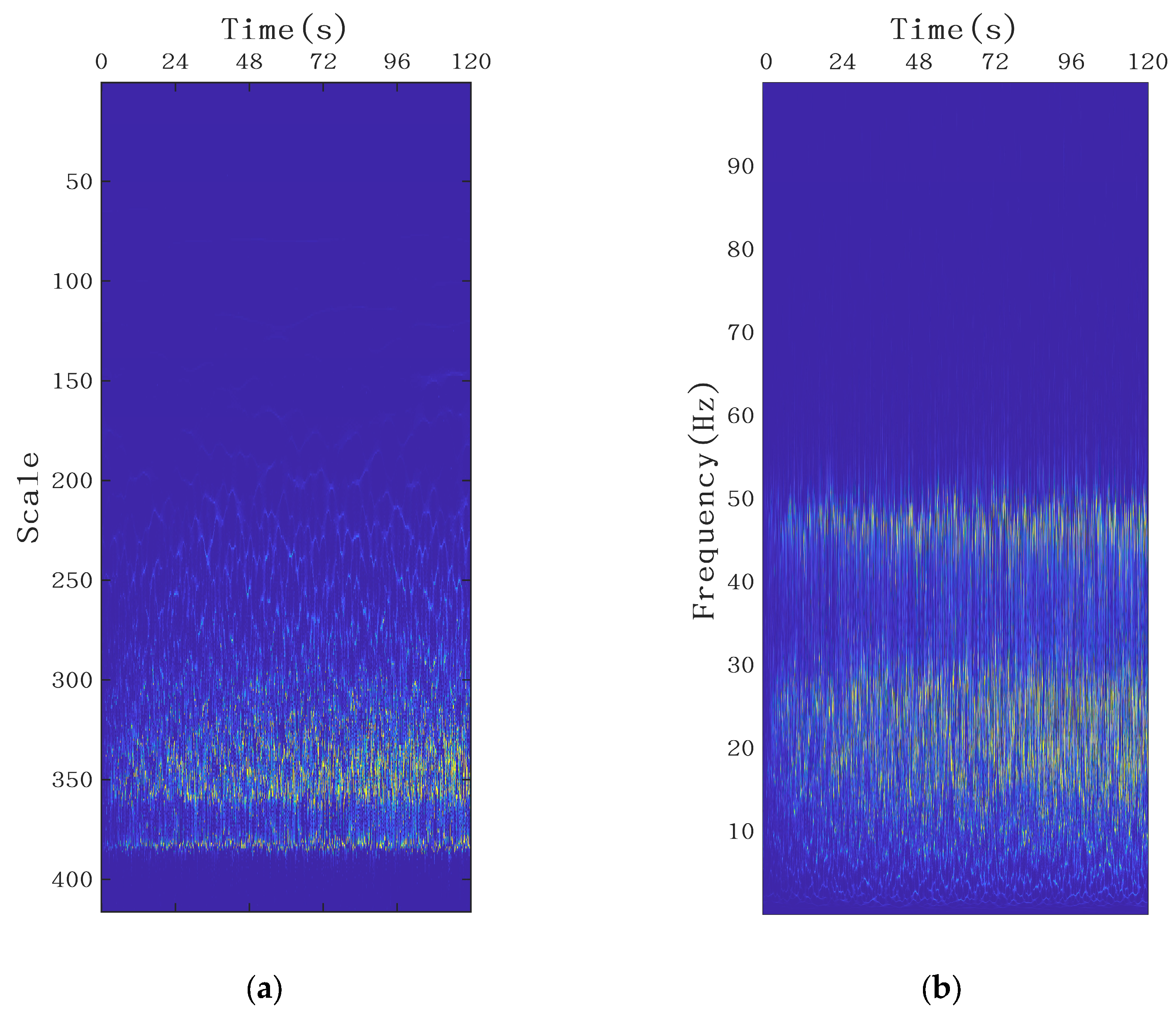
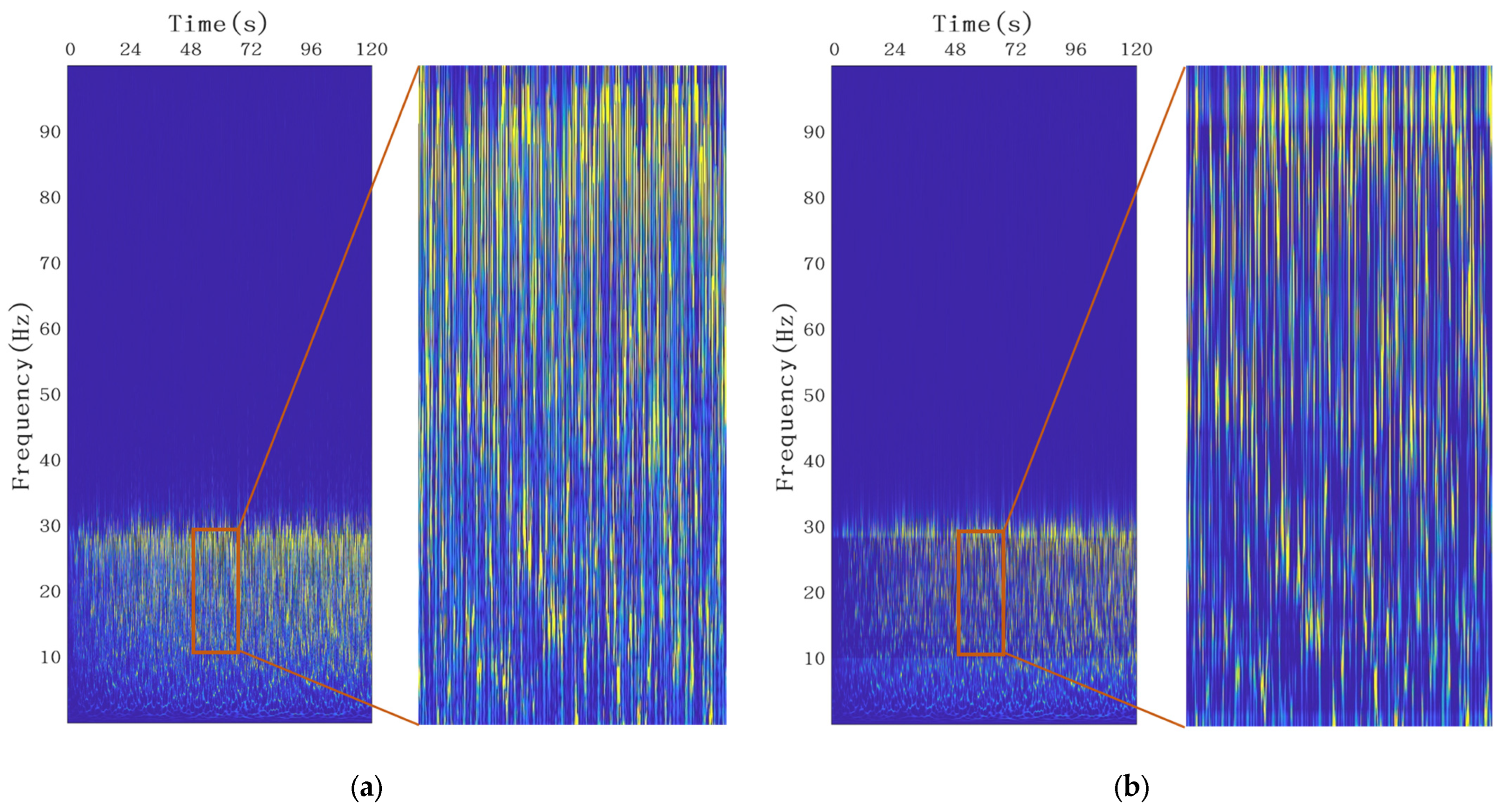
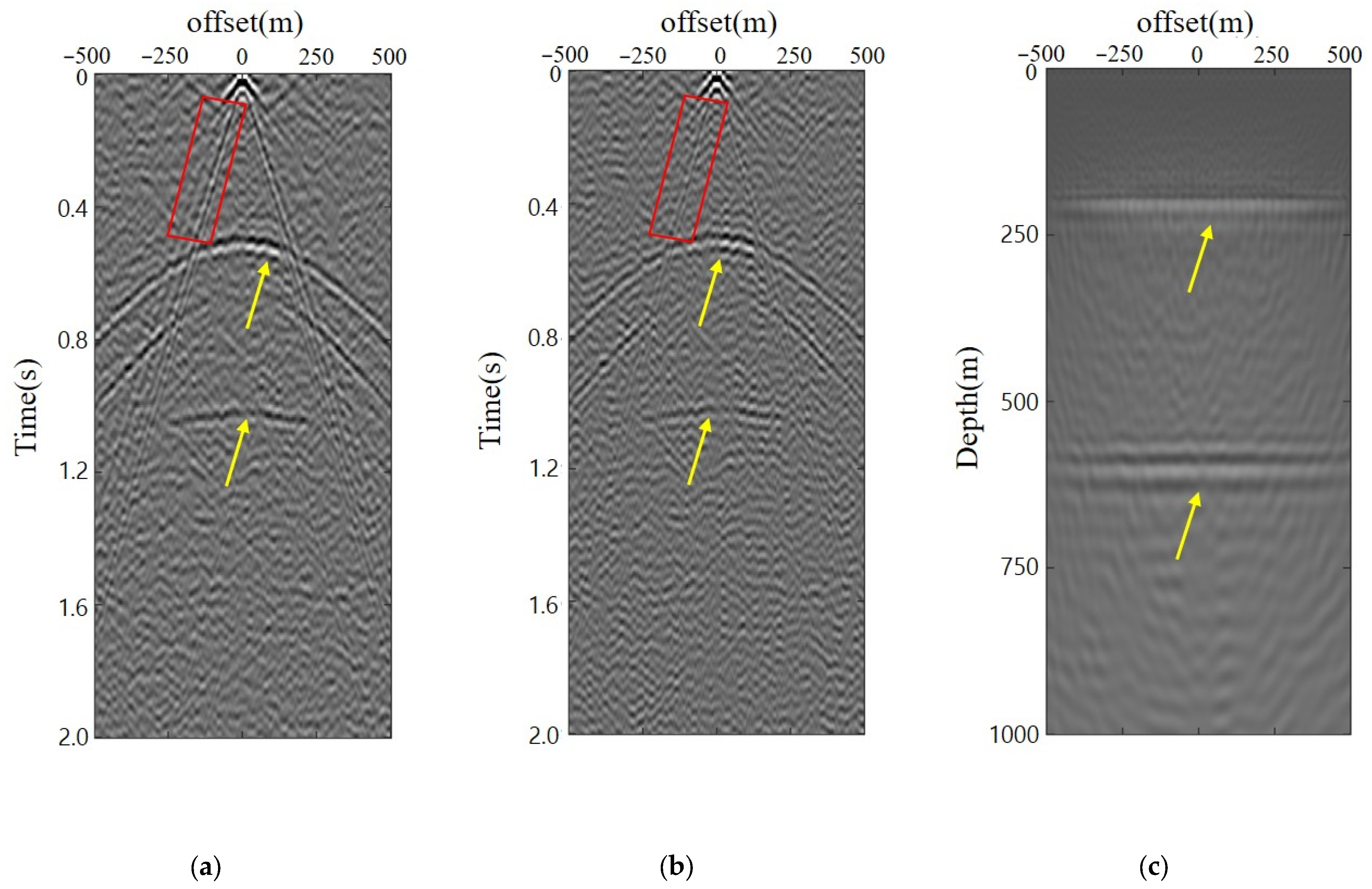
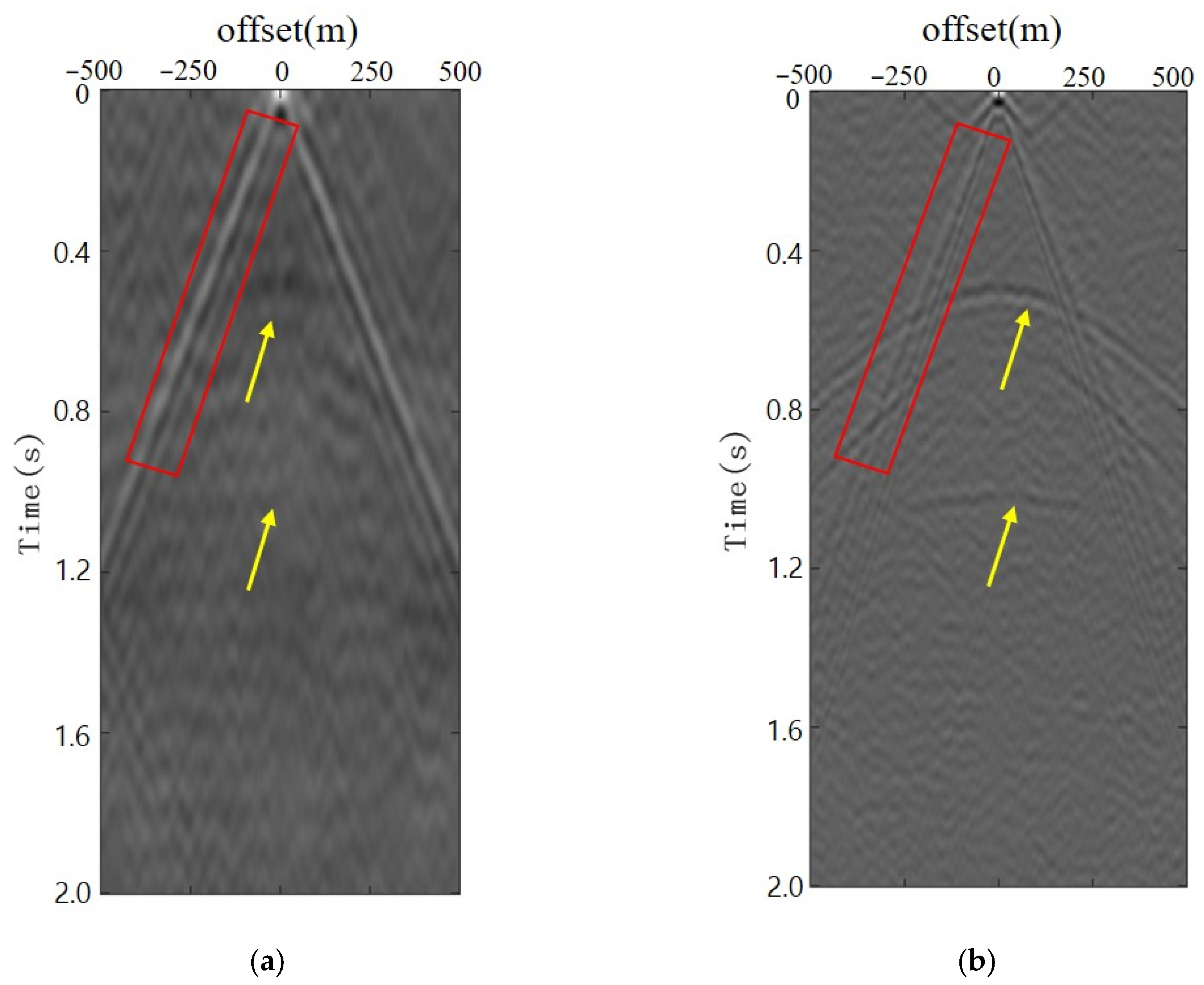
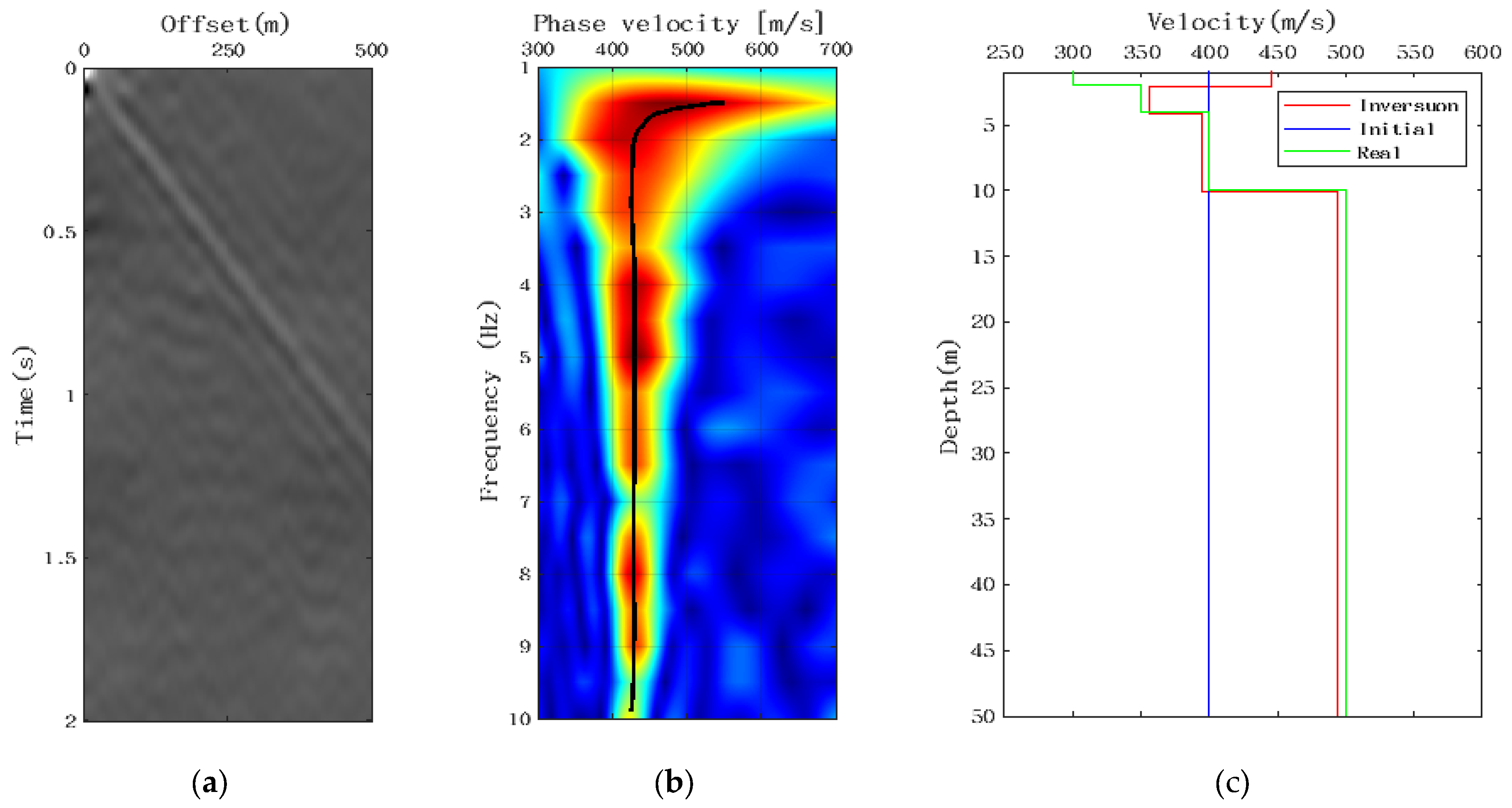
4. Numerical Experiments
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| SI | Seismic Interferometry |
| HVSR | Horizontal-to-Vertical Spectral Ratio |
| MAPS | Multi-Channel Analysis of Passive Surface Waves |
| MASW | Multi-Channel Analysis of Surface Waves |
| F-J | Frequency–Bessel Transform |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DAS | Distributed Fiber Acoustic Sensing |
| CWT | Continuous Wavelet Transform |
| SWT | Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform |
| EMD | Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| CMSL | CREWES MATLAB Software Library |
| Boundary | |
| Green’s Function | |
| Angular Frequency | |
| Wavelet Coefficients | |
| Time-Domain Signal | |
| Mother Wavelet | |
| Fourier Transforms of | |
| Dirac Delta Function | |
| Synchronized Wavelet Coefficient | |
| Instantaneous Frequency | |
| a | Scale Parameter |
| b | Translation Parameter |
| s | Second |
| m | Meter |
References
- Shang, X.; Han, L.; Qi, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Passive seismic full waveform inversion based on random interferometry reconstruction. Prog. Geophys. 2021, 36, 2557–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xue, S.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, Y. Progress in data acquisition and processing technology of portable node seismographs. Prog. Geophys. 2021, 36, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tian, X.; Guo, L.; Yan, J.; Lyu, Q. High-Resolution Crustal Velocity Imaging Using Ambient Noise Recordings from a High-Density Seismic Array: An Example from the Shangrao Section of the Xinjiang Basin, China. Earthq. Sci. 2018, 31, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landar, S.; Velychkovych, A.; Ropyak, L.; Andrusyak, A. A Method for Applying the Use of a Smart 4 Controller for the Assessment of Drill String Bottom-Part Vibrations and Shock Loads. Vibration 2024, 7, 802–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claerbout, J.F. Synthesis of a Layered Medium from Its Acoustic Transmission Response. Geophysics 1968, 33, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickett, J.; Claerbout, J. Acoustic Daylight Imaging via Spectral Factorization; Helioseismology and Reservoir Monitoring. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 957–960. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, G.T. Theory of Daylight/Interferometric Imaging: Tutorial. In Seismic Interferometry: History and Present Status; Wapenaar, K., Draganov, D., Robertsson, J.O.A., Pelissier, M.A., Eds.; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2008; Volume 26, pp. 77–81. ISBN 978-1-56080-150-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wapenaar, K.; Fokkema, J. Green’s Function Representations for Seismic Interferometry. Geophysics 2006, 71, SI33–SI46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wapenaar, K.; van der Neut, J.; Ruigrok, E. Passive Seismic Interferometry by Multidimensional Deconvolution. Geophysics 2008, 73, A51–A56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakata, N.; Snieder, R.; Tsuji, T.; Larner, K.; Matsuoka, T. Shear Wave Imaging from Traffic Noise Using Seismic Interferometry by Cross-Coherence. Geophysics 2012, 76, SA97–SA106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.A.; Draganov, D.; van der Neut, J.; Drijkoningen, G.; Wapenaar, K. Retrieval of Reflections from Ambient Noise Using Illumination Diagnosis. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiana-Merino, J.J.; Rosa-Herranz, J.; Giner, J.; Molina, S.; Botella, F. De-Noising of Short-Period Seismograms by Wavelet Packet Transform. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2003, 93, 2554–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, S.; Craven, J.A.; Bellefleur, G. Feasibility of Virtual Source Reflection Seismology Using Interferometry for Mineral Exploration: A Test Study in the Lalor Lake Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Mining Area, Manitoba, Canada. Geophys. Prospect. 2015, 63, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.M.; Chen, M.C.; Liu, Z.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Xu, Z.W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.G. Review of progress in passive seismic reflection exploration. Rev. Geophys. Planet. Phys. 2023, 54, 150–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y. A Method for Dynamic Characteristics Estimation of Subsurface Using Microtremor on the Ground Surface. Q. Rep. RTRI 1989, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Cheng, F.; Xu, Z.; Shen, C.; Liu, R. Advantages of Multi-Channel Analysis of Passive Surface Waves (MAPS). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Geophysics, Al Ain, United Arab Emirates, 9–12 October 2017; SEG Global Meeting Abstracts. Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, G.; Chen, X. Frequency-Bessel Transform Method for Effective Imaging of Higher-Mode Rayleigh Dispersion Curves From Ambient Seismic Noise Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 3708–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, J.; Pang, J.; Zhou, C.; Mi, B. Deep Learning Inversion of Rayleigh-Wave Dispersion Curves with Geological Constraints for near-Surface Investigations. Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 231, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B.; Xia, J.; Xu, Y.; You, B.; Chen, Y. Retrieval of Surface Waves from High-Speed-Train-Induced Vibrations Using Seismic Interferometry. Geophysics 2023, 88, KS113–KS126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tran, K.T.; Cox, B.R.; Vantassel, J.P. Geotechnical Site Characterization with 3D Ambient Noise Tomography. Geophysics 2023, 88, KS101–KS112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakulin, A.; Golikov, P.; Erickson, K.; Silvestrov, I.; Kim, Y.S.; Smith, R.; Al-Ali, M. Seismic Imaging of Vertical Array Data Acquired Using Smart DAS Uphole Acquisition System. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018; SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 4050–4054. [Google Scholar]
- Velychkovych, A.; Mykhailiuk, V.; Andrusyak, A. Numerical Model for Studying the Properties of a New Friction Damper Developed Based on the Shell with a Helical Cut. Appl. Mech. 2025, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, S.; White, D.J.; Draganov, D.; Bellefleur, G.; Craven, J.A.; Roberts, B. Passive Seismic Reflection Interferometry: A Case Study from the Aquistore CO2 Storage Site, Saskatchewan, Canada. Geophysics 2017, 82, B79–B93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G. Enhancing Body Waves in Passive Seismic Reflection Exploration: A Case Study in Inner Mongolia, China. Interpretation 2022, 10, B13–B24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-Y.; Lu, Z.-W.; Fu, W.; Hou, H.-S. A Seismic Ambient Noise Data Classification Method Based on Waveform and Frequency-Wavenumber Analysis: Application to Reliable Geological Interpretation Adjacent to Well Songke-2, Northeast China. Geophysics 2024, 89, Q1–Q12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; van der Baan, M. Empirical Mode Decomposition for Seismic Time-Frequency Analysis. Geophysics 2013, 78, O9–O19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Huo Liu, Q. Wavelet Transform with Generalized Beta Wavelets for Seismic Time-Frequency Analysis. Geophysics 2017, 82, O47–O56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Langston, C.A. Automatic Noise-Removal/Signal-Removal Based on General Cross-Validation Thresholding in Synchrosqueezed Domain and Its Application on Earthquake Data. Geophysics 2017, 82, V211–V227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I.; Lu, J.; Wu, H.-T. Synchrosqueezed Wavelet Transforms: An Empirical Mode Decomposition-like Tool. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2011, 30, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liang, M. Time–Frequency Signal Analysis for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis Using a Generalized Synchrosqueezing Transform. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 26, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, G.; Brevdo, E.; Fučkar, N.S.; Wu, H.-T. The Synchrosqueezing Algorithm for Time-Varying Spectral Analysis: Robustness Properties and New Paleoclimate Applications. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Lv, Q. High-Resolution Characterization of Geologic Structures Using the Synchrosqueezing Transform. Interpretation 2017, 5, T75–T85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Man, W. Reservoir Prediction Based on Synchrosqueezed Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the International Geophysical Conference, Qingdao, China, 17–20 April 2017; SEG Global Meeting Abstracts. Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA; Chinese Petroleum Society: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 256–259. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Langston, C.A.; Horton, S.P. Automatic Microseismic Denoising and Onset Detection Using the Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform. Geophysics 2016, 81, V341–V355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngui, W.K.; Leong, M.S.; Hee, L.M.; Abdelrhman, A.M. Wavelet Analysis: Mother Wavelet Selection Methods. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 393, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitmar, A. Plancherel Theorem. In A First Course in Harmonic Analysis; Deitmar, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 89–104. ISBN 978-1-4757-3834-6. [Google Scholar]
- Averbuch, G.; Assink, J.D.; Smets, P.S.M.; Evers, L.G. Extracting Low Signal-to-Noise Ratio Events with the Hough Transform from Sparse Array Data. Geophysics 2018, 83, WC43–WC51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, G.; Brenguier, F.; Campillo, M.; Lynch, R.; Roux, P. Body-Wave Reconstruction from Ambient Seismic Noise Correlations in an Underground Mine. Geophysics 2015, 80, KS11–KS25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. The W Transform. Geophysics 2021, 86, V31–V39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Ideal Spatial Adaptation by Wavelet Shrinkage. Biometrika 1994, 81, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Nozaki, T. Application of Wavelet Cross-Correlation Analysis to a Plane Turbulent Jet. JSME Int. J. Ser. B 1997, 40, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorbecke, J.W.; Draganov, D. Finite-Difference Modeling Experiments for Seismic Interferometry. Geophysics 2011, 76, H1–H18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panea, I.; Draganov, D.; Almagro Vidal, C.; Mocanu, V. Retrieval of Reflections from Ambient Noise Recorded in the Mizil Area, Romania. Geophysics 2014, 79, Q31–Q42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, M.B.; Anas, M.; Rizvi, Z.H.; Ali, A.H.; Zain, M.; Cascante, G.; Wuttke, F. Enhancement of In-Plane Seismic Full Waveform Inversion with CPU and GPU Parallelization. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, M.; Karavelić, E.; Ibrahimbegovic, A.; Miščević, P. Lattice Element Models and Their Peculiarities. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2018, 25, 753–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, Z.H.; Mustafa, S.H.; Sattari, A.S.; Ahmad, S.; Furtner, P.; Wuttke, F. Dynamic Lattice Element Modelling of Cemented Geomaterials. In Advances in Computer Methods and Geomechanics; Prashant, A., Sachan, A., Desai, C.S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolic, M.; Ibrahimbegovic, A.; Miscevic, P. Discrete Element Model for the Analysis of Fluid-Saturated Fractured Poro-Plastic Medium Based on Sharp Crack Representation with Embedded Strong Discontinuities. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 298, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Z.; Gong, X. Separation of Body and Surface Wave Background Noise and Passive Seismic Interferometry Based on Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073917
Li X, Zhang F, Xu Z, Gong X. Separation of Body and Surface Wave Background Noise and Passive Seismic Interferometry Based on Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073917
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaolong, Fengjiao Zhang, Zhuo Xu, and Xiangbo Gong. 2025. "Separation of Body and Surface Wave Background Noise and Passive Seismic Interferometry Based on Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073917
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, F., Xu, Z., & Gong, X. (2025). Separation of Body and Surface Wave Background Noise and Passive Seismic Interferometry Based on Synchrosqueezed Continuous Wavelet Transform. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073917







