Abstract
Aeolian sand serves as the principal foundation material for construction in desert regions, yet its stabilization predominantly relies on cement, presenting critical carbon emission challenges. This study developed a cementitious material utilizing complementary industrial solid wastes (ISWs)—steel slag (SS), ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS), phosphorus slag (PS), and carbide slag (CS)—based on clinker three chemical moduli (TCM) and simplex lattice design, aiming to replace cement for aeolian sand stabilization. ISW dosage effects on stabilized sand strength and mechanical properties were investigated, with stabilization mechanisms studied via phase and microstructural analysis. Results demonstrated that GGBFS exerted the most significant positive influence on the strength of stabilized sand. The optimal proportion was determined as SS:GGBFS:PS:CS = 5:35:20:40, achieving strength comparable to cement-stabilized aeolian sand in the literature. The elastic modulus and ductility of stabilized sand exhibited linear positive and exponential negative correlation with uniaxial compressive strength. The hydration products of ISWs, including C(-A)-S-H gel and ettringite similar to clinker, effectively enhanced interparticle bonding strength and pore-filling capacity. ISW proportions governed the composition and distribution of hydration products, thereby modulating microstructural density and strength, ultimately dictating macroscopic performance variations. The conclusions provide an environmentally friendly solution for aeolian sand stabilization in desert regions.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the intensification of desertification due to global climate change coupled with the increasing level of urbanization has necessitated the construction of numerous buildings on aeolian sand foundations [1,2,3,4,5]. In regions with extensive desert areas such as Northwest China, the Middle East and North Africa, the majority of new construction projects must address the geotechnical challenges posed by aeolian sand foundations [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. However, aeolian sand is a special type of material characterized by excessive fluidity (angle of repose < 28°), negligible cohesion (<1 kPa in natural state), and a loose granular structure (void ratio > 0.65) [14,15,16,17,18]. These properties result in critically low bearing capacities and pronounced susceptibility to differential settlement under load, which significantly increase the difficulty of foundation construction and severely restrict engineering development in desert regions [19,20,21,22].
The traditional method for aeolian sand foundation treatment involves complete excavation and replacement with imported clay or crushed stone [23,24,25]. Unfortunately, although it can significantly enhance the bearing capacity of the foundation, the scarcity of replacement materials and the limited transportation conditions in remote deserts render this method costly [26]. By contrast, the in situ improvement of aeolian sand using cementitious materials to enhance its bearing capacity represents a more economical treatment method. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), as the most widely used inorganic cementitious material globally, has been a common curing stabilizer in past research and applications of aeolian sand stabilization. Previous studies demonstrate that the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and shear strength of cement-stabilized aeolian sand exhibit positive correlations with cement content and curing age [20,27,28,29]. At an optimal water–cement ratio with 8–10% cement dosage, the 28-day UCS of stabilized aeolian sand exceeds 1.5 MPa [30], accompanied by a cohesive strength surpassing 90 kPa [26]. However, the decarbonization of limestone during OPC clinker production, coupled with fossil fuel combustion in kilns, results in substantial carbon emissions, which renders the application of OPC in the stabilization of aeolian sand increasingly incompatible with the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals.
Utilization of industrial solid wastes (ISWs) to develop cementitious materials as alternatives to OPC has been recognized as an environmentally sustainable soil stabilization strategy that effectively enhances soil bearing capacity while mitigating the challenges of ISW stockpiling, therefore garnering significant attention [31]. Similar to the OPC clinker, ISWs containing reactive calcium silicates (C2S/C3S) and calcium aluminates (C3A) generate calcium (aluminate) silicate hydrate [C-(A)-S-H] gels under alkaline conditions, strengthening interparticle bonding to achieve stabilization performance comparable to or superior to OPC [32,33,34,35]. Current research has extensively investigated partial OPC replacement with fly ash (FA) [36,37,38,39] and ground granulated blast-furnace slag [40,41,42,43], accompanied by the progressive establishment of relevant standards. On the other hand, studies exploring the use of solid wastes such as steel slag [44,45,46], red mud (RM) [47,48,49], and desulfurized gypsum (DG) [50,51,52] to develop fully industrial solid waste-based cementitious materials (ISW-CMs) as complete replacements for OPC have also been reported. It is noteworthy that the oxide content and reactivity vary significantly among different ISWs, making it crucial to determine their proportions according to specific principles in order to optimize the strength and workability of ISW-CMs. However, current studies predominantly rely on empirical data and trial-and-error experiments, resulting in inefficiency and inconsistent performance.
In the production of the OPC clinker, to obtain the desired oxide proportions and subsequently achieve the targeted clinker properties, the admixture ratio of raw materials is adjusted through the use of the three chemical moduli (TCM), which encompass the silicon modulus (SM), iron modulus (IM), and lime saturation coefficient (KH) [53]. Nowadays, TCM have been extensively utilized in the quality control of the OPC clinker and also provide a design framework for the proportioning of raw materials in ISW-CMs. Studies have shown that the soft soil stabilized using ISW-CMs developed with TCM achieve comparable or even higher strength than that stabilized with OPC [53,54]. In addition, mixture experimental design based on the simplex lattice/centroid method is another approach to determine proportion, with advantages including a reduced number of experimental points, high prediction accuracy, and the ability to swiftly identify optimal proportion. This approach involves strategically designing a few experiments with varying proportions in a simplex of two or more dimensions to obtain a regression equation between the response values and raw material percentages. Consequently, the optimal proportion can be determined, and further investigation into the inherent relationship between proportions and response values can be conducted. Currently, studies employing this method to develop ISW-CMs that simultaneously meet multiple property requirements have been reported [55,56].
Despite numerous practical applications of ISW-CMs as an alternative to OPC for soil stabilization, the current literature primarily focuses on the stabilizing of clays with certain bearing capacity in their natural state. Research on aeolian sand, which exhibits inferior engineering properties and necessitates higher solidification demands, remains limited. Furthermore, trial-and-error-based development approaches for ISW-CMs frequently exhibit inefficiency and theoretical deficiencies, often yielding materials that fail to concurrently satisfy strength and workability requirements, thereby imposing significant barriers to their widespread implementation.
This study prepared a fully ISW-based cementitious material for stabilizing aeolian sand in desert regions using four complementary industrial solid wastes—blast-furnace slag (GGBFS), steel slag (SS), phosphorous slag (PS), and carbide slag (CS)—as raw materials. The TCM theory of the cement clinker and the simplex lattice design were used to systematically investigate the influence of ISW dosages on the UCS of stabilized aeolian sand and determine the optimal proportion of ISWs. Phase and microstructural analyses were employed to investigate the content of hydration products and their cementitious effects on particle bonding in aeolian sand stabilized with varying proportions of the cementitious materials. The findings provide novel insights and references for the development of ISW-based cementitious material for aeolian sand stabilization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The aeolian sand utilized in this study was sourced from the Taklamakan Desert in Xinjiang, China. Sand samples were excavated from a depth of 1.5 m below the surface, immediately packed in sealed bags, and transported to the laboratory. Natural moisture content, bulk density, and porosity were measured in the laboratory, with these parameters detailed in our previously published work [30]. Figure 1a illustrates the natural morphology and microstructural characteristics of the untreated aeolian sand particles. Observations reveal that the aeolian sand particles exhibited angular to sub-rounded shapes with smooth surfaces and minimal fines content, indicating limited interparticle cohesion and weak natural cementation. Results of laser particle size analysis (LPSA, as shown in Figure 2) indicate that the limiting particle size d60 of aeolian sand was 345 μm, with uniformity coefficient Cu of 2.62 and curvature coefficient Cc of 0.88.
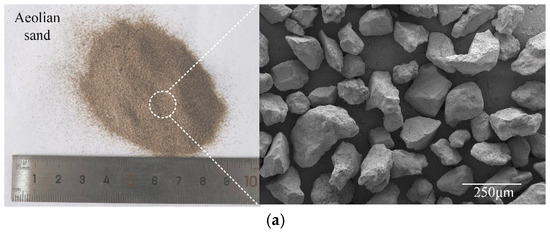

Figure 1.
Materials used in this study: (a) macro/microscopic morphologies of aeolian sand; (b) ISWs.
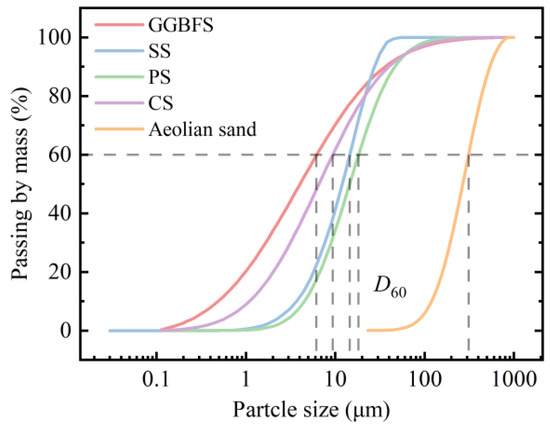
Figure 2.
Particle size distribution of materials.
GGBFS employed in this study was provided by a mineral powder plant in Hebei, China. As shown in Figure 1b, the GGBFS appears as a pale powder with a specific surface area of approximately 0.43 m2/g, produced by crushing and grinding waste slag generated during blast-furnace iron smelting. The d60, Cu, and Cc of GGBFS were measured as 6.31 μm, 12.6, and 1.0, respectively. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy results (Table 1) reveal that the primary oxides in GGBFS are SiO2 and CaO (30% and 40%, respectively), along with minor Al2O3 (14%) and MgO (8%). These oxides predominantly exist as amorphous glassy phases with weak intermolecular bonding due to the rapid cooling rate during discharge, thereby endowing the material with high pozzolanic reactivity.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of materials.
SS and PS are two additional ISWs employed to provide reactants for pozzolanic reactions. Coarse SS and coarse PS were collected from a steel plant and a phosphate chemical plant in Henan, China, respectively. In the laboratory, the coarse slags were milled into black and white powder, respectively, via high-energy ball milling and fully passed through a 150-mesh sieve (aperture size: 106 μm). The elevated temperature generated during this process evaporated residual moisture in the raw materials. The d60, Cᵤ, and Cc of SS were 15.1 μm, 4.08, and 1.0, respectively, while those of PS were 17.9 μm, 3.9, and 1.13, respectively. XRF results revealed that SS contains 30% CaO and 30% Fe2O3, along with 17% SiO2, while PS is composed of 40% SiO2 and 40% CaO, with minor contributions from other oxides. These compositions enabled precise modulation of the oxide ratios within the binder system.
CS was a by-product generated during acetylene production via calcium carbide hydrolysis. The employed CS in this study was collected from an acetylene chemical plant in Hebei, China, presented as white powder. Results of LPSA indicated that d60, Cu and Cc of CS were 10.0 μm, 9.1, and 0.87, respectively. Chemical composition analysis identified it as comprising 70% CaO with trace impurities of silicon- and iron-phase compounds. In the binder system, CS primarily functions as a CaO supplement to enhance alkalinity due to its high CaO content.
2.2. Specimen Design
The proportioning design of ISWs in stabilized aeolian sand specimens was programmed according to the following steps: (a) determination of a basic dosage based on TCM of OPC; (b) establishment of the ISW dosage range using the basal dosage as a reference point; and (c) configuration of experimental points by defining the dosage range’s supper and lower limits within the simplex lattice design framework.
The reference OPC, compliant with Chinese Portland cement standards [57] and supplied by China United Cement Corporation, was used to determine the basic proportion of ISWs through TCM methodology. Based on the oxide composition of the clinker (SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, and CaO as listed in Table 1), its TCM were calculated using Equations (1)–(3), yielding values of SM = 2.29, IM = 1.47, and KH = 0.91. By integrating the oxide compositions of ISWs, a quaternary linear equation system (Equation (4)) was formulated. In Equation (4), rows of the coefficient matrix represent oxide contents within ISWs, while columns correspond to distinct oxide components. The right-hand vector denotes the required oxide quantities to achieve TCM equivalence with the reference OPC. As a result, the basic proportion of ISWs was determined as SS:GGBFS:PS:CS = 10.0:18.1:26.8:57.1.
where mi stand for dosages of ISWs i.
The experimental determination of cementitious material for aeolian sand stabilization constitutes a typical mixture design with specific constraints requiring the summation of all component dosages to equal 100%. The simplex lattice method (SLM) serves as a conventional framework for such experimental configurations. Given that the binder developed in this study comprises four types of ISWs, the experimental points were distributed within a regular tetrahedron, as illustrated in Figure 3, where each axis represents a distinct ISW component and each vertex corresponds to a specific proportion. The lattice degree of SLM was specified as three, establishing three compositional levels for each ISW, and the design was augmented with axial points and centroid point. A total of 26 test specimens were designed, comprising 25 SLM-designed proportions and one basic proportion. Additionally, the binder content was set at 11% of the aeolian sand mass, while water content was set at 9%, which has the maximum stabilization aeolian sand strength according to previous study [30]. The proportion of experiment points is listed in Table 2. Additionally, to compare the effectiveness of ISW-CMs and cement in stabilizing aeolian sand, a control group utilizing cement with an equivalent dosage was established.
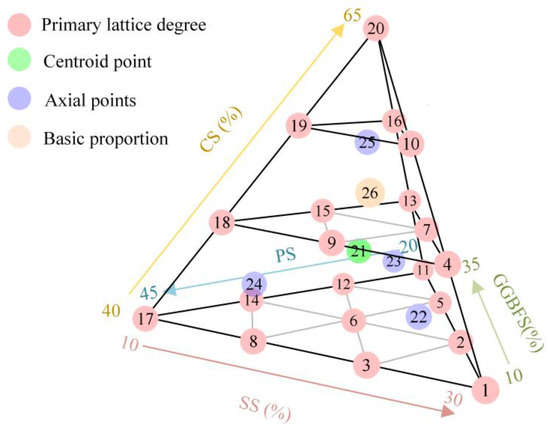
Figure 3.
Distribution of experiment points.

Table 2.
Proportion of ISWs in design experiment points.
2.3. Specimen Preparation
The specimens of stabilized aeolian sand were prepared in accordance with American standards [58]. ISWs and aeolian sand were oven-dried at 105 °C for 6 h to eliminate absorbed moisture, followed by precise weighing according to the designed proportion. The blended ISWs were initially homogenized using a planetary mixer, until uniform coloration was achieved. Subsequently, the aeolian sand was incrementally introduced into the mixture until visual homogeneity was re-established. Distilled water was then added in a controlled stream, followed by high-speed mixing for an additional 5 min.
The homogenized mixture was transferred via funnel into stainless-steel cylindrical molds (50 mm in diameter × 100 mm height) and compacted in three successive layers. Each layer underwent 15 compactive blows using a stainless-steel tamper, applied radially from the periphery inward, with interlayer surface scarification to enhance bonding. Then, the top surfaces were immediately sealed with laboratory-grade polyethylene sealing film to prevent moisture dissipation. After 3 days of in-mold curing, the specimens were demolded and transferred to a humidity-controlled curing chamber maintained at 23 °C for continued curing over 25 days, achieving a total curing time of 28 days. Three parallel samples were prepared for each experiment points.
2.4. UCS Test
UCS of stabilized aeolian sand specimens was evaluated using an electronically universal compression testing machine. This apparatus employs a hydraulic jack-driven link rod to vertically displace specimens against pressure sensor (10 kN capacity, ±0.001 kN accuracy). A displacement sensor integrated with the link rod recorded real-time specimen deformation. The load was applied under displacement control, commencing at 0.1 mm/min until the sensor registered 0.5 kN, confirming proper specimen–sensor contact. The loading rate was then reduced to 0.08 mm/min for the formal test phase. Specimen failure was defined as a post-peak force reduction exceeding 30% of the maximum recorded load, at which point testing was terminated. Failed specimens were subsequently milled, oven-dried, and stored in sealed bags for subsequent analysis.
2.5. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was employed to analyze the phase composition of solidified aeolian sand, utilizing a D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer (Bruker, Hongkong) with Cu Kα radiation generated at 60 kV and 80 mA. The scanning range was set from 15° to 80°, with a step size of 0.02°/step and a scanning speed of 30 steps/s.
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope
The microstructure of stabilized eolian sand was observed using an SU8220 field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, HITACHI High-tech Co., Tokyo, Japan) with the voltage set at 5 kV. Due to the poor electrical conductivity of both eolian sand and ISWs (immobilized sand–water mixtures, presumably), gold sputtering was performed on the sample surfaces for 2 min with a current of 10 mA using an ion sputter coater prior to observation. Additionally, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) mapping was employed to determine the elemental composition of the observed materials.
2.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Differential Scanning Calorimetry
The hydrated products and thermal stability of stabilized aeolian sand samples were analyzed using Thermogravimetric Analysis/Differential Scanning Calorimetry (TG/DSC) with an SDT Q600 synchronous thermal analyzer (TA Instruments Inc., New Castle, DE, USA). A 10 mg powder sample was first stabilized at room temperature for 30 min and then heated to 800 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min under a nitrogen atmosphere. During the heating process, the curves of sample weight and heat flow as a function of temperature were recorded.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Stress–Strain Response
Figure 4a–e present the stress (σ)–strain (ε) curves for all specimens, and Figure 4f demonstrates a typical characteristic of the σ–ε curve. It can be observed that, at the initial stage of loading, the curves undergo a relatively short phase with increasing slope, reflecting the gradual enhancement of the specimen resistance to deformation due to being progressively compressed and densified. The slope of the curves gradually stabilizes as the load increases, representing the elastic phase of the specimens. Subsequently, the curves become nonlinear again and reach a peak. Finally, the curves begin to decline, indicating that the specimens have lost their load-bearing capacity, which is accompanied by the appearance of obvious shear cracks on specimens. Based on these characteristics, the UCS of the specimens was determined as the stress corresponding to the peak of the curve; the elastic modulus E was calculated as the ratio of the change in stress (Δσ) to the change in strain (Δε) during the stable slope phase; and the ductility DI was taken as the ratio of the strain at failure (εf) to the peak strain (εu). The UCS, E, and DI of test specimens are summarized in Table 3.
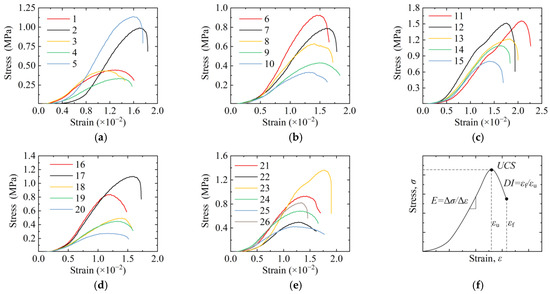
Figure 4.
Stress–strain curves of test specimens: (a) 1–5, (b) 6–10, (c) 11–15, (d) 16–20, (e) 21–26, and (f) typical characteristic of σ–ε curve.

Table 3.
UCS, E and DI of test specimens.
3.2. Effect of Proportion of ISWs on UCS and the Optimal Proportion
The ternary plot in Figure 5 illustrates the variation in the UCS of stabilized aeolian sand with the proportions of ISWs, where the name of ISWs represents their dosages. Since four types of ISWs were utilized as raw materials in this study and a single ternary plot can only accommodate three variables, to depict their synergistic effects and mutual influences, each ternary plot fixes one variable at a specific level. Subsequently, the changes in UCS with respect to the other three variables are investigated for different levels of the fixed variable.
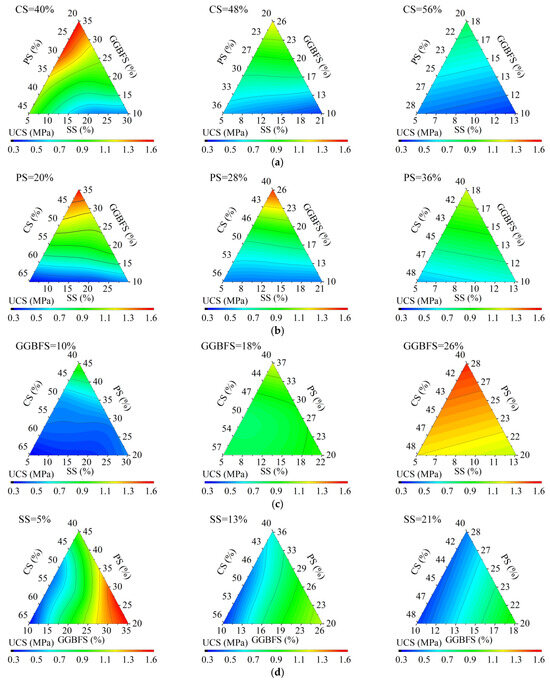
Figure 5.
Effect of proportion of ISWs on UCS of stabilized aeolian sand, where fixed factor is (a) CS, (b) PS, (c) GGBFS, and (d) SS.
The fixed factor of Figure 5a is CS. It can be observed that, regardless of the CS dosages, the UCS of stabilized aeolian sand increases with the increment in the GGBFS dosage but decreases with the increase in PS and SS dosages. When the CS dosage is 40%, the UCS of stabilized aeolian sand reaches its maximum value at a PS dosage below 30% and GGBFS dosage above 32%, while the SS dosage above 17% leads to a significant decrease in UCS. When the CS content is increased to 48.3% and 56.7%, the changes in UCS become more pronounced, and the contour lines gradually become perpendicular to the GGBFS axis, indicating that the influence of the GGBFS dosage on UCS is most significant at these levels. The main chemical component of CS is CaO, and changes in its dosage can alter the alkalinity of the system. The increase in alkalinity caused by an increase in CS dosage may be the reason why the influence of GGBFS becomes more significant.
In Figure 5b, with PS serving as the fixed factor, the variation trend of UCS of stabilized aeolian sand is similar to that observed when the dosage of is fixed. However, it exhibits a slight increase with the elevation of SS dosage. This trend becomes more pronounced when the PS dosage reaches 21.6%. This can be explained by the fact that a higher PS dosage limits the incorporation of GGBFS with the highest reactivity. At this point, increasing the SS dosage can, to a certain extent, supplement the reactants for the pozzolanic reaction. Nevertheless, due to the inherently low reactivity of SS, it fails to elicit particularly significant changes in strength. Meanwhile, an increase in CS leads to a notable decrease in UCS, indicating that excessively high alkalinity is detrimental to the strength of stabilized aeolian sand.
The fixed factor of Figure 5c is GGBFS. It can be indicated that the UCS of stabilized aeolian sand increases with the elevation of PS dosage. Notably, when the GGBFS dosage reaches 18%, a CS content higher than 47% (with SS dosage less than 12% and PS dosage less than 30%) results in a rapid decline in UCS. This is attributed to the fact that both PS and GGBFS, which serve as reactants for the pozzolanic reaction, are present at relatively low levels at this point, and CaO constitutes the majority of CS, with its hydration product almost exclusively Ca(OH)2, which leads to an excessively high alkalinity in the system and a relative scarcity of hydration products with a gelling effect.
SS serves as the fixed factor in Figure 5d. It can be observed that, regardless of the level of SS, the influence pattern of the proportion of the other three ISWs on the strength of stabilized aeolian sand remains consistent. Specifically, the UCS increases with the increase in GGBFS dosage but decreases with the increase in PS and CS dosages. This is because the primary role of SS in the system is to provide Fe2O3, which is one of the precursors of C4AF and mainly affects the working properties of the cementitious material rather than its strength.
The analysis above elucidates a prevailing pattern in experiment results: the incremental dosage of GGBFS substantially enhances the strength of stabilized aeolian sand. This phenomenon primarily stems from GGBFS’s superior pozzolanic reactivity compared to other investigated ISWs, attributable to its vitreous microstructure containing reactive compounds that readily participate in hydration processes. PS demonstrates comparatively lower reactivity, while SS exhibits the least reactive characteristics. These observations suggest that the exclusive utilization of GGBFS could theoretically yield cementitious materials with maximum compressive strength. However, practical engineering considerations regarding the workability of cementitious composites and long-term stability of stabilized aeolian sand necessitate maintaining oxide proportions within reasonable ranges. Therefore, through dual optimization employing TCM theory and SLM, the optimal proportion of ISWs used to stabilize aeolian sand was determined as 5:35:20:40, which corresponds to the specimen exhibiting the highest UCS in SLM experiments. Furthermore, comparative analysis with the cement-stabilized aeolian sand control group (CE) revealed that the UCS of aeolian sand that stabilized ISW-CMs with the basic proportion was 45% lower than that of CE, whereas the ISW-CMs with optimal proportion stabilized specimen exhibited a 3% strength enhancement over CE. This demonstrates the following: (a) the proportion determined by the dual optimization strategy incorporating TCM and the SLM was superior than that determined solely by TCM; (b) synergistically prepared ISW-CMs achieve comparable effectiveness to cement in aeolian sand stabilization.
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Stabilized Aeolian Sand
The elastic modulus E and ductility coefficient DI, derived from stress–strain curves, were employed to quantify the specimen’s deformation resistance during the elastic phase and post-failure ductility. Figure 6 illustrates the variations in E and DI with UCS for specimens in SLM experiments. The results reveal a positive correlation between the strength of stabilized aeolian sand and its elastic modulus. Specimens with higher UCS values exhibited a rapid increase in deformation resistance following the compaction phase, typically accompanied by pronounced shear-induced cracks at failure. This enhancement is attributable to two synergistic mechanisms: (1) the abundance of cementitious compounds reinforcing interparticle bonds and (2) the presence of high-hardness crystalline phases (e.g., ettringite), which fill intergranular voids and inhibit particle displacement. These microstructural features collectively improve the cohesion and friction angle along shear planes.
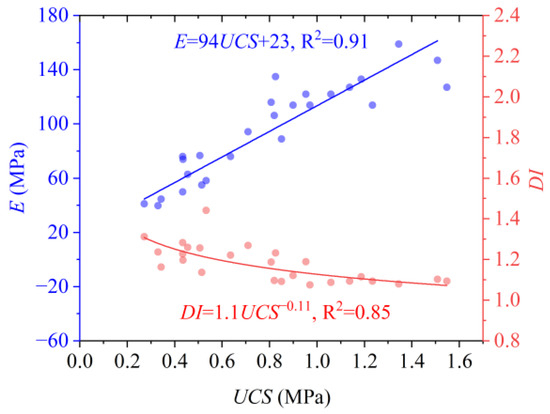
Figure 6.
Variations in E and DI with UCS for specimens.
Conversely, ductility inversely correlated with strength. Specimens with lower UCS displayed broader stress–strain curve peaks, characterized predominantly by axial splitting fractures parallel to the specimen axis. This behavior arises from two factors: (1) reduced cumulative strain energy under lower loads, resulting in gradual post-peak stress dissipation and (2) diminished hydration products, leading to weaker particle bonding and more micropores (a critical contributor to splitting failure modes). After specimen failure, the partial closure of these micropores generates residual strength, thereby decelerating the descending phase of stress–strain curves.
The quantitative relationships between UCS and the mechanical parameters can be mathematically expressed by linear and exponential functions, respectively, as shown in Figure 6.
3.4. Phase Composition and Microstructure
Figure 7 presents the XRD patterns of selected specimens from the SLM experiments along with their corresponding UCS values and ISW proportions (SS:GGBFS:PS:CS). Significant variations in phase composition were observed among specimens with different ISW proportions. The characteristic diffraction peak around 2θ = 29.5°, attributed to C(-A)-S-H gel formation, is recognized as the primary contributor to the strength development of aeolian sand consolidation. Specimens NO. 4 and NO. 8 with low UCS demonstrated attenuated C(-A)-S-H gel diffraction intensities. In contrast, specimens NO. 12 and NO. 11 with higher mechanical performance displayed enhanced peak intensities at this position, with specimen NO. 11 manifesting an additional characteristic peak, which indicates the increased gel formation—a phenomenon consistent with its elevated GGBFS content.
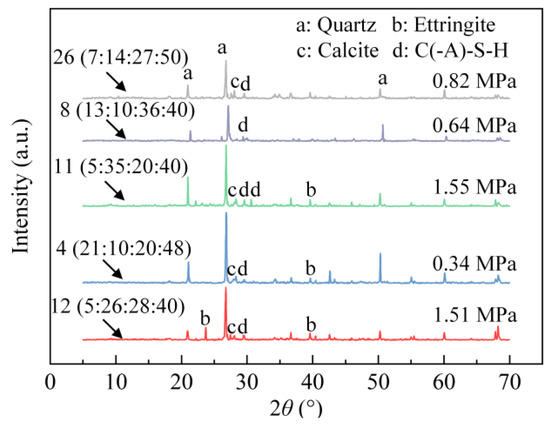
Figure 7.
XRD patterns of specimens in SLM experiment.
Ettringite diffraction peaks at 2θ = 40° were detected in all specimens except specimen NO. 8, with specimen NO. 12 exhibiting supplementary ettringite-related peaks. This absence in specimen NO. 8 may be attributed to its higher SS content and reduced CS proportion, resulting in excessive Fe-phase oxides and diminished alkalinity within the system. These conditions potentially inhibited the synthesis of ettringite through the reaction pathway described in Equation (5):
Additionally, characteristic peaks of calcite (CaCO3) were identified, with their formation attributed to the carbonation of Ca(OH)2 during the curing process. Similar to ettringite, calcite contributes to strength enhancement by filling the pores between particles and increasing the density of stabilized aeolian sand. The highest calcite peak intensities were observed in Specimens NO. 4, 11, and 26, while its diminished presence in Specimen NO. 8 correlates with the absence of CS. However, despite their pronounced calcite content, Specimens NO. 4 and 26 exhibited suboptimal mechanical performance. This phenomenon may stem from the formation of weaker particle connections by the limited amount of C(-A)-S-H gel, which could be disrupted by the volumetric expansion caused by excessive calcite crystal generation.
Figure 8 displays the TG and DSC curves of selected specimens in the SLM experiment. The TG curve quantifies mass loss during heating, enabling the clear comparison of hydrated phase contents across specimens due to distinct decomposition temperatures of different hydration products. Concurrently, the DSC curve monitors the heat flux differential between the sample and reference, providing insights into endothermic and exothermic events within the material. The combined analysis of TG-DSC data enhances the characterization of ISW hydration products in stabilized aeolian sand. Three prominent thermal mass loss stages can be observed in Figure 8: (a) 60–120 °C: Attributed to the loss of bound water from hydration products such as C(-A)-S-H gel and ettringite, corresponding to the P1 endothermic peak in the DSC curve; (b) 380–500 °C: Associated with hydroxyl group removal from Ca(OH)2 in the matrix, marked by the P2 endothermic peak; and (c) 600–720 °C: Corresponding to the decomposition of carbonate phases (e.g., calcite). Specimens with lower UCS such as specimens NO. 4 and 8 exhibited reduced mass loss and diminished peak areas in the first stage, indicative of limited gel and ettringite formation. Notably, Specimen NO. 4 demonstrated significantly higher mass loss in the second stage, consistent with its elevated CS content, which also contributed to enhanced thermal decomposition (third-stage mass loss and peak area). Conversely, Specimen NO. 4 displayed minimal third-stage mass loss, likely due to suppressed carbonation during curing, resulting in diminished calcite production.
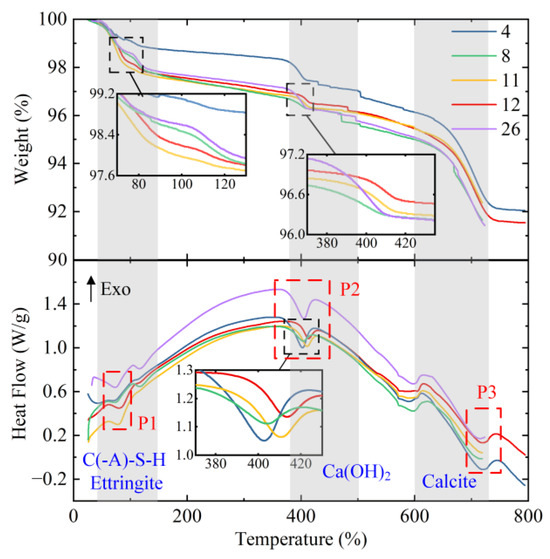
Figure 8.
TG and DSC curve of specimens in SLM experiment.
The TG/DSC results, corroborated by XRD analysis, collectively demonstrate that Specimen No. 11 achieved superior mechanical performance through optimized hydration product, validating its ISW proportion as the most effective composition.
Figure 9 presents the particle morphology of Sample No. 11 observed using SEM. Figure 9a demonstrates a typical characteristic of aeolian sand particles encapsulated by cementitious materials. Through comparative analysis with untreated aeolian sand particles shown in Figure 1, it can be observed that a dense layer of hydration products composed of gel and ettringite thoroughly coats the particle surface. At 500× magnification, neither distinct pores nor the original surface texture of soil particles can be clearly discerned; however, small and shallow pores became discernible upon magnification to 5000×. This observation corresponds to the higher gel production detected in the phase analysis of this specimen, as well as the elevated GGBFS dosage and enhanced UCS observed at macroscopic scale. Figure 9b illustrates the interconnections formed between multiple soil particles through hydration products. As previously discussed, the natural aeolian sand exhibits a loose microstructure with minimal interparticle bonding under untreated conditions, resulting in load-bearing capacity that relies solely on mechanical interlocking. After stabilization using ISW-based cementitious materials, multiple particles encapsulated by gel and other hydration products gradually establish stable connections during compaction and curing processes. The matrix of these connections primarily consists of C(-A)-S-H gel, internally reinforced by crystalline phases including ettringite, Ca(OH)2, and calcite, which collectively provide robust structural support. However, a limited quantity of unhydrated ISW particles can still be detected under high magnification, which may be attributed to the weak hydration activity of specific ISW components. These findings exhibit similarities with previously reported microstructures of cement-stabilized aeolian sand. Nevertheless, compared to the porous interparticle connections observed in cement-treated specimens, the ISW-stabilized aeolian sand demonstrates significantly denser and more compact bonding configurations. This evidence confirms that ISW cementitious materials can establish a more reliable and higher-strength microstructure at the microscopic scale.
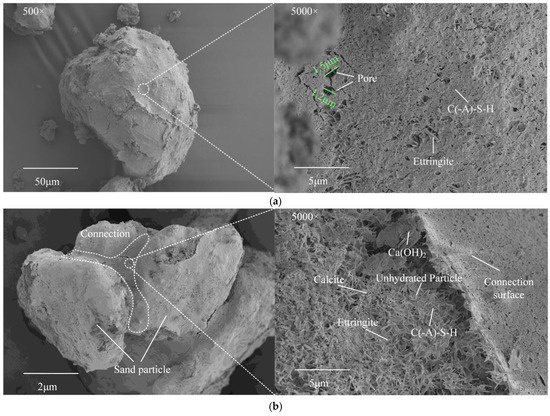
Figure 9.
Particle morphology of Sample No. 11. (a) aeolian sand particles encapsulated by cementitious materials; (b) connection between sand particles.
For comparative analysis, Figure 10 exhibits the microstructural morphologies of lower-strength specimens No. 4, 8, and 26, through which the influence of ISW proportions on the microstructure of stabilized aeolian sand can be systematically elucidated. In Figure 10a, depicting the particle encapsulation status of Specimen No. 4, it is evident that, although hydration products such as gel and ettringite were generated, the particle surfaces were merely covered by an exceedingly thin layer, leaving the significant exposure of sand particle surfaces. Upon further magnification to 10,000×, the C(-A)-S-H gel predominantly exhibited flocculent structures with limited spatial coverage and short filament lengths, cementing sparse ettringite and Ca(OH)2 crystals. Unlike the integrated matrix observed in Specimen No. 13, these hydration products failed to form a continuous network, while unhydrated ISW particles were ubiquitously distributed. Such microstructural configurations resulted in feeble interparticle connections prone to external load-induced damage, ultimately manifesting as substantially reduced bearing capacity at the microscopic scale.
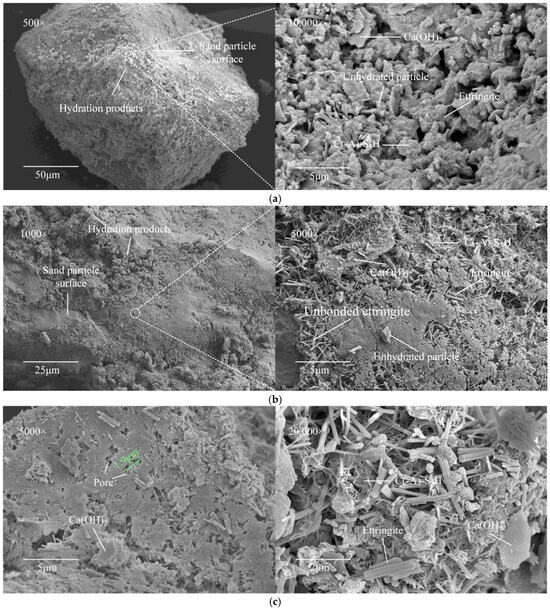
Figure 10.
Particle morphology of sample with low strength: (a) specimen No. 4; (b) specimen No. 8 and (c) specimen No. 26.
Figure 10b illustrates the particle surface morphology of Specimen No. 8. Although the hydration product layer appeared thicker compared to Specimen No. 4, the residual exposure of sand particle surfaces was still detected. At higher magnification, localized interconnected systems of gel–ettringite–calcium hydroxide were partially observable; however, the scarcity of the gel matrix rendered such systems spatially limited, with unbonded ettringite crystals persisting. This trend correlates with the increased hydration reaction products induced by reduced SS and elevated GGBFS and PS dosages, corresponding macroscopically to a marginal increase in UCS. Furthermore, this progressive trend persists in the microstructural morphology of Specimen No. 26 shown in Figure 10c. A substantial interconnected network of hydration products was observed, with minimal independent ettringite or Ca(OH)2 crystals detectable even under high magnification. Nevertheless, excessive CS dosage in this specimen constrained gel production, resulting in comparatively porous and sparse particle encapsulation relative to Specimen No. 11. Trace amounts of unhydrated ISW particles were also identified, collectively contributing to its inferior mechanical performance.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of ISW Interactions and Hydration Phase Quantification
The synergistic interplay between SS, GGBFS, PS, and CS in hydration reactions critically governs the mechanical performance of stabilized aeolian sand. As evidenced by the chemical compositions in Table 1, GGBFS contributes high SiO2 (30.07%) and CaO (38.22%), serving as the primary source of reactive silicates for C-(A)-S-H gel formation. PS, with its elevated SiO2 (44.89%) and CaO (43.97%), complements GGBFS by supplying additional amorphous silica, while CS (70.35% CaO) acts as a pH regulator to sustain alkaline conditions for sustained pozzolanic activity. SS, despite its lower reactivity, introduces Fe2O3 (29.1%), which facilitates the formation of ferrite phases (e.g., C4AF) that enhance microstructural strength.
Quantitative TG/DSC analysis (Figure 8) and XRD results (Figure 7) highlight distinct hydration behaviors across ISW proportions. Specimens with optimal ISW proportions (No. 11) exhibited markedly higher mass loss in the 60–120 °C range compared to suboptimal mixtures (e.g., No. 4), correlating with enhanced C-(A)-S-H and ettringite formation. The stoichiometric synergy between GGBFS-derived silicates and CS-provided Ca2+ ensures balanced C/S ratios in hydration products, maximizing gel polymerization and pore-filling efficiency. Conversely, excessive CS disrupts this equilibrium, promoting Ca(OH)2 precipitation and calcite overgrowth, as observed in SEM micrographs (Figure 10c), which weaken interparticle bonding through crystalline expansion.
4.2. Long-Term Durability and Field Application Prospects
The hyper-arid desert environment imposes multifactorial challenges to the long-term stability of stabilized aeolian sand, including diurnal thermal cycling, UV radiation, and salt-laden winds particularly regarding potential degradation mechanisms induced by salt crystallization (e.g., sulfate-chloride interactions), acid attacks from pH fluctuations in contaminated soils, and ion-exchange reactions with heavy metal pollutants that may alter the pozzolanic reaction kinetics. The chemical compatibility between ISW-derived alkaline components (e.g., free CaO) and acidic contaminants (H⁺/SO42−) could critically influence the stability of hydration products like C-(A)-S-H gels, while chloride infiltration might accelerate matrix deterioration through Friedel’s salt formation-disintegration cycles under thermal stresses. Such physicochemical interactions necessitate the systematic evaluation of long-term phase evolution using accelerated aging protocols simulating multi-factor desert environmental conditions. While the current study focuses on 28-day mechanical properties, the intrinsic characteristics of ISW-CM hydration products suggest potential durability advantages over conventional cement-based systems. The dense C-(A)-S-H gel matrix observed in SEM micrographs (Figure 9a,b) and the absence of large ettringite clusters (compared to OPC systems) may mitigate crack propagation under thermal stresses. Additionally, the high calcite content detected in XRD patterns (Figure 7) could enhance carbonation resistance, though excessive crystallization risks interfacial debonding as evidenced in low-strength specimens (Figure 10c).
In field applications, the workability (e.g., fluidity, setting time), volume stability of the cementitious materials, and their applicability to other specialty soils represent pivotal determinants for large-scale implementation, warranting systematic exploration to validate technological scalability. Additionally, both current and previous studies reveal that cement and ISW-based cementitious materials stabilized aeolian sand typically exhibit limited ductility, posing reliability risks in engineering applications through sudden load-bearing capacity loss upon reaching critical stress thresholds—a phenomenon detrimental to life and property protection under extreme conditions. While geosynthetics (geomembranes, geotextiles) or reinforcement techniques may partially mitigate this issue, enhancing intrinsic ductility through fiber incorporation into stabilized sand matrices presents a promising research direction.
4.3. Limits and Future Perspectives
The primary objective of this study is to develop cementitious materials using four types of ISWs for aeolian sand stabilization. Although the prepared materials achieved compressive strength comparable to cement-stabilized sand reported in the literature, limited research outcomes are available for direct comparison. This scarcity arises from the historical predominance of transportation infrastructure (e.g., roads, railways) in desert construction projects, with existing cement stabilization studies predominantly focusing on subgrade filler performance. Notably, fundamental disparities exist between subgrade and building foundation requirements regarding cement dosage, service environments, and loading patterns, rendering direct strength comparisons between these distinct applications scientifically invalid. Consequently, while preliminary strength comparisons were made between ISW-based materials and cement-stabilized sand, comprehensive evaluations of stabilization efficacy, including compressive, shear, and tensile strengths, should be further investigated.
Among the ISWs employed, GGBFS demonstrated substantial pozzolanic reactivity, accounting for its dominant influence on UCS variations in stabilized sand. A widely accepted paradigm suggests that alkaline activation can enhance the reactivity of most ISWs, with various alkali excitation techniques having been extensively applied in soft soil and sludge stabilization. However, the inherent low moisture content of aeolian sand in desert environments raises critical questions regarding the efficacy of alkali activation for ISW-based stabilization systems, necessitating dedicated investigation.
5. Conclusions
This study developed a quaternary industrial solid waste (ISW)-based cementitious material composed of steel slag (SS), granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS), phosphorus slag (PS), and carbide slag (CS) for the stabilization of aeolian sand in desert regions using a four-factor simplex lattice experiment (SLM) based on the three chemical moduli (TCM) theory referenced standard cement. The optimal proportion of ISWs is determined, and the solidification effects are evaluated in terms of mechanical properties, hydration product levels, and microstructure. The main conclusions obtained are as follows:
- (1)
- The results of the simplex lattice point experiment indicate that an increase in the dosage of GGBFS has a significant positive effect on the UCS of stabilized aeolian sand due to its highest pozzolanic reactivity. Conversely, higher SS incorporation reduced UCS. Considering the workability of the cementitious material in conjunction with the TCM theory, the optimal proportion of ISWs was determined to be 5:35:20:40, and the UCS of aeolian sand stabilized using ISWs with optimal proportion was comparable with that stabilized by OPC.
- (2)
- The UCS of stabilized aeolian sand exhibited a linear positive correlation with its elastic modulus but a negative correlation with ductility. The failure mode of stabilized aeolian sand specimens was related to their strength: specimens with higher strength exhibited pronounced inclined shear cracks upon failure, while specimens with lower strength mostly displayed splitting cracks.
- (3)
- The abundance of hydration products such as C(-A)-S-H gel and ettringite was the primary reason for the high strength of stabilized aeolian sand with the optimal proportion. A higher content of CS can increase the level of Ca(OH)2 in the system, leading to an increase in calcite formed through carbonation. However, an unreasonable proportion results in insufficient gel in the system, causing an incomplete particle encapsulation and weak connections between particles, which can be disrupted by the expansion of crystals such as ettringite and calcite, leading to a porous and loose microstructure and thus reducing the strength of stabilized aeolian sand.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.X., B.Y. and Z.Q.; methodology, Z.X. and Z.Q.; software, Z.Q.; validation, H.W. and Y.Q.; formal analysis, Z.X.; investigation, Z.X., H.W. and Y.Q.; resources, Z.Q.; data curation, B.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.Q. and B.Y.; visualization, Z.X.; supervision, Z.Q. and H.W.; project administration, Y.Q.; funding acquisition, Z.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42372318).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Akin, I.D.; Tirkes, S.; Collins, C.E. Geotechnical insights of mammal burrows in loose desert sand. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Qiao, G.F.; Wang, R. Turning desert sand into building material products: An ambitious attempt of solar 3D printing. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ordoñez, C.; Crespo-Cabillo, I.; Calzada, J.R.; Garcia-Nevado, E.; Coch, H. Reducing residential cooling demand in a sprawling desert city through vertical urban densification. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.G.; Li, X.F. Experiments on the State Boundary Surface of Aeolian Sand for Road Building in the Tengger Desert. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherzad, M.F.; Goossens, D. Wind Tunnel Experiments and Field Observations of Aeolian Sand Encroachment around Vernacular Settlements in the Saharan and Arabian Deserts. Buildings 2022, 12, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammala, P.K.; Kolli, S.; Garaga, R.; Reddy, K.R.; Kumar, P. Aeolian sand dune fixation—Critical review of measures, challenges and future perspectives with a case study on Thar Desert. Catena 2025, 250, 108786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathali, M.; Nasrabad, M.M.K.; Abbasi, H.R.; Amrollahi, A.; Soleymani, M. Aeolian sand challenges in desert rail infrastructures, overview of Iran’s experience and advancement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 136953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.Q.; Liu, W.B.; Jiang, W.J.; Wang, G.Z. Mechanics and road performance of mudstone modified stabilized gravel subgrade in arid desert areas. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Zani, N.; Ghidini, L.; Petrogalli, C.; Yu, L.; Mazzù, A.; Ding, H.; Wang, W. Wear and damage behaviors of wheel-rail with different material matchings under various sand deposition densities of rail top in desert environments. Wear 2025, 560–561, 205622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.J.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.X.; Xie, X.Y.; Mao, X.; Ren, Z.F.; Liu, J.K. Comparison and Optimization of Bearing Capacity of Three Kinds of Photovoltaic Support Piles in Desert Sand and Gravel Areas. Buildings 2024, 14, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, S.X.; Sun, L.Y.; Huang, S.P.; Zhu, H.; Zou, H.H.; Li, G.R. Analysis of significant risk factors for sand accumulation on desert expressways. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 095802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.F. Effect of high temperature on residual splitting strength of desert sand concrete. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 3208–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Dai, P.Z.; Yan, H.M.; Zhou, L. Effect of sand and crosswind on the performance of solar chimney power plant. Energy Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sanad, H.; Ismael, N.; Nayfeh, A. Geotechnical properties of dune sands in Kuwait. Eng. Geol. 1993, 34, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Taie, A.J.; Al-Shakarchi, Y.J.; Mohammed, A.A. Investigation of geotechnical specifications of sand dune soil: A case study around Baiji in Iraq. IIUM Eng. J. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Fang, Y.Q.; Gu, X.D. Experimental Investigation on the Strength and Microscopic Properties of Cement-Stabilized Aeolian Sand. Buildings 2023, 13, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmakumar, G.P.; Srinivas, K.; Uday, K.V.; Iyer, K.R.; Pathak, P.; Keshava, S.M.; Singh, D.N. Characterization of aeolian sands from Indian desert. Eng. Geol. 2012, 139, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, S.H. Evaluation of wind erosion resistance of EICP solidified desert sand based on response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 447, 138119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ding, S. Prototype tests of assembly foundation of transmission line in aeolian sand area. Rock Soil Mech. 2012, 33, 3230–3236. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Qian, Z.; Yang, W.; Zheng, W. Cement-stabilization of aeolian sand foundation and performance test. Ind. Constr. 2018, 48, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, M.; Zou, C.; Qian, Z.; Lu, X. Experiments on the bearing capacity of aeolian sand stabilized by cement stabilizers. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, J.; Cai, J.; Pan, H.; She, X. Study on the bearing capacity and engineering performance of aeolian sand. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 3426280. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, P.; Song, X.T.; Shen, Y.P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, P.C. Hydraulic behavior of sandy subgrade under extreme rainfall in Alashan, China. Transp. Geotech. 2023, 42, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.Z.; Sheng, M.Q.; Huang, F.M.; Lu, X.L. Uplift Performance of Plate Anchors in Cement-Stabilised Aeolian Sand. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 783148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.Z.; Lu, X.L.; Shijun, D. Experimental study of assembly foundation for transmission line tower in Taklimakan desert. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 32, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.Z.; Huang, X.J.; Yin, W.H.; Liu, G.Y. Static and dynamic characteristics of cement-treated and untreated aeolian sand from the Tengger desert hinterland: Laboratory tests and prediction models. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J. Experiment on the splitting tensile strength of cemented aeolian sand reinforced with different kinds of fibers. J. Rail Way Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Hu, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.L. Aeolian sand stabilized by using fiber- and silt-reinforced cement: Mechanical properties, microstructure evolution, and reinforcement mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Geng, J.; Pang, S.; Su, L.J.; Cai, G.J.; Zhou, Z.C. Microscopic Properties and Splitting Tensile Strength of Fiber-Modified Cement-Stabilized Aeolian Sand. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qian, Z.Z.; Yue, B.; Xie, Z.L. Effects of Cement Dosage, Curing Time, and Water Dosage on the Strength of Cement-Stabilized Aeolian Sand Based on Macroscopic and Microscopic Tests. Materials 2024, 17, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Liu, X.M.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.X.; Yue, J.W. Synergistic effect of red mud, desulfurized gypsum and fly ash in cementitious materials: Mechanical performances and microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulinska, S.; Sujak, A.; Pyzalski, M. Sustainable Management of Photovoltaic Waste Through Recycling and Material Use in the Construction Industry. Materials 2025, 18, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, F.F.G.; Tamashiro, J.R.; Silva, L.H.P.; Kinoshita, A. Utilization of inorganic solid wastes in cementitious materials—A systematic literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.L.; Yu, Z.H.; Bao, R.; Xiong, J.; Yan, K.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, X.B. Manufacture of tailings-based cementitious materials: Insights into tailings activation strategies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 439, 137194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, P.; Park, S.; Pyo, S. A Review on Sustainable Fabrication of Futuristic Cementitious Binders Based on Application of Waste Concrete Powder, Steel Slags, and Coal Bottom Ash. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2022, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.W.; Shi, C.J.; De Schutter, G. Estimation of Magnetic Force between Micrometer-Sized Fly-Ash Particles in Cementitious Suspensions. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04022421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Ramanathan, S.; Suraneni, P.; Hale, W.M. Mitigating calcium oxychloride formation in cementitious paste using alternative supplementary cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 377, 130756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tan, J.J.; Qiu, H.F.; Zhang, J.B.; Guo, Y. Study on microstructural and mechanical properties of cementitious materials composed of fly ash and dacite powder. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1267197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.C.; Yin, H.; Ge, P. Design and microstructural analysis of the mixture proportion of alkali-activated fly ash-slag composite cementitious material. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, P.T.; Ho, L.S.; Shi, J.Y.; Huynh, T.P. Effect of low-calcium fly ash inclusion on long-term mechanical properties and durability of ground granulated blast furnace slag-based cement-free mortars. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L-J. Mater.-Des. Appl. 2024, 238, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.L.; Huang, J.G.; Han, X.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Liu, T.A.; Zhou, J.Y.; Yang, Y.Z. Mass GGBFS Concrete Mixed with Recycled Aggregates as Alkali-Active Substances: Workability, Temperature History and Strength. Materials 2023, 16, 5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.P.; Yang, L.B.; Wang, D.F.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, M.G.; Xue, G.B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Effect of GGBFS on the mechanical properties of metakaolin-based self-compacting geopolymer concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejic, J.S.; Basic, A.D.; Grubor, M.; Serdar, M. Link between the Reactivity of Slag and the Strength Development of Calcium Aluminate Cement. Materials 2024, 17, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baalamurugan, J.; Kumar, V.G.; Padmapriya, R.; Raja, V.K.B. Recent applications of steel slag in construction industry. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 2865–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.H.; Zhou, W.T.; Lyu, X.; Liu, X.; Su, H.L.; Li, C.M.; Wang, H. Comprehensive utilization of steel slag: A review. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhao, D.N.; Lei, J.L.; Song, S.Q. Preparation and Performance Testing of Steel Slag Concrete from Steel Solid Waste. Buildings 2024, 14, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.G. Investigation on the mechanical and microstructure properties of masonry cement-red mud-carbide slag-based paste. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, W.T.; Yan, S.Y. Study on the strength characteristics and micro-mechanism of modified solidified red mud. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1461198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, T.; Zhang, G. Deformation characteristics of red-mud embankment under monotonic and cyclic loads. In Proceedings of the 5th GeoShanghai International Conference, Shanghai, China, 26–29 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.Z.; Dong, X.; Chen, H.X.; Zhou, F.; Liu, G.; Chang, W.; Zhu, R. Study on the Improvement Performance of Different Clay Components with Desulfurization Gypsum-Containing Cementitious Material. Buildings 2024, 14, 3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.Y.; Zhang, G.F.; Ren, Y.L. Properties and microstructure of soil solidified by titanium slag-flue gas desulfurized gypsum-Portland cement composites as solidifiers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Hao, J.Y.; Cheng, G.J.; Guo, B.; Li, X.J. Preparation and Hardening Performance of Lightweight Gypsum Mortar Based on Desulfurization Gypsum. Iran. J. Sci. Technol.-Trans. Civ. Eng. 2023, 47, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Q.W.; Deng, Y.F.; Yu, X.B.; Feng, Q.; Yan, C. Expansive soil modified by waste steel slag and its application in subbase layer of highways. Soils Found. 2019, 59, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Deng, Y.F.; Zhang, G.P.; Zhou, A.N.; Tan, Y.Z.; Xiao, H.L.; Zheng, Q.S. A Generic Framework of Unifying Industrial By-products for Soil Stabilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Figueroa, O.; Escamilla, A.C.; Varum, H.; Amaya, R.J.G. Effect of cassava starch, hydrated lime, and carboxymethylcellulose on the physicomechanical behavior of mixtures with clay matrix. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, R.X.; Ni, J.J. Study on the preparation, performance, and mechanism for solid waste cementitious materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 175-2023; Common Portland Cement. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2023.
- ASTM D5102-2017; Standard Test Method for Unconfined Compressive Strength of Compacted Soil-Lime Mixtures. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).