Research on Performance Predictive Model and Parameter Optimization of Pneumatic Drum Seed Metering Device Based on Backpropagation Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A discussion of the dataset required for ANN training and testing through seeding performance experiments;
- An explanation of using the backpropagation neural network (BPNN) to establish a predictive model of seeding performance from the input physical properties of seeds (geometric mean diameter, sphericity, thousand-grain weight, and kernel density), operational parameters (vacuum pressure and drum rotational speed), and structural parameters (suction hole diameter), producing seeding performance indices (missing index and reseeding index);
- A description of the efficient optimization method of the combination of the BPNN predictive model and MOPSO algorithm (BPNN-MOPSO) to search for optimal device parameters, with the lowest missing and reseeding indexes as the optimization objectives.
2. Materials and Methods
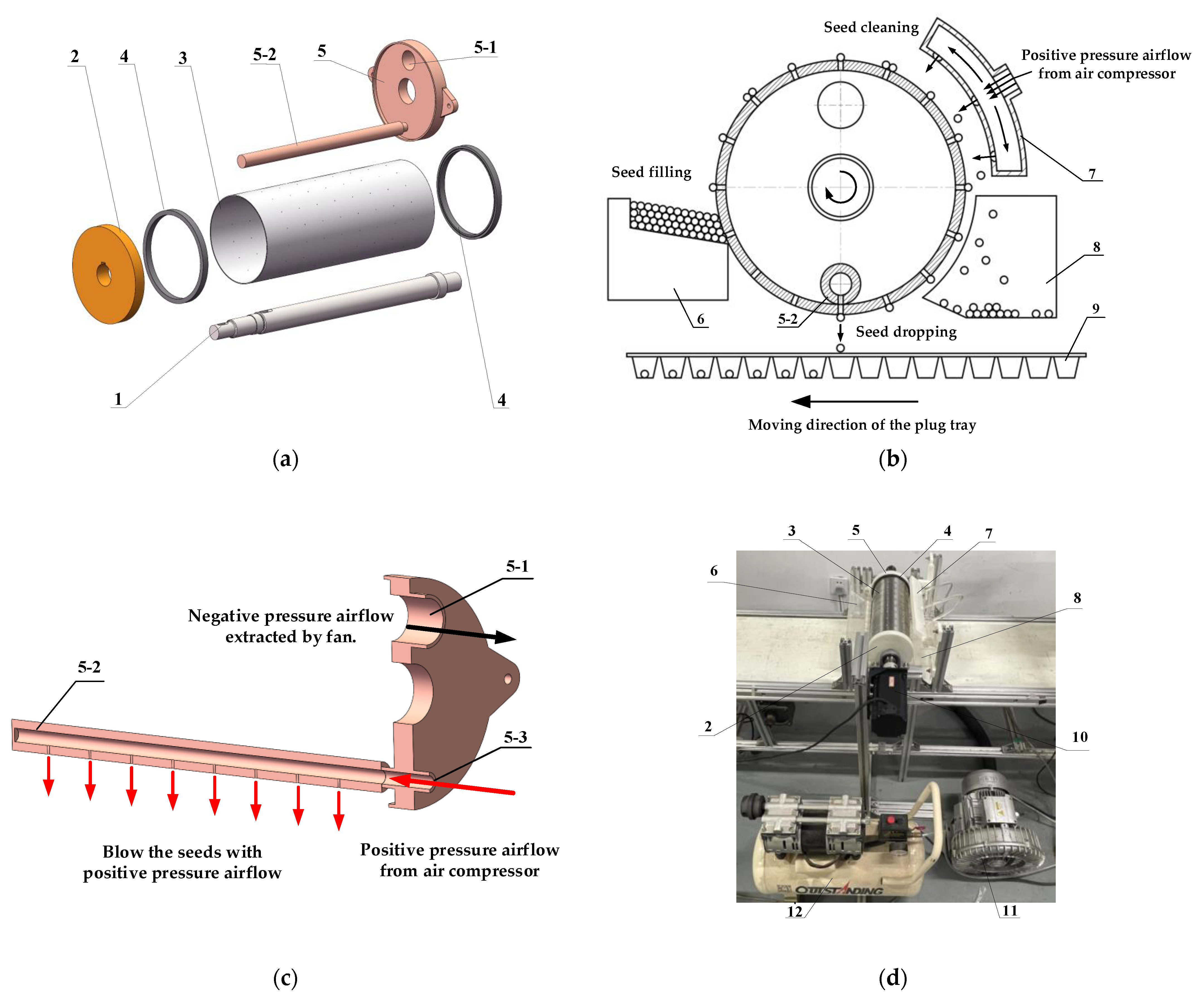
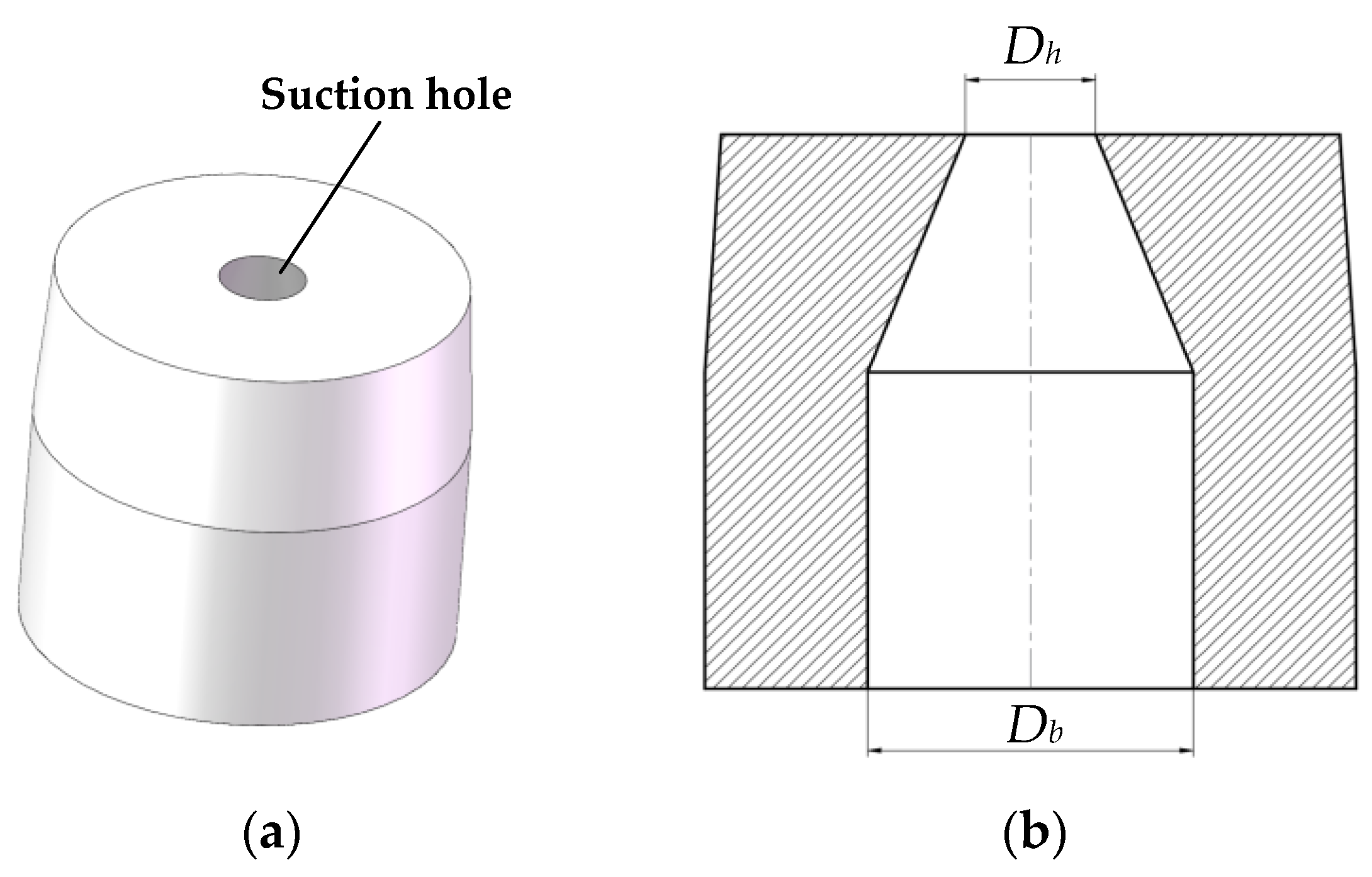
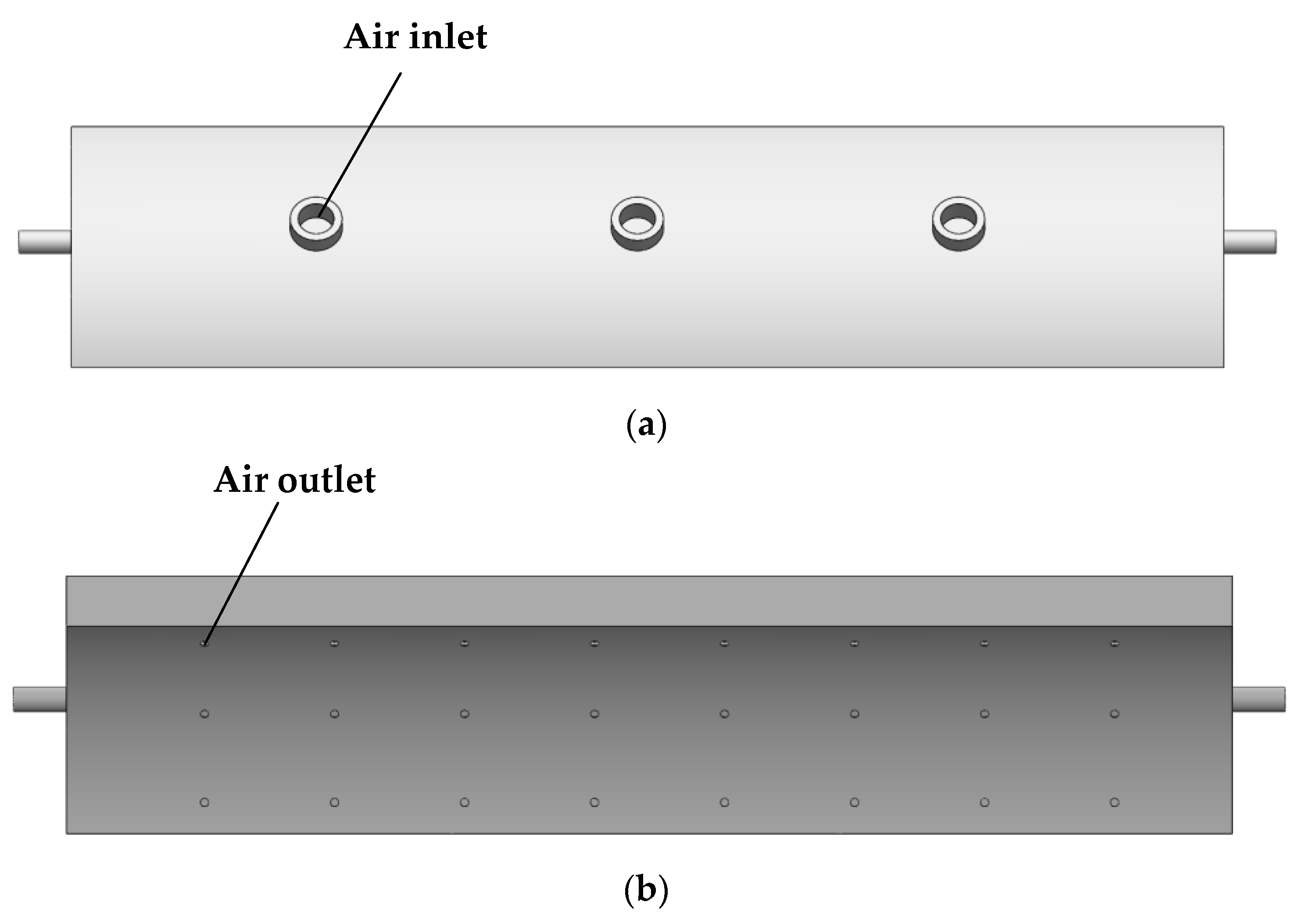
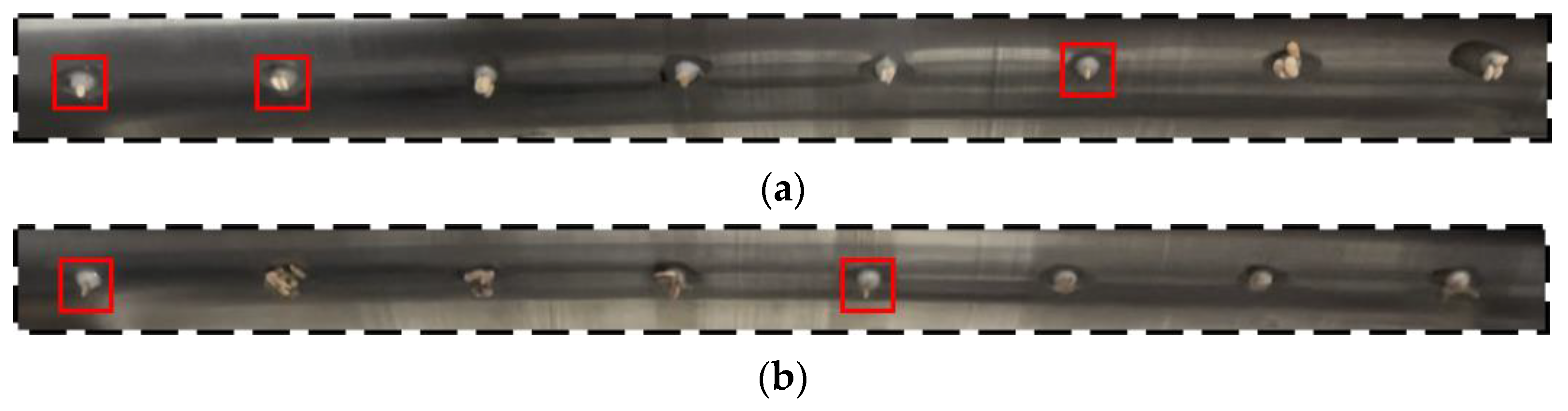
2.1. Overall Structure and Working Principle
2.2. Experimental Seeds and Physical Properties
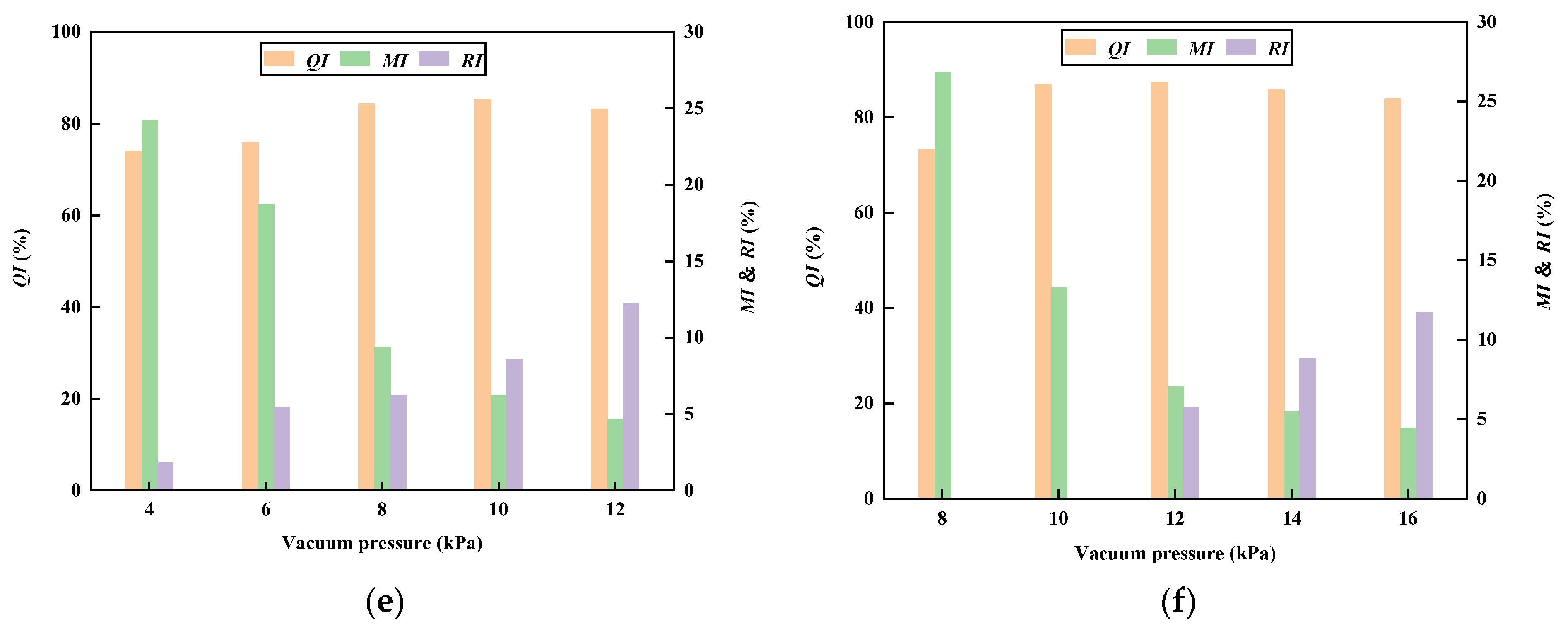
2.3. Influencing Factors and Seeding Performance Indices
2.4. Value Range of Factors
2.5. Orthogonal Experiments
2.6. Backpropagation Neural Network Predictive Model
2.6.1. Seeding Performance Dataset
2.6.2. Backpropagation Neural Network
2.6.3. Evaluation Indices for Network Performance
2.6.4. Establishment of BPNN Predictive Model
2.7. BPNN-MOPSO Parameter Optimization of the Seed Metering Device
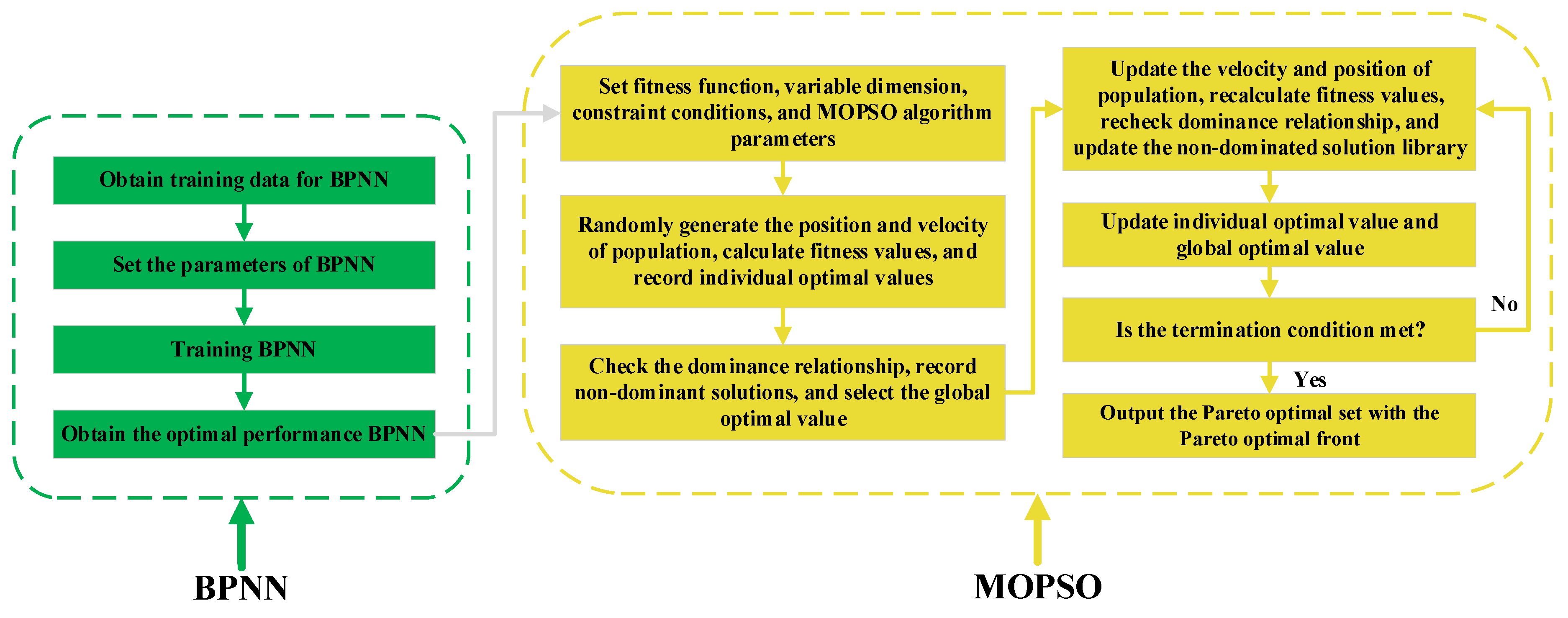
2.7.1. Principle and Flow of the MOPSO Algorithm
- Define a fitness function based on optimization objectives, determine the dimensions and constraints for each input variable, and set MOPSO algorithm parameters;
- Randomly generate position and velocity vectors for the initial population; then, calculate and record the fitness value of each particle as the individual optimal value;
- Based on Pareto dominance, check the dominance relationship of all particles, record all non-dominated solutions, and select one as the global optimal value;
- Update the velocity and position vectors of the population, recalculate each particle’s fitness value, recheck the domination relationship, and update the non-domination solution library;
- Update individual and global optimal values;
- Check whether the maximum number of iterations is reached. If so, the algorithm terminates; otherwise, return to Step 4;
- Output the Pareto optimal set and the Pareto optimal front.
2.7.2. Settings of the MOPSO Algorithm Parameters
2.7.3. Mathematical Model for the Multi-Objective Optimization Problem
2.7.4. Scoring Method for Solutions
2.7.5. Process of BPNN-MOPSO
3. Results and Discussion
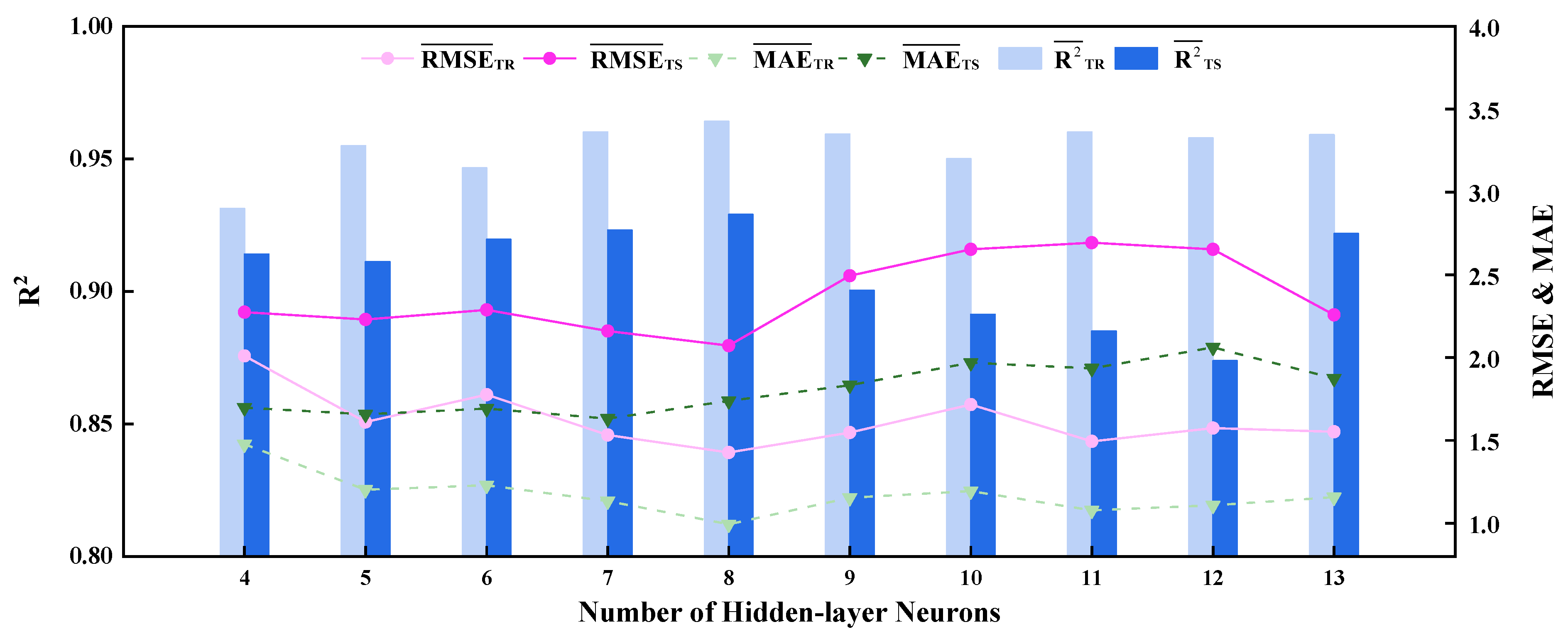
3.1. Determination of the Number of Hidden-Layer Neurons
3.2. Determination of the Activation Functions for the Hidden and Output Layers
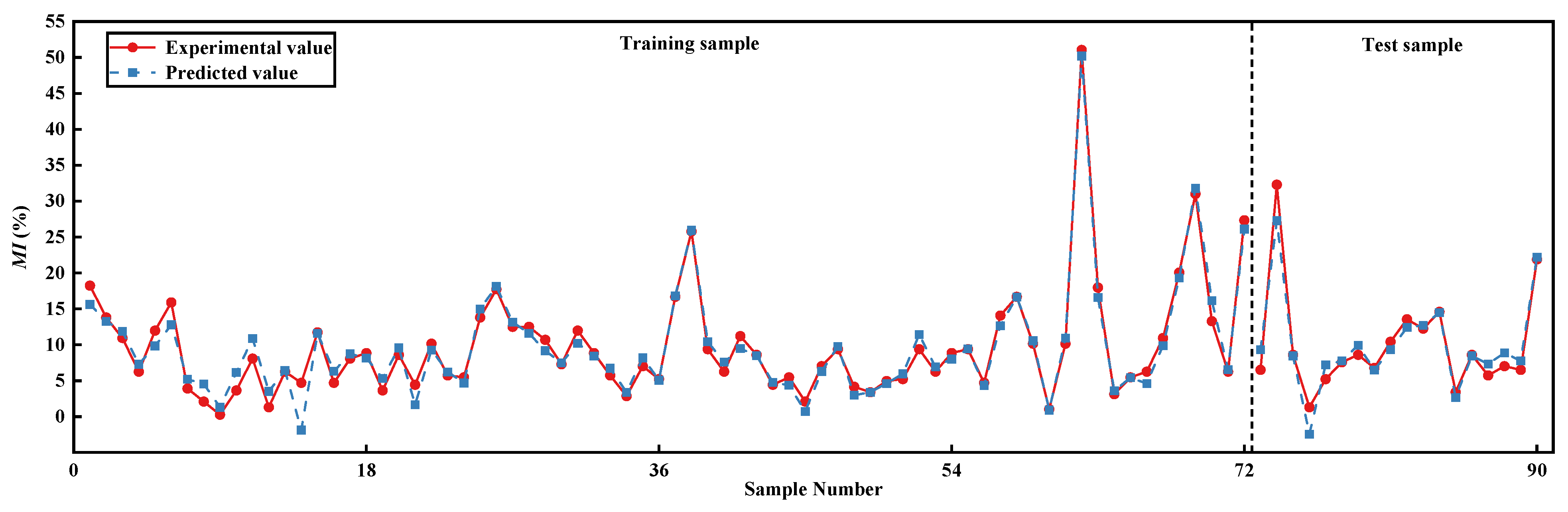
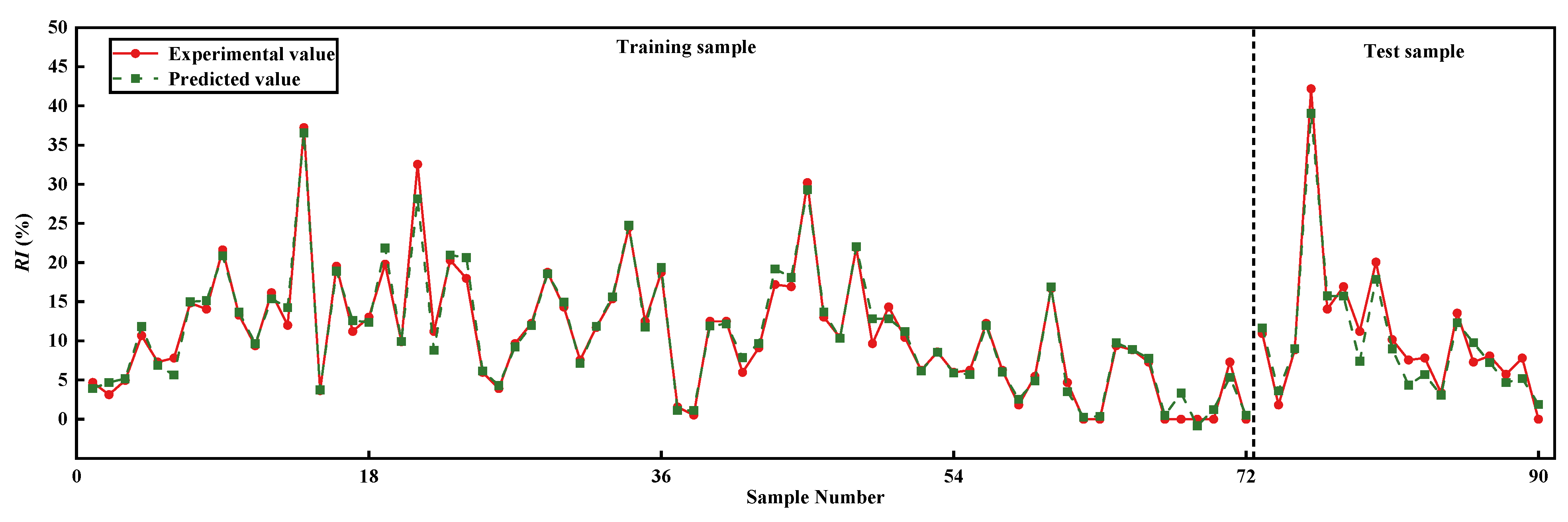
3.3. Determination of the Optimal BPNN Performance
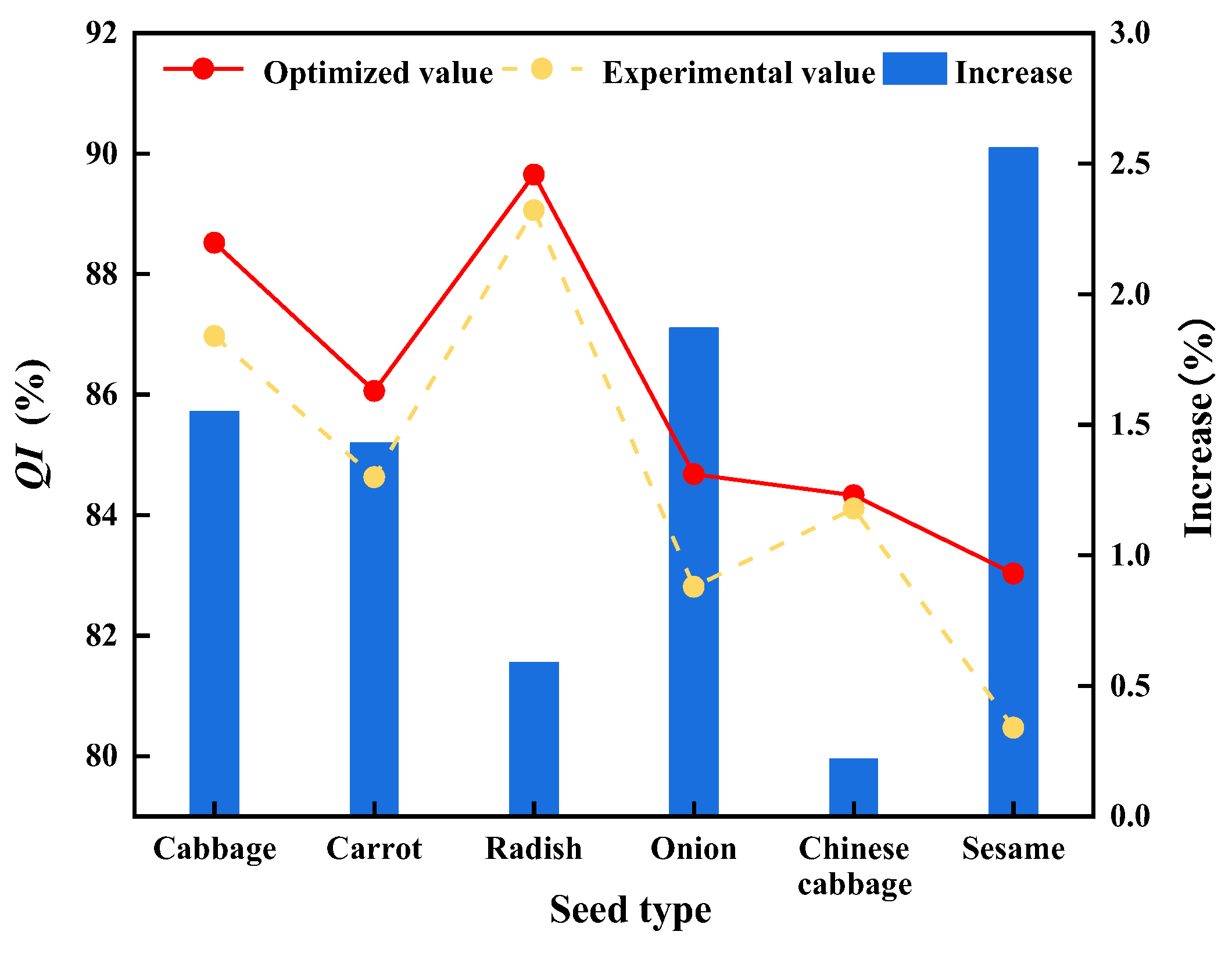
3.4. Verification of Optimization Capability of BPNN-MOPSO
3.5. BPNN-MOPSO Efficient Parameter Optimization Results and Experimental Verification
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- For six types of seeds (cabbage, carrot, radish, onion, Chinese cabbage, and sesame seeds), the range of the suction hole diameter was determined to be from 0.6 to 1.0 mm through the testing and analysis of the seed adsorption process. The suitable range of vacuum pressure for each seed type was determined by single-factor experiments: 6 to 10 kPa for Chinese cabbage, carrot, sesame, and onion seeds; 8 to 12 kPa for cabbage seeds; and 10 to 14 kPa for radish seeds. The seeding performance experiments were carried out, and the dataset used for network training and testing was obtained.
- (2)
- For the BPNN predictive model, when the number of the hidden-layer neurons and the combination of the activation functions of the hidden layer and output layer are eight and logsig/purelin, respectively, the training set (0.9641) and test set (0.9290) are at a high level, and the values of the error indices ( and ) are basically within 2%, which are better than those obtained under other network parameters, showing good network performance. Thus, the number of the hidden-layer neurons and the combination of the activation functions were determined to be eight and logsig/purelin, respectively. Under the above values of network parameters, the BPNN with the optimal performance was obtained through training and testing. The R2 values of two outputs for the training set are both above 0.96; the R2 values of two outputs for the test set are both above 0.92; and the values of the error indices (RMSE and MAE) are basically within 2%, demonstrating the excellent fitting performance and strong generalization ability of the optimal BPNN predictive model.
- (3)
- In the validation of optimization capability, the values of QI optimized by the BPNN-MOPSO algorithm are higher than the optimal experimental ones for cabbage, carrot, radish, onion, Chinese cabbage, and sesame seeds, and the increases are 1.55%, 1.43%, 0.59%, 1.87%, 0.22%, and 2.53%, respectively.
- (4)
- Using the BPNN-MOPSO algorithm to carry out the efficient parameter optimization, the optimal device parameters and seeding performance for three untested seed types (tomato, pepper, and bok choi seeds) were sought. For tomato seeds, with a hole diameter of 0.75 mm, vacuum pressure of 5.6 kPa, and drum rotational speed of 13.7 rpm, the MI, RI, and QI were 11.85%, 2.66%, and 85.50%, respectively. For pepper seeds, with a hole diameter of 1.0 mm, vacuum pressure of 10.4 kPa, and drum rotational speed of 18.0 rpm, the MI, RI, and QI were 11.54%, 2.94%, and 85.52%, respectively. For bok choi seeds, with a hole diameter of 0.67 mm, vacuum pressure of 8.6 kPa, and drum rotational speed of 14.0 rpm, the MI, RI, and QI were 10.72%, 4.41%, and 84.87%, respectively. The bench experiments verified the optimization results. The results show that the absolute errors between the predicted and experimental values were all less than 3%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.S.; Hu, J. Seed Science, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Yang, Y.N.; Meng, F.C.; Liang, L.N.; Ge, Y.X. Improved design and performance experiment on air-suction drum-type seed metering device for rice with auto-cleaning block. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Z.M.; Zhang, D.X.; Li, C.; Cui, T.; He, X.T. Design and test of the T-shaped hole of centrifugal high-speed maize precision seed metering device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Huang, Z.S.; Qin, W.; He, S.Y.; Qian, C.; Jiang, Y.C.; Tao, W.Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, Z.M. Design of hybrid rice air-suction single-seed metering device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Yu, L.Y.; Wu, X.P.; Huang, Y.X.; Yan, X.L. Design and Experiment of Intelligent Seed Supply System of Air-assisted High Speed Precision Maize Seed Metering Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.D. Research on the Movement Characteristics of Flat Seeds in the Seed Box of Metering Device with Air-Blowing Seed Feeding. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Hou, J.W.; Wu, W.B.; Han, C.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Tang, T.; Sun, S.L. Key Structure Design and Experiment of Air-Suction Vegetable Seed-Metering Device. Agronomy 2022, 12, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, S.L.; He, Z.K.; Wang, X.M.; Zeng, Z.H.; Li, J.; Wu, W.B. Design and optimization of seed-metering plate of air-suction vegetable seed-metering device based on DEM-CFD. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 230, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Jiang, Y.C.; He, S.Y.; Huang, Z.S.; Qin, W.; Qian, C.; Tao, W.Y.; Zang, Y. Design and experiment of the air suction wheel precision seed metering device for vegetables. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Q.; Liu, L.J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wu, H.H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, F.J. Design and Test of Four-stage Seed Cleaning Mechanism for Air-suction Vegetables Seed-metering Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liao, Q.X.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.S.; Liu, H. Seed suction performance and experiment of sesame precision hole seeding metering device. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2021, 40, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Yu, H.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Sun, X.P.; Yin, J.Q. Design and Experiment of Group Air-suction Type Celery Seed Metering Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Q. Optimization Design and Test of Gas-suction Seeding Unit of Small-Sized Spherical Vegetable. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Mechanization Sciences, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.X.; Tan, B.; Wei, S.; Xie, H. Structural Design and Analysis of Air Suction Precision Metering Device for White Radish. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liao, Y.T.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.S.; Du, Z.; Liao, Q.X. Design and Experiment of Positive and Negative Pressure Combination Precision Metering Device for Pakchoi. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayel, D.; Güngör, O.; Šarauskis, E. Estimation of Optimum Vacuum Pressure of Air-Suction Seed-Metering Device of Precision Seeders Using Artificial Neural Network Models. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolahzare, Z.; Mehdizadeh, S.A. Nonlinear Mathematical Modeling of Seed Spacing Uniformity of a Pneumatic Planter Using Genetic Programming and Image Processing. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 29, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Sun, S.M.; Zhang, Z.G. Performance test and forecast analysis for air suction seed metering device. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2015, 41, 440–442. [Google Scholar]
- Anantachar, M.; Kumar, P.G.V.; Guruswamy, T. Neural Network Prediction of Performance Parameters of an Inclined Plate Seed Metering Device and Its Reverse Mapping for the Determination of Optimum Design and Operational Parameters. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 72, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.M.; Pareek, C.M.; Machavaram, R. Optimizing the Aeration Performance of a Perforated Pooled Circular Stepped Cascade Aerator Using Hybrid ANN-PSO Technique. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022, 9, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, C.M.; Tewari, V.K.; Machavaram, R. Multi-Objective Optimization of Seeding Performance of a Pneumatic Precision Seed Metering Device Using Integrated ANN-MOPSO Approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Study on WC-10Co-4Cr Coating Prediction Model and Multi-objective Optimization by High Velocity Oxy-Fuel spraying Based on Neural Network. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.C.; Kan, C.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Wu, C.; Du, Q.; Pan, W.J. Design and Test of Precision Seed Metering Device for Panax notoginseng Seedling and Seeding by Air Suction. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.R. Design and Experiment of Pneumatic Roller Type Precision Seed-Metering Device for Tomato Seedlings. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, S.D. Research on Virtual Prototype of Pneumatic Drum Seed Metering Device Based on Seed Characteristics. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Zeng, X.G.; Kou, H.Q.; Chen, H.Y. A Kind of Numerical Model Combined with Genetic Algorithm and Back Propagation Neural Network for Creep-Fatigue Life Prediction and Optimization of Double-Layered Annulus Metal Hydride Reactor and Verification of ASME-NH Code. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 54, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X.S.; Pu, J.; Jiao, S.S. Kinetic Analysis and Back Propagation Neural Network Model for Shelf-Life Estimation of Stabilized Rice Bran. J. Food Eng. 2024, 380, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.Y.; Pan, X.L.; Qiu, Z.F.; Zhou, H.B. Design of Intelligent Quantitative Seeding System Based on BP Neural Network. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.C.; Li, D.W. Neural Network and Deep Learning: Simulation and Realization Based on MATLAB, 1st ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2022; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Kuang, C.W.; Chen, Y.X. Prediction Model of Soil Moisture in Hainan Island Based on Meteorological Factors. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2023, 43, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xu, K.L.; Qi, Y. Study on neural network-based prediction model for biomass ash softening temperature. J. Saf. Environ. 2024, 24, 3801–3808. [Google Scholar]




| Seed Type | L/mm | W/mm | T/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese cabbage | 3.44 ± 0.25 | 2.61 ± 0.21 | 2.01 ± 0.25 |
| Carrot | 3.43 ± 0.54 | 1.58 ± 0.20 | 0.71 ± 0.11 |
| Sesame | 2.97 ± 0.20 | 2.03 ± 0.18 | 1.43 ± 0.20 |
| Onion | 3.08 ± 0.16 | 1.85 ± 0.14 | 0.87 ± 0.08 |
| Cabbage | 2.04 ± 0.16 | 1.75 ± 0.13 | 1.52 ± 0.20 |
| Radish | 1.94 ± 0.14 | 1.73 ± 0.12 | 1.54 ± 0.11 |
| Tomato | 1.71 ± 0.11 | 1.59 ± 0.10 | 1.49 ± 0.11 |
| Pepper | 4.02 ± 0.42 | 3.28 ± 0.35 | 0.80 ± 0.12 |
| Bok choi | 3.41 ± 0.25 | 2.50 ± 0.29 | 0.67 ± 0.10 |
| Seed Type | Geometric Mean Diameter (mm) | Sphericity (%) | Thousand-Grain Weight (g) | Kernel Density (g·cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese cabbage | 1.73 ± 0.11 | 89.27 ± 2.96 | 3.13 ± 0.10 | 0.977 ± 0.026 |
| Carrot | 1.56 ± 0.17 | 46.10 ± 5.19 | 1.84 ± 0.07 | 1.155 ± 0.016 |
| Sesame | 1.71 ± 0.10 | 55.34 ± 2.43 | 3.06 ± 0.07 | 0.930 ± 0.027 |
| Onion | 2.04 ± 0.11 | 68.99 ± 4.69 | 3.28 ± 0.02 | 1.131 ± 0.014 |
| Cabbage | 1.75 ± 0.13 | 86.25 ± 5.73 | 3.64 ± 0.16 | 0.940 ± 0.021 |
| Radish | 2.62 ± 0.19 | 76.25 ± 3.64 | 11.27 ± 0.44 | 1.042 ± 0.014 |
| Tomato | 1.78 ± 0.13 | 52.33 ± 4.17 | 3.02 ± 0.06 | 1.147 ± 0.058 |
| Pepper | 2.19 ± 0.21 | 54.60 ± 3.77 | 5.47 ± 0.05 | 0.937 ± 0.054 |
| Bok choi | 1.60 ± 0.10 | 93.14 ± 2.79 | 2.60 ± 0.05 | 0.975 ± 0.039 |
| Seed Type | Range | Level (kPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Radish | 8–16 kPa | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
| Chinese cabbage, carrot, sesame, onion, cabbage | 4–12 kPa | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| Seed Type | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Hole Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese cabbage | 6–10 | 10–14 | 0.61.0 |
| Carrot | |||
| Sesame | |||
| Onion | |||
| Cabbage | 8–12 | ||
| Radish | 1014 |
| Factor | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Hole diameter (mm) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| Vacuum pressure (kPa) | 6/8/10 | 8/10/12 | 10/12/14 |
| Rotational speed (rpm) | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| Seed Type | Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese cabbage | 0.6 | 6 | 10 | 18.23 | 4.69 | 77.08 |
| 6 | 14 | 32.29 | 1.82 | 65.89 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 13.80 | 3.13 | 83.07 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 10.94 | 4.95 | 84.11 | ||
| 10 | 10 | 6.51 | 10.94 | 82.55 | ||
| 0.8 | 8 | 10 | 6.25 | 10.68 | 83.07 | |
| 8 | 14 | 11.98 | 7.29 | 80.73 | ||
| 6 | 12 | 15.89 | 7.81 | 76.30 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 8.59 | 8.85 | 82.55 | ||
| 10 | 12 | 3.91 | 14.84 | 81.25 | ||
| 1.0 | 8 | 12 | 2.08 | 14.06 | 83.86 | |
| 10 | 10 | 0.26 | 21.61 | 78.13 | ||
| 6 | 10 | 3.65 | 13.28 | 83.07 | ||
| 6 | 14 | 8.07 | 9.38 | 82.55 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 1.30 | 16.15 | 82.55 |
| Seed Type | Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrot | 0.6 | 6 | 10 | 8.59 | 9.89 | 81.52 |
| 6 | 14 | 11.72 | 3.65 | 84.63 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 8.07 | 11.20 | 80.73 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 7.55 | 16.93 | 75.52 | ||
| 10 | 10 | 5.73 | 20.31 | 73.96 | ||
| 0.8 | 8 | 10 | 4.69 | 19.53 | 75.78 | |
| 8 | 14 | 8.85 | 13.02 | 78.13 | ||
| 6 | 12 | 10.16 | 11.20 | 78.64 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 5.21 | 14.06 | 80.73 | ||
| 10 | 12 | 3.65 | 19.79 | 76.56 | ||
| 1.0 | 8 | 12 | 4.43 | 32.55 | 63.02 | |
| 10 | 10 | 1.30 | 42.19 | 56.51 | ||
| 6 | 10 | 5.47 | 17.97 | 76.56 | ||
| 6 | 14 | 6.25 | 11.98 | 81.77 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 4.69 | 37.24 | 58.07 |
| Seed Type | Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sesame | 0.6 | 6 | 10 | 13.80 | 5.99 | 80.21 |
| 6 | 14 | 17.71 | 3.91 | 78.39 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 12.50 | 9.64 | 77.86 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 12.50 | 12.24 | 75.26 | ||
| 10 | 10 | 10.68 | 18.75 | 70.57 | ||
| 0.8 | 8 | 10 | 7.29 | 14.32 | 78.39 | |
| 8 | 14 | 10.42 | 10.16 | 79.42 | ||
| 6 | 12 | 11.98 | 7.55 | 80.47 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 8.85 | 11.72 | 79.43 | ||
| 10 | 12 | 6.77 | 20.05 | 73.18 | ||
| 1.0 | 8 | 12 | 5.73 | 15.36 | 78.91 | |
| 10 | 10 | 2.86 | 24.48 | 72.66 | ||
| 6 | 10 | 7.03 | 12.50 | 80.47 | ||
| 6 | 14 | 8.59 | 11.20 | 80.21 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 5.21 | 18.75 | 76.04 |
| Seed Type | Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onion | 0.6 | 6 | 10 | 16.67 | 1.56 | 81.77 |
| 6 | 14 | 25.78 | 0.52 | 73.70 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 14.58 | 3.39 | 82.03 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 12.24 | 7.81 | 79.95 | ||
| 10 | 10 | 9.38 | 12.50 | 78.13 | ||
| 0.8 | 8 | 10 | 6.25 | 12.50 | 81.25 | |
| 8 | 14 | 11.20 | 5.99 | 82.81 | ||
| 6 | 12 | 13.54 | 7.55 | 78.91 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 8.59 | 9.11 | 82.29 | ||
| 10 | 12 | 4.43 | 17.19 | 78.39 | ||
| 1.0 | 8 | 12 | 5.47 | 16.93 | 77.60 | |
| 10 | 10 | 2.08 | 30.21 | 67.71 | ||
| 6 | 10 | 7.03 | 13.02 | 79.95 | ||
| 6 | 14 | 9.38 | 10.42 | 80.21 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 4.17 | 21.88 | 73.96 |
| Seed Type | Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cabbage | 0.6 | 12 | 14 | 10.16 | 5.47 | 84.37 |
| 10 | 12 | 9.38 | 6.25 | 84.37 | ||
| 8 | 10 | 14.06 | 6.25 | 79.69 | ||
| 8 | 14 | 16.67 | 1.82 | 81.51 | ||
| 12 | 10 | 8.59 | 7.29 | 84.12 | ||
| 0.8 | 10 | 10 | 5.21 | 10.42 | 84.37 | |
| 10 | 14 | 8.85 | 5.99 | 85.16 | ||
| 8 | 12 | 9.38 | 6.25 | 84.37 | ||
| 10 | 12 | 6.25 | 8.59 | 85.16 | ||
| 12 | 12 | 4.69 | 12.24 | 83.07 | ||
| 1.0 | 8 | 14 | 5.73 | 8.07 | 86.20 | |
| 8 | 10 | 4.95 | 14.32 | 80.73 | ||
| 10 | 12 | 3.39 | 9.64 | 86.97 | ||
| 12 | 14 | 3.39 | 13.54 | 83.07 | ||
| 12 | 10 | 1.04 | 16.67 | 82.29 |
| Seed Type | Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radish | 0.6 | 12 | 12 | 27.34 | 0.00 | 72.66 |
| 10 | 14 | 51.04 | 0.00 | 48.96 | ||
| 10 | 10 | 30.99 | 0.00 | 69.01 | ||
| 14 | 10 | 20.05 | 0.00 | 79.95 | ||
| 14 | 14 | 21.88 | 0.00 | 78.12 | ||
| 0.8 | 12 | 10 | 6.51 | 7.81 | 85.68 | |
| 12 | 14 | 10.16 | 4.69 | 85.15 | ||
| 10 | 12 | 13.28 | 0.00 | 86.72 | ||
| 12 | 12 | 7.03 | 5.73 | 87.24 | ||
| 14 | 12 | 5.47 | 8.85 | 85.68 | ||
| 1.0 | 14 | 14 | 6.25 | 7.29 | 86.46 | |
| 14 | 10 | 3.13 | 9.38 | 87.49 | ||
| 12 | 12 | 6.25 | 7.29 | 86.46 | ||
| 10 | 10 | 10.94 | 0.00 | 89.06 | ||
| 10 | 14 | 17.97 | 0.00 | 82.03 |
| No. | Geometric Mean Diameter (mm) | Sphericity (%) | Thousand-Grain Weight (g) | Kernel Density (g·cm−3) | Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.73 | 89.27 | 3.13 | 0.977 | 0.6 | 10 | 10 | 6.51 | 10.94 |
| 2 | 1.73 | 89.27 | 3.13 | 0.977 | 0.6 | 6 | 14 | 32.29 | 1.82 |
| 3 | 1.73 | 89.27 | 3.13 | 0.977 | 0.8 | 8 | 12 | 8.59 | 8.85 |
| 4 | 1.56 | 46.10 | 1.84 | 1.155 | 1.0 | 10 | 10 | 1.30 | 42.19 |
| 5 | 1.56 | 46.10 | 1.84 | 1.155 | 0.8 | 8 | 12 | 5.21 | 14.06 |
| 6 | 1.56 | 46.10 | 1.84 | 1.155 | 0.6 | 10 | 14 | 7.55 | 16.93 |
| 7 | 1.71 | 55.34 | 3.06 | 0.930 | 1.0 | 6 | 14 | 8.59 | 11.20 |
| 8 | 1.71 | 55.34 | 3.06 | 0.930 | 0.8 | 10 | 12 | 6.77 | 20.05 |
| 9 | 1.71 | 55.34 | 3.06 | 0.930 | 0.8 | 8 | 14 | 10.42 | 10.16 |
| 10 | 2.04 | 68.99 | 3.28 | 1.131 | 0.8 | 6 | 12 | 13.54 | 7.55 |
| 11 | 2.04 | 68.99 | 3.28 | 1.131 | 0.6 | 10 | 14 | 12.24 | 7.81 |
| 12 | 2.04 | 68.99 | 3.28 | 1.131 | 0.6 | 8 | 12 | 14.58 | 3.39 |
| 13 | 1.75 | 86.25 | 3.64 | 0.940 | 1.0 | 12 | 14 | 3.39 | 13.54 |
| 14 | 1.75 | 86.25 | 3.64 | 0.940 | 0.6 | 12 | 10 | 8.59 | 7.29 |
| 15 | 1.75 | 86.25 | 3.64 | 0.940 | 1.0 | 8 | 14 | 5.73 | 8.07 |
| 16 | 2.62 | 76.25 | 11.27 | 1.042 | 0.8 | 12 | 12 | 7.03 | 5.73 |
| 17 | 2.62 | 76.25 | 11.27 | 1.042 | 0.8 | 12 | 10 | 6.51 | 7.81 |
| 18 | 2.62 | 76.25 | 11.27 | 1.042 | 0.6 | 14 | 14 | 21.88 | 0.00 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum no. of iterations | 1000 |
| Target error | 1 × 10−4 |
| Learning rate | 0.01 |
| Training algorithm | Levenberg–Marquardt |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Population size | 100 |
| Non-dominated solution library size | 100 |
| No. of iterations | 200 |
| Individual learning coefficient | 1.5 |
| Global learning coefficient | 1.5 |
| Number of grids per dimension | 40 |
| Inertia weight | Max: 0.9 |
| Min: 0.4 |
| Seed Type | x2 | x3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| e | f | g | h | |
| Cabbage | 8 | 12 | 10 | 18 |
| Carrot | 4 | 8 | 14 | |
| Radish | 10 | 16 | ||
| Tomato | 4 | 10 | ||
| Chinese cabbage | 6 | |||
| Sesame | ||||
| Onion | ||||
| Bok choi | ||||
| Pepper | 18 | |||
| No. of Hidden-Layer Neurons | Average Value of Network Performance Indices for Two Outputs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Indices for the Training Set | Performance Indices for the Test Set | |||||
| 4 | 2.0104 | 1.4775 | 0.9313 | 2.2744 | 1.6981 | 0.9141 |
| 5 | 1.6113 | 1.2020 | 0.9549 | 2.2306 | 1.6582 | 0.9112 |
| 6 | 1.7768 | 1.2297 | 0.9466 | 2.2881 | 1.6919 | 0.9196 |
| 7 | 1.5325 | 1.1333 | 0.9601 | 2.1607 | 1.6319 | 0.9231 |
| 8 | 1.4273 | 0.9935 | 0.9641 | 2.0728 | 1.7391 | 0.9290 |
| 9 | 1.5477 | 1.1539 | 0.9593 | 2.4943 | 1.8335 | 0.9004 |
| 10 | 1.7167 | 1.1945 | 0.9500 | 2.6538 | 1.9693 | 0.8913 |
| 11 | 1.4944 | 1.0783 | 0.9602 | 2.6942 | 1.9353 | 0.8850 |
| 12 | 1.5744 | 1.1079 | 0.9579 | 2.6539 | 2.0620 | 0.8738 |
| 13 | 1.5520 | 1.1576 | 0.9591 | 2.2583 | 1.8748 | 0.9218 |
| Hidden-Layer Activation Function | Output-Layer Activation Function | Average Value of Network Performance Indices for Two Outputs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Indices for the Training Set | Performance Indices for the Test Set | ||||||
| Logsig | Tansig | 2.2038 | 1.5565 | 0.9179 | 2.8172 | 2.1504 | 0.8766 |
| Logsig | Purelin | 1.4273 | 0.9935 | 0.9641 | 2.0728 | 1.7391 | 0.9290 |
| Tansig | Tansig | 2.0002 | 1.3602 | 0.9323 | 2.6083 | 1.9306 | 0.8949 |
| Tansig | Purelin | 1.4303 | 1.0685 | 0.9646 | 2.1444 | 1.8452 | 0.9281 |
| Purelin | Tansig | 3.0668 | 2.2387 | 0.8409 | 3.4141 | 2.4209 | 0.8192 |
| Purelin | Purelin | 3.8248 | 2.6658 | 0.7512 | 4.2289 | 3.0312 | 0.7071 |
| Network | Output | Dataset | Performance Indices | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPNN (7-8-2) | Missing index | Training set | 1.4883 | 1.0937 | 0.9627 |
| Test set | 1.8807 | 1.3440 | 0.9287 | ||
| Reseeding index | Training set | 1.2064 | 0.8436 | 0.9753 | |
| Test set | 2.0178 | 1.7559 | 0.9497 | ||
| Connection Weight Between Input and Hidden Layers W1 | Connection Weight Between Hidden and Output Layers (Transposition) W2T | Hidden-Layer Bias bh | Output-Layer Bias bo | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −2.7320 | −1.3529 | −0.6447 | 0.5044 | 0.7261 | 3.9120 | −0.9372 | −2.1289 | −0.5536 | 6.0500 | 3.1567 |
| 2.2852 | 2.0053 | −1.2572 | 0.5124 | 3.9060 | 0.9832 | 0.1191 | 0.5815 | −1.7001 | −4.0843 | −2.1084 |
| −2.3290 | 0.2466 | 0.3522 | 0.8968 | 4.4255 | 0.5757 | −0.0804 | −1.4565 | 0.3460 | 6.4274 | |
| −1.6748 | −0.3326 | 0.8352 | 0.3386 | 0.3735 | 2.1485 | −0.5065 | −0.2870 | 1.3906 | 0.0285 | |
| 0.4245 | 0.2209 | 4.0421 | −0.1324 | −0.7695 | −2.7666 | −1.7444 | 0.0490 | −0.2990 | −3.8582 | |
| −0.1538 | −1.4328 | 1.3190 | −2.7081 | −0.5418 | −1.2597 | −0.6917 | −0.0582 | 0.2649 | −0.5468 | |
| 0.5534 | 1.7438 | −0.7404 | 1.0796 | 2.8059 | 1.2724 | 0.0536 | −0.8076 | 2.3069 | −2.5635 | |
| 1.8411 | −1.7465 | −3.2982 | 2.4162 | −0.7691 | −1.9419 | 0.2147 | −0.0975 | 1.2290 | 3.1703 | |
| Seed Type | Parameter | Indices | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) | ||
| Cabbage | Experimental value | 1.00 | 10.0 | 12 | 3.39 | 9.64 | 86.97 |
| Optimized value | 1.00 | 11.6 | 18 | 5.20 | 6.28 | 88.52 | |
| Carrot | Experimental value | 0.60 | 6.0 | 14 | 11.72 | 3.65 | 84.63 |
| Optimized value | 0.77 | 4.3 | 14 | 11.70 | 2.24 | 86.06 | |
| Radish | Experimental value | 1.00 | 10.0 | 10 | 10.94 | 0.00 | 89.06 |
| Optimized value | 0.98 | 10.6 | 10 | 8.76 | 1.59 | 89.65 | |
| Onion | Experimental value | 0.80 | 8.0 | 14 | 11.20 | 5.99 | 82.81 |
| Optimized value | 0.71 | 6.2 | 10 | 11.96 | 3.36 | 84.68 | |
| Chinese cabbage | Experimental value | 0.60 | 10.0 | 14 | 10.94 | 4.95 | 84.11 |
| Optimized value | 0.70 | 9.0 | 14 | 10.48 | 5.19 | 84.33 | |
| Sesame | Experimental value | 1.00 | 6.0 | 10 | 7.03 | 12.50 | 80.47 |
| Optimized value | 0.85 | 6.3 | 14 | 10.52 | 6.46 | 83.03 | |
| Seed Type | Parameter | Indices | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hole Diameter (mm) | Vacuum Pressure (kPa) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) | |
| Tomato | 0.75 | 5.6 | 13.7 | 11.85 | 2.66 | 85.50 |
| Pepper | 1.00 | 10.4 | 18.0 | 11.54 | 2.94 | 85.52 |
| Bok choi | 0.67 | 8.6 | 14.0 | 10.72 | 4.41 | 84.87 |
| Seed Type | Missing Index (%) | Reseeding Index (%) | Qualified Index (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomato | Predicted value | 11.85 | 2.66 | 85.50 |
| Experimental value | 11.19 | 2.08 | 86.73 | |
| Absolute error | 0.66 | 0.58 | 1.23 | |
| Pepper | Predicted value | 11.54 | 2.94 | 85.52 |
| Experimental value | 8.85 | 3.65 | 87.50 | |
| Absolute error | 2.69 | 0.71 | 1.98 | |
| Bok choi | Predicted value | 10.72 | 4.41 | 84.87 |
| Experimental value | 9.11 | 5.21 | 85.68 | |
| Absolute error | 1.61 | 0.80 | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qin, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Research on Performance Predictive Model and Parameter Optimization of Pneumatic Drum Seed Metering Device Based on Backpropagation Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073682
Pan Y, Yu Y, Zhou J, Qin W, Wang Q, Wang Y. Research on Performance Predictive Model and Parameter Optimization of Pneumatic Drum Seed Metering Device Based on Backpropagation Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073682
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yilong, Yaxin Yu, Junwei Zhou, Wenbing Qin, Qiang Wang, and Yinghao Wang. 2025. "Research on Performance Predictive Model and Parameter Optimization of Pneumatic Drum Seed Metering Device Based on Backpropagation Neural Network" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073682
APA StylePan, Y., Yu, Y., Zhou, J., Qin, W., Wang, Q., & Wang, Y. (2025). Research on Performance Predictive Model and Parameter Optimization of Pneumatic Drum Seed Metering Device Based on Backpropagation Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073682





