Microplastic Retention in Secondary Sewage Sludge: Characterization and Influence of Solid Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
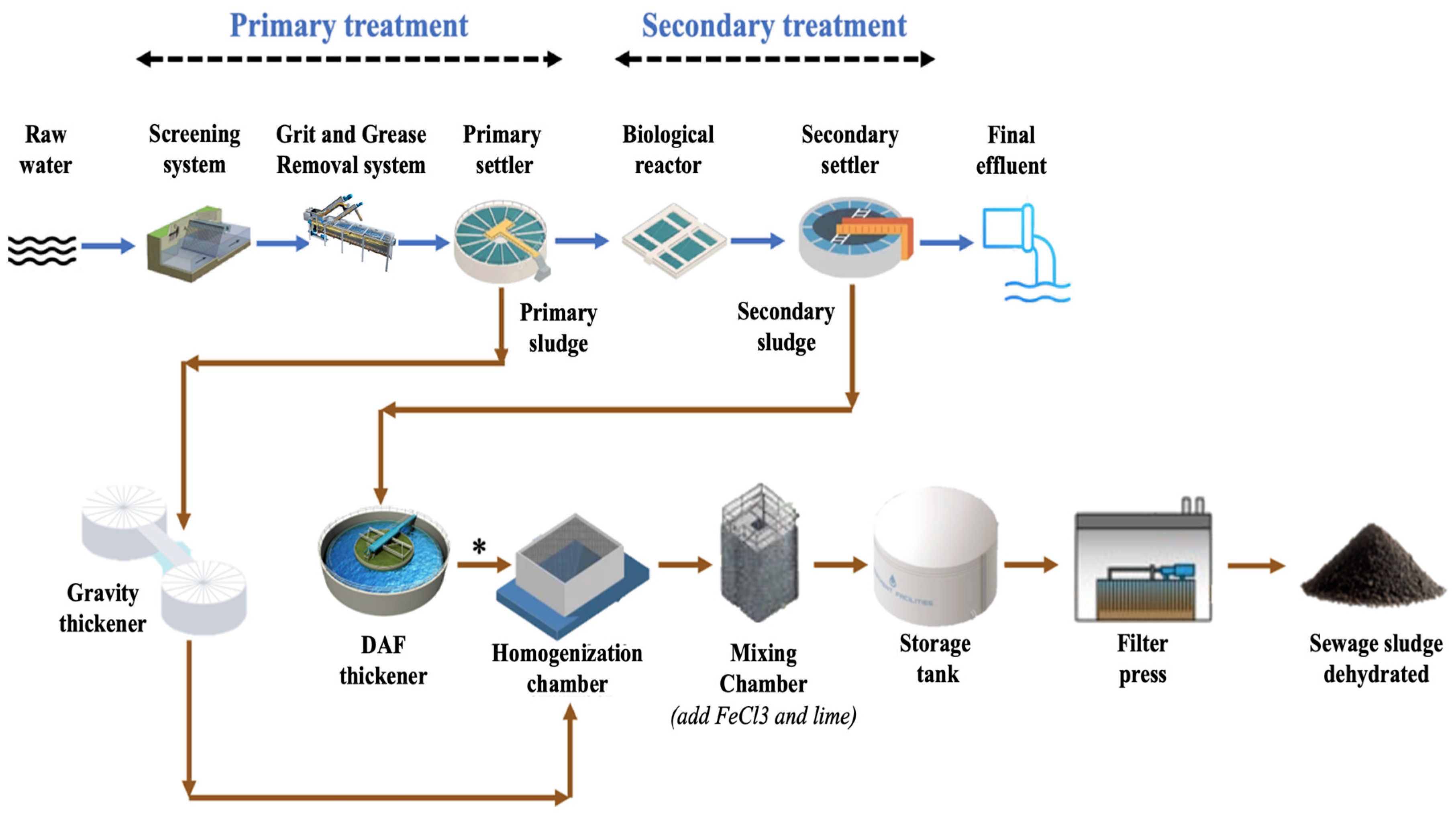
2.1. WWTP Characteristics
2.2. Sludge Characteristics
2.3. Treatment of Sludge Samples for MP Analysis
2.4. Mixing–Settling Experiments
- (a)
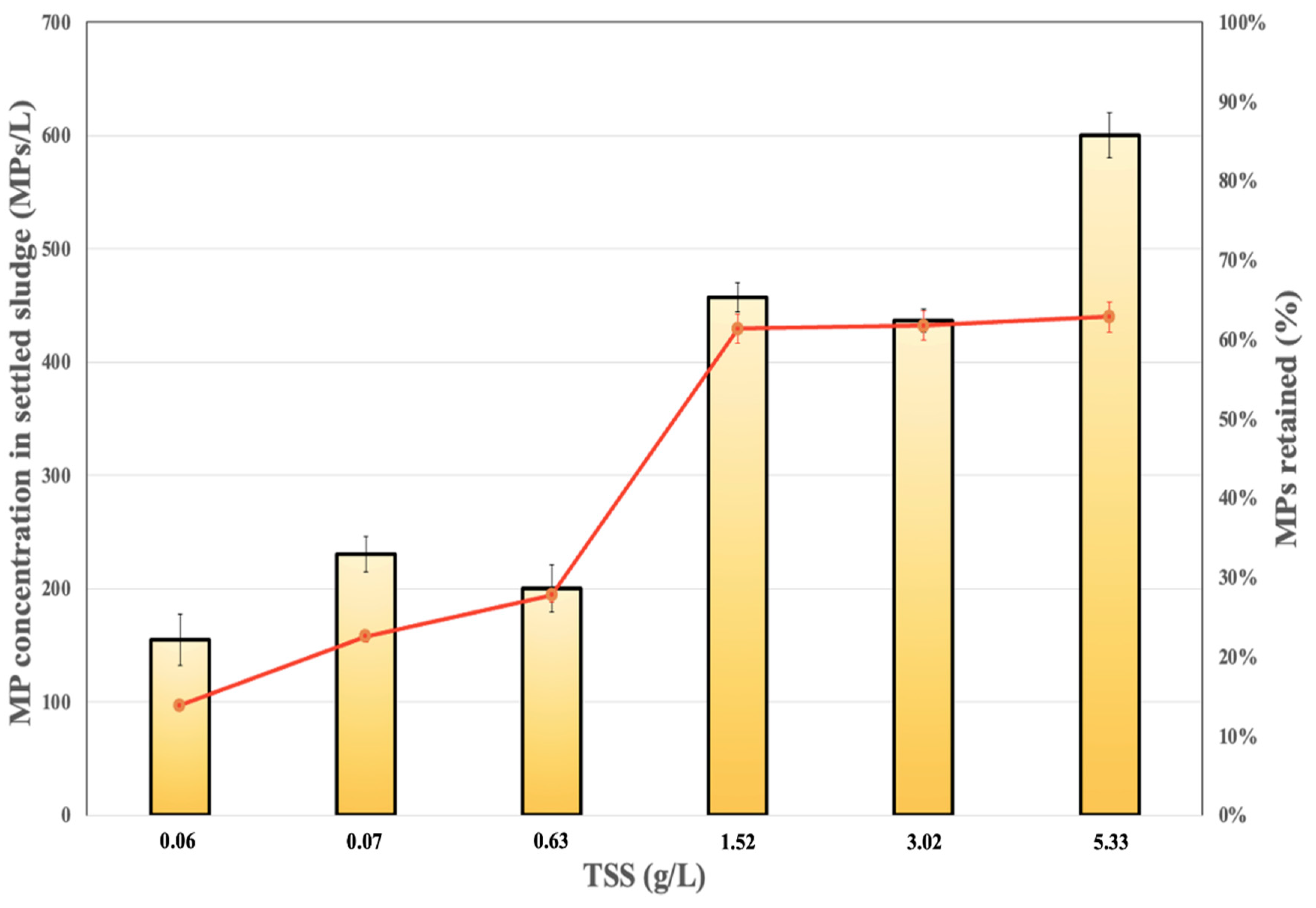
- To test the effect of solid concentration, different sludge:water ratios were used. Six different weights of sewage sludge (1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 g) were diluted with 500 mL of filtered distilled water (enriched with field-obtained MPs, within the range of 120 to 220 MPs) and were shaken for 30 min at 30 rpm. Afterward, the samples were left to rest for 3 h to favour the sedimentation process, and the supernatant was collected. The settled sludge and the supernatant were then treated following the same experimental procedure described in Section 2.3.
- (b)
- To test the effect of adding a coagulant (FeCl3, 5%, Sigma Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany) and a flocculant (non-ionic granular PAM, 5 ppm, Thermo Scientific, Shangai, China), the same sludge:water ratio was used [25,26,27]. Specifically, 10 g of sewage sludge was diluted with 500 mL of filtered distilled water (enriched with field-obtained MPs, ranging from 164 to 174 MPs). Subsequently, 10 mL of coagulant and 10 mL of flocculant were added to two glass beakers containing the diluted sludge. A 5% solution of FeCl3 (97%, Sigma-Aldrich, Germany) was used as the coagulant, while a 5ppm solution of non-ionic granular PAM (97.5%, Thermo Scientific, China) was used as the flocculant. Jar test experiments and the sample collection were carried out as described above.
2.5. Microplastic Analysis
2.6. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Native MPs in the Sewage Sludge
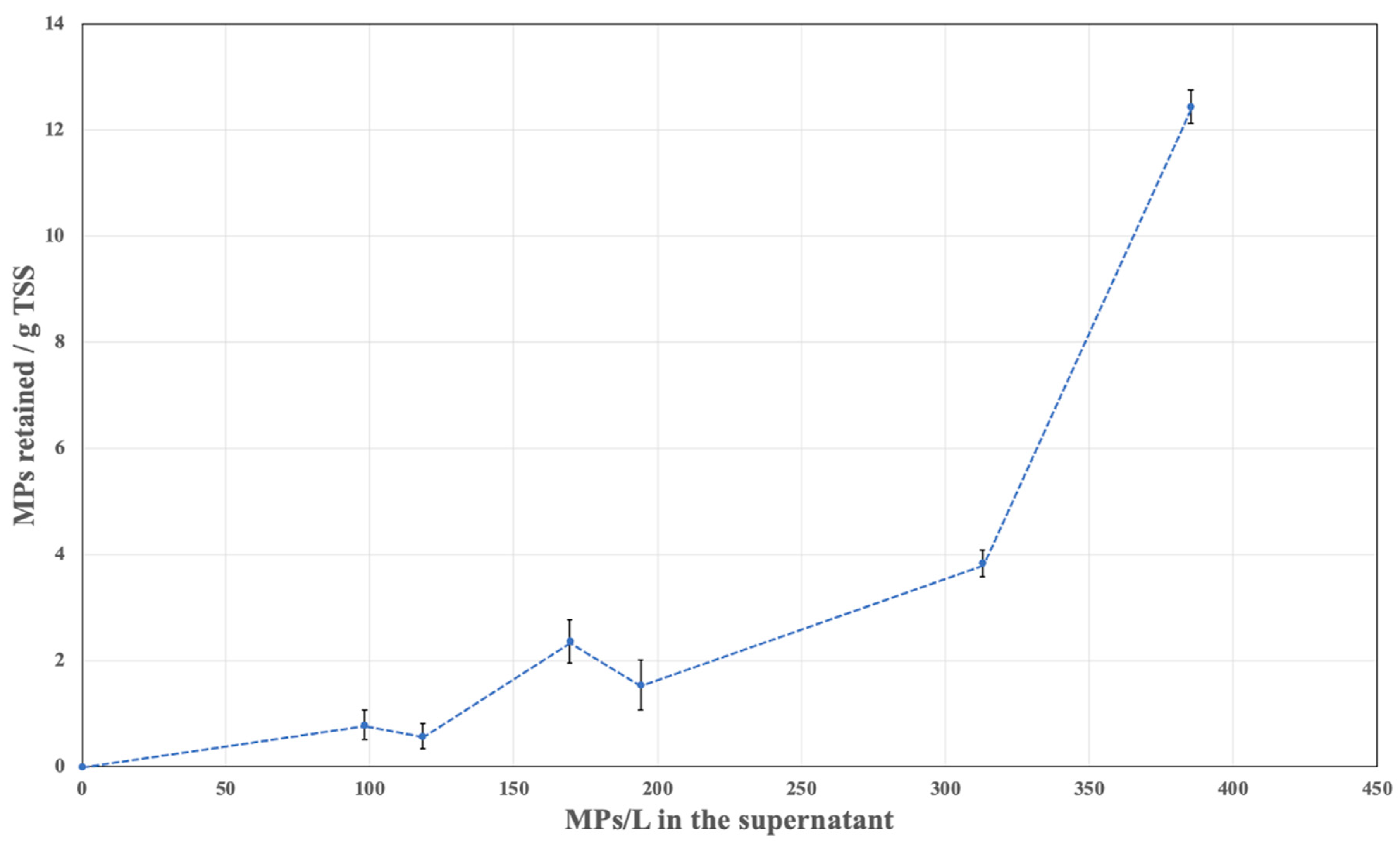
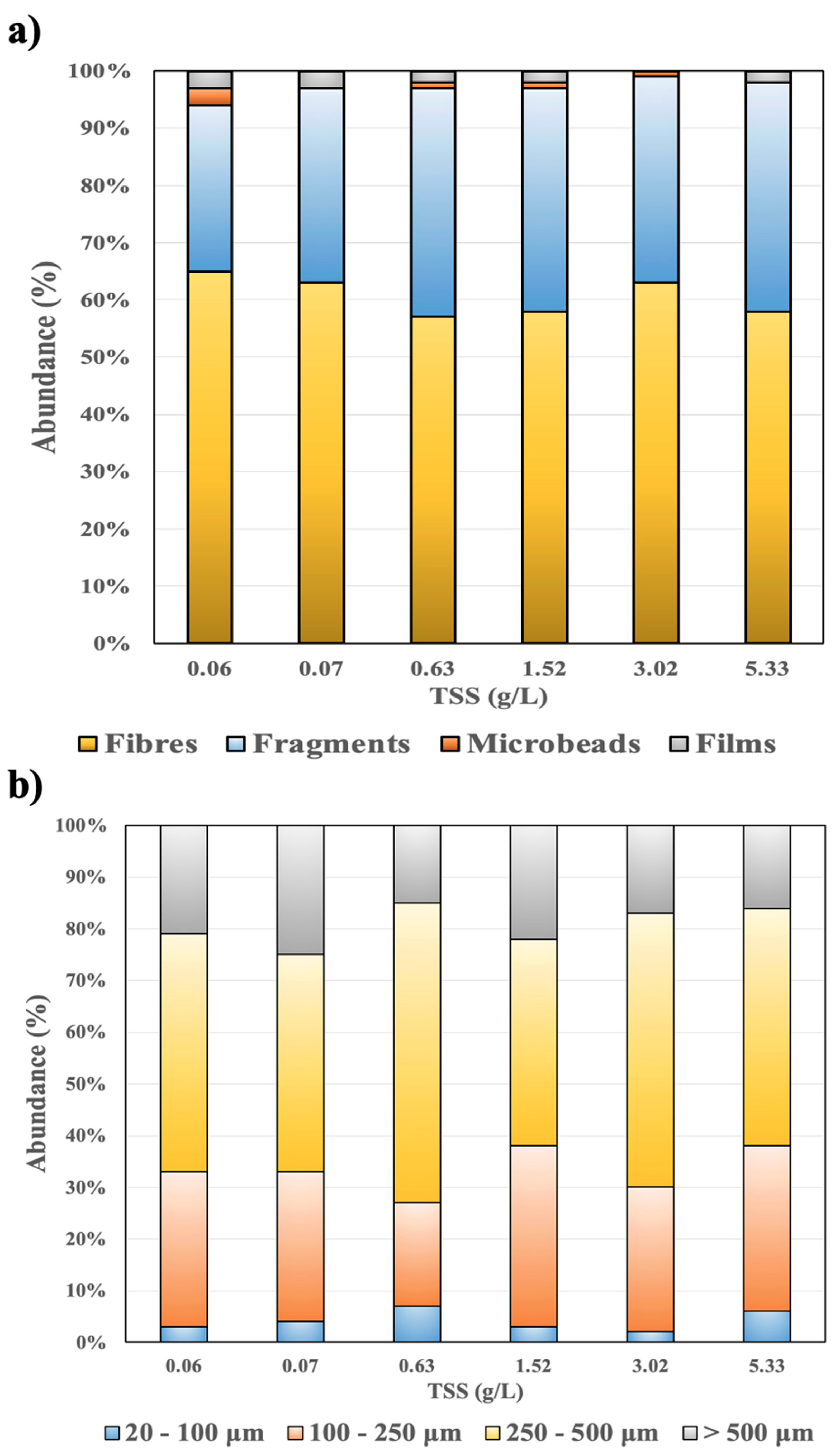
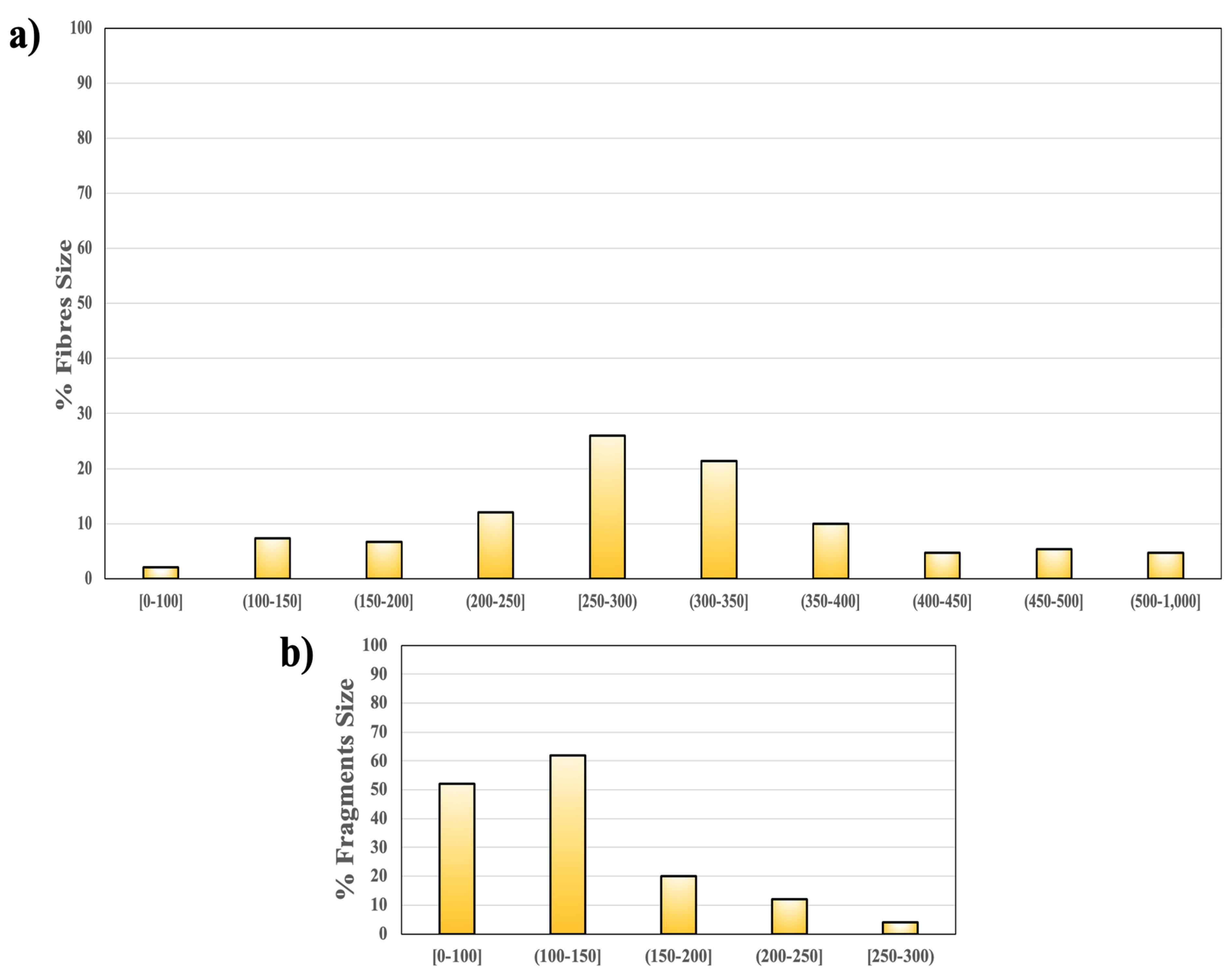
3.2. Effect of Solid Concentration on MP Retention
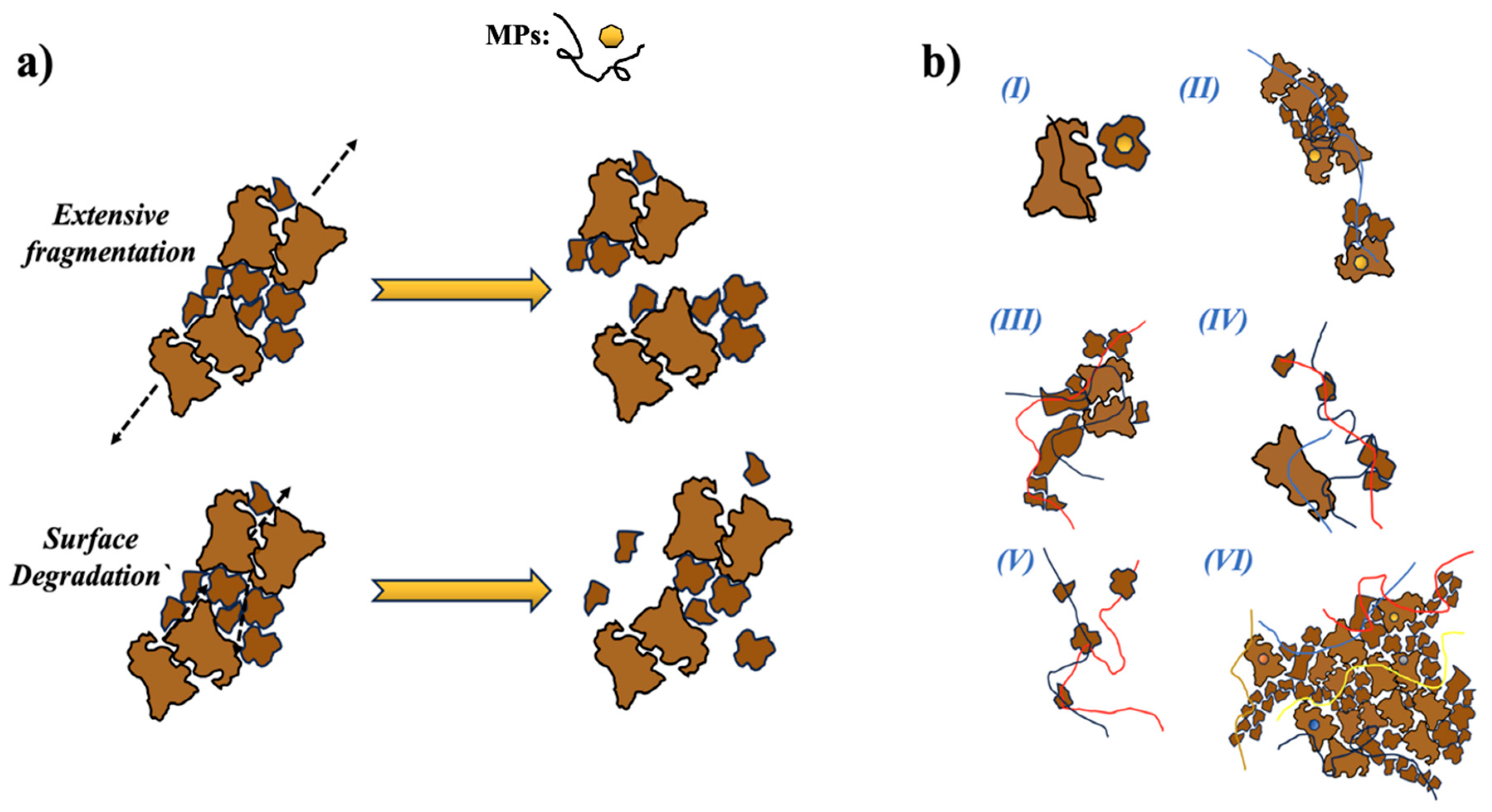
3.3. Floc Stability and MP Entrapment Mechanism
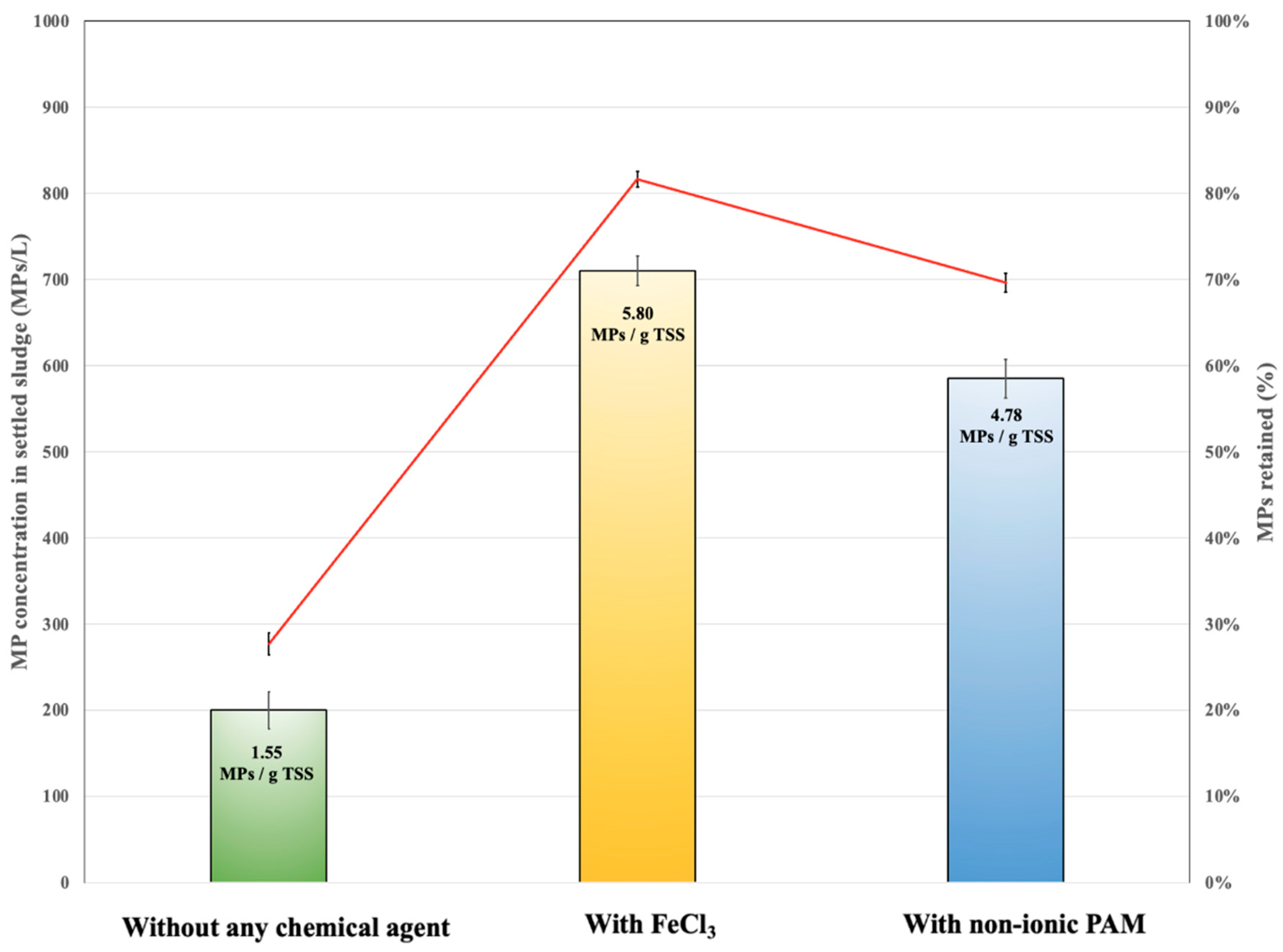
3.4. Effect of Adding Coagulant/Flocculant Agents on MP Retention
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CE | Cellulose |
| DAF | Dissolved air flotation |
| DM | Dry matter |
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| ER | Epoxy resim |
| EVA | Ethylene-vynil acetate |
| GLP | Good laboratory procedures |
| MPs | Microplastics |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PAA | Polyacrylic acid |
| PAC | Polyaluminum chloride |
| PAM | Polyacrylamide |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PEEU | Polyether ester urethane |
| PEI | Polyethylenimine |
| PEST | Polyester |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| PEUR | Polyether urethane |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PVC | Polyvinvyl chloride |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| QA/QC | Quality assurance/quality control |
| RA | Rayon |
| SS | Suspended solids |
| tCOD | Total chemical oxygen demand |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| TSS | Total suspended solids |
| WWTP | Wastewater treatment plant |
References
- Franco, A.A.; Martín-García, A.P.; Egea-Corbacho, A.; Arellano, J.M.; Albendín, G.; Rodríguez-Barroso, R.; Coello, M.D. Assessment and accumulation of microplastics in sewage sludge at wastewater treatment plants located in Cádiz, Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley-Nyang, D.; Memon, F.A.; Baquero, A.O.; Galloway, T. Variation in microplastic concentration, characteristics and distribution in sewage sludge & biosolids around the world. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, C.; Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Microplastics in Sewage Sludge: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63382–63415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Wastewater treatment approaches to remove microplastics. Polluting Textiles: The Problem with Microfibres. In Polluting Textiles; Routledge: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, D.; Solís-Balbín, C.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. A standard analytical approach and establishing criteria for microplastic concentrations in wastewater, drinking water and tap water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiá, P.; Sol, D.; Ardura, A.; Laca, A.; Borrell, Y.J.; Dopico, E.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Bioremediation as a promising strategy for microplastics removal in wastewater treatment plants. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Fate of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental dispersion with effluent and sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolsky, C.; Kelkar, V.; Driver, E.; Halden, R.U. Municipal sewage sludge as a source of microplastics in the environment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 14, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, P.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Corradini, F.; Geissen, V. Sewage sludge application as a vehicle for microplastics in eastern Spanish agricultural soils. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.Y.; Sun, Q.; Xia, S.Y.; Tong, D.; Ni, H.G. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and their contributions to surface water and farmland pollution in China. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Fatemi, S.S.; Talebi, P.; Dalvand, A. Investigating the efficiency of coagulation and flocculation process in wastewater treatment of paper and cardboard recycling industry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 5860–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Ge, W.; Li, W.; Yuan, H. Coagulation-flocculation performance and floc properties for microplastics removal by magnesium hydroxide and PAM. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliwan, T.; Pungrasmi, W.; Lohwacharin, J. Effects of microplastic accumulation on floc characteristics and fouling behavior in a membrane bioreactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Ren, S.Y.; Ni, H.G. Incidence of microplastics in personal care products: An appreciable part of plastic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, Y. A comprehensive study on the performance and mechanism of microplastics removal by enhanced coagulation methods. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Bueno, Y.; Castillo-Suárez, L.A.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Garduño-Pineda, L.; Alanis, C.; Natividad, R. Denim washing wastewater treatment by coupling coagulation–flocculation/Fe-garnet filtration: Life cycle assessment and the fertilization with the sludge. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 6109–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Approaching the environmental problem of microplastics: Importance of WWTP treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Lu, F.H.; Ni, H.G. Microplastic-water partitioning of two states halogenated PAHs: Solute and sol. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarer, S. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Sources, properties, removal efficiency, removal mechanisms, and interactions with pollutants. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 685–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, M.; Farner, J.M.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Understanding and improving microplastic removal during water treatment: Impact of coagulation and flocculation. Environ. Sci Technol. 2020, 54, 8719–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.T.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Chung, J.; Kim, E.J. Microplastic removal in conventional drinking water treatment processes: Performance, mechanism, and potential risk. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Hidayaturrahman, H.; Peera, S.G.; Lee, T.G. Elimination of microplastics at different stages in wastewater treatment plants. Water 2022, 14, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Li, H.; Fei, L.; Wei, B.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, H. The removal of microplastics from water by coagulation: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayaturrahman, H.; Lee, T.G. A study on characteristics of microplastic in wastewater of South Korea: Identification, quantification, and fate of microplastics during treatment process. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Ding, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Removal characteristics of microplastics by Fe-based coagulants during drinking water treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 78, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Li, L. Characteristics of microplastic removal via coagulation and ultrafiltration during drinking water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.M.; Malkoske, T.; Almuhtaram, H.; Andrews, R.C. Microplastic removal in batch and dynamic coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation systems is controlled by floc size. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA-AWWA-WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 21th Edition. New York, Total Solids Suspended, Method 2540 D, 2-55 a 2-59. 2005.
- Solís-Balbín, C.; Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Destruction and entrainment of microplastics in ozonation and wet oxidation processes. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 51, 103456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Shruti, V.C.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Elizalde-Martínez, I. Common laboratory reagents: Are they a double-edged sword in microplastics research? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shruti, V.C.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. Blanks and bias in microplastic research: Implications for future quality assurance. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 38, e00203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Effects of chronic exposure to different sizes and polymers of microplastics on the characteristics of activated sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Ji, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, B.; Qian, G.; Dai, X. Effects of chemical pretreatments on microplastic extraction in sewage sludge and their physicochemical characteristics. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.B.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) producing bacterial strains of municipal wastewater sludge: Isolation, molecular identification, EPS characterization and performance for sludge settling and dewatering. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2253–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Menéndez, C.; Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Interrelation between extracellular polymer substances (EPSs) and MPs in an MBR. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorowska-Kaufman, M.; Marciniak, W. Removal of microplastic particles during municipal wastewater treatment: A current review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Song, L.; Liu, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Dai, X. The effect of repeated energy inputs on the release profiles of extracellular organic substances in sewage sludge. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zeng, S.; Chen, Z.; Lv, M.; Tang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, J. Synergistic effect of organic matter-floc size-bound water and multifactorial quantitative model of optimal reagent demand in sewage sludge conditioning process prior to dewatering. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gies, E.A.; LeNoble, J.L.; Noël, M.; Etemadifar, A.; Bishay, F.; Hall, E.R.; Ross, P.S. Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongprasith, N.; Kittimethawong, C.; Lertluksanaporn, R.; Eamchotchawalit, T.; Kittipongvises, S.; Lohwacharin, J. IR microspectroscopic identification of microplastics in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18557–18564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, S.; Akita, K.; Ozaki, A.; Masumoto, K.; Okuda, T. Circulation of fibrous microplastic (microfiber) in sewage and sewage sludge treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadsuwan, K.; Babel, S. Microplastic contamination in a conventional wastewater treatment plant in Thailand. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardar, S.; Onay, T.T.; Demirel, B.; Kideys, A.E. Evaluation of microplastics removal efficiency at a wastewater treatment plant discharging to the Sea of Marmara. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shi, J.; Huang, H.; Xie, B. Distribution and removal characteristics of microplastics in different processes of the leachate treatment system. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Chen, L. Microplastics profile in sludge from a university wastewater treatment plant and the influence of chemical digestions on Nile red stained microplastics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Silveira, I.T.; Chua, A.; Leusch, F.D. An audit of microplastic abundance throughout three Australian wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, A.M.; O’Connell, B.; Healy, M.G.; O’Connor, I.; Officer, R.; Nash, R.; Morrison, L. Microplastics in sewage sludge: Effects of treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Caccamo, F.M.; Milanese, C. Microplastics in sewage sludge: A known but underrated pathway in wastewater treatment plants. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Ben-Haddad, M.; Abelouah, M.R.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Alla, A.A. Sludge drying and dewatering processes influence the abundance and characteristics of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, L.; Cizdziel, J.; Huang, Y. Research progress on microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: A holistic review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, I.; Yusoff, M.S.; Halim, H.B. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: A review of the occurrence, removal, impact on ecosystem, and abatement measures. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 104039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhao, H.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xia, T. Investigation of microplastics in sludge from five wastewater treatment plants in Nanjing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, D.; Shaikh, M.A.N.; Nawaz, T. Remediation of emerging contaminants by naturally derived adsorbents. New Trends Emerg. Environ. Contam. 2022, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Hadi, M.; Lin, C.; Nguyen, H.L.; Thai, V.B.; Hoang, H.G.; Tran, H.T. Microplastics in sewage sludge: Distribution, toxicity, identification methods, and engineered technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez-Manjón, A.; Martínez-Díez, R.; Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Rancaño, A.; Díaz, M. Long-term occurrence and fate of microplastics in WWTPs: A case study in southwest Europe. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, C.; Ruan, Z.; Bürger, R.; Hou, H. Research on floc structure and physical properties based on pipeline flocculation. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensi, E.; Alemany, E. A hindered settling velocity model related to the fractal dimension and activated sludge flocs characteristics: Application to a sludge with a previous fragmentation and flocculation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilén, B.M.; Jin, B.; Lant, P. Impacts of structural characteristics on activated sludge floc stability. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3632–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alioua, W.; Lapointe, M. Fiber-based super-bridging agents enable efficient contaminant removal via settling and screening: Impact on microplastics, textile fibers, and turbidity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Huang, Q.S.; Luo, T.Y.; Wu, R.L.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.J. Coagulation removal and photocatalytic degradation of microplastics in urban waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Zhou, C.; Wang, C. Internal interaction between chemically-pretreated polypropylene microplastics and floc growth during flocculation: Critical effect on floc properties and flocculation mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C.; Wu, R.; Lam, P.K. A preliminary screening of HBCD enantiomers transported by microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radityaningrum, A.D.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Soedjono, E.S.; Herumurti, W. Microplastic contamination in water supply and the removal efficiencies of the treatment plants: A case of Surabaya City, Indonesia. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


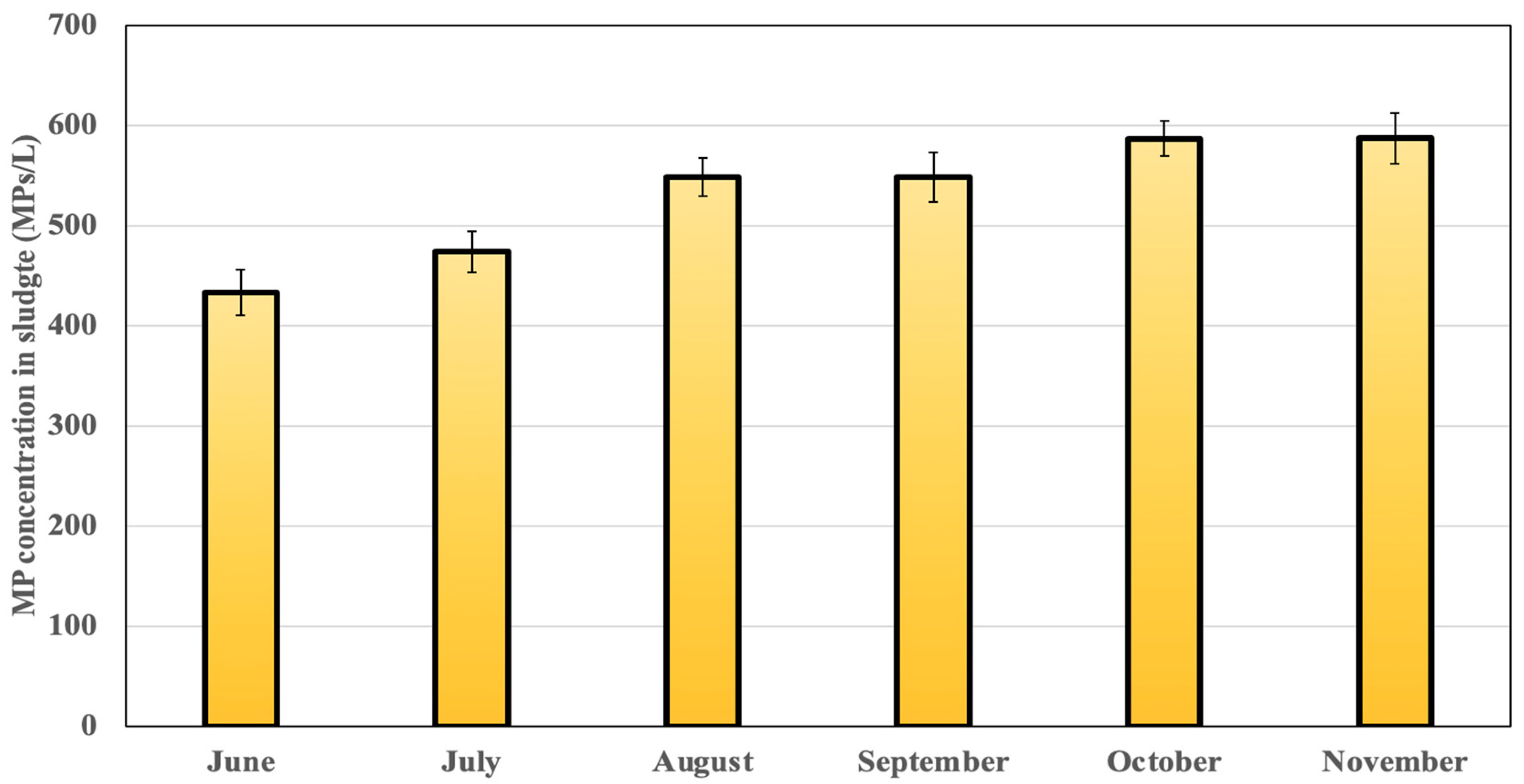

| Month (2023) | TSS (g/L) | pH | Moisture (%) | Dry Matter (g DM/kg Sludge) | tCOD (g O2/kg DM) | TOC (g C/kg DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| June | 32.6 ± 2.6 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 93.5 ± 1.7 | 31 ± 2 | 1050 ± 30 | 420 ± 3 |
| July | 32.6 ± 4.1 | 7.4 ± 0.2 | 94.9 ± 2.1 | 32 ± 3 | 1050 ± 30 | 415 ± 2 |
| August | 31.4 ± 3.2 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 95.2± 1.6 | 34 ± 3 | 1046 ± 27 | 416 ± 1 |
| September | 31.4 ± 4.4 | 7.3 ± 0.4 | 95.2 ± 2.3 | 34 ± 3 | 1041 ± 32 | 419 ± 2 |
| October | 33.9 ± 2.8 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 94.4 ± 1.2 | 33 ± 2 | 1055 ± 21 | 415 ± 1 |
| November | 33.9 ± 3.7 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 94.4 ± 2.2 | 33 ± 2 | 1045 ± 31 | 417 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casella, C.; Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Microplastic Retention in Secondary Sewage Sludge: Characterization and Influence of Solid Concentration. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073557
Casella C, Sol D, Laca A, Díaz M. Microplastic Retention in Secondary Sewage Sludge: Characterization and Influence of Solid Concentration. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073557
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasella, Claudio, Daniel Sol, Adriana Laca, and Mario Díaz. 2025. "Microplastic Retention in Secondary Sewage Sludge: Characterization and Influence of Solid Concentration" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073557
APA StyleCasella, C., Sol, D., Laca, A., & Díaz, M. (2025). Microplastic Retention in Secondary Sewage Sludge: Characterization and Influence of Solid Concentration. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3557. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073557






