Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of Low-Cost Seismic Isolators Exposed to Environmental Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Development
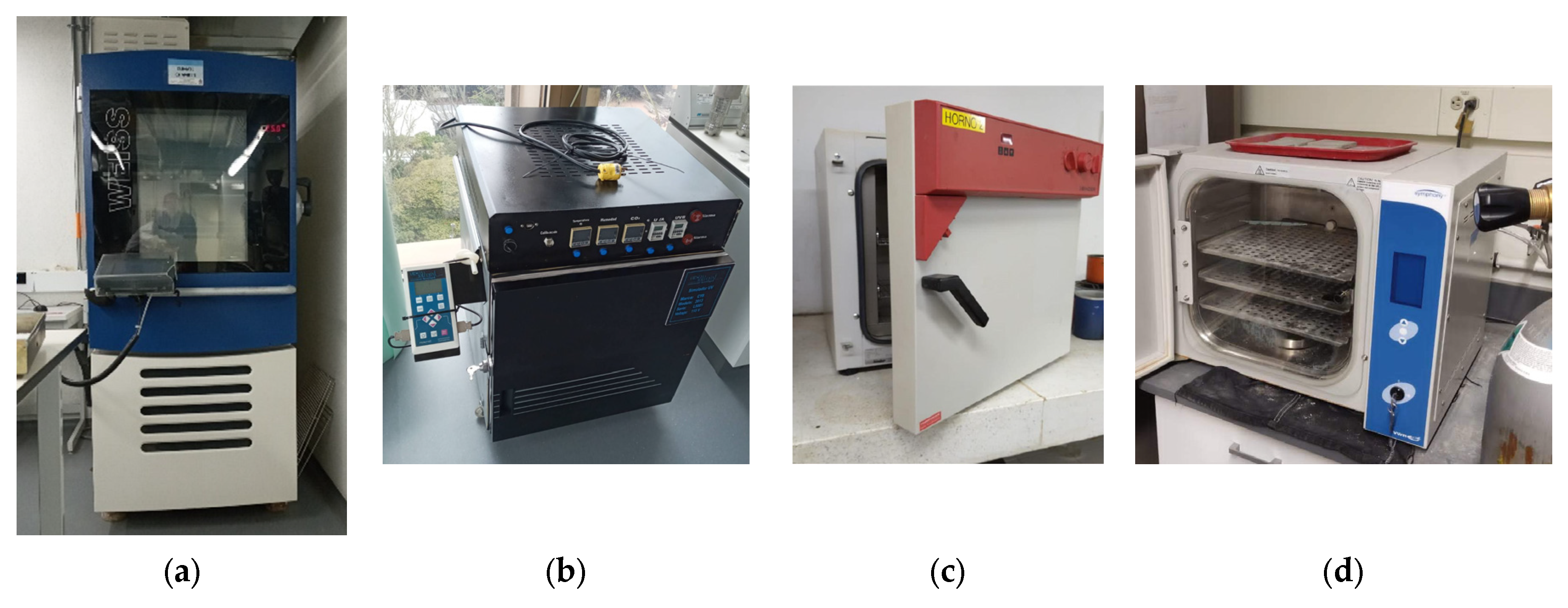
2.1. Exposure to Environmental Conditions
2.1.1. Relative Humidity (RH)
2.1.2. UV Radiation
2.1.3. Saltwater (SW)
2.1.4. Accelerated Carbonation (CO2)
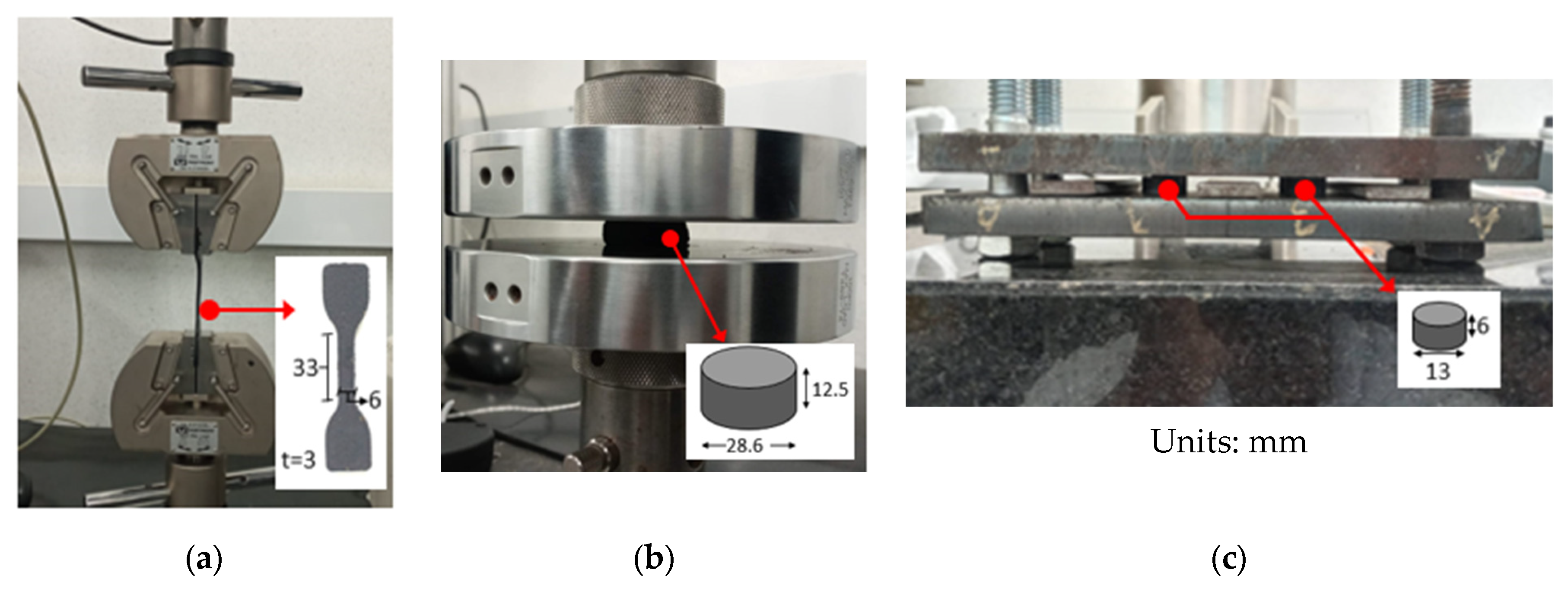
2.2. Mechanical Characterization of Specimens
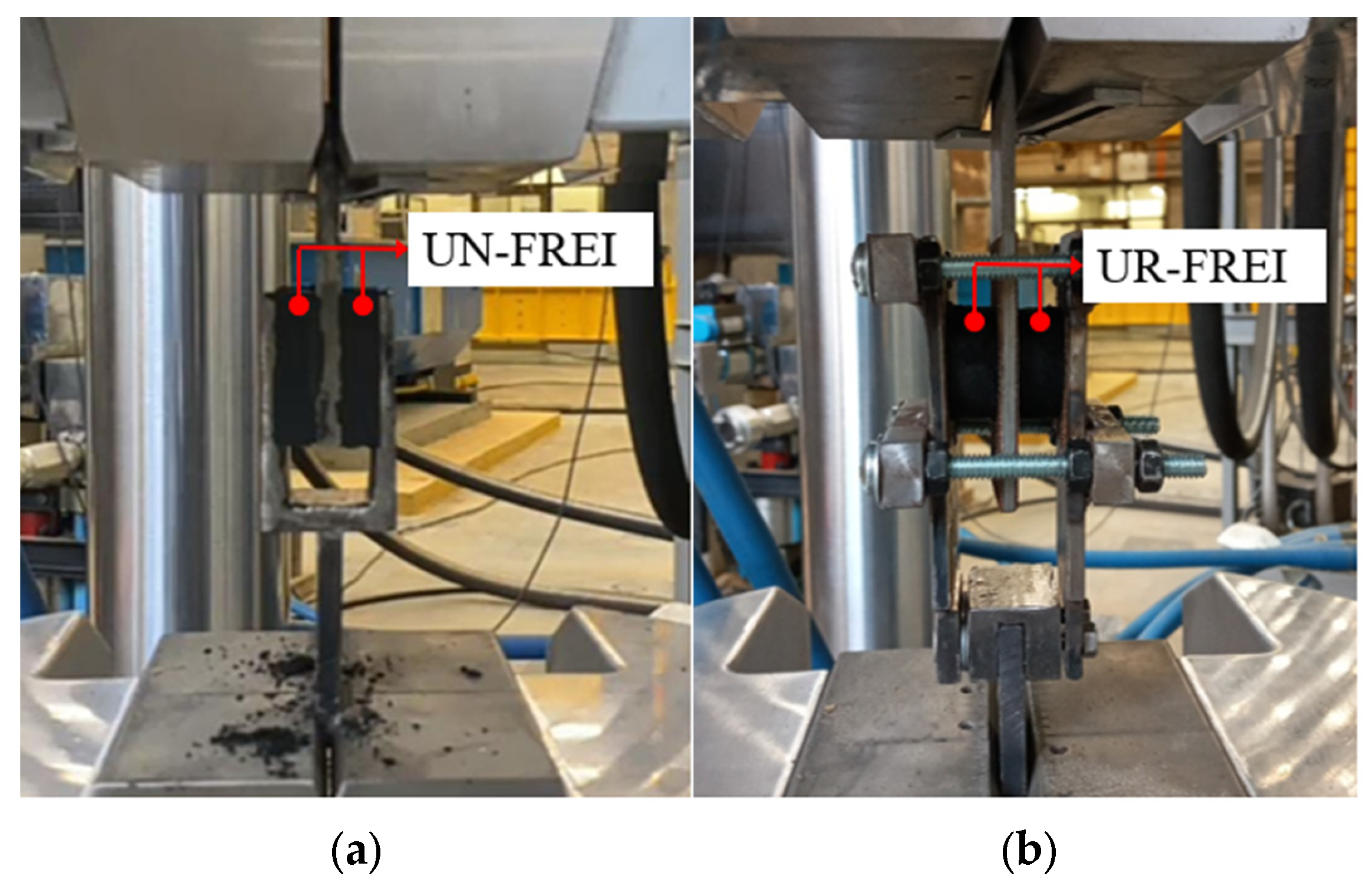
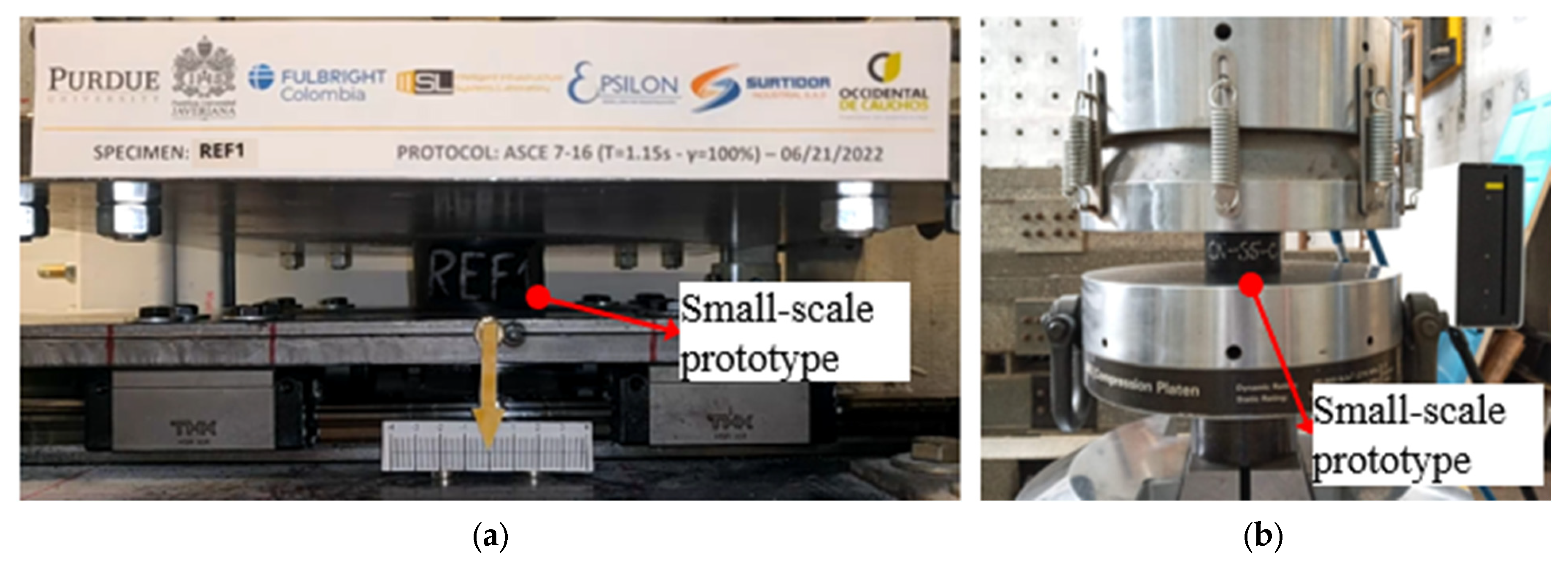
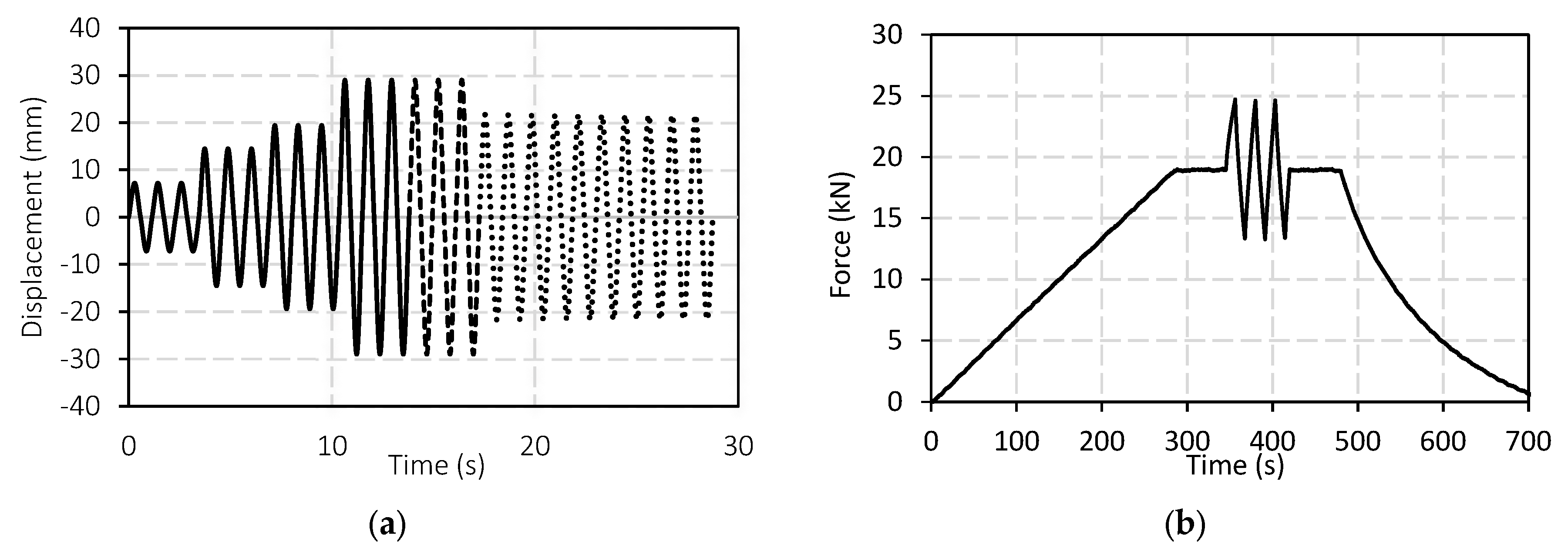
2.3. Mechanical Characterization of Small-Scale Prototypes
2.4. Characteristics of the Isolated Building
3. Results and Discussion
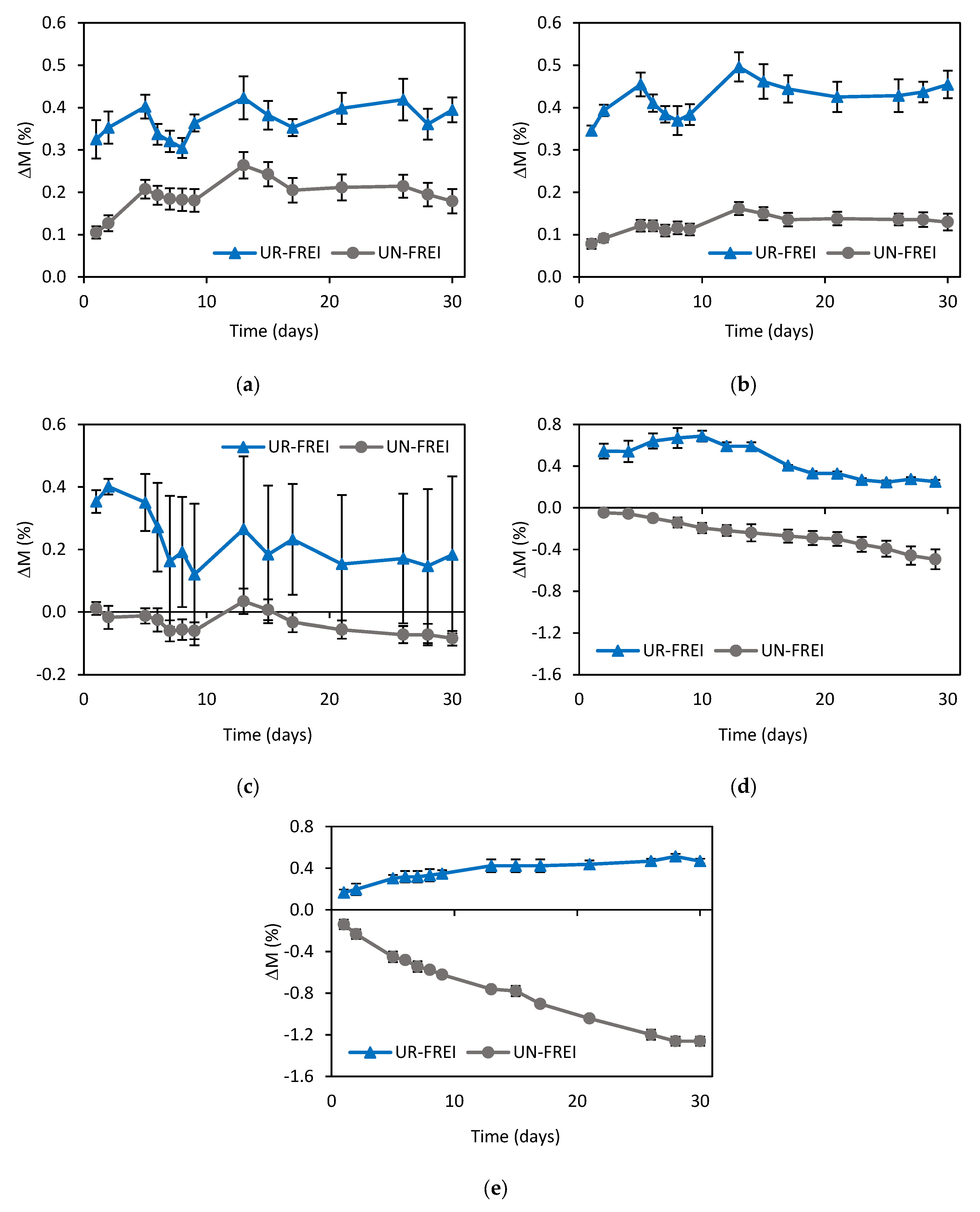
3.1. Mechanical Characterization of Specimens
3.1.1. Relative Humidity (RH)
3.1.2. UV Radiation
3.1.3. Saltwater (SW)
3.1.4. Summary of Specimen Results
3.2. Mechanical Characterization of Small-Scale Prototypes
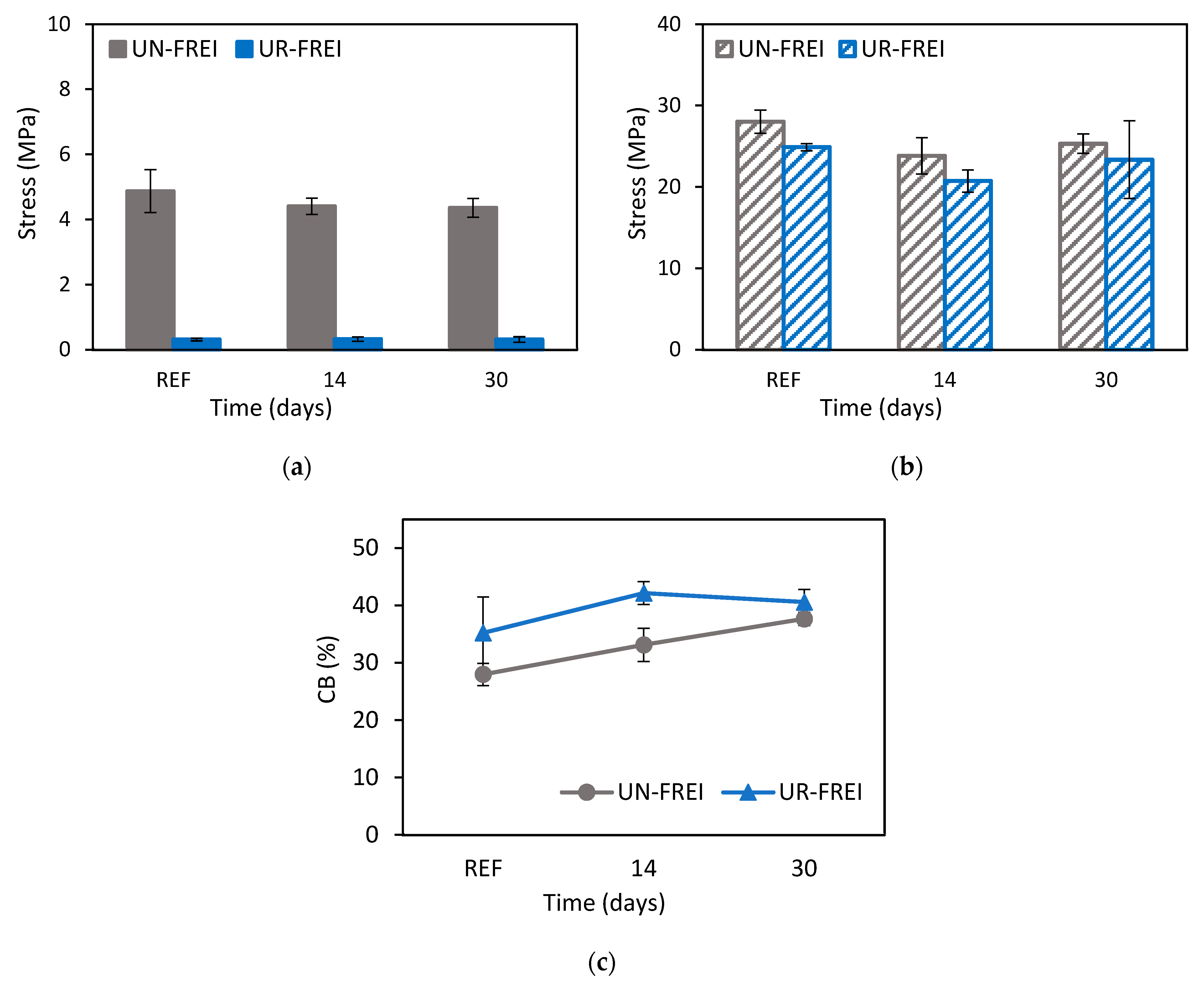
3.2.1. Shear Compression Test
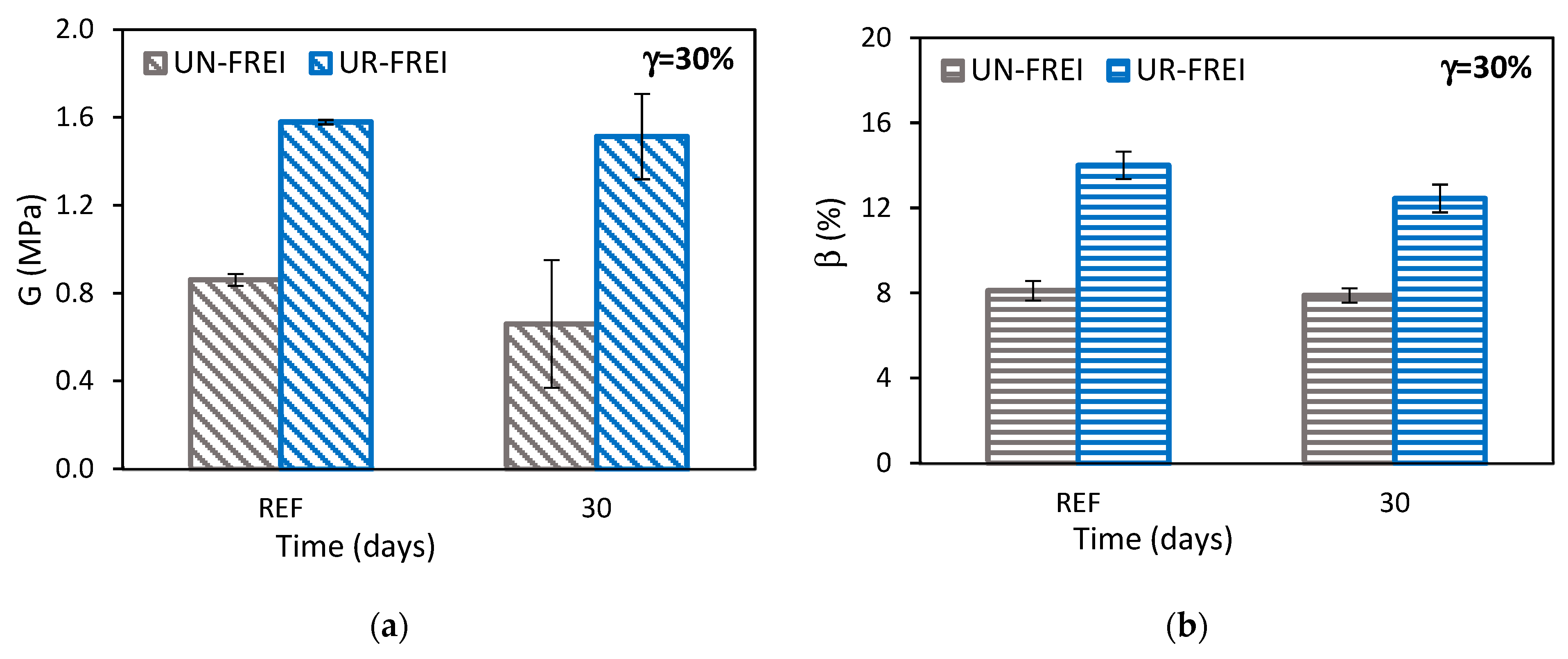
3.2.2. Cyclic Compression Test
3.2.3. Summary of Small-Scale Prototypes Results
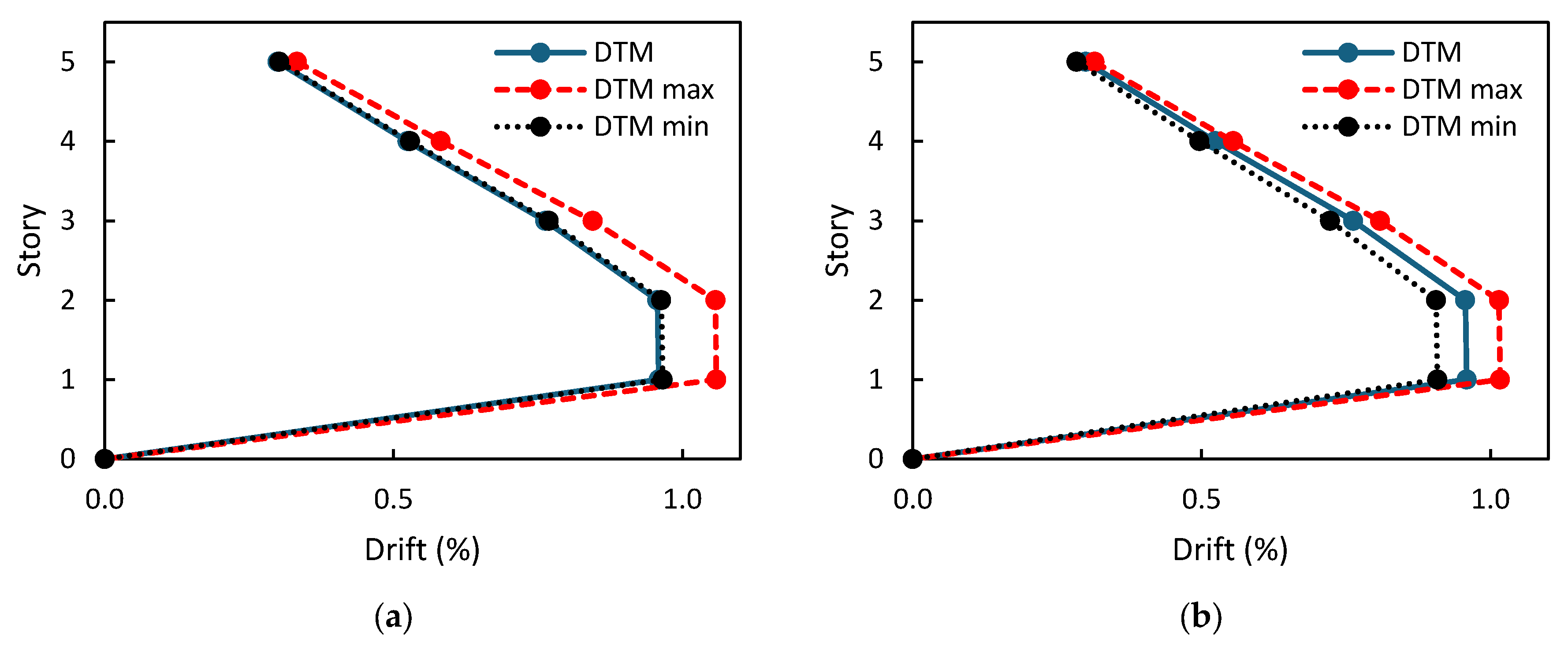
3.3. Evaluation of the Seismic Response of a Base-Isolated Structure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madera Sierra, I.E.; Losanno, D.; Strano, S.; Marulanda, J.; Thomson, P. Development and experimental behavior of HDR seismic isolators for low-rise residential buildings. Eng. Struct. 2019, 183, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenozhi, S.; Yu, W. Advances in modeling and vibration control of building structures. Annu. Rev. Control 2013, 37, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ali, A. The advancement of seismic isolation and energy dissipation mechanisms based on friction. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 146, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, D.; Longo, P.; Losanno, D.; Maugeri, N.; Ricciardi, G.; Vaiana, N. Full-scale experimental tests on unbonded fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators under bidirectional excitation. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2023, 44, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, D. Response of frames seismically protected with passive systems in near-field areas. Int. J. Struct. Eng. 2014, 5, 326–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losanno, D.; De Domenico, D.; Madera-Sierra, I.E. Experimental testing of full-scale fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators (FREIs) in unbounded configuration. Eng. Struct. 2022, 260, 114234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losanno, D.; Madera Sierra, I.E.; Spizzuoco, M.; Marulanda, J.; Thomson, P. Experimental assessment and analytical modeling of novel fiber-reinforced isolators in unbounded configuration. Compos. Struct. 2019, 212, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losanno, D.; Madera Sierra, I.E.; Spizzuoco, M.; Marulanda, J.; Thomson, P. Experimental performance of unbonded polyester and carbon fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators under bidirectional seismic excitation. Eng. Struct. 2020, 209, 110003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanikzai, M.H.; Elias, S.; Matsagar, V.A.; Jain, A.K. Seismic response control of base-isolated buildings using multiple tuned mass dampers. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2019, 28, e1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanikzai, M.H.; Elias, S.; Matsagar, V.A.; Jain, A.K. Seismic response control of base-isolated buildings using tuned mass damper. Aust. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 21, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toopchi-Nezhad, H.; Tait, M.J.; Drysdale, R.G. Bonded versus unbonded strip fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators: Finite element analysis. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engelen, N.C. Fiber-reinforced elastomeric isolators: A review. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 125, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habieb, A.B.; Valente, M.; Milani, G. Base seismic isolation of a historical masonry church using fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 120, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habieb, A.B.; Valente, M.; Milani, G. Implementation of a simple novel Abaqus user element to predict the behavior of unbonded fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators in macro-scale computations. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 2741–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera-Sierra, I.E. Desarrollo Tecnológico de un Aislador Sísmico de Bajo Costo Para Edificaciones Bajas [Technological Development of a Low-Cost Seismic Isolator for Low-Rise Buildings]. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad del Valle, Cali, Colombia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega Escobar, L.F. Prototipos de Aisladores Sísmicos Con Matriz de Caucho Reciclado Para la Mitigación de Riesgo en Estructuras [Prototypes of Seismic Isolators with Recycled Rubber Matrix for Risk Mitigation in Structures]. Master’s Thesis, Universidad del Valle, Cali, Colombia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- De Domenico, D.; Losanno, D.; Vaiana, N. Experimental tests and numerical modeling of full-scale unbonded fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators (UFREIs) under bidirectional excitation. Eng. Struct. 2023, 274, 115118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, L.-O. Corrosion of steel in concrete. In Developments in the Formulation and Reinforcement of Concrete; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Yu, K.; Zhong, G.; Chen, F.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y. Effects of temperature, humidity and CO2 concentration on carbonation of cement-based materials: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, M.H.; Alrashidi, R.S.; Mosavi, H.; Almarshoud, M.A.; Riding, K.A. Potential accelerated test methods for physical sulfate attack on concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Li, W.; Dong, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Yu, T. Durability deterioration of concrete under marine environment from material to structure: A critical review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B.; Zhang, K. Effects of saltwater intrusion and sea level rise on aging and corrosion rates of iron pipes in water distribution and wastewater collection systems in coastal areas. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Guermazi, N.; Elleuch, K.; Ayedi, H.F. Study of UV-aging of thermoplastic polyurethane material. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepens, M.; Gijsman, P. Photo-oxidative degradation of bisphenol A polycarbonate and its possible initiation processes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, T.; Bryant, P.; Kurusingal, V.; Colwell, J.M.; Laycock, B. Degradation and stabilization of polyurethane elastomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 211–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Itoh, Y.; Satoh, K. Effect of rubber bearing ageing on seismic response of base-isolated steel bridges. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Advances in Steel Structures, Shanghai, China, 13–15 June 2005; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.S.; Itoh, Y. Ageing Behaviour of Natural Rubber and High Damping Rubber Materials Used in Bridge Rubber Bearings. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2010, 13, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, H. Time-dependent seismic reliability of isolated bridges considering ageing deterioration of lead rubber bearings. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 18, 1526–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D573-04; Standard Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air Oven. Volume 4, Issue Reapproved; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Gu, H.S. Prediction of Aging Characteristics in Natural Rubber Bearings Used in Bridges. J. Bridge Eng. 2009, 14, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, G. Mechanical properties and seismic isolation behavior of scrap tire pads subjected to thermal-cold cycles in rural construction. Structures 2022, 40, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, A.; Spizzuoco, M.; Serino, G.; Della Corte, G.; Maddaloni, G. Shaking table investigation of a novel, low-cost, base isolation technology using recycled rubber. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2015, 22, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizzuoco, M.; Calabrese, A.; Serino, G. Innovative low-cost recycled rubber–fiber reinforced isolator: Experimental tests and Finite Element Analyses. Eng. Struct. 2014, 76, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habieb, A.B.; Milani, F.; Milani, G.; Cerchiaro, R. Rubber compounds made of reactivated EPDM for fiber-reinforced elastomeric isolators: An experimental study. Iran. Polym. J. 2020, 29, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habieb, A.B.; Milani, G.; Cerchiaro, R.; Quaglini, V.; Milani, F. Numerical study on rubber compounds made of reactivated ethylene propylene diene monomer for fiber reinforced elastomeric isolators. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losanno, D.; Palumbo, F.; Calabrese, A.; Barrasso, T.; Vaiana, N. Preliminary Investigation of Aging Effects on Recycled Rubber Fiber Reinforced Bearings (RR-FRBs). J. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 26, 5407–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragni, L.; Micozzi, F.; Gioiella, L.; Castellano, M.G.; Infanti, S.; Dall’Asta, A. λ-Factors for the Upper and Lower Bound Analyses of Base-Isolated Structures: Historical Review of Code Provisions for Elastomeric Bearings. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, A.; Losanno, D.; Barjani, A.; Spizzuoco, M.; Strano, S. Effects of the long-term aging of glass-fiber reinforced bearings (FRBs) on the seismic response of a base-isolated residential building. Eng. Struct. 2020, 221, 110735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, L.F.; Herazo, M.Z.; Ortiz, A.R.; Thomson, P.; Marulanda, J. Performance of prototype seismic isolators reinforced with fiber and a recycled rubber tire matrix. Eng. Struct. 2023, 278, 115422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, A.; Kärhä, P.; Tanskanen, A.; Kaunismaa, M.; Koskela, T.; Kaurola, J.; Ture, T.; Syrjälä, S. Characterizing a UV chamber with mercury lamps for assessment of comparability to natural UV conditions. Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambier, S.M.; Frankel, G.S. Coating and Interface Degradation of Coated steel, Part 2: Accelerated Laboratory Tests. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 136, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Tokuta, Y.; Oishi, A.; Kuriyama, T.; Kunioka, M. Weatherability of Polypropylene by Accelerated Weathering Tests and Outdoor Exposure Tests in Japan. J. Polym. 2016, 2016, 6539567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gac, P.Y.; Le Saux, V.; Paris, M.; Marco, Y. Ageing mechanism and mechanical degradation behaviour of polychloroprene rubber in a marine environment: Comparison of accelerated ageing and long term exposure. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auroy, M.; Poyet, S.; Le Bescop, P.; Torrenti, J.M.; Charpentier, T.; Moskura, M.; Bourbon, X. Comparison between natural and accelerated carbonation (3% CO2): Impact on mineralogy, microstructure, water retention and cracking. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 109, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ju, X.; Wu, L.; Guo, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. Carbonation depth model for loaded reinforced concrete (RC) beams under time-dependent relative humidity conditions. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 65, 105618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Bishnoi, S. Carbonation resistance of cements containing supplementary cementitious materials and its relation to various parameters of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heede, P.; Thiel, C.; De Belie, N. Natural and accelerated carbonation behaviour of high-volume fly ash (HVFA) mortar: Effects on internal moisture, microstructure and carbonated phase proportioning. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 113, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D412-16; Standard Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 1–14. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D575-91; Standard Test Methods for Rubber Properties in Compression. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D395-18; Standard Test Methods for Rubber Property—Residual compression. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- ATC-17; ATC-17-2 Seminar on Response Modification Performance-Based Seismic Design. A.T.C.: Carson, CA, USA, 2002.
- ASTM D4014-03; Standard Specification for Plain and Steel-Laminated Elastomeric Bearings for Bridges. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- AIS. Reglamento Colombiano de Construcción Sismo Resistente, NSR 10; Asociación Colombiana de Ingeniería Sísmica (AIS): Bogotá, Colombia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- FEMA 450. Recommended Provisions for Seismic Regulations for New Buildings and Other Structures (FEMA 450); Building Seismic Safety Council (BSSC) of the National Institute of Building Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ASCE. Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, J.E.; Coyle, D.J. Hydrolysis kinetics of condensation polymers under humidity aging conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Gu, H.S. Effect of ultraviolet irradiation on surface rubber used in bridge bearing. J. Struct. Eng. 2007, 53A, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, F. Experimental research on the time-varying law of performance for natural rubber laminated bearings subjected to seawater dry-wet cycles. Eng. Struct. 2019, 195, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmo, A.; Mualla, I.H.; Hasan, H.T. The Behavior of Multi-Story Buildings Seismically Isolated System Hybrid Isolation (Friction, Rubber and with the Addition of Rotational Friction Dampers). Open J. Earthq. Res. 2015, 4, 52406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


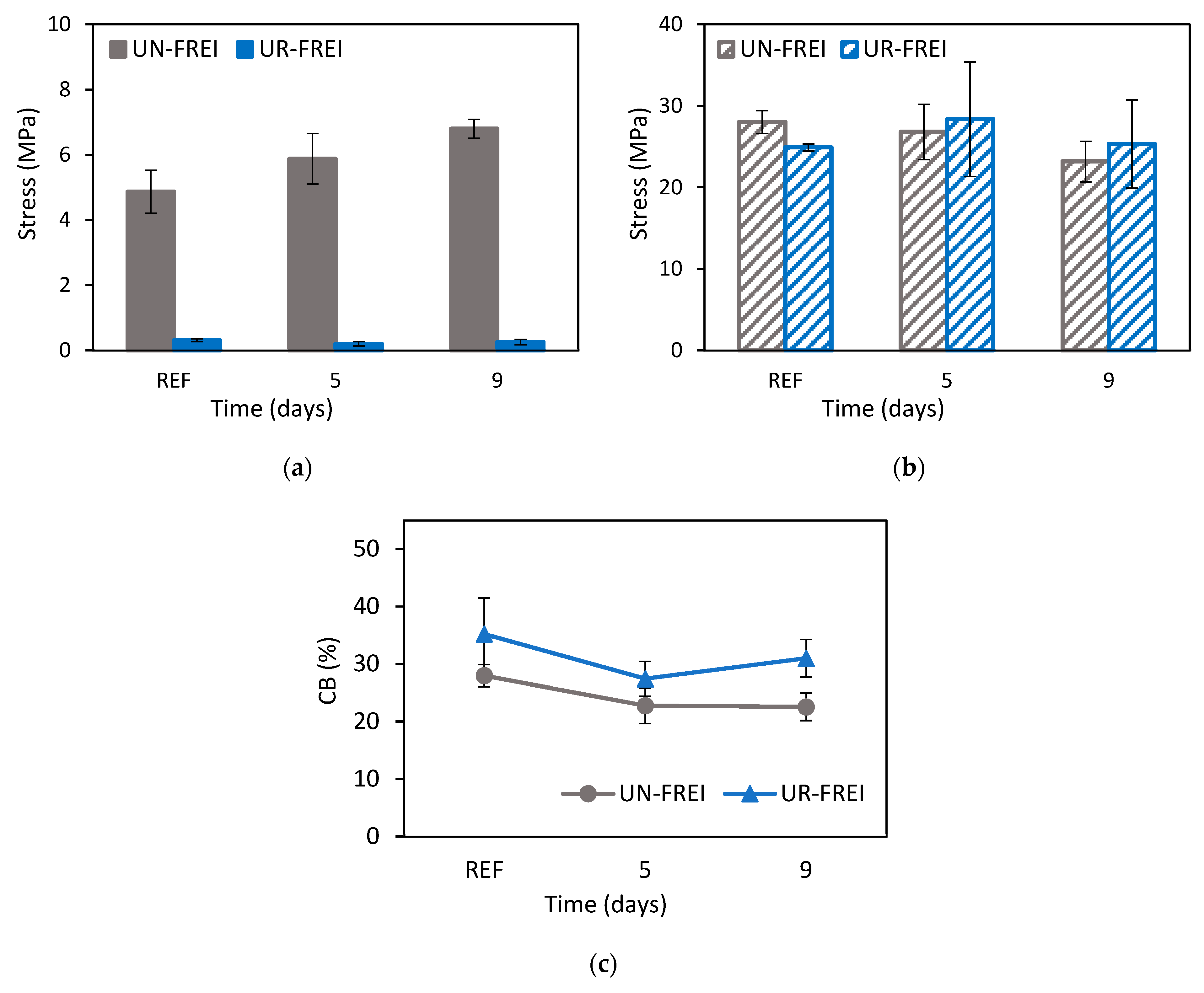
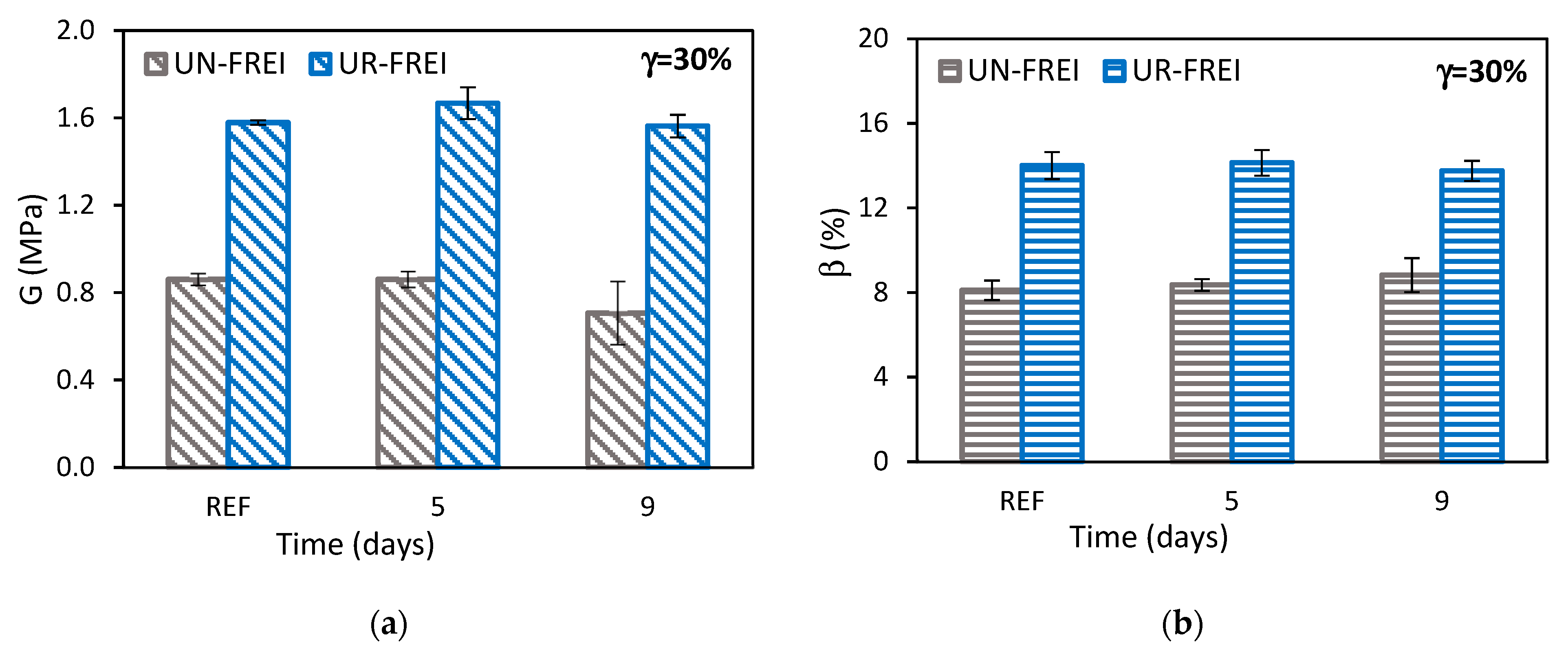
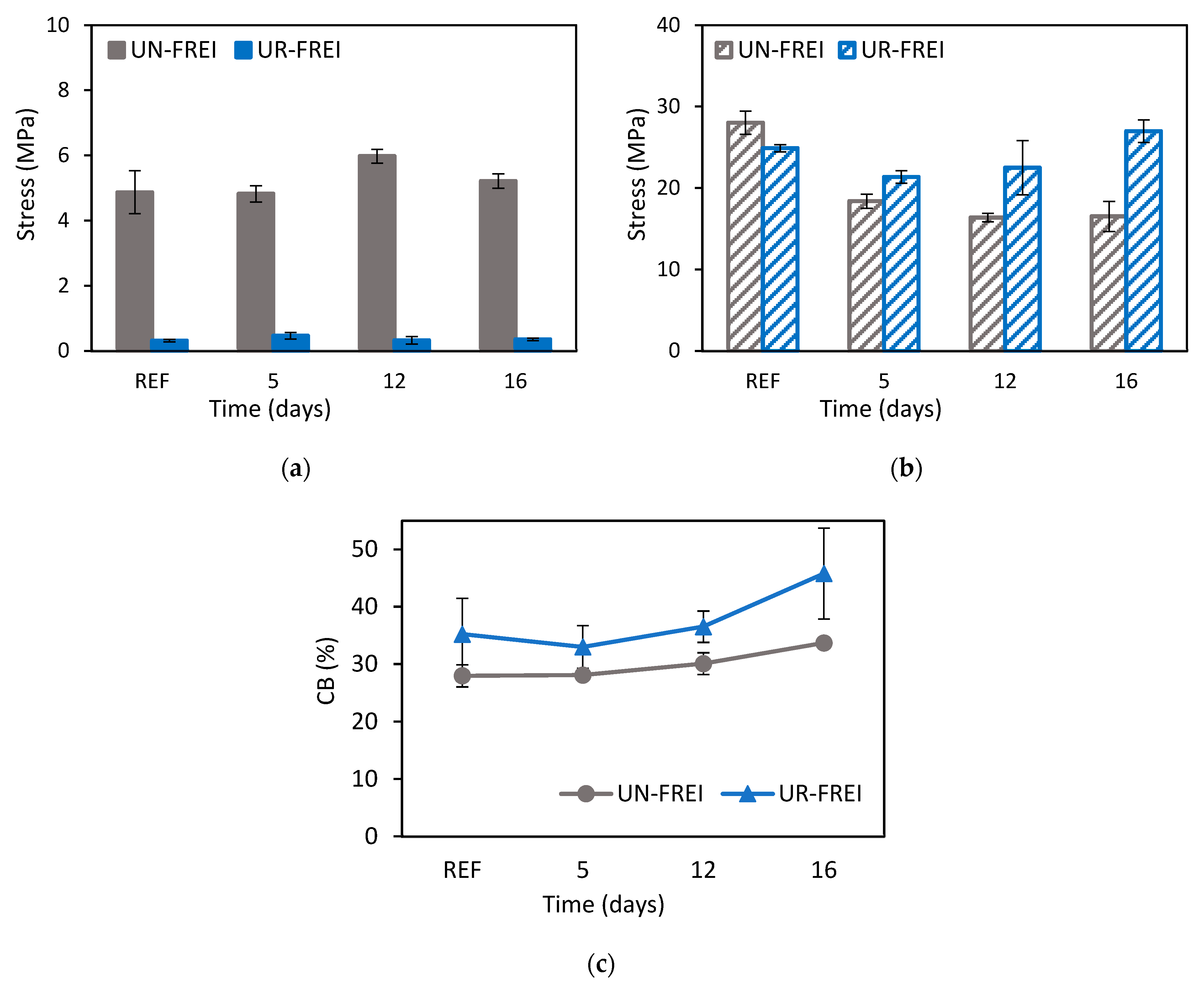
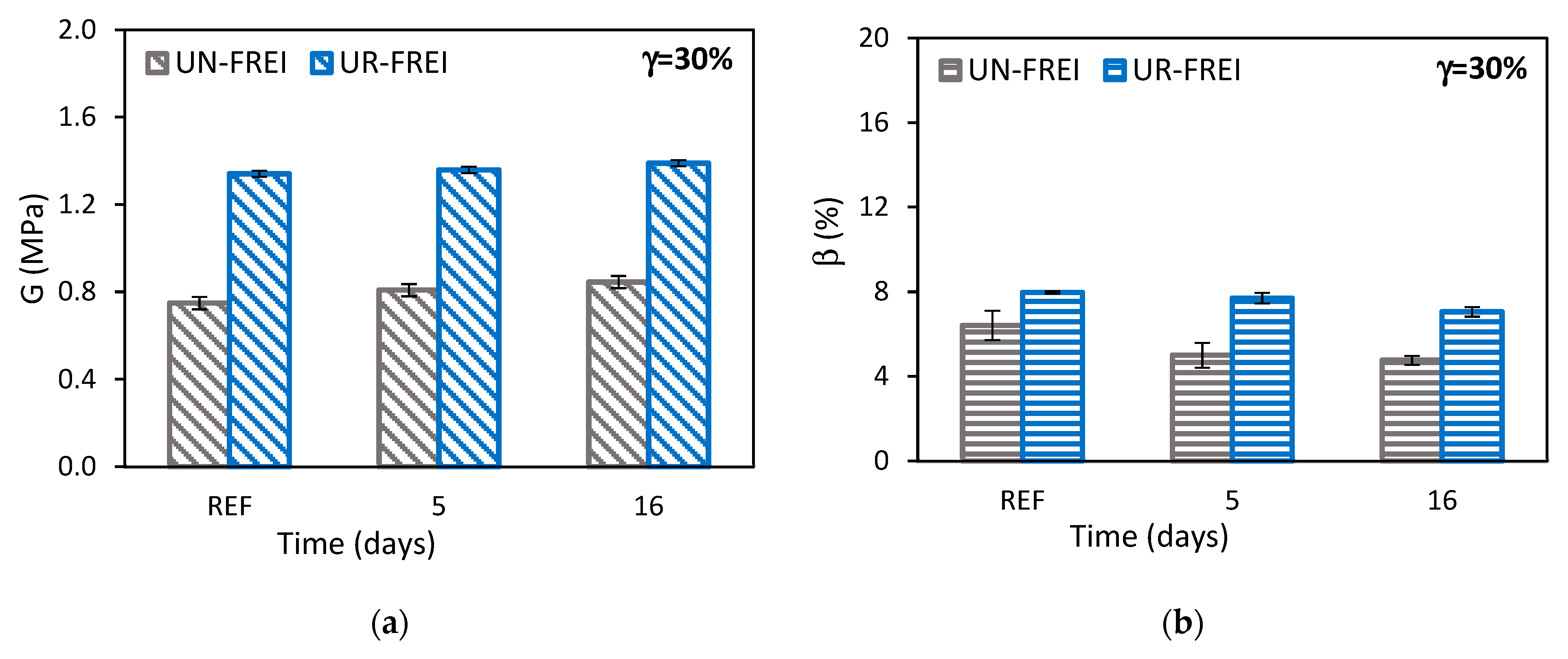



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Concrete (MPa) (f’c) | 24 |
| Steel (MPa) (fy) | 420 |
| Columns | 45 × 45 cm |
| Beams | 35 × 40 cm, 40 × 50 cm |
| Number of stories | 5 |
| Story height (m) | 3 |
| Number of isolators | 20 |
| Dead load (kN/m2) | 5.0 |
| Live load (kN/m2) | 1.8 |
| Weight of structure (kN) | 19,760 |
| Design period | 2.5 s |
| Horizontal damping (γ = 160%) | 6.10% |
| Property | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness of rubber layers (mm) | tr | 9.0 |
| Number of layers | n | 24 |
| Polyester fiber thickness (mm) | tf | 1.1 |
| Total thickness of rubber (mm) | Hr | 216.0 |
| Total thickness of isolator (mm) | H | 241.3 |
| Isolator diameter (mm) | D | 750 |
| Total maximum displacement (m) | DTM | 0.345 |
| Period isolated structure (s) | TM | 2.42 |
| Fiber density (kg/m3) | γfibra | 1000 |
| Rubber density (kg/m3) | γcaucho | 1200 |
| Isolator mass (kg) | Miso | 125 |
| Isolator weight (N) | Wiso | 1233 |
| Vertical displacement characteristics U1 | ||
| Effective stiffness (N/m) | Kv | 146,303,417.64 |
| Effective damping (N⋅s/m) | Cv | 76,525.09 |
| Horizontal displacement characteristics U2 = U3 | ||
| Effective stiffness (N/m) | Keff | 850,121.57 |
| Effective damping (N⋅s/m) | Ch | 41,266.82 |
| Elastic stiffness (N/m) | Ke | 2,151,572.72 |
| Yield stress (N) | fy | 46,473.97 |
| Post-yield stiffness ratio | Kp/Ke | 0.35 |
| Range (%) | State | * Increase | * Decrease | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | Slight | ~↑ | ~↓ |
| 5 | 10 | Moderate | ↑ | ↓ |
| 10 | 20 | Severe | ↑↑ | ↓↓ |
| 20 | 50 | Critical | ↑↑↑ | ↓↓↓ |
| UN-FREI | UR-FREI | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Exposure | T | C | R.C. | G | β | T | C | R.C. | G | β |
| RH | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↑↑↑ | ↓↓↓ | ~↓ | ~↓ | ↓↓ | ↑↑ | ~↓ | ↓↓ |
| UV | ↑↑↑ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↑ | ↑↑↑ | ↑↑ | ↓↓↓ | ↑ | ~↓ |
| SW | ↑↑↑ | ↓↓↓ | ↑↑↑ | ↑↑ | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↑↑↑ | ~↑ | ↓↓ |
| UN-FREI | UR-FREI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Exposure | Kh | β | C | Kh | β | C |
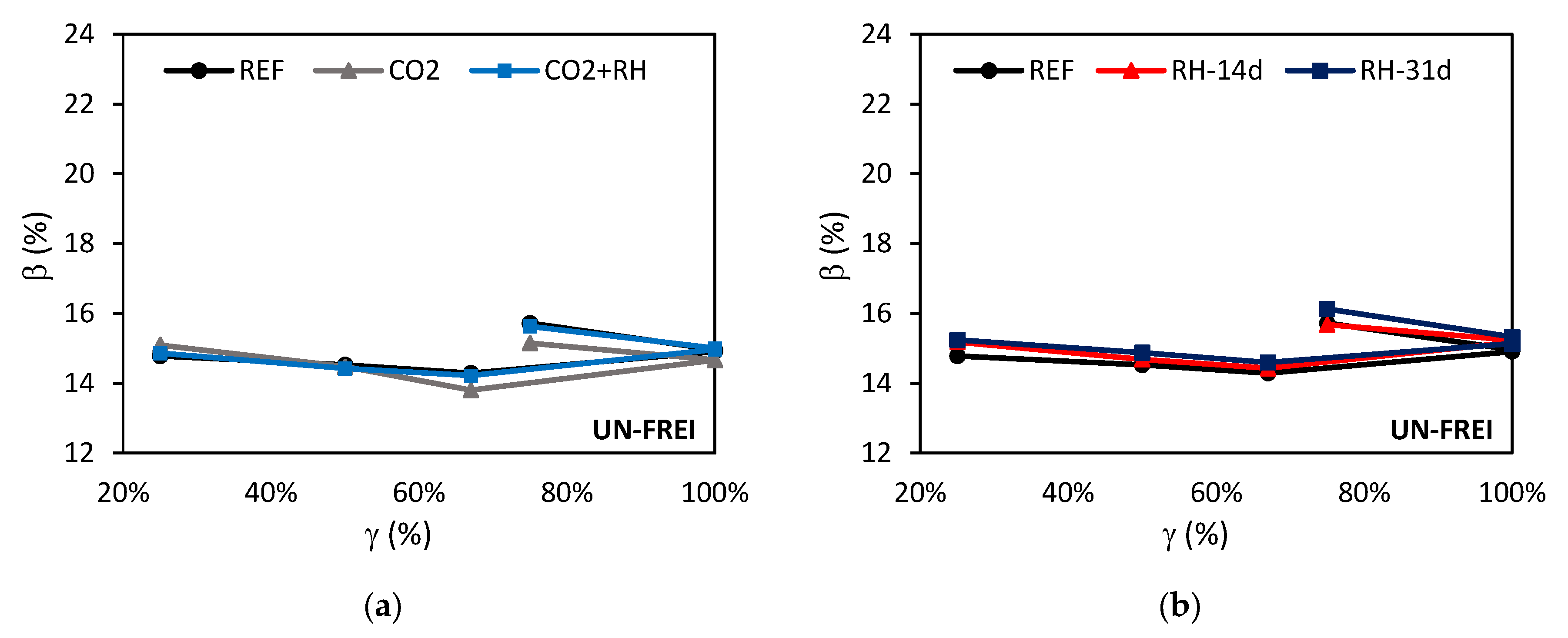
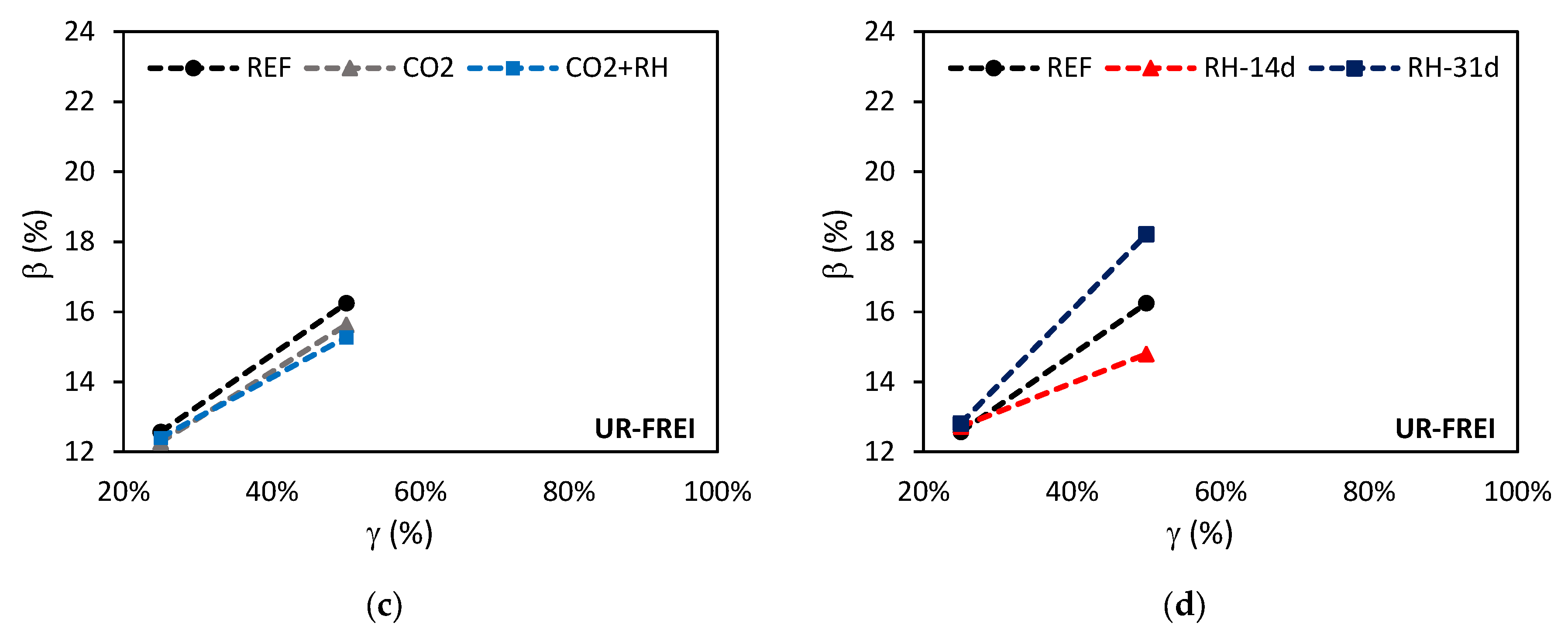
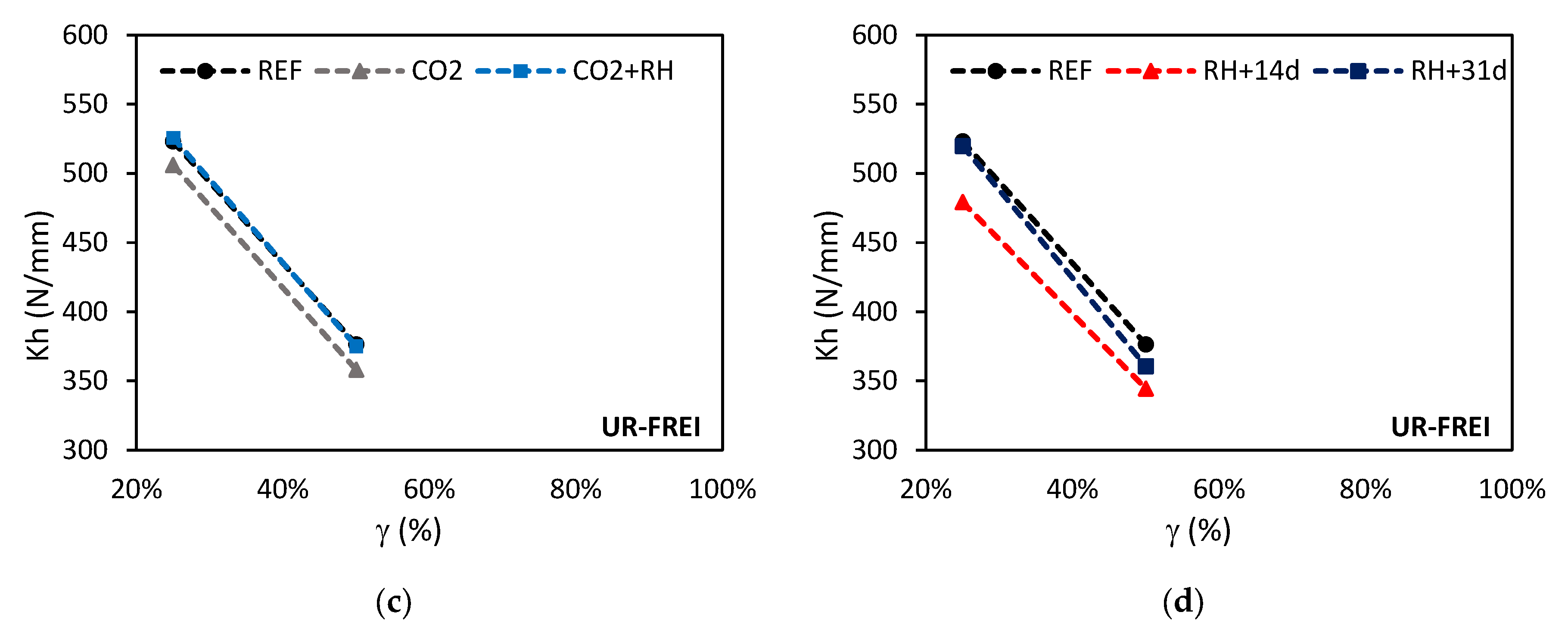
| CO2 | ↑ | ~↓ | ~↓ | ~↓ | ||
| CO2+RH | ↑ | ~↓ | ~↑ | ↓ | ||
| RH-14d | ~↑ | ~↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ||
| RH-31d | ↑↑ | ~↑ | ~↓ | ↑↑ | ||
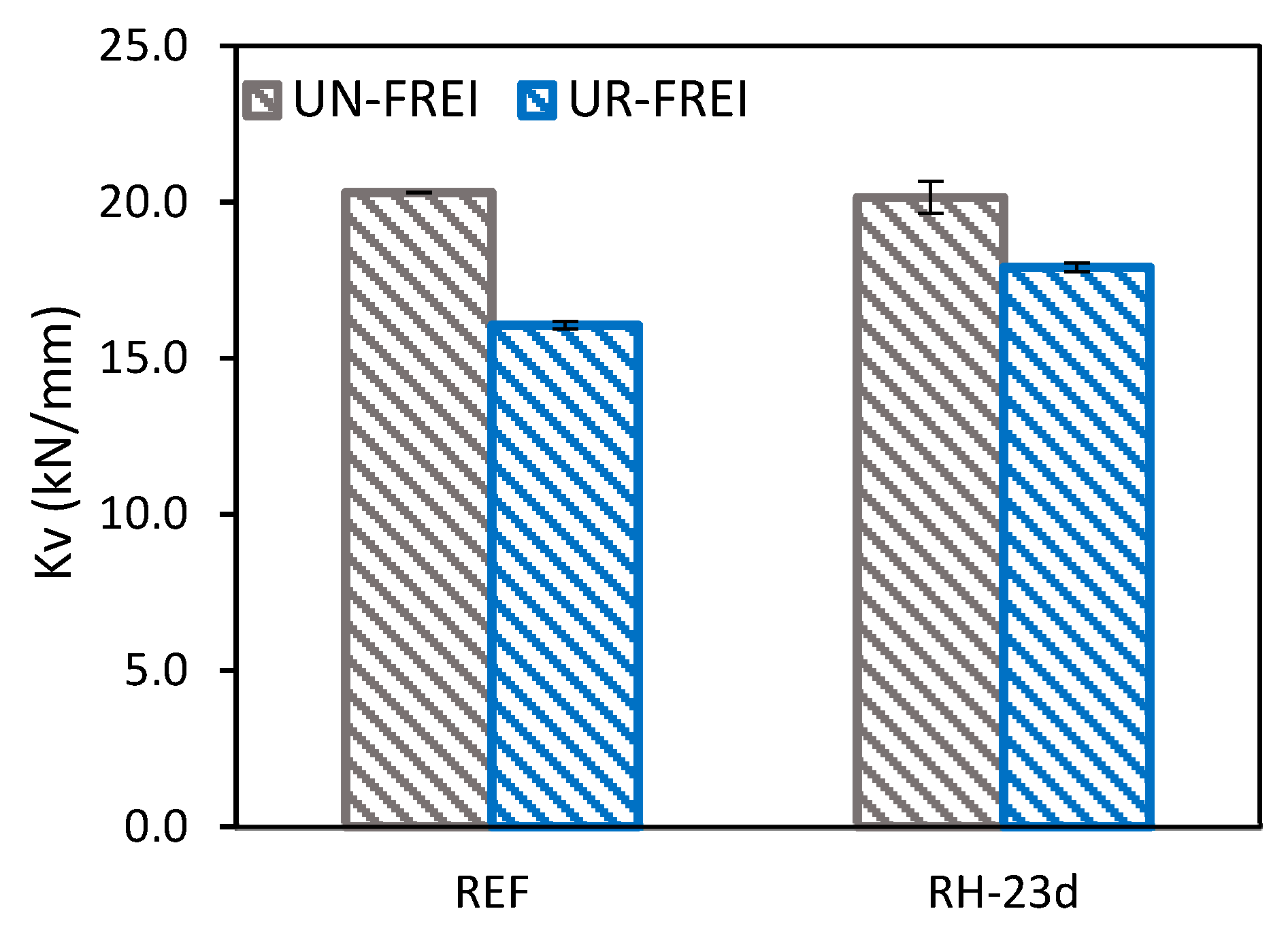
| RH-23d | ~↓ | ↑↑ | ||||
| Maximum Values | Minimum Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Factor for aging effects and environmental conditions | ||
| Factor for heating, rate of loading, and scragging. | ||
| Factor or permissible manufacturing variation |
| UN-FREI | UR-FREI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ(ae,max) | λ(ae,min) | λ(ae,max) | λ(ae,min) | ||||
| Kh | 1.07 | Kh | 1.00 | Kh | 1.00 | Kh | 0.94 |
| β | 1.03 | β | 0.98 | β | 1.12 | β | 0.94 |
| Kv | 1.00 | Kv | 0.99 | Kv | 1.11 | Kv | 1.00 |
| Period | UN-FREI | UR-FREI |
|---|---|---|
| T DTM (s) | 2.42 | 2.42 |
| T DTM min (s) | 2.43 | 2.50 |
| T DTM max (s) | 2.34 | 2.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lemos-Micolta, E.D.; Velasco-Cuervo, I.C.; Madera-Sierra, I.E.; Rojas-Manzano, M.A.; Cundumí, O.; Patino, E.; Salmeron-Becerra, M.; Lopez-Arias, M.; Dyke, S.J.; Velay-Lizancos, M. Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of Low-Cost Seismic Isolators Exposed to Environmental Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073467
Lemos-Micolta ED, Velasco-Cuervo IC, Madera-Sierra IE, Rojas-Manzano MA, Cundumí O, Patino E, Salmeron-Becerra M, Lopez-Arias M, Dyke SJ, Velay-Lizancos M. Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of Low-Cost Seismic Isolators Exposed to Environmental Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073467
Chicago/Turabian StyleLemos-Micolta, Erika D., Isabel C. Velasco-Cuervo, Ingrid E. Madera-Sierra, Manuel Alejandro Rojas-Manzano, Orlando Cundumí, Edwin Patino, Manuel Salmeron-Becerra, Marina Lopez-Arias, Shirley J. Dyke, and Mirian Velay-Lizancos. 2025. "Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of Low-Cost Seismic Isolators Exposed to Environmental Conditions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073467
APA StyleLemos-Micolta, E. D., Velasco-Cuervo, I. C., Madera-Sierra, I. E., Rojas-Manzano, M. A., Cundumí, O., Patino, E., Salmeron-Becerra, M., Lopez-Arias, M., Dyke, S. J., & Velay-Lizancos, M. (2025). Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of Low-Cost Seismic Isolators Exposed to Environmental Conditions. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073467





