Abstract
The sustainable management of biowaste, mainly food and pruning waste, is currently a challenge due to the increase in its production. The CaMPuSTAJE program, which has been implemented on the campus of the Public University of Navarre (UPNA) since 2019, is an excellent example of how the institution is addressing its strategic interests in sustainable waste management. The principal aim of this program is to manage the biowastes generated by the campus canteens through a simple community composting facility, involving UPNA students and graduates. This program aims to promote experiential learning and applied research in sustainability and circular economy, managing their own waste in a circular and local way. Thus, four composting sets of the CaMPuSTAJE program were evaluated by monitoring the process and the main chemical properties of the composting samples. Also, final composts were fully characterized to ensure the process reproducibility and efficiency and the absence of any hazard in the end-products. The final composts showed a significant agronomic quality, had low content of potentially toxic elements, and were free from phytotoxicity, thus being able to be reintroduced as an organic amendment at the university campus itself.
1. Introduction
Waste generation at a global level is one of the challenges of our constantly growing society [1]. In particular, the sustainable management of biowaste, which mainly includes food and pruning organic wastes, implies a challenge due to their increasing production in recent decades, but also an opportunity to transform them into a resource, also avoiding impacts on the environment [2]. This waste stream, with a high potential to become an added-value resource, plays a key role in the path towards a more circular economy, as it can be used to obtain high-value organic fertilizers such as compost [3]. Composting as a method to treat and valorize organic waste is based on the aerobic decomposition of the organic matter contained in the waste, in order to obtain a final material (compost), with maturity, stability, and humification properties; with fertilizing capacity; and without pathogens. This allows its use in agriculture as a growing medium, as a substitute for chemical fertilizers, without posing hazards to human health or the environment [4,5]. Thus, the European Union, through Directive (EU) 2018/851, establishes the separate collection and treatment of municipal organic waste, which includes, among other materials, biodegradable organic waste from food and kitchen waste from households, restaurants, catering establishments, and retail premises. Furthermore, it stipulates that the preparation for re-use and recycling of municipal waste should be augmented to a minimum of 55% by weight by 2025, progressively increasing this amount up to 65% by weight by 2035 [6]. Thus, traditionally, large-scale municipal solid waste management has been based on landfilling [7] and management in centralized facilities, where the environmental costs associated with transport and the long distances over which waste is transported have made waste management a serious issue [8]. Moreover, this type of large-scale composting facilities requires large areas and contributes to increased greenhouse gas emissions [9]. However, in recent decades, new environmentally friendly management models have emerged as decentralized composting models, such as community composting [3,10,11]. Different studies on this type of decentralized composting model have been conducted around the world, particularly in universities, municipal markets, and groups of households [12,13,14,15,16]. In this regard, in 2019, the campus of the Public University of Navarre (UPNA) launched the CaMPuSTAJE program, which aims to manage the biowaste generated in campus canteens through a simple community composting facility. In addition, the CaMPuSTAJE program is an excellent example of how the institution can address its strategic interests in sustainable waste management and how educational programs can be created to raise environmental and circular economy awareness among future graduates. Thus, UPNA students and graduates are actively engaged in the daily management of the program, whose one of these main aims is to promote experiential learning and applied research in sustainability and the circular economy [12]. As in other examples of community composting, this alternative method can be possible if the composting process is properly followed, from the design and dimensioning of the decentralized composting sites, as well as the characteristics of the used materials and final composts, to the training of staff in charge [17]. However, community composting, despite being extensively used in many countries and having increasingly attracted attention in the recent years, has been very little assessed [18]. Furthermore, until now, community composting has been only conceived as a reproduction of experiences from other places, without an analysis of the real needs of each case, a technical criterion or social perspective when making decisions [17]. Therefore, one of the main concerns on this scale of management is the lack of information regarding the process and of the quality of the end-products obtained, reflected in a lack of specific legislation and regulations. For these reasons, in order to assure the process reproducibility and the agronomic value, quality, and hygienic conditions of the final product, it is essential to monitor both the process and the end-product in this composting model [19]. Thus, this study evaluated four composting sets of the CaMPuSTAJE by monitoring the process and the composting samples at chemical and biological levels. In addition, a complete characterization of the agronomic and hygienic-sanitary quality of the end-products was conducted to ensure the reproducibility and efficiency of both the process and the compost produced.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composting Scenario
The Arrosadia campus of UPNA has a central canteen building where more than 500 meals are prepared and consumed every day from Monday to Friday during the academic year (from September to July). In addition to the kitchen where the meals are prepared and the self-service canteen, the building also has a cafeteria. All the biowastes generated in the building are separated and kept separate from the rest of the waste generated in the building. In 2019, an outdoor community composting site was installed 5 m from the door of the kitchen place in the building to manage biowaste from the campus (Figure 1). The community composting site consisted of 6 composting modules, each with a capacity of 1 m3 (1 m long × 1 m wide × 1 m high), forming a batch system with two parallel management lines. Each of the management lines comprises three composting modules. The first management line is constituted by the input module 1, the intermediate compost module 2, and the maturation module 3. The second management line is formed by the input module 6, the intermediate compost module 5, and the maturation module 4. Daily biowaste, mainly food waste, is stored in the input module 1 or 6 (Figure 2).
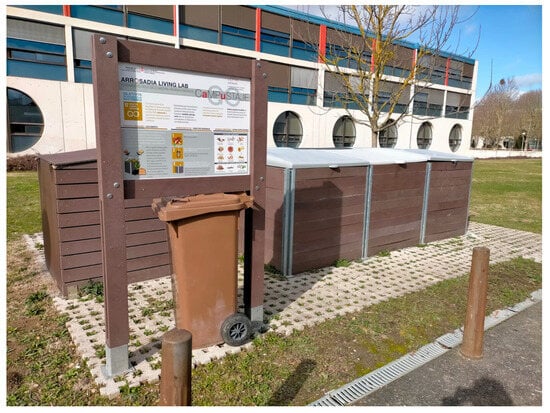

Figure 1.
CaMPuSTAJE project community composting site located at the Arrosadia campus of the UPNA.
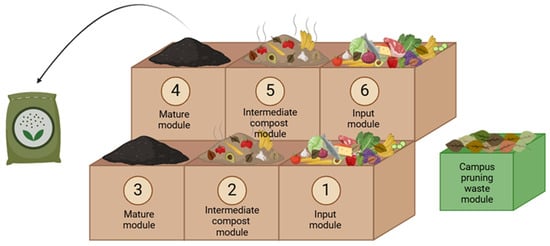
Figure 2.
Diagram of composting process monitoring at the point of management.
In this input module, university staff mixed food waste (FW) collected from the canteen building with pruning waste from the campus itself, which acts as a bulking agent. Campus pruning waste (CPW) was collected and stored at the community composting site by the campus gardening service. As is described in Figure 2, the modules 1 and 6 were used alternated as input modules, where the mixture of food waste (FW) + campus pruning waste (CPW) is deposited, adding layers of canteen biowaste and bulking material each day. When these modules were completed with material, the composting mixtures were transferred alternatively to the intermediate compost modules 2 and 5. Finally, the maturation stage was carried out in the alternated maturation modules 3 and 4, once the intermediate modules 2 and 5 were also completed. The surface of the formed set, which was in contact with the environment, was coated with a thin layer of bulking material to prevent the proliferation of flies and nuisance insects. This was accompanied by the use of a synthetic geotextile or a wet jute net. The transfer of all materials from one composter to another was conducted throughout the process, with each set passing through the three composting modules of each line. Once the material from each set reaches the maturation modules, it is considered mature and may be used on the campus.
In all sets, to maintain the homogeneity of the composted materials, the new material from each input was mixed with the material already in the composter on each input day using a hand-held spiral aerator tool. The transfers were conducted on two occasions for each of the sets. To keep the moisture content above 40% for proper composting, the moisture content of the material was adjusted by irrigation each time it was loaded or transferred to the next composter and when the material seemed dry. The ‘first test’ was used to qualitatively check the moisture content during the composting process [20]. As the composting sets were prepared in different periods of the year (sets 1 and 2 in spring-summer and sets 3 and 4 in autumn–winter), the watering requirements were different in the sets. For each material input, the temperature was monitored by measuring directly with a thermometer at 3 different points on the surface of the material, starting from the center and moving towards the edges. In addition, university staff carry out daily checks on the quantities of fresh weight of biowaste added to the mix, the amount of campus pruning waste used in the mix, irrigation, and transfers, as well as any incidents or other need-to-know information (occurrence of odors, flies, insects, etc.).
2.2. Characteristics of the Initial Materials and Composting Procedure
Four composting sets were prepared by mixing food waste (FW), coming from the central canteen building located at the Arrosadia campus of the UPNA (Pamplona, Navarre, Spain), with the campus pruning waste (CPW). The amounts of each type of waste used in each of the composting sets are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Amount of food waste and campus pruning waste managed in each composting set (kg on a fresh weight basis).
Timing differences between the different sets and canteen service days resulted in small variations in the amount of waste managed. The principal properties of the biowastes used in each composting set are shown in Table 2 and Table 3. The composting sets were formed inside the compost modules at the UPNA community composting site. Manual turning was carried out with each addition of new material, as well as with transfers to another composting module, as the various sets were completed to a height of approximately 80 cm, filling the composting module. The end of the bio-oxidation was considered reached when the temperature in the sets fell to the temperature of the environment and the difference between the set material temperature and environment temperature was ≤ 10 °C for at least 10 consecutive days [21].

Table 2.
Characteristics of the biowastes used in the composting processes (sets 1 and 2). Data expressed on a dry weight basis.

Table 3.
Characteristics of the biowastes used in composting processes (sets 3 and 4). Data expressed on a dry weight basis.
The bio-oxidative phase lasted 162, 137, 170, and 89 days for sets 1 to 4, respectively. After this, the composts were maintained for maturation during 67, 80, 64, and 76 days for sets 1 to 4, respectively. The sets were sampled at four different times: the initial phase (M1), the thermophilic stage (M2), the end of the bio-oxidation stage (M3), and the maturity phase (M4). Composite samples were obtained by collecting, mixing, and homogenizing seven subsamples from seven different places of the sets, considering the whole profile from the top to the deepest part, following the procedure detailed by Bustamante et al. [22]. Three parts were obtained from each sample: a first sample was immediately frozen and preserved for subsequent analyses, another fresh sample was used for pathogen analysis, and a third sample was air-dried and ground to 0.5 mm for the rest of determinations.
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.3.1. Physico-Chemical, Chemical, and Biological Methods
Dry matter in the initial wastes and in the composting samples was analyzed after samples drying for 12 h at 105 °C. Electrical conductivity (EC) and pH were assessed after a water-soluble extraction using the ratio 1:10 (w/v) with a conductivity/pH meter (Crison Instruments, S.A., Barcelona, Spain). After combustion at 550 °C for 24 h, organic matter (OM) was determined following the standard method CEN13039 [23]. Total organic carbon (TOC) and total nitrogen (TN) were assessed in an elemental analyzer (Truspec CN, Leco, St. Joseph, MO, USA) at 950 °C by dry combustion. Extractable organic carbon (Cex) was obtained after extraction with 0.1 M NaOH, while fulvic-acid-like carbon (Cfa) was obtained after precipitating the humic-acid-like carbon (Cha) of the NaOH extract at pH 2.0, following the procedure detailed by Bustamante et al. [24]. All these fractions and that of water-soluble carbon (Cw), obtained in a water-soluble extract (1:20 w:v), were assessed with an automatic carbon analyzer (TOCV-CSN, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan).
The humification indices for each set were assessed using the formulas used by Bustamante et al. [22]:
- Humification ratio (HR) = 100;
- Humification index (HI) = 100;
- Percentage of humic acids (Pha) = 100;
- Polymerization rate =.
Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was assessed in the end-products with the BaCl2-triethanolamine method, as described in Bustamante et al. [24]. In addition, microelements, P, and heavy metals were determined in these samples by means of ICP-OES (ICAP 6500 DUO, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA), after digestion with HNO3/HClO4. Phytotoxicity was assessed with the methodology described by Zucconi et al. [25] with Lepidium sativum L. The stability test was conducted using the method described by Brinton et al. [26]. All the analytical determinations were conducted in triplicate.
OM losses were calculated from the concentrations of OM losses calculated from the ash concentrations at the beginning (X1) and at the end (X2) of the process, according to the following equation Bustamante et al. [24]:
OM loss (%) = 100 − 100 [(X1 (100 − X2))/(X2 (100 − X1))]
2.3.2. Determination of the Pathogen Content in the Final Composts
The potential presence of pathogens was investigated to guarantee the absence of biological risk in the final composts. For this, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and fecal coliforms (E. coli) were assessed in triplicate following the methodology described by Alvarez-Alonso et al. [21]. The results obtained were expressed as the number of colony-forming units per gram of fresh compost (CFU/g compost) for E. coli and as presence/absence of Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
The statistical methods were conducted using ANOVA. The Tukey-b post hoc test and the least significant difference (LSD) test at p < 0.05 were used to evaluate the significant differences among the different composting stages and the parameters studied during composting, respectively. To check the normality and homogeneity of the variances before ANOVA, the Shapiro–Wilk and Levene tests were used. The standard error of the mean values of each parameter and the standard deviation of the sets were also calculated. These statistical determinations were made with the IBM SPSS Statistics v. 29.0 software.
OM loss data during composting were fitted to a kinetic function by the Marquardt–Levenberg algorithm using the Sigmaplot 14.0 software. Organic matter decomposition during composting was explained using a first-order kinetic model [25]:
where A corresponds to the maximum OM degradation (% C), k is the rate constant (d−1), and t is the composting time (days). The coefficient of determination (R2), F-values, and the standard error of estimate (SEE) were calculated to compare the goodness of curve fitting, the fittings of different functions, and the statistical significance of curve fitting, respectively.
OM losses (%) = A (1 − e−kt)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Behaviour of the Composting Sets
The study of the temperature development during the composting process allows us to verify the evolution of the biological processes that enhance the reduction of pathogens in the compost [27]. Figure 3 shows the evolution of temperatures in the four processes studied. It can be observed that, in the initial phases of the process, temperatures higher than 60 °C were reached in practically all the composting sets in the first 2–3 process days. Similarly, during the first days of the process and until the maximum filling of the composter was reached (about 80% of composter capacity) (until process day 70, 60, and 52 for sets 2, 3, and 4, respectively), the temperature remained in thermophilic values (≤40 °C) in all cases, except for set 1, which showed a higher variability in the thermal profile. Gaspar et al. [28] also reported a rapid increase in the temperature in the first few days during the composting of food waste. However, throughout the processes, several drastic drops and rises in the temperature values of the composting sets were observed (Figure 3). The high temperatures reached in the processes diminished water content in the mixtures due to evaporation losses, reducing the microbial activity in the composting mass, with this being reflected in a temperature decrease. With water incorporation, the temperature increased due to the recovery of the process (blue points in Figure 3). Moreover, the transfer of the mass to the corresponding module (yellow lines in Figure 3) also implied a temperature increase, due to the homogenization and aeration of the mixture. The maximum temperatures observed in the composting sets were 73, 79, 78, and 77 °C for sets 1 to 4, respectively, with these values being higher than the optimal temperature range that ensures sanitization in the composting mass [27]. These temperatures were higher than those recorded in previous studies using similar wastes [1,29] and were in line with those obtained by Wang et al. [27] in a composting experiment using kitchen waste and Storino et al. [30] in a study of composting of vegetable food waste with garden waste. In addition, the duration of the bio-oxidative phase of the composting sets was very long, lasting more than 130 days in all the sets, except for set 4, whose bio-oxidative stage lasted 89 days, probably due to this module managing the least amount of biowaste (674 kg, Table 4). However, the duration of the bio-oxidative phase, even in set 4, was similar to that observed by Álvarez-Alonso et al. [21] in a study with compost made from organic fraction collected separately from municipal waste mixed with urban pruning waste. Extended periods of thermophilic temperatures indicate a good evolution of the composting process [29]. In contrast, the duration of the bio-oxidative phase is significantly longer than that described in studies where the mixtures are inoculated with microorganisms [28]. Thus, all the four composting sets fulfilled the European Union requirements for the temporary duration of certain temperatures with the aim of ensuring compost sanitization [31] and maximum pathogen reduction [30].
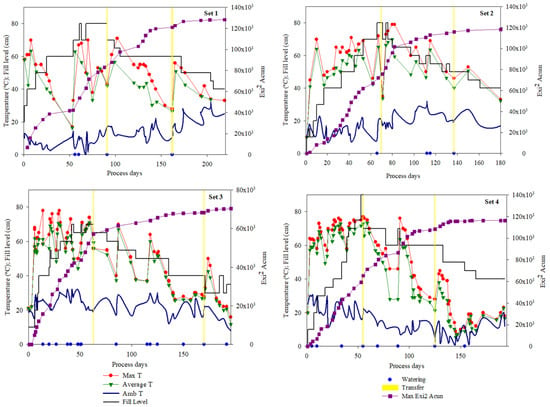
Figure 3.
Evolution of temperature and EXI2 index in the four composting sets studied.

Table 4.
Evolution of the main parameters during composting time (dry weight basis).
In addition, the degree of exothermicity was assessed using the cumulative quadratic exothermicity index (EXI2) [32], which indicates the intensity of the bio-oxidative phase (Figure 3). This index was determined as the quadratic sum of the daily difference between the temperature inside the set and the temperature of the environment during the bio-oxidative phase of composting [32]. Sets 1, 2, and 3 obtained the highest EXI2 value with 127,252, 118,568, and 116,225 °C2, respectively, while set 3 showed the lowest value with 70,289 °C2. The sets with the highest values obtained (sets 1 and 2) were the ones with the highest amount of waste managed (in kg, Table 1). The incorporation of important quantities of waste produced a raise in the temperature values during the process and enhanced its maturity [30]. This EXI2 value was in the range of those recorded by Alvarez-Alonso et al. [21] during composting of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and, consequently, lower than those recorded by Vico et al. [32] and Pelegrín et al. [33] in composting processes using agro-industrial organic wastes. As observed by Wang et al. [27] in small-scale composting, all the composting sets showed a slight reactivation of the process after each addition of material and subsequent mixture, although only in set 2 was this increase higher than the temperatures reached during the first few days of the process. This reactivation was greater in the cases where the material was transferred to the next composting module and irrigation was also applied.
3.2. Organic Matter Development
As shown in Figure 4, the OM degradation was most pronounced during the bio-oxidative composting phase, when temperatures were at their maximum values, with sets 2 and 4 showing the highest degradation during the first days of the process. The degradation of OM remained stable from about day 80 onwards. This demonstrates the microbial stability of the organic compounds in the final compost.
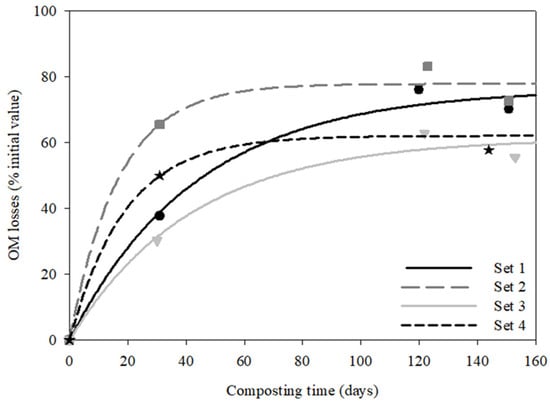
Figure 4.
Organic matter (OM) losses (%) in the composting sets. Lines represent the curve fitting for each set.
The following parameter values (A: maximum degradation; k: rate constant; R2: coefficient of determination; standard deviation in parentheses; SEE: standard error of estimate; and **: significant at p < 0.01) were obtained by fitting the OM loss to a first-order kinetic equation:
Set 1: A = 76.38 (0.02); k = 0.02 (0.005); R2 = 0.9900; F = 198.0 (**); SEE = 4.28
Set 2: A = 77.89 (3.75); k = 0.05 (0.016); R2 = 0.9870; F = 151.3 (**); SEE = 5.26
Set 3: A = 61.39 (4.66); k= 0.02 (0.006); R2 = 0.9828; F = 114.3 (**); SEE = 4.57
Set 4: A = 62.13 (3.06); k = 0.05 (0.013); R2 = 0.9791; F = 141.5 (**); SEE = 4.30
All of the equations were significant at p < 0.01. As can be seen from the values of F, sets 1, 2, and 4 fit this equation better than set 3, which obtained the lowest value (114.3). The values obtained from the equations were slightly higher than those obtained by Pelegrin et al. [33] in a composting experiment with agri-food sludge and similar to those obtained by Saez et al. [34] with livestock waste. Comparing the values of A, associated with the maximum degradation of OM, and of k, related to the rate of the process, it can be observed that set 2 showed the highest values. This could be due to this set showing the greatest initial OM contents, probably more degradable than in set 1, which could be explained by the important heterogeneity of the food waste used in the mixtures. Conversely, set 3 showed the lowest A and k values and the worst fit of the model. Previous studies of composting using similar wastes have reported that high fat contents in the raw materials inhibit the decomposition of organic matter in a composting process, since the development of the microbiota associated with the composting process is inhibited at high fat concentrations, reducing the conversion of OM to humus [35]. In this study, set 3 was the mixture with the highest proportion of FW, and thus this composting set probably contained a higher fat content than the rest, which could explain the lowest degradation rate observed in this composting set.
3.3. Evolution of the Physico-Chemical and Chemical Parameters
Table 4 shows the evolution of the most relevant parameters in the sets during the composting process. The initial pH values in the set mixtures (Table 4) were within the optimal range (5.0–8.0) for the suitable development of the bacteria and fungi typical of the composting process [23].
During the process, a progressive increase in pH was observed in the sets, up to values in the alkali range of 8.1 to 8.9 at the end of the composting period (Table 4), values that are in line with those previously observed in composting experiments using similar organic wastes [25,28,36]. The EC showed a similar trend to pH with initial values range from 3.6 to 5.8 dS m−1 and an increase to final values between 4.6 to 7.5 dS m−1. This increase could be associated with the observed organic matter degradation (Figure 4) and the subsequent concentration of soluble salts in the composting mass, as well as due to the absence of excessive irrigation, since the process was carried out in closed composting modules [37]. In general, the final composts showed high EC values, mainly due to the mineralization processes associated to the composting process, but especially due to the initial EC values showed by the FW, with EC initial values higher than 5 dS m−1 (Table 2 and Table 3). Salt concentrations in the final composts above 4 dS m−1 can be detrimental to crops [38,39], so it would be advisable to mix such materials with others prior to their use to reduce their salt content [4].
On the other hand, OM concentrations were high at the beginning of the process in all the sets, with values of 92.0, 93.4, 87.6, and 92.1% for sets 1 to 4, respectively (Table 4). These values decreased with the composting process to final values of 76.7, 78.5, 75.3, and 78.9% for sets 1 to 4, respectively, with these values widely fulfilling EU regulations, which stipulate that a compost must contain a minimum of 15% organic matter calculated on a dry matter basis following the composting process [31].
As a consequence of the loss of the composting mass due to the decomposition of the raw materials, the TN concentration increased in sets 1, 2 and 4. In contrast, this parameter exhibited a slight decline in set 3 during the composting process, which showed the highest value at the beginning of the process (Table 4). This decline could be attributed to the lower proportion of bulking material in the mixture, which avoids N losses by volatilization. Pardo et al. [40] also reported in a review about gaseous emissions during organic waste management the significant effect of the bulking agent in the reduction of N losses during composting. In this sense, the minimization of the N losses during composting not only increases the N contents of the compost obtained but also reduces odor emissions and thus environmental impacts, providing both economically and agronomically added value to the final compost, which can be used as a substitute for inorganic fertilizers in agriculture [3].
3.4. Agronomic Quality of the Final Composts
The main characteristics related to the agronomic value of the final composts are shown in Table 5. Macronutrient and micronutrient contents were high at the end of the process, showing TN values above 20 g kg−1 in all sets. These values were similar to those found by Alvarez-Alonso et al. [21] and Gómez-López et al. [6] in compost obtained from similar raw materials. On the other hand, these results were slightly higher than those found by other researchers in compost from livestock waste [34] or agro-industrial waste [23]. The final P content was higher than 10 g kg−1 in compost from sets 1 and 3 and lower in compost from sets 2 and 4. If these data are expressed as fertilizer units (P2O5), the values of 2.8, 2.0, 3.4, and 2.1 g kg−1 are observed for sets 1 to 4, respectively. The K content was higher than 15 g kg−1 in all cases. With regard to the fertilizer units (K2O), the values observed were 2.3, 2.6, 2.6, and 1.7 g kg−1 for sets 1 to 4, respectively. The differences in the macronutrient contents observed among the different composting sets could be explained by the significant heterogeneity of the canteen biowastes, which also determines the contents in the final composts. Moreover, the development of the composting process also influences the nutrient contents in the final composts, as a consequence of the concentration effect due to the mass loss, reported in previous works [18,25,27]. However, these values were similar to those found in composts from canteen and/or kitchen biowastes [11,41]. The agronomic value of the composts, in terms of NPK content obtained, were 2.9–2.8–2.3, 3.3–2.0–2.6, 3.3–3.4–2.6, and 3.5–2.1–1.7 for compost from sets 1 to 4, respectively. These values were within the ranges reported in the literature by other researchers [6].

Table 5.
Main agronomic and quality characteristics of final compost (data expressed on a dry weight basis).
The main parameters for the evaluation of the maturity and stability of the final composts are presented in Table 6. It is well established that organic carbon is microbially metabolized to fulvic acids and then polymerized to stable humic acids to increase humic substances content during composting [38].

Table 6.
Parameters of compost maturity and stability (data expressed on a dry weight basis).
All the final composts showed values of Cex, HA, and FA similar to those reported by other studies using organic wastes with similar nature [19,25,35]. However, while the compost from set 1 showed the lowest values for the humic acid-like C, the compost from set 4 showed the best results, indicating that when a lower amount of waste is managed per set and the FW:CPW ratio is adjusted (approximately 80:20), the degree of humification of the compost and its agronomic quality are improved. The humification indices calculated in this study (Table 6) exceeded in all the composts the values established by Roletto et al. [42] (RH > 7; HI > 3.5; Pha > 62 and polymerization ratio > 1) and by Iglesias-Jimenez and Pérez-Garcia [43] (HI > 13 and polymerization ratio > 1.6) for mature composts. The compost from set 1 was the only compost that did not verify the limit value for HI established by Iglesias-Jimenez and Pérez-Garcia [43]. In general, all the composts, except that from set 1, showed CEC values higher than 60–67 meq/100 g OM, the range established for compost maturity [43]. On the other hand, the germination index (GI) was above 50% in all the composts (Table 6), the limit value established by Zucconi et al. [25] to demonstrate the absence of phytotoxicity in organic materials. These values are similar to those found in kitchen waste-derived compost [30], municipal waste compost [44,45], and livestock compost [46]. Furthermore, all composts showed an adequate level of stability, according to the stability test described by Brinton et al. [26].
3.5. Potentially Toxic Elements and Pathogens
The contents of heavy metals and pathogens were assessed in the final composts to evaluate the potential chemical and sanitary risks associated with their use, also comparing them with the limit values established in the European normative on fertilizers [31] (Table 7 and Table 8). Concerning the heavy metals, all the composts fulfilled the criteria established by the European normative [31] (Table 7), the levels being even lower than those reported in composts from similar organic wastes (Table 7), such as those from the organic fraction of municipal solid wastes mixed with different bulking materials [8,11,25].

Table 7.
Heavy metal content in the final composts from each composting set (data expressed on a dry weight basis) compared to the limit values of the European legislation on fertilizers.

Table 8.
Pathogenic groups in the final composts.
Furthermore, to assure the sanitary quality of the end-products, the final materials were tested for organisms that could cause a biological risk, such as fecal coliforms (E. coli), Salmonella spp., included in the European normative on fertilizers [31], and Listeria monocytogenes (Table 8). All the composts verified the sanitary criteria established by the European legislation [31], with the absence of Salmonella spp./25 g compost and levels of E. coli < 1000 CFU/g compost, with the exception of the compost obtained in the composting set 2, which exceeded the limit proposed by European legislation for this pathogenic group [31].
Listeria monocytogenes was not detected in the composts from sets 1 and 2, whereas it was present in the composts from sets 3 and 4. The higher contents of E. coli in the compost from set 2 and the presence of Listeria in composts from sets 3 and 4 could be related to a possible re-contamination of the samples after their collection. This fact was also reported by Alvarez-Alonso et al. [21] in composts from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste, since no high values of E. coli or presence, in the case of Listeria, were observed in the samples prior to maturation (61 CFU/g and absence, respectively). Moreover, the thermophilic phase of the composting process in these sets also fulfilled the criteria established in the European normative (55 °C or more at least 14 days), which guarantee the sanitization of the compost. Thus, these results have shown that to ensure the hygienic quality of the biowaste composts, not only is a proper process development required, reaching thermophilic temperature values during the established period of time to ensure pathogen elimination, but also the adequate management of the final composts, avoiding an improper handling of the material that can reintroduce pathogens.
4. Conclusions
The community composting of food waste from small producers, such as the canteen services of the UPNA’s Arrosadia university campus, together with pruning waste from the same campus, represents an initiative that allows the management and valorization of this type of waste within a circular economy framework. The study of the thermal evolution of the four composting sets has demonstrated the capacity of the mixtures studied to reach temperatures of over 70 °C, which are effective in sanitizing the compost. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that this type of proximity management allows the production of mature and stable composts with optimal characteristics, with high contents in macro- and micronutrients and the absence of environmental and sanitary risks, without pathogens and potentially toxic elements. Thus, these composts could be safely used in not only the campus gardening to close the loop in the university campus itself, but also with agricultural purposes due to their suitable agronomic and maturity characteristics. In addition, the assessment of the composting sets has revealed an important process uniformity and homogeneity in the quality of the final products, which guarantees the reproducibility of the system. The results obtained have confirmed the consistency and efficiency of this biological treatment in this scenario, encouraging the implementation of criteria aimed at standardizing this approach to biowaste management. Therefore, this approach allows to close the loop with the transformation of this type of waste in a resource in a local way, reducing the impacts associated with the traditional disposal of these biowastes, but also contributing to increase the environmental awareness at an educational level.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M., J.S.-A., R.P., I.I. and C.Á.-A.; methodology, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M., C.Á.-A., E.M.-S. and I.I.; software, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M. and C.Á.-A.; validation, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M., C.Á.-A., I.N., I.I. and M.L.; formal analysis, C.Á.-A., E.M.-S. and I.I.; investigation, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M., C.Á.-A., I.I., I.N., E.M.-S. and M.L.; resources, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M., J.S.-A., R.P. and I.I.; data curation, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M., C.Á.-A. and E.M.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Á.B. and C.Á.-A.; writing—review and editing, M.Á.B., C.Á.-A., I.I. and I.N.; visualization, M.Á.B., M.D.P.-M., C.Á.-A., I.I., R.P., J.S.-A. and M.L.; supervision, M.Á.B. and M.D.P.-M.; project administration, M.Á.B. and M.D.P.-M.; funding acquisition, M.Á.B. and M.D.P.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the research project NEOCOMP (ref. PID2020-113228RB-I00) funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033, and it was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Universities with a PhD contract (FPU21/01207) to the first author.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Public University of Navarre (UPNA-NUP) and the UPNA canteens for their participation in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Ramon Plana was employed by the company Organic Wastes Management Consultancy. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FW | food waste |
| CPW | campus pruning waste |
| UPNA | Public University of Navarre |
References
- Bello, H.; Ajao, J.O.; Sadiku, N.A. Co-composting of sawdust with food waste: Effects of physical properties on composting process and products quality. Detritus 2022, 23, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Prats, M.; González, D.; Moral-Vico, J.; Madrid-López, C.; Sánchez, A. Implementing community composting in primary schools: First experiences at Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Spain. Eng. Proc. 2023, 37, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungría, J.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Siles, J.A.; Martín, M.A. Advantages and drawbacks of OFMSW and winery waste co-composting at pilot scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Pandey, A.K.; Khan, J.; Bundela, P.S.; Wong, J.W.C.; Selvam, A. Evaluation of thermophilic fungal consortium for organic municipal solid waste composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.N.; Parsai, T. A comprehensive review on the decentralized composting systems for household biodegradable waste management. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-López, M.D.; El Bied, O.; Beltrá, J.C.; Yanardag, I.H.; Gómez, C.; Faz, Á.; Zornoza, R. Strategies for the sustainable management of the organic fraction of municipal waste. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaretou, V.; Vakalis, S.; Ntolka, A.; Sotiropoulos, A.; Moustakas, K.; Malamis, D.; Loizidou, M. Assessing the alteration of physicochemical characteristics in composted organic waste in a prototype decentralized composting facility. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Resear. 2019, 26, 20232–20247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.; Akyol, Ç.; Cipolletta, G.; Eusebi, A.L.; Caniani, D.; Masi, S.; Colón, J.; Fatone, F. Decentralized community composting: Past, present and future aspects of Italy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.Q.; Wang, G.X.; Huo, Z.C.; Yan, L.; Gao, Y.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Gu, J.-D.; Wang, W.D. Effect of aeration rates on the composting processes and nitrogen loss during composting. Appl. Environ. Biotech. 2017, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storino, F.; Plana, R.; Usanos, M.; Morales, D.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.; Muro, J.; Irigoyen, I. Integration of a communal henhouse and community composter to increase motivation in recycling programs: Overview of a three-year pilot experience in Noáin (Spain). Sustainability 2018, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keng, Z.X.; Chong, S.; Ng, C.G.; Ridzuan, N.I.; Hanson, S.; Pan, G.T.; Lau, P.L.; Supramaniam, C.V.; Singh, A.; Chin, C.F.; et al. Community-scale composting for food waste: A life-cycle assessment supported case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrijos, V.; Dopico, D.C.; Soto, M. Integration of food waste composting and vegetable gardens in a university campus. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcello, B.; Di Gennaro, V.; Ferrini, S. Let the citizens speak: An empirical economic analysis of domestic organic waste for community composting in Tuscany. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.; Ai, N.; Zheng, J. Decentralized community composting feasibility analysis for residential food waste: A Chicago case study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Horowitz, N.; Casey, M.; Jones, K. Environmental and economic analysis of an in-vessel food waste composting system at Kean University in the U.S. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Lee, L.H.; Wu, T.Y. Sustainability of using composting and vermicomposting technologies for organic solid waste biotransformation: Recent overview, greenhouse gases emissions and economic analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 111, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sierra, R.P.; Arizmendiarrieta, S.J.; Sánchez, B.P.; Irigoien, I.; Duarte, G.N. Community Composting. A Practice Guide for Local Management of Biowaste. Zero Waste Europa. 2019. Available online: https://sites.google.com/view/fearesiduos/ (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Sánchez, A. Decentralized composting of food waste: A perspective on scientific knowledge. Front. Chem. Eng. 2022, 4, 850308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, F.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.C.; Nghiem, L.D.; Li, G.; Luo, W. Humification and maturation of kitchen waste during indoor composting by individual households. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 814, 152509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FCQAO, Federal Compost Quality Assurance Organization. Method Books for the Analysis of Compost; University of Essen: Duisburg, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Alonso, C.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Sánchez-Méndez, S.; Martínez-Sabater, E.; Irigoyen, I.; López, M.; Nogués, I.; Paredes, C.; Orden, L.; García-Rández, A.; et al. Municipal Solid Waste Management in a Decentralized Composting Scenario: Assessment of the Process Reproducibility and Quality of the Obtained Composts. Agronomy 2024, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.A.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Restrepo, A.P.; de la Fuente, C.; Paredes, C.; Moral, R.; Bernal, M.P. Co-composting of the solid fraction of anaerobic digestates, to obtain added-value materials for use in agriculture. Biomass Bioener. 2012, 43, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN EN 13039:1999 E; European Committee for Standardization. Soil Improvers and Growing Media-Determination of Organic Matter and Ash. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- Bustamante, M.A.; Paredes, C.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Pérez-Espinosa, A.; Bernal, M.P.; Moral, R. Co-composting distillery wastes with animal manure: Carbon and nitrogen transformations and evaluation of compost stability. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucconi, F.; Pera, A.; Forte, M.; de Bertoldi, M. Evaluating toxicity of immature compost. Biocycle 1981, 22, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Brinton, W.F.; Evans, E.; Droffner, M.L.; Brinton, R.B. A standardized Dewar test for evaluation of compost self-heating. Biocycle 1995, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Yuan, Z. Aeration rate improves the compost quality of food waste and promotes the decomposition of toxic materials in leachate by changing the bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, S.S.; Assis, L.L.R.; Carvalho, C.A.; Buttrós, V.H.; Ferreira, G.M.R.; Schwan, R.F.; Pasqual, M.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Rigobelo, E.C.; Castro, R.P.; et al. Dynamics of microbiota and physicochemical characterization of food waste in a new type of composter. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 960196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Ocaña, E.R.; Dominguez, I.; Komilis, D.; Sánchez, A. Co-composting of green waste mixed with unprocessed and processed food waste: Influence on the composting process and product quality. Waste Biomass Valor. 2019, 10, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storino, F.; Menéndez, S.; Muro, J.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; Irigoyen, I. Effect of feeding regime on composting in bins. Compost Sci. Util. 2017, 25, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Regulation (EU) 2019/1009, 2019. Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 laying down rules on the making available on the market of EU fertiliser products, amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 and repealing Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, L 170, 1–114. [Google Scholar]
- Vico, A.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Bustamante, M.A.; Agulló, E.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Sáez, J.A.; Paredes, C.; Pérez- Espinosa, A.; Moral, R. Valorization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) pruning biomass by co-composting with urban and agri-food sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 226, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrín, M.; Sáez-Tovar, J.A.; Andreu-Rodríguez, J.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Martínez-Sabater, E.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Pérez-Espinosa, A.; Bustamante, M.A.; Agulló, E.; Vico, A.; et al. Composting of the invasive species Arundo donax with sewage and agri-food sludge: Agronomic, economic and environmental aspects. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, J.A.; Clemente, R.; Bustamante, M.Á.; Yañez, D.; Bernal, M.P. Evaluation of the slurry management strategy and the integration of the composting technology in a pig farm—Agronomical and environmental implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shen, Y.; Ding, J.; Luo, W.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, P.; et al. High oil content inhibits humification in food waste composting by affecting microbial community succession and organic matter degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandpe, A.; Tyagi, L.; Paliya, S.; Chaudhry, S.; Motghare, A.; Kumar, S. Rapid-in-house composting of organic solid wastes with fly ash supplementation: Performance evaluation at thermophilic exposures. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, C.; Bernal, M.P.; Roig, A.; Cegarra, J. Effects of Olive Mill Wastewater Addition in Composting of Agro Industrial and Urban Wastes. Biodegradation 2001, 12, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, X.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J. Biochar influences the succession of microbial communities and the metabolic functions during rice straw composting with pig manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Garg, A. Performance assessment of improved composting system for food waste with varying aeration and use of microbial inoculum. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, G.; Moral, R.; Aguilera, E.; Del Prado, A. Gaseous emissions from management of solid waste: A systematic review. Global Change Biol. 2015, 21, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.; Villar, I.; Mato, S. Community composting strategies for biowaste treatment: Methodology, bulking agent and compost quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 9873–9885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roletto, E.; Barberis, R.; Consiglio, M.; Jodice, R. Chemical parameters for evaluating compost maturity. Biocycle 1985, 26, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias Jiménez, E.; Pérez García, V. Determination of maturity indices for city refuse composts. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1992, 38, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Ocaña, E.R.; Marmolejo-Rebellon, L.F.; Torres-Lozada, P. Evaluation of the addition of wood ash to control the pH of substrates in municipal biowaste composting. Ing. Investig. Tecnol. 2014, 15, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Pandey, A.K.; Bundela, P.S.; Khan, J. Co-composting of organic fraction of municipal solid waste mixed with different bulking waste: Characterization of physicochemical parameters and microbial enzymatic dynamic. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Bai, X.; Gao, H.; Huang, Y. Enzymatic mechanism of organic nitrogen conversion and ammonia formation during vegetable waste composting using two amendments. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).