SVR-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Using a Hybrid FISA-Rao and Firefly Algorithm for Feature and Hyperparameter Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- To the best of the author’s knowledge, this study is the first to propose a plug-in hybrid optimization framework combining the Firefly optimization algorithm and FISA for joint feature selection and parameter optimization, used here with SVR for cryptocurrency price prediction. The proposed modular structure can be easily integrated into other machine learning or deep learning models, enabling broader applicability and improved predictive performance.
- (ii)
- A wide set of technical indicators was used in the prediction model, and feature selection was applied using the proposed hybrid FISA and Firefly algorithm to improve prediction accuracy.
- (iii)
- A correlation-based feature selection technique was integrated into the Firefly algorithm to adapt the feature selection process for the target problem. Consequently, the algorithm selects different feature sets, offering deeper insights into the varying dynamics of different cryptocurrency markets.
- (iv)
- While most existing studies utilize daily data, this study used hourly data as the primary input for model training and forecasting, which is critical for intra-day trading in the cryptocurrency market.
2. Literature Review and Background
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Methodological Background
3.2.1. Support Vector Regression
3.2.2. Firefly Algorithm
- Generate an initial population of fireflies.
- Apply the following iterative steps (main loop) until termination criteria are met:
- Calculate the brightness of each firefly based on the objective function.
- Move fireflies towards brighter ones, modifying their position according to attractiveness (population update).
- If there is a new one brighter than the previous iteration, determine this as the global best solution (best brighter).
- Display the global best solution.
3.2.3. FISA and Rao Algorithms
3.3. General Framework of the Proposed Model
3.3.1. Firefly Algorithm Adaptation and Improvement for the Joint Optimization of Features and Hyperparameters
3.3.2. FISA-Rao Algorithm Adaption to Fine-Tune the Parameters of the Firefly Algorithm
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Benchmark Results
4.2. Analysis of the Selected Features for Different Cryptocurrencies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACO | Ant Colony Optimization |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| BNB | Binance |
| BTC | Bitcoin |
| ETH | Ethereum |
| FISA | Fully Informed Search Algorithm |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| OHLC | Open High Low Close |
| OHLCV | Open High Low Close Volume |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| SOL | Solana |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| XRP | Ripple |
Appendix A
| No | Feature Technical Indicator Description | Binance | Bitcoin | Ethereum | Solana | Ripple |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Open Price | X | X | |||
| 2 | High Price | X | X | X | X | |
| 3 | Low Price | X | X | X | X | |
| 4 | Volume | |||||
| 5 | Hilbert Transform—Dominant Cycle Period | X | X | |||
| 6 | Hilbert Transform—Dominant Cycle Phase | X | ||||
| 7 | Hilbert Transform—Phasor In-Phase Component | X | X | |||
| 8 | Hilbert Transform—Phasor Quadrature Component | X | X | |||
| 9 | Hilbert Transform—Sine Wave | X | ||||
| 10 | Hilbert Transform—Lead Sine Wave | X | ||||
| 11 | Hilbert Transform—Trend vs. Cycle Mode | X | X | |||
| 12 | Average Directional Movement Index | X | X | |||
| 13 | Average Directional Movement Index Rating | X | X | |||
| 14 | Absolute Price Oscillator | X | ||||
| 15 | Aroon Indicator—Aroon Down | |||||
| 16 | Aroon Indicator—Aroon Up | X | ||||
| 17 | Aroon Oscillator | X | X | X | ||
| 18 | Balance of Power | X | X | X | X | |
| 19 | Commodity Channel Index | X | X | |||
| 20 | Chande Momentum Oscillator | X | ||||
| 21 | Directional Movement Index | X | ||||
| 22 | MACD—MACD Line | X | ||||
| 23 | MACD—Signal Line | |||||
| 24 | MACD—Histogram | X | X | |||
| 25 | MACDEXT—MACD Line | X | ||||
| 26 | MACDEXT—Signal Line | X | ||||
| 27 | MACDEXT—Histogram | X | X | |||
| 28 | MACDFIX—MACD Line | X | X | |||
| 29 | MACDFIX—Signal Line | X | ||||
| 30 | MACDFIX—Histogram | X | ||||
| 31 | Money Flow Index | X | ||||
| 32 | Negative Directional Indicator (-DI) | X | X | |||
| 33 | Negative Directional Movement (-DM) | X | X | |||
| 34 | Momentum | X | ||||
| 35 | Positive Directional Indicator (+DI) | |||||
| 36 | Positive Directional Movement (+DM) | X | ||||
| 37 | Percentage Price Oscillator | |||||
| 38 | Rate of Change | |||||
| 39 | Rate of Change (Percentage) | |||||
| 40 | Rate of Change Ratio | X | X | X | ||
| 41 | Rate of Change Ratio (×100) | X | ||||
| 42 | Relative Strength Index | X | ||||
| 43 | Stochastic Oscillator—Slow %K | X | X | |||
| 44 | Stochastic Oscillator—Slow %D | |||||
| 45 | Stochastic Fast—%K | X | X | |||
| 46 | Stochastic Fast—%D | |||||
| 47 | Stochastic RSI—%K | X | X | |||
| 48 | Stochastic RSI—%D | X | ||||
| 49 | TRIX (Triple Exponential Average) | X | ||||
| 50 | Ultimate Oscillator | X | X | |||
| 51 | Williams %R | X | ||||
| 52 | Bollinger Bands—Upper Band | X | X | |||
| 53 | Bollinger Bands—Middle Band | X | X | X | ||
| 54 | Bollinger Bands—Lower Band | X | X | X | X | |
| 55 | Double Exponential Moving Average | X | X | X | X | |
| 56 | Exponential Moving Average | X | X | X | ||
| 57 | Hilbert Transform—Instantaneous Trendline | X | X | X | ||
| 58 | Kaufman Adaptive Moving Average | X | X | X | ||
| 59 | Moving Average | X | X | X | X | |
| 60 | MESA Adaptive Moving Average—MAMA | X | X | X | X | |
| 61 | MESA Adaptive Moving Average—FAMA (Following) | X | X | X | ||
| 62 | Midpoint (Average of Price) | X | X | X | X | |
| 63 | Midprice (Average of High and Low) | X | X | X | X | X |
| 64 | Parabolic SAR | X | X | X | ||
| 65 | Parabolic SAR Extended | X | ||||
| 66 | Simple Moving Average | X | X | X | X | |
| 67 | Triple Exponential Moving Average (T3) | X | X | X | ||
| 68 | Triple Exponential Moving Average (TEMA) | X | X | X | ||
| 69 | Triangular Moving Average | X | X | X | ||
| 70 | Weighted Moving Average | X | X | X | ||
| 71 | Average True Range | X | ||||
| 72 | Normalized Average True Range | |||||
| 73 | True Range | |||||
| 74 | Chaikin A/D Line | X | X | X | ||
| 75 | Chaikin A/D Oscillator | X | ||||
| 76 | On Balance Volume | X | X | X |
References
- Kuznetsov, O.; Kostenko, O.; Klymenko, K.; Hbur, Z.; Kovalskyi, R. Machine Learning Analytics for Blockchain-Based Financial Markets: A Confidence-Threshold Framework for Cryptocurrency Price Direction Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Fiszeder, P.; Kobus, P.; Orzeszko, W. Forecasting cryptocurrencies volatility using statistical and machine learning methods: A comparative study. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 151, 111132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, S.; Roozkhosh, P.; Farimani, N. MLP-based Learnable Window Size for Bitcoin price prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 129, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.M.; Arif, I.; Pravija, V.P.R.; El-Bannany, M.; Alhashmi, S.M.; Sreedharan, M. Cryptocurrency price prediction using traditional statistical and machine-learning techniques: A survey. Intell. Syst. Account. Financ. Manag. 2021, 28, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, C.; Kong, X.; Baltas, K.; Zureigat, Q. Past, present, and future of the application of machine learning in cryptocurrency research. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2022, 63, 101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Machado, M. High-Frequency Cryptocurrency Price Forecasting Using Machine Learning Models: A Comparative Study. Information 2025, 16, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, M.A.; Hajizadeh, E. Time series prediction for cryptocurrency markets with transformer and parallel convolutional neural networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 177, 113229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, R.; Raza Ur Rehman, H.M.; Choi, G.S. Crypto foretell: A novel hybrid attention-correlation based forecasting approach for cryptocurrency. J. Big Data 2025, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, E.; Martin-Barreiro, C.; Cabezas, X. A Novel Hybrid Approach Using an Attention-Based Transformer + GRU Model for Predicting Cryptocurrency Prices. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, L.; Armas, J.; Masip, D.; Juan, A. Learnheuristics: Hybridizing metaheuristics with machine learning for optimization with dynamic inputs. Open Math. 2017, 15, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Priyanka, S.; Dhanashree, K.; Praveen, V.; Rekha, R. Efficient binary grasshopper optimization based neural network algorithm for bitcoin value prediction. Int. J. Nonlinear Anal. Appl. 2022, 13, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strumberger, I.; Zivkovic, M.; Thumiki, V.; Djordjevic, A.; Gajic, J.; Bacanin, N. Multivariate Bitcoin Price Prediction Based on Tuned Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network and Enhanced Reptile Search Algorithm. In Information and Software Technologies (ICIST 2023); Lopata, A., Gudonienė, D., Butkienė, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2024; Volume 1979, pp. 38–52. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, S.; Nayak, S.; Das, S. Modeling and Forecasting Cryptocurrency Closing Prices with Rao Algorithm-Based Artificial Neural Networks: A Machine Learning Approach. FinTech 2022, 1, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmiri, S.; Bekiros, S.; Bezzina, F. Complexity analysis and forecasting of variations in cryptocurrency trading volume with support vector regression tuned by Bayesian optimization under different kernels: An empirical comparison from a large dataset. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchtadi-Alamsyah, I.; Viltoriano, R.; Harjono, F.; Nazaretha, M.; Susilo, M.; Bayu, A.; Josaphat, B. Support vector regression-based heteroscedastic models for cryptocurrency risk forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 162, 111792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Rahimnejad, A.; Akbari, E.; Rao, R.V.; Trojovský, P.; Trojovská, E.; Gadsden, S.A. A new metaphor-less simple algorithm based on Rao algorithms: A Fully Informed Search Algorithm (FISA). PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Tiwari, S.; Khaled, D.; Mahendru, M.; Shahzad, U. Forecasting Bitcoin prices using artificial intelligence: Combination of ML, SARIMA, and Facebook Prophet models. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 198, 122938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Chen, Y.; Lin, W.; Wang, J. Attention-based CNN–LSTM for high-frequency multiple cryptocurrency trend prediction. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizdrakovic, V.; Kljajic, M.; Zivkovic, M.; Bacanin, N.; Jovanovic, L.; Deveci, M.; Pedrycz, W. Forecasting bitcoin: Decomposition aided long short-term memory based time series modeling and its explanation with Shapley values. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 299, 112026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Ling, M.; Wei, J.; Chen, C. Dynamic Market Behavior and Price Prediction in Cryptocurrency: An Analysis Based on Asymmetric Herding Effects and LSTM. Comput. Econ. 2024, 65, 3325–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Dai, H.-N. Enhancing Bitcoin Price Fluctuation Prediction Using Attentive LSTM and Embedding Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Nalavade, J. Metaheuristic Assisted Hybrid Classifier for Bitcoin Price Prediction. Cybern. Syst. 2023, 54, 1037–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, H.; Biehl, M.; Petkov, N. Survey of feature selection and extraction techniques for stock market prediction. Financ. Innov. 2023, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htay, H.S.; Ghahremani, M.; Shiaeles, S. Enhancing Bitcoin Price Prediction with Deep Learning: Integrating Social Media Sentiment and Historical Data. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, H.; Hajizadeh, E. Designing a cryptocurrency trading system with deep reinforcement learning utilizing LSTM neural networks and XGBoost feature selection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 175, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Yang, J.; Dai, J. Verifying Technical Indicator Effectiveness in Cryptocurrency Price Forecasting: A Deep Learning Time Series Model Based on Sparrow Search Algorithm. Cogn. Comput. 2025, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirshahi, B.; Lahmiri, S. Investigating the effectiveness of Twitter sentiment incryptocurrency close price prediction by using deep learning. Expert. Syst. 2025, 42, 13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Khalili Damghani, K.; Abdi, F.; Sardar, S. A Hybrid Model for Predicting Bitcoin Price Using Machine Learning and Metaheuristic Algorithms. J. Appl. Res. Ind. Eng. 2022, 9, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafidi, N.; Khoudi, Z.; Nachaoui, M.; Lyaqini, S. Enhancing Cryptocurrency Price Prediction through Inter-Coin Volatility and Hyperparameter Optimization. Comput. Econ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Chauhan, J.; Tiwari, N.K.; Upaddhyay, V.; Bajpai, A. A Deep Learning Framework for Hourly Bitcoin Price Prediction Using Bi-LSTM and Sentiment Analysis of Twitter Data. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Khanna, R. Support Vector Regression. In Efficient Learning Machines; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S. Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms; Luniver Press: Frome, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fister, I.; Fister, I.; Yang, X.; Brest, J. A comprehensive review of firefly algorithms. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2013, 13, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, D. A Systematic Review on Firefy Algorithm: Past, Present, and Future. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 3269–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fister, I.; Perc, M.; Kamal, S.; Fister, I. A review of chaos-based firefly algorithms: Perspectives and research challenges. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 252, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.V. Rao algorithms: Three metaphor-less simple algorithms for solving optimization problems. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 2020, 11, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
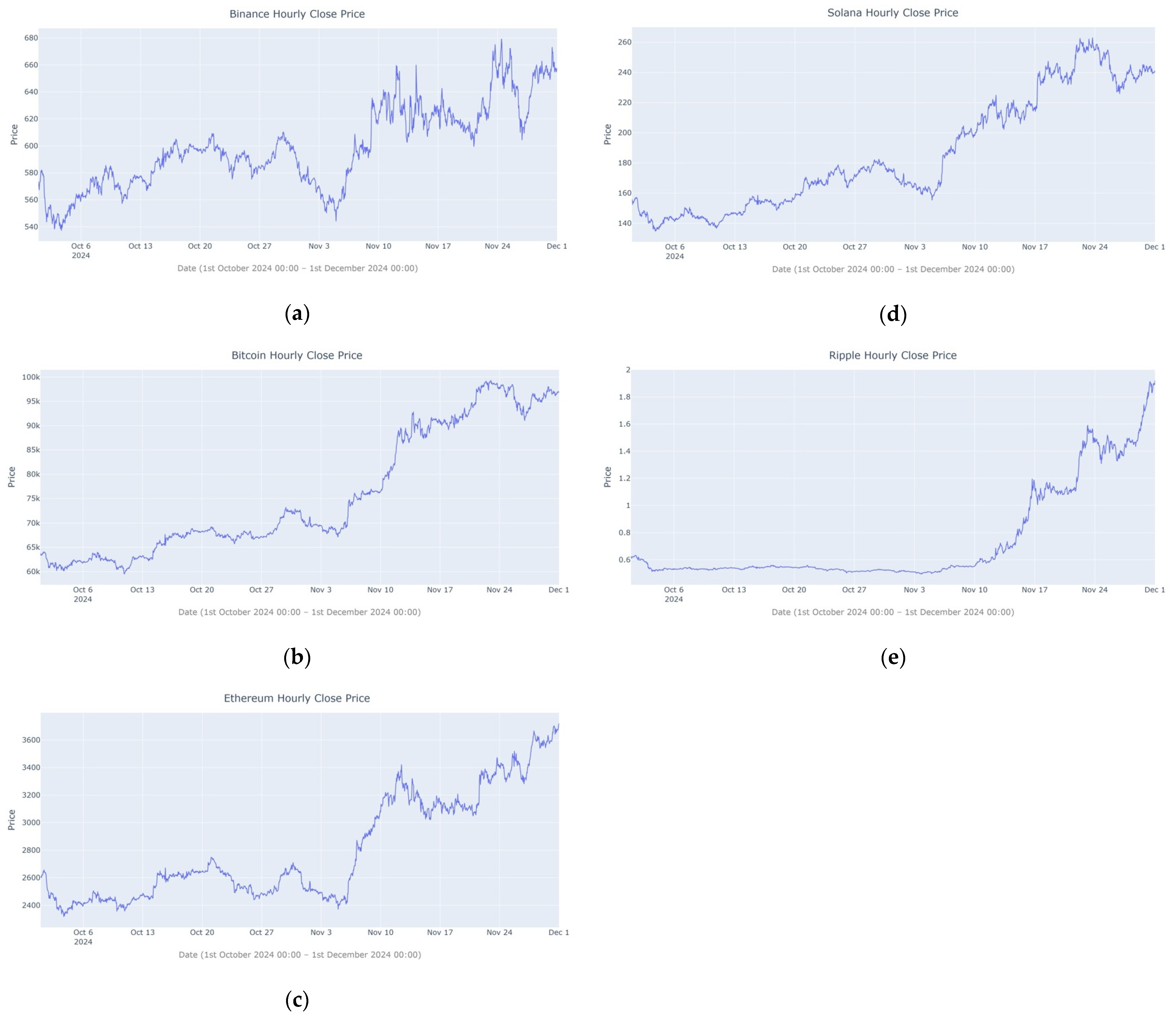
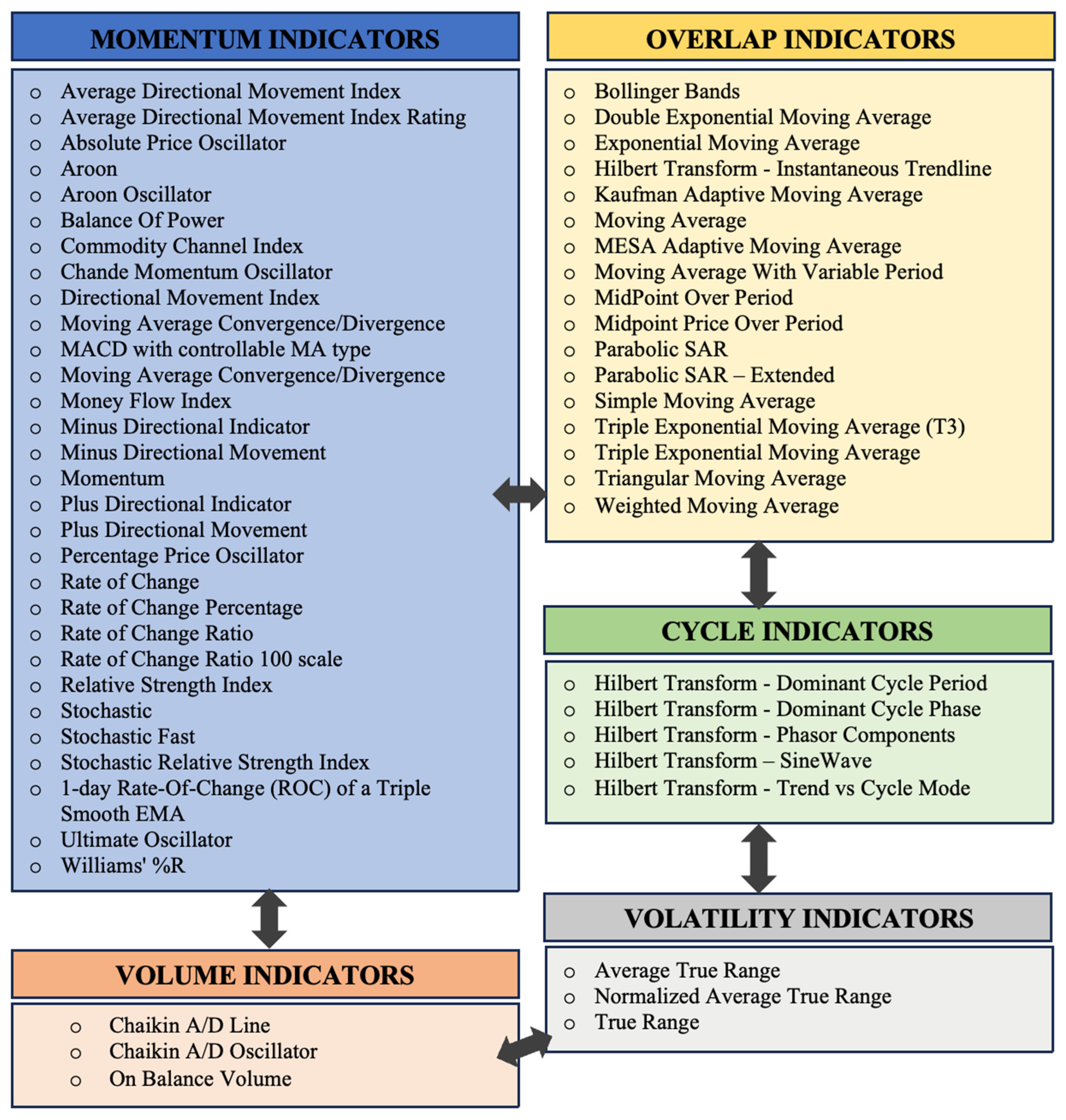

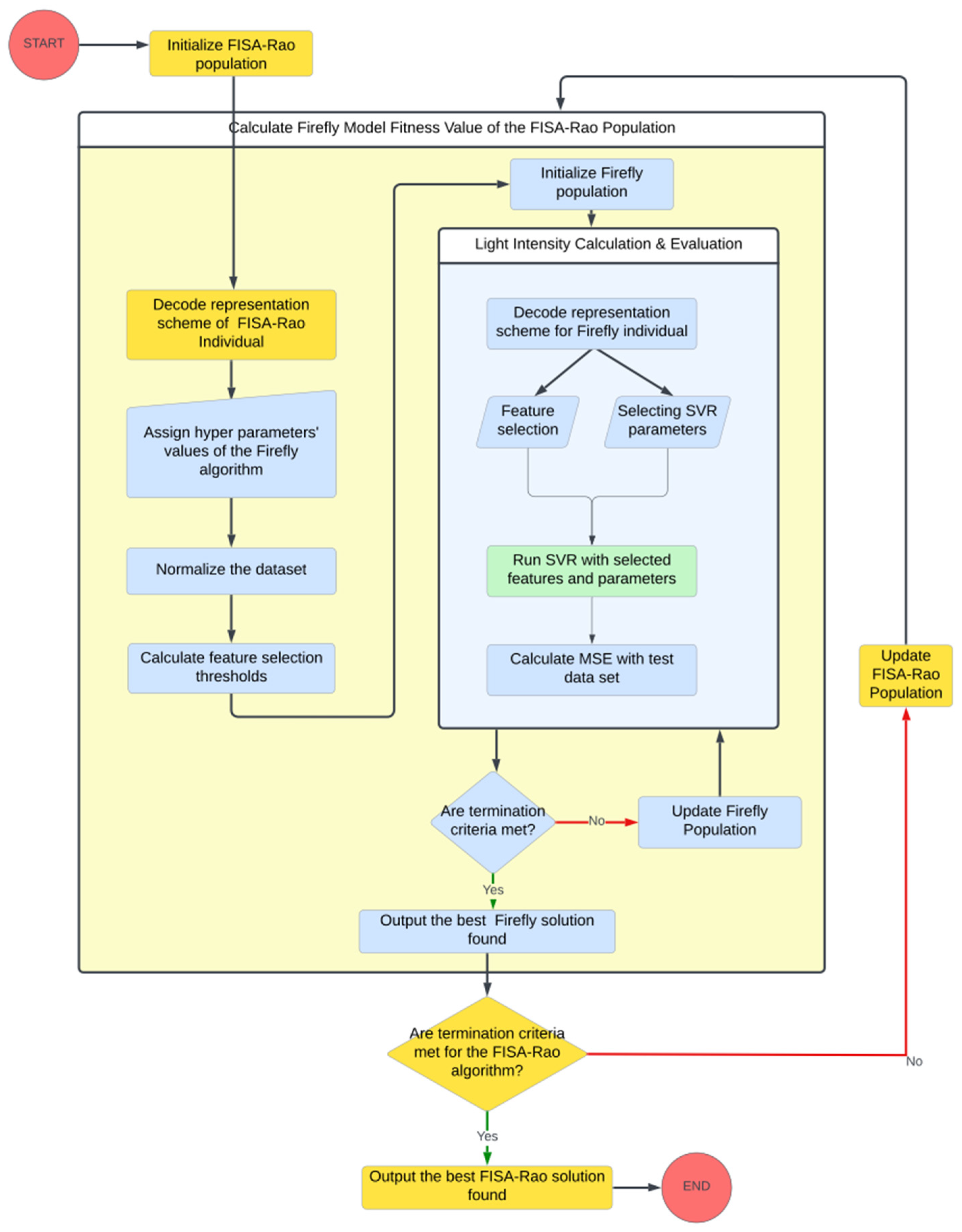
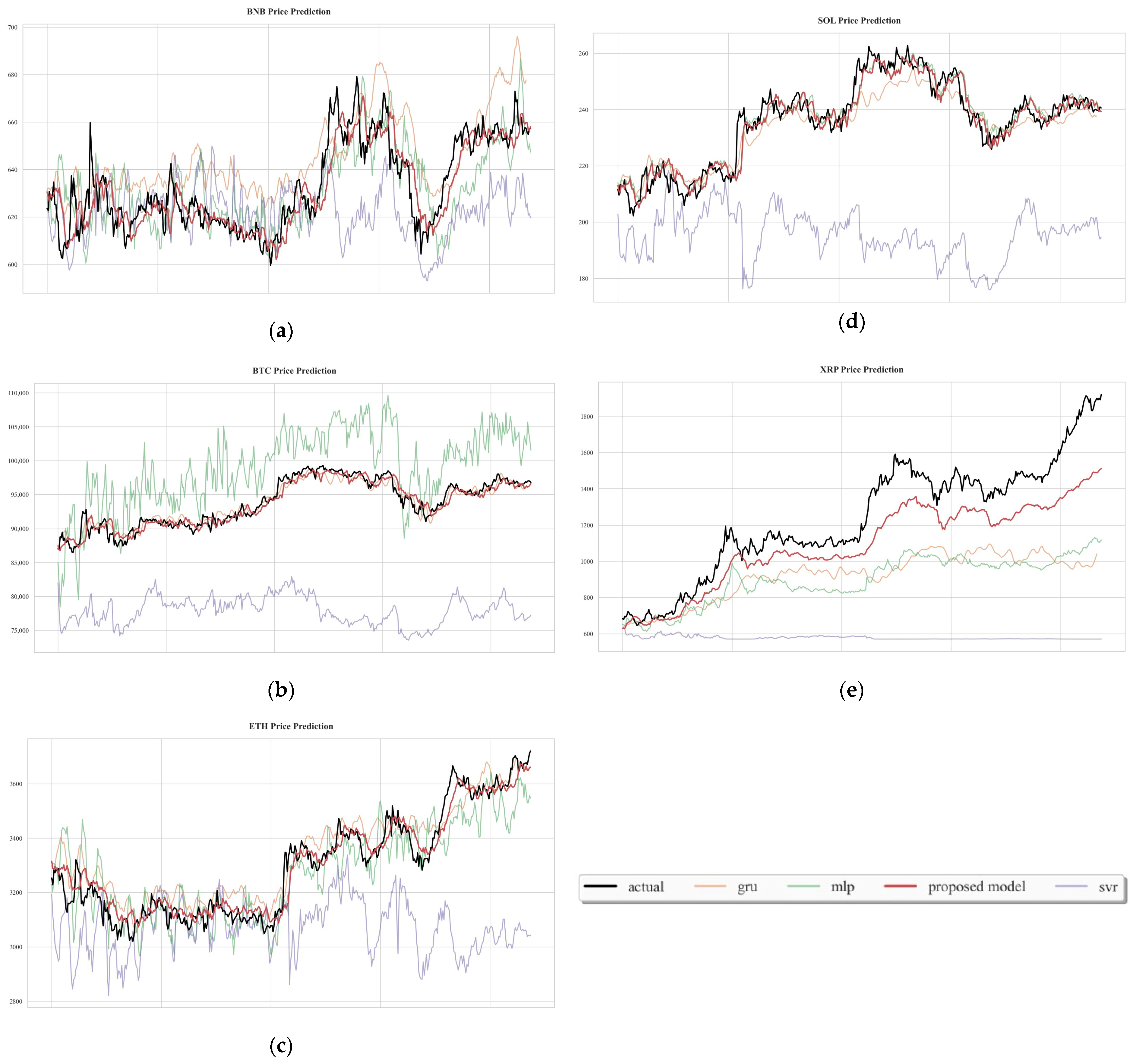
| BNB | BTC | ETH | SOL | XRP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 1465 | 1465 | 1465 | 1465 | 1465 |
| Min | 537.3 | 59,502.01 | 2317.55 | 134.82 | 0.4948 |
| Mean | 598.8354 | 75,697.74 | 2805.907 | 185.7587 | 0.747284 |
| Std | 30.45049 | 12,896.92 | 385.1328 | 37.67042 | 0.363906 |
| 25% | 576 | 66,490 | 2476.44 | 154.23 | 0.5283 |
| 50% | 595.8 | 69,210.89 | 2633.8 | 173.2 | 0.5448 |
| 75% | 620.58 | 90,260.01 | 3134.82 | 218.24 | 0.8722 |
| Max | 679.17 | 99,272.72 | 3720.2 | 262.83 | 1.9209 |
| Skewness | 0.352382 | 0.587923 | 0.675721 | 0.509854 | 1.484177 |
| Kurtosis | −0.57016 | −1.24594 | −0.94955 | −1.16438 | 0.829053 |
| Cryptocurrency | Alpha | Beta | Gamma | Feature Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | 0.10 | 3.88871113 | 0.53142280 | 0.10 |
| Bitcoin | 0.10899655 | 2.05456144 | 0.10005020 | 0.10 |
| Ethereum | 0.10 | 2.71845964 | 0.90 | 0.10 |
| Solana | 0.90 | 4.00 | 0.90 | 0.10 |
| Ripple | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.11195953 | 0.10 |
| Cryptocurrency | Number of Selected Features | C | Gamma | Epsilon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | 24 | 1.71251507 | 0.00031585 | 0.06085070 |
| Bitcoin | 26 | 1.92974892 | 0.00041844 | 0.04702257 |
| Ethereum | 26 | 1.90682945 | 0.00040813 | 0.04588806 |
| Solana | 33 | 2.61428180 | 0.00062762 | 0.00696581 |
| Ripple | 33 | 2.87812035 | 0.00088860 | 0.00271578 |
| Cryptocurrency | Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GRU | MLP | SVR (Kernel: RBF) | |
| Binance | 50 neurons 2 layers | Activation function: ReLU Hidden layer size: (100, 100, 100) | C: 601.6744848632667 ε: 0.001 γ: 0.016682100811756757 |
| Bitcoin | 50 neurons 2 layers | Activation function: ReLU Hidden layer size: (200) | C: 67,020.49366740837 ε: 0.1 γ: 0.01700055555320537 |
| Ethereum | 50 neurons 2 layers | Activation function: ReLU Hidden layer size: (300, 200, 100) | C: 2621.2502950923654 ε: 0.1 γ: 0.016707224581714062 |
| Solana | 50 neurons 2 layers | Activation function: Logistic Hidden layer size: (500) | C: 151.8565094362226 ε: 0.1 γ: 0.017531376423040763 |
| Ripple | 50 neurons 2 layers | Activation function: Logistic Hidden layer size: (500) | C: 685.4619764331517 ε: 0.1 γ: 0.030590208767187797 |
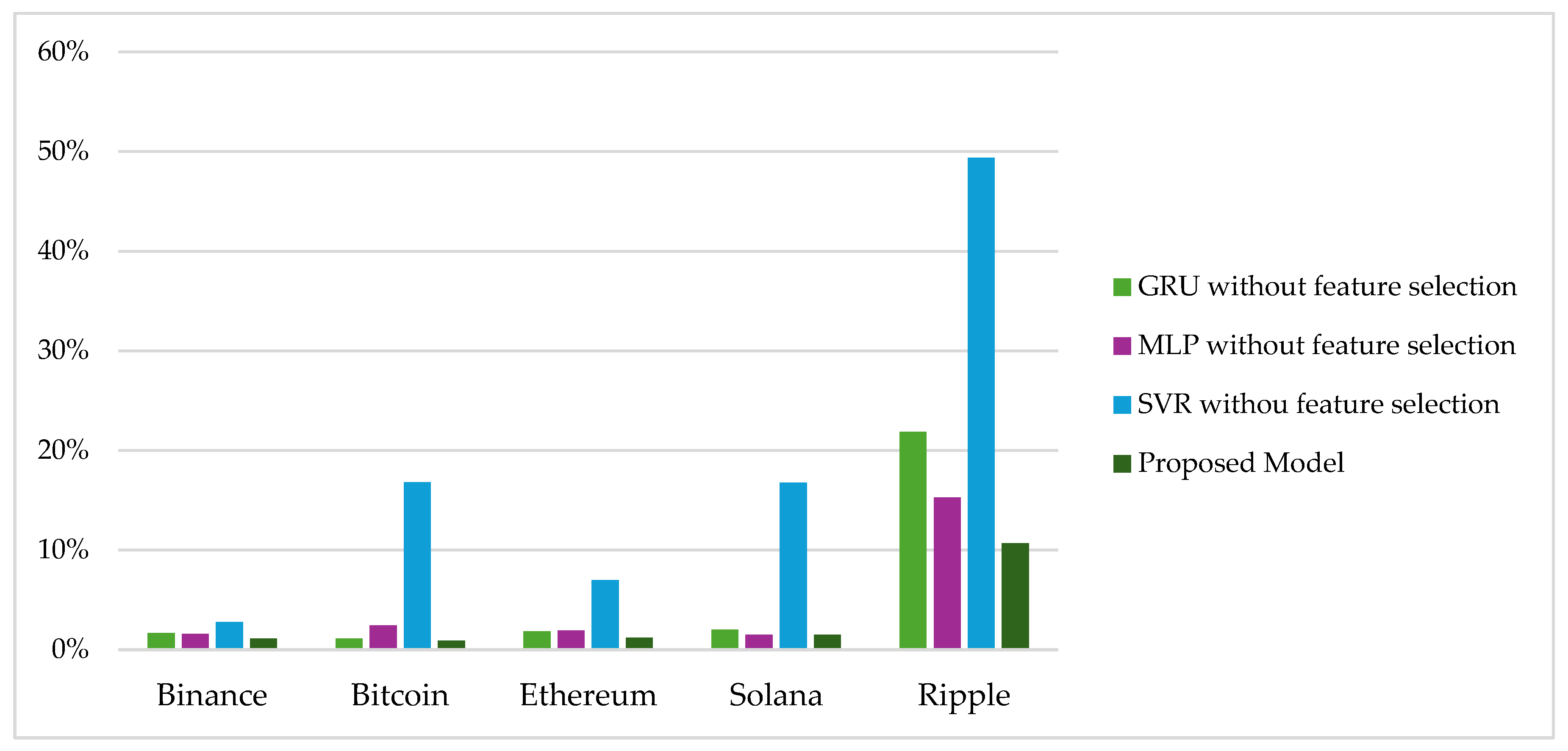
| Coin Type | Model | MSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | GRU | 166.434 | 10.421 | 1.653% |
| MLP | 168.556 | 10.068 | 1.585% | |
| SVR | 492.112 | 17.778 | 2.769% | |
| Proposed Model | 87.247 | 7.063 | 1.100% | |
| Bitcoin | GRU | 1,671,160.784 | 1014.896 | 1.093% |
| MLP | 7,979,731.089 | 2268.121 | 2.422% | |
| SVR | 265,932,562.476 | 15,866.991 | 16.817% | |
| Proposed Model | 1,203,594.201 | 834.689 | 0.900% | |
| Ethereum | GRU | 5877.340 | 60.388 | 1.830% |
| MLP | 6115.215 | 62.739 | 1.919% | |
| SVR | 97,587.330 | 239.332 | 6.969% | |
| Proposed Model | 2695.571 | 39.273 | 1.200% | |
| Solana | GRU | 34.725 | 4.687 | 2.001% |
| MLP | 22.417 | 3.548 | 1.513% | |
| SVR | 1964.356 | 40.404 | 16.752% | |
| Proposed Model | 21.465 | 3.515 | 1.500% | |
| Ripple | GRU | 137,573.672 | 302.340 | 21.857% |
| MLP | 61,041.568 | 208.582 | 15.258% | |
| SVR | 537,991.248 | 658.389 | 49.375% | |
| Proposed Model | 31,128.558 | 145.748 | 10.700% |
| Coin Type | Compared Model with the Proposed Model | p-Value | r | Test Statistic | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNB | GRU | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| BNB | MLP | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| BNB | SVR | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| BTC | GRU | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| BTC | MLP | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| BTC | SVR | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| ETH | GRU | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| ETH | MLP | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| ETH | SVR | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| SOL | GRU | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| SOL | MLP | 0.784126 | 0.461905 | 97 | FALSE |
| SOL | SVR | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| XRP | GRU | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| XRP | MLP | 1.34 × 10−5 | 0.019048 | 4 | TRUE |
| XRP | SVR | 1.91 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | TRUE |
| Coin Type | OHLC | Momentum | Overlap | Cycle | Volatility | Volume | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | 1 | 12 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 24 | |
| Bitcoin | 3 | 2 | 18 | 3 | 26 | ||
| Ethereum | 3 | 3 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 26 | |
| Solana | 1 | 18 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 33 |
| Ripple | 2 | 16 | 12 | 3 | 33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Er, M.; Bayaz, K.; Oktay Fırat, S.Ü. SVR-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Using a Hybrid FISA-Rao and Firefly Algorithm for Feature and Hyperparameter Selection. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 13177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413177
Er M, Bayaz K, Oktay Fırat SÜ. SVR-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Using a Hybrid FISA-Rao and Firefly Algorithm for Feature and Hyperparameter Selection. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(24):13177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413177
Chicago/Turabian StyleEr, Merve, Kenan Bayaz, and Seniye Ümit Oktay Fırat. 2025. "SVR-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Using a Hybrid FISA-Rao and Firefly Algorithm for Feature and Hyperparameter Selection" Applied Sciences 15, no. 24: 13177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413177
APA StyleEr, M., Bayaz, K., & Oktay Fırat, S. Ü. (2025). SVR-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Using a Hybrid FISA-Rao and Firefly Algorithm for Feature and Hyperparameter Selection. Applied Sciences, 15(24), 13177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413177






